JP2005065184A - Solid state image sensor and its driving method, and video camera and still camera using it - Google Patents
Solid state image sensor and its driving method, and video camera and still camera using it Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005065184A JP2005065184A JP2003296326A JP2003296326A JP2005065184A JP 2005065184 A JP2005065184 A JP 2005065184A JP 2003296326 A JP2003296326 A JP 2003296326A JP 2003296326 A JP2003296326 A JP 2003296326A JP 2005065184 A JP2005065184 A JP 2005065184A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- imaging device
- solid
- state imaging
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 25
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 title abstract 3
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims description 62
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 claims description 29
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 29
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 26
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 abstract description 55
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 25
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 17
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 101150082606 VSIG1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000593 degrading effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005375 photometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、ビデオカメラやデジタルスチルカメラ用等のイメージ入力装置等として広範に用いられる固体撮像装置及びその駆動方法、並びにその固体撮像装置を用いたビデオカメラ及びスチルカメラに関するものである。 The present invention relates to a solid-state imaging device widely used as an image input device for a video camera or a digital still camera, a driving method thereof, and a video camera and a still camera using the solid-state imaging device.
近年、高解像化のため、微細化プロセスを用いた光電変換素子のセルサイズ縮小が精力的に行われる一方、光電変換信号出力が低下すること等から、光電変換信号を増幅して出力することが可能な増幅型の光電変換装置が注目されている。このような増幅型光電変換装置には、MOS型、AMI、CMD、BASIS等がある。 In recent years, the cell size of photoelectric conversion elements using a miniaturization process has been vigorously reduced for high resolution, while the photoelectric conversion signal output has been reduced, and the photoelectric conversion signal is amplified and output. An amplifying photoelectric conversion device capable of this is attracting attention. Such amplification type photoelectric conversion devices include MOS type, AMI, CMD, BASIS and the like.
このうち、MOS型はフォトダイオードで発生した光キャリアをMOSトランジスタのゲート電極に蓄積し、走査回路からの駆動タイミングに従ってその電位変化を出力部へ電荷増幅して出力するものである。近年、このMOS型のうち光電変換部やその周辺回路部を含め全てCMOSプロセスで実現するCMOS型光電変換装置が特に注目されている。 Among these, the MOS type stores light carriers generated in the photodiode in the gate electrode of the MOS transistor, and amplifies the potential change to the output unit according to the drive timing from the scanning circuit and outputs it. In recent years, a CMOS type photoelectric conversion device that is realized by a CMOS process, including the photoelectric conversion unit and its peripheral circuit unit, of the MOS type has attracted particular attention.
ところが、CMOS型光電変換装置は画素内の電荷増幅アンプで信号電荷の増幅を行う反面、電荷増幅アンプの入力MOSのVthやアンプゲインのバラツキが、信号のSNの劣化を招くという課題があった。 However, while the CMOS type photoelectric conversion device amplifies the signal charge with the charge amplification amplifier in the pixel, there is a problem that the variation of the Vth of the input MOS of the charge amplification amplifier and the variation of the amplifier gain causes the SN of the signal to deteriorate. .
そこで、本願発明者等は、この課題を解決した固体撮像装置を特開平11−274454号公報で提案している(特許文献1参照)。図10は同公報の画素構成を示す等価回路図、図11は図10の画素を用いた光電変換装置を示す等価回路図である。 Accordingly, the inventors of the present application have proposed a solid-state imaging device that solves this problem in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 11-274454 (see Patent Document 1). FIG. 10 is an equivalent circuit diagram showing the pixel configuration of the publication, and FIG. 11 is an equivalent circuit diagram showing a photoelectric conversion device using the pixel of FIG.
まず、同公報のものは、図10に示すようにフォトダイオードPD、MOSトランジスタから成る転送スイッチQ1を備えている。また、Q2は拡散浮遊領域をリセットするためのリセットMOSトランジスタのリセットスイッチ、Q3は拡散浮遊領域がゲートに接続され、ソース側の負荷として定電流源812が接続されたソースフォロワ増幅回路の入力MOSトランジスタ、Q4は読み出し画素を選択するための選択スイッチである。
First, as shown in FIG. 10, the publication includes a photodiode PD and a transfer switch Q1 composed of a MOS transistor. Q2 is a reset switch of a reset MOS transistor for resetting the diffusion floating region, and Q3 is an input MOS of a source follower amplifier circuit in which the diffusion floating region is connected to the gate and a constant
図11はこの画素セルを用いた固体撮像装置を示す等価回路図であるが、簡単のため画素を3行3列として示す。動作を説明すると、まず、リセットスイッチQ2によりソースフォロワ増幅回路の入力ゲートにリセット電圧を入力するリセット動作と、選択スイッチQ4による行選択を行う。 FIG. 11 is an equivalent circuit diagram showing a solid-state imaging device using this pixel cell. For simplicity, the pixels are shown in 3 rows and 3 columns. The operation will be described. First, a reset operation for inputting a reset voltage to the input gate of the source follower amplifier circuit by the reset switch Q2 and row selection by the selection switch Q4 are performed.
次に、ソースフォロワ増幅回路の入力ノードにおける拡散浮遊領域のゲートをフローティングにし、リセットノイズ及びソースフォロワ入力MOSトランジスタQ3の閾値電圧のばらつき等の固定パターンノイズからなるノイズ成分の読み出しを行い、その情報を信号蓄積部805に一旦保持する。その後、転送スイッチQ1を開閉し、光信号により生成されたフォトダイオードPDの蓄積電荷をソースフォロワ増幅回路の入力ノードに転送し、前述のノイズ成分と光信号成分の和を読み出し、信号蓄積部805に保持する。
Next, the gate of the diffusion floating region at the input node of the source follower amplifier circuit is floated, and a noise component consisting of reset noise and fixed pattern noise such as variations in the threshold voltage of the source follower input MOS transistor Q3 is read out. Is temporarily held in the
次いで、転送スイッチ808、808′を介して共通信号線809、809′にノイズ成分の信号と、ノイズ成分と光信号成分の和の信号とをそれぞれ読み出し、各出力アンプ810、810′を介して出力811、811′として出力する。その後、出力811、811′の差をとることでリセットノイズ及び固定パターンノイズを除去して、光信号成分のみを取り出すことで、SNの高い画像信号が得られる。
Next, the signal of the noise component and the signal of the sum of the noise component and the optical signal component are read out to the
また、固体撮像装置の全行の蓄積タイミングを同時とする方法が、特開2002−320141号公報で提案されている(特許文献2参照)。同公報の方法は、全行のフォトダイオードを同時にリセット解除することによって信号蓄積を開始し、全行のフォトダイオードの蓄積電荷を同時にソースフォロワ増幅回路の入力ノードに転送することによって信号蓄積を終了する。その後、一行毎にソースフォロワ増幅回路の出力を読み出し、次にソースフォロワ増幅回路の入力ゲートにリセット電圧を入力してリセット動作を行った後、ソースフォロワ入力MOSトランジスタの閾値電圧のばらつき等の固定パターンノイズからなるノイズ成分を読み出し、この2つの出力値の差分をとって信号を得るものである。
特許文献1の固体撮像装置は、一行づつ順次、読み出しを行うものである。このような固体撮像装置では、光信号により生成されたフォトダイオードの蓄積電荷がソースフォロワ増幅回路の入力ノードに転送されると、次の信号電荷蓄積が開始されるので、各行毎に信号蓄積開始、終了のタイミングがずれてしまう。そのため、撮像する被写体が早い動きをしている場合には、被写体の形状が歪んで捕らえられたり、蛍光灯のフリッカが画像に現れる場合があった。
The solid-state imaging device disclosed in
また、特許文献2の方法は、差分をとるリセット出力が信号電荷が転送される前のリセットによるものではない。従って、拡散浮遊領域をリセットする時のリセットノイズを差し引くことができず、得られる出力のSNが悪くなってしまう問題があった。
Further, the method of
本発明は、上記従来の問題点に鑑みなされたもので、その目的は、出力のSNが劣化することなく、全画素の信号蓄積開始と終了のタイミングを同時に行うことが可能な固体撮像装置及びその駆動方法、並びにそれを用いたビデオカメラ及びスチルカメラを提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above-described conventional problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a solid-state imaging device capable of simultaneously performing signal accumulation start and end timings of all pixels without degradation of output SN. It is an object of the present invention to provide a driving method and a video camera and a still camera using the driving method.
