EP4001488B1 - Device for the manufacture of non-woven fabrics from continuous filaments - Google Patents
Device for the manufacture of non-woven fabrics from continuous filaments Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP4001488B1 EP4001488B1 EP20208671.6A EP20208671A EP4001488B1 EP 4001488 B1 EP4001488 B1 EP 4001488B1 EP 20208671 A EP20208671 A EP 20208671A EP 4001488 B1 EP4001488 B1 EP 4001488B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- roller
- nonwoven web
- nose
- mesh belt
- lift
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 title description 8
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title description 4
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 34
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 claims description 27
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 claims 7
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims 5
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 166
- 238000007596 consolidation process Methods 0.000 description 26
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 4
- -1 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012815 thermoplastic material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001634 Copolyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011258 core-shell material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005283 ground state Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/02—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of forming fleeces or layers, e.g. reorientation of yarns or filaments
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H20/00—Advancing webs
- B65H20/02—Advancing webs by friction roller
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D13/00—Complete machines for producing artificial threads
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/08—Melt spinning methods
- D01D5/088—Cooling filaments, threads or the like, leaving the spinnerettes
- D01D5/092—Cooling filaments, threads or the like, leaving the spinnerettes in shafts or chimneys
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/08—Melt spinning methods
- D01D5/098—Melt spinning methods with simultaneous stretching
- D01D5/0985—Melt spinning methods with simultaneous stretching by means of a flowing gas (e.g. melt-blowing)
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/08—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating
- D04H3/14—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating with bonds between thermoplastic yarns or filaments produced by welding
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/20—Belts
- B65H2404/25—Driving or guiding arrangements
- B65H2404/256—Arrangement of endless belt
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/20—Belts
- B65H2404/26—Particular arrangement of belt, or belts
- B65H2404/261—Arrangement of belts, or belt(s) / roller(s) facing each other for forming a transport nip
- B65H2404/2614—Means for engaging or disengaging belts into or out of contact with opposite belts, rollers or balls
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/20—Belts
- B65H2404/26—Particular arrangement of belt, or belts
- B65H2404/262—Arrangements of belts facing rollers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2701/00—Handled material; Storage means
- B65H2701/10—Handled articles or webs
- B65H2701/17—Nature of material
- B65H2701/177—Fibrous or compressible material
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for producing nonwovens from continuous filaments, wherein a spinning device for spinning the filaments and a cooling device for cooling the filaments are present, wherein a depositing screen belt is also provided on which the filaments can be deposited in a depositing area to form a nonwoven web, wherein the depositing screen belt can be deflected from its transport direction in a deflection area by at least one nose roller and wherein at least one follow-up device for the nonwoven web is present downstream of the depositing screen belt in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web.
- the invention also relates to a method for transporting and treating a nonwoven web made of continuous filaments.
- - Continuous filaments differ from staple fibers due to their practically endless length, which have significantly shorter lengths of, for example, 10 mm to 60 mm.
- Devices and methods of the type mentioned at the beginning are basically known in different embodiments from practice and from the state of the art.
- the filaments are spun using a spinning device, then cooled in a cooling device and finally deposited on a depositing screen belt to form the nonwoven web.
- WO 00/46434 A1 describes a device and a method for producing nonwovens, wherein the spun filaments are deposited on a deposit belt to form a nonwoven web, detached from the deposit belt by means of a lifting roller and then consolidated in a calender.
- US$5,807,795 discloses a device and a method for producing a nonwoven fabric, wherein the filaments are spun in a spinning device and deposited on a deposit belt to form the nonwoven web. The nonwoven web is detached from the deposit belt by means of a roller arrangement.
- EP 3 495 543 A1 describes a system and a method for producing a spunbonded nonwoven from continuous filaments, whereby the filaments are deposited on a first depositing belt to form the nonwoven web and are then transferred to a second depositing belt.
- the nonwoven web is guided by the second depositing belt around a suction drum arranged above the second depositing belt and is thus detached from the depositing belt.
- US 2007/0271749 A1 relates to a device for producing nonwovens, whereby filaments are spun in a spinning device and deposited on a deposit belt to form a nonwoven web. It is possible for the nonwoven web to be guided over a drum arranged above the deposit belt.
- the depositing screen belt of the devices known from practice is usually designed as an endlessly rotating depositing screen belt that is deflected from its transport direction in a deflection area by a nose roller. In this deflection area arranged at the end of the depositing screen belt, the nonwoven web is transferred from the depositing screen belt or from the nose roller to a subsequent device and is detached from the depositing screen belt in the deflection area.
- detaching the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt requires a relatively high level of force and is therefore not always easy or reliable.
- a sufficiently good adhesion of the nonwoven web to the depositing screen belt is generally desirable, at least in the depositing area, so that there is a conflict of objectives between good detachment behavior and sufficient adhesion to the depositing screen belt.
- the strong deflection of the depositing screen belt can lead to jamming or trapping of the continuous filaments in the depositing screen belt, particularly in the deflection area.
- the A great deal of force is required to detach the fleece web from the depositing screen belt, and the fleece web can be damaged by filaments being torn out.
- filament residues can remain on the depositing screen belt, which are torn out of the fleece web during the detachment process. - There is a need for improvement in this regard.
- the invention is based on the technical problem of specifying a device of the type mentioned at the beginning with which the nonwoven web can be detached from the depositing screen belt in a simple and functionally reliable manner, with which in particular damage to the nonwoven web can be avoided during the detachment process and the amount of force required to detach the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt can be reduced.
- the invention is also based on the technical problem of specifying a corresponding method for transporting and treating a nonwoven web.
- the invention teaches a device for producing nonwovens from continuous filaments, wherein a spinning device for spinning the filaments and a cooling device for cooling the filaments are present, wherein a depositing screen belt is also provided on which the filaments can be deposited in a depositing area to form a nonwoven web, wherein the depositing screen belt can be deflected from its transport direction in a deflection area by at least one nose roller, wherein at least one follow-up device for the nonwoven web is provided downstream of the depositing screen belt in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web, wherein the nonwoven web can be detached from the depositing screen belt before the deflection area and then transferred to the follow-up device, wherein at least one lifting roller is provided for detaching the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt, wherein the lifting roller is arranged or is arranged above the depositing screen belt can be detached from the depositing screen belt by means of the at least one lifting roller in a detachment area which is arranged at a distance A from
- the spinning device according to the invention is designed in particular as a spinnerette within the scope of the invention.
- the transport direction of the depositing screen belt means in particular the direction in which the depositing screen belt or the endlessly rotating depositing screen belt moves to convey the nonwoven web.
- the transport direction of the depositing screen belt means in particular the deflection area at the end of the depositing screen belt in which the depositing screen belt is deflected from its transport direction by the nose roller and thus leaves its transport direction.
- the detachment area or detachment area of the nonwoven web means in particular the area in which the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt.
- the detachment area is a detachment line which extends in particular transversely, preferably perpendicularly to the transport direction of the depositing screen belt.
- the detachment area or detachment line is preferably arranged in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt in front of the deflection area and/or in front of the nose roller.
- the distance A is measured in particular between a projection of the axis of rotation of the nose roller onto the depositing screen belt and the detachment area or the detachment line, whereby the projection of the axis of rotation is perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt in the area of the distance A.
- the deposit area refers expediently to the area of the deposit screen belt in which the spun filaments are deposited to form the nonwoven web.
- the device according to the invention is a spunbond device, wherein a stretching device is provided for stretching the filaments.
- a stretching device is provided for stretching the filaments.
- Another embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the device according to the invention is a meltblown device.
- spunbond nonwovens or nonwoven webs are produced with the device according to the invention.
- monocomponent filaments and/or multicomponent filaments or bicomponent filaments are produced as continuous filaments.
- the multicomponent filaments or bicomponent filaments can be, for example, continuous filaments with a core-shell configuration or continuous filaments with a side-by-side configuration.
- the multicomponent filaments or bicomponent filaments can have a tendency to curl.
- the continuous filaments produced with the device according to the invention or with the method according to the invention consist of at least one thermoplastic material, in particular of at least one polyolefin, preferably of polypropylene and/or polyethylene.
- the at least one thermoplastic material is a polyester or copolyester, in particular polyethylene terephthalate and/or a polyethylene terephthalate copolymer.
- a cooling device for cooling the filaments.
- the cooling device preferably has a cooling chamber through which the continuous filaments are guided for cooling. It is preferred that air supply cabins for supplying cooling air are arranged on two opposite sides of the cooling chamber. According to a preferred embodiment, air supply cabins arranged one above the other are present on two opposite sides of the cooling chamber, in particular two air supply cabins arranged one above the other, from which air of different temperatures is preferably introduced into the cooling chamber. It has proven useful to provide a monomer extraction device between the spinning device and the cooling device, with which disruptive gases that occur during the spinning process can be removed from the device or the spunbond device. The disruptive gases can be monomers, oligomers and similar substances.
- a stretching device for stretching the filaments is expediently arranged downstream of the cooling device in the direction of filament flow.
- the unit comprising the cooling device and the stretching device is designed as a closed unit in which, apart from the supply of cooling air in the cooling device, no further air is supplied to the closed unit.
- At least one diffuser is arranged between the stretching device and the deposition screen belt.
- the continuous filaments emerging from the stretching device are guided through the diffuser and then deposited on the deposition screen belt, in particular deposited in the deposition area of the deposition screen belt.
- Two diffusers connected in series are provided.
- the depositing sieve belt or the endlessly rotating depositing sieve belt is also expediently designed to be permeable to air, so that process air can be extracted from below through the depositing sieve belt. Expediently, at least in the depositing area of the depositing sieve belt, process air is sucked through the depositing sieve belt by means of at least one extraction device, in particular from below.
- a preferred embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the at least one lifting roller is or can be arranged in relation to the nose roller in such a way that the detachment area is located in front of the deflection area in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt. It is recommended that the at least one lifting roller is or can be arranged in front of or behind the nose roller in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt. It is within the scope of the invention that the nonwoven web can be or is guided over the top of the at least one lifting roller. It is recommended that the at least one lifting roller is designed as a non-vacuum-fed lifting roller.
- the distance A is smaller than the distance C between the nose roller and a deflection roller.
- deflection roller means in particular a roller which is set up in addition to the nose roller for transporting the depositing screen belt and which is arranged in front of the nose roller in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt.
- the deflection roller is provided in particular between the depositing area and the deflection area.
- the depositing screen belt can be guided along the deflection roller without being deflected from its transport direction.
- the depositing screen belt deflected from its transport direction by the deflection roller, as will be explained in more detail below.
