JP2004056984A - Power converting device - Google Patents
Power converting device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2004056984A JP2004056984A JP2002215303A JP2002215303A JP2004056984A JP 2004056984 A JP2004056984 A JP 2004056984A JP 2002215303 A JP2002215303 A JP 2002215303A JP 2002215303 A JP2002215303 A JP 2002215303A JP 2004056984 A JP2004056984 A JP 2004056984A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- terminal
- conductor
- arm
- side arm
- filter capacitor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Inverter Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、自己消弧型半導体素子とそれに逆並列接続されるダイオードを内蔵したパワーモジュールを適用したインバータ部を含む電力変換装置に関するものである。特に電力変換装置内における浮遊インダクタンスを極力抑制してパワーモジュールのスイッチング動作により発生するサージを軽減すると同時に、パワーモジュールに設けられている複数端子間の電流不平衡を抑制する電力変換装置の実装技術に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
図14は特開2002−044949号公報に開示されている従来の電力変換装置の基本回路構成を示す図である。図14において、1は直流電源、2はフィルタコンデンサ、3はインバータ部である。インバータ部3はパワーモジュール4と出力端子5を備えており、パワーモジュール4はIGBT(Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor)6a、6bとIGBT6a、6bの各々に逆並列接続されるダイオード7a、7bから構成される。
【0003】
一方、図15は図14におけるインバータ部3のパワーモジュール4とフィルタコンデンサ2との接続構成を説明した図である。フィルタコンデンサ2はコンデンサ群8a、8bに分割されており、コンデンサ群8a、8bは複数のコンデンサエレメント9a〜9fから成る。また、各コンデンサエレメント9a〜9fの電極端子は向き合わせて面対称的に配置されている。フィルタコンデンサ2とパワーモジュール4は平行配置された導体10a、10bによって接続されている。図16(a)(b)は各々、図15のコンデンサ群8a及びコンデンサ群8bの実態を示す図であり、例えばコンデンサ群8aは3つのコンデンサエレメント9a、9b、9cを一組として複数組配列し、板状導体11a〜11dによって並列接続されている。コンデンサ群8bも同様に、3つのコンデンサエレメント9d、9e、9fを一組として複数組配列し、板状導体11e〜11hによって並列接続されている。この板状導体11a〜11hは積層板状導体、所謂ラミネートブスバーによって構成される。導体10aは導体11a、11hと電気的に接続された状態で、コンデンサ群8a、8bとパワーモジュール4とを接続する。導体10bは導体11d、11eと電気的に接続された状態で、コンデンサ群8a、8bとパワーモジュール4とを接続する。
【0004】
フィルタコンデンサ2を前記のようにコンデンサ群8a、8bに分割配置し、パワーモジュール4と前記フィルタコンデンサ2とを近接平行に配置された板状導体10a、10bによって接続することにより、板状導体10a、10bは向き合った導体に流れる電流の向きが相反する関係となる。これにより、電流によって発生する磁力線が互いに打ち消し合うことになり、サージの発生を抑制することが可能となる。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、前記のような従来の電力変換装置においては、フィルタコンデンサ2からインバータ部3までの配線が原因で発生するサージを軽減するためのコンデンサ配列方法及び各コンデンサとパワーモジュール4との接続方法が示されているのみであり、フィルタコンデンサ内部の配線とインバータ部内部の配線との関係、直流電源1からフィルタコンデンサ2への配線と他の配線との関係、パワーモジュール4から出力端子5への配線や出力端子5と負荷との間の配線と他の配線との関係等に関しては何ら考慮されておらず、これらの配線間でサージの発生を十分に抑制することができなかった。従って、結局はサージ吸収のための部品が増加することとなり、装置コストが高くなるとともに信頼性が低下するという問題があった。
【0006】
また、図15に示すようにコンデンサ群8a、8bを構成すると、陽極と陰極とを適宜低インダクタンス化を図りながら接続するためには、接続導体自体が絶縁されて複数重ねられた形状をもつ積層板状導体(所謂ラミネートブスバー)を用いる必要がある。これは部品コストが高くなり、ひいては装置コストが高くなるという問題があった。
更に、コンデンサエレメントの電極面で低インダクタンス化を図る必要があるが、特に板状導体10aと板状導体10bとの間において、電極とラミネートブスバーとを接続するボルトなどの締め付け部品のための空間を確保せねばならず、板状導体10aと板状導体10bとを十分近接配置できないという問題があった。
【0007】
また、車両推進システムに適用するような比較的大容量な電力変換装置の場合には、負荷となる電動機の容量が大きく大電流を出力する必要があるため、パワーモジュールは同一電位かつ少なくとも2つ以上に分割されたエミッタ端子、コレクタ端子を備える。このようなパワーモジュールを用いる場合には分割された複数の端子に流れる電流の不平衡状態を回避しなければならない。もしパワーモジュール以外の外的要因によって前記不平衡状態が発生する場合には不平衡電流に応じて出力電流を減じなければならず、インバータ部の出力容量が低下する。従って、パワーモジュールを複数並列接続することによって低下するであろう出力電流を補償して、必要な出力容量を確保しなければならない。これは部品コストが高くなり、ひいては装置コストが高くなるという問題があった。
【0008】
本発明は前記のような問題点を解消するためになされたものであり、電力変換装置における配線インダクタンスを減少させ、サージ発生要因自体を大幅に低減させることが可能な電力変換装置を提供することを目的とする。また、これにより、サージ抑制部品の寸法や容量を小さくし、あるいは不要にして、装置自体の信頼性向上と小形化、低コスト化を図ることが可能な電力変換装置を提供することを目的としている。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明の電力変換装置は、少なくとも1つ以上のコンデンサエレメントにより構成され、直流電圧を受電または送電するフィルタコンデンサ、前記フィルタコンデンサのP側に接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるP側アーム、前記フィルタコンデンサのN側に接続されると共に、前記P側アームと直列接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるN側アーム、及び前記P側アームと前記N側アームとの直列接続点と接続される出力端子を備えた電力変換装置において、前記フィルタコンデンサは、直流電圧を受電または送電するP側端子とN側端子とで構成された一対の第1直流端子と、前記P側アームに接続されるP側端子と前記N側アームに接続されるN側端子とで構成された一対の第2直流端子と、前記第1直流端子のP側端子と前記第2直流端子のP側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのP側に接続されるP側導体と、前記第1直流端子のN側端子と前記第2直流端子のN側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのN側に接続されるN側導体とを備え、前記P側導体と前記N側導体とは少なくとも一部分が略平行に配置された構成のものである。
【0010】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、少なくとも1つ以上のコンデンサエレメントにより構成され、直流電圧を受電または送電するフィルタコンデンサ、前記フィルタコンデンサのP側に接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるP側アーム、前記フィルタコンデンサのN側に接続されると共に、前記P側アームと直列接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるN側アーム、及び前記P側アームと前記N側アームとの直列接続点と接続される出力端子を備えた電力変換装置において、前記フィルタコンデンサは、直流電圧を受電または送電するP側端子とN側端子とで構成された一対の第1直流端子と、前記P側アームに接続されるP側端子と前記N側アームに接続されるN側端子とで構成された一対の第2直流端子と、前記第1直流端子のP側端子と前記第2直流端子のP側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのP側に接続されるP側導体と、前記第1直流端子のN側端子と前記第2直流端子のN側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのN側に接続されるN側導体とを備え、前記P側導体と前記N側導体の少なくとも第2直流端子側部分は、前記P側アームと前記N側アームとを直列接続するアーム接続導体と略平行に配置され、かつ電流の流れる方向が逆方向となるように構成されたものである。
