JP2008040420A - Image heating device - Google Patents
Image heating device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008040420A JP2008040420A JP2006218281A JP2006218281A JP2008040420A JP 2008040420 A JP2008040420 A JP 2008040420A JP 2006218281 A JP2006218281 A JP 2006218281A JP 2006218281 A JP2006218281 A JP 2006218281A JP 2008040420 A JP2008040420 A JP 2008040420A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- belt
- image
- speed
- mode
- image heating
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Fixing For Electrophotography (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、電子写真、静電記録、磁気記録等の作像プロセス手段を採用した、複写機、LBP、ファクシミリ、マイクロフィルムリーダプリンタ、ディスプレイ装置、記録機等の画像形成装置に用いられ、記録材上の画像を加熱する画像加熱装置に関する。 The present invention is used in an image forming apparatus such as a copying machine, an LBP, a facsimile, a microfilm reader printer, a display device, and a recording machine that employs an image forming process means such as electrophotography, electrostatic recording, and magnetic recording. The present invention relates to an image heating apparatus for heating an image on a material.
この画像加熱装置としては、例えば、記録材上の未定着画像を定着する定着装置や、記録材に定着された画像を加熱することにより画像の光沢を増大させる光沢増大化装置等を挙げることができる。 Examples of the image heating device include a fixing device that fixes an unfixed image on the recording material, and a gloss increasing device that increases the gloss of the image by heating the image fixed on the recording material. it can.
上記のような画像形成装置において、記録材上に形成した未定着画像を定着処理する定着装置の実用装置の一つとしてベルト(フィルム)加熱方式の画像加熱装置が有る。この画像加熱装置は、記録材上の画像を加熱するためのエンドレスベルトと、このベルトとの間で加熱ニップを形成するニップ形成部材と、ベルトの回転に伴いベルトと摺動自在に設けられた摺動部材と、を有する。 In the image forming apparatus as described above, there is a belt (film) heating type image heating apparatus as one of practical apparatuses of a fixing apparatus for fixing an unfixed image formed on a recording material. This image heating device is provided with an endless belt for heating an image on a recording material, a nip forming member for forming a heating nip with the belt, and a belt slidable as the belt rotates. And a sliding member.
より具体的には、固定支持された加熱体と、該加熱体に密着して摺動しつつ搬送されるエンドレスベルトと、該ベルトを介して記録材を加熱体に密着させる加圧体を有する。そして、加熱体の熱をベルトを介して記録材に付与して記録材上の画像を加熱する装置である。 More specifically, it has a fixedly supported heating body, an endless belt that is conveyed while being in close contact with the heating body, and a pressure body that causes the recording material to be in close contact with the heating body via the belt. . The apparatus heats the image on the recording material by applying heat from the heating body to the recording material via a belt.
このようなベルト加熱方式の装置は、昇温の速い低熱容量の加熱体や薄膜のベルトを用いることができる。そのため、省電力化やウエイトタイムの短縮化(クイックスタート性)が可能となる、画像形成装置等の本機の機内昇温を低めることができる等の利点を有し、効果的なものである。 Such a belt heating type apparatus can use a low heat capacity heating element or a thin film belt that is rapidly heated. Therefore, it has advantages such as power saving and shortening of the wait time (quick start property), and lowering the temperature rise in the apparatus such as an image forming apparatus, which is effective. .
しかしながら、低温環境下においては、クイックスタートを行うと定着性が不十分となってしまう場合がある。そこで、低温環境下では定着性確保のために、記録材搬送前に、一定時間ベルトを加熱した状態で回転させ、十分に加圧ローラ、ベルトなどが暖まった状態で、記録材搬送を開始させるモード(前回転モード)を持たせている。 However, in a low temperature environment, fixing performance may be insufficient when performing a quick start. Therefore, in order to ensure fixability in a low-temperature environment, the belt is heated while it is heated for a certain period of time before the recording material is transported, and the recording material transport is started while the pressure roller, belt, etc. are sufficiently warmed. A mode (pre-rotation mode) is provided.
また、このようなベルト加熱方式の定着装置は、ヒートローラ方式などの他の定着装置に比べて熱容量が非常に小さい。そのため、連続して小サイズ記録材(搬送方向に対して直角方向の幅が狭い記録材)を通紙した場合、非通紙部昇温しやすく、紙シワや、カール、記録材後端ハネなどの問題が発生する場合がある。そこで、小サイズ記録材の連続通紙時において、非通紙部昇温が進んでくると、通紙を一旦停止し、一定時間ベルトを回転させることにより、非通紙部昇温を是正するモード(後回転モード)を持つ場合がある。また、ジョブ終了後に一定時間ベルトを回転させることにより非通紙部昇温を是正するモード(後回転モード)を持つ場合がある。 Further, such a belt heating type fixing device has a very small heat capacity compared to other fixing devices such as a heat roller type. For this reason, when a small-size recording material (a recording material having a narrow width in the direction perpendicular to the conveyance direction) is continuously fed, the temperature of the non-sheet passing portion is likely to increase, and paper wrinkles, curls, Such problems may occur. Therefore, when the non-sheet passing portion temperature rises during continuous feeding of small size recording materials, the sheet passing is temporarily stopped and the belt is rotated for a certain time to correct the non-sheet passing portion temperature rise. May have a mode (post-rotation mode). Further, there is a case where a mode (post-rotation mode) for correcting the temperature rise of the non-sheet passing portion by rotating the belt for a certain time after the job is completed may be provided.
これら前回転モードや後回転モードは、ベルトの回転スピードよりも回転時間が重要であるため、多くの場合、ベルトの耐久性の観点などから、できるだけ遅いスピードで回転させている(プロセススピードよりも十分遅いスピード)。 In these pre-rotation mode and post-rotation mode, since the rotation time is more important than the rotation speed of the belt, in many cases, it is rotated at the lowest possible speed from the viewpoint of belt durability (rather than the process speed). Slow enough).
特許文献1には、低温時の定着性確保のために、記録材搬送前に、搬送時よりも遅いスピードで一定時間ベルトを温調した状態で回転させることが示されている。これにより、低温環境下においても、定着性を確保することが可能となり、また、ベルトの走行距離も短くてすむ。
しかしながら、耐久が進むにつれて、ベルト内面のグリースの劣化や、ベルトの内面削れの進行により、ベルトの回転抵抗が増加する。そうすると、ベルトと、ベルトが加圧されている(密着している)加熱体(ヒータ面等)との間で、スティックスリップが発生する場合がある。特にベルトの回転スピードが遅いほど、スティックスリップになりやすく、それが異音となり問題となる場合があった。 However, as the durability progresses, the rotational resistance of the belt increases due to the deterioration of grease on the inner surface of the belt and the progress of shaving of the inner surface of the belt. If it does so, stick slip may generate | occur | produce between a belt and the heating body (heater surface etc.) to which the belt is pressurized (contact | adhered). In particular, the slower the rotation speed of the belt, the more likely it becomes stick-slip, which may become a problem due to abnormal noise.
それを回避する為に、あらかじめ前回転モードと、後回転モードでのベルト回転速度をスティックスリップが起こらない程度の速さに設定する方法も考えられる。しかし、この場合は、それほど耐久が進んでいない状況であっても、すなわち、スティックスリップが発生する心配がない時にも、一律回転スピードを速めてしまうので、必要以上にベルトの走行距離が伸び、ベルトの耐久性能に影響を与えてしまう。 In order to avoid this, it is conceivable to set the belt rotation speed in the pre-rotation mode and the post-rotation mode in advance so that stick slip does not occur. However, in this case, even in a situation where durability has not progressed so much, that is, when there is no concern about stick slip, the uniform rotation speed is increased, so the mileage of the belt extends more than necessary, This will affect the durability of the belt.