本発明の固体撮像装置は、上記目的を達成するため、光信号を信号電荷に変換して蓄積する光電変換手段と、前記光電変換手段に蓄積された信号電荷をリセットする第一のリセット手段と、前記信号電荷を読み出す読み出し手段と、前記読み出し手段を通して読み出された信号電荷を増幅する増幅手段と、前記増幅手段の信号電荷をリセットする第二のリセット手段と、特定の画素を選択する選択手段とを画素の構成要素として含み、前記第一のリセット手段と前記読み出し手段が、光電変換手段の同一の辺に接して配置されていることを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above object, the solid-state imaging device of the present invention converts photoelectric signals into signal charges and accumulates them, and first reset means that resets the signal charges accumulated in the photoelectric conversion means, A reading means for reading out the signal charge; an amplifying means for amplifying the signal charge read through the reading means; a second reset means for resetting the signal charge of the amplifying means; and a selection for selecting a specific pixel And the first reset means and the readout means are arranged in contact with the same side of the photoelectric conversion means.
また、本発明の固体撮像装置の駆動方法は、光信号を信号電荷に変換して蓄積する光電変換手段と、前記光電変換手段に蓄積された信号電荷をリセットする第一のリセット手段と、前記信号電荷を読み出す読み出し手段と、前記読み出し手段を通して読み出された信号電荷を増幅する増幅手段と、前記増幅手段の信号電荷をリセットする第二のリセット手段と、特定の画素を選択する選択手段とを画素の構成要素として含む固体撮像装置の駆動方法であって、
前記第二のリセット手段によって前記増幅手段の入力をリセットした後に、前記増幅手段の入力がフローティングの状態で行順次に画素からノイズ信号の読み出しを行い、
前記第一のリセット手段によって全画素の光電変換手段を同時にリセットし、
一定の蓄積期間の後に、前記読み出し手段によって前記光電変換手段に蓄積された信号電荷を全画素同時に前記増幅手段の入力に読み出し、
行順次に画素から前記ノイズ信号に重畳された光信号の読み出しを行い、
前記ノイズ信号と前記光信号の差分処理
を行うことを特徴とする。
The solid-state imaging device driving method of the present invention includes a photoelectric conversion unit that converts an optical signal into a signal charge and stores the signal, a first reset unit that resets the signal charge stored in the photoelectric conversion unit, Read means for reading signal charges, amplification means for amplifying signal charges read through the read means, second reset means for resetting signal charges of the amplification means, and selection means for selecting a specific pixel A solid-state imaging device including a pixel as a component of a pixel,
After resetting the input of the amplifying means by the second reset means, the noise signal is read out from the pixels sequentially in a row with the input of the amplifying means floating,
Simultaneously resetting the photoelectric conversion means of all pixels by the first reset means;
After a certain accumulation period, the signal charges accumulated in the photoelectric conversion means by the readout means are simultaneously read out to the input of the amplification means,
Read out the optical signal superimposed on the noise signal from the pixels row by row,
Difference processing between the noise signal and the optical signal is performed.
本発明によれば、出力のSNが劣化することなく、全画素の蓄積開始及び終了のタイミングを同時とすることができる。そのため、動きの早い被写体を撮像する場合であっても、被写体の形状を歪んで捕らえたり、或いは蛍光灯のフリッカが画像に現われることがなく、良質の画像を撮像することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to make the accumulation start and end timings of all the pixels at the same time without degrading the output SN. Therefore, even when capturing a fast-moving subject, it is possible to capture a high-quality image without distorting and capturing the shape of the subject or causing flicker of a fluorescent lamp to appear in the image.
次に、発明を実施するための最良の形態について図面を参照して詳細に説明する。 Next, the best mode for carrying out the invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
(第1の実施形態)
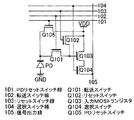
図1は本発明による固体撮像装置の第1の実施形態を示す等価回路図である。図1は画素部の構成を示す。図中PDはフォトダイオード、Q101はMOSトランジスタから成る転送スイッチである。Q102は拡散浮遊領域をリセットするためのMOSトランジスタから成るリセットスイッチ、Q104は読み出し画素を選択するためのMOSトランジスタから成る選択スイッチ、Q103は拡散浮遊領域がゲートに接続され、ソースが選択スイッチQ104のドレインに接続されたソースフォロワの入力MOSトランジスタ、Q105はフォトダイオードPDをリセットするためのMOSトランジスタから成るPDリセットスイッチである。
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is an equivalent circuit diagram showing a first embodiment of a solid-state imaging device according to the present invention. FIG. 1 shows the configuration of the pixel portion. In the figure, PD is a photodiode, and Q101 is a transfer switch composed of a MOS transistor. Q102 is a reset switch composed of a MOS transistor for resetting the diffusion floating region, Q104 is a selection switch composed of a MOS transistor for selecting a readout pixel, Q103 is connected to the gate of the diffusion floating region, and the source is the selection switch Q104. A source follower input MOS transistor Q105 connected to the drain is a PD reset switch composed of a MOS transistor for resetting the photodiode PD.
