JP2004252228A - Device and method for smoothing release layer of heat fixing roller - Google Patents
Device and method for smoothing release layer of heat fixing roller Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2004252228A JP2004252228A JP2003043408A JP2003043408A JP2004252228A JP 2004252228 A JP2004252228 A JP 2004252228A JP 2003043408 A JP2003043408 A JP 2003043408A JP 2003043408 A JP2003043408 A JP 2003043408A JP 2004252228 A JP2004252228 A JP 2004252228A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- fixing roller
- release layer
- heat fixing
- heating
- heat
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Processing And Handling Of Plastics And Other Materials For Molding In General (AREA)
- Fixing For Electrophotography (AREA)
- Rolls And Other Rotary Bodies (AREA)
Abstract
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、電子写真式画像形成装置に使用される加熱定着ローラを構成する芯金表面のフッ素樹脂膜を平滑化するための装置、及び方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
電子写真複写機、レーザプリンタ、ファクシミリ等の電子写真方式の画像形成装置においては、感光体上に形成された静電潜像を現像装置から供給されるトナーによって現像し、このトナー像を転写紙上に転写してから、定着装置によって加熱しながら加圧することによって定着している。定着装置は、通常内部にヒータを備えた加熱定着ローラと、この加熱定着ローラに圧接する加圧ローラと、を備えており、両ローラのニップに未定着トナー像を保持した転写紙を通過させる際に、トナー像の定着を行う。
加熱定着ローラは、中空円筒状の芯金の表面に少なくとも一層の熱可塑性樹脂から成る樹脂離型層を備え、この離型層を平滑化した構成を備えている。即ち、従来の加熱定着ローラは、芯金上にプライマ層及び樹脂離型層を順次積層した構成を有している。樹脂離型層は、予めプライマ層を形成した芯金表面に熱可塑性樹脂を被覆することにより形成される。このような熱可塑性樹脂としては、トナーに対する離型性、トナー定着温度(通常180〜200℃)での連続耐久性等の要求に対応するために、フッ素樹脂等の離型性樹脂が用いられている。
このフッ素樹脂としては、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン共重合(PTFE)が一般に用いられているが、最近では、テトラフルオロエチレン−ポリエチレンフルオロビニルエーレル共重合(PFA)の方が加工性がよいので、PFAが主に加熱定着ローラ用の樹脂離型層の材料として使用されている。
【0003】
ところで、フッ素樹脂等の樹脂離型層の表面は、熱により溶融したトナーに対する十分な離型性を確保する必要があるので、十点平均粗さ(Rz):1〜3μm、及び、うねり:2〜4μm程度の平滑性が要求される。
従来、芯金表面に形成された樹脂離型層を平滑化する場合は、加熱定着ローラの軸方向へ移動可能であり、且つ回転自在に支持された押圧ローラを、加熱定着ローラ表面の樹脂離型層に圧接しつつ連れ回り回転させながら軸方向に移動させて、樹脂離型層を押つぶすことによって、樹脂離型層の表面の平滑性を向上させる方法(バニッシュ工法)が採用されていた。
従来、このようなバニッシュ工法を適用して平滑な加熱定着ローラを製造するには、前記した押圧ローラに加える加圧力を20〜60kgfにする必要があった。加熱定着ローラの芯金の肉厚が1〜2mm以上であれば、定着ローラに前記20〜60kgf程度の加圧力を加えたとしても、加圧による加熱定着ローラの変形量は、芯金の弾性変形の範囲内に止めることが可能であった。
しかしながら、加熱定着ローラの消費電力を低減する目的で、芯金の肉厚を1mm未満に薄肉化すると、押圧ローラの加圧力によって、芯金が塑性変形してしまい、不良品になるという問題がある。
このような場合、押圧ローラの加圧力を小さくすることによって、加熱定着ローラの変形を抑制することも可能ではあるが、押圧ローラの加圧力を小さくした場合には、樹脂離型層の平滑性が十分に得られないという問題が発生する。
【0004】
ところで、芯金表面の樹脂離型層をその溶融温度以上に熱した後で急速冷却することで、樹脂離型層の結晶化度を低くし、且つ樹脂離型層の強度を高める結果として、耐久性と平滑性を向上できることが知られている。
ところが、急冷工程が全表面に対して均一に行われない場合、結晶化度が不均一な箇所を起点としてトナーの固着や、オフセットの発生を誘引してしまうという問題がある。
ところで、特公平6−51373号公報、特許第2646263号、特公平6−82257号公報には、何れも樹脂離型層の溶融温度以上に加熱した後に冷却する方法として、加熱定着ローラを水に浸漬する方法が示されている。しかし、水中への浸漬を行うと冷却速度がローラ全体において均一化しないばかりか、その後の乾燥工程が必要となって工程数の増大、生産性の低下が発生するばかりでなく、品質上においても種々の不具合が発生し易い。
【特許文献1】特公平6−51373号公報
【特許文献2】特許第2646263号
【特許文献3】特公平6−82257号公報
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
本発明は上記に鑑みてなされたものであり、1mmを下回る薄肉の芯金表面に樹脂離型層を被覆形成した加熱定着ローラにおける樹脂離型層の平滑化を、樹脂離型層を溶融温度まで加熱してから急冷することによって実施する装置、及び方法において、加熱定着ローラの全表面に対して均一に急冷工程を行うことを可能にすることによって、樹脂離型層の結晶化度を均一に低くし、平滑性及び耐久性を高めることを可能とした加熱定着ローラの樹脂離型層の平滑化装置、及び平滑化方法を提供することを目的とする。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記課題を解決するため、請求項1の発明は、中空円筒状の芯金の表面に樹脂離型層を備えた加熱定着ローラにおける樹脂離型層の平滑化装置であって、平滑化されていない樹脂離型層を備えた加熱定着ローラを加工位置に搬入する搬入手段と、前記搬入手段によって加工位置に搬入されてきた加熱定着ローラの軸方向両端部を把持する把持手段と、前記把持手段によって把持された加熱定着ローラを、前記樹脂離型層の溶融温度以上に加熱する加熱手段と、前記加熱手段によって溶融温度以上に加熱された加熱定着ローラを急冷する急冷手段と、前記急冷手段によって急冷された加熱定着ローラを把持手段から受け取って搬出する搬出手段と、を備えたことを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、芯金上に樹脂離型層を形成してから、加熱、急冷することにより平滑化を図る際に、樹脂離型層表面の結晶化度が低くなり、高耐久の加熱定着ローラを連続して製造することができる。