【0011】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、少なくとも1つ以上のコンデンサエレメントにより構成され、直流電圧を受電または送電するフィルタコンデンサ、前記フィルタコンデンサのP側に接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるP側アーム、前記フィルタコンデンサのN側に接続されると共に、前記P側アームと直列接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるN側アーム、及び前記P側アームと前記N側アームとの直列接続点と接続される出力端子を備えた電力変換装置において、前記フィルタコンデンサは、直流電圧を受電または送電するP側端子とN側端子とで構成された一対の第1直流端子と、前記P側アームに接続されるP側端子と前記N側アームに接続されるN側端子とで構成された一対の第2直流端子と、前記第1直流端子のP側端子と前記第2直流端子のP側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのP側に接続されるP側導体と、前記第1直流端子のN側端子と前記第2直流端子のN側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのN側に接続されるN側導体とを備え、前記P側導体と前記N側導体とは少なくとも一部分が略平行に配置され、前記P側導体と前記N側導体の少なくとも第2直流端子側部分は、前記P側アームと前記N側アームとを直列接続するアーム接続導体と略平行に配置され、かつ電流の流れる方向が逆方向となるように構成されたものである。
【0012】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、P側アームとN側アームとの直列接続点と出力端子とを接続する出力端子接続導体は、少なくともP側導体またはN側導体の一部と略平行に配置されているものである。
【0013】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、フィルタコンデンサは、P側導体とN側導体との間に出力端子接続導体を貫通させることができる空間を有し、前記出力端子接続導体は、前記空間を貫通して取り出せるように配置されているものである。
【0014】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、空間を貫通する出力端子接続導体とP側導体との間、及び空間を貫通する前記出力端子接続導体とN側導体との間に絶縁物が挿入されているものである。
【0015】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、フィルタコンデンサは、少なくとも2つ以上の複数のコンデンサエレメントと、これら複数のコンデンサエレメントを並列接続するP側導体及びN側導体とをモールド成形した構成のものである。
【0016】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、一対の第2直流端子は、フィルタコンデンサの本体より外側に突出して設けられ、突出した前記一対の第2直流端子に、P側アームの自己消弧型半導体素子のコレクタ端子とN側アームの自己消弧型半導体素子のエミッタ端子とをそれぞれ接続するものである。
【0017】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、フィルタコンデンサはP側アームとN側アームとの直列接続点と常に同電位にある出力端子を備えた構成のものである。
【0018】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、P側アームおよびN側アームは、それぞれ複数個の直列接続された自己消弧型半導体素子とこれら自己消弧型半導体素子の各々に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されたものである。
【0019】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、P側導体とN側導体の少なくとも第2直流端子側部分は、P側アームおよびN側アームを構成する複数個の自己消弧型半導体素子を直列接続する接続導体と略平行に配置され、かつ電流の流れる方向が逆方向となるように構成されているものである。
【0020】
また、本発明の電力変換装置は、前記装置において、フィルタコンデンサとP側アームとN側アームと出力端子とで構成される電力変換ユニットを複数組有し、各フィルタコンデンサの第1直流端子におけるN側端子同士、及び各フィルタコンデンサの第1直流端子におけるP側端子同士を並列に接続したものである。
【0021】
【発明の実施の形態】
実施の形態1.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図を用いて説明する。
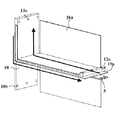
なお、すべての図面において同一符号は同一若しくは相当部材とする。図1は本発明の実施の形態1による電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図である。図2、図3は本実施の形態1による電力変換装置の構造を具体的に示す斜視図であり、特にフィルタコンデンサ2の構造を異なる方向からみた図である。また、図4はP側導体の具体的な構成を、図5はアーム接続導体および出力端子接続導体の構成を具体的に示す。
図1において、1は陽極(Pと記す)と陰極(Nと記す)の電位を持つ直流電源、2は直流電源1からの直流電圧を受電するフィルタコンデンサ(負荷から電流が流れ込む場合は直流電圧を送電する)、3はインバータ部である。フィルタコンデンサ2は複数のコンデンサエレメント9から構成され、直流電源1に接続されるP側端子12aとN側端子12bとで構成された一対の第1直流端子と、インバータ部3に接続されるP側端子13aとN側端子13bとで構成された一対の第2直流端子と、第1直流端子のP側端子12aと第2直流端子のP側端子13aとを接続すると共に、コンデンサエレメント9のP側に接続されるP側導体16aと、第1直流端子のN側端子12bと第2直流端子のN側端子13bとを接続すると共に、コンデンサエレメント9のN側に接続されるN側導体16bとを備える。また、インバータ部3はIGBT6aおよびフリーホイールダイオード7aを内蔵したパワーモジュール4aで構成されるP側アームと、IGBT6bおよびフリーホイールダイオード7bを内蔵したパワーモジュール4bで構成されるN側アームとを備える。14a、15aはそれぞれパワーモジュール4aのコレクタ端子、エミッタ端子であり、14b、15bはパワーモジュール4bのコレクタ端子、エミッタ端子である。P側アームとN側アームとは直列接続され、IGBT6aのエミッタ端子15aとIGBT6bのコレクタ端子14bとがアーム接続導体18により直列接続される。またP側アームとN側アームとの直列接続点から負荷に接続される出力端子5が引き出されており、前記直列接続点と出力端子5とを接続する出力端子接続導体17は、フィルタコンデンサ2のP側導体16aとN側導体16bとの間に設けられた空間を貫通して、一対の第1直流端子12a、12bの間から外部に引き出されている。
【0022】
フィルタコンデンサ2は、図2、3に示すように、複数のコンデンサエレメント9で構成され、各コンデンサエレメント9はそれぞれのP側端子が幅広の板状のP側導体16a1、16a2に、それぞれのN側端子が幅広の板状のN側導体16b1、16b2に接続されており、複数のコンデンサエレメント9は並列接続されている。また、P側導体16a1、16a2は、第1直流端子のP側端子12aと第2直流端子のP側端子13aとを接続する幅広の板状のP側導体16a3、16a4に接続されている。N側導体16b1、16b2も同様に、第1直流端子のN側端子12bと第2直流端子のN側端子13bとを接続する幅広の板状のN側導体16b3、16b4に接続されている。前記P側導体16a1、16a2、16a3、16a4は、図4に示すような構成であり、電気的に接続されてP側導体16aを構成する。また、P側導体16a4は第2直流端子のP側端子13aを有し、P側導体16a3は第1直流端子のP側端子12aを有する。N側導体16b1、16b2、16b3、16b4も同様の構成であり、N側導体16bを構成する。配置は板状導体16aを180度回転した状態に置かれ、P側導体16a3とN側導体16b3とは略平行に配置される。
P側導体16a4及びN側導体16b4はアーム接続導体18と略平行に配置され、第2直流端子のP側端子13aにはパワーモジュール4aのコレクタ端子14aが直接接続され、第2直流端子のN側端子13bにはパワーモジュール4bのエミッタ端子15bが直接接続される。
【0023】
出力端子接続導体17は、幅広の板状の導体で構成されており、出力端子5を有する。アーム接続導体18も幅広の板状の導体で構成されており、端子18a、18bを有する。これら幅広の板状の接続導体17、18は、図5に示すように、一体化されている。端子18aはパワーモジュール4aのエミッタ端子15aと直接接続され、端子18bはパワーモジュール4bのコレクタ端子15bと直接接続される。図5において、接続導体17の出力端子5に至る部分については、出力端子5に近づく程、幅が小さくなっているが、全く同じ幅のものを適用しても良い。
【0024】
また、、出力端子接続導体17とP側導体16aとの間、及びアーム接続導体18とP側導体16aとの間には、図2、図3に示すように、幅広の板状の絶縁物19aが挿入されており、出力端子接続導体17とN側導体16bとの間、及びアーム接続導体18とN側導体16bとの間には幅広の板状の絶縁物19bが挿入されている。
【0025】