また、101はPDリセットスイッチQ105を駆動するPDリセットスイッチ線、102は転送スイッチQ101を駆動する転送スイッチ線、103はリセットスイッチQ102を駆動するリセットスイッチ線、104は選択スイッチQ104を駆動する選択スイッチ線、105は画素部の信号を読み出す信号出力線を示す。
次に、画素部の動作について説明する。まず、リセットスイッチ線103の駆動によりリセットスイッチQ102をオンすることでソースフォロワの入力ゲートにリセット電圧を入力するリセット動作と、選択スイッチ線104の駆動に従い選択スイッチQ104による行選択を行う。次に、ソースフォロワの入力ノードの拡散浮遊領域をフローティングにし、リセットノイズ及びソースフォロワの入力MOSトランジスタQ103の閾値電圧ばらつき等の固定パターンノイズからなるノイズ成分の読み出しを行う。
Next, the operation of the pixel portion will be described. First, by turning on the reset switch Q102 by driving the
更に、PDリセットスイッチ線101の駆動によりPDリセットスイッチQ105をオンすることでフォトダイオードPDをリセットし蓄積を開始する。所望の蓄積時間が経過すると、転送スイッチQ101を開閉し、光信号により生成されたフォトダイオードPDの蓄積電荷をソースフォロワの入力ノードに転送し、前述のノイズ成分と光信号成分の和を読み出す。その後、両信号の差分をとることでリセットノイズ及び固定パターンノイズを除去して、光信号成分を取り出すことでSNの高い画像信号が得られる。
Further, the PD reset switch Q105 is turned on by driving the PD
本実施形態の構成によれば、フォトダイオードPDへの信号電荷の蓄積開始と、フォトダイオードPDからソースフォロワの入力ノードへの蓄積電荷の転送とを独立に制御できるため、蓄積開始、終了を全行同時に行うことができる。 According to the configuration of the present embodiment, since the start of signal charge accumulation in the photodiode PD and the transfer of accumulated charge from the photodiode PD to the input node of the source follower can be controlled independently, the start and end of accumulation are completely controlled. Lines can be done simultaneously.
図2は図1の画素の各素子の配置を示す画素部の平面図、図3は図2をA−A線で切断した場合の断面図である。図1と同一部位には同一符号を付している。図中301はn基板であり、そのn基板301上にp型ウエル302が形成され、その上にフォトダイオードのn層303が形成されている。また、その上にフォトダイオードのp層304が表面を濃くして形成され、転送スイッチQ101及びPDリセットスイッチQ105のゲート領域305、307がフォトダイオード側面に絶縁層316を介して形成され、更に、リセットスイッチQ102のゲート領域306が絶縁層316を介して形成されている。
2 is a plan view of a pixel portion showing the arrangement of each element of the pixel of FIG. 1, and FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view of FIG. 2 taken along the line AA. The same parts as those in FIG. 1 are denoted by the same reference numerals. In the figure,
転送スイッチQ101及びPDリセットスイッチQ105のゲート領域305、307とフォトダイオード側面の間には、フォトダイオードのn層303から連続するバイパス領域308、309が形成されている。また、転送スイッチQ101及びリセットスイッチQ102のゲート領域305、306の側面下部に拡散浮遊領域310が形成されており、拡散浮遊領域310はコンタクト311、配線層312を介してソースフォロワの入力MOSトランジスタQ103のゲートに接続され、ソースには選択スイッチQ104のドレインが接続されている。
Between the
更に、PDリセットスイッチQ105及びリセットスイッチQ102のゲート領域307、306の側面下部にn型のソースドレイン領域313が形成され、ソースドレイン領域313はコンタクト314、配線層315を介して電源VDDに接続されている。なお、ゲート領域305と307はその二つのMOSトランジスタの特性を揃えるため、ゲート長、ゲート幅の少なくとも1つを等しくすることが望ましい。
Further, an n-type source /
次に、前述の読み出し動作に基づいて本実施形態による特徴について説明する。本実施形態による特徴は、拡散浮遊領域310のリセット直後の出力信号Vr1を一旦保持した後、転送スイッチQ101のゲート領域305に正の電圧を印加してフォトダイオードPDのn層303の蓄積電荷を拡散浮遊領域310に転送し、リセット信号に転送電荷Qsig/拡散浮遊領域容量Cfd分だけ重畳された信号Vsig1との差分(Vsig1−Vr1)をとることで、拡散浮遊領域310のリセットノイズの大部分を除去することである。特に、フォトダイオードPDのn層303に蓄積された電荷をより高い割合でリセットし、且つ、拡散浮遊領域310に転送することが重要である。
Next, features of the present embodiment will be described based on the read operation described above. The feature of this embodiment is that the output signal Vr1 immediately after resetting the
フォトダイオードのn層303のリセット動作に関して更に説明すると、PDリセットスイッチQ105が充分なオン状態であるならば、フォトダイオードPDのn層303にはp型ウエル302と表面の濃いp層304のGND電位に対し電源電圧VDDの逆バイアスが印加される。この時、フォトダイオードPDのn層303には、p型ウエル302と表面の濃いp層304から空乏層が延び、フォトダイオードPDのn層303全体を空乏化させることでフォトダイオードPDに信号電荷をほとんど残さずにリセットすることができる。フォトダイオードPDのn層303から拡散浮遊領域310への転送についても同様にフォトダイオードPDに信号電荷をほとんど残さずに信号電荷を読み出すことができる。
The reset operation of the n-
このような動作を実現するためには、PDリセットスイッチQ105及び転送スイッチQ101を充分なオン状態にする必要がある。本実施形態では、そのための技術として、転送スイッチQ101及びPDリセットスイッチQ105と、埋め込み型のフォトダイオードとの間にバイパス領域308、309を形成している。
In order to realize such an operation, it is necessary to turn on the PD reset switch Q105 and the transfer switch Q101 sufficiently. In this embodiment, as a technique for that purpose, bypass
バイパス領域を形成する方法としては、フォトダイオードPDのn層303や表面の濃いp層304を、転送スイッチQ101及びPDリセットスイッチQ105のゲート領域、例えば、多結晶シリコンをマスク材にし、斜めにイオン注入することによって形成する方法がある。また、フォトダイオードPDのn層303を転送スイッチQ101及びPDリセットスイッチQ105のゲート領域をマスク材にしてセルフアラインで形成し、表面の濃いp層304をゲート領域に対してオフセットをつけて露光して形成する方法等がある。
As a method of forming the bypass region, the
前者の方法をとる場合には、転送スイッチQ101のゲート領域305とバイパス領域308との位置関係と、PDリセットスイッチQ105のゲート領域307とバイパス領域309との位置関係が同一方向(即ち、フォトダイオードのn層303、ゲート領域305、コンタクト311の並び方向と、フォトダイオードのn層303、ゲート領域307、コンタクト314の並び方向が同一方向である)ことが重要となる。また、後者の方法をとる場合においても、両者を同一方向に配置することによって露光装置の位置合わせずれに対してバイパス領域の幅が同じように変化するため製造工程の管理が容易になる。
When the former method is used, the positional relationship between the
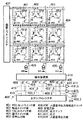
図4は図1〜図3の画素セルを用いた固体撮像装置の一実施形態を示すブロック図である。なお、図4では簡単のため画素セルを3行3列としている。図中406は水平シフトレジスタ、407は垂直シフトレジスタ、408は共通信号出力線415への転送スイッチ、408_1、408_2、408_3は水平シフトレジスタ406から転送スイッチ408への駆動パルスである。また、409は定電流源、410は出力アンプ、411は出力、412はADコンバータ、413は信号蓄積部、414はフレームメモリを示す。
FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing an embodiment of a solid-state imaging device using the pixel cells of FIGS. In FIG. 4, pixel cells are arranged in 3 rows and 3 columns for simplicity. In the figure, 406 is a horizontal shift register, 407 is a vertical shift register, 408 is a transfer switch to the common