請求項2の発明は、請求項1において、前記急冷手段は、圧縮空気を前記加熱定着ローラの表面に噴射することによって、前記加熱定着ローラを急冷することを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、圧縮空気を噴射するだけの簡便な装置を使って効果的な急冷を行うことができる。
請求項3の発明は、請求項2において、前記圧縮空気を噴射する急冷手段は、前記加熱定着ローラの軸方向全長にわたって均一な噴射が得られるスリット状の噴射ノズルを備えていることを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、加熱定着ローラ全長にわたって均一に結晶化度が低く高耐久の加熱定着ローラを提供することができる。
請求項4の発明は、請求項2又は3において、前記圧縮空気を噴射する急冷手段は、複数の噴射ノズルを備えていることを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、複数の噴射ノズルを夫々適所に配置して加熱定着ローラに対する全体的な冷却を行うので、冷却速度をより速くすることが可能になり、離型層表面のより深い所まで結晶化度を低くすることができる。
請求項5の発明は、請求項1、2、3又は4において、前記把持手段によって把持された加熱定着ローラの表面に帯電した静電気を除電する除電手段を備えることを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、加熱定着ローラ表面に帯電した静電気の影響によって、離型層が溶融状態にあるとき、空気中の塵埃が加熱定着ローラ上に付着し、不良品になるのを未然に防止することができる。
【0007】
請求項6の発明は、請求項1乃至6において、前記把持手段は、前記加熱定着ローラの両端部を夫々把持するチャック部と、該各チャック部を回転自在に支持すると共に軸方向へ進退可能に支持された軸受ユニットと、少なくとも一方のチャック部を回転駆動するモータと、少なくとも一方の軸受ユニットを軸方向へ進退させる駆動源と、を備え、前記加熱手段は、前記各チャック部により支持された加熱定着ローラの軸方向端部開口からその内部に加熱源を着脱自在に挿着する構成を備えていることを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、定速回転した状態で加熱定着ローラの離型層を溶融することが可能になるので、ローラの表面温度が均一な状態で急冷を開始することができ、均一な結晶化度を得ることが可能になる。
請求項7の発明は、請求項6において、前記加熱源は、前記加熱定着ローラの軸方向に配光を有する赤外線ヒータであることを特徴とする。
この発明によれば離型層が溶融状態になるまでの加熱昇温時間が短い、効率の良い加熱源を提供することが可能になる。
請求項8の発明は、請求項1乃至7において、前記加熱手段は、前記加熱定着ローラの外周面を加熱する加熱源を備えることを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、離型層が溶融状態になるまでの加熱昇温時間をさらに短くすることができ、生産性の高い製造装置を提供することが可能になる。
請求項9の発明は、中空円筒状の芯金の表面に樹脂離型層を備えた加熱定着ローラにおける樹脂離型層の平滑化方法であって、平滑化されていない樹脂離型層を備えた加熱定着ローラを加工位置に搬入する搬入工程と、加工位置に搬入されてきた加熱定着ローラを把持した状態で、前記樹脂離型層をその溶融温度以上に加熱する加熱工程と、前記加熱工程において溶融温度以上に加熱された加熱定着ローラを急冷する急冷工程と、前記急冷工程において急冷された加熱定着ローラを加工位置から搬出する搬出工程と、を備えたことを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、表面の結晶化度が低く高耐久の加熱定着ローラを連続して製造できる製造方法を提供することが可能になる。
【0008】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施例を図面に基づいて説明する。
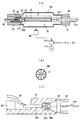
図1(a)及び(b)は本発明の一実施形態としての加熱定着ローラの平滑化装置の側面図、及び加熱定着ローラの構成図であり、図2はその正面図であり、図3(a)(b)及び(c)は加熱部周辺の部分拡大断面図、要部断面図、及び要部拡大図である。
本実施形態に係る平滑化装置0は、加熱定着ローラ100を自動的に加工位置Aに搬入してから、これを把持した状態で加熱を行い、加熱後に急冷してから、加工位置から搬出する各工程を自動的に連続して実施することを可能としたものである。平滑化装置0は、図1(b)に示すように、中空円筒状の薄肉の芯金101の表面にプライマ層102、樹脂離型層103を順次積層した構成を備えている。樹脂離型層103としては、例えばテトラフルオロエチレン−ポリエチレンフルオロビニルエーレル共重合(PFA)を使用する。
本発明の平滑化装置0による加工前の加熱定着ローラ100は、芯金表面の樹脂離型層103が未平滑の状態にあるため、樹脂離型層103の溶融温度以上に加熱してから急速冷却させることによって、樹脂離型層の結晶化度を均一に低くして平滑化し、且つ耐久性を高める。
平滑化装置0は、複数の加熱定着ローラ100を所定のピッチにて連続的に加工位置Aまで搬送すると共に把持手段によって把持可能な位置まで移動させる搬入手段1と、搬入手段1によって加工位置Aに搬入されてきた加熱定着ローラ100を一個ずつ支持する把持手段10と、把持手段10によって把持された加熱定着ローラ100を離型層103の溶融温度以上に加熱する加熱手段20と、加熱手段20によって溶融温度以上に加熱された加熱定着ローラを急冷する急冷手段35と、急冷手段35によって急冷された加熱定着ローラを把持手段10から受け取って搬出する搬出手段50と、加熱定着ローラ表面上に帯電した静電気を除電するための除電手段55と、これらを制御する図示しない制御部と、を概略備えて構成されている。
【0009】
搬入手段1は、例えば搬送ローラ2間にエンドレスに張設されて矢印方向へ駆動されるコンベア3と、コンベア3上に所定のピッチで固定配置されたローラ受け台4と、昇降移載手段5と、を備える。コンベア3は、搬送ローラ2の内の一方を図示しないモータにより回転駆動することにより間欠駆動される。コンベア3は細幅の2本のベルトから成り、2本のベルト間には後述する昇降移載手段5が水平方向へ移動したり、上下動するための空間が確保される。
各受け台4の凹状の座には平滑化を受けていない加熱定着ローラ100が載置され、加熱定着ローラを支持した受け台4がコンベア3の反転位置(加工位置Aの手前)に達したときに、その直下位置に昇降移載手段5が待機しており、受け台4が停止したタイミングでワーク受け9を上昇させて受け台4上の加熱定着ローラ100の両端部を支持し、更に受け台4より所定高さだけ持ち上げて完全に離脱させてから、後述する直動アクチュエータ7を作動させて実線で示した加工位置に移動させる。
なお、空になった受け台4上への加熱定着ローラ100の搭載作業は、搭載位置Bにおいて、人手或いは搭載装置によって行う。
