JP2007069061A - Sorting system of vegetables and fruits - Google Patents
Sorting system of vegetables and fruits Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007069061A JP2007069061A JP2005255579A JP2005255579A JP2007069061A JP 2007069061 A JP2007069061 A JP 2007069061A JP 2005255579 A JP2005255579 A JP 2005255579A JP 2005255579 A JP2005255579 A JP 2005255579A JP 2007069061 A JP2007069061 A JP 2007069061A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- vegetables
- fruits
- fruit
- residual
- detection means
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Sorting Of Articles (AREA)
- Attitude Control For Articles On Conveyors (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、収穫された青果物の表面に付着した残留農薬によって該青果物を選別する青果物選別システムの技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a technique for a fruit and vegetable sorting system that sorts the fruit and vegetables by a residual pesticide attached to the surface of the harvested fruit and vegetables.
従来より、青果物の糖度や酸度等を測定する内部品質センサによって、青果物を選別する青果物選別システムが公知となっている(例えば、特許文献1参照。)。また、青果物に付着した残留農薬については、該残留農薬濃度等が食品衛生法残留農薬基準値に適合しているか否か測定する必要があるため、従来は委託分析やELISA法を用いた簡易分析による破壊検査にて検査していた(例えば、特許文献2参照。)。
しかし、前記委託分析においては、委託費用が高価であり、且つ分析結果が出るまでに長い時間がかかる等の問題点があった。一方のELISA法を用いた簡易分析においては、数時間で分析結果が出るものの、試料作成作業に時間がかり面倒であった。また、破壊検査であるため、全数検査は不可能であった。
そこで、本発明においては、焦点距離の調節を自動で行うことによって、青果物を破壊したり傷ませることなく付着した残留農薬の種類や量や濃度を測定し、該残留農薬の種類や量や濃度によって青果物を選別する青果物選別システムを提供することを課題としている。
However, the commissioned analysis has a problem that the commissioned cost is expensive and it takes a long time to obtain an analysis result. On the other hand, in the simple analysis using the ELISA method, although an analysis result was obtained in a few hours, the sample preparation work took time and was troublesome. Moreover, since it is a destructive inspection, 100% inspection was impossible.
Therefore, in the present invention, by automatically adjusting the focal length, the type, amount and concentration of the residual agricultural chemical attached without destroying or damaging the fruits and vegetables are measured, and the type, amount or concentration of the residual agricultural chemical is measured. It is an object to provide a fruit and vegetable sorting system that sorts fruits and vegetables by using the above method.
本発明の解決しようとする課題は以上の如くであり、次にこの課題を解決するための手段を説明する。 The problem to be solved by the present invention is as described above. Next, means for solving the problem will be described.
即ち、請求項1においては、赤外分光光度計を利用して青果物の表面における残留農薬濃度等を測定する残留農薬検知手段を備えた青果物選別システムであって、
該青果物を搬送する搬送手段と、
該青果物表面と該残留農薬検知手段との距離が予め定められた焦点距離に達したことを検知する位置検知手段とを具備し、
該青果物表面が焦点距離に達した地点において、該搬送手段を停止して、残留農薬濃度等を測定することを特徴とするものである。
That is, in claim 1, a fruit and vegetable sorting system provided with a residual pesticide detection means for measuring the residual pesticide concentration on the surface of the fruit and vegetables using an infrared spectrophotometer,
Conveying means for conveying the fruits and vegetables;
Position detecting means for detecting that the distance between the fruit and vegetable surface and the residual pesticide detecting means has reached a predetermined focal length;
At the point where the surface of the fruits and vegetables reaches the focal length, the conveying means is stopped and the residual agricultural chemical concentration and the like are measured.
請求項2においては、前記搬送手段にバイパス経路を接続し、該バイパス経路上に前記残留農薬検知手段及び前記位置検知手段を配設したものである。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, a bypass path is connected to the conveying means, and the residual pesticide detecting means and the position detecting means are disposed on the bypass path.
請求項3においては、青果物を載置する載置台を備え、前記残留農薬検知手段近傍に、該載置台を水平回転させる回動手段を設けたものである。 According to a third aspect of the present invention, a mounting table for mounting fruits and vegetables is provided, and a rotating means for horizontally rotating the mounting table is provided in the vicinity of the residual agricultural chemical detecting means.
本発明の効果として、以下に示すような効果を奏する。 As effects of the present invention, the following effects can be obtained.
請求項1においては、大掛かりな装置を利用することなく青果物の位置調節が可能となる。つまり、残留農薬検知手段から青果物表面までの距離を焦点距離に容易に合せることができる。その結果、成分分析精度を高めることができ、高価な委託分析の必要が無くなり、ELISA法のように試料を作成する必要がなくなり、青果物を破壊することなく選別できるので、時間をかければ全数検査ができる。 In claim 1, the position of the fruits and vegetables can be adjusted without using a large-scale device. That is, the distance from the residual pesticide detection means to the fruit and vegetable surface can be easily adjusted to the focal length. As a result, the accuracy of component analysis can be improved, the need for expensive commissioned analysis is eliminated, and there is no need to prepare samples as in the ELISA method, and it is possible to sort without destroying fruits and vegetables. Can do.