図6はパワーモジュール4a(もしくは4b)に適したパワーモジュール構造を示す図であり、IGBT6a(もしくは6b)とフリーホイールダイオード7a(もしくは7b)とが同一モジュール内に収納されている。14aは例えば3つに分割されたコレクタ端子、15aは3つに分割されたエミッタ端子である。これら3端子構成のコレクタ端子14a、14b、及びエミッタ端子15a、15bにそれぞれP側導体16aの第2直流端子13a、接続導体18の端子18a、18b、N側導体16bの第2直流端子13bが取り付けられるが、本実施の形態においては、第2直流端子13aから第1直流端子12aへの電流経路、端子18aから端子18bへの電流経路、および第2直流端子13bから第1直流端子12bへの電流経路については、全て幅の等しい幅広の板状導体を用いて構成されており、ねじれの位置に無いため、各々の3端子に対してインピーダンスが均等に配分される構成となっている。つまり、パワーモジュールの外部要因によって各3端子間に流れる電流を不均衡にする要因が未然に排除されるような構造になっている。
【0026】
以上の構造物を用いた電力変換装置の組立方法を説明する。
まず、パワーモジュール4aのエミッタ端子15aと接続導体18の端子18aとを接続し、パワーモジュール4bのコレクタ端子14bと接続導体18の端子18bとを接続する。次に、P側導体16aに複数個のコンデンサエレメント9のうちの半分のコンデンサエレメント9のP側端子を、またN側導体16bに残りの複数個のコンデンサエレメント9のN側端子を接続する。次に、コンデンサエレメント9が接続されたP側導体16aとN側導体16bとを組合せ、コンデンサエレメント9をすべて導体16aと導体16bに接続して、フィルタコンデンサ2を形成する。P側導体16aとN側導体16bとを組合せる際には、P側導体16a3とN側導体16b3との間に空間を有するように組み合わせる。次に、フィルタコンデンサ2の前記空間に絶縁物19a、19bを適宜挿入したのち、前記空間に接続導体17を貫通させる。なお、絶縁物19a、19bは接続導体18とP側導体16a4及びN側導体16b4との間にも挿入される。この後、パワーデバイス4aのコレクタ端子14aと第2直流端子のP側端子13a、パワーデバイス4bのエミッタ端子15bと第2直流端子のN側端子13bとを接続して組立を完了する。
なお、この組立過程のうち、少なくとも導体16a、16bと複数のコンデンサエレメント9、望ましくは絶縁物19a、19bも含めて、予め樹脂などでモールド一体形成することによって、フィルタコンデンサ2を1つの導体内蔵型のフィルタコンデンサとして構成することにより、更に組立を容易にし、組立て時間を短縮することが可能である。
【0027】
次に、本実施の形態による電力変換装置において用いられる各導体は、常に同じ値の逆方向の電流が流れる導体と平行近接の位置関係を持つことを示す。特に定常時に流れる負荷電流と負荷電流の転流時に流れるダイオードの逆回復電流との2つの場合について説明する。
【0028】
まず、負荷電流が流れる経路について図7、図8を用いて説明する。図7はこの説明のためにP側導体16aと接続導体17、18とを作為的に抽出した図であり、図8は電流経路を説明するための回路図である。なおコンデンサエレメント9は省略する。
パワーデバイス4aが導通している場合には、負荷電流は図8に矢印で示す経路で流れる。負荷に流れ出る電流について記載したが、負荷から流れ込む電流については矢印の向きが変わるだけで、本質的な違いは無い。図8に示した電流は、図7において、矢印に示すように、第1直流端子のP側端子12aから接続導体16aの中心部を通って第2直流端子のP側端子13a、パワーデバイス4aのコレクタ端子14a、エミッタ端子15a、端子18aを経、接続導体18、17を介して出力端子5に至る経路を流れる。図7より、前記経路において、各導体のどの部分を見ても必ず同じ大きさの電流が流れるような対となる平行導体部分が存在する。この条件は負荷電流の大きさが変化しても成立する。従って、この経路を流れる電流によって生じる磁力線を相殺する効果は最大限に発揮されるような構造になっている。
【0029】
次に、負荷電流の転流時に流れる経路について図9、図10を用いて説明する。図9はこの説明のためにP側導体16aの一部分(16a4)と、N側導体16bの一部分(16b4)と、接続導体、17、18を作為的に抽出した図であり、図10は電流経路を説明するための回路図である。
負荷電流がパワーモジュール4bのダイオード7bに流れている状態で、IGBT6bにオフ信号が与えられた後にIGBT6aがターンオンするとダイオード7bの逆回復動作を伴うことから、図10に示す直流電源1を短絡するような経路で電流が過渡的に流れる。即ち、図10において矢印に示すように、第1直流端子のP側端子12aから、第2直流端子のP側端子13a、パワーモジュール4aのコレクタ端子14a、エミッタ端子15a、端子18a、接続導体18、端子18b、パワーモジュール4bのコレクタ端子14b、エミッタ端子15b、第2直流端子のN側端子13b、第1直流端子のN側端子12bに至る経路を流れる。このような経路においては、図9に示すように、特にP側導体の第2直流端子側部分16a4、及びN側導体の第2直流端子側部分16b4において、必ず電流の変化率が等しくなるような対となる平行導体部分が存在する。即ち、アーム接続導体18がP側導体16a4、16b4に略平行に配置され、かつ電流の流れる方向が逆方向となるように構成されている。図9には図示されていないが、P側導体の第1直流端子側部分16a3、及びN側導体の第1直流端子側部分16b3においても、これらは互いに略平行に配置されており、かつ電流の流れる方向が逆方向となるように構成されている。従って、この経路を流れる電流の変化率によって生じる磁力線を相殺する効果は最大限に発揮されると同時に、相互結合によって浮遊インダクタンスの最小化効果は最大限に発揮されるような構造になっている。
【0030】
なお、本実施の形態においては、図2、図3に示すように、一対の第2直流端子13a、13bは、フィルタコンデンサ2の本体より外側に突出して設けられており、突出した前記一対の第2直流端子13a、13bに、パワーモジュール4aのコレクタ端子とパワーモジュール4bのエミッタ端子とをそれぞれ接続するので、組立てが容易であり、装置のコストを低減することができる。
【0031】
以上のように、本実施の形態では、P側端子とN側端子とで構成される1対の直流端子を2組備え、それぞれのP側端子間、及びN側端子間を接続する導体をフィルタコンデンサ内に内蔵し、かつこれら導体の配置を工夫したので、配線インダクタンスを減少させ、サージ発生要因自体を大幅に低減させることが可能となる。また、これにより、サージ抑制部品の寸法や容量を小さくし、あるいは不要にして、装置自体の信頼性向上と小形化、低コスト化を図ることが可能となる。また、パワーモジュールとの接続を簡素化でき、装置の組立コストを低減することができる。
また、P側導体、N側導体、アーム接続導体、出力端子接続導体等の各導体を幅広の板状導体で構成したので、さらに配線インダクタンスを減少させることが可能となる。
また、パワーモジュールの電極が分割されている場合にはインピーダンスが均等に配分される構成となり、分割された各電極に流れる電流が不平衡になることがない。
【0032】
また、出力端子5は、フィルタコンデンサ内に空間を設けて接続導体によりフィルタコンデンサ内を貫通させて取り出すようにしたので、使用する導体として積層導体を使用する必要がないので、装置コストを低減することができる。
【0033】
また、フィルタコンデンサ2としてモールドタイプコンデンサを適用することにより、必要な導体をフィルタコンデンサ内に内蔵でき、装置の組立を簡素化できる。また、積層導体、所謂ラミネートブスバーを用いる必要がなくなるため、装置コストを低減することができる。
【0034】
また、第1直流端子と第2直流端子との間で複数のコンデンサエレメントを板状の導体により並列に接続しているので、フィルタコンデンサの必要容量が大きくなり、フィルタコンデンサの筐体寸法が大きくなった場合にも、内部インダクタンスを下げることができるため、パワーモジュールのスイッチング時に発生するサージ電圧が抑制でき、装置の信頼性を向上できる。
【0035】
また、接続導体17、18とP側導体16aとの間、及び接続導体17、18とN側導体16bとの間に、それぞれ絶縁物を挿入しているので、絶縁距離を空間によって確保するのではなく、絶縁物の沿面で確保でき、各導体を近接配置できるため、相互インダクタンスによる浮遊インダクタンスの低減が図れ、パワーモジュールのスイッチング時に発生するサージ電圧が抑制でき、装置の信頼性が向上できる。
【0036】
また、IGBTとダイオードとが同一モジュールに収納されたIGBTモジュールを用いているので、パワーモジュールとして標準品を使用することができ、装置コストを低減することができる。
【0037】
なお、本実施の形態においては、フィルタコンデンサ2は第1の直流端子12a、12bと、第2の直流端子13a、13bとを有し、かつフィルタコンデンサ2に形成された空間内を、出力端子5に接続される接続導体17が貫通するように構成して、出力端子5を第1の直流端子側から取り出せるように構成したが、上記接続導体17をフィルタコンデンサ内に内蔵して、例えばフィルタコンデンサ2の第1直流端子側に、出力端子5と常に同電位にある出力端子を備えた構成としてもよく、パワーモジュールとの接続等が簡素化でき、装置の組立コストを低減することができる。
【0038】
また、コンデンサエレメント9の形状については、一例として円柱形状のものを適用した図を示したが、特に円柱状の形状である必要はなく、例えば直方体状の形状であっても同様の効果が得られる。
【0039】
なお、図4、図5において、例えば導体16a、16b、17、18などを一体成形された導体として図示したが、特に一体成形される必要はなく、幾つかの導体を繋ぎあわせて形成しても良いことは言うまでもない。
また、パワーモジュールの具体例としてIGBTとダイオードが内蔵されたものについて説明したが、特にIGBTに限定される必要はなく、MOSFETや他の自己消弧型半導体素子であっても構わない。また、自己消弧型半導体素子やダイオードの材質についてはシリコンであっても良いし、新しい半導体材料として例えばシリコンカーバイドであっても構わない。
【0040】
本実施の形態において、パワーモジュール4a、4bの冷却フィンについては触れなかったが、冷却フィンはパワーモジュール4a、4bに個別に装着しても良いし、共通な冷却フィンに2つのパワーモジュール4a、4bを装着しても良い。
【0041】
実施の形態2.