昇降移載手段5は、ベース6上に配置された直動アクチュエータ7、8と、ワーク受け9と、を備えている。水平方向(定着加熱ローラの径方向)への直動アクチュエータ7は、制御部からの制御によって上下方向への直動アクチュエータ8を水平方向へ進退させる。直動アクチュエータ8は制御部からの制御によってワーク受け9を上下方向へ進退させる。直動アクチュエータ7によるワーク受け9の可動範囲は、搬入用のコンベア3の右端部の下方位置から、搬出用コンベア52の左端部の下方位置までに設定する。これにより、搬入手段1及び搬出手段50との間のワークの受け渡しが可能となる。
【0010】
把持手段10は、ベース6上に配置された左右2つの水平方向への直動ガイド部材11と、加熱定着ローラ100の両端部を夫々着脱自在に把持するチャック部12と、各チャック部12を回転自在に支持する図示しない軸受を有すると共に各直動ガイド部材11によって矢印で示す加熱定着ローラの軸方向へ進退可能に支持される軸受ユニット13と、各軸受ユニット13に配置されて各チャック部12を回転駆動させるモータ14と、各軸受ユニット13を軸方向へ移動させる直動アクチュエータ(駆動源)15と、を備えている。
搬入手段1から受け渡された加熱定着ローラ100をワーク受け9上に支持した状態で直動アクチュエータ8を作動させて各チャック部12の高さ位置まで上昇させておき、各直動アクチュエータ15を作動させてそれまで外側に退避していた各軸受ユニット13を加工位置A側へ向けて移動させることにより、各チャック部12のテーパー状の先端を加熱定着ローラ100の両端の開口内に嵌合させてこれを把持する。その後、直動アクチュエータ8を下降退避させる。各軸受ユニット13に配置されたモータ14を同期駆動することにより、各チャック部12は回転駆動され、把持した加熱定着ローラ100を回転させる。なお、チャック部12を回転させるモータは、何れか一方の軸受ユニット13側にのみ設け、他方のチャック部は従動回転するようにしてもよい。
加熱手段20は、図3(a)(b)に示すように、両端部をチャック部12によって把持された加熱定着ローラ100の内部に一方の開口端から差込み挿着される加熱源21を備えている。加熱源21は、例えば図示のように細長い赤外線ヒータを用いる。加熱定着ローラ100表面の離型層をその融点以上の温度に加熱する加熱源21の一端部には、保持部材23aを介して直動アクチュエータ22のアームが固定され、この直動アクチュエータ22により加熱源21は加熱定着ローラ100の開口端からその内外へ進退可能に構成されている。加熱源21の右側の端子から延びるリード線21aは保持部材23a、直動アクチュエータ22のアームを介して図示しない電源と接続されている。
加熱源21の他端には保持部材23bが配置され、両保持部材23a、23bは、撓みに対する剛性を高めるための管状の補強部材24により一体化されている。補強部材24の内部には、赤外線ヒータ25が配置されている。赤外線ヒータ25は、両保持部材23a、23bによって両端部を保持されている。
【0011】
補強部材24の他端には、絶縁材料から成る略円錐状のガイド部材26が設けられ、このガイド部材26は、左側のチャック部12内に配置した他の絶縁性ガイド部材27のテーパー状の嵌合凹所内に着脱自在に嵌合する。ガイド部材26の中空内部には赤外線ヒータ25の他方の端子から延びるリード線21bが位置しており、ガイド部材26の先端開口に固定された電力供給用の電極26aと、電気的に接続されている。ガイド部材27の内部には前記電極26aと接離可能な伸縮可動電極27aが配置されている。伸縮可動電極27aは固定基部27bによって軸方向へ突出入自在に支持されると共に固定基部内のバネによって突出方向へ弾性付勢されている。伸縮可動電極27aは、配線28により電源と接続されている。ガイド部材27は、右側の軸受ユニット13に設けた固定部29によって固定されている。
従って、直動アクチュエータ22の作動によってそのアームに固定された加熱源21が、右側のチャック部12内から加熱定着ローラ100内に挿入され、加熱源21の左端部のガイド部材26が他方のガイド部材27の凹所内に嵌合した際に、電極26aが伸縮可動電極27aと電気的に接続されて図示しない電源からの給電を受けることが可能となる。このため、加熱定着ローラ100を内側から加熱して、樹脂離型層103を融点以上に加熱することができる。なお、両ガイド部材26、27は、加熱源21を所定位置に位置決めするための手段でもある。
逆に、直動アクチュエータ22の作動により、加熱源21が右側のチャック部12内を経て右側の軸受ユニット13内に退避する場合には、電極26aと伸縮可動電極27aとの間の接続がスムーズに遮断され、加熱定着ローラに対する内部からの加熱が中断される。
【0012】
急冷手段35は、加熱工程を終了した加熱定着ローラ100の外周面に対して圧縮エアーを噴射することによって急冷を行う手段であり、この急冷手段35は、圧縮エアー源36と、圧縮エアー源36からの圧縮エアーを噴出するエアーノズル(噴射手段)37と、を備えている。又、エアーノズル37の近傍には、加熱中の加熱定着ローラの表面温度を非接触で測定する非接触温度計38を配置する。非接触温度計38は、図3(a)に示すように制御部110に計測したローラ温度を出力し、制御部110は測定された温度に基づいて加熱源21の温度(ON、OFF)を制御する。
この急冷手段35を用いることにより、冷却速度をより速くすることができ、加熱定着ローラ表面のより深い位置まで結晶化度を低くすることができる。
エアーノズル37として、ローラ軸方向全長に亘って均一な噴射が得られるスリット状のノズルを用いることにより、ローラ全長にわたって均一に結晶化度を低くし、高耐久とすることができる。
また、加熱定着ローラ表面に帯電した静電気を除電する除電手段55を配置したため、静電気の影響によって離型層が溶融状態にあるときに空気中の塵埃が加熱定着ローラ表面に付着し、不良品となることを未然に防止できる。
搬出手段50は、ローラ51間にエンドレスに張設されたコンベア52上に所定のピッチで固定配置されたローラ受け台53と、を備える。コンベア52は、搬送ローラ51の内の一方を図示しないモータにより回転駆動することにより間欠駆動される。搬入側のコンベア3の場合と同様に、このコンベア52も平行に離間して配置された2本のベルトから成り、ベルト間の空間を利用して昇降移載手段が加工位置とコンベア52内部との間を自由に進退することが可能となり、搬入手段1の場合と同様にワーク受け9上のワークをローラ受け台53上に移載することができる。各受け台53の凹状の座には平滑化を受けた加熱定着ローラ100が載置され、搬出される。
把持手段10によって把持された状態にある加熱定着ローラ100を受け台53に移載する際には、昇降用直動アクチュエータ8を作動させてワーク受け9を上昇させて加熱定着ローラ100の両端部を支持してから、各軸受ユニット13を外側へ退避させる。次いで、横移動用直動アクチュエータ7を用いてワーク受け9をコンベア52側へ移動させて、2本のベルト間の空間に進入し、停止した状態にある空の受け台53上に加熱定着ローラを載置し、載置後にワーク受け9だけを退避させる。
【0013】
次に、図4は、本発明の他の実施形態に係る平滑化装置の変形例を示したものであり、急冷手段35として、急冷エアーノズル40をローラの径方向に沿って複数個、例えば3個並列に設けた場合の実施形態である。なお、本実施形態では、急冷エアーノズル40の数量は3個であるが、これは一例に過ぎず、これよりも多くてもかまわない。また、本実施形態では、3個並列に配置しているが、ローラ100とノズル40のなす角度を必要に応じて適宜調整することも可能である。