本発明は、このような技術的課題に鑑みてなされたものである。その目的は、ベルト加熱方式の画像加熱装置において、ベルトのスティックスリップによる異音対策と耐久性能の両立を可能にすることである。 The present invention has been made in view of such technical problems. The purpose of the image heating apparatus of the belt heating method is to make it possible to achieve both noise countermeasures and durability performance due to stick-slip of the belt.
上記の目的を達成するための本発明に係る画像加熱装置の代表的な構成は、記録材上の画像を加熱するためのエンドレスベルトと、このベルトとの間で加熱ニップを形成するニップ形成部材と、ベルトの回転に伴いベルトと摺動自在に設けられた摺動部材と、ベルトの周速を検出する検出手段と、この検出手段の出力に応じて少なくとも画像加熱処理時のベルトの周速が設定速度となるように制御する制御手段と、を有し、この制御手段による速度制御を行うことなく非画像加熱処理時にベルトを設定時間に亘って画像加熱処理時よりも遅い設定速度で回転させるモードを実行可能な画像加熱装置において、このモード時に検出されたベルトの周速が設定速度を下回った場合、このモード時のベルトの設定速度を速い速度へ変更することを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above object, a typical configuration of an image heating apparatus according to the present invention includes an endless belt for heating an image on a recording material, and a nip forming member for forming a heating nip between the belt. A sliding member provided slidably with the belt as the belt rotates, a detecting means for detecting the peripheral speed of the belt, and at least the peripheral speed of the belt during image heating processing according to the output of the detecting means And a control means for controlling the belt so as to become a set speed, and the belt is rotated at a set speed slower than that during the image heating process during the non-image heating process without performing the speed control by the control means. In the image heating apparatus capable of executing the mode, the belt setting speed in this mode is changed to a higher speed when the belt peripheral speed detected in this mode falls below the setting speed. To.
また、上記の目的を達成するための本発明に係る画像加熱装置の他の代表的な構成は、記録材上の画像を加熱するためのエンドレスベルトと、このベルトとの間で加熱ニップを形成するニップ形成部材と、ベルトの回転に伴いベルトと摺動自在に設けられた摺動部材と、を有し、非画像加熱処理時にベルトを設定時間に亘って画像加熱処理時よりも遅い設定速度で回転させるモードを実行可能な画像加熱装置において、このモードにおけるベルトの使用後期の設定速度をベルトの使用初期の設定速度よりも速くすることを特徴とする。 Another typical configuration of the image heating apparatus according to the present invention for achieving the above object is to form a heating nip between an endless belt for heating an image on a recording material and the belt. And a slidable member that is slidable with the belt as the belt rotates, and the belt is set at a slower setting speed during the non-image heating process than during the image heating process. In the image heating apparatus capable of executing the rotation mode, the set speed in the latter half of use of the belt in this mode is set to be higher than the set speed in the initial use of the belt.
本発明によれば、ベルトのスティックスリップによる異音対策と、耐久性能の両立が可能となる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to achieve both noise countermeasures due to stick-slip of the belt and durability.
(1)画像形成装置例の概略構成
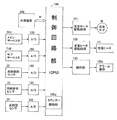
図1は本発明に従う画像加熱装置を定着装置として搭載させた画像形成装置例の概略構成図である。本例の画像形成装置は、画像読み取りスキャナ部を具備させた、転写方式電子写真プロセス利用の多機能型画像形成装置である。
(1) Schematic Configuration of Example Image Forming Apparatus FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration diagram of an example image forming apparatus in which an image heating apparatus according to the present invention is mounted as a fixing device. The image forming apparatus of this example is a multifunctional image forming apparatus using a transfer type electrophotographic process, which includes an image reading scanner unit.
この画像形成装置本体Aは、上部に原稿の画像情報を読み取る画像読み取り手段である画像読み取りスキャナ部Bを有し、その下部に画像形成手段となる画像形成部Cを有し、更にその下部にシートデッキDを組み付けて構成されている。 The image forming apparatus main body A has an image reading scanner unit B as an image reading unit for reading image information of a document at the upper part, an image forming unit C as an image forming unit at the lower part, and further at the lower part. The seat deck D is assembled.
a)画像読み取りスキャナ部B
202は水平に固定配設したプラテンガラスであり、その上に本や厚紙・カール紙等の、ブック原稿やシート状原稿を読み取りすべき画像面を下側にして所定の載置基準に従って載置し、原稿圧板203により背面を押圧して静止状態でセットする。
a) Image reading scanner section B
読み取り開始キーを押すと、ガラス202の下面側に配設の、走査系光源201・走査系ミラー204等を含む走査ユニットが、ガラス左辺側の実線示のホームポジションからガラス下面に沿って右辺側方向である矢印a方向に所定の速度で往動駆動される。
When the reading start key is pressed, the scanning unit including the
これにより、ガラス202上に載置セットされている原稿の下向きの画像面が左辺側から右辺側に順次に照明走査される。そして、その照明走査光の原稿面反射光がレンズ205を通して受光素子(光電変換素子)206に入射して光電読み取りされ、画像処理部で処理され、画像情報電気信号に変換されて、画像形成部Cのレーザスキャナ111に伝送される。
As a result, the downward image surface of the document placed and set on the
移動した走査ユニット201・204は所定の往動終点まで移動すると復動に転じられて、始めのホームポジションに戻される。
When the moved
b)画像形成部C
図2は画像形成部Cの要部の拡大図である。図1と図2をして、112は像担持体としての回転ドラム型の電子写真感光体(以下、ドラムと記す)である。このドラム112は矢印の時計方向に所定の周速度(プロセススピード)をもって回転駆動される。その回転過程において、ドラム112は帯電器122による所定の極性・電位の一様帯電処理を受け、その一様帯電面にレーザスキャナ111・画像書き込み光学系113から画像情報に対応するレーザ光走査露光bを受ける。これにより、ドラム面に走査露光パターンに対応した静電潜像が形成される。
b) Image forming unit C
FIG. 2 is an enlarged view of a main part of the image forming unit C. 1 and 2,