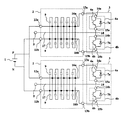
図11は本発明の実施の形態2による電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図であり、各アームは、直列接続された複数(ここでは2個)のパワーモジュールで構成されている。図において、4a、4bはP側アームを構成するパワーモジュール、4c、4dはN側アームを構成するパワーモジュールである。各アームにおいて、直列接続されるパワーモジュールの数は任意に設定できる。第2直流端子のP側端子13aは最も高電位にあるパワーモジュール4aのコレクタ端子14aに接続され、第2直流端子のP側端子13bは最も低電位にあるパワーモジュール4dのエミッタ端子15dに接続される。出力端子5はパワーモジュール4bのエミッタ端子15bとパワーモジュール4cのコレクタ端子14cとの接続点の延長として設けられている。また、P側アームのパワーモジュール4bのエミッタ端子15bとN側アームのパワーモジュール4dのコレクタ端子14cとを接続するアーム接続導体18の他に、各アームのパワーモジュール間を接続する接続導体、即ち接続導体パワーモジュール4aとパワーモジュール4b、パワーモジュール4cとパワーモジュール4dの各々エミッタ端子とコレクタ端子を接続するための接続導体20a、20bが必要となり、これら接続導体20a、20bは接続導体18と同様、P側導体16a及びN側導体16bの第2直流端子側部分、即ちP側導体16a4及びN側導体16b4と略平行に配置される。
【0042】
電力変換装置としての構造の考え方は図2、図3に記載したものと変更なく適用することができ、各導体は、常に同じ値の逆方向の電流が流れる導体と平行近接の位置関係を持つ。
【0043】
本実施の形態の構成では、各アームにおいて、複数のパワーモジュールを直列接続しているので、実施の形態1の効果に加え、装置の高圧出力化を図ることができるため、装置の適用範囲が拡大する。
【0044】
なお、パワーモジュールの冷却フィンについては、本実施の形態のような直列接続の場合には各パワーモジュールの電位が異なることから、各々のパワーモジュールに個別に冷却フィンを装着することが、パワーモジュールに過度な絶縁を持たせないようにする意味でも適当である。
【0045】
実施の形態3.
図12は本発明の実施の形態3による電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図であり、多相構成の電力変換装置の回路構成を示す。本実施の形態3では、図1に示す回路構成の電力変換ユニットを複数組有し、各フィルタコンデンサ2の第1直流端子におけるN側端子12a同士、及び各フィルタコンデンサ2の第1直流端子におけるP側端子12b同士を並列に接続する。なお、図12において、相数は2としたが、相数は任意に選ぶことが可能である。
例えば車両用推進装置においては、一般に3相インバータとブレーキ回路が必要となるが、このブレーキ回路が同じユニットとして構成可能な場合には、4相構成が適用されることになる。このような構成を実現するためには、各ユニットにおける第1直流端子12a、12bを並列に接続することが有利である。なぜならフィルタコンデンサ2の等価合成容量を増加できるため、直流電圧のリップル低減、即ち安定化に貢献することになるからである。特に互いの第1直流端子12a、12bを平行導体によって並列接続することは、並列接続部の低インダクタンス化が図れることから好ましい方策である。
【0046】
このような構成とすることにより、容易に多相出力構成が実現できる。また、直流電圧を制御するチョッパ機能をこのモジュールに持たせることによって、同じ電力変換ユニットを汎用的に用いることが可能となり、装置コストを低減することができる。
【0047】
実施の形態4.
図13は本発明の実施の形態4による電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図であり、出力端子5をフィルタコンデンサ2の第1直流端子12a、12bの間から取り出さない構成の電力変換装置である。この場合には、出力端子5は図1に図示された出力端子と反対の方向に取り出すため、負荷電流による磁力線をP側導体16aとN側導体16bとによって打ち消すことはできないが、逆回復電流による磁力線を打ち消すことはできる。
フィルタコンデンサ2としては、前述したものをそのまま適用することができるし、その際、絶縁物19a、19bを取り除いた構造のものを接続してもよい。また、フィルタコンデンサ2は出力端子5とは無関係となるので、第1直流端子12a、12bと第2直流端子13a、13bとを備えたものとなる。
【0048】
なお、図11に示す構成と同様の電力変換装置に対しても、上記実施の形態と同様に、出力端子を反対方向に取り出すようにしても良い。
【0049】
また、出力端子5を取り出す位置は、上記各実施の形態の位置でなくともよい。例えば、フィルタコンデンサ2の第1直流端子12a、12bの間ではなく、第1直流端子12a、12b側の他の位置であっても良く、出力端子接続導体17がP側導体16aまたはN側導体16bの一部と略平行に配置されるような位置であっても良い。
【0050】
【発明の効果】
以上のように、本発明によれば、少なくとも1つ以上のコンデンサエレメントにより構成され、直流電圧を受電または送電するフィルタコンデンサ、前記フィルタコンデンサのP側に接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるP側アーム、前記フィルタコンデンサのN側に接続されると共に、前記P側アームと直列接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるN側アーム、及び前記P側アームと前記N側アームとの直列接続点と接続される出力端子を備えた電力変換装置において、前記フィルタコンデンサは、直流電圧を受電または送電するP側端子とN側端子とで構成された一対の第1直流端子と、前記P側アームに接続されるP側端子と前記N側アームに接続されるN側端子とで構成された一対の第2直流端子と、前記第1直流端子のP側端子と前記第2直流端子のP側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのP側に接続されるP側導体と、前記第1直流端子のN側端子と前記第2直流端子のN側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのN側に接続されるN側導体とを備え、前記P側導体と前記N側導体とは少なくとも一部分が略平行に配置された構成としたので、電力変換装置の導体配線の不均衡によるノイズの発生が抑制できる効果がある。また、配線インダクタンスを減少させ、サージ発生要因自体を大幅に低減させることが可能となる。また、ノイズやサージの抑制部品の寸法や容量を小さくし、あるいは不要にして、装置自体の信頼性向上と小形化、低コスト化を図ることが可能となる。
【0051】
また、本発明によれば、少なくとも1つ以上のコンデンサエレメントにより構成され、直流電圧を受電または送電するフィルタコンデンサ、前記フィルタコンデンサのP側に接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるP側アーム、前記フィルタコンデンサのN側に接続されると共に、前記P側アームと直列接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるN側アーム、及び前記P側アームと前記N側アームとの直列接続点と接続される出力端子を備えた電力変換装置において、前記フィルタコンデンサは、直流電圧を受電または送電するP側端子とN側端子とで構成された一対の第1直流端子と、前記P側アームに接続されるP側端子と前記N側アームに接続されるN側端子とで構成された一対の第2直流端子と、前記第1直流端子のP側端子と前記第2直流端子のP側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのP側に接続されるP側導体と、前記第1直流端子のN側端子と前記第2直流端子のN側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのN側に接続されるN側導体とを備え、前記P側導体と前記N側導体の少なくとも第2直流端子側部分は、前記P側アームと前記N側アームとを直列接続するアーム接続導体と略平行に配置され、かつ電流の流れる方向が逆方向となるように構成したので、前記効果と同様の効果がある。
【0052】
また、本発明によれば、少なくとも1つ以上のコンデンサエレメントにより構成され、直流電圧を受電または送電するフィルタコンデンサ、前記フィルタコンデンサのP側に接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるP側アーム、前記フィルタコンデンサのN側に接続されると共に、前記P側アームと直列接続され、自己消弧型半導体素子とこの自己消弧型半導体素子に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成されるN側アーム、及び前記P側アームと前記N側アームとの直列接続点と接続される出力端子を備えた電力変換装置において、前記フィルタコンデンサは、直流電圧を受電または送電するP側端子とN側端子とで構成された一対の第1直流端子と、前記P側アームに接続されるP側端子と前記N側アームに接続されるN側端子とで構成された一対の第2直流端子と、前記第1直流端子のP側端子と前記第2直流端子のP側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのP側に接続されるP側導体と、前記第1直流端子のN側端子と前記第2直流端子のN側端子とを接続すると共に、前記コンデンサエレメントのN側に接続されるN側導体とを備え、前記P側導体と前記N側導体とは少なくとも一部分が略平行に配置され、前記P側導体と前記N側導体の少なくとも第2直流端子側部分は、前記P側アームと前記N側アームとを直列接続するアーム接続導体と略平行に配置され、かつ電流の流れる方向が逆方向となるように構成したので、前記効果と同様の効果がある。
【0053】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、P側アームとN側アームとの直列接続点と出力端子とを接続する出力端子接続導体は、少なくともP側導体またはN側導体の一部と略平行に配置されているので、浮遊インダクタンスが低減できるため、スイッチング時のサージ電圧が抑制でき、装置の信頼性を向上させることが可能となる。
【0054】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、フィルタコンデンサは、P側導体とN側導体との間に出力端子接続導体を貫通させることができる空間を有し、前記出力端子接続導体は、前記空間を貫通して取り出せるように配置されているので、上記効果に加え、積層導体を使用する必要が無いため、装置コストを低減できる効果がある。