図5は、本発明の他の実施形態に係る加熱手段の構成説明図であり、加熱定着ローラ100の外周面に急冷ノズル40と加熱手段20を近接配置している。加熱手段20は、ローラ外部加熱ヒータ(加熱源)21と、反射・防眩板45と、を備えている。加熱手段20と急冷ノズル40を直動自在に可動にさせるための直動アクチュエータ46が装備されている。
この実施形態の構成によれば、離型層103が溶融状態になるまでの加熱昇温時間をさらに短くすることができ、生産性の高い製造装置を提供することが可能になる。ローラ外部からの加熱手段と、ローラ内部からの加熱手段を併用しても良いし、ローラ外部からのみ加熱するようにしてもよい。
【0014】
次に、以上の構成を備えた平滑化装置0による平滑化手順は次の通りである。
1.加熱定着ローラ100を搭載位置Bにてコンベア3上の各受け台4上に順次セットする。
2.加熱定着ローラ100がコンベア3の前進端部まで搬送されると、除電装置55によりローラ表面上に帯電した静電気を除電する。(なお、除電は後述するチャック部により把持した状態で行っても良い。)
3.直動アクチュエータ7、8を用いて、除電を完了したローラ100を、ワーク受け9上に移載し、チャック位置まで上昇させる(搬入工程)。
4.各直動アクチュエータ15を作動させて各軸受ユニット13を接近方向へ移動し、各軸受ユニット13により支持されたチャック部12により、ローラ100の両端部をチャックする(把持工程)。次いで、モータ14を作動させてローラ100を定速回転させる。この際、直動アクチュエータ22を作動させて右側のチャック部12内に位置している加熱源21をローラ100の一端開口からローラ内部に挿入し、先端の電極26aを伸縮可動電極27aと導通させる。即ち、加熱源21の左端部のガイド部材26が他方のガイド部材27の凹所内に嵌合した際に、加熱源21が位置決めされると共に、電極26aが伸縮可動電極27aと電気的に接続されて図示しない電源からの給電を受けることが可能となる(加熱工程)。
5.加熱源21を発熱させて所定温度まで昇温させることにより、ローラ100を離型層103の融点以上の温度まで加熱させる(加熱工程)。
6.ローラ100の樹脂離型層103を所定の加熱温度に昇温して溶融させた後、加熱源による加熱を停止させると同時に、エアーノズル40からローラ周面に向けてエアーを噴出させて急冷する(急冷工程)。なお、加熱源21は、直動アクチュエータ22を用いて加熱停止後に(できれば冷却開始前に)、右側の軸受ユニット13内に退避させる。
7.ローラ100が所定の温度まで冷却された後、ローラを搬出コンベア52の受け台53上に移載し搬出させる(搬出工程)。
8.1〜7の工程を繰り返す。
9.樹脂離型層103の平滑化のための加工を完了した加熱定着ローラ100を取出し位置Cにて順次取り出す。
【0015】
(実施結果)
図6は、エアーノズル40を1個使用し、350℃から急冷させたときの温度変化を示す。
この条件下では、結晶度の低い良好な樹脂離型層103を得ることができた。急冷開始温度を変えてみても離型層に大きな変化は発生しなかったが、320℃より低い温度から急冷を介しした場合には結晶化度が高くなる変化が見られたことから、320℃以上の温度から急冷を開始することが望ましい。
なお、本発明は、加熱定着ローラのみならず、表面が熱可塑性樹脂で被覆された円筒形状物の表面の平滑化に応用可能である。
【0016】
【発明の効果】
以上のように本発明によれば、1mmを下回る薄肉の芯金表面に形成された樹脂離型層の平滑化を、樹脂離型層を溶融温度まで加熱してから急冷することによって実施する加熱定着ローラの加工装置、及び方法において、ローラの全表面に対して均一に急冷を行うことによって、樹脂離型層の結晶化度を均一に低くし、平滑性及び耐久性を高めることができる。
即ち、請求項1記載の発明によれば、溶融温度まで加熱してから急冷した際に、加熱定着ローラの離型層の結晶化度を低くすることが可能になり、ローラの耐久性を向上させることができる。さらに、本装置単体のみを使ってバッチ処理にて加工が行えるので、既存の製造設備に何ら影響を与えることなく製造することできる効果がある。
請求項2、3記載の発明によれば、圧縮空気を噴射するだけの簡便な冷却手段を使って急冷させることが可能になる。
請求項4記載の発明によれば、複数のエアーノズルを用いるので、より冷却速度を早める効果がある。
請求項5記載の発明によれば、溶融前に事前に除電を行うので、空気中に浮遊する塵埃の付着を防ぎ、塵埃の付着による不良品の発生を未然に防ぐ効果がある。
請求項6、7記載の発明によれば、ローラ軸方向に沿った長さを有した熱源を用いているので、ローラ全長に亘って均一な加熱を行い、迅速に昇温することが可能になる。
請求項8記載の発明によれは、ローラ内部のみならず、外部からも加熱することにより、加熱昇温を一層速くすることが可能になる。
請求項9記載の発明によれば、加熱定着ローラの離型層の結晶化度を低くすることが可能になり、ローラの耐久を向上させることができる。さらに、本装置単体のみを使ってバッチ処理にて加工が行えるので、既存の製造設備に何ら影響を与えることなく製造することできる効果がある。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】(a)及び(b)は本発明の一実施形態としての加熱定着ローラの平滑化装置の側面図、及び加熱定着ローラの構成図。
【図2】図1の正面図。
【図3】(a)(b)及び(c)は加熱部周辺の部分拡大断面図、要部断面図、及び要部拡大図。
【図4】本発明の他の実施形態に係る平滑化装置の変形例を示した図。
【図5】本発明の他の実施形態に係る加熱手段の構成説明図。
【図6】急冷したときの温度変化を示す図。
【符号の説明】
A 加工位置、B 搭載位置、 0 平滑化装置、1 搬入手段、2 ローラ、3コンベア、4 ローラ受け台、5 昇降移載手段、6 ベース、7、8 直動アクチュエータ、9 ワーク受け、10 把持手段、11 直動ガイド部材、12 チャック部、13 軸受ユニット、15 直動アクチュエータ、20 加熱手段、21 加熱源、22 直動アクチュエータ、23a、23b 保持部材、24 補強部材、25 赤外線ヒータ、26 ガイド部材、26a 電極、27 絶縁性ガイド部材、27 伸縮可動電極、27b 固定基部、28 配線、29 固定部、35 急冷手段、36 圧縮エアー源、37 エアーノズル(噴射手段)、38 非接触温度計、100 加熱定着ローラ、101 芯金、102 プライマ層、103 樹脂離型層、110 制御部、50 搬出手段。[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for smoothing a fluororesin film on the surface of a metal core constituting a heat fixing roller used in an electrophotographic image forming apparatus.
[0002]
[Prior art]