- the at least one nose roller is arranged behind the depositing area and behind the unit comprising the spinning device and the cooling device in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt or in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web.
- the at least one deflection roller is expediently arranged behind the depositing area or behind the unit comprising the spinning device and the cooling device in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt or in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web, but in front of the nose roller.
- Distance C between the nose roller and the deflection roller means in the context of the invention in particular the distance between the axes of rotation of the nose roller and the deflection roller, which is expediently measured between the projections of the axes of rotation onto the depositing screen belt, the projections of the axes of rotation being perpendicular to the longitudinal extent of the depositing screen belt in the region of the distance C.
- the region between the deflection roller and the nose roller represents a transfer table, the length of which is defined in particular by the distance C.
- the transfer table essentially has the function of transferring the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt to the subsequent device.
- the distance A is a maximum of 50%, preferably a maximum of 25%, preferably a maximum of 10%, particularly preferably a maximum of 5%, very particularly preferably a maximum of 2.5%, for example 1% of the distance C.
- the distance A is at least 25% of the diameter n of the nose roller, preferably at least 50%, preferably at least 75%, particularly preferably at least 100% and very particularly preferably at least 125% of the diameter n of the nose roller.
- the distance A is further preferably between 10% and 500%, particularly preferably between 25% and 400%, most preferably between 50% and 350% of the diameter n of the nose roller.
- the at least one lifting roller is height-adjustable in relation to the depositing screen belt and can preferably be moved in a vertical direction for this purpose. It is recommended that the at least one lifting roller can be moved from a basic position to various lifting positions and back due to its height adjustability or vertical mobility. In the basic position of the at least one lifting roller, for example, cleaning work can be carried out on the device or the nonwoven web can be threaded. The device is then not in its operating state or in its operating position. In the lifting position, the at least one lifting roller is expediently arranged in relation to the nose roller in such a way that the distance A between the detachment area or the detachment line of the nonwoven web and the nose roller results in the operating state of the device.
- a preferred embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the at least one lifting roller is designed as a rotating lifting roller, in particular as a drivable rotating lifting roller.
- the at least one lifting roller is designed as a simple round profile that is not rotating and not drivable. Such a round profile has a longitudinal axis instead of an axis of rotation.
- the at least one lifting roller is designed as a rotating lifting roller.
- a further preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention is characterized in that the at least one lifting roller is arranged at a distance D from the depositing screen belt or can be arranged can, wherein this distance D is expediently greater than 50% of the diameter d of the lifting roller and preferably at least 55%, particularly preferably at least 60% of the diameter d of the lifting roller.
- distance D means in particular the distance of the axis of rotation of the at least one lifting roller to the depositing screen belt, wherein this distance D is expediently measured perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt in the region of the at least one lifting roller or to the imaginary extension of this longitudinal extension.
- the diameter d of the at least one lifting roller is 10 to 500 mm, preferably 25 to 400 mm, preferably 50 to 300 mm, particularly preferably 100 to 250 mm.
- the diameter d of the at least one lifting roller is expediently smaller than 8 times the diameter n of the nose roller.
- An embodiment which is of particular importance within the scope of the invention is characterized in that at least two, in particular two lifting rollers are provided, wherein a second lifting roller is preferably arranged or can be arranged in front of the nose roller in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt and wherein a first or the first lifting roller is preferably arranged or can be arranged in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt between the second lifting roller and the nose roller or behind the nose roller.
- the at least two, in particular the two lifting rollers are designed as rotating lifting rollers.
- the at least two, in particular the two lifting rollers are designed as drivable rotating lifting rollers.
- the first lifting roller and the second lifting roller have the same diameter d or essentially the same diameter d.
- the first and second lifting rollers it is also possible for the first and second lifting rollers to have different diameters d 1 and d 2.
- the diameters d 1 and d 2 are then expediently between 10 and 500 mm, preferably between 25 and 400 mm, more preferably between 50 and 300 mm, particularly preferably between 100 and 250 mm.
- the distance between the axes of rotation m of the two lifting rollers is preferably at least 105%, preferably at least 110%, particularly preferably at least 115% of the diameter d of the lifting rollers. If the two lifting rollers have different diameters d 1 or d 2 , these details refer to the diameter of the lifting roller with the larger diameter.
- the rotation axis distance m is expediently measured between the projections of the rotation axes of the lifting rollers onto the depositing screen belt, with the projections of the rotation axes being perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt in the area of the lifting rollers.
- the rotation axis distance m of the two lifting rollers is less than 300%, preferably less than 250%, particularly preferably less than 200% of the diameter d of the lifting rollers. If the lifting rollers have a different diameter, these details refer to the diameter of the lifting roller with the larger diameter.
- the two lifting rollers are or can be arranged at a distance D or D 1 and D 2 from the depositing screen belt, and wherein this distance D 1 and/or D 2 is preferably greater than 50% of the respective diameter d 1 or d 2 of the lifting roller, particularly preferably at least 55% and very particularly preferably at least 60% of the respective diameter d 1 or d 2 of the lifting roller.
- the at least two, in particular the two lifting rollers are arranged with the same distance D or essentially with the same distance D in relation to the depositing screen belt.
- the distance between the respective axis of rotation of the lifting roller and the depositing screen belt is then the same or essentially the same.
- the lifting rollers are arranged at a different distance D 1 and D 2 from the depositing screen belt, wherein the distance D 1 of the first lifting roller from the depositing screen belt is then preferably greater than the distance D 2 of the second lifting roller from the depositing screen belt.
- the nonwoven web can be guided over the top of the at least one lifting roller. If, according to a preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention, at least two lifting rollers, in particular two lifting rollers, are provided, the nonwoven web can expediently be guided over the underside of the second lifting roller and over the top of the first lifting roller. In this context, it is preferred that the second lifting roller is arranged in front of the first lifting roller in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt.
- the nonwoven web can be guided over the underside of the second lifting roller and over the top of the first lifting roller, the first lifting roller is responsible in particular for detaching the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt and the second lifting roller is then recommended for holding the nonwoven web down near the depositing screen belt.
- This The embodiment is based on the knowledge that the second lifting roller, which holds down the nonwoven web, means that the detachment area is or can be arranged close to the second lifting roller and in particular in the area of the second lifting roller.
- the distance A from the nose roller can be further limited so that it is in particular a maximum of 25%, preferably a maximum of 10%, preferably a maximum of 5%, particularly preferably a maximum of 2.5% of the distance C, very particularly preferably a maximum of 1%, for example 0.1% of the distance C.
- the use of two lifting rollers, with a first lifting roller being provided for the detachment process and a second lifting roller being provided for holding it down, is also based on the knowledge that the detachment area or the detachment line can be defined very reliably by the second lifting roller.
- the distance D 2 of the second lifting roller from the depositing screen belt has a significant influence on the distance A of the detachment area or the detachment line from the nose roller.
- the ratio of the distance D 1 of the first lifting roller to the depositing screen belt to the distance D 2 of the second lifting roller to the depositing screen belt (D 1 /D 2 ) preferably influences the position of the detachment area or the detachment line in such a way that, with a larger wrap angle of the nonwoven web around the second lifting roller, the detachment area or the detachment line is arranged closer to an intersection point of a straight line running perpendicular to the depositing screen belt and passing through the center of the second lifting roller. It is within the scope of the invention that the detachment area or the detachment line is located in the area of the second lifting roller and in particular below the second lifting roller.
- both lifting rollers are arranged in relation to the depositing screen belt are height-adjustable and can preferably be moved in a vertical direction for this purpose. It is possible for both lifting rollers to be able to be moved from a basic position to a lifting position or to various lifting positions and back. In the basic position, it is recommended that the device according to the invention can be cleaned and/or the fleece web can be threaded. When the device is in operation, the lifting rollers are expediently arranged in their lifting positions.
- the device can also be operated with the lifting rollers in the basic position if it is not necessary to remove the fleece web using the lifting rollers. It is recommended that the first lifting roller is arranged in its basic position below the depositing screen belt and/or that the second lifting roller is arranged in its basic position above the depositing screen belt. In principle, however, both lifting rollers can also be arranged above or below the depositing screen belt in their basic position.
- the depositing sieve belt or the transfer table is arranged parallel or essentially parallel to the device base or the ground when the device is in operation.
- the nose roller can be moved or lowered in the vertical direction. It is recommended that the nose roller can be moved or lowered in the vertical direction in such a way that the depositing sieve belt is oriented towards the device base at least between the deflection roller and the nose roller in the transport direction and preferably has a gradient of greater than 0° to 20°, in particular from 3° to 20°, preferably from 4° to 18°, particularly preferably from 5° to 16°.
- the depositing sieve belt has a gradient in the direction of the device base
- the depositing sieve belt is expediently moved by the deflection roller from its - previously in particular parallel to the device base - transport direction.
- the ability of the nose roller to move in the vertical direction means in particular the ability of the nose roller to move in the direction of the device base and back.
- a further preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention is characterized in that the nose roller can be moved or telescoped in a horizontal direction.
- horizontal direction means in particular in a direction parallel to the device base. Due to the horizontal moveability or telescoping of the nose roller, the nose roller can thus be moved closer to the following device, for example.
- the distance C between the nose roller and the deflection roller is expediently increased when moving or telescoping and reduced when the nose roller is retracted.
- the nose roller can be moved or telescoped in a horizontal direction and can be moved or lowered in a vertical direction. This embodiment is based on the knowledge that the nose roller can be set to a wide variety of positions.
- a deposit screen belt oriented towards the device base can be realized and at the same time the nose roller can be moved close to the following device.
- horizontal movability or telescoping also expediently means the movability or telescoping of the nose roller in the transport direction of the deposit screen belt, i.e. in accordance with the set gradient of the deposit screen belt or the transfer table between the deflection roller and the nose roller.
- the nose roller can be moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction and lowered or moved in the vertical direction and, in addition, the lifting roller or the lifting rollers can be moved in the vertical direction, different positions of the nose roller can be set and the lifting rollers can be arranged in their lifting positions in such a way that the above-described distances between the rollers and between the detachment area A and the nose roller are achieved. These distances and positions therefore relate to the operating state of the device.
- the distance A of the detachment area from the nose roller can be adjusted (also) by the vertical mobility and/or the horizontal mobility or telescoping of the nose roller.
- the nose roller can only be moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction and not moved or lowered in the vertical direction.
- the depositing sieve belt is arranged parallel or substantially parallel to the device base or the ground and the nose roller can be moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction.
- the nose roller can neither be moved or lowered in the vertical direction nor moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction, so that there is a rigid depositing sieve belt that is arranged parallel or substantially parallel to the device base or the ground.