ドラム面に形成された静電潜像は現像器114によりトナー画像として現像される。そのトナー画像がドラム112と転写帯電ローラ115との当接部である転写ニップ部Tにおいて、該転写ニップ部Tに後述する給紙部側から所定の制御タイミングにて給送された記録材P(以下、用紙と記す)に対して順次に転写されていく。
The electrostatic latent image formed on the drum surface is developed as a toner image by the developing
転写ニップ部Tを通ってトナー画像の転写を受けた用紙Pはドラム面から順次に分離されて搬送ガイド部117を通り、定着装置118に搬送される。そして、用紙Pは該定着装置118の定着ニップ部Nで挟持搬送される過程で加熱及び加圧されて未定着トナー画像の定着処理を受ける。
The paper P that has received the transfer of the toner image through the transfer nip T is sequentially separated from the drum surface, and is conveyed to the
一方、用紙分離後のドラム面は、クリーニング器123で転写残トナー等の残留付着汚染物の除去処理を受け、またイレーサランプ124等による除電処理を受けて、繰り返して作像に供される。
On the other hand, the drum surface after paper separation is subjected to a removal process of residual adhered contaminants such as transfer residual toner by a cleaning device 123 and subjected to a charge removal process by an
定着装置118を通った用紙Pは、片面プリントモードの場合には、排出ローラ119によって機外に配置された排紙トレイ(若しくはソーター)120に排出、積載される。
In the single-sided printing mode, the paper P that has passed through the
両面プリントモードの場合には、定着装置118から排出された第1面に対する画像形成済みの用紙が排出ローラ119に挟持され、その用紙の後端が分岐点207を通過した時点で排出ローラ119が逆転し、両面トレイ121上に一旦載置される。その後、搬送ローラ104・105により搬送されて、レジストローラ106に到達し、転写ニップ部Tに所定の制御タイミングにて再給送される。これにより、反転された該用紙の第2面に対して前述と同様にして画像が形成された後、排紙トレイ120に排出、積載される。
In the duplex printing mode, the sheet on which the image is formed on the first surface discharged from the fixing
レジストローラ106は、互いに当接させた駆動ローラとピンチローラとのローラ対からなり、駆動停止状態において該両ローラ対の圧接ニップ部Rで給紙部から給送された用紙の先端辺を一旦受止めた状態にして用紙を一時待機状態に保持する。また用紙の斜行矯正の機能も有している。そして所定の制御タイミングにて駆動ローラが所定の周速度にて回転駆動されることで、用紙が転写ニップ部Tへ給送される。用紙の後端がレジストローラ106の圧接ニップ部Rを抜けると、次の用紙の先端を受止めるために駆動ローラの駆動が停止される。
The
22と23は用紙検知センサとしてのフォトインタラプタであり、それぞれフラグ部(アクチュエータ)24と25を設けてある。用紙検知センサ22はレジストローラ106の用紙出口側位置における用紙の到着及び通過を検知する。用紙検知センサ23は定着装置118の用紙出口側位置における用紙の到着及び通過を検知する。用紙検知センサ22と23の用紙検知信号が、それぞれ、A/D変換器103(図7)を介して制御回路部(CPU)100に入力する。制御回路部100は用紙検知センサ22・23からの入力信号に基いて、作像シーケンスの制御をしたり、レジストローラ106と定着装置118との間における用紙ジャムの発生を検知したりする。
22 and 23 are photo-interrupters as paper detection sensors, which are provided with flag portions (actuators) 24 and 25, respectively. The
ここで、画像形成装置本体Aは、上記のようにレーザスキャナ111に画像読み取りスキャナ部Bの画像処理部の処理信号を入力すれば複写機として機能する。外部コンピューターの出力信号を入力すればプリンターとして機能する。また、他のファクシミリ装置からの信号を受信したり、画像読み取りスキャナ部Bの画像処理部の信号を他のファクシミリ装置に送信したりすれば、ファクシミリ装置としても機能する。図7において、200は外部コンピューターや他のファクシミリ装置等の外部機器であり、インターフェイスIFを介して画像形成装置本体Aの制御回路部100に接続されている。
Here, the image forming apparatus main body A functions as a copying machine if the processing signal of the image processing section of the image reading scanner section B is input to the
c)シートデッキD
画像形成部Cの下部にはシートカセット1を装着させている。このシートカセット1は下段カセット1aと上段カセット1bの2個で1つの給送ユニットとして構成されている。本例では、2つの給送ユニットU1・U2を装着して4個のカセットを装着するようにしている。上方に位置する1つの給送ユニットU1は装置本体Aに対して着脱可能に取り付けられ、下方の給送ユニットU2はシートデッキDに着脱可能に取り付けられている。そして選択指定されたカセットからそれに収容の用紙が一枚宛自動給紙される。
c) Seat deck D
A
即ち、前記カセット1a・1b内に収容された用紙は、給送回転体となるピックアップローラ3により繰り出され、フィードローラ4とリタードローラ5との協働作用により1枚ずつ分離・給送される。そして、その用紙は搬送ローラ104・105によって搬送され、レジストローラ106へと導かれ、該ローラ106によって画像形成動作に同期するようにして画像形成部Cの転写ニップ部Tへ給送される。
That is, the sheets stored in the
また、上記用紙カセット1とは別に、手差しトレイ6が装置本体Aの側面に配置されており、該トレイ6上の用紙は、手差し給紙ローラ7によりレジストローラ106へと繰り出される。
In addition to the
(2)定着装置118
本実施例における定着装置118は、基本的には特開平4−44075〜44083、4−204980〜204984号公報等に開示のベルト加熱方式・加圧部材駆動方式(テンションレスタイプ)の加熱装置である。
(2)
The fixing
以下の説明において、定着装置又はこれを構成している部材について長手方向とは記録材(用紙)搬送路面内において記録材搬送方向に直交する方向に並行な方向である。定着装置に関して、正面とは記録材導入側の面、左右とは装置を正面から見て左又は右である。記録材の幅とは記録材面において記録材搬送方向に直交する方向の記録材寸法である。 In the following description, the longitudinal direction of the fixing device or the members constituting the fixing device is a direction parallel to the direction orthogonal to the recording material conveyance direction in the recording material (paper) conveyance path surface. Regarding the fixing device, the front is the surface on the recording material introduction side, and the left and right are the left or right when the device is viewed from the front. The width of the recording material is a recording material dimension in a direction orthogonal to the recording material conveyance direction on the recording material surface.
図3はこの定着装置118の要部の拡大横断面模型図、図4の(a)は同じく要部の正面模型図、(b)は縦断正面模型図である。
3 is an enlarged cross-sectional model view of the main part of the fixing
10は定着ベルトアセンブリ(以下、アセンブリと記す)、18は加圧回転体(ニップ形成部材)としての弾性加圧ローラである。アセンブリ10と加圧ローラ18との圧接により定着ニップ部(加熱ニップ)Nを形成させている。
アセンブリ31において、12は記録材上の画像を加熱するためのエンドレスベルト(加熱回転体)としての、円筒状(スリーブ状)で可撓性を有する耐熱性ベルトである。11は横断面略半円弧状樋型の耐熱性樹脂製の定着ステイ(ヒータ保持部材兼フィルムガイド部材:以下、ステイと記す)である。13は熱源(加熱体)としてのセラミックヒータ(摺動部材:以下、ヒータと記す)であり、ステイ11の外面に、該ステイの長手に沿って設けた凹溝部に嵌め入れて固定して配設してある。ベルト12はヒータ13を取り付けたステイ11に対してルーズに外嵌させてある。14は横断面コ字型の剛性を有する加圧部材であり、ステイ11の内側に配設してある。15は加圧部材14の左右両端部の外方突出腕部14aにそれぞれ嵌着した端部ホルダ、15aはこの端部ホルダ15と一体のフランジ部である。
In the
ベルト12は熱容量を小さくしてクイックスタート性を向上させるため、その膜厚は総厚40〜100μm程度としてある。そして、少なくとも、耐熱性・離型性・強度・耐久性等のあるポリイミドフィルム等の耐熱素材で構成されたベース層の外周に、PTFE・PFA等のフッ素系樹脂に導電剤を添加したコート層を設けたものである。