請求項2においては、搬送手段による搬送を止めることなく、容易に抜取検査を行なうことができ、バイパス経路で残留農薬を検知する時間に合わせて抜き取り作業ができる。 According to the second aspect of the present invention, the sampling inspection can be easily performed without stopping the conveyance by the conveying means, and the sampling operation can be performed in accordance with the time for detecting the residual agricultural chemicals by the bypass route.
請求項3においては、載置台を回転させるだけで、一つの検体(青果物)に対して複数箇所を容易に測定することが可能となり、残留農薬の検出精度を高めることが可能となる。大掛かりな装置を利用することなく青果物の位置調節が可能となる。つまり、残留農薬検知手段から青果物表面までの距離を容易に焦点距離に合せることができる。その結果、高価な委託分析の必要が無くなり、ELISA法のように試料を作成する必要がなくなり、青果物を破壊することなく選別できるので、時間をかければ全数検査ができる。 According to the third aspect, it is possible to easily measure a plurality of locations for one specimen (fruits and vegetables) only by rotating the mounting table, and it is possible to improve the detection accuracy of residual agricultural chemicals. The position of fruits and vegetables can be adjusted without using a large-scale device. That is, the distance from the residual pesticide detection means to the fruit and vegetable surface can be easily adjusted to the focal length. As a result, there is no need for expensive commissioned analysis, and there is no need to prepare a sample as in the ELISA method, and it is possible to sort without destroying the fruits and vegetables.
次に、発明の実施の形態を説明する。
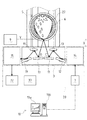
図1は実施例1に係る青果物選別システム1aの平面模式図、図2は載置台6の平面図と側面図、図3は残留農薬検知手段20近傍を示す正面図、図4は同じく一部断面平面図、図5は内部品質センサ4の側面模式図、図6は実施例2に係る残留農薬検知手段20近傍示す平面図、図7は同じく一部断面側面図、図8は実施例2に係る青果物選別システム1bの平面模式図である。
Next, embodiments of the invention will be described.
1 is a schematic plan view of a fruit and
以下では図1から図5を用いて本発明の青果物選別システムの実施の一形態である青果物選別システム1aの詳細構成について説明する。なお、以後の説明では、図1の矢印A・Bで表される方向を青果物6が搬送される方向(搬送方向A・B)とし、青果物6は搬送手段2の上流側の青果物供給装置16から、後述する搬送手段2やバイパス経路30を通過して、階級別ライン2a・2b・2cや廃棄ライン30bへと搬送されるものである。
The detailed configuration of the fruit and
図1に示すように、青果物選別システム1aは、赤外線を用いて青果物6表面に付着した残留農薬の種類や量や濃度(以下、残留農薬濃度等という。)を測定して該測定結果に基づき第1段階目の選別(残留農薬濃度等選別)を行い、光を用いて青果物6の糖度や酸度等の内部品質を測定して該測定結果に基づき第2段階目の選別(内部品質選別)を行なうものである。青果物選別システム1aは主に搬送手段2、バイパス経路30、位置検知手段9、残留農薬検知手段20、農薬選別手段22、内部品質センサ4、内部品質選別手段29、制御手段10等から構成される。
As shown in FIG. 1, the fruit and
青果物選別システム1aで取り扱う青果物6は、イチゴ、蜜柑、オレンジ、メロン、トマトその他の果物類または野菜類の総称であり、残留農薬濃度等や糖度(甘味)や酸度(酸味)等の内部品質によって選別されるものである。詳しくは、後述するように、バイパス経路30に搬送された青果物6が、残留農薬濃度等によって出荷青果物6a(残留農薬濃度等が基準値未満の青果物)と廃棄青果物6b(残留農薬濃度等が基準値以上の青果物)とに選別され、出荷青果物6a及びバイパス経路30に搬送されなかった青果物6は、糖度や酸度等の内部品質によって階級別に選別される。
The fruits and
載置台5はトレイやパンといった搬送用容器の実施の一形態であり、青果物6の表面を傷めることなく搬送するためのものである。
図2に示すように、載置台5は全体が樹脂など剛性の高い材質にて構成されているが、前記青果物6を載置する皿表面はシリコン又はゴムなど剛性の低い弾性を有する材質で構成されており、該皿表面の下部にある底部は吸収をやわらげるゲル剤などが注入されている。これらの構成により搬送中の青果物6の損傷を防いでいる。