- the distance A between the detachment area or the detachment line and the nose roller is smaller than the distance E between the nose roller and the deposit area of the deposit screen belt.
- the distance E is measured in the context of the invention in particular between a projection of the axis of rotation of the nose roller onto the deposit screen belt and the deposit area, in particular the middle of the deposit area, wherein the projection of the axis of rotation of the nose roller is perpendicular to the longitudinal extent of the deposit screen belt in the region of the distance E.
- the distance A is a maximum of 50%, preferably a maximum of 25%, preferably a maximum of 10%, particularly preferably a maximum of 5%, very particularly preferably a maximum of 2.5%, for example 1% of the distance E.
- the distance E expediently refers to a state of the device in which the deposit screen belt is arranged parallel or essentially parallel to the device base or to the ground and in particular to an embodiment in which the device does not have a deflection roller and/or in which the nose roller cannot be moved or lowered in the vertical direction and/or cannot be moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction.
- the downstream device is a consolidation device, in particular a hot-air bonder, for example an oven, and/or a calender and/or that the downstream device is a winder.
- the device it is possible for the device to have at least two downstream devices, for example a consolidation device, in particular a calender and a winder.
- the consolidation device or calender is then expediently arranged first in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web and the winder is provided behind the consolidation device or calender.
- the consolidation device or calender serves in particular for the consolidation or final consolidation of the Nonwoven web. After the detachment process, the nonwoven web is conveniently transferred to the bonding device or calender in the detachment area.
- the consolidation device or the calender has at least one calender roller, in particular at least one pair of calender rollers, with at least one calender roller preferably being movable in the vertical direction.
- the nonwoven web is guided in particular through the gap or nip between the at least two - preferably arranged one above the other - calender rollers of the at least one pair of calender rollers.
- the nonwoven web can either be guided in such a way that it does not touch any of the calender rollers, since the calender or the at least one pair of calender rollers is open, or it can be guided in such a way that it only touches one of the calender rollers in order to influence the properties of the corresponding side of the nonwoven web, or it can be guided in such a way that it touches both calender rollers, since the calender or the at least one pair of calender rollers is closed. It is also within the scope of the invention that the nonwoven web is consolidated as it passes between the two calender rollers - in particular by thermal bonding.
- At least three calender rolls are provided for the consolidation device or for the calender, whereby preferably at least one calender roll is movable in the vertical direction and whereby the at least three calender rolls are particularly preferably arranged one above the other.
- This arrangement results in two calender roll pairs each consisting of the uppermost calender roll and the middle calender roll and of the lowermost calender roll and the middle calender roll.
- the nonwoven web is expediently guided through one of the resulting gaps for consolidation or final consolidation.
- the position of the nose roll and/or the lifting rolls is dependent on the The operating mode of the calender is adjustable or is set.
- the consolidation device or the calender is recommended to have at least one consolidation area in which the nonwoven web is consolidated or finally consolidated.
- consolidation area means the area in which the nonwoven web is consolidated or finally consolidated or otherwise treated by interaction or contact with at least one calender roller. It is recommended that the consolidation area of the consolidation device or the calender is arranged above the nose roller and/or above the deposit screen belt. The arrangement of the consolidation area relates to the operating position or the operating state of the device.
- the calender is a consolidation calender and/or a coating calender and/or a calibration calender and/or a laminating calender and/or an activation calender.
- the device expediently has a pre-consolidation device, which is preferably arranged in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt in front of the detachment area. It is possible that the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt before the nonwoven web is finally consolidated. In principle, however, it is also possible for the device to be set up in such a way that the nonwoven web is finally consolidated before the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt.
- Such an embodiment, in which the nonwoven web is finally consolidated before the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt, is particularly preferred if the nonwoven web is immediately subjected to a coating calender and/or a calibration calender and/or a laminating calender and/or an activation calender and/or a hot air bonder, for example an oven.
- the at least one lifting roller and/or the second lifting roller has a distance U from the nose roller that is at least 50% of the diameter of the respective lifting roller.
- the distance U is expediently measured between the projections of the axes of rotation of the lifting roller and the nose roller onto the depositing screen belt, wherein the projections of the axes of rotation are perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt or to the imaginary extension of this longitudinal extension in the region of the distance U.
- both lifting rollers preferably have a distance U 1 and U 2 from the nose roller that is at least 50% of the diameter of the respective lifting roller.
- the invention further teaches a method for transporting and treating a nonwoven web made of continuous filaments, in particular with a device described above, wherein the nonwoven web is guided over a depositing screen belt that can be deflected from its transport direction in a deflection area by a nose roller, wherein the nonwoven web is transferred to a downstream device, wherein the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt before the deflection area.
- the method according to the invention is characterized in that the nonwoven web is guided over at least one lifting roller for detachment from the depositing screen belt, which is arranged above the depositing screen belt, wherein the at least one lifting roller is height-adjustable in relation to the depositing screen belt and is preferably movable in the vertical direction for this purpose, wherein the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt by means of the at least one lifting roller in a detachment region which is arranged at a distance A from the nose roller and wherein the nonwoven web is subsequently fed to the subsequent device.
- the nonwoven web is subsequently wound and/or coated and/or calibrated and/or activated and/or consolidated in the subsequent device(s).
- the invention is based on the finding that the device according to the invention enables the nonwoven web to be detached from the depositing screen belt in a functionally reliable and simple manner and that, in particular, the amount of force required to detach the nonwoven web can be reduced compared to known measures. This is achieved by detaching the nonwoven web by means of at least one lifting roller in a detachment area that is arranged in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt in front of the deflection area.
- the nonwoven web can be detached by the measures according to the invention in particular without damaging the nonwoven web, for example by tearing out filaments, so that no unwanted filament residues remain on the depositing screen belt. It should also be emphasized that the measures according to the invention can be implemented relatively easily and without any significant effort or cost.
- the detachment area or the detachment line and thus the distance A from the nose roller can be set very precisely. Due to the preferred vertical mobility of the lifting roller(s) and/or the horizontal mobility or telescopicity of the nose roller and/or the vertical mobility of the nose roller, different operating states of the device can be set and in particular the distance of the nose roller to a subsequent device, for example to a calender, can be adjusted and/or a gradient of the depositing screen belt can be realized, whereby the lifting roller or the lifting rollers can nevertheless be arranged in relation to the depositing screen belt such that the detachment of the nonwoven web takes place or can take place in a detachment area or on a detachment line in front of the deflection area.
- the device or the method according to the invention can therefore be used very flexibly, whereby in the various operating positions a simple and functionally reliable detachment of the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt is possible, for which a relatively small amount of force is required and which can take place in particular without damaging the nonwoven web.
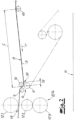
- the figures show a device for producing nonwovens from continuous filaments, with a spinning device 1 designed as a spinneret for spinning the filaments and a cooling device 2 for cooling the filaments.
- a depositing screen belt 3 is also provided, on which the filaments can be deposited in a depositing area 4 to form the nonwoven web 5.
- the device is a spunbond device, with a stretching device 17 being provided for stretching the filaments.
- the continuous filaments can expediently be monocomponent filaments made of at least one thermoplastic.
- the cooling device 2 has, as recommended and in the exemplary embodiment, a cooling chamber 18 through which the continuous filaments are guided for cooling.
- two air supply cabins 19, 20 arranged one above the other are arranged on two opposite sides of the cooling chamber 18, from which air of different temperatures is preferably introduced into the cooling chamber 18.
- a monomer extraction device 21 is provided between the spinning device 1 and the cooling device 2, with which interfering gases that occur during the spinning process can be removed from the device or the spunbond device.
- the interfering gases can be monomers, oligomers and similar substances.
- the stretching device 17 for stretching the filaments is arranged downstream of the cooling device 2 in the filament flow direction FS.
- the unit comprising the cooling device 2 and the stretching device 17 is designed as a closed unit in which, apart from the supply of cooling air in the cooling device 2, no further air is supplied to the closed unit.
- a diffuser 23 through which the continuous filaments are guided is arranged between the stretching device 17 and the depositing screen belt 3.
- secondary air inlet gaps 24 for the introduction of secondary air into the diffuser 23 are provided between the stretching device 17 and the diffuser 23.
- the continuous filaments are deposited on the depositing screen belt 3 in the depositing area 4 to form the nonwoven web 5 and are then expediently transported away with the depositing screen belt 3 in the transport direction T of the depositing screen belt 3.
- a suction device 22 is provided under the depositing screen belt 3 for sucking air or process air through the depositing screen belt 3.
- the depositing screen belt 3 can be deflected from its transport direction T in a deflection area 6 by at least one nose roller 7.
- the fleece web 5 is in the operating state of the device ( Figures 2 to 4 ) can be detached from the depositing screen belt 3 before the deflection area 6 and then transferred to at least one subsequent device 8.
- two subsequent devices 8, a calender 16 and a winder 26 are provided.
- two lifting rollers 9, 14 are preferably provided in the embodiment according to the figures. It is recommended and in the embodiment the lifting rollers 9, 14 are designed to be height-adjustable in relation to the depositing screen belt 3 and preferably and in the embodiment they are movable in the vertical direction. This is particularly the case in the Fig.1
- the lifting rollers 9, 14 can be conveniently adjusted in height or moved vertically from a basic position to various lifting positions and back. In a basic position of the lifting rollers 9, 14, which are in the Fig.1 As shown, cleaning of the device according to the invention and/or threading of the fleece web is possible, so that the device is not yet in its operating state.
- FIG. 2 and 3 Two different lifting positions of the lifting rollers 9, 14 are shown in the Figures 2 and 3 These figures show the device in the operating state.
- the lifting rollers 9, 14 are expediently arranged above the depositing screen belt 3 and the fleece web 5 can be detached from the depositing screen belt 3 by means of the lifting rollers 9, 14 in a detachment area 10 or on a detachment line, which is arranged at a distance A from the nose roller 7 and is arranged in particular in front of the nose roller 7 in the transport direction T.
- Distance A between the nose roller 7 and the detachment area 10 or the detachment line means in particular the distance between the axis of rotation of the nose roller 7 and the detachment area or the detachment line 10.
- the distance A is expediently measured between a projection of the axis of rotation of the nose roller 7 onto the depositing screen belt 3 and the detachment area 10 or the detachment line, whereby the projection of the axis of rotation is perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt 3 in the area of the distance A ( Figures 2 to 4 ).
- the first lifting roller 9 is arranged in the transport direction T of the depositing screen belt 3 behind the nose roller 7 ( Fig.2 ) or arranged in front of the nose roller 7 ( Fig.3 ).