The
本実施例におけるベルト12は、少なくとも、ポリイミド等で構成されたベース層と、その外周に薄膜のフッ素系樹脂等でコーティングしたコーティング層と、ベース層とコーティング層の間に設けたプライマー層と、の3層以上を有する。プライマー層とコーティング層は導電または半導電の電気特性を有し、ベース層は絶縁の電気特性を有する。
The
本実施例におけるヒータ13は、ベルト12の移動方向に直交する方向を長手とする低熱容量の横長・薄板形の加熱体であり、薄板状のセラミック基板と、該基板の面に長手に沿って形成した抵抗発熱体を基本構成体とする全体に低熱容量の部材である。抵抗発熱体への電力供給により迅速に発熱・昇温し、温調系で所定の定着温度に温調管理される。
The
図5はそのようなヒータ13の一例の構成模式図である。13aは高絶縁性・高熱伝導性のヒータ基板としての薄板状のセラミック基板であり、アルミナ・窒化アルミニウム・炭化ケイ素等のセラミックスでできている。13bはAg/Pd、RuO2、Ta2N等の抵抗発熱体の層であり、セラミック板13aの表面側に長手に沿ってスクリーン印刷等により線状若しくは細帯状に塗工し、焼成して形成してある。13cは抵抗発熱体層13bに対するAg/Pt等の給電電極部であり、抵抗発熱体層13bの両端部に電気的に導通させてセラミック板面に形成してある。13dはセラミック板13aの表面側に形成した絶縁保護層であり、抵抗発熱体層13bと、給電電極部13cの一部を被わせている。この絶縁保護層13dは、抵抗発熱体層13bと、給電電極部13cの一部を電気的に絶縁保護するとともに、ベルト内面との摺擦に耐えることが可能な、薄層のガラスコート層やフッ素コート層等である。TH1とTH2はセラミック板13aの裏面側に設けた第1と第2の温度検知手段としてのメインサーミスタとサブサーミスタである。L13bは抵抗発熱体層13bの全長域であり、給電電極部13c・13c間に給電されることで、抵抗発熱体層13bの全長域L13bが発熱する。すなわち、この抵抗発熱体層13bの全長域L13bがヒータ13の有効発熱長さ領域である。
FIG. 5 is a schematic configuration diagram of an example of such a
ヒータ13は、ステイ11の下面に長手に沿って形成したヒータ嵌め込み溝部内に、ヒータ表面側(絶縁保護層13dを形成した面側)を外側にして嵌め込んで耐熱性接着剤で接着して保持させてある。
The
加圧ローラ18は、アルミニウム・鉄・ステンレス等の芯軸18aと、この軸に外装したシリコンゴム等の離型性の良い耐熱ゴム弾性体からなるローラ部18bと、フッ素樹脂を分散させた表面コート層18cとからなる。表面コート層18cは、用紙Pやベルト12の搬送性、トナー汚れ防止等の理由から設けてある。
The
加圧ローラ18は、芯金18aの左右両端部を装置フレーム16の左右の側板16L・16R間に軸受部材17を介して回転自由に軸受保持させて配設してある。
The
上記の加圧ローラ18に対して、アセンブリ10を、ヒータ13側を対向させて並行に配列する。そして、左右の端部ホルダ15を、それぞれ、加圧バネ19により所定の力で加圧ローラ18の軸線方向に附勢する。これにより、ヒータ13の面をベルト12を介して加圧ローラ18に対して弾性層18bの弾性に抗して圧接させて、ベルト12と加圧ローラ18との間に加熱定着に必要な、用紙搬送方向cに関して所定幅の定着ニップ部()Nを形成させてある。20と21は装置フレーム16に組付けた入り口ガイドと出口ガイドである。
The
Gは加圧ローラ18の芯金18aの一端部に固着したドライブギアである。このギアGに定着モータMの回転力が不図示の動力伝達機構を介して伝達されることで、加圧ローラ18が図3において矢印の時計方向に回転駆動される。この加圧ローラ18の回転駆動により、加圧ローラ18とベルト12の外面との定着ニップ部Nにおける摩擦力でベルト12に回転力が作用する。これにより、ベルト12が、その内面が定着ニップ部Nにおいてヒータ13に密着して摺動しながら矢印の反時計方向にステイ11の外回りを回転する。ベルト12は加圧ローラ18の回転スピードにほぼ対応したスピードをもって回転する。左右のフランジ部15aは、回転するベルト12がステイ11の長手に沿って左方または右方に寄り移動したとき寄り側のベルト端部を受け止めて移動を規制する役目をする。ベルト12の内面にはグリース(潤滑剤)を塗布して、ヒータ13・ステイ11に対するベルト12の摺動性を確保している。
G is a drive gear fixed to one end of the cored
定着ニップ部Nに導入された記録材Pは、加圧ローラ18とベルト12の回転により挟持搬送される。本実施例では、記録材Pの搬送は記録材中心の、いわゆる中央基準搬送で行われる。すなわち、装置に通紙使用可能な大小いかなる幅の記録材も、記録材幅方向中央部がベルト12の長手方向中央部を通過することになる。Sはその記録材中央通紙基準線(仮想線)である。
The recording material P introduced into the fixing nip N is nipped and conveyed by the rotation of the
WP1は装置に通紙使用可能な最大幅の用紙(最大サイズ用紙)の通紙域幅である。WP2は最大サイズ用紙よりも小さい幅の用紙(小サイズ用紙)の通紙域幅である。WP3は小サイズ用紙を通紙したときに生じる非通紙部幅(最大サイズ通紙域幅WP1と小サイズ通紙域幅WP2の差域)である。ヒータ13の有効発熱長さ領域である抵抗発熱体層全長域L13bは、最大サイズ用紙の幅と同じか、少し大きい長さとしてある。
WP1 is a sheet passing area width of the maximum width sheet (maximum size sheet) that can be used in the apparatus. WP2 is a sheet passing area width of a sheet (small size sheet) having a width smaller than the maximum size sheet. WP3 is a non-sheet passing portion width (a difference between the maximum size sheet passing area width WP1 and the small size sheet passing area width WP2) generated when a small size sheet is passed. The resistance heating element layer full length region L13b, which is the effective heat generation length region of the
メインサーミスタTH1は、大小いかなる幅の用紙も通紙部となるヒータ部分の温度を検出するように、ヒータ13の有効発熱長さ領域L13bのほぼ中央部位置においてヒータ裏面に対して接触させて配設してある。サブサーミスタTH2は、小サイズ用紙を通紙したときの非通紙部に対応するヒータ部分の温度を検出するように、ヒータ13の有効発熱長さ領域L13bの端部位置においてヒータ裏面に対して接触させて配設してある。サブサーミスタTH2は、非通紙部に対応するフィルム部分の温度を検出するように、ベルト12の内面に弾性的に接触させて配設させる構成にすることもできる。
The main thermistor TH1 is arranged in contact with the back surface of the heater at a substantially central position of the effective heat generation length region L13b of the
ヒータ13は、電力供給部としての定着ヒータ駆動回路102(図7)から、抵抗発熱体層13bに対して通電がなされることで、通電発熱層13bが発熱して、ヒータ13が有効発熱長さ領域L13bの全域において急速に昇温する。そのヒータ温度がメインサーミスタTH1とサブサーミスタTH2により検出され、ヒータ温度に関する電気的情報がA/Dコンバータ103を介して制御回路部100に入力する。制御回路部100は、メインサーミスタTH1、サブサーミスタTH2の出力をもとに、ヒータ13の温調制御内容を決定し、ヒータ駆動回路101からヒータ13への通電を制御する。
When the
而して、制御回路部100は、所定の制御信号に基づいて、定着モータ駆動回路101を制御して、加圧ローラ18の回転駆動を開始させる。また、定着ヒータ駆動回路102を制御して、ヒータ13のヒートアップを開始させる。ステイ11はヒータ13を断熱保持するとともに、ベルト内面ガイド部材となる。ベルト12の回転スピードが定常化し、ヒータ13の温度が所定に立ち上がった状態において、画像形成部側から定着ニップ部Nに未定着トナー像tを担持した用紙Pが入り口ガイド20に沿って案内されて導入される。用紙Pのトナー画像担持面側がベルト12に対面する。用紙Pは定着ニップ部Nにおいてベルト12を介してヒータ13に密着して定着ニップ部Nをベルト12と一緒に移動通過していく。その移動通過過程においてヒータ13で加熱されるベルト12により用紙Pに熱が付与されてトナー画像tが用紙面に加熱定着される。定着ニップ部Nを通過した用紙Pはベルト12の面から曲率分離されて排出搬送される。
Thus, the
また、回転するベルト12の周速を検出する検出手段(ベルト回転速度検知手段)を具備させている。本実施例においては、その検出手段として、図4の(a)、図6のように、ベルト12の最大サイズ通紙域幅WP1外のベルト部分外面の一部に、周辺のベルト部分より光反射率が高い反射材(マーキング部)12aをコートした。また、その反射材12aを形成具備させたベルト端部側において、ベルト12の回転に伴う反射材12aの回転軌跡位置の上方に、反射型センサ26を位置固定して配設した。反射材12aは、ベルト12の回転に伴い回転して反射型センサ26の下をベルト12の1回転につき1回通過する。反射型センサ26は、その反射材12aの通過時毎の反射材12aからの反射光を検知し、その検知信号をA/Dコンバータ103を介して制御回路部100に送っている。制御回路部100は、その検知信号の入力間隔とベルト周長より、ベルト12が一周に要する時間を計算し、ベルト12の実際の周速を検出する。制御回路部100は、検出手段の出力、すなわち検出周速に応じて、少なくとも画像定着処理時(画像加熱処理時)のベルト12の周速が設定速度となるように、定着モータ駆動回路101を制御している。
18dは反射材12aをクリーニングする部材であり、ベルト12の回転に伴う反射材12aの回転軌跡位置に対応する加圧ローラ端部領域にローラ周方向に具備させてある。