【0055】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、空間を貫通する出力端子接続導体とP側導体との間、及び空間を貫通する前記出力端子接続導体とN側導体との間に絶縁物が挿入されているので、各導体を近接配置できるため、相互インダクタンスによる浮遊インダクタンスの低減が図れ、パワーモジュールのスイッチング時に発生するサージ電圧が抑制でき、装置の信頼性が向上できる。
【0056】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、フィルタコンデンサは、少なくとも2つ以上の複数のコンデンサエレメントと、これら複数のコンデンサエレメントを並列接続するP側導体及びN側導体とをモールド成形した構成であるので、必要な導体をフィルタコンデンサ内に内蔵でき、装置の組立を簡素化できる。また、積層導体を用いる必要がなくなるため、装置コストを低減することができる。
【0057】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、一対の第2直流端子は、フィルタコンデンサの本体より外側に突出して設けられ、突出した前記一対の第2直流端子に、P側アームの自己消弧型半導体素子のコレクタ端子とN側アームの自己消弧型半導体素子のエミッタ端子とをそれぞれ接続するので、組立てが容易であり、装置のコストを低減することができる。
【0058】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、フィルタコンデンサはP側アームとN側アームとの直列接続点と常に同電位にある出力端子を備えたので、パワーモジュールとの接続等が簡素化でき、装置の組立コストを低減することができる。
【0059】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、P側アームおよびN側アームを、それぞれ複数個の直列接続された自己消弧型半導体素子とこれら自己消弧型半導体素子の各々に逆並列に接続されるダイオードとで構成したので、装置の高圧出力化を図ることができるため、装置の適用範囲が拡大する。
【0060】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、P側導体とN側導体の少なくとも第2直流端子側部分は、P側アームおよびN側アームを構成する複数個の自己消弧型半導体素子を直列接続する接続導体と略平行に配置され、かつ電流の流れる方向が逆方向となるように構成されているので、配線インダクタンスを減少させ、サージ発生要因自体を大幅に低減させることが可能となる。
【0061】
また、本発明によれば、前記装置において、フィルタコンデンサとP側アームとN側アームと出力端子とで構成される電力変換ユニットを複数組有し、各フィルタコンデンサの第1直流端子におけるN側端子同士、及び各フィルタコンデンサの第1直流端子におけるP側端子同士を並列に接続したので、容易に多相出力構成が実現できる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の形態1による電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図である。
【図2】本発明の実施の形態1による電力変換装置の構造を示す斜視図である。
【図3】本発明の実施の形態1による電力変換装置の構造を示す斜視図である。
【図4】本発明の実施の形態1に係わるP側導体の構造を示す図である。
【図5】本発明の実施の形態1に係わる接続導体の構造を示す図である。
【図6】本発明の実施の形態1に係わるパワーモジュールの具体的構造を示す図である。
【図7】本発明の実施の形態1に係わる負荷電流の経路を示す図である。
【図8】本発明の実施の形態1に係わる負荷電流の経路を示す回路図である。
【図9】本発明の実施の形態1に係わる逆回復現象によって流れる電流の経路を示す図である。
【図10】本発明の実施の形態1に係わる逆回復現象によって流れる電流の経路を示す回路図である。
【図11】本発明の実施の形態2による電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図である。
【図12】本発明の実施の形態3による電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図である。
【図13】本発明の実施の形態4による電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図である。
【図14】従来の電力変換装置の回路構成を示す図である。
【図15】従来の電力変換装置におけるパワーモジュールとフィルタコンデンサとの接続構造を示す図である。
【図16】従来の電力変換装置におけるコンデンサ群8の構造を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1 直流電源、2 フィルタコンデンサ、3 インバータ部、4,4a,4b,4c,4d パワーモジュール、5 出力端子、6a,6b,6c,6d IGBT、7a、7b,7c,7d ダイオード、8a,8b コンデンサ群、9,9a,9b,9c,9d,9e,9f コンデンサエレメント、10a,10b導体、11a,11b,11c,11d,11e,11f,11g,11h 板状導体、12a 第1直流端子のP側端子、12b 第1直流端子のN側端子、13a 第2直流端子のP側端子、13b 第2直流端子のN側端子、14a,14b,14c,14d コレクタ端子、15a,15b,15c,15d エミッタ端子、16a,16a1,16a2,16a3,16a4 P側導体、16b,16b1,16b2,16b3,16b4 N側導体、17 出力端子接続導体、18 アーム接続導体、18a,18b 端子、19a,19b 絶縁物、20a,20b 接続導体。[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a power conversion device including an inverter unit using a power module including a self-extinguishing semiconductor device and a diode connected in anti-parallel to the semiconductor device. In particular, a power conversion device mounting technology that suppresses stray inductance in the power conversion device as much as possible to reduce surges generated by switching operations of the power module and also suppresses current imbalance between multiple terminals provided in the power module. It is about.
[0002]
[Prior art]
FIG. 14 is a diagram showing a basic circuit configuration of a conventional power converter disclosed in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2002-0444949. In FIG. 14, 1 is a DC power supply, 2 is a filter capacitor, and 3 is an inverter unit. The
[0003]
On the other hand, FIG. 15 is a diagram illustrating a connection configuration between the
[0004]
The
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in the conventional power converter as described above, a capacitor arrangement method for reducing a surge generated due to a wiring from the
[0006]
Further, when the
Further, it is necessary to reduce the inductance on the electrode surface of the capacitor element. Particularly, between the plate-
[0007]
Also, in the case of a relatively large-capacity power conversion device applied to a vehicle propulsion system, since the capacity of a motor serving as a load is large and a large current needs to be output, the power module has the same potential and at least two power modules. An emitter terminal and a collector terminal divided as described above are provided. When such a power module is used, it is necessary to avoid an unbalanced state of the current flowing through the plurality of divided terminals. If the unbalanced state occurs due to an external factor other than the power module, the output current must be reduced according to the unbalanced current, and the output capacity of the inverter unit decreases. Therefore, it is necessary to compensate for an output current that would be reduced by connecting a plurality of power modules in parallel, and to secure a necessary output capacity. This has a problem that the component cost is high and the device cost is high.