- the second lifting roller 14 is preferably arranged in front of the nose roller 7 in the transport direction T of the depositing screen belt 3.
- the distance A is smaller than the distance C between the nose roller 7 and a deflection roller 15.
- the deflection roller 15 is expediently a roller set up in addition to the nose roller 7 for transporting the depositing screen belt 3, which is arranged in front of the nose roller 7 in the transport direction T of the depositing screen belt 3.
- the deflection roller 15 is recommended and in the exemplary embodiment provided between the depositing area 4 and the deflection area 6.
- the depositing screen belt 3 can be guided along the deflection roller 15 either without deflection from its transport direction ( Fig.1 ) or be deflected from its transport direction by the deflection roller 15 ( Figures 2 and 3 ), as explained in more detail below.
- Distance C between the nose roller 7 and the deflection roller 15 means in the context of the invention in particular the distance between the axes of rotation of the nose roller 7 and the deflection roller 15, which is expediently measured between the projections of the axes of rotation onto the depositing screen belt 3, whereby the projections of the axes of rotation are perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt 3 in the area of the distance C. It is recommended that the distance A is a maximum of 30%, preferably a maximum of 20% of the distance C. In the embodiment according to the Fig.2 the distance A may be about 5% of the distance C. In the embodiment according to the Fig.3 the distance A may be about 15% of the distance C.
- the lifting rollers 9, 14 are designed as rotating lifting rollers.
- the diameter d of the lifting rollers 9, 14 is preferably 25 to 400 mm, particularly preferably 100 to 250 mm.
- the first lifting roller 9 and the second lifting roller 14 have the same diameter d or essentially the same diameter d.
- the rotational axis distance m of the two lifting rollers 9, 14 in the operating state of the device is at least 115% of the diameter d of the lifting rollers 9, 14.
- the rotational axis distance m of the two lifting rollers 9, 14 may be approximately 130% of the diameter d of the lifting rollers 9, 14.
- Rotational axis distance m in this context means in particular the distance between the rotational axes of the two lifting rollers 9, 14, wherein this rotational axis distance m is expediently measured between the projections of the rotational axes of the lifting rollers 9, 14 onto the depositing screen belt 3, wherein the projections of the rotational axes are perpendicular to the longitudinal extent of the depositing screen belt 3 or to the imaginary extension of this longitudinal extent.
- the lifting rollers 9, 14 are arranged at a distance D in relation to the depositing screen belt 3.
- Distance D in this context means in particular the distance of the axis of rotation of the respective lifting roller 9, 14 to the depositing screen belt 3.
- the distance D to the depositing screen belt 3 is thereby conveniently measured or determined perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt 3 in the area of the lifting rollers 9, 14 or to the imaginary extension of this longitudinal extension.
- the distance of the first lifting roller 9 from the depositing screen belt 3 is marked with D 1 and the distance of the second lifting roller 14 from the depositing screen belt 3 is marked with D 2.
- the distance D or the distances D 1 and D 2 are greater than 50% of the diameter d of the respective lifting roller 9, 14.
- the distance D 1 of the first lifting roller 9 from the depositing screen belt 3 is greater than the distance D 2 of the second lifting roller 14 from the depositing screen belt 3.
- the fleece web 5 can be guided expediently and in the embodiment in the operating state of the device over the underside of the second lifting roller 14 and over the top of the first lifting roller 9. This is particularly the case in the Figures 2 to 4
- the first lifting roller 9 is preferably responsible for detaching the nonwoven web 5 from the depositing screen belt 3.
- the second lifting roller 14 is recommended for holding down the nonwoven web 5 close to the depositing screen belt 3.
- the detachment area 10 or the detachment line is expediently and in the exemplary embodiment close to the second lifting roller 14 and in particular below the second lifting roller 14.
- the nose roller 7 can be moved or lowered in the vertical direction in such a way that the depositing screen belt 3 between the deflection roller 15 and the nose roller 7 is oriented in the transport direction T towards the device base 11.
- the depositing screen belt has a gradient of 3° to 20° in this area.
- the sieve belt 3 may have a gradient of about 7° and in the embodiment according to the Fig.3 have a gradient of about 15°.
- the deflection roller 15 thus deflects the depositing screen belt 3 from its transport direction T, which previously ran parallel to the device base 11 ( Figures 2 and 3 ).
- the ability of the nose roller 7 to move in the vertical direction means in particular the ability to move in the direction of the device base 11 and back.
- the nose roller 7 is movable or telescopic in the horizontal direction.
- Horizontal direction means in this context in particular in the direction parallel to the device base 11. Due to the horizontal mobility or telescoping of the nose roller 7, this nose roller 7 can, for example, be moved closer to the following device 8 or the calender 16.
- the nose roller 7 can be moved or telescopic in the horizontal direction and can be moved or lowered in the vertical direction, so that a wide variety of positions of the nose roller can be set.
- the nose roller 7 can be moved or telescopic in the horizontal direction and can be lowered in the vertical direction and in addition the lifting rollers 9, 14 can be moved in the vertical direction, different positions of the nose roller 7 can be set and the lifting rollers 9, 14 can be arranged in their lifting positions in such a way that in particular the distance A of the detachment area 10 from the nose roller 7 can be realized in the operating state of the device.
- a follow-up device 8 is designed as a calender 16.
- a further follow-up device 8 in the form of a winder 26 can be provided, with the calender 16 and then the winder 26 being arranged in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web 5.
- the calender 16 has three calender rollers 12.1, 12.2 and 12.3, which can be moved in the vertical direction.
- the nonwoven web 5 is guided in particular through the gap or nip between two of the calender rollers 12.1, 12.2, 12.3.
- the three calender rollers 12.1, 12.2, 12.3 are expediently arranged one above the other in the exemplary embodiment.
- the nonwoven web 5 is solidified or final consolidation is expediently and in the exemplary embodiment through a gap or nip that is formed between the calender rolls 12.1, 12.2, 12.3.
- a consolidation area 13 of the calender 16 the nonwoven web 5 can then be consolidated or finally consolidated.
- Consolidation area 13 in this context means the area in which the nonwoven web 5 can be consolidated or finally consolidated by the action of at least one calender roll 12.1, 12.2, 12.3.
- the consolidation region 13 of the calender 16 is arranged above the nose roller 7 and above the deposition screen belt 3.
- the detachment of the nonwoven web 5 from the depositing screen belt 3 takes place after a pre-consolidation of the nonwoven web 5.
- the nonwoven web is thus recommended and in the embodiment before detachment from the depositing screen belt 3 pre-consolidated by means of a pre-consolidation device 25. This is particularly the case in the Fig.1 to recognize.
- first lifting roller 9 and/or the second lifting roller 14 has a distance U from the nose roller 7 which is at least 50% of the diameter of the respective lifting roller 9, 14.
- Distance U in this context means in particular the distance of the axis of rotation of the at least one lifting roller 9, 14 from the axis of rotation of the nose roller 7, wherein the distance U is expediently measured between the projections of the axes of rotation of the lifting roller 9, 14 and the nose roller 7 onto the depositing screen belt 3, wherein the projections of the axes of rotation are perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt 3 or to the imaginary extension of this longitudinal extension in the region of the distance U.
- both lifting rollers 9, 14 each have a center distance U 1 and U 2 from the nose roller 7, which is at least 50% of the diameter d of the respective lifting roller 9, 14 ( Fig.4 ).
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Nonwoven Fabrics (AREA)
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Vliesstoffen aus Endlosfilamenten, wobei eine Spinneinrichtung zum Erspinnen der Filamente und eine Kühleinrichtung zum Kühlen der Filamente vorhanden ist, wobei weiterhin ein Ablagesiebband vorgesehen ist, auf dem die Filamente in einem Ablagebereich zu einer Vliesbahn ablegbar sind, wobei das Ablagesiebband in einem Umlenkungsbereich durch zumindest eine Nasenwalze aus seiner Transportrichtung ablenkbar ist und wobei zumindest eine dem Ablagesiebband in Förderrichtung der Vliesbahn nachgeschaltete Folgevorrichtung für die Vliesbahn vorhanden ist. Die Erfindung betrifft weiterhin ein Verfahren zum Transport und zur Behandlung einer Vliesbahn aus Endlosfilamenten. - Endlosfilamente unterscheiden sich aufgrund ihrer praktisch endlosen Länge von Stapelfasern, die deutlich geringere Längen von beispielsweise 10 mm bis 60 mm aufweisen.The invention relates to a device for producing nonwovens from continuous filaments, wherein a spinning device for spinning the filaments and a cooling device for cooling the filaments are present, wherein a depositing screen belt is also provided on which the filaments can be deposited in a depositing area to form a nonwoven web, wherein the depositing screen belt can be deflected from its transport direction in a deflection area by at least one nose roller and wherein at least one follow-up device for the nonwoven web is present downstream of the depositing screen belt in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web. The invention also relates to a method for transporting and treating a nonwoven web made of continuous filaments. - Continuous filaments differ from staple fibers due to their practically endless length, which have significantly shorter lengths of, for example, 10 mm to 60 mm.
Vorrichtungen und Verfahren der eingangs genannten Art sind in unterschiedlichen Ausführungsformen aus der Praxis und aus dem Stand der Technik grundsätzlich bekannt. Bei derartigen Vorrichtungen werden die Filamente mittels einer Spinneinrichtung ersponnen, anschließend in einer Kühleinrichtung gekühlt und schließlich auf einem Ablagesiebband zur Vliesbahn abgelegt.