Further, a detecting means (belt rotational speed detecting means) for detecting the peripheral speed of the
18d is a member for cleaning the reflecting
(3)定着装置118の前回転モード
制御回路部100は、低温環境下でのプリント動作時は、定着性確保のために、未定着トナーtを担持した用紙Pが定着装置118に到達する以前(非画像加熱処理時)に、ベルト12と加圧ローラ18を予熱する「前回転モード」を実行する。この前回転モードでは、ベルト12の速度制御を行うことなく、ベルト12を所定時間に亘って画像加熱処理時(用紙挟持搬送時、プリント実行時)よりも遅い設定速度で回転させる。
(3) Pre-rotation mode of the fixing
制御回路部100は、例えば、定着装置の温度検知手段が検知する温度が所定温度以下(例えば、15℃以下)であるときに低温環境下であると判断して、上記の前回転制御モードを実行する。
For example, when the temperature detected by the temperature detection unit of the fixing device is equal to or lower than a predetermined temperature (for example, 15 ° C. or lower), the
前回転モードは、ヒータ13に対する電力供給をONにし、また定着モータMをONにして、ベルト12を所定の時間(例えば、約10秒)、所定の回転速度設定値で温調回転させて、ベルト12と加圧ローラ18を予め温める制御モードである。
In the pre-rotation mode, the power supply to the
この前回転モードは、定着ニップ部Nにて用紙を挟持搬送するわけではないため、ベルト12の耐久性を考慮し、ベルト回転速度は出来るだけ低速に設定される。例えば、画像加熱処理時におけるベルト12の回転速度設定値の1/4の回転速度値に設定される。
In this pre-rotation mode, the sheet is not nipped and conveyed at the fixing nip portion N, so the belt rotation speed is set as low as possible in consideration of the durability of the
そして、前回転モードが所定の時間(例えば約10秒間)実行されて、ベルト12及び加圧ローラ18が十分暖まった後に、定着装置118に対する用紙の搬送が開始される。
Then, after the pre-rotation mode is executed for a predetermined time (for example, about 10 seconds) and the
制御回路部100は、低温環境下でなければ、上記の前回転モードは実行しない。
The
(4)定着装置118の後回転モード
小サイズ用紙を連続通紙するプリント動作時においては、定着装置118の非通紙部域WP3で昇温が大きくなり(端部昇温)、様々な問題を引き起こす。制御回路部100は、端部昇温を検知するサブサーミスタTH2の検知温度を元に、ある一定以上の端部昇温が起こった場合に、端部昇温を是正する「後回転モード」を実行する。この後回転モードも、ベルト12の速度制御を行うことなく、ベルト12を所定時間に亘って画像加熱処理時(用紙挟持搬送時、プリント実行時)よりも遅い設定速度で回転させる。
(4) Post-rotation mode of the fixing
後回転モードは、小サイズ記録材の連続通紙時において、非通紙部昇温が進んでくると、通紙を一旦停止し、ベルト12を所定の一定時間(例えば約10秒)、所定の回転速度設定値で回転させて、端部昇温を十分是正する。そして、その是正後に、次の通紙を受け付けるものである。また、ジョブ終了後に、ベルト12を所定の一定時間(例えば約10秒)所定の回転速度設定値で回転させて、端部昇温を十分是正した後に、次のジョブの通紙を受け付けるものである。
In the post-rotation mode, when the temperature of the non-sheet passing portion advances during continuous feeding of the small size recording material, the feeding is temporarily stopped and the
この後回転モードも、上記の前回転モードと同様に、定着ニップ部Nにて用紙を挟持搬送するわけではないため、ベルト12の耐久性を考慮し、ベルト回転速度は出来るだけ低速に設定される。例えば、画像加熱処理時におけるベルト12の回転速度設定値の1/4の回転速度値に設定される。
In the post-rotation mode, as in the case of the pre-rotation mode, the sheet is not nipped and conveyed by the fixing nip portion N. Therefore, considering the durability of the
後回転モードは、画像加熱処理に引き続いて実行するとともに、該後回転モードの終了に伴いベルト12の回転が停止される。
The post-rotation mode is executed following the image heating process, and the rotation of the
(5)前回転モードと後回転モードにおけるベルト回転速度設定値の変更制御
前述したように、前回転モードや後回転モードにおいては、ベルト12の回転は、回転スピードよりも回転時間が重要であるため、ベルトの耐久性の観点などから、できるだけ遅いスピードで回転させている。すなわち、プロセススピードよりも十分遅いスピードで回転させている。しかしながら、耐久が進むにつれて、ベルト内面のグリースの劣化や、ベルトの内面削れの進行により、ベルトの回転抵抗が増加する。そうすると、ベルト12と、ベルト内面が密着して摺動する内側部材であるヒータ13やステイ11との間で、スティックスリップが発生する場合がある。そして、スティックスリップは、ベルトの回転スピードが遅いほど発生しやすく、特に、後回転にベルト12の回転速度を減速させる場合に発生しやすい。そして、そのスティックスリップが異音となり問題となる場合があった。
(5) Belt rotation speed setting value change control in the front rotation mode and the rear rotation mode As described above, in the front rotation mode and the rear rotation mode, the rotation time of the
そこで、耐久が進んでも、スティックスリップに起因する異音の発生を防止するために、本実施例においては、前回転モードと後回転モードにおけるスティックスリップの発生(又は、スティックスリップによる異音が発生しやすい状態:以下同じ)を検知する。そして、スティックスリップの発生を検知したときは、前回転モードと後回転モードにおけるベルト回転速度設定値を所定に上げる設定値変更制御を行わせ、その後は変更した新しい設定値により前回転モード又は後回転モードを実行させるようにしている。これにより、耐久が進んでも、前回転モードと後回転モードにおいてベルトのスティックスリップの発生が防止され、異音の発生が防止される。 Therefore, in order to prevent the occurrence of abnormal noise due to stick-slip even if the durability is advanced, in this embodiment, the occurrence of stick-slip in the front rotation mode and the rear rotation mode (or abnormal noise due to stick-slip occurs). Detectable status: the same applies hereinafter). When the occurrence of stick-slip is detected, set value change control for increasing the belt rotation speed set value in the pre-rotation mode and the post-rotation mode to a predetermined value is performed. The rotation mode is executed. As a result, even if the durability progresses, the occurrence of stick-slip of the belt is prevented in the front rotation mode and the rear rotation mode, and the generation of abnormal noise is prevented.
本実施例では、ベルトのスティックスリップの発生を検知する手段として、前記のベルト周速検出手段12a・26を用いている。すなわち、制御回路部100は、定着装置118の前回転モード及び後回転モードの実行時において、検出手段12a・26により実際のベルト周速を検出する。そして、その検出周速値と、所定の判定値とを対比する。検出周速値が判定値以下の場合は、スティックスリップが発生した、或いは発生しやすい状態になっていると判断して、前回転モード及び後回転モードの実行時におけるベルト回転速度設定値を変更し、元の設定値よりも速い速度の設定値を再設定する。そして、ベルト回転速度再設定値にあうように、定着モータMの回転数を一律変更する。
In this embodiment, the belt peripheral
前回転モード又は後回転モードにおいて、ベルトのスティックスリップが発生した、或いは発生しやすい状態になっていると判断する上記の判定値について説明する。 The above-described determination value for determining that a stick-slip of the belt has occurred or is likely to occur in the pre-rotation mode or the post-rotation mode will be described.