The mounting table 5 is an embodiment of a transport container such as a tray or a pan, and is used for transporting the surface of the
As shown in FIG. 2, the mounting table 5 is entirely made of a material having high rigidity such as resin, but the surface of the dish on which the fruits and
ここで、前記載置台5の中央には上下方向に貫通する孔部26が設けられており、図5に示すように、後述する内部品質センサ4の投光部24から照射される光が載置台5によって遮られることがないように構成されている。つまり、該投光部24からの照射光は、後述するバイパス経路30のベルト13a・13b間と、前記載置台5の中央の孔部26を通過して、青果物6を透過して、該受光部25にて検知される。
Here, a
載置台5の側面若しくは底面には、ICタグ35が添付されており、該ICタグ35には予め前記青果物6の生産者番号や収穫日等の生産者情報が記憶されている。これは、後述するように、バイパス経路30を通った青果物6の残留農薬濃度等の測定結果を、後述する演算記憶部10bに記憶しておき、営農指導等に利用するためである。
An
図1に戻って、搬送手段2は青果物6・6・・・を搬送用容器である載置台5・5・・・上に載置して上流側(青果物供給装置16側)から下流側(内部品質選別手段29側)に搬送するものである(搬送方向A)。本実施例における搬送手段2はベルトコンベアであり、図1に示す如く所定の間隔を空けて巻回されたベルト13a・13b等によって構成されている。搬送手段2や、後述するバイパス経路30や、階級別ライン2a・2b・2cは、図3に示すモータ21等によって、駆動される。
Returning to FIG. 1, the transport means 2 places the fruits and
搬送手段2の中途部には、バイパス経路30が接続されており、詳しくは搬送手段2上の前記青果物供給装置16の直下流にバイパス経路30の始端部が接続されて分岐部31が構成され、搬送手段2上の後述する内部品質センサ4にバイパス経路30の終端部が接続されて合流部が構成されている。本実施例では、内部品質センサ4が合流部の役割を担っているが、このような形態に限定するものではなく、内部品質センサ4より上流側の搬送手段2上に別途合流部を設けても良いし、該終端部を他の選別経路に連結しても良い。
A
バイパス経路30は、搬送手段2のように2本のベルト間に間隔を設ける必要は無く、1本のライン等で構成すると、後述する青果物6の位置調節に大掛かりな装置が不要となり好適である。
バイパス経路30には、位置検知手段9と、残留農薬検知手段20と、農薬選別手段22と、該農薬選別手段22から分岐して延設される出荷ライン30aと廃棄ライン30bとが配設されている。前述したように、該出荷ライン30aの終端部(バイパス経路30の終端部)は、搬送手段2上の内部品質センサ4に接続される。
The
In the
図1、図3、図4に示すように、バイパス経路30においては、青果物6が載置された載置台5は残留農薬検知手段20の拡散反射装置3の近傍を通過させるようにしている。
拡散反射装置3は、投光手段7から発した赤外線を分割して合成(干渉)し、照射用反射手段12へと投光する干渉計14と、該合成された赤外線を下記照射用ミラー11へと導く照射用反射手段12・13と、該照射用反射手段12・13によって導かれた該赤外線を反射して載置台5上の青果物6側面に照射(図中、矢印C)する照射用ミラー11と、該青果物6で反射(図中、矢印D)した赤外線を受光用反射手段18・19及び光路変更手段15へと反射する受光用ミラー17と、該受光用ミラー17から投光された赤外線を後方の検知器32に投光する光路変更手段15等から構成されるものである。
残留農薬検知手段20は、前記投光手段7と、前記拡散反射装置3と、前記光路変更手段15の後方に配設されて、光路変更手段15からの赤外線を検知し、検知した赤外線の光学的情報を出力信号としてAD変換器33へ送信する検知器32と、該出力信号をデジタル化した後に制御手段10へ送信するAD変換器33等から構成されている。
As shown in FIGS. 1, 3, and 4, in the
The diffuse
The residual pesticide detection means 20 is disposed behind the
残留農薬検知手段20では、後述するように、バイパス経路30に搬送された青果物6が該残留農薬検知手段20近傍に送られてくると、投光手段7より干渉計14や照射用ミラー11を介して赤外線を照射し、該青果物6で反射した反射光を受光用ミラー17や光路変更手段15を介して検知器32にて検知する。該検知器32で検知された反射光の光学的情報は、AD変換器33にてデジタル信号に変換されて、制御手段10へと送信される。そして、後述する制御手段10にて、スペクトル分析を行なうことにより、バイパス経路30を通過した青果物6表面に付着した残留農薬濃度等の測定や、及び該青果物6が出荷できる青果物であるか出荷できない青果物であるかの判断を行なう。
In the residual pesticide detection means 20, as will be described later, when the fruits and
本実施例では、赤外線による残留農薬検知手段20を用いて青果物6の表面に付着した残留農薬濃度等を測定するシステムであるため、照射用ミラー11及び受光用ミラー17と測定される青果物6表面との距離を最適な距離(以下、焦点距離とする。)に調節しなければ、正確な青果物6表面のスペクトルを得ることができない。
詳しくは、照射用ミラー11及び受光用ミラー17と測定される青果物6表面との距離が最適でない場合は、検知器32で受ける反射光の強度が弱くなるため、スペクトルの波形において波長に応じた強度の違い(スペクトルの凹凸)がはっきりと識別できなくなり、その結果残留農薬の種類や濃度が正確に判断できなくなるのである。