Das Ablagesiebband der aus der Praxis bekannten Vorrichtungen ist in der Regel als endlos umlaufendes Ablagesiebband ausgebildet, das in einem Umlenkungsbereich durch eine Nasenwalze aus seiner Transportrichtung abgelenkt wird. Die Vliesbahn wird in diesem am Ende des Ablagesiebbandes angeordneten Umlenkungsbereich von dem Ablagesiebband bzw. von der Nasenwalze an eine Folgevorrichtung übergeben und dazu in dem Umlenkungsbereich von dem Ablagesiebband abgelöst. Bei den aus der Praxis bekannten Vorrichtungen und Verfahren hat sich aber gezeigt, dass das Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband eine relativ hohe Kraft erfordert und insoweit nicht immer einfach und funktionssicher möglich ist. Hinzu kommt, dass in der Regel eine ausreichend gute Haftung der Vliesbahn an dem Ablagesiebband zumindest im Ablagebereich wünschenswert ist, sodass gleichsam ein Zielkonflikt zwischen einem guten Ablöseverhalten und einer ausreichenden Haftung auf dem Ablagesiebband besteht. Darüber hinaus kann es insbesondere im Umlenkungsbereich aufgrund der starken Umlenkung des Ablagesiebbandes zu einer Verklemmung bzw. Einklemmung der Endlosfilamente in dem Ablagesiebband kommen. In der Folge ist für das Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband ein hoher Kraftaufwand erforderlich und es kann zu Beschädigungen der Vliesbahn durch Herausreißen von Filamenten kommen. Zudem können in unerwünschter Weise Filamentreste auf dem Ablagesiebband verbleiben, die beim Ablösevorgang aus der Vliesbahn herausgerissen werden. - Insoweit besteht Verbesserungsbedarf.The depositing screen belt of the devices known from practice is usually designed as an endlessly rotating depositing screen belt that is deflected from its transport direction in a deflection area by a nose roller. In this deflection area arranged at the end of the depositing screen belt, the nonwoven web is transferred from the depositing screen belt or from the nose roller to a subsequent device and is detached from the depositing screen belt in the deflection area. However, with the devices and methods known from practice, it has been shown that detaching the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt requires a relatively high level of force and is therefore not always easy or reliable. In addition, a sufficiently good adhesion of the nonwoven web to the depositing screen belt is generally desirable, at least in the depositing area, so that there is a conflict of objectives between good detachment behavior and sufficient adhesion to the depositing screen belt. In addition, the strong deflection of the depositing screen belt can lead to jamming or trapping of the continuous filaments in the depositing screen belt, particularly in the deflection area. As a result, the A great deal of force is required to detach the fleece web from the depositing screen belt, and the fleece web can be damaged by filaments being torn out. In addition, filament residues can remain on the depositing screen belt, which are torn out of the fleece web during the detachment process. - There is a need for improvement in this regard.
Der Erfindung liegt demgegenüber das technische Problem zugrunde, eine Vorrichtung der eingangs genannten Art anzugeben, mit der die Vliesbahn einfach und funktionssicher von dem Ablagesiebband abgelöst werden kann, mit der insbesondere eine Beschädigung der Vliesbahn beim Ablösevorgang vermieden werden kann und wobei der Kraftaufwand für das Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband reduziert werden kann. Der Erfindung liegt darüber hinaus das technische Problem zugrunde, ein entsprechendes Verfahren zum Transport und zur Behandlung einer Vliesbahn anzugeben.The invention is based on the technical problem of specifying a device of the type mentioned at the beginning with which the nonwoven web can be detached from the depositing screen belt in a simple and functionally reliable manner, with which in particular damage to the nonwoven web can be avoided during the detachment process and the amount of force required to detach the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt can be reduced. The invention is also based on the technical problem of specifying a corresponding method for transporting and treating a nonwoven web.
Zur Lösung dieses technischen Problems lehrt die Erfindung eine Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Vliesstoffen aus Endlosfilamenten, wobei eine Spinneinrichtung zum Erspinnen der Filamente und eine Kühleinrichtung zum Kühlen der Filamente vorhanden ist, wobei weiterhin ein Ablagesiebband vorgesehen ist, auf dem die Filamente in einem Ablagebereich zu einer Vliesbahn ablegbar sind, wobei das Ablagesiebband in einem Umlenkungsbereich durch zumindest eine Nasenwalze aus seiner Transportrichtung ablenkbar ist, wobei zumindest eine dem Ablagesiebband in Förderrichtung der Vliesbahn nachgeschaltete Folgevorrichtung für die Vliesbahn vorhanden ist, wobei die Vliesbahn vor dem Umlenkungsbereich von dem Ablagesiebband ablösbar und anschließend an die Folgevorrichtung übergebbar ist, wobei zur Ablösung der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband zumindest eine Abhebewalze vorgesehen ist, wobei die Abhebewalze oberhalb des Ablagesiebbandes angeordnet ist bzw. angeordnet werden kann, wobei die Vliesbahn mittels der zumindest einen Abhebewalze in einem Ablösebereich von dem Ablagesiebband ablösbar ist, der mit einem Abstand A zu der Nasenwalze angeordnet ist. Die erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die zumindest eine Abhebewalze in Bezug auf das Ablagesiebband höhenverstellbar ist und dazu vorzugsweise in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar ist.To solve this technical problem, the invention teaches a device for producing nonwovens from continuous filaments, wherein a spinning device for spinning the filaments and a cooling device for cooling the filaments are present, wherein a depositing screen belt is also provided on which the filaments can be deposited in a depositing area to form a nonwoven web, wherein the depositing screen belt can be deflected from its transport direction in a deflection area by at least one nose roller, wherein at least one follow-up device for the nonwoven web is provided downstream of the depositing screen belt in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web, wherein the nonwoven web can be detached from the depositing screen belt before the deflection area and then transferred to the follow-up device, wherein at least one lifting roller is provided for detaching the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt, wherein the lifting roller is arranged or is arranged above the depositing screen belt can be detached from the depositing screen belt by means of the at least one lifting roller in a detachment area which is arranged at a distance A from the nose roller. The device according to the invention is characterized in that the at least one lifting roller is height-adjustable in relation to the depositing screen belt and is preferably movable in the vertical direction for this purpose.
Die erfindungsgemäße Spinneinrichtung ist im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere als Spinnerette ausgebildet. Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes meint im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere die Richtung, in die sich das Ablagesiebband bzw. das endlos umlaufende Ablagesiebband zur Förderung der Vliesbahn bewegt. Förderrichtung der Vliesbahn meint insbesondere die Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes. Umlenkungsbereich meint im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere den Bereich am Ende des Ablagesiebbandes, in dem das Ablagesiebband durch die Nasenwalze aus seiner Transportrichtung abgelenkt wird und somit seine Transportrichtung verlässt. Ablösebereich bzw. Ablösebereich der Vliesbahn meint im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere den Bereich, in dem die Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband abgelöst wird. Gemäß einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform handelt es sich bei dem Ablösebereich um eine Ablöslinie, die sich insbesondere quer, bevorzugt senkrecht zu der Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes erstreckt. Der Ablösebereich bzw. die Ablöselinie ist vorzugsweise in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes vor dem Umlenkungsbereich und/oder vor der Nasenwalze angeordnet. Der Abstand A wird insbesondere zwischen einer Projektion der Drehachse der Nasenwalze auf das Ablagesiebband und dem Ablösebereich bzw. der Ablöselinie gemessen, wobei die Projektion der Drehachse senkrecht zu der Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes im Bereich des Abstandes A erfolgt. Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes meint im Rahmen der Erfindung die Erstreckung in Transportrichtung. Ablagebereich meint zweckmäßigerweise denjenigen Bereich des Ablagesiebbandes, in dem die ersponnenen Filamente zur Vliesbahn abgelegt werden. Hier und nachfolgend wird insbesondere auf die Betriebsposition bzw. den Betriebszustand der Vorrichtung Bezug genommen, soweit nichts anderes angegeben ist.The spinning device according to the invention is designed in particular as a spinnerette within the scope of the invention. In the scope of the invention, the transport direction of the depositing screen belt means in particular the direction in which the depositing screen belt or the endlessly rotating depositing screen belt moves to convey the nonwoven web. In the scope of the invention, the transport direction of the depositing screen belt means in particular the deflection area at the end of the depositing screen belt in which the depositing screen belt is deflected from its transport direction by the nose roller and thus leaves its transport direction. In the scope of the invention, the detachment area or detachment area of the nonwoven web means in particular the area in which the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt. According to a preferred embodiment, the detachment area is a detachment line which extends in particular transversely, preferably perpendicularly to the transport direction of the depositing screen belt. The detachment area or detachment line is preferably arranged in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt in front of the deflection area and/or in front of the nose roller. The distance A is measured in particular between a projection of the axis of rotation of the nose roller onto the depositing screen belt and the detachment area or the detachment line, whereby the projection of the axis of rotation is perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt in the area of the distance A. Longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt means in the context of the invention the extension in Transport direction. The deposit area refers expediently to the area of the deposit screen belt in which the spun filaments are deposited to form the nonwoven web. Here and below, reference is made in particular to the operating position or operating state of the device, unless otherwise stated.
Nach einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform der Erfindung handelt es sich bei der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung um eine Spunbond-Vorrichtung, wobei eine Verstreckeinrichtung zum Verstrecken der Filamente vorgesehen ist. Eine andere Ausführungsform der Erfindung ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung eine Meltblown-Vorrichtung ist.According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, the device according to the invention is a spunbond device, wherein a stretching device is provided for stretching the filaments. Another embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the device according to the invention is a meltblown device.
Wenn die erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung gemäß bevorzugter Ausführungsform als Spunbond-Vorrichtung ausgebildet ist, werden mit der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung Spunbond-Vliese bzw. Vliesbahnen hergestellt. Dabei werden Monokomponentenfilamente und/oder Mehrkomponentenfilamente bzw. Bikomponentenfilamente als Endlosfilamente erzeugt. Bei den Mehrkomponentenfilamenten bzw. Bikomponentenfilamenten kann es sich beispielsweise um Endlosfilamente mit Kern-Mantel-Konfiguration oder um Endlosfilamente mit Seite-an-Seite-Konfiguration handeln. Die Mehrkomponentenfilamente bzw. Bikomponentenfilamente können eine Kräuselneigung aufweisen. Gemäß einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform der Erfindung bestehen die mit der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung bzw. mit dem erfindungsgemäßen Verfahren hergestellten Endlosfilamente aus zumindest einem thermoplastischen Kunststoff, insbesondere aus zumindest einem Polyolefin, vorzugsweise aus Polypropylen und/oder Polyethylen. Gemäß einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausführungsform ist der zumindest eine thermoplastische Kunststoff ein Polyester bzw. Copolyester, insbesondere Polyethylenterephthalat und/oder ein Polyethylenterephthalat-Copolymer.If the device according to the invention is designed as a spunbond device according to a preferred embodiment, spunbond nonwovens or nonwoven webs are produced with the device according to the invention. In this case, monocomponent filaments and/or multicomponent filaments or bicomponent filaments are produced as continuous filaments. The multicomponent filaments or bicomponent filaments can be, for example, continuous filaments with a core-shell configuration or continuous filaments with a side-by-side configuration. The multicomponent filaments or bicomponent filaments can have a tendency to curl. According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, the continuous filaments produced with the device according to the invention or with the method according to the invention consist of at least one thermoplastic material, in particular of at least one polyolefin, preferably of polypropylene and/or polyethylene. According to a further preferred embodiment, the at least one thermoplastic material is a polyester or copolyester, in particular polyethylene terephthalate and/or a polyethylene terephthalate copolymer.