[0008]
The present invention has been made in order to solve the above-described problems, and to provide a power conversion device capable of reducing a wiring inductance in a power conversion device and greatly reducing a cause of a surge itself. With the goal. Further, with this, it is an object of the present invention to provide a power conversion device capable of reducing the size and capacity of a surge suppression component or making it unnecessary, thereby improving the reliability of the device itself and achieving downsizing and cost reduction. I have.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
A power conversion device according to the present invention includes at least one or more capacitor elements, a filter capacitor that receives or transmits a DC voltage, is connected to the P side of the filter capacitor, and has a self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and a self-extinguishing type. A P-side arm composed of a diode connected in anti-parallel to the type semiconductor element, connected to the N side of the filter capacitor, and connected in series with the P-side arm to form a self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and In a power converter including an N-side arm composed of a diode connected in antiparallel to an arc-extinguishing semiconductor element and an output terminal connected to a series connection point of the P-side arm and the N-side arm The filter capacitor includes a pair of first DC terminals each including a P-side terminal for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage and an N-side terminal; A pair of second DC terminals including a P-side terminal connected to the N-side arm and an N-side terminal connected to the N-side arm; a P-side terminal of the first DC terminal; and a P-side terminal of the second DC terminal. And a P-side conductor connected to the P-side of the capacitor element, an N-side terminal of the first DC terminal and an N-side terminal of the second DC terminal, and An N-side conductor connected to the N-side of the element is provided, and the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor are configured to be at least partially arranged substantially in parallel.
[0010]
Further, the power converter of the present invention comprises at least one or more capacitor elements, a filter capacitor for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage, connected to the P side of the filter capacitor, and a self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and a self-extinguishing semiconductor element. A P-side arm composed of a diode connected in antiparallel to the arc-extinguishing type semiconductor element, connected to the N-side of the filter capacitor, connected in series with the P-side arm, A power converter having an N-side arm composed of a diode connected in anti-parallel to the self-extinguishing type semiconductor element, and an output terminal connected to a series connection point between the P-side arm and the N-side arm. In the device, the filter capacitor includes a pair of first DC terminals each including a P-side terminal and an N-side terminal for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage; A pair of second DC terminals each including a P-side terminal connected to the side arm and an N-side terminal connected to the N-side arm; and a P-side terminal of the first DC terminal and a pair of second DC terminals. While connecting a P-side terminal, connecting a P-side conductor connected to the P-side of the capacitor element, an N-side terminal of the first DC terminal and an N-side terminal of the second DC terminal, An N-side conductor connected to the N-side of the capacitor element, wherein at least the second DC terminal side portion of the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor is an arm for connecting the P-side arm and the N-side arm in series It is arranged so as to be substantially parallel to the connection conductor, and is configured such that the direction of current flow is opposite.
[0011]
Further, the power converter of the present invention comprises at least one or more capacitor elements, a filter capacitor for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage, connected to the P side of the filter capacitor, and a self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and a self-extinguishing semiconductor element. A P-side arm composed of a diode connected in antiparallel to the arc-extinguishing type semiconductor element, connected to the N-side of the filter capacitor, connected in series with the P-side arm, A power converter having an N-side arm composed of a diode connected in anti-parallel to the self-extinguishing type semiconductor element, and an output terminal connected to a series connection point between the P-side arm and the N-side arm. In the device, the filter capacitor includes a pair of first DC terminals each including a P-side terminal and an N-side terminal for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage; A pair of second DC terminals each including a P-side terminal connected to the side arm and an N-side terminal connected to the N-side arm; and a P-side terminal of the first DC terminal and a pair of second DC terminals. While connecting a P-side terminal, connecting a P-side conductor connected to the P-side of the capacitor element, an N-side terminal of the first DC terminal and an N-side terminal of the second DC terminal, An N-side conductor connected to the N-side of the capacitor element, wherein the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor are at least partially arranged substantially in parallel, and at least a second direct current of the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor is provided. The terminal-side portion is arranged substantially parallel to an arm connection conductor for connecting the P-side arm and the N-side arm in series, and is configured such that a current flows in the opposite direction.
[0012]
Further, in the power conversion device of the present invention, in the device, the output terminal connection conductor connecting the series connection point of the P-side arm and the N-side arm and the output terminal is at least a part of the P-side conductor or the N-side conductor. Are arranged substantially in parallel.
[0013]
Further, in the power conversion device according to the present invention, in the device, the filter capacitor has a space between the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor so that the output terminal connection conductor can pass therethrough. , Are arranged so as to be able to be taken out through the space.
[0014]
Further, in the power conversion device of the present invention, in the device, an insulator may be provided between the output terminal connection conductor penetrating the space and the P-side conductor and between the output terminal connection conductor penetrating the space and the N-side conductor. Is inserted.
[0015]
Further, in the power conversion device of the present invention, in the device, the filter capacitor is formed by molding at least two or more capacitor elements and a P-side conductor and an N-side conductor that connect the plurality of capacitor elements in parallel. It is of a configuration.
[0016]
Further, in the power conversion device according to the present invention, in the device described above, the pair of second DC terminals are provided to protrude outside the main body of the filter capacitor. The collector terminal of the arc-extinguishing type semiconductor element is connected to the emitter terminal of the self-extinguishing type semiconductor element of the N-side arm.
[0017]
Further, the power conversion device of the present invention is configured such that in the device, the filter capacitor has an output terminal which is always at the same potential as a series connection point of the P-side arm and the N-side arm.
[0018]
In the power converter according to the present invention, the P-side arm and the N-side arm each include a plurality of self-extinguishing semiconductor elements connected in series and anti-parallel to each of the self-extinguishing semiconductor elements. And a diode connected to the switch.
[0019]
Further, in the power conversion device according to the present invention, in the device, at least the second DC terminal side portion of the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor includes a plurality of self-extinguishing semiconductor elements forming the P-side arm and the N-side arm. Are arranged substantially in parallel with the connection conductors that connect in series, and the current flows in the opposite direction.
[0020]
Further, the power conversion device of the present invention, in the above device, includes a plurality of sets of power conversion units each including a filter capacitor, a P-side arm, an N-side arm, and an output terminal. The N-side terminals and the P-side terminals of the first DC terminals of each filter capacitor are connected in parallel.
[0021]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
In all the drawings, the same reference numerals are the same or equivalent members. FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of the power conversion device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. 2 and 3 are perspective views specifically showing the structure of the power conversion device according to the first embodiment, and particularly, the views of the structure of the
In FIG. 1,
[0022]
As shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, the
[0023]
The output
[0024]
Further, between the output
[0025]
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a power module structure suitable for the
[0026]
A method of assembling the power conversion device using the above structure will be described.
First, the
In this assembling process, at least the
[0027]
Next, it is shown that each conductor used in the power converter according to the present embodiment has a parallel and close positional relationship with a conductor through which a current of the same value flows in the opposite direction at all times. In particular, two cases of a load current flowing in a steady state and a reverse recovery current of a diode flowing in a commutation of the load current will be described.
[0028]
First, the path through which the load current flows will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 7 is a diagram in which the P-
When the
[0029]
Next, a path that flows when the load current is commutated will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 9 shows a portion (16a) of the P-
When the load current is flowing through the
[0030]
In the present embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, the pair of
[0031]
As described above, in the present embodiment, two pairs of DC terminals each including a P-side terminal and an N-side terminal are provided, and a conductor connecting between each P-side terminal and between the N-side terminals is provided. Since the conductors are built in the filter capacitor and the arrangement of these conductors is devised, the wiring inductance can be reduced, and the cause of surge generation itself can be greatly reduced. This also makes it possible to reduce or eliminate the size and capacity of the surge suppression component, thereby improving the reliability of the device itself, miniaturizing the device, and reducing the cost. Further, the connection with the power module can be simplified, and the assembly cost of the device can be reduced.