In this embodiment, since the residual agricultural chemical concentration attached to the surface of the fruits and
Specifically, when the distance between the
そこで、本青果物選別システム1aにおいては、図1に示すように、バイパス経路30上の残留農薬検知手段20の直前に、青果物6の搬送位置の位置検知手段9が配設されている。該位置検知手段9は、バイパス経路30上を搬送されてきた青果物6の表面(残留農薬検知手段20側の先端)が、残留農薬検知手段20から焦点距離だけ離れた位置に達したか否かを判断するものである。
詳しくは、位置検知手段9は、残留農薬検知手段20の焦点の高さと略一致する高さの青果物6の表面と、換言すれば青果物6の焦点高さにおける残留農薬検知手段側の先端と、残留農薬検知手段20との距離Xが、残留農薬検知手段20固有の焦点距離と略一致したことを検知するものである。つまり、載置台5の位置ではなく青果物6の先端位置を直接検知するようにしている。
Therefore, in the present fruit and
Specifically, the position detection means 9 includes a surface of the fruit and
具体的には、後述するように演算記憶部10bで得られるスペクトルのエネルギー若しくは強度若しくは強度の凹凸が大きくなる、青果物6の表面と残留農薬検知手段20との距離を、予め焦点距離として設定しておき、残留農薬検知手段20から該焦点距離だけ離れた地点に光センサ等の位置検知手段9を配設する。そして、該光センサ等の位置検知手段9から発せられる赤外線Y等が遮られたり、反射したことを感知することにより、青果物6表面が残留農薬検知手段20から焦点距離だけ離れた位置に到達したことを検知するのである。そして、該位置検知手段9は、青果物6が焦点距離に到達すると到達信号を制御手段10の演算記憶部10bに送信し、搬送を停止する構成となっている。後述するように、到達信号が直接バイパス経路30のモータ21や残留農薬検知手段20に送られる構成であっても良い。但し、残留農薬検知手段20の近傍に超音波センサ等の距離センサを配置して、前記焦点距離に青果物6が達すると搬送を停止する構成とすることも可能である。
Specifically, as will be described later, the distance between the surface of the fruits and
図1に戻って、農薬選別手段22は、バイパス経路30上の前記残留農薬検知手段20より下流側に設けられ、残留農薬検知手段20及び制御手段10による判断結果(測定された残留農薬濃度等が基準値未満であるか否か)に基づいて青果物6を出荷青果物6aと廃棄青果物6bとに選別し、該出荷青果物6aを前記出荷ライン30aへ、該廃棄青果物6bを前記廃棄ライン30bへと載置する。
Returning to FIG. 1, the agrochemical sorting means 22 is provided on the downstream side of the residual pesticide detection means 20 on the
読取手段34は、残留農薬検知手段20の直後に配設されており、前記残留農薬検知手段20によって残留農薬濃度等が測定された青果物6の載置台5に添付されたICタグ35に記憶された生産者情報を読み取ることができる。前記残留農薬検知手段20で測定された青果物6の残留農薬濃度等が基準値以上である場合に、該ICタグ35に記憶された青果物6の生産者情報が読取られ、読取られた生産者情報は後述する制御手段10へ送られて、残留農薬検知手段20によって測定された残留農薬濃度等と共に演算記憶部10bに記憶される。
但し、読取手段34は、残留農薬検知手段20の上流側や、廃棄ライン30b上に配設されても良いものである。
The
However, the
青果物供給装置16は搬送手段2の最上流部に設けられ、搬送手段2に青果物6を載置する前の載置台5・5・・・を供給する。
The fruit and
内部品質センサ4は青果物6の内部品質である糖度(甘味)や酸度(酸味)等の内部品質を光学的に(光を用いて非破壊で)判断するものであり、搬送手段2とバイパス経路30の合流部に設けられている。
The
図5に示す如く、内部品質センサ4は主に筐体23、投光部24、受光部25等で構成される。
筐体23は内部品質センサ4の他の部材を固定する構造体であるとともに投光部24および受光部25に外部からの光が影響することを防止するための被覆手段を兼ねる。筐体23は略直方体の箱であり、開口部23aおよび開口部23bが筐体23の互いに対向する側面に穿設され、搬送手段2が開口部23a・開口部23bを貫通している。搬送手段2上を搬送されてきた青果物6は、載置台5に載置されたまま開口部23aより筐体23の内部に進入し、開口部23bから筐体23の外部に排出される。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
The
投光部24は青果物6の糖度または酸度等の内部品質を測定するための光(赤外線やレーザー光等)を青果物6に照射するものであり、ケーブル24aにより制御手段10に接続されている。投光部24は具体的にはランプまたはLED等で構成される。なお、投光部24により青果物6に照射される光は、該青果物6の種類等に応じてその種類や波長、強度等を適宜選択する必要がある。また、投光部24はランプ等の光源やレンズが設けられ、ケーブル24aにより該光源に電力が供給される形式でも良く、あるいは光源が制御手段10側に設けられ、ケーブル24aを光ファイバーとして投光部24のレンズに光を供給する形式としても良い。
受光部25は、投光部24により照射され青果物6内を通過してきた透過光を受けるものであり、ケーブル25aにより制御手段10に接続されている。受光部25は具体的にはフォトダイオードやフォトトランジスタやCCD等で構成される。