先に述べたように、このベルト加熱方式の定着装置118は、加圧ローラ駆動により、ベルト12が従動回転する構成であるため、加圧ローラ18の温度が低い状態と、高い状態で、加圧ローラの熱膨張状態が変わる。そのために、結果として、ベルト12の回転速度が変化する。この回転速度の変化量は、加圧ローラ18のゴム部18bの厚みに依存するが、最大概ね±1〜2%程度である。また、Φ24のベルトの場合、ベルト一周分での上記速度変化は、もっと小さく、最大でも±0.5%程度である。それに対して、スティックスリップは、瞬間的なベルト回転ストップが連続する現象であり、ベルト1周期では少なくとも3.0%以上回転速度が遅くなる。
As described above, the belt heating
以上より、加圧ローラ18のゴム厚や、ゴムの熱膨張率にもよるが、ベルト周速検出手段12a・26で検出される実際のベルト回転速度が、所定の設定値に対して概ね3%以上のスピードダウンしている場合に、上記の設定値の変更制御を実行させる。即ち、[所定の設定値×0.97]を判定値にして、実際のベルト回転速度測定値がそれ以下の場合にスティックスリップが発生した、或いは発生しやすい状態になっていると判断させる。新しい速度設定値は、例えば、旧設定値の10%UPにする。この場合、定着モータMの回転数を10%UPさせる。
From the above, although depending on the rubber thickness of the
そして、上記の設定値変更の繰り返しにより、前回転モード及び後回転モードの実行時におけるベルト回転速度設定値が、最終的に、画像加熱処理時のベルト回転速度設定値を超えた場合には、ベルト12が寿命に達したと判断する。この場合には、制御回路部100は、操作部130(図7)上にアラーム表示130aをして、サービスマンコールを促す。
And by repeating the above set value change, when the belt rotation speed setting value at the time of execution of the pre-rotation mode and the post-rotation mode finally exceeds the belt rotation speed setting value at the time of image heating processing, It is determined that the
制御回路部100は、通常の定着処理時(画像加熱処理時)には、上述のベルト周速検出手段12a・26により検知されるベルト12の回転速度が目標速度である所定の設定値となるようにフィードバック制御を行っている。具体的には、加圧ローラ18の回転速度を増減させる、つまり、定着モータMの回転速度を増減させることによりベルトの回転速度が所定の設定値を維持するように構成されている。
一方、上述したように、前回転モード時や後回転モード時(非画像加熱処理時)には、制御回路部100は、ベルト12の回転速度のフィードバック制御は行っていない。つまり、制御回路部100は、ベルト周速検出手段12a・26により検知されるベルト12の回転速度に応じて加圧ローラ12の回転速度を増減させるといったフィードバック制御は行っていない。
In the normal fixing process (at the time of image heating process), the
On the other hand, as described above, the
図8は前回転モードについての具体的な制御例のフローチャートである。 FIG. 8 is a flowchart of a specific control example for the pre-rotation mode.
ステップS1・S2:画像形成装置本体の電源をONしたとき、定着装置内のサーミスタ(例えば、メインサーミスタTH1)により温度を検知し、そのデータを制御回路部100が拾い上げる。
Steps S1 and S2: When the power of the image forming apparatus main body is turned on, the temperature is detected by a thermistor (for example, main thermistor TH1) in the fixing device, and the
ステップS3・S4・S12:サーミスタの検知温度Tが15℃以下である場合には低温環境下と判断して、定着装置118を予熱する前回転モードに入る。検知温度Tが15℃よりも高い場合は、前回転モードなしで、通常プリント動作モードに移行する。
Steps S3, S4, and S12: If the thermistor detection temperature T is 15 ° C. or lower, it is determined that the temperature is low and the pre-rotation mode for preheating the fixing
ステップS5:前回転モードに入った場合は、まず、ヒータ13がONされてヒータ温度が所定に立ち上げられて温調される。このヒータ13のONとほぼ同時に定着モータMがONされて、加圧ローラ18の駆動によるフィルム回転が開始される。
Step S5: When the pre-rotation mode is entered, first, the
この前回転モードにおけるベルト回転速度設定値Vaは、初期値として、画像加熱処理時(用紙挟持搬送時、リント実行時)のベルト回転速度設定値をVとしたとき、その1/4速(Va=1/4V)に設定している。 The belt rotation speed setting value Va in the pre-rotation mode is set to an initial value of the 1/4 rotation speed (Va) when the belt rotation speed setting value at the time of image heating processing (at the time of paper nipping conveyance and lint execution) is V. = 1 / 4V).
ステップS6・S7:定着モータMのONから回転が安定する駆動開始1秒後に、ベルト周速検出手段12a・26によりベルト回転速度を測定して、実際のベルト回転速度を判断する。
Steps S6 and S7: One second after the start of driving when the rotation of the fixing motor M is stabilized, the belt rotational speed is measured by the belt peripheral
ステップS8:ベルト回転速度測定値Vxと、所定のスティックスリップ判定値Vyとを対比する。判定値Vyは、[Va×0.97](ベルト回転速度設定値Vaを3%ダウンした速度値)に設定してある。 Step S8: The belt rotation speed measurement value Vx is compared with a predetermined stick-slip determination value Vy. The determination value Vy is set to [Va × 0.97] (speed value obtained by reducing the belt rotation speed setting value Va by 3%).
ステップS9・S10・S11:ステップS8で、測定値Vxが判定値Vyよりも大きい場合は、スティックスリップは発生していないと判断して、判定値Vyは据え置きにする。そして、ステップS4で前回転モードに入ってからの時間Aが10秒を経過しないうちは、ベルト回転速度の測定、ベルト回転速度判断、判定値Vyとの対比のステップが繰り返えされる。 Steps S9, S10, and S11: If the measured value Vx is larger than the determination value Vy in step S8, it is determined that stick slip has not occurred, and the determination value Vy is deferred. Then, as long as the time A after entering the pre-rotation mode in step S4 does not pass 10 seconds, the steps of measuring the belt rotation speed, judging the belt rotation speed, and comparing with the determination value Vy are repeated.
ステップS13:ステップS8で、測定値Vxが判定値Vy以下である場合は、スティックスリップが発生した、或いは発生しやすい状態になっているとしていると判断し、即座に、ベルト回転速度設定値Vaを、新しい設定値Vbに変更する。新設定値Vbは、変更前の旧設定値Vaの10%UPの速度値としている。 Step S13: If the measured value Vx is less than or equal to the determination value Vy in step S8, it is determined that stick slip has occurred or is in a state where it is likely to occur, and the belt rotation speed setting value Va is immediately determined. Is changed to a new set value Vb. The new set value Vb is a speed value that is 10% UP of the old set value Va before the change.
ステップS14・S15:新設定値Vbと、画像加熱処理時のベルト回転速度設定値Vとを対比し、新設定値Vbが設定値Vよりも大きい場合は、ベルト12が寿命に達したと判断し、寿命アラーム表示をする。
Steps S14 and S15: The new set value Vb is compared with the belt rotation speed set value V during the image heating process, and if the new set value Vb is larger than the set value V, it is determined that the
ステップS16:ステップS14で、新設定値Vbが設定値V以下の場合は、定着モータMを新設定値Vbにて駆動させる。この新設定値Vbにての定着モータMの回転が安定する駆動開始1秒後に、回転速度検知手段12a・26によりベルト回転速度を測定し、再びステップS7に移行して実際のベルト回転速度を判断する。
Step S16: If the new set value Vb is less than or equal to the set value V in step S14, the fixing motor M is driven with the new set value Vb. One second after the start of driving when the rotation of the fixing motor M at the new set value Vb is stabilized, the belt rotational speed is measured by the rotational
次のステップS8においては、スティックスリップ判定値Vyを、新設定値Vbを3%ダウンした速度値に変更し、その変更後の判定値Vyと、新設定値Vbのもとでの実際のベルト回転速度測定値Vxを対比させて、再びスティックスリップを判定させる。スティックスリップの判定開始は、新設定値Vbの回転速度で定着モータMを駆動し始めてから1秒後とする。 In the next step S8, the stick-slip determination value Vy is changed to a speed value that is 3% lower than the new set value Vb, and the actual belt under the changed set value Vy and the new set value Vb. The stick-slip is determined again by comparing the rotation speed measurement value Vx. The stick-slip determination is started one second after the fixing motor M starts to be driven at the rotation speed of the new setting value Vb.