Erfindungsgemäß ist eine Kühleinrichtung zum Kühlen der Filamente vorgesehen. Die Kühleinrichtung weist empfohlenermaßen eine Kühlkammer auf, durch die die Endlosfilamente zur Kühlung geführt werden. Es ist bevorzugt, dass an zwei gegenüberliegenden Seiten der Kühlkammer Luftzufuhrkabinen für die Zufuhr der Kühlluft angeordnet sind. Gemäß einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform sind an zwei gegenüberliegenden Seiten der Kühlkammer übereinander angeordnete Luftzufuhrkabinen vorhanden, insbesondere zwei übereinander angeordnete Luftzufuhrkabinen, aus denen bevorzugt Luft unterschiedlicher Temperatur in die Kühlkammer eingeführt wird. Es hat sich bewährt, dass zwischen der Spinneinrichtung und der Kühleinrichtung eine Monomer-Absaugungseinrichtung vorgesehen ist, mit der störende Gase, die beim Spinnprozess auftreten aus der Vorrichtung bzw. der Spunbond-Vorrichtung entfernt werden können. Bei den störenden Gasen kann es sich etwa um Monomere, Oligomere und dergleichen Substanzen handeln.According to the invention, a cooling device is provided for cooling the filaments. The cooling device preferably has a cooling chamber through which the continuous filaments are guided for cooling. It is preferred that air supply cabins for supplying cooling air are arranged on two opposite sides of the cooling chamber. According to a preferred embodiment, air supply cabins arranged one above the other are present on two opposite sides of the cooling chamber, in particular two air supply cabins arranged one above the other, from which air of different temperatures is preferably introduced into the cooling chamber. It has proven useful to provide a monomer extraction device between the spinning device and the cooling device, with which disruptive gases that occur during the spinning process can be removed from the device or the spunbond device. The disruptive gases can be monomers, oligomers and similar substances.
Zweckmäßigerweise ist der Kühleinrichtung in Filamentströmungsrichtung eine Verstreckeinrichtung zum Verstrecken der Filamente nachgeschaltet. Nach besonders empfohlener Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung ist das Aggregat aus der Kühleinrichtung und der Verstreckeinrichtung als geschlossenes Aggregat ausgebildet, bei dem außer der Zufuhr der Kühlluft in der Kühleinrichtung keine weitere Luftzufuhr in das geschlossene Aggregat stattfindet.A stretching device for stretching the filaments is expediently arranged downstream of the cooling device in the direction of filament flow. According to a particularly recommended embodiment of the device according to the invention, the unit comprising the cooling device and the stretching device is designed as a closed unit in which, apart from the supply of cooling air in the cooling device, no further air is supplied to the closed unit.
Es ist bevorzugt, dass zwischen der Verstreckeinrichtung und dem Ablagesiebband zumindest ein Diffusor angeordnet ist. Die aus der Verstreckeinrichtung austretenden Endlosfilamente werden durch den Diffusor hindurchgeführt und dann auf dem Ablagesiebband abgelegt, insbesondere in dem Ablagebereich des Ablagesiebbandes abgelegt. Gemäß einer Ausführungsform der Erfindung sind zwei hintereinander geschaltete Diffusoren vorgesehen. Das Ablagesiebband bzw. das endlos umlaufende Ablagesiebband ist im Übrigen zweckmäßigerweise luftdurchlässig ausgebildet, sodass eine Absaugung von Prozessluft von unten durch das Ablagesiebband erfolgen kann. Zweckmäßigerweise wird zumindest im Ablagebereich des Ablagesiebbandes Prozessluft mittels zumindest einer Absaugungseinrichtung, insbesondere von unten, durch das Ablagesiebband gesaugt.It is preferred that at least one diffuser is arranged between the stretching device and the deposition screen belt. The continuous filaments emerging from the stretching device are guided through the diffuser and then deposited on the deposition screen belt, in particular deposited in the deposition area of the deposition screen belt. According to one embodiment of the invention Two diffusers connected in series are provided. The depositing sieve belt or the endlessly rotating depositing sieve belt is also expediently designed to be permeable to air, so that process air can be extracted from below through the depositing sieve belt. Expediently, at least in the depositing area of the depositing sieve belt, process air is sucked through the depositing sieve belt by means of at least one extraction device, in particular from below.
Eine bevorzugte Ausführungsform der Erfindung ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die zumindest eine Abhebewalze derart zu der Nasenwalze angeordnet ist bzw. angeordnet werden kann, dass der Ablösebereich in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes vor dem Umlenkungsbereich liegt. Es empfiehlt sich, dass die zumindest eine Abhebewalze in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes vor oder hinter der Nasenwalze angeordnet ist bzw. angeordnet werden kann. Es liegt im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die Vliesbahn über die Oberseite der zumindest einen Abhebewalze geführt werden kann bzw. geführt wird. Es empfiehlt sich, dass die zumindest eine Abhebewalze als nicht-besaugte Abhebewalze ausgeführt ist.A preferred embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the at least one lifting roller is or can be arranged in relation to the nose roller in such a way that the detachment area is located in front of the deflection area in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt. It is recommended that the at least one lifting roller is or can be arranged in front of or behind the nose roller in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt. It is within the scope of the invention that the nonwoven web can be or is guided over the top of the at least one lifting roller. It is recommended that the at least one lifting roller is designed as a non-vacuum-fed lifting roller.
Gemäß einer besonders bevorzugten Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung ist der Abstand A kleiner als der Abstand C zwischen der Nasenwalze und einer Umlenkungswalze. Umlenkungswalze meint in diesem Zusammenhang insbesondere eine zusätzlich zu der Nasenwalze zum Transport des Ablagesiebbandes eingerichtete Walze, die in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes vor der Nasenwalze angeordnet ist. Die Umlenkungswalze ist insbesondere zwischen dem Ablagebereich und dem Umlenkungsbereich vorgesehen. An der Umlenkungswalze kann das Ablagesiebband gemäß einer Ausführungsform ohne Ablenkung aus seiner Transportrichtung entlang geführt werden. Gemäß einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform wird das Ablagesiebband durch die Umlenkungswalze aus seiner Transportrichtung abgelenkt, wie unten stehend noch näher erläutert wird. Es ist bevorzugt, dass die zumindest eine Nasenwalze in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes bzw. in Förderrichtung der Vliesbahn hinter dem Ablagebereich und hinter dem Aggregat aus Spinneinrichtung und Kühleinrichtung angeordnet ist. Zweckmäßigerweise ist die zumindest eine Umlenkungswalze in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes bzw. in Förderrichtung der Vliesbahn ebenfalls hinter dem Ablagebereich bzw. hinter dem Aggregat aus Spinneinrichtung und Kühleinrichtung, aber vor der Nasenwalze, angeordnet. Abstand C zwischen der Nasenwalze und der Umlenkungswalze meint im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere den Abstand der Drehachsen der Nasenwalze und der Umlenkungswalze, der zweckmäßigerweise zwischen den Projektionen der Drehachsen auf das Ablagesiebband gemessen wird, wobei die Projektionen der Drehachsen senkrecht zu der Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes im Bereich des Abstandes C erfolgen. Zweckmäßigerweise stellt der Bereich zwischen der Umlenkungswalze und der Nasenwalze einen Übergabetisch dar, dessen Länge insbesondere durch den Abstand C definiert ist. Der Übergabetisch hat zweckmäßigerweise im Wesentlichen die Funktion, die Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband an die Folgevorrichtung zu übergeben.According to a particularly preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention, the distance A is smaller than the distance C between the nose roller and a deflection roller. In this context, deflection roller means in particular a roller which is set up in addition to the nose roller for transporting the depositing screen belt and which is arranged in front of the nose roller in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt. The deflection roller is provided in particular between the depositing area and the deflection area. According to one embodiment, the depositing screen belt can be guided along the deflection roller without being deflected from its transport direction. According to a preferred embodiment, the depositing screen belt deflected from its transport direction by the deflection roller, as will be explained in more detail below. It is preferred that the at least one nose roller is arranged behind the depositing area and behind the unit comprising the spinning device and the cooling device in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt or in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web. The at least one deflection roller is expediently arranged behind the depositing area or behind the unit comprising the spinning device and the cooling device in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt or in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web, but in front of the nose roller. Distance C between the nose roller and the deflection roller means in the context of the invention in particular the distance between the axes of rotation of the nose roller and the deflection roller, which is expediently measured between the projections of the axes of rotation onto the depositing screen belt, the projections of the axes of rotation being perpendicular to the longitudinal extent of the depositing screen belt in the region of the distance C. Expediently, the region between the deflection roller and the nose roller represents a transfer table, the length of which is defined in particular by the distance C. The transfer table essentially has the function of transferring the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt to the subsequent device.
Es ist bevorzugt, dass der Abstand A maximal 50 %, vorzugsweise maximal 25 %, bevorzugt maximal 10 %, besonders bevorzugt maximal 5 %, ganz besonders bevorzugt maximal 2,5 %, beispielsweise 1 % von dem Abstand C beträgt. Gemäß einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung beträgt der Abstand A zumindest 25 % des Durchmessers n der Nasenwalze, vorzugsweise zumindest 50 %, bevorzugt zumindest 75 %, besonders bevorzugt zumindest 100 % und ganz besonders bevorzugt zumindest 125 % des Durchmessers n der Nasenwalze. Weiter bevorzugt beträgt der Abstand A zwischen 10 % und 500 %, besonders bevorzugt zwischen 25 % und 400 %, ganz besonders bevorzugt zwischen 50 % und 350 % des Durchmessers n der Nasenwalze.It is preferred that the distance A is a maximum of 50%, preferably a maximum of 25%, preferably a maximum of 10%, particularly preferably a maximum of 5%, very particularly preferably a maximum of 2.5%, for example 1% of the distance C. According to a further preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention, the distance A is at least 25% of the diameter n of the nose roller, preferably at least 50%, preferably at least 75%, particularly preferably at least 100% and very particularly preferably at least 125% of the diameter n of the nose roller. The distance A is further preferably between 10% and 500%, particularly preferably between 25% and 400%, most preferably between 50% and 350% of the diameter n of the nose roller.