The
The
投光部24は筐体23内部において搬送手段2の下方に配置され、かつ受光部25は筐体23内部において搬送手段2の上方に配置される。そして、投光部24より照射される光は載置台5の中央部に穿設された孔部26を通過し、該載置台5上に載置された青果物6を透過して受光部25に受光される。
前述したように、搬送手段2のベルト13aおよびベルト13bは所定の間隔を空けて巻回されており、ベルト13aとベルト13bとの間を投光部24からの光が通過するように構成されている。従って、搬送手段2が光路(投光部24から受光部25までの光の経路)を遮ることがない。
The
As described above, the
受光部25により受光される光(青果物6の透過光)は、投光部24により照射される光と比較すると、特定の波長成分が減少している。これは、青果物6中に含まれる糖度に係る成分や酸度に係る成分等が特定の波長成分を吸収することに起因している。
従って、この吸収量を測定する(青果物6が光路を遮っていない状態で受光部25が受光している時の特定波長成分と、青果物6が光路を遮っている状態で受光部25が受光している時の特定波長成分とを比較する)ことにより、光が透過した部位に存在する青果物6の糖度に係る成分や、酸度に係る成分等の量(より厳密には、糖度に係る成分分子の個数や酸度に係る成分分子等の個数)を測定することが可能である。
The light received by the light receiving unit 25 (transmitted light from the fruits and vegetables 6) has a reduced specific wavelength component as compared with the light irradiated by the
Therefore, the amount of absorption is measured (the specific wavelength component when the
なお、本実施例においては投光部24が搬送手段2の下方、受光部25が搬送手段2の上方に配置される構成であるが搬送手段の側方に配置しても良く、光路の方向と搬送方向Aとの関係(成す角度および位置関係)は限定されない。
In the present embodiment, the
図1に戻って、内部品質選別手段29は搬送手段2の最下流部に設けられ、内部品質センサ4による判断結果(内部品質に係る情報)に基づいて青果物6を選別する。換言すれば、該内部品質選別手段29は、内部品質センサ4によって測定された階級別(内部品質別)に、青果物6・6aを階級別ライン2a・2b・2cへと載置するものである。
Returning to FIG. 1, the internal quality selection means 29 is provided in the most downstream part of the transport means 2, and selects the fruits and
制御手段10は、図1に示すように、青果物選別システム1を構成する搬送手段2、分岐部31、バイパス経路30、位置検知手段9、残留農薬検知手段20、農薬選別手段22、内部品質センサ4、内部品質選別手段29、読取手段34等を制御するものであり、これらの動作を制御するためのプログラムが格納されており、位置検知手段9や残留農薬検知手段20や読取手段34や内部品質センサ4等から種々の情報を取得したり、該残留農薬検知手段20等へ電力を供給したり、あるいは該バイパス経路30や残留農薬検知手段20や農薬選別手段22等に動作指令(信号)を送信したりすることが可能である。
As shown in FIG. 1, the control means 10 includes a transport means 2, a
図1及び図4に示すように、制御手段10は、表示部10aと演算記憶部10bから構成されている。該演算記憶部10bは、位置検知手段9からの到達信号を受信した際に、モータ21を停止してバイパス経路30を停止させたり、残留農薬検知手段20に青果物6の残留農薬濃度等の測定を開始させたりする。
但し、該到達信号が、演算記憶部10bを介さずに、直接モータ21や残留農薬検知手段20に送信される構成としても良い。即ち、青果物6表面と残留農薬検知手段20との距離Xが焦点距離となった際に、位置検知手段9が、直接モータ21を停止させ、残留農薬検知手段20に青果物6表面の残留農薬濃度等の測定を開始させる構成であっても良い。
As shown in FIG.1 and FIG.4, the control means 10 is comprised from the
However, the arrival signal may be transmitted directly to the
そして、演算記憶部10bでは、前記残留農薬検知手段20から送信されてきた反射光に関する出力信号をスペクトルに変換する。詳しくは、前記検知器32で検知した反射光の情報がAD変換器33を介してデジタル信号として制御手段10に送信され、該制御手段10の演算記憶部10bでは、受信した反射光の時間関数としての波形を、周波数の関数としてのスペクトルにフーリエ変換する。
Then, the
そして、図4に示すように、該フーリエ変換の結果はスペクトルとして表示部10aにて表示される。
演算記憶部10bでは、演算されたスペクトルを画像処理し、青果物6毎に求められた残留農薬濃度等が基準値以内であるか否かを自動で判断して、農薬選別手段22によって青果物6・6・・・を出荷青果物6a(基準値以内の青果物)と廃棄青果物6b(基準値超の青果物)に選別する。つまり、出荷青果物のみ、出荷ライン30aに載せて前記内部品質センサ4へ搬送することができるのである。
但し、作業者が、表示されたスペクトルを目視で判断し、青果物6毎に求められた残留農薬濃度等が基準値以内であるか否かを判断し、該判断結果によって作業者が青果物6・6・・・を出荷青果物6aと廃棄青果物6bに選別する構成であっても良い。