その後の前回転モードは、その前の前回転モードで更新された新しい設定値Vbを元に同様の制御を行う。 In the subsequent pre-rotation mode, similar control is performed based on the new set value Vb updated in the previous pre-rotation mode.
以上は前回転モードの場合である。後回転モードの場合も、同様にして、実際のベルト回転速度測定値Vxとスティックスリップ判定値Vyとの対比によるスティックスリップの判定と、後回転モードにおけるベルト回転速度設定値Vaの新設定値Vbへの更新変更制御がなされる。 The above is the case of the pre-rotation mode. Similarly, in the case of the post-rotation mode, the stick-slip determination based on the comparison between the actual belt rotation speed measured value Vx and the stick-slip determination value Vy and the new set value Vb of the belt rotation speed set value Va in the post-rotation mode are performed. Update change control is performed.
実施例1では、ベルト回転速度検知のための反射部材12aは1個としてある。ベルト12のスティックスリップは、瞬間的なブレーキが連続的に起こることを考慮すると、反射部材12aはベルト12の周方向に複数個具備させるのも良い。これにより、ベルト速度サンプリング時間を短くすることができて、スティックスリップを捉える精度を上げることができる。
In the first embodiment, the number of the reflecting
実施例1,2では、ベルト周速検出手段として、反射部材12aと、反射光検知部としての反射型センサ26の組み合わせを用いた。ベルト周速検出手段は、これに限られず、その他、例えば、ベルト12の端部に複数のスリットを切り、フォトインタラプタでスリット間の通過時間を測定することでベルト回転速度を検知する手段構成にすることも可能である。
In Examples 1 and 2, a combination of the
実施例1〜3では、ベルト回転速度を検知することで、ベルト12のスティックスリップを検知し、前回転モードと後回転モードとにおけるベルト回転速度の設定値を変更制御している。
In the first to third embodiments, by detecting the belt rotation speed, stick slip of the
これ以外にも、実際にベルト12のスティックスリップを検知することなしに、予め実験的に、ベルト回転速度設定値と、その設定値においてスティックスリップが発生するベルト総回転時間(積算回転時間)の関係を求めておく。そして、制御回路部100でベルト12の総回転時間をカウンター機能部100aで積算カウントさせる。カウンター機能部100aで積算カウントされる所定の累積記録材搬送枚数に応じて、すなわち、所定の時間に達する毎に、前回転モードと後回転モードとにおけるベルト回転速度設定値を段階的に上げる設定値変更制御構成にすることも可能である。
In addition to this, without actually detecting stick-slip of the
図9はその制御例のフローチャートである。前回転モードと後回転モードとにおいて、初期設定値Va(=1/4V)によるベルト回転の総回転時間Taが所定の時間T1に到達したら、ベルト回転速度設定値を第2の設定値Vbに変更制御する。この第2の設定値Vbは初期設定値Vaよりも10%UPの速度値である。 FIG. 9 is a flowchart of the control example. In the pre-rotation mode and the post-rotation mode, when the total rotation time Ta of the belt rotation by the initial setting value Va (= 1 / 4V) reaches a predetermined time T1, the belt rotation speed setting value is changed to the second setting value Vb. Change control. The second set value Vb is a speed value that is 10% higher than the initial set value Va.
この第2の設定値Vbによるベルト回転の総回転時間Tbが所定の時間T2に到達したら、ベルト回転速度設定値を第3の設定値Vcに変更制御する。この第3の設定値Vcは第2の設定値Vbよりも10%UPの速度値である。 When the total rotation time Tb of the belt rotation by the second set value Vb reaches a predetermined time T2, the belt rotation speed set value is changed to the third set value Vc. The third set value Vc is a speed value that is 10% higher than the second set value Vb.
このようにして、制御回路部100で、そのときのベルト回転速度設定値によるベルト12の総回転時間をカウントさせ、所定時間に達する毎に、前回転モードと後回転モードとにおけるベルト回転速度設定値を段階的に上げる。そして、段階的に上げられていく設定値が最終的に用紙挟持搬送時のベルト回転速度設定値Vよりも大きくなった場合に、ベルト12が寿命に達したと判断し、寿命アラーム表示をする。
In this way, the
ここで、上記のベルト総回転時間(積算回転時間)は、累積の記録材搬送枚数としても等価である。すなわち、予め、どのくらいの累積記録材搬送枚数によって、スティックスリップが発生するかを予測しておき、制御回路部100で累積記録材搬送枚数をカウンター機能部100aで積算カウントさせる。そして、所定の累積記録材搬送枚数に応じて、すなわち、所定の累積記録材搬送枚数に達する毎に、前回転モードと後回転モードとにおけるベルト回転速度設定値を段階的に上げる設定値変更制御構成にすることも可能である。
Here, the total belt rotation time (integrated rotation time) is equivalent to the cumulative number of recording material conveyed. That is, it is predicted in advance how many cumulative recording material transported sheets will cause stick slip, and the
また、スティックスリップの発生を、定着モータMの負荷トルクの増加を捉えることで検知することも可能である。モータ電流をサンプリングし、所定の電流値を超えた場合、スティックスリップが発生したと判断する。 It is also possible to detect the occurrence of stick-slip by capturing the increase in the load torque of the fixing motor M. When the motor current is sampled and exceeds a predetermined current value, it is determined that stick-slip has occurred.
すなわち、この実施例4では、前回転モードや後回転モードにおけるベルト12の使用後期の設定速度をベルトの使用初期の設定速度よりも速くすること、ベルトの使用後期の設定速度は画像加熱処理時の設定速度以下であることを特徴としている。後回転モードは、画像加熱処理に引き続いて実行するとともに、該後回転モードの終了に伴いベルト12の回転が停止される。
That is, in the fourth embodiment, the setting speed of the
実施例1〜4は、前回転モードと後回転モードの2つのモードにおけるスティックスリップの判定と、ベルト回転速度設定値の変更制御を行っているが、どちらか一方のモードだけについて上記の判定と、設定値変更制御をする構成にすることもできる。 In the first to fourth embodiments, the stick-slip determination in the two modes of the pre-rotation mode and the post-rotation mode and the change control of the belt rotation speed setting value are performed. Further, it is possible to adopt a configuration in which setting value change control is performed.
図10の定着装置は、電磁誘導加熱方式の画像加熱装置である。31は加熱回転体としてのエンドレスの定着ベルトである。このベルト31は電磁誘導発熱性で可撓性を有するものであり、駆動ローラ32と、テンションローラ33と、加圧パッド34との間に懸回張設されている。加圧パッド34に対しては、ベルト31を挟ませて弾性加圧ローラ35を圧接させて所定幅の定着ニップ部Nを形成させてある。36は励磁コイルユニットであり、駆動ローラ32とテンションローラ33との間のベルト部分の外面に対して近接対面させて配設してある。駆動ローラ32が定着モ−タMにより矢印の時計方向に回転駆動されることで、ベルト31がその内面側が定着ニップ部Nにおいて加圧パッド34の面に摺動しながら矢印の時計方向に回転駆動される。加圧ローラ35はベルト31の回転に従動して回転する。
The fixing device shown in FIG. 10 is an image heating device using an electromagnetic induction heating method.