また、401はPDリセット線、402は転送スイッチ線、403はリセットスイッチ線、404は選択スイッチ線、405は信号出力線である。これらのPDリセット線401、転送スイッチ線402、リセットスイッチ線403、選択スイッチ線404、信号出力線405は、それぞれ図1のPDリセット線101、転送スイッチ線102、リセットスイッチ線103、選択スイッチ線104、信号出力線105に対応している。
次に、本実施形態の固体撮像装置の基本動作を図5のタイミング図を用いて説明する。まず、読み出しに先立ち、全行のPDリセットスイッチ線401をハイレベル、転送スイッチ線402をロウレベル、リセットスイッチ線403をハイレベルとし、PDリセットスイッチQ105、リセットスイッチQ102をオンし、転送スイッチQ101をオフすることで、全画素のフォトダイオードPDとソースフォロワの入力ノードの拡散浮遊領域をリセット状態とする。PDリセットスイッチ線101、転送スイッチ線102、リセットスイッチ線103、選択スイッチ線404は垂直シフトレジスタ407によって駆動される。
Next, the basic operation of the solid-state imaging device of this embodiment will be described with reference to the timing chart of FIG. First, prior to reading, PD reset
次に、図5に示すように全行のリセットスイッチ線403(図5の403_1は1行目、403_2は2行目、403_3は3行目のリセットスイッチ線)をロウレベルとし、リセットスイッチQ102をオフすることで、ソースフォロワの入力ノードの拡散浮遊領域をフローティングにする。その後、1行目の選択スイッチ線404_1(図5の404_2は2行目、404_3は3行目の選択スイッチ線)をハイレベルとし、1行目の選択スイッチQ104をオンして行選択を行い、リセットノイズ及びソースフォロワの入力MOSトランジスタQ103の閾値電圧ばらつき等の固定パターンノイズからなるノイズ成分を信号蓄積部413に読み出す。
Next, as shown in FIG. 5, the
次いで、図5に示すように水平シフトレジスタ406からの駆動パルス408_1〜408_3を順次ハイレベルとし、MOSトランジスタの転送スイッチ408を順次オンすることでアンプ410を介して出力411に1行目のノイズ成分を順次読み出す。読み出されたノイズ成分はAD(Analog to Digital)コンバータ412によりAD(Analog to Digital)変換され、フレームメモリ414に保持される。2行目以降についても図5に示すように同様に読み出され、全画素分のノイズ成分がフレームメモリ414に保持される。
Next, as shown in FIG. 5, the drive pulses 408_1 to 408_3 from the
次に、図5に示すように全行のPDリセットスイッチ線401をロウレベルとし、PDリセットスイッチQ105をオフすることでフォトダイオードPDのn層303に光電変換された信号電荷の蓄積を開始する。所望の蓄積時間が経過すると、全行の転送スイッチ線402の駆動により転送スイッチQ101を開閉することでフォトダイオードPDの蓄積電荷をソースフォロワの入力ノードに転送する。図5の矢印で示す範囲は蓄積期間である。
Next, as shown in FIG. 5, the PD reset
次いで、ノイズ成分の読み出しと同様に1行目の選択スイッチ線404_1をハイレベルとして行選択を行い、前述のノイズ成分と光信号成分の和を信号蓄積部413に読み出す。次に、水平シフトレジスタ406からの駆動パルス408_1、408_2、408_3を順次ハイレベルとし、転送スイッチ408を順次オンすることで、出力411に出力アンプ410を介して1行目のノイズ成分と光信号成分の和を順次読み出す。読み出されたノイズ成分と光信号成分の和はADコンバータ412によりAD変換され、予めフレームメモリ414に保持されている1行目のノイズ成分との差分をとることで、リセットノイズ及び固定パターンノイズを除去して、光信号成分のみを取り出す。2行目以降についても同様に読み出され、SNの高い画像信号が得られる。
Next, the row selection is performed by setting the selection switch line 404_1 of the first row to the high level in the same manner as the reading of the noise component, and the sum of the noise component and the optical signal component is read out to the
上記動作によれば、全行の信号蓄積開始、終了のタイミングは同時であり、被写体が早い動きをしている場合でも、被写体の形状が歪んで捕らえられたり、或いは蛍光灯のフリッカが画像に現れることがなく、良質の画像を撮像することが可能である。 According to the above operation, the signal accumulation start and end timings of all rows are the same, and even when the subject is moving fast, the shape of the subject is distorted or the flicker of the fluorescent lamp appears in the image. A high-quality image can be taken without appearing.
また、蓄積期間以外は全行のPDリセットスイッチ線401がハイレベルにあり、全画素のPDリセットスイッチQ105がオン状態であるため、蓄積以外の期間に光が入射し、蓄積電荷がフォトダイオードPDのn層303の飽和電荷量を超えたとしても、溢れ出て隣接する拡散浮遊領域やフォトダイオードPDに混入してしまうブルーミング現象が起きることはない。
In addition, since the PD reset
更に、各行の拡散浮遊領域がフローティングとなっている時間が、ノイズ成分読み出しの時(リセットスイッチが閉じてから転送スイッチが開くまでの期間)と信号成分読み出しの時(転送スイッチが閉じてから信号蓄積部に読み出されるまでの期間)とで等しいため、拡散浮遊領域への光の漏れ込みによる光電荷や暗電流による影響も前述の差分処理で除去することが可能である。なお、本実施形態では、簡易的に画素が3行3列の場合を説明したが、これに限るものではない。 Furthermore, the time when the diffusion floating area of each row is floating is determined when the noise component is read (period from when the reset switch is closed until the transfer switch is opened) and when the signal component is read (the signal is output after the transfer switch is closed). The period until the data is read out by the storage unit) is equal, so that the influence of photoelectric charges and dark current due to light leakage into the diffusion floating region can be removed by the above-described differential processing. In the present embodiment, the case where the pixels are arranged in 3 rows and 3 columns has been described, but the present invention is not limited to this.
(第2の実施形態)
図6は図1〜3の画素を用いた固体撮像装置の他の実施形態を示すブロック図である。図6では図4と同一部分は同一符号を付している。また、簡単のため画素セルを3行3列としている。図4の実施形態とは後述するように読み出し方法が異なっている。図中408はノイズ成分を読み出す転送スイッチ、408′はノイズ成分と光信号成分との和を読み出す転送スイッチ、410、410′は出力アンプ、411、411′は出力である。
(Second Embodiment)
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing another embodiment of the solid-state imaging device using the pixels of FIGS. In FIG. 6, the same parts as those in FIG. 4 are denoted by the same reference numerals. For simplicity, the pixel cells are arranged in 3 rows and 3 columns. The reading method is different from the embodiment of FIG. 4 as described later. In the figure, 408 is a transfer switch for reading out noise components, 408 'is a transfer switch for reading out the sum of noise components and optical signal components, 410 and 410' are output amplifiers, and 411 and 411 'are outputs.