Then, as shown in FIG. 4, the result of the Fourier transform is displayed as a spectrum on the
The
However, the operator visually determines the displayed spectrum, determines whether or not the residual pesticide concentration obtained for each of the fruits and
具体的には、演算記憶部10bが、該スペクトルと残留農薬の種類ごとに予め実験的に得られた変換テーブルに基いて、残留農薬の種類を判別し、残留農薬濃度を求める。
該残留農薬濃度等の測定が終了すると、制御手段10はモータ21を始動して前記バイパス経路30の駆動を再開させる。前述同様、制御手段10を介さずに、残留農薬濃度等の測定が終了すると、残留農薬検知手段20が直接モータ21を始動してバイパス経路30の駆動を再開させる構成であっても良い。
Specifically, the
When the measurement of the residual pesticide concentration and the like is completed, the control means 10 starts the
このとき、演算記憶部10bは、読取手段34で読取られた出荷青果物6aや廃棄青果物6bの生産者情報等を記憶するものとする。また、生産者毎の出荷青果物6aと廃棄青果物6bの割合が演算されて、該割合や出荷青果物数や廃棄青果物数等が記憶されており、表示部10aにてそれらの数値が閲覧できる。これによって、廃棄青果物6bと判断される頻度が高い生産者には、出荷停止等の対策をとることも可能となる。
At this time, the
さらに、該制御手段10は分岐部31における載置台5のバイパス経路30への抜き取りも制御している。
また、該演算記憶部10bでは、内部品質センサ4によって測定された内部品質に基づいて青果物6・6・・・を階級付けし、内部品質選別手段29に該青果物6・6・・・を階級別に選別させる。
Further, the control means 10 controls the extraction of the mounting table 5 from the branching
Further, in the
以下では本実施例の青果物選別システム1による選別作業について説明する。
図1に示すように、搬送手段2上を搬送されてきた青果物6・6・・・のうち、制御手段10にて予め設定された割合の青果物6・6・・・が分岐部31からバイパス経路30へと搬送される(搬送方向B)。青果物6は該バイパス経路30上を残留農薬検知手段20へと向って搬送され、青果物6表面(残留農薬検知手段20側の先端)が残留農薬検知手段20から焦点距離だけ離れた位置に達すると、到達信号が位置検知手段9からバイパス経路30のモータ21及び残留農薬検知手段20へと送られる。
Hereinafter, the sorting operation by the fruit and vegetable sorting system 1 of the present embodiment will be described.
As shown in FIG. 1, among the
図3及び図4に示すように、該モータ21は、前記到達信号を受信するとバイパス経路30の搬送を停止し、残留農薬検知手段20では、図4に示すように、投光手段7から干渉計14や照射用ミラー11を介して赤外線が青果物6に照射され、該青果物6で反射した反射光は受光用ミラー17や光路変更手段15を介して検知器32にて検知される。そして、吸収された赤外線の光学的情報はAD変換器33にてデジタル信号に変換されて制御手段10に送信される(すなわち、制御手段10は残留農薬検知手段20から青果物6の光学的情報を取得する)。
演算記憶部10bでは、該光学的情報をスペクトルに変換して、スペクトル分析を行なう。詳しくは、該スペクトルに基いて残留農薬濃度等を演算し、該残留農薬濃度等が食品衛生法残留農薬基準値に適合しているか否かの判断を行う。
As shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, when the
The
次に、青果物選別システム1bの実施例2について説明する。
青果物選別システム1bは、青果物選別システム1aに、青果物6が載置された載置台5を水平面内で回転(自転)させる手段を具備したものである。具体的には、図6に示すように、前記残留農薬検知手段20近傍のバイパス経路30上に、載置台5の直径と略同距離だけ離間した二つのローラ40・40を配設する。図7に示すように、該ローラ40・40は下方にはモータ41・41が配設されており、該モータ41・41によってローラ軸42・42等を介して該ローラ40・40が回動する構成となっている。
前記位置検知手段9は、ローラ40の残留農薬検知手段20側に配設される。
Next, Example 2 of the fruit and
The fruit and
The position detection means 9 is disposed on the
つまり、残留農薬検知手段20の手前において、該ローラ40・40によって該載置台5を回動させて、位置検知手段9によって青果物6表面が残留農薬検知手段20から焦点距離だけ離れた位置に到達したことを検知することによって、残留農薬濃度等の測定を行なうのである。
本実施例では、2つのローラ40・40によって載置台5を挟持して回動する構成としたが、配設するローラ40の個数は2つに限定するものではなく、載置台5の挟持を安定させるために3つ以上のローラ40・40・・・によって載置台5を挟持する構成としても良い。また、本実施例では載置台5の両側の側面にローラ40・40を当接させて回転させる構成としているが、青果物6の測定位置の下方に昇降可能に円盤を設けて、円盤上に載置台5を載せて持ち上げ、回転してから降ろす構成とすることも可能である。