Further, since each conductor such as the P-side conductor, the N-side conductor, the arm connection conductor, and the output terminal connection conductor is formed of a wide plate-shaped conductor, it is possible to further reduce the wiring inductance.
Further, when the electrodes of the power module are divided, the configuration is such that the impedance is evenly distributed, and the current flowing through each divided electrode does not become unbalanced.
[0032]
In addition, since the
[0033]
In addition, by applying a mold type capacitor as the
[0034]
In addition, since a plurality of capacitor elements are connected in parallel by the plate-shaped conductor between the first DC terminal and the second DC terminal, the required capacity of the filter capacitor increases, and the housing size of the filter capacitor increases. Even in such a case, since the internal inductance can be reduced, a surge voltage generated at the time of switching of the power module can be suppressed, and the reliability of the device can be improved.
[0035]
Further, since insulators are inserted between the
[0036]
Further, since the IGBT module in which the IGBT and the diode are housed in the same module is used, a standard product can be used as the power module, and the device cost can be reduced.
[0037]
In the present embodiment, the
[0038]
Further, as an example of the shape of the
[0039]
In FIGS. 4 and 5, for example, the
Also, a power module incorporating an IGBT and a diode has been described as a specific example of the power module. However, the power module is not particularly limited to the IGBT, and may be a MOSFET or another self-extinguishing semiconductor element. Further, the material of the self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and the diode may be silicon, or a new semiconductor material such as silicon carbide may be used.
[0040]
In the present embodiment, the cooling fins of the
[0041]
FIG. 11 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of a power conversion device according to
[0042]
The concept of the structure as the power conversion device can be applied without change to those described in FIGS. 2 and 3, and each conductor has a parallel and close positional relationship with a conductor through which a current of the same value flows in the opposite direction at all times. .
[0043]
In the configuration of the present embodiment, in each arm, a plurality of power modules are connected in series. In addition to the effect of the first embodiment, the output of the device can be increased to a high voltage. Expanding.
[0044]
As for the cooling fins of the power module, since the potential of each power module is different in the case of the series connection as in the present embodiment, it is necessary to attach the cooling fin to each power module individually. It is also appropriate in the sense that it does not have excessive insulation.
[0045]
FIG. 12 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of a power converter according to
For example, a vehicle propulsion device generally requires a three-phase inverter and a brake circuit. If the brake circuit can be configured as the same unit, a four-phase configuration is applied. In order to realize such a configuration, it is advantageous to connect the
[0046]
With such a configuration, a multi-phase output configuration can be easily realized. In addition, by providing the module with a chopper function for controlling a DC voltage, the same power conversion unit can be used for general purposes, and the cost of the apparatus can be reduced.
[0047]
FIG. 13 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of a power conversion device according to
As the
[0048]
Note that the output terminal may be taken out in the opposite direction, similarly to the above-described embodiment, for a power converter having the same configuration as that shown in FIG.
[0049]
Further, the position from which the
[0050]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, a self-extinguishing type semiconductor device, which is constituted by at least one or more capacitor elements, receives or transmits a DC voltage, is connected to the P side of the filter capacitor, A P-side arm composed of a diode connected in anti-parallel to the self-extinguishing semiconductor element, connected to the N side of the filter capacitor, and connected in series with the P-side arm, And an N-side arm composed of a diode connected in anti-parallel to the self-extinguishing semiconductor element, and an output terminal connected to a series connection point of the P-side arm and the N-side arm. In the converter, the filter capacitor includes a pair of first DC terminals each including a P-side terminal and an N-side terminal for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage; A pair of second DC terminals each including a P-side terminal connected to the side arm and an N-side terminal connected to the N-side arm; and a P-side terminal of the first DC terminal and a pair of second DC terminals. While connecting a P-side terminal, connecting a P-side conductor connected to the P-side of the capacitor element, an N-side terminal of the first DC terminal and an N-side terminal of the second DC terminal, An N-side conductor connected to the N-side of the capacitor element is provided, and the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor are arranged at least in part substantially in parallel. This has the effect of suppressing the generation of noise due to noise. In addition, it is possible to reduce the wiring inductance and greatly reduce the cause of the surge itself. Further, it is possible to reduce the size and capacity of the noise and surge suppression components or to eliminate them, thereby improving the reliability of the device itself, reducing the size, and reducing the cost.
[0051]
Further, according to the present invention, a filter capacitor configured of at least one or more capacitor elements for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage, connected to the P side of the filter capacitor, and having a self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and this self-extinguishing type A P-side arm composed of a diode connected in anti-parallel to the type semiconductor element, connected to the N side of the filter capacitor, and connected in series with the P-side arm to form a self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and In a power converter including an N-side arm composed of a diode connected in antiparallel to an arc-extinguishing semiconductor element and an output terminal connected to a series connection point of the P-side arm and the N-side arm The filter capacitor includes a pair of first DC terminals each including a P-side terminal for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage and an N-side terminal; A pair of second DC terminals each including a P-side terminal connected to the N-side arm and an N-side terminal connected to the N-side arm; a P-side terminal of the first DC terminal; and a P-side of the second DC terminal. And a P-side conductor connected to the P-side of the capacitor element, an N-side terminal of the first DC terminal and an N-side terminal of the second DC terminal, and An N-side conductor connected to the N-side of the first arm, and at least a second DC terminal side portion of the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor is an arm connection conductor for connecting the P-side arm and the N-side arm in series Are arranged substantially in parallel with each other, and the direction in which the current flows is the opposite direction.
[0052]
Further, according to the present invention, a filter capacitor configured of at least one or more capacitor elements for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage, connected to the P side of the filter capacitor, and having a self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and this self-extinguishing type A P-side arm composed of a diode connected in anti-parallel to the type semiconductor element, connected to the N side of the filter capacitor, and connected in series with the P-side arm to form a self-extinguishing type semiconductor element and In a power converter including an N-side arm composed of a diode connected in antiparallel to an arc-extinguishing semiconductor element and an output terminal connected to a series connection point of the P-side arm and the N-side arm The filter capacitor includes a pair of first DC terminals each including a P-side terminal for receiving or transmitting a DC voltage and an N-side terminal; A pair of second DC terminals each including a P-side terminal connected to the N-side arm and an N-side terminal connected to the N-side arm; a P-side terminal of the first DC terminal; and a P-side of the second DC terminal. And a P-side conductor connected to the P-side of the capacitor element, an N-side terminal of the first DC terminal and an N-side terminal of the second DC terminal, and An N-side conductor connected to the N-side of the P-side conductor, the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor are at least partially arranged substantially in parallel, and at least a second DC terminal side of the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor The portion is arranged substantially parallel to the arm connection conductor that connects the P-side arm and the N-side arm in series, and is configured so that the direction of current flow is opposite. is there.
[0053]
Further, according to the present invention, in the device, the output terminal connection conductor connecting the series connection point of the P-side arm and the N-side arm and the output terminal is substantially at least a part of the P-side conductor or the N-side conductor. Since they are arranged in parallel, stray inductance can be reduced, so that surge voltage during switching can be suppressed, and reliability of the device can be improved.
[0054]
Further, according to the present invention, in the device, the filter capacitor has a space between the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor so that the output terminal connection conductor can penetrate, and the output terminal connection conductor is Since it is arranged so that it can be taken out through the space, in addition to the above effects, there is no need to use a laminated conductor, so that there is an effect that the cost of the apparatus can be reduced.
[0055]
According to the invention, in the device, an insulator is inserted between the output terminal connection conductor penetrating the space and the P-side conductor, and between the output terminal connection conductor penetrating the space and the N-side conductor. Since the conductors can be arranged close to each other, stray inductance due to mutual inductance can be reduced, surge voltage generated at the time of switching of the power module can be suppressed, and reliability of the device can be improved.