Erfindungsgemäß ist die zumindest eine Abhebewalze in Bezug auf das Ablagesiebband höhenverstellbar und dazu vorzugsweise in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar. Empfohlenermaßen kann die zumindest eine Abhebewalze durch ihre Höhenverstellbarkeit bzw. vertikale Verfahrbarkeit von einer Grundposition in verschiedene Abhebepositionen und zurück verfahren werden. In der Grundposition der zumindest einen Abhebewalze können beispielsweise Reinigungsarbeiten an der Vorrichtung vorgenommen werden oder es kann eine Einfädelung der Vliesbahn erfolgen. Dann befindet sich die Vorrichtung nicht in ihrem Betriebszustand bzw. in ihrer Betriebsposition. In der Abhebeposition ist die zumindest eine Abhebewalze zweckmäßigerweise derart zu der Nasenwalze angeordnet, dass sich im Betriebszustand der Vorrichtung der Abstand A zwischen dem Ablösebereich bzw. der Ablöselinie der Vliesbahn und der Nasenwalze ergibt.According to the invention, the at least one lifting roller is height-adjustable in relation to the depositing screen belt and can preferably be moved in a vertical direction for this purpose. It is recommended that the at least one lifting roller can be moved from a basic position to various lifting positions and back due to its height adjustability or vertical mobility. In the basic position of the at least one lifting roller, for example, cleaning work can be carried out on the device or the nonwoven web can be threaded. The device is then not in its operating state or in its operating position. In the lifting position, the at least one lifting roller is expediently arranged in relation to the nose roller in such a way that the distance A between the detachment area or the detachment line of the nonwoven web and the nose roller results in the operating state of the device.
Eine bevorzugte Ausführungsform der Erfindung ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die zumindest eine Abhebewalze als rotierende Abhebewalze, insbesondere als antreibbare rotierende Abhebewalze, ausgebildet ist. Grundsätzlich liegt es auch im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die zumindest eine Abhebewalze als einfaches Rundprofil ausgebildet ist, das nicht rotierend und nicht antreibbar ausgebildet ist. Ein solches Rundprofil weist anstelle einer Drehachse eine Längsachse auf. Bevorzugt ist die zumindest eine Abhebewalze aber als rotierende Abhebewalze ausgebildet.A preferred embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the at least one lifting roller is designed as a rotating lifting roller, in particular as a drivable rotating lifting roller. In principle, it is also within the scope of the invention that the at least one lifting roller is designed as a simple round profile that is not rotating and not drivable. Such a round profile has a longitudinal axis instead of an axis of rotation. Preferably, however, the at least one lifting roller is designed as a rotating lifting roller.
Eine weitere bevorzugte Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die zumindest eine Abhebewalze in einem Abstand D zu dem Ablagesiebband angeordnet ist bzw. angeordnet werden kann, wobei dieser Abstand D zweckmäßigerweise größer als 50 % des Durchmessers d der Abhebewalze ist und bevorzugt mindestens 55 %, besonders bevorzugt mindestens 60 % des Durchmessers d der Abhebewalze beträgt. Abstand D meint im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere den Abstand der Drehachse der zumindest einen Abhebewalze zu dem Ablagesiebband, wobei dieser Abstand D zweckmäßigerweise senkrecht zu der Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes im Bereich der zumindest einen Abhebewalze bzw. zu der imaginären Verlängerung dieser Längserstreckung gemessen wird.A further preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention is characterized in that the at least one lifting roller is arranged at a distance D from the depositing screen belt or can be arranged can, wherein this distance D is expediently greater than 50% of the diameter d of the lifting roller and preferably at least 55%, particularly preferably at least 60% of the diameter d of the lifting roller. In the context of the invention, distance D means in particular the distance of the axis of rotation of the at least one lifting roller to the depositing screen belt, wherein this distance D is expediently measured perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt in the region of the at least one lifting roller or to the imaginary extension of this longitudinal extension.
Es empfiehlt sich, dass der Durchmesser d der zumindest einen Abhebewalze 10 bis 500 mm, vorzugsweise 25 bis 400 mm, bevorzugt 50 bis 300 mm, besonders bevorzugt 100 bis 250 mm beträgt. Zweckmäßigerweise ist der Durchmesser d der zumindest einen Abhebewalze kleiner als das 8-fache des Durchmessers n der Nasenwalze.It is recommended that the diameter d of the at least one lifting roller is 10 to 500 mm, preferably 25 to 400 mm, preferably 50 to 300 mm, particularly preferably 100 to 250 mm. The diameter d of the at least one lifting roller is expediently smaller than 8 times the diameter n of the nose roller.
Eine Ausführungsform, der im Rahmen der Erfindung ganz besondere Bedeutung zukommt ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass zumindest zwei, insbesondere zwei Abhebewalzen vorgesehen sind, wobei eine zweite Abhebewalze vorzugsweise in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes vor der Nasenwalze angeordnet ist bzw. angeordnet werden kann und wobei eine erste bzw. die erste Abhebewalze bevorzugt in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes zwischen der zweiten Abhebewalze und der Nasenwalze oder hinter der Nasenwalze angeordnet ist bzw. angeordnet werden kann.An embodiment which is of particular importance within the scope of the invention is characterized in that at least two, in particular two lifting rollers are provided, wherein a second lifting roller is preferably arranged or can be arranged in front of the nose roller in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt and wherein a first or the first lifting roller is preferably arranged or can be arranged in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt between the second lifting roller and the nose roller or behind the nose roller.
Es ist bevorzugt, dass die zumindest zwei, insbesondere die zwei Abhebewalzen als rotierende Abhebewalzen ausgebildet sind. Gemäß einer Ausführungsform sind die zumindest zwei, insbesondere die zwei Abhebewalzen als antreibbare rotierende Abhebewalzen ausgebildet. Es liegt weiterhin im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die erste Abhebewalze und die zweite Abhebewalze den gleichen Durchmesser d bzw. im Wesentlichen den gleichen Durchmesser d aufweisen. Es ist aber auch möglich, dass die erste und die zweite Abhebewalze einen unterschiedlichen Durchmesser d1 und d2 aufweisen. Zweckmäßigerweise betragen die Durchmesser d1 und d2 dann jeweils zwischen 10 und 500 mm, vorzugsweise zwischen 25 und 400 mm, bevorzugt zwischen 50 und 300 mm, besonders bevorzugt zwischen 100 und 250 mm. Vorzugsweise beträgt der Drehachsenabstand m der beiden Abhebewalzen zumindest 105 %, bevorzugt zumindest 110 %, besonders bevorzugt zumindest 115 % des Durchmessers d der Abhebewalzen. Wenn die beiden Abhebewalzen einen unterschiedlichen Durchmesser d1 bzw. d2 aufweisen, beziehen sich diese Angaben auf den Durchmesser der Abhebewalze mit dem größeren Durchmesser. Der Drehachsenabstand m wird zweckmäßigerweise zwischen den Projektionen der Drehachsen der Abhebewalzen auf das Ablagesiebband gemessen, wobei die Projektionen der Drehachsen senkrecht zu der Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes im Bereich der Abhebewalzen erfolgt. Es ist bevorzugt, dass der Drehachsenabstand m der beiden Abhebewalzen weniger als 300 %, bevorzugt weniger als 250 %, besonders bevorzugt weniger als 200 % des Durchmessers d der Abhebewalzen beträgt. Wenn die Abhebewalzen einen unterschiedlichen Durchmesser aufweisen, beziehen sich diese Angaben auf den Durchmesser der Abhebewalze mit dem größeren Durchmesser.It is preferred that the at least two, in particular the two lifting rollers are designed as rotating lifting rollers. According to one embodiment, the at least two, in particular the two lifting rollers are designed as drivable rotating lifting rollers. It is also within the scope of the invention that the first lifting roller and the second lifting roller have the same diameter d or essentially the same diameter d. However, it is also possible for the first and second lifting rollers to have different diameters d 1 and d 2. The diameters d 1 and d 2 are then expediently between 10 and 500 mm, preferably between 25 and 400 mm, more preferably between 50 and 300 mm, particularly preferably between 100 and 250 mm. The distance between the axes of rotation m of the two lifting rollers is preferably at least 105%, preferably at least 110%, particularly preferably at least 115% of the diameter d of the lifting rollers. If the two lifting rollers have different diameters d 1 or d 2 , these details refer to the diameter of the lifting roller with the larger diameter. The rotation axis distance m is expediently measured between the projections of the rotation axes of the lifting rollers onto the depositing screen belt, with the projections of the rotation axes being perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt in the area of the lifting rollers. It is preferred that the rotation axis distance m of the two lifting rollers is less than 300%, preferably less than 250%, particularly preferably less than 200% of the diameter d of the lifting rollers. If the lifting rollers have a different diameter, these details refer to the diameter of the lifting roller with the larger diameter.
Es ist bevorzugt, dass die beiden Abhebewalzen jeweils in einem Abstand D bzw. D1 und D2 zu dem Ablagesiebband angeordnet sind bzw. angeordnet werden können und wobei dieser Abstand D1 und/oder D2 vorzugsweise größer als 50 % des jeweiligen Durchmessers d1 bzw. d2 der Abhebewalze ist, besonders bevorzugt mindestens 55 % und ganz besonders bevorzugt mindestens 60 % des jeweiligen Durchmessers d1 bzw. d2 der Abhebewalze beträgt.It is preferred that the two lifting rollers are or can be arranged at a distance D or D 1 and D 2 from the depositing screen belt, and wherein this distance D 1 and/or D 2 is preferably greater than 50% of the respective diameter d 1 or d 2 of the lifting roller, particularly preferably at least 55% and very particularly preferably at least 60% of the respective diameter d 1 or d 2 of the lifting roller.
Gemäß einer Ausführungsvariante der Erfindung sind die zumindest zwei, insbesondere die zwei Abhebewalzen in Bezug auf das Ablagesiebband mit dem gleichen Abstand D bzw. im Wesentlichen mit dem gleichen Abstand D angeordnet. Dann ist der Abstand zwischen der jeweiligen Drehachse der Abhebewalze und dem Ablagesiebband gleich bzw. im Wesentlichen gleich. Es liegt aber auch im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die Abhebewalzen in einem unterschiedlichen Abstand D1 und D2 zu dem Ablagesiebband angeordnet sind, wobei dann vorzugsweise der Abstand D1 der ersten Abhebewalze zu dem Ablagesiebband größer ist als der Abstand D2 der zweiten Abhebewalze zu dem Ablagesiebband. Es liegt bezüglich der Durchmesser d1 und d2 der zwei Abhebewalzen und der Abstände D1 und D2 dieser Abhebewalzen im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass diese die Gleichung: D1 + d1 > D2 - d2 erfüllen. Es ist somit bevorzugt, dass die Summe aus D1 und d1 größer als die Differenz aus D2 und d2 ist.According to one embodiment of the invention, the at least two, in particular the two lifting rollers are arranged with the same distance D or essentially with the same distance D in relation to the depositing screen belt. The distance between the respective axis of rotation of the lifting roller and the depositing screen belt is then the same or essentially the same. However, it is also within the scope of the invention that the lifting rollers are arranged at a different distance D 1 and D 2 from the depositing screen belt, wherein the distance D 1 of the first lifting roller from the depositing screen belt is then preferably greater than the distance D 2 of the second lifting roller from the depositing screen belt. With regard to the diameters d 1 and d 2 of the two lifting rollers and the distances D 1 and D 2 of these lifting rollers, it is within the scope of the invention that these satisfy the equation: D 1 + d 1 > D 2 - d 2. It is therefore preferred that the sum of D 1 and d 1 is greater than the difference between D 2 and d 2 .