次に、図7のタイミング図を用いて本実施形態の基本的な動作を説明する。まず、読み出しに先立ち、全行のPDリセットスイッチ線401をハイレベル、転送スイッチ線402をロウレベル、リセットスイッチ線403をハイレベルとすることにより、全画素のフォトダイオードPDとソースフォロワの入力ノードの拡散浮遊領域をリセット状態とする。
Next, the basic operation of this embodiment will be described with reference to the timing chart of FIG. First, prior to reading, the PD reset
次いで、図7に示すように1行目のリセットスイッチ線403_1をロウレベルとし、リセットスイッチQ102をオフすることでソースフォロワの入力ノードの拡散浮遊領域をフローティングとする。その後、1行目の選択スイッチ線404_1をハイレベルとして行選択を行い、リセットノイズ及びソースフォロワの入力MOSトランジスタの閾値電圧ばらつき等の固定パターンノイズからなるノイズ成分を信号蓄積部413に読み出す。
Next, as shown in FIG. 7, the reset switch line 403_1 in the first row is set to a low level, and the reset switch Q102 is turned off to make the diffusion floating region of the input node of the source follower floating. Thereafter, the selection switch line 404_1 in the first row is set to a high level to perform row selection, and noise components including reset pattern noise and fixed pattern noise such as threshold voltage variations of input MOS transistors of the source follower are read out to the
次に、2行目、3行目のリセットスイッチ線403_2、403_3を順次ロウレベルとし、選択スイッチ線404_2、404_3を順次ハイレベルとして行選択を行い、信号蓄積部413にノイズ成分を順次読み出す。この時点で信号蓄積部413には3行分のノイズ成分が保持される。次に、図7に示すように全行のPDリセットスイッチ線401をロウレベルとし、PDリセットスイッチQ105をオフすることでフォトダイオードPDのn層303に光電変換された信号電荷の蓄積を開始する。
Next, the reset switch lines 403_2 and 403_3 in the second row and the third row are sequentially set to a low level, and the selection switch lines 404_2 and 404_3 are sequentially set to a high level to perform row selection, and noise components are sequentially read out to the
所望の蓄積時間が経過すると、図7に示すように全行の転送スイッチ線402の駆動により転送スイッチQ101を開閉することで、フォトダイオードPDの蓄積電荷をソースフォロワの入力ノードに転送する。図7の矢印で示す範囲は蓄積期間である。
When a desired accumulation time elapses, as shown in FIG. 7, the transfer switch Q101 is opened / closed by driving the
次いで、ノイズ成分の読み出しと同様に1行目の選択スイッチ線404_1をハイレベルとして行選択を行い、ノイズ成分と光信号成分の和を信号蓄積部413に読み出す。次に、水平シフトレジスタ406からの駆動パルス408_1〜408_3、駆動パルス408′_1〜408′_3を順次ハイレベルとすることで、転送スイッチ408と転送スイッチ408′を順次オンする。転送スイッチ408はノイズ成分の転送、転送スイッチ408′はノイズ成分と光信号成分との和の転送に用いられ、水平シフトレジスタ106からの駆動パルス408_1と駆動パルス408′_1、駆動パルス408_2と駆動パルス408′_2、駆動パルス408_3と駆動パルス408′_3はそれぞれ同時にハイレベルになる。
Next, similarly to the readout of the noise component, the selection switch line 404_1 in the first row is set to the high level to perform row selection, and the sum of the noise component and the optical signal component is read out to the
このように転送スイッチ408、408′を駆動することで、予め信号蓄積部413に保持されていた1行目のノイズ成分が出力411に、ノイズ成分と信号成分の和が出力411′に順次読み出される。なお、図7には駆動パルス408_1〜408_3のみしか示していないが、駆動パルス408′_1〜408′_3のハイレベルとロウレベルのタイミングは駆動パルス408_1〜408_3と同様である。
By driving the transfer switches 408 and 408 ′ in this way, the noise component in the first row previously stored in the
次に、2行目以降についても同様に選択スイッチをオンし、駆動パルス408_1〜408_3、駆動パルス408′_1〜408′_3を順次ハイレベルとすることで、転送スイッチ408と転送スイッチ408′を順次オンする。これにより、信号蓄積部413に蓄積されていたノイズ成分が出力411に、ノイズ成分と信号成分の和が出力411′に順次読み出される。また、両信号の差分をとることでリセットノイズ及び固定パターンノイズを除去して、光信号成分のみを取り出すことで、SNの高い画像信号が得られる。
Next, in the second and subsequent rows, the selection switches are turned on in the same manner, and the drive pulses 408_1 to 408_3 and the
上記動作によれば、全行の信号蓄積開始、終了のタイミングは同時であり、撮像する被写体が早い動きをしている場合でも、被写体の形状が歪んで捕らえられることはなく、蛍光灯のフリッカが画像に現れることもない。 According to the above operation, the signal accumulation start and end timings of all rows are the same, and even when the subject to be imaged moves quickly, the shape of the subject is not distorted and flickering of the fluorescent lamp Does not appear in the image.
また、蓄積期間以外は全行のPDリセットスイッチ線401がハイレベルにあり、全画素のPDリセットスイッチQ105がオン状態であるため、蓄積以外の期間に光が入射し、蓄積電荷がフォトダイオードPDのn層303の飽和電荷量を超えたとしても、溢れ出て隣接する拡散浮遊領域310やフォトダイオードPDに混入してしまうようなブルーミング現象が起きることはない。なお、本実施形態においても簡易的に画素を3行3列としているが、これに限ることはない。また、本実施形態の信号蓄積部413は画素部と同一半導体基板上に配置することが配線接続を簡単化する上で望ましい。
In addition, since the PD reset
なお、図6の実施形態では全画素のノイズ成分を保持するためのフレームメモリ及び信号蓄積部が必要となる。一方で、全行の信号蓄積開始、終了のタイミングを同時とすることが必要なモードは動画を撮像するモードである場合が多く、この場合には、全行を読み出さずに不要な行を間引くことにより、読み出す画素数を削減し、フレームレートを向上させることが可能である。また、不要な行を間引いて読み出す場合には、必要な画素数分のフレームメモリ及び信号蓄積部があれば良い。 In the embodiment of FIG. 6, a frame memory and a signal storage unit for holding noise components of all pixels are required. On the other hand, a mode that requires the signal accumulation start and end timings of all rows to be simultaneous is often a mode for capturing a moving image. In this case, unnecessary rows are thinned out without reading all the rows. Thus, the number of pixels to be read can be reduced and the frame rate can be improved. Further, when thinning out unnecessary rows and reading them out, it suffices if there are as many frame memories and signal storage units as necessary.