[0056]
Further, according to the present invention, in the above device, the filter capacitor has a configuration in which at least two or more capacitor elements and a P-side conductor and an N-side conductor that connect the plurality of capacitor elements in parallel are molded. As a result, necessary conductors can be incorporated in the filter capacitor, and assembly of the device can be simplified. In addition, since it is not necessary to use a laminated conductor, the apparatus cost can be reduced.
[0057]
Further, according to the present invention, in the device, the pair of second DC terminals are provided to protrude outside the main body of the filter capacitor, and the pair of protruding second DC terminals are connected to the self-extinguishing of the P-side arm. Since the collector terminal of the semiconductor element is connected to the emitter terminal of the self-extinguishing semiconductor element of the N-side arm, assembly is easy and the cost of the device can be reduced.
[0058]
Further, according to the present invention, in the above device, since the filter capacitor has an output terminal which is always at the same potential as the series connection point of the P-side arm and the N-side arm, connection with the power module can be simplified. Therefore, the assembly cost of the apparatus can be reduced.
[0059]
Further, according to the present invention, in the above-mentioned device, the P-side arm and the N-side arm are respectively connected to a plurality of self-extinguishing semiconductor elements connected in series and each of these self-extinguishing semiconductor elements in anti-parallel. Since the high-voltage output of the device can be achieved, the application range of the device is expanded.
[0060]
Further, according to the present invention, in the device, at least the second DC terminal side portion of the P-side conductor and the N-side conductor includes a plurality of self-extinguishing semiconductor elements forming the P-side arm and the N-side arm in series. Since it is arranged so as to be substantially parallel to the connection conductor to be connected and the direction in which the current flows in the opposite direction, it is possible to reduce the wiring inductance and greatly reduce the cause of surge generation itself.
[0061]
Further, according to the present invention, in the device, the power conversion unit includes a plurality of sets each including a filter capacitor, a P-side arm, an N-side arm, and an output terminal. Since the terminals and the P-side terminal of the first DC terminal of each filter capacitor are connected in parallel, a multi-phase output configuration can be easily realized.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of a power conversion device according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a perspective view showing a structure of the power conversion device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a perspective view showing a structure of the power conversion device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a structure of a P-side conductor according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a structure of a connection conductor according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a specific structure of the power module according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a path of a load current according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 8 is a circuit diagram showing a path of a load current according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a path of a current flowing by a reverse recovery phenomenon according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 10 is a circuit diagram showing a path of a current flowing by a reverse recovery phenomenon according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 11 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of a power conversion device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 12 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of a power conversion device according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 13 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of a power conversion device according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 14 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration of a conventional power converter.
FIG. 15 is a diagram showing a connection structure between a power module and a filter capacitor in a conventional power converter.
FIG. 16 is a diagram showing a structure of a capacitor group 8 in a conventional power converter.
[Explanation of symbols]
Claims (12)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002215303A JP2004056984A (en) | 2002-07-24 | 2002-07-24 | Power converting device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002215303A JP2004056984A (en) | 2002-07-24 | 2002-07-24 | Power converting device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004056984A true JP2004056984A (en) | 2004-02-19 |
Family
ID=31937370
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002215303A Pending JP2004056984A (en) | 2002-07-24 | 2002-07-24 | Power converting device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2004056984A (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005278384A (en) * | 2004-02-24 | 2005-10-06 | Fuji Electric Systems Co Ltd | Semiconductor power converter |
| JP2007006584A (en) * | 2005-06-22 | 2007-01-11 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Power converter |
| JP2008099397A (en) * | 2006-10-10 | 2008-04-24 | Denso Corp | Smoothing capacitor module and power conversion device using the same |
| WO2011122279A1 (en) * | 2010-03-29 | 2011-10-06 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Motor drive circuit module |
| JP2016158342A (en) * | 2015-02-24 | 2016-09-01 | 株式会社明電舎 | Inverter apparatus |
| US9467067B2 (en) | 2012-03-12 | 2016-10-11 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Power converter |
| US10128625B2 (en) | 2014-11-18 | 2018-11-13 | General Electric Company | Bus bar and power electronic device with current shaping terminal connector and method of making a terminal connector |
| JP2020167787A (en) * | 2019-03-28 | 2020-10-08 | 株式会社デンソー | Power conversion device |
| JPWO2021186888A1 (en) * | 2020-03-18 | 2021-09-23 | ||
| CN113890386A (en) * | 2020-07-02 | 2022-01-04 | 富士电机株式会社 | Power conversion device |
-
2002
- 2002-07-24 JP JP2002215303A patent/JP2004056984A/en active Pending
Cited By (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005278384A (en) * | 2004-02-24 | 2005-10-06 | Fuji Electric Systems Co Ltd | Semiconductor power converter |
| JP2007006584A (en) * | 2005-06-22 | 2007-01-11 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Power converter |
| JP2008099397A (en) * | 2006-10-10 | 2008-04-24 | Denso Corp | Smoothing capacitor module and power conversion device using the same |
| JP4655020B2 (en) * | 2006-10-10 | 2011-03-23 | 株式会社デンソー | Smoothing capacitor module and power converter using the same |
| WO2011122279A1 (en) * | 2010-03-29 | 2011-10-06 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Motor drive circuit module |
| CN102812629A (en) * | 2010-03-29 | 2012-12-05 | 本田技研工业株式会社 | Motor drive circuit module |
| JPWO2011122279A1 (en) * | 2010-03-29 | 2013-07-08 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Motor drive circuit module |
| US9467067B2 (en) | 2012-03-12 | 2016-10-11 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Power converter |
| US10128625B2 (en) | 2014-11-18 | 2018-11-13 | General Electric Company | Bus bar and power electronic device with current shaping terminal connector and method of making a terminal connector |
| WO2016136516A1 (en) * | 2015-02-24 | 2016-09-01 | 株式会社明電舎 | Inverter device |
| US9954459B2 (en) | 2015-02-24 | 2018-04-24 | Meidensha Corporation | Inverter device |
| JP2016158342A (en) * | 2015-02-24 | 2016-09-01 | 株式会社明電舎 | Inverter apparatus |
| JP2020167787A (en) * | 2019-03-28 | 2020-10-08 | 株式会社デンソー | Power conversion device |
| JP7088112B2 (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2022-06-21 | 株式会社デンソー | Power converter |
| JPWO2021186888A1 (en) * | 2020-03-18 | 2021-09-23 | ||
| WO2021186888A1 (en) * | 2020-03-18 | 2021-09-23 | 富士電機株式会社 | Electric circuit and semiconductor module |
| CN113890386A (en) * | 2020-07-02 | 2022-01-04 | 富士电机株式会社 | Power conversion device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10153708B2 (en) | Three-level power converter | |
| US9899283B2 (en) | Power module with low stray inductance | |
| JP4920677B2 (en) | Power conversion device and assembly method thereof | |
| JP6096881B2 (en) | Power converter for vehicle | |
| JP5132175B2 (en) | Power converter | |
| JP6836201B2 (en) | Power converter | |
| JP6848073B2 (en) | Main circuit wiring member and power converter | |
| JP3622782B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2004214452A (en) | Semiconductor module for power and method for connecting to external electrode | |
| JP3652934B2 (en) | Power converter | |
| JP2005216876A (en) | Power semiconductor module | |
| JP2004056984A (en) | Power converting device | |
| JP2005287267A (en) | Power converting device | |
| JP2004096974A (en) | Snubber module and power converter | |
| WO2019146179A1 (en) | Power conversion device and electric railroad vehicle equipped with power conversion device | |
| US10284111B2 (en) | Power conversion apparatus having connection conductors having inductance which inhibits ripple current | |
| US10554123B2 (en) | Power converter with a parallel flat plate conductor electrically connected with a capacitor and a power module | |
| US11128235B2 (en) | Power conversion device | |
| JP2004031590A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2003018860A (en) | Power converter | |
| JP4697025B2 (en) | Power semiconductor module | |
| CN116800106A (en) | Laminated busbar of double-tube parallel NPC three-level inverter and inverter | |
| JP2002044960A (en) | Power converter | |
| JP2005192328A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP4156258B2 (en) | Resonant type inverter |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20040712 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20041224 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080131 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080219 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080417 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080701 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20081028 |