Es liegt im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die Vliesbahn über die Oberseite der zumindest einen Abhebewalze führbar ist. Wenn gemäß bevorzugter Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung zumindest zwei Abhebewalzen, insbesondere zwei Abhebewalzen vorgesehen sind, ist die Vliesbahn zweckmäßigerweise über die Unterseite der zweiten Abhebewalze und über die Oberseite der ersten Abhebewalze führbar. Es ist in diesem Zusammenhang bevorzugt, dass die zweite Abhebewalze in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes vor der ersten Abhebewalze angeordnet ist. Wenn die Vliesbahn gemäß bevorzugter Ausführungsform über die Unterseite der zweiten Abhebewalze und über die Oberseite der ersten Abhebewalze führbar ist, ist die erste Abhebewalze insbesondere für die Ablösung der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband verantwortlich und die zweite Abhebewalze ist dann empfohlenermaßen für das Niederhalten der Vliesbahn nahe des Ablagesiebbandes verantwortlich. Dieser Ausführungsform liegt die Erkenntnis zugrunde, dass durch die zweite Abhebewalze, die die Vliesbahn niederhält, der Ablösebereich nahe der zweiten Abhebewalze und insbesondere im Bereich der zweiten Abhebewalze angeordnet ist bzw. angeordnet werden kann. Auf diese Weise kann der Abstand A von der Nasenwalze weiter begrenzt werden, sodass er insbesondere maximal 25 %, vorzugsweise maximal 10 %, bevorzugt maximal 5 %, besonders bevorzugt maximal 2,5 % von dem Abstand C, ganz besonders bevorzugt maximal 1 %, beispielsweise 0,1 % von dem Abstand C beträgt. Der Verwendung von zwei Abhebewalzen, wobei eine erste Abhebewalze für den Ablösevorgang und eine zweite Abhebewalze zum Niederhalten vorgesehen ist, liegt weiterhin die Erkenntnis zugrunde, dass der Ablösebereich bzw. die Ablöselinie durch die zweite Abhebewalze sehr funktionssicher definiert werden kann. Hierbei hat insbesondere der Abstand D2 der zweiten Abhebewalze von dem Ablagesiebband einen maßgeblichen Einfluss auf den Abstand A des Ablösebereiches bzw. der Ablöselinie von der Nasenwalze. Insbesondere beeinflusst das Verhältnis des Abstandes D1 der ersten Abhebewalze zu dem Ablagesiebband zu dem Abstand D2 der zweiten Abhebewalze zu dem Ablagesiebband (D1/D2) vorzugsweise die Lage des Ablösebereiches bzw. der Ablöselinie derart, dass bei größerem Umschlingungswinkel der Vliesbahn um die zweite Abhebewalze der Ablösebereich bzw. die Ablöselinie umso näher zu einem Schnittpunkt einer senkrecht zum Ablagesiebband verlaufenden Geraden, die durch den Mittelpunkt der zweiten Abhebewalze verläuft, angeordnet ist. Es liegt im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass sich der Ablösebereich bzw. der Ablöselinie im Bereich der zweiten Abhebewalze und insbesondere unterhalb der zweiten Abhebewalze befindet.It is within the scope of the invention that the nonwoven web can be guided over the top of the at least one lifting roller. If, according to a preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention, at least two lifting rollers, in particular two lifting rollers, are provided, the nonwoven web can expediently be guided over the underside of the second lifting roller and over the top of the first lifting roller. In this context, it is preferred that the second lifting roller is arranged in front of the first lifting roller in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt. If, according to a preferred embodiment, the nonwoven web can be guided over the underside of the second lifting roller and over the top of the first lifting roller, the first lifting roller is responsible in particular for detaching the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt and the second lifting roller is then recommended for holding the nonwoven web down near the depositing screen belt. This The embodiment is based on the knowledge that the second lifting roller, which holds down the nonwoven web, means that the detachment area is or can be arranged close to the second lifting roller and in particular in the area of the second lifting roller. In this way, the distance A from the nose roller can be further limited so that it is in particular a maximum of 25%, preferably a maximum of 10%, preferably a maximum of 5%, particularly preferably a maximum of 2.5% of the distance C, very particularly preferably a maximum of 1%, for example 0.1% of the distance C. The use of two lifting rollers, with a first lifting roller being provided for the detachment process and a second lifting roller being provided for holding it down, is also based on the knowledge that the detachment area or the detachment line can be defined very reliably by the second lifting roller. In particular, the distance D 2 of the second lifting roller from the depositing screen belt has a significant influence on the distance A of the detachment area or the detachment line from the nose roller. In particular, the ratio of the distance D 1 of the first lifting roller to the depositing screen belt to the distance D 2 of the second lifting roller to the depositing screen belt (D 1 /D 2 ) preferably influences the position of the detachment area or the detachment line in such a way that, with a larger wrap angle of the nonwoven web around the second lifting roller, the detachment area or the detachment line is arranged closer to an intersection point of a straight line running perpendicular to the depositing screen belt and passing through the center of the second lifting roller. It is within the scope of the invention that the detachment area or the detachment line is located in the area of the second lifting roller and in particular below the second lifting roller.
Wenn gemäß bevorzugter Ausführungsform der Erfindung zumindest zwei Abhebewalzen, insbesondere zwei Abhebewalzen vorgesehen sind, liegt es im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass beide Abhebewalzen in Bezug auf das Ablagesiebband höhenverstellbar sind und dazu vorzugsweise in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar sind. Es ist möglich, dass beide Abhebewalzen von einer Grundposition in eine Abhebeposition bzw. in verschiedene Abhebepositionen und zurück verfahrbar sind. In der Grundposition ist empfohlenermaßen eine Reinigung der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung und/oder eine Einfädelung der Vliesbahn möglich. Wenn sich die Vorrichtung im Betriebszustand befindet, sind die Abhebewalzen zweckmäßigerweise in ihren Abhebepositionen angeordnet. Grundsätzlich kann die Vorrichtung auch mit den Abhebewalzen in der Grundposition betrieben werden, wenn eine Ablösung der Vliesbahn mittels der Abhebewalzen nicht erforderlich ist. Es empfiehlt sich, dass die erste Abhebewalze in ihrer Grundposition unterhalb des Ablagesiebbandes angeordnet ist und/oder dass die zweite Abhebewalze in ihrer Grundposition oberhalb des Ablagesiebbandes angeordnet ist. Grundsätzlich können in ihrer Grundposition aber auch beide Abhebewalzen oberhalb oder unterhalb des Ablagesiebbandes angeordnet sein.If, according to a preferred embodiment of the invention, at least two lifting rollers, in particular two lifting rollers, are provided, it is within the scope of the invention that both lifting rollers are arranged in relation to the depositing screen belt are height-adjustable and can preferably be moved in a vertical direction for this purpose. It is possible for both lifting rollers to be able to be moved from a basic position to a lifting position or to various lifting positions and back. In the basic position, it is recommended that the device according to the invention can be cleaned and/or the fleece web can be threaded. When the device is in operation, the lifting rollers are expediently arranged in their lifting positions. In principle, the device can also be operated with the lifting rollers in the basic position if it is not necessary to remove the fleece web using the lifting rollers. It is recommended that the first lifting roller is arranged in its basic position below the depositing screen belt and/or that the second lifting roller is arranged in its basic position above the depositing screen belt. In principle, however, both lifting rollers can also be arranged above or below the depositing screen belt in their basic position.
Es liegt grundsätzlich im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass das Ablagesiebband bzw. der Übergabetisch im Betriebszustand der Vorrichtung parallel bzw. im Wesentlichen parallel zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund bzw. zum Erdboden angeordnet ist. Nach besonders bevorzugter Ausführungsform der Erfindung ist die Nasenwalze in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. absenkbar. Empfohlenermaßen ist die Nasenwalze in vertikaler Richtung derart verfahrbar bzw. absenkbar, dass das Ablagesiebband zumindest zwischen der Umlenkungswalze und der Nasenwalze in Transportrichtung zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund hin orientiert ist und vorzugsweise ein Gefälle von größer als 0° bis 20°, insbesondere von 3° bis 20°, bevorzugt von 4° bis 18°, besonders bevorzugt von 5° bis 16° aufweist. Wenn das Ablagesiebband ein Gefälle in Richtung des Vorrichtungsuntergrundes aufweist, wird das Ablagesiebband zweckmäßigerweise durch die Umlenkungswalze aus seiner - zuvor insbesondere parallel zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund verlaufenden - Transportrichtung abgelenkt. Mit der Verfahrbarkeit der Nasenwalze in vertikaler Richtung ist insbesondere eine Verfahrbarkeit der Nasenwalze in Richtung des Vorrichtungsuntergrundes und zurück gemeint.It is fundamentally within the scope of the invention that the depositing sieve belt or the transfer table is arranged parallel or essentially parallel to the device base or the ground when the device is in operation. According to a particularly preferred embodiment of the invention, the nose roller can be moved or lowered in the vertical direction. It is recommended that the nose roller can be moved or lowered in the vertical direction in such a way that the depositing sieve belt is oriented towards the device base at least between the deflection roller and the nose roller in the transport direction and preferably has a gradient of greater than 0° to 20°, in particular from 3° to 20°, preferably from 4° to 18°, particularly preferably from 5° to 16°. If the depositing sieve belt has a gradient in the direction of the device base, the depositing sieve belt is expediently moved by the deflection roller from its - previously in particular parallel to the device base - transport direction. The ability of the nose roller to move in the vertical direction means in particular the ability of the nose roller to move in the direction of the device base and back.
Eine weitere bevorzugte Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Nasenwalze in horizontaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. teleskopierbar ist. Horizontale Richtung meint in diesem Zusammenhang insbesondere in Richtung parallel zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund. Durch die horizontale Verfahrbarkeit bzw. Teleskopierbarkeit der Nasenwalze kann die Nasenwalze somit beispielsweise näher an die Folgevorrichtung herangefahren werden. Weiterhin wird der