That is, before the residual pesticide detection means 20, the mounting table 5 is rotated by the
In this embodiment, the mounting table 5 is sandwiched and rotated by the two
青果物選別システム1bでは、ローラ40・40によって載置台5を回動させことにより、1つの青果物6に対して残留農薬濃度等の測定を複数箇所について行なうことができる。そのため、青果物6表面に付着した残留農薬濃度等に濃淡があった場合にも、最大値や平均値を算出することができ、残留農薬濃度等の測定の信頼性を向上させることができる。
また、青果物6のヘタ等の残留農薬濃度等を測定してしまうと、ヘタ等の葉緑素等によって残留農薬濃度等の正常なスペクトルが得られないが、そのようなスペクトルを異常値として処理して、再度青果物6を回動させて別の箇所(可食部等)の残留農薬濃度等を測定することが可能である。つまり、青果物6の載置台5への載置方向(載置状態)を問わず、残留農薬濃度等の測定が可能となる。
In the fruit and
In addition, if the residual agricultural chemical concentration such as the spatter of fruits and
上記のように、ローラ40・40による載置台5の回動中に、青果物6表面の位置を検知する構成の場合には、バイパス経路30上の載置台5の搬送をスムーズなものとするために、図8に示す如く、残留農薬検知手段20手前にてバイパス経路30が側方に折れ曲がった構成とすると好適である。
As described above, in the case of detecting the position of the surface of the fruits and
このように、赤外分光光度計を利用して青果物6の表面における残留農薬濃度等を測定する残留農薬検知手段20を備えた青果物選別システム1a・1bであって、該青果物6を搬送する搬送手段2と、該青果物6表面と該残留農薬検知手段20との距離が予め定められた焦点距離に達したことを検知する位置検知手段9とを具備し、該青果物6表面が焦点距離に達した地点において、該搬送手段を停止して、残留農薬濃度等を測定するので、大掛かりな装置を利用することなく青果物6の位置調節が可能となる。つまり、残留農薬検知手段20から青果物6表面までの距離を容易に焦点距離に合せることができる。その結果、成分分析精度を高めることができ、高価な委託分析の必要が無くなり、ELISA法のように試料を作成する必要がなくなり、青果物6を破壊することなく選別できるので、時間をかければ全数検査ができる。
As described above, the fruit and
また、前記搬送手段2にバイパス経路30を接続し、該バイパス経路30上に前記残留農薬検知手段20及び前記位置検知手段9を配設したので、搬送手段2による搬送を止めることなく、容易に抜取検査を行なうことができ、バイパス経路30で残留農薬を検知する時間に合わせて抜き取り作業ができる。
Further, since the
また、青果物6を載置する載置台5を備え、前記残留農薬検知手段20近傍に、該載置台5を水平回転させる回動手段40を設けたので、載置台5を回転させるだけで、一つの検体(青果物6)に対して複数箇所を容易に測定することが可能となり、残留農薬の検出精度を高めることが可能となる。大掛かりな装置を利用することなく青果物6の位置調節が可能となる。つまり、残留農薬検知手段20から青果物6表面までの距離を容易に焦点距離に合せることできる。その結果、高価な委託分析の必要が無くなり、ELISA法のように試料を作成する必要がなくなり、青果物を破壊することなく選別できるので、時間をかければ全数検査ができる。
Further, since the mounting table 5 for mounting the fruits and
1a・1b 青果物選別システム
2 搬送手段
4 内部品質センサ
5 載置台
6 青果物
9 位置検知手段
10 制御手段
20 残留農薬検知手段
22 農薬選別手段
30 バイパス経路
40 回動手段(ローラ)
1a, 1b Fruits and
Claims (3)
該青果物を搬送する搬送手段と、
該青果物表面と該残留農薬検知手段との距離が予め定められた焦点距離に達したことを検知する位置検知手段とを具備し、
該青果物表面が焦点距離に達した地点において、該搬送手段を停止して、残留農薬濃度等を測定することを特徴とする青果物選別システム。 A fruit and vegetable sorting system equipped with a residual pesticide detection means for measuring the residual pesticide concentration on the surface of the fruit and vegetables using an infrared spectrophotometer,
Conveying means for conveying the fruits and vegetables;
Position detecting means for detecting that the distance between the fruit and vegetable surface and the residual pesticide detecting means has reached a predetermined focal length;
A fruit and vegetable sorting system characterized by measuring the concentration of residual agricultural chemicals and the like by stopping the conveying means at a point where the surface of the fruit and vegetables reaches a focal length.