2. Description of the Related Art In an electrophotographic image forming apparatus such as an electrophotographic copying machine, a laser printer, and a facsimile, an electrostatic latent image formed on a photoreceptor is developed with toner supplied from a developing device, and the toner image is formed on transfer paper. After the image is transferred to the fixing device, the image is fixed by applying pressure while heating with a fixing device. The fixing device usually includes a heat-fixing roller having a heater inside, and a pressure roller pressed against the heat-fixing roller, and the transfer paper holding the unfixed toner image passes through the nip of both rollers. At this time, the toner image is fixed.
The heat fixing roller has a configuration in which at least one resin release layer made of a thermoplastic resin is provided on the surface of a hollow cylindrical cored bar, and the release layer is smoothed. That is, the conventional heat fixing roller has a configuration in which a primer layer and a resin release layer are sequentially laminated on a cored bar. The resin release layer is formed by coating the surface of a core metal on which a primer layer has been formed in advance with a thermoplastic resin. As such a thermoplastic resin, a release resin such as a fluororesin is used in order to meet requirements such as releasability from a toner and continuous durability at a toner fixing temperature (usually 180 to 200 ° C.). ing.
As this fluororesin, polytetrafluoroethylene copolymer (PTFE) is generally used, but recently, tetrafluoroethylene-polyethylene fluorovinyl ether copolymer (PFA) has better processability, so PFA Is mainly used as a material of a resin release layer for a heat fixing roller.
[0003]
By the way, since the surface of a resin release layer made of a fluororesin or the like needs to ensure sufficient releasability with respect to toner melted by heat, ten-point average roughness (Rz): 1 to 3 μm, and undulation: Smoothness of about 2 to 4 μm is required.
Conventionally, when a resin release layer formed on the surface of a cored bar is smoothed, a pressing roller that is movable in the axial direction of the heat-fixing roller and that is rotatably supported is used to release the resin from the surface of the heat-fixing roller. A method of improving the smoothness of the surface of the resin release layer by moving the shaft in the axial direction while rotating while rotating while pressing against the mold layer (vanish method) has been adopted. .
Conventionally, in order to manufacture a smooth heat-fixing roller by applying such a burnishing method, it is necessary to set the pressure applied to the pressing roller to 20 to 60 kgf. If the thickness of the core metal of the heat fixing roller is 1 to 2 mm or more, even if the above-mentioned pressing force of about 20 to 60 kgf is applied to the fixing roller, the amount of deformation of the heat fixing roller due to the pressure is limited by the elasticity of the core metal. It was possible to stop within the range of deformation.
However, if the thickness of the cored bar is reduced to less than 1 mm for the purpose of reducing the power consumption of the heat fixing roller, there is a problem that the cored bar is plastically deformed by the pressing force of the pressing roller, resulting in a defective product. is there.
In such a case, it is possible to suppress the deformation of the heat-fixing roller by reducing the pressing force of the pressing roller, but when the pressing force of the pressing roller is reduced, the smoothness of the resin release layer is reduced. However, there arises a problem that sufficient is not obtained.