また、このような間引き動作において、読み出さない行のPDリセットスイッチ線401やリセットスイッチ線403を常にハイレベルとすることにより、不要な行のフォトダイオードPDのn層303に蓄積された電荷が飽和電荷量を超えたとしても、溢れ出て隣接する拡散浮遊領域やフォトダイオードに混入してしまうブルーミング現象が起きることはない。
Further, in such a thinning-out operation, the charge accumulated in the
(第3の実施形態)
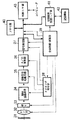
図8は本発明の固体撮像装置をビデオカメラに使用した場合の一実施形態を示すブロック図である。図中1Aは撮影レンズで焦点調節を行うためのフォーカスレンズ、1Bはズーム動作を行うズームレンズ、1Cは結像用のレンズである。また、2は絞り、3は撮像面に結像された被写体像を光電変換して電気的な撮像信号に変換する固体撮像装置であり、図4或いは図6の実施形態で説明した固体撮像装置を用いるものとする。
(Third embodiment)
FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing an embodiment when the solid-state imaging device of the present invention is used in a video camera. In the figure, reference numeral 1A denotes a focus lens for adjusting the focus with a photographing lens, 1B denotes a zoom lens for performing a zoom operation, and 1C denotes a lens for image formation. 2 is a solid-state imaging device that photoelectrically converts an object image formed on the imaging surface into an electrical imaging signal, and is described in the embodiment of FIG. 4 or FIG. Shall be used.
4は固体撮像装置3から出力された撮像信号をサンプルホールドし、更に、レベルをアンプするサンプルホールド回路(S/H回路)であり、映像信号を出力する。5はサンプルホールド回路4から出力された映像信号にガンマ補正、色分離、ブランキング処理等の所定の処理を施すプロセス回路で、輝度信号Y及びクロマ信号Cを出力する。
プロセス回路5から出力されたクロマ信号Cは、色信号補正回路21でホワイトバランス及び色バランスの補正が施され、色差信号R−Y,B−Yとして出力される。また、プロセス回路5から出力された輝度信号Yと、色信号補正回路21から出力された色差信号R−Y,B−Yは、エンコーダ回路(ENC回路)24で変調され、標準テレビジョン信号として出力される。このテレビジョン信号は図示しないビデオレコーダ或いは電子ビューファインダ等のモニタEVFへと供給される。更に、色信号補正回路21から出力された色差信号R−Y、B−Yは、ゲート回路22でゲートされ、積分回路25で積分値が検出されて論理制御回路17に入力される。この信号は、主にホワイトバランスの調節(不図示)に利用される。
The chroma signal C output from the
6はアイリス制御回路であり、サンプルホールド回路4から供給される映像信号に基づいてアイリス駆動回路7を制御し、映像信号のレベルが所定レベルの一定値となるように絞り2の開口量を制御すべくigメータ8を自動制御する。13、14はサンプルホールド回路4から出力された映像信号中より合焦検出を行うために必要な高周波成分を抽出する、異なった帯域制限のバンドパスフィルタ(BPF)である。
第一のバンドパスフィルタ13(BPF1)及び第二のバンドパスフィルタ14(BPF2)から出力された信号は、ゲート回路15及びフォーカスゲート枠信号で各々ゲートされ、ピーク検出回路16でピーク値が検出されてホールドされると共に論理制御回路17に入力される。この信号を焦点電圧と呼び、この焦点電圧によってフォーカスを合わせている。
The signals output from the first bandpass filter 13 (BPF1) and the second bandpass filter 14 (BPF2) are gated by the gate circuit 15 and the focus gate frame signal, respectively, and the
また、18はフォーカスレンズ1Aの移動位置を検出するフォーカスエンコーダ、19はズームレンズ1Bの焦点距離を検出するズームエンコーダ、20は絞り2の開口量を検出するアイリスエンコーダである。これらのエンコーダの検出値はシステムコントロールを行う論理制御回路17へ供給される。論理制御回路17は設定された合焦検出領域内に相当する映像信号に基づいて被写体に対する合焦検出を行い焦点調節を行う。
即ち、各々のバンドパスフィルタ13、14より供給された高周波成分のピーク値情報を取り込み、高周波成分のピーク値が最大となる位置へとフォーカスレンズ1Aを駆動すべくフォーカス駆動回路9にフォーカスモータ10の回転方向、回転速度、回転/停止等の制御信号を供給し、これを制御する。
That is, the peak value information of the high frequency components supplied from the respective band pass filters 13 and 14 is taken in, and the
(第4の実施形態)
図9は本発明の固体撮像装置をスチルカメラに使用した場合の一実施形態を示すブロック図である。図中31はレンズのプロテクトとメインスイッチを兼ねるバリア、32は被写体の光学像を固体撮像装置34に結像させるレンズ、33はレンズ32を通った光量を可変するための絞り、34はレンズ32で結像された被写体を画像信号として取り込むための固体撮像装置であり、図4或いは図6の実施形態で説明したものを用いるものとする。
(Fourth embodiment)
FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing an embodiment when the solid-state imaging device of the present invention is used in a still camera. In the figure, 31 is a barrier that serves as a lens protect and main switch, 32 is a lens that forms an optical image of a subject on the solid-
36は固体撮像装置34から出力される画像信号のアナログーディジタル変換を行うA/D変換器、37はA/D変換器36から出力された画像データに各種の補正を行ったり、データを圧縮したりする信号処理部、38は固体撮像装置34、撮像信号処理回路35、A/D変換器36、信号処理部37に各種タイミング信号を出力するタイミング発生部である。
An A /
また、39は各種演算とスチルカメラ全体を制御する全体制御・演算部、40は画像データを一時的に記憶する為のメモリ部、41は記録媒体に記録又は読み出しを行うための記録媒体制御I/F(インターフェース)部、42は画像データの記録又は読み出しを行う為の半導体メモリ等の着脱可能な記録媒体、43は外部コンピュータ等と通信する為の外部I/F(インターフェース)部である。 Also, 39 is an overall control / arithmetic unit for controlling various calculations and the entire still camera, 40 is a memory unit for temporarily storing image data, and 41 is a recording medium control I for recording or reading on a recording medium. An / F (interface) unit, 42 is a removable recording medium such as a semiconductor memory for recording or reading image data, and 43 is an external I / F (interface) unit for communicating with an external computer or the like.