定着モ−タMがONされ、ベルト31が回転している状態において、励磁コイルユニットの励磁コイルに励磁回路37から高周波電流が供給される。そうすると、励磁コイルユニット36で発生する交番磁束の作用によりベルト31が電磁誘導発熱して昇温する。そのベルト31の温度が温度検知手段TH1・TH2により検知され、制御回路部100にフィードバックされる。制御回路部100は温度検知手段TH1・TH2からの温度検知信号に基づいて、ベルト31が所定の定着温度に温調維持されるように励磁回路37から励磁コイルユニット36の励磁コイルへの供給電力を制御する。この状態において、画像形成部から未定着トナー画像tを担持した用紙Pが定着ニップ部Nに導入されて、トナー画像tが用紙面に加熱・加圧定着される。
In a state where the fixing motor M is turned on and the
このように、ベルト31が、加圧パッド34に密着して摺動する構成の定着装置においても、加圧パッド34とベルト31との摺動によりスティックスリップが発生する。その対策についても、実施例1〜4と同様の方法で対応が可能である。
As described above, even in the fixing device in which the
A・・画像形成装置本体、B・・画像読み取りスキャナ部、C・・画像形成部、D・・シートデッキ、112・・感光体ドラム、115・・転写ローラ、N・・転写ニップ部、118・・定着装置、11・・ステイ、12・・定着ベルト、13・・ヒータ(加熱体)、18・・加圧ローラ、M・・定着モータ、12a・・光反射材(マーキング部)、26・・反射型センサ、22,23・・第1と第2の紙検知センサ(フォトインタラプタ)、24,25・・フラグ部(アクチュエータ)、100・・制御回路部(CPU)
A..Image forming apparatus main body, B..Image reading scanner section, C..Image forming section, D..Sheet deck, 112..Photosensitive drum, 115..Transfer roller, N..Transfer nip section, 118. ..Fusing device, 11 ..Stay, 12 ..Fusing belt, 13 ..Heater (heating body), 18 ..Pressure roller, M ..Fixing motor, 12 a ..Light reflecting material (marking part), 26 ..
Claims (8)
このモード時に検出されたベルトの周速が設定速度を下回った場合、このモード時のベルトの設定速度を速い速度へ変更することを特徴とする画像加熱装置。 An endless belt for heating an image on a recording material, a nip forming member for forming a heating nip with the belt, a sliding member provided slidably with the belt as the belt rotates, and a belt Detecting means for detecting the peripheral speed of the belt, and control means for controlling at least the peripheral speed of the belt during the image heating process to be a set speed in accordance with the output of the detecting means. In an image heating apparatus capable of executing a mode in which a belt is rotated at a set speed slower than that at the time of image heating processing over a set time during non-image heating processing without performing control,
An image heating apparatus characterized in that when the peripheral speed of the belt detected in this mode falls below a set speed, the set speed of the belt in this mode is changed to a high speed.
このモードにおけるベルトの使用後期の設定速度をベルトの使用初期の設定速度よりも速くすることを特徴とする画像加熱装置。 An endless belt for heating the image on the recording material, a nip forming member that forms a heating nip with the belt, and a sliding member that is slidable with the belt as the belt rotates. In an image heating apparatus capable of executing a mode in which a belt is rotated at a set speed slower than that during image heating processing over a set time during non-image heating processing,
An image heating apparatus characterized in that a set speed in the latter half of use of the belt in this mode is made faster than a set speed in the early stage of using the belt.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006218281A JP2008040420A (en) | 2006-08-10 | 2006-08-10 | Image heating device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006218281A JP2008040420A (en) | 2006-08-10 | 2006-08-10 | Image heating device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008040420A true JP2008040420A (en) | 2008-02-21 |
Family
ID=39175446
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006218281A Pending JP2008040420A (en) | 2006-08-10 | 2006-08-10 | Image heating device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2008040420A (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011028037A (en) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-02-10 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Fixing device and image forming apparatus using the same |
| JP2013105112A (en) * | 2011-11-16 | 2013-05-30 | Konica Minolta Business Technologies Inc | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2014215581A (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2014-11-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image formation device |
| JP2017107086A (en) * | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-15 | 株式会社リコー | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2017167333A (en) * | 2016-03-16 | 2017-09-21 | 株式会社リコー | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2018025595A (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-02-15 | キヤノンファインテックニスカ株式会社 | Thermal fixation device |
| US10001734B2 (en) | 2015-12-25 | 2018-06-19 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Fixing device and image forming apparatus including fixing device with vibration dampening |
| JP2020067528A (en) * | 2018-10-23 | 2020-04-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fixing device |
| JP2020126168A (en) * | 2019-02-05 | 2020-08-20 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Fixing device, image forming apparatus, method for controlling fixing device, and computer program |
| JP7533002B2 (en) | 2020-08-07 | 2024-08-14 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
-
2006
- 2006-08-10 JP JP2006218281A patent/JP2008040420A/en active Pending
Cited By (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011028037A (en) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-02-10 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Fixing device and image forming apparatus using the same |
| US8346106B2 (en) | 2009-07-27 | 2013-01-01 | Ricoh Company, Limited | Fixing device and image forming apparatus using same having a second heater outside the recording medium passing area |
| JP2013105112A (en) * | 2011-11-16 | 2013-05-30 | Konica Minolta Business Technologies Inc | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| US8843010B2 (en) | 2011-11-16 | 2014-09-23 | Konica Minolta, Inc. | Fixation unit and image forming apparatus |
| JP2014215581A (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2014-11-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image formation device |
| JP2017107086A (en) * | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-15 | 株式会社リコー | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| US10001734B2 (en) | 2015-12-25 | 2018-06-19 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Fixing device and image forming apparatus including fixing device with vibration dampening |
| JP2017167333A (en) * | 2016-03-16 | 2017-09-21 | 株式会社リコー | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2018025595A (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-02-15 | キヤノンファインテックニスカ株式会社 | Thermal fixation device |
| JP2020067528A (en) * | 2018-10-23 | 2020-04-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fixing device |
| JP7187258B2 (en) | 2018-10-23 | 2022-12-12 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fixing device |
| JP2023011048A (en) * | 2018-10-23 | 2023-01-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fixing device |
| JP7472246B2 (en) | 2018-10-23 | 2024-04-22 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fixing device |
| US12025931B2 (en) | 2018-10-23 | 2024-07-02 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Fixing unit having a sliding sheet with a width in a longitudinal direction smaller than the width of first and second contact members |
| JP2020126168A (en) * | 2019-02-05 | 2020-08-20 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Fixing device, image forming apparatus, method for controlling fixing device, and computer program |
| JP7230548B2 (en) | 2019-02-05 | 2023-03-01 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | FIXING DEVICE, IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS, FIXING DEVICE CONTROL METHOD, AND COMPUTER PROGRAM |
| JP7533002B2 (en) | 2020-08-07 | 2024-08-14 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2008040420A (en) | Image heating device | |
| JP5173464B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP6032898B2 (en) | Fixing device | |
| JP5943559B2 (en) | Fixing device | |
| JP2010164930A (en) | Heat fixing apparatus | |
| JP2002287560A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP4442858B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP4898258B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2006163017A (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP3605042B2 (en) | Fixing device | |
| JP4594013B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP3486571B2 (en) | Fixing device | |
| JP2010164725A (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP2009075439A (en) | Image heating device | |
| JP2009008898A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP4677220B2 (en) | Image heating apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| JPH10142975A (en) | Heating device and image forming device | |
| JP3605069B2 (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP2007058083A (en) | Control method in image forming apparatus | |
| JP2007310077A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2006317512A (en) | Heat fixing-device | |
| JP2007199582A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2000200006A (en) | Heating device | |
| JP3958108B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2010139954A (en) | Image forming apparatus |