[0004]
By the way, by rapidly cooling after heating the resin release layer on the core metal surface to the melting temperature or higher, the crystallinity of the resin release layer is reduced, and as a result of increasing the strength of the resin release layer, It is known that durability and smoothness can be improved.
However, when the quenching step is not performed uniformly on the entire surface, there is a problem that the toner may be fixed or an offset may be generated starting from a portion where the crystallinity is not uniform.
By the way, Japanese Patent Publication No. 6-51373, Japanese Patent No. 2646263 and Japanese Patent Publication No. 6-82257 all disclose a method in which a heating and fixing roller is heated with water to a temperature higher than the melting temperature of a resin release layer. A method of immersion is shown. However, when immersed in water, not only does the cooling speed not become uniform throughout the roller, but also a subsequent drying step is required, which increases the number of steps, lowers productivity, and also reduces quality. Various troubles are likely to occur.
[Patent Document 1] Japanese Patent Publication No. 6-51373
[Patent Document 2] Japanese Patent No. 2646263
[Patent Document 3] Japanese Patent Publication No. 6-82257
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
The present invention has been made in view of the above, and is intended to smooth a resin release layer in a heat-fixing roller in which a resin release layer is formed on a thin metal core having a thickness of less than 1 mm, and to apply a melting temperature to the resin release layer. In the apparatus and method carried out by heating to quenching and then quenching, the quenching process can be performed uniformly on the entire surface of the heat fixing roller, so that the crystallinity of the resin release layer is uniform. It is an object of the present invention to provide a smoothing device and a smoothing method for a resin release layer of a heat fixing roller, which are capable of improving the smoothness and the durability of the heat fixing roller.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to solve the above problem, the invention of claim 1 is a smoothing device for a resin release layer in a heat fixing roller having a resin release layer on the surface of a hollow cylindrical cored bar, wherein the smoothing is performed. Carrying-in means for carrying a heat-fixing roller provided with no resin release layer to a processing position; gripping means for grasping both ends in the axial direction of the heat-fixing roller carried into the processing position by the carrying-in means; A heating unit that heats the heat-fixing roller gripped by the melting temperature of the resin release layer or higher, a quenching unit that rapidly cools the heat-fixing roller heated to a melting temperature or higher by the heating unit, and the quenching unit. And a carry-out means for receiving the quenched heated fixing roller from the holding means and carrying it out.
According to the present invention, the crystallinity of the surface of the resin release layer is reduced when smoothing is performed by heating and quenching after forming the resin release layer on the cored bar, and high durability heating is achieved. The fixing roller can be manufactured continuously.
According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the first aspect, the rapid cooling means rapidly cools the heat fixing roller by injecting compressed air to a surface of the heat fixing roller.
According to the present invention, effective rapid cooling can be performed using a simple device that only injects compressed air.
According to a third aspect of the present invention, in the second aspect, the quenching means for injecting the compressed air includes a slit-shaped injection nozzle capable of obtaining uniform injection over the entire axial length of the heat fixing roller. I do.
According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a highly durable heat fixing roller having low crystallinity uniformly over the entire length of the heat fixing roller.
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, in the second or third aspect, the quenching means for injecting the compressed air includes a plurality of injection nozzles.
According to the present invention, since a plurality of injection nozzles are respectively arranged at appropriate locations to perform overall cooling on the heating and fixing roller, it is possible to increase the cooling speed, and to a deeper part of the release layer surface. Crystallinity can be reduced.
According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, in any one of the first, second, third, and fourth aspects, the apparatus further comprises a static eliminator for eliminating static electricity charged on the surface of the heat fixing roller gripped by the gripper.
According to the present invention, when the release layer is in a molten state due to the influence of static electricity charged on the surface of the heat fixing roller, dust in the air is prevented from adhering to the heat fixing roller and becoming defective. can do.
[0007]
According to a sixth aspect of the present invention, in the first to sixth aspects, the gripping means includes chuck portions for gripping both ends of the heat-fixing roller, and rotatably supports the chuck portions and is capable of axially moving back and forth. Bearing unit, a motor for rotating and driving at least one of the chuck units, and a drive source for moving at least one of the bearing units in the axial direction, wherein the heating means is supported by each of the chuck units. A heating source is detachably inserted into the heat fixing roller from an axial end opening thereof.
According to the present invention, it is possible to melt the release layer of the heat fixing roller while rotating at a constant speed, so that rapid cooling can be started in a state where the surface temperature of the roller is uniform, and uniform crystallization can be achieved. It is possible to gain the degree.
The invention according to claim 7 is characterized in that, in claim 6, the heating source is an infrared heater having a light distribution in an axial direction of the heat fixing roller.
According to the present invention, it is possible to provide an efficient heating source in which the heating and heating time until the release layer is in a molten state is short.
According to an eighth aspect of the present invention, in any one of the first to seventh aspects, the heating means includes a heating source for heating the outer peripheral surface of the heat fixing roller.
According to the present invention, the heating and heating time until the release layer is brought into a molten state can be further shortened, and a manufacturing apparatus with high productivity can be provided.
The invention according to
According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a manufacturing method capable of continuously manufacturing a highly durable heat fixing roller having low surface crystallinity.
[0008]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
1A and 1B are a side view of a heat fixing roller smoothing device according to an embodiment of the present invention, and a configuration diagram of the heat fixing roller. FIG. 2 is a front view of FIG. (A), (b) and (c) are a partial enlarged cross-sectional view, a main part cross-sectional view, and a main part enlarged view around a heating unit.
The smoothing device 0 according to the present embodiment automatically carries the heating /
The heat-fixing
The smoothing device 0 transports the plurality of heat-fixing
[0009]
The carry-in means 1 includes, for example, a
On the concave seat of each
The operation of mounting the
The lifting / lowering transfer means 5 includes
[0010]
The gripping means 10 includes two linear
With the heat-fixing
As shown in FIGS. 3A and 3B, the
A holding
[0011]
At the other end of the reinforcing
Accordingly, the
Conversely, when the
[0012]
The quenching
By using the quenching means 35, the cooling rate can be further increased, and the crystallinity can be lowered to a deeper position on the surface of the heat fixing roller.