次に、スチルカメラの撮影時の動作について説明する。まず、バリア31がオープンされると、メイン電源がオンされ、次にコントロール系の電源がオンし、更に、A/D変換器36等の撮像系回路の電源がオンされる。それから、露光量を制御する為に、全体制御・演算部39は絞り33を開放にし、固体撮像装置34から出力された信号はA/D変換器36で変換された後、信号処理部37に入力される。
Next, the operation at the time of shooting with the still camera will be described. First, when the
全体制御・演算部39ではそのデータに基づいて露出の演算を行う。この測光を行った結果により明るさを判断し、その結果に応じて全体制御・演算部39は絞り32を制御する。次に、固体撮像装置34から出力された信号をもとに高周波成分を取り出し、被写体までの距離の演算を全体制御・演算部39で行う。その後、レンズ32を駆動して合焦か否かを判断し、合焦していないと判断した時は、再びレンズ32を駆動し測距を行う。
The overall control /
そして、合焦が確認された後に本露光が始まる。露光が終了すると、固体撮像装置34から出力された画像信号はA/D変換器36でA/D変換され、信号処理部37を通り全体制御・演算部39によりメモリ部40に書き込まれる。その後、メモリ部40に蓄積されたデータは全体制御・演算部39の制御により記録媒体制御I/F部41を通り、半導体メモリ等の着脱可能な記録媒体42に記録される。また、外部I/F部43を通り直接コンピュータ等に入力して画像の加工を行っても良い。
Then, after the in-focus state is confirmed, the main exposure starts. When the exposure is completed, the image signal output from the solid-
1A フォーカスレンズ
1B ズームレンズ
1C 結像用レンズ
2 絞り
3 固体撮像装置
4 サンプルホールド回路
5 プロセス回路
6 アイリス制御回路
7 アイリス駆動回路
8 igメータ
9 フォーカス駆動回路
10、12 モータ
11 ズーム駆動回路
13、14 BPF
15、22 ゲート回路
16 ピーク検出回路
17 論理制御回路
18 フォーカスエンコーダ
19 ズームエンコーダ
20 アイリスエンコーダ
21 色信号補正回路
23 ゲートパルス発生回路
24 ENC回路
25 積分回路
31 バリア
32 レンズ
33 絞り
34 固体撮像装置
35 撮像信号処理回路
36 A/D変換器
37 信号処理回路
38 タイミング発生部
39 全体制御・演算部
40 メモリ部
41 記録媒体制御I/F部
42 記録媒体
43 外部I/F部
101、401 PDリセットスイッチ線
102、402 転送スイッチ線
103、403 リセットスイッチ線
104、404 選択スイッチ線
105、405 信号出力線
301 n基板
302 p型ウェル
303 フォトダイオードのn層
304 表面の濃いp層
305 転送スイッチのゲート領域
306 リセットスイッチのゲート領域
307 PDリセットスイッチのゲート領域
308、309 バイパス領域
310 拡散浮遊領域
311、314 コンタクト
312、315 配線層
313 ソースドレイン領域
316 絶縁層
406 水平シフトレジスタ
407 垂直シフトレジスタ
408、408′ 転送スイッチ
409 定電流源
410、410′ 出力アンプ
411、411′ 出力
412 A/Dコンバータ
413 信号蓄積部
414 フレームメモリ
415、415′ 共通信号出力線
PD フォトダイオード
Q101 転送スイッチ
Q102 リセットスイッチ
Q103 入力MOSトランジスタ
Q104 選択スイッチ
Q105 PDリセットスイッチ
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1A Focus lens 1B Zoom lens
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 15, 22 Gate circuit 16 Peak detection circuit 17 Logic control circuit 18 Focus encoder 19 Zoom encoder 20 Iris encoder 21 Color signal correction circuit 23 Gate pulse generation circuit 24 ENC circuit 25 Integration circuit 31 Barrier 32 Lens 33 Diaphragm 34 Solid-state imaging device 35 Imaging Signal processing circuit 36 A / D converter 37 Signal processing circuit 38 Timing generation unit 39 Overall control / calculation unit 40 Memory unit 41 Recording medium control I / F unit 42 Recording medium 43 External I / F unit 101, 401 PD reset switch line 102, 402 transfer switch line 103, 403 reset switch line 104, 404 selection switch line 105, 405 signal output line 301 n substrate 302 p type well 303 photodiode n layer 304 dark p layer 305 surface transfer Switch gate region 306 Reset switch gate region 307 PD reset switch gate region 308, 309 Bypass region 310 Diffusion floating region 311, 314 Contact 312, 315 Wiring layer 313 Source drain region 316 Insulating layer 406 Horizontal shift register 407 Vertical shift register 408, 408 ′ transfer switch 409 constant current source 410, 410 ′ output amplifier 411, 411 ′ output 412 A / D converter 413 signal storage unit 414 frame memory 415, 415 ′ common signal output line PD photodiode Q101 transfer switch Q102 reset switch Q103 Input MOS transistor Q104 Selection switch Q105 PD reset switch
Claims (11)
前記第二のリセット手段によって前記増幅手段の入力をリセットした後に、前記増幅手段の入力がフローティングの状態で行順次に画素からノイズ信号の読み出しを行い、
前記第一のリセット手段によって全画素の光電変換手段を同時にリセットし、
一定の蓄積期間の後に、前記読み出し手段によって前記光電変換手段に蓄積された信号電荷を全画素同時に前記増幅手段の入力に読み出し、
行順次に画素から前記ノイズ信号に重畳された光信号の読み出しを行い、
前記ノイズ信号と前記光信号の差分処理
を行うことを特徴とする固体撮像装置の駆動方法。 A photoelectric conversion unit that converts an optical signal into a signal charge and stores it, a first reset unit that resets the signal charge stored in the photoelectric conversion unit, a read unit that reads the signal charge, and a read unit that reads the signal charge. A solid-state imaging device driving method including amplification means for amplifying the output signal charge, second reset means for resetting the signal charge of the amplification means, and selection means for selecting a specific pixel as constituent elements of the pixel Because
After resetting the input of the amplifying means by the second reset means, the noise signal is read out from the pixels sequentially in a row with the input of the amplifying means floating,
Simultaneously resetting the photoelectric conversion means of all pixels by the first reset means;
After a certain accumulation period, the signal charges accumulated in the photoelectric conversion means by the readout means are simultaneously read out to the input of the amplification means,
Read out the optical signal superimposed on the noise signal from the pixels row by row,
A method of driving a solid-state imaging device, wherein difference processing between the noise signal and the optical signal is performed.