前記残留農薬検知手段近傍に、該載置台を水平回転させる回動手段を設けたことを特徴とする請求項1若しくは請求項2に記載の青果物選別システム。 It has a mounting table for mounting fruits and vegetables,
The fruit and vegetable sorting system according to claim 1 or 2, wherein a rotating means for horizontally rotating the mounting table is provided in the vicinity of the residual pesticide detecting means.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005255579A JP2007069061A (en) | 2005-09-02 | 2005-09-02 | Sorting system of vegetables and fruits |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005255579A JP2007069061A (en) | 2005-09-02 | 2005-09-02 | Sorting system of vegetables and fruits |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007069061A true JP2007069061A (en) | 2007-03-22 |
Family
ID=37930983
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005255579A Pending JP2007069061A (en) | 2005-09-02 | 2005-09-02 | Sorting system of vegetables and fruits |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2007069061A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102645405A (en) * | 2012-03-29 | 2012-08-22 | 中国农业大学 | Rotary positioning device and detection system for detecting pesticide residue on surface of fruits |
| JP2012192999A (en) * | 2011-03-15 | 2012-10-11 | Yanmar Co Ltd | Fruit sorting system |
| JP2016142556A (en) * | 2015-01-30 | 2016-08-08 | 株式会社島津製作所 | Resin identification device |
| JP2020535412A (en) * | 2017-09-26 | 2020-12-03 | エルジー・ケム・リミテッド | Optical film adhesion system |
| JP2021000618A (en) * | 2019-06-20 | 2021-01-07 | 済南申塗鎖具有限公司 | Automatic sampling inspection system used for measuring quality of electronic components |
| JP2021059478A (en) * | 2019-10-09 | 2021-04-15 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Manufacturing method of glass sheet and manufacturing apparatus of glass sheet |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001252625A (en) * | 2000-03-14 | 2001-09-18 | Kyowa Kikai Kk | Article inspection apparatus |
| JP2004066157A (en) * | 2002-08-08 | 2004-03-04 | Maki Mfg Co Ltd | Measurement method and measurement instruments for agricultural product sorting |
| JP2005177627A (en) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-07 | Yanmar Co Ltd | Sorting method of vegetables and fruits |
-
2005
- 2005-09-02 JP JP2005255579A patent/JP2007069061A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001252625A (en) * | 2000-03-14 | 2001-09-18 | Kyowa Kikai Kk | Article inspection apparatus |
| JP2004066157A (en) * | 2002-08-08 | 2004-03-04 | Maki Mfg Co Ltd | Measurement method and measurement instruments for agricultural product sorting |
| JP2005177627A (en) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-07 | Yanmar Co Ltd | Sorting method of vegetables and fruits |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012192999A (en) * | 2011-03-15 | 2012-10-11 | Yanmar Co Ltd | Fruit sorting system |
| CN102645405A (en) * | 2012-03-29 | 2012-08-22 | 中国农业大学 | Rotary positioning device and detection system for detecting pesticide residue on surface of fruits |
| JP2016142556A (en) * | 2015-01-30 | 2016-08-08 | 株式会社島津製作所 | Resin identification device |
| JP2020535412A (en) * | 2017-09-26 | 2020-12-03 | エルジー・ケム・リミテッド | Optical film adhesion system |
| JP7141449B2 (en) | 2017-09-26 | 2022-09-22 | 杉金光電(蘇州)有限公司 | Optical film deposition system |
| JP2021000618A (en) * | 2019-06-20 | 2021-01-07 | 済南申塗鎖具有限公司 | Automatic sampling inspection system used for measuring quality of electronic components |
| JP2021059478A (en) * | 2019-10-09 | 2021-04-15 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Manufacturing method of glass sheet and manufacturing apparatus of glass sheet |
| WO2021070588A1 (en) * | 2019-10-09 | 2021-04-15 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Method and device for manufacturing glass plate |
| JP7366344B2 (en) | 2019-10-09 | 2023-10-23 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Glass plate manufacturing method and its manufacturing device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7091388B2 (en) | Methods and devices for detecting substances | |
| AU2004304823B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for detecting damage in plant products | |
| JP3693361B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for optical inspection of transparent containers | |
| JP4209926B1 (en) | Packaged food inspection equipment using near infrared rays | |
| JP2007069061A (en) | Sorting system of vegetables and fruits | |
| NZ517460A (en) | Apparatus for inspection of fruit and vegetables by spectral analysis of light transmitted through the fruit body | |
| JP2006267037A (en) | Internal quality evaluating apparatus and internal quality evaluation method of fresh product | |
| JP2007044659A (en) | Vegetable and fruit sorting system | |
| JP2008014873A (en) | Device for determining internal quality | |
| JP2007069060A (en) | Sorting system of vegetables and fruits | |
| AU2019326499B2 (en) | Light condensing device for inspecting quality inside fruits and vegetables, system comprising same, and use method thereof | |
| JP5386114B2 (en) | Fruit and vegetable quality judgment device | |
| JP2011112575A (en) | Non-destructive quality determination device | |
| JP4733490B2 (en) | Fruit and vegetable sorting system | |
| JP2007029847A (en) | Vegetable and fruit sorting mechanism | |
| JP2007044658A (en) | Vegetable and fruit sorting apparatus | |
| JP4713731B2 (en) | Equipment for measuring the internal quality of fruits and vegetables | |
| JP4340492B2 (en) | Agricultural product sorting equipment | |
| JP2007071550A (en) | Sensor of agricultural chemicals | |
| JP2005046794A5 (en) | ||
| JP2007327906A (en) | Component analyzing system | |
| JP7325383B2 (en) | Article inspection device | |
| JP2004219376A (en) | Quality evaluation system for fruits and vegetables | |
| JP2004361346A (en) | Agricultural product non-destructive quality determining apparatus | |
| JP2006337255A (en) | Apparatus for nondestructively determining residual agricultural chemical |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20071128 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100831 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100921 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101118 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Effective date: 20101214 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Effective date: 20110412 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 |