By using, as the
In addition, since the static elimination means 55 for eliminating static electricity charged on the surface of the heat fixing roller is disposed, dust in the air adheres to the surface of the heat fixing roller when the release layer is in a molten state due to the influence of static electricity, and the defective product is regarded as defective. Can be prevented from occurring.
The carrying-out means 50 includes a
When the heating and fixing
[0013]
Next, FIG. 4 shows a modification of the smoothing device according to another embodiment of the present invention. As the quenching means 35, a plurality of quenching
FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram of a configuration of a heating unit according to another embodiment of the present invention. A quenching
According to the configuration of this embodiment, the heating and heating time until the
[0014]
Next, a smoothing procedure by the smoothing device 0 having the above configuration is as follows.
1. The
2. When the heating and fixing
3. Using the
4. The respective
5. By causing the
6. After the
7. After the
Repeat steps 8.1 to 7.
9. The heat-fixing
[0015]
(Implementation results)
FIG. 6 shows a temperature change when one
Under these conditions, a good
The present invention is applicable not only to the heat fixing roller but also to the smoothing of the surface of a cylindrical object whose surface is coated with a thermoplastic resin.
[0016]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, the smoothing of the resin release layer formed on the surface of the thin metal core having a thickness of less than 1 mm is performed by heating the resin release layer to a melting temperature and then rapidly cooling the resin release layer. In the processing apparatus and method of the fixing roller, by uniformly quenching the entire surface of the roller, the crystallinity of the resin release layer can be uniformly reduced, and the smoothness and durability can be increased.
That is, according to the first aspect of the present invention, when heated to a melting temperature and then rapidly cooled, the crystallinity of the release layer of the heat-fixing roller can be reduced, and the durability of the roller is improved. Can be done. Furthermore, since processing can be performed by batch processing using only the present apparatus alone, there is an effect that manufacturing can be performed without affecting existing manufacturing equipment at all.
According to the second and third aspects of the present invention, it is possible to rapidly cool using a simple cooling means that only injects compressed air.
According to the fourth aspect of the present invention, since a plurality of air nozzles are used, there is an effect that the cooling speed is further increased.
According to the fifth aspect of the present invention, since static elimination is performed before melting, there is an effect of preventing adhesion of dust floating in the air and preventing occurrence of defective products due to the attachment of dust.
According to the sixth and seventh aspects of the present invention, since a heat source having a length along the roller axis direction is used, uniform heating can be performed over the entire length of the roller, and the temperature can be quickly raised. Become.
According to the eighth aspect of the present invention, the heating temperature can be further increased by heating not only the inside of the roller but also the outside.
According to the ninth aspect of the invention, the crystallinity of the release layer of the heat fixing roller can be reduced, and the durability of the roller can be improved. Furthermore, since processing can be performed by batch processing using only the present apparatus alone, there is an effect that manufacturing can be performed without affecting existing manufacturing equipment at all.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIGS. 1A and 1B are a side view of a heat fixing roller smoothing device according to an embodiment of the present invention, and a configuration diagram of the heat fixing roller.
FIG. 2 is a front view of FIG. 1;
FIGS. 3A, 3B, and 3C are a partially enlarged cross-sectional view, a main part cross-sectional view, and a main part enlarged view around a heating unit.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a modification of the smoothing device according to another embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a configuration explanatory view of a heating unit according to another embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a change in temperature when rapid cooling is performed.
[Explanation of symbols]
A processing position, B mounting position, 0 smoothing device, 1 loading means, 2 rollers, 3 conveyors, 4 roller cradle, 5 lifting and lowering transfer means, 6 base, 7, 8 linear actuator, 9 work receiving, 10 gripping Means, 11 linear guide member, 12 chuck portion, 13 bearing unit, 15 linear actuator, 20 heating means, 21 heating source, 22 linear actuator, 23a, 23b holding member, 24 reinforcing member, 25 infrared heater, 26 guide Member, 26a electrode, 27 insulating guide member, 27 telescopic movable electrode, 27b fixed base, 28 wiring, 29 fixed part, 35 quenching means, 36 compressed air source, 37 air nozzle (injection means), 38 non-contact thermometer, REFERENCE SIGNS
Claims (9)
平滑化されていない樹脂離型層を備えた加熱定着ローラを加工位置に搬入する搬入手段と、
前記搬入手段によって加工位置に搬入されてきた加熱定着ローラの軸方向両端部を把持する把持手段と、
前記把持手段によって把持された加熱定着ローラを、前記樹脂離型層の溶融温度以上に加熱する加熱手段と、
前記加熱手段によって溶融温度以上に加熱された加熱定着ローラを急冷する急冷手段と、
前記急冷手段によって急冷された加熱定着ローラを把持手段から受け取って搬出する搬出手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする加熱定着ローラの離型層平滑化装置。A flattening device for a resin release layer in a heat fixing roller having a resin release layer on the surface of a hollow cylindrical cored bar,
Carrying means for carrying a heat fixing roller having a non-smoothed resin release layer to a processing position,
Gripping means for gripping both axial ends of the heat-fixing roller which has been carried into the processing position by the carrying-in means;
A heating unit that heats the heat fixing roller gripped by the gripping unit to a temperature equal to or higher than the melting temperature of the resin release layer,
Quenching means for quenching the heat fixing roller heated to a melting temperature or higher by the heating means,
An unloading unit that receives the heated fixing roller quenched by the quenching unit from the gripping unit and unloads it,
An apparatus for smoothing a release layer of a heat fixing roller, comprising:
前記加熱手段は、前記各チャック部により支持された加熱定着ローラの軸方向端部開口からその内部に加熱源を着脱自在に挿着する構成を備えていることを特徴とする請求項1乃至5の何れか一項に記載の加熱定着ローラの離型層平滑化装置。The gripping unit includes a chuck unit that grips both ends of the heat fixing roller, a bearing unit that rotatably supports the chuck units and is supported so as to be able to advance and retreat in the axial direction, and at least one chuck unit. A motor that rotates and has a drive source that moves at least one bearing unit in the axial direction,