The solid-state imaging device according to claim 1, a lens that forms a subject image on the solid-state imaging device, and a signal processing unit that processes a signal from the solid-state imaging device. A feature still camera.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003296326A JP2005065184A (en) | 2003-08-20 | 2003-08-20 | Solid state image sensor and its driving method, and video camera and still camera using it |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003296326A JP2005065184A (en) | 2003-08-20 | 2003-08-20 | Solid state image sensor and its driving method, and video camera and still camera using it |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005065184A true JP2005065184A (en) | 2005-03-10 |
Family
ID=34372267
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003296326A Pending JP2005065184A (en) | 2003-08-20 | 2003-08-20 | Solid state image sensor and its driving method, and video camera and still camera using it |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005065184A (en) |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008167178A (en) * | 2006-12-28 | 2008-07-17 | Denso Corp | Image data generator, and photoreceptor device |
| US7612320B2 (en) | 2007-02-21 | 2009-11-03 | Olympus Corporation | Solid-state imaging apparatus with reset operation |
| JP2010183195A (en) * | 2009-02-03 | 2010-08-19 | Olympus Imaging Corp | Imaging pickup apparatus |
| WO2010107200A2 (en) * | 2009-03-16 | 2010-09-23 | (주) 지안 | Cmos image sensor having wide dynamic range and sensing method thereof |
| JP2010245891A (en) * | 2009-04-07 | 2010-10-28 | Olympus Imaging Corp | Imaging device and imaging method |
| JP2010252067A (en) * | 2009-04-16 | 2010-11-04 | Olympus Corp | Solid-state image sensor, camera system, and signal readout method |
| KR20100135548A (en) * | 2009-06-17 | 2010-12-27 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Optical modulator, methods of manufacturing and operating the same and optical apparatus comprising optical modulator |
| US7999871B2 (en) | 2007-05-08 | 2011-08-16 | Olympus Corporation | Solid-state imaging apparatus, and video camera and digital still camera using the same |
| JP2011530920A (en) * | 2008-08-13 | 2011-12-22 | トムソン ライセンシング | CMOS image sensor with selectable hard-wired binning |
| JP2011259102A (en) * | 2010-06-07 | 2011-12-22 | Olympus Corp | Readout control apparatus, readout control method, program, imaging apparatus, and solid state image pickup device |
| JP2012010074A (en) * | 2010-06-24 | 2012-01-12 | Olympus Corp | Readout control apparatus, readout control method, imaging apparatus, solid-state imaging apparatus and program |
| WO2012047057A2 (en) * | 2010-10-08 | 2012-04-12 | 주식회사 지안 | Cmos image sensor having wide dynamic range and image sensing method |
| US8174590B2 (en) | 2009-02-03 | 2012-05-08 | Olympus Imaging Corp. | Image pickup apparatus and image pickup method |
| JP2012134756A (en) * | 2010-12-21 | 2012-07-12 | Olympus Corp | Imaging apparatus |
| US8300122B2 (en) | 2009-04-10 | 2012-10-30 | Olympus Corporation | Solid-state imaging device, camera system, and signal reading method |
| JP2013118698A (en) * | 2013-03-06 | 2013-06-13 | Sony Corp | Image sensor and control method |
| US9111837B2 (en) | 2007-09-10 | 2015-08-18 | Sony Corporation | Image sensor |
| US10645325B2 (en) | 2016-09-30 | 2020-05-05 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Solid-state imaging device, method of driving solid-state imaging device, and imaging system having detection pixels and image acquisition pixels |
-
2003
- 2003-08-20 JP JP2003296326A patent/JP2005065184A/en active Pending
Cited By (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008167178A (en) * | 2006-12-28 | 2008-07-17 | Denso Corp | Image data generator, and photoreceptor device |
| US7612320B2 (en) | 2007-02-21 | 2009-11-03 | Olympus Corporation | Solid-state imaging apparatus with reset operation |
| US7999871B2 (en) | 2007-05-08 | 2011-08-16 | Olympus Corporation | Solid-state imaging apparatus, and video camera and digital still camera using the same |
| US9111837B2 (en) | 2007-09-10 | 2015-08-18 | Sony Corporation | Image sensor |
| US8704926B2 (en) | 2008-08-13 | 2014-04-22 | Thomson Licensing | CMOS image sensor with selectable hard-wired binning |
| JP2011530920A (en) * | 2008-08-13 | 2011-12-22 | トムソン ライセンシング | CMOS image sensor with selectable hard-wired binning |
| US8174590B2 (en) | 2009-02-03 | 2012-05-08 | Olympus Imaging Corp. | Image pickup apparatus and image pickup method |
| JP2010183195A (en) * | 2009-02-03 | 2010-08-19 | Olympus Imaging Corp | Imaging pickup apparatus |
| US8390692B2 (en) | 2009-02-03 | 2013-03-05 | Olympus Imaging Corp. | Image pick up apparatus and image pick up method capable of reading signal charge for image display by newly performing exposure while reading signal charge for still image by simultaneous exposure of all pixels |
| CN101795345B (en) * | 2009-02-03 | 2012-05-09 | 奥林巴斯映像株式会社 | Image pickup apparatus and image pickup method |
| US8797434B2 (en) | 2009-03-16 | 2014-08-05 | Zeeann Co., Ltd | CMOS image sensor having wide dynamic range and sensing method thereof |
| WO2010107200A2 (en) * | 2009-03-16 | 2010-09-23 | (주) 지안 | Cmos image sensor having wide dynamic range and sensing method thereof |
| WO2010107200A3 (en) * | 2009-03-16 | 2010-11-25 | (주) 지안 | Cmos image sensor having wide dynamic range and sensing method thereof |
| JP2010245891A (en) * | 2009-04-07 | 2010-10-28 | Olympus Imaging Corp | Imaging device and imaging method |
| US8300122B2 (en) | 2009-04-10 | 2012-10-30 | Olympus Corporation | Solid-state imaging device, camera system, and signal reading method |
| JP2010252067A (en) * | 2009-04-16 | 2010-11-04 | Olympus Corp | Solid-state image sensor, camera system, and signal readout method |
| KR101638974B1 (en) | 2009-06-17 | 2016-07-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Optical modulator, methods of manufacturing and operating the same and optical apparatus comprising optical modulator |
| KR20100135548A (en) * | 2009-06-17 | 2010-12-27 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Optical modulator, methods of manufacturing and operating the same and optical apparatus comprising optical modulator |
| JP2011259102A (en) * | 2010-06-07 | 2011-12-22 | Olympus Corp | Readout control apparatus, readout control method, program, imaging apparatus, and solid state image pickup device |
| JP2012010074A (en) * | 2010-06-24 | 2012-01-12 | Olympus Corp | Readout control apparatus, readout control method, imaging apparatus, solid-state imaging apparatus and program |
| WO2012047057A3 (en) * | 2010-10-08 | 2012-06-28 | 주식회사 지안 | Cmos image sensor having wide dynamic range and image sensing method |
| WO2012047057A2 (en) * | 2010-10-08 | 2012-04-12 | 주식회사 지안 | Cmos image sensor having wide dynamic range and image sensing method |
| US9407828B2 (en) | 2010-10-08 | 2016-08-02 | Zeeann Co., Ltd. | Wide dynamic range CMOS image sensor and image sensing method |
| KR101728713B1 (en) | 2010-10-08 | 2017-04-21 | (주) 지안 | Wide Dynamic Range CMOS Image Sensor and Image Sensing Method |
| JP2012134756A (en) * | 2010-12-21 | 2012-07-12 | Olympus Corp | Imaging apparatus |
| JP2013118698A (en) * | 2013-03-06 | 2013-06-13 | Sony Corp | Image sensor and control method |
| US10645325B2 (en) | 2016-09-30 | 2020-05-05 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Solid-state imaging device, method of driving solid-state imaging device, and imaging system having detection pixels and image acquisition pixels |
| US11159759B2 (en) | 2016-09-30 | 2021-10-26 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Solid-state imaging device, method of driving solid-state imaging device, and imaging system that can detect a failure while performing capturing |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20240006427A1 (en) | Imaging device and imaging system | |
| JP4794877B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and camera | |
| JP4416668B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device, control method thereof, and camera | |
| US7466003B2 (en) | Solid state image pickup device, camera, and driving method of solid state image pickup device | |
| JP5247007B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging system | |
| US8883526B2 (en) | Image pickup device, its control method, and camera | |
| US7821551B2 (en) | Solid-state image pickup device with an analog memory and an offset removing unit | |
| JP2005333462A (en) | Solid state imaging device and imaging system | |
| JP2005065184A (en) | Solid state image sensor and its driving method, and video camera and still camera using it | |
| JP2006261597A (en) | Solid state imaging device, manufacturing method thereof, and camera | |
| EP1596579A2 (en) | Solid-state image pickup device and camera utilizing the same | |
| JP2001024948A (en) | Solid-state image pickup device and image pickup system using the same | |
| JP5627728B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging system | |
| JP2007143067A (en) | Image sensing device and image sensing system | |
| JP2007214791A (en) | Imaging element, imaging apparatus, and driving method of imaging element | |
| JP2011155306A (en) | Solid state imaging device and camera |