6. The heating unit according to claim 1, wherein the heating unit has a configuration in which a heating source is removably inserted into an axial end opening of the heating / fixing roller supported by the chucks. The release layer smoothing device for a heat fixing roller according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
平滑化されていない樹脂離型層を備えた加熱定着ローラを加工位置に搬入する搬入工程と、
加工位置に搬入されてきた加熱定着ローラを把持した状態で、前記樹脂離型層をその溶融温度以上に加熱する加熱工程と、
前記加熱工程において溶融温度以上に加熱された加熱定着ローラを急冷する急冷工程と、
前記急冷工程において急冷された加熱定着ローラを加工位置から搬出する搬出工程と、
を備えたことを特徴とする加熱定着ローラの離型層平滑化方法。A method for smoothing a resin release layer in a heat fixing roller having a resin release layer on the surface of a hollow cylindrical cored bar,
A carrying-in step of carrying a heat-fixing roller having a non-smoothed resin release layer to a processing position,
A heating step of heating the resin release layer to a temperature equal to or higher than its melting temperature while holding the heat fixing roller that has been carried into the processing position;
A quenching step of quenching the heated fixing roller heated to a melting temperature or higher in the heating step,
An unloading step of unloading the heat fixing roller quenched in the quenching step from the processing position,
A method for smoothing a release layer of a heat fixing roller, characterized by comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003043408A JP2004252228A (en) | 2003-02-20 | 2003-02-20 | Device and method for smoothing release layer of heat fixing roller |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003043408A JP2004252228A (en) | 2003-02-20 | 2003-02-20 | Device and method for smoothing release layer of heat fixing roller |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004252228A true JP2004252228A (en) | 2004-09-09 |
Family
ID=33026392
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003043408A Pending JP2004252228A (en) | 2003-02-20 | 2003-02-20 | Device and method for smoothing release layer of heat fixing roller |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2004252228A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006163089A (en) * | 2004-12-08 | 2006-06-22 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Manufacture method and apparatus of resin coated roller |
| JP2007160526A (en) * | 2005-12-09 | 2007-06-28 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Quenching treatment apparatus of resin coated cylindrical body |
| CN101892018A (en) * | 2010-05-14 | 2010-11-24 | 上海天洋热熔胶有限公司 | Hot-melt adhesive film forming, delivering and winding device |
| JP2016177175A (en) * | 2015-03-20 | 2016-10-06 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Tubular body, fixation device and image formation device |
| CN108262999A (en) * | 2018-01-22 | 2018-07-10 | 杨康君 | PVC film produces humidification apparatus |
| CN116394553A (en) * | 2023-02-13 | 2023-07-07 | 湖州森诺氟材料科技有限公司 | Equipment and method for enhancing interlayer binding force of polytetrafluoroethylene microporous membrane |
-
2003
- 2003-02-20 JP JP2003043408A patent/JP2004252228A/en active Pending
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006163089A (en) * | 2004-12-08 | 2006-06-22 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Manufacture method and apparatus of resin coated roller |
| JP2007160526A (en) * | 2005-12-09 | 2007-06-28 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Quenching treatment apparatus of resin coated cylindrical body |
| CN101892018A (en) * | 2010-05-14 | 2010-11-24 | 上海天洋热熔胶有限公司 | Hot-melt adhesive film forming, delivering and winding device |
| JP2016177175A (en) * | 2015-03-20 | 2016-10-06 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Tubular body, fixation device and image formation device |
| CN108262999A (en) * | 2018-01-22 | 2018-07-10 | 杨康君 | PVC film produces humidification apparatus |
| CN108262999B (en) * | 2018-01-22 | 2020-12-04 | 浙江宏鑫减震系统股份有限公司 | PVC membrane production humidifying equipment |
| CN116394553A (en) * | 2023-02-13 | 2023-07-07 | 湖州森诺氟材料科技有限公司 | Equipment and method for enhancing interlayer binding force of polytetrafluoroethylene microporous membrane |
| CN116394553B (en) * | 2023-02-13 | 2024-01-30 | 湖州森诺氟材料科技有限公司 | Equipment and method for enhancing interlayer binding force of polytetrafluoroethylene microporous membrane |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6214300B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for manufacturing fixing member | |
| CN1202641A (en) | Fixing apparatus | |
| JP2004252228A (en) | Device and method for smoothing release layer of heat fixing roller | |
| JP4894962B1 (en) | Manufacturing method of cylindrical member | |
| JP2011136461A (en) | Embossing apparatus | |
| US20090067903A1 (en) | Coil unit for induction heating fixing device | |
| JPH10180797A (en) | Method and apparatus for molding insert molded article | |
| JP2006255679A (en) | Manufacturing method and apparatus for cylinder with coated film | |
| JP2009291949A (en) | Method and apparatus for molding thermoplastic resin | |
| JP3595695B2 (en) | Method for transferring surface pattern of transfer member to fluororesin surface on cylindrical substrate | |
| JP2004245880A (en) | Toner fixing member, method for manufacturing toner fixing member, and device for manufacturing toner fixing member | |
| JP2004212411A (en) | Fixing roller and method and apparatus for producing the roller | |
| EP0781644A2 (en) | Heat-treating method of a thermoplastic resin film | |
| JP2004148757A (en) | Method and apparatus for manufacturing resin coated roller | |
| JP4739809B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of large-diameter tubular product | |
| JP2002361139A (en) | Method and device for forming coating film on surface of shaft | |
| JP4012835B2 (en) | Plastic coating roller surface smoothing device | |
| EP3136183A1 (en) | Fixing device using stainless steel material | |
| JP6457889B2 (en) | Rubber hose manufacturing apparatus and manufacturing method | |
| JP2006163089A (en) | Manufacture method and apparatus of resin coated roller | |
| JP2592937B2 (en) | Fixing device | |
| JP2883346B2 (en) | Electrostatic coating method and apparatus therefor | |
| JP2006334937A (en) | Method and apparatus for producing rubber roller | |
| JPH07199691A (en) | Heat-resistant fixing film and heating/fixing device using the same | |
| JP6776860B2 (en) | A sizing die, an extrusion molding device, and a method for manufacturing a tubular member using them. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050621 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20071022 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20071030 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Effective date: 20080401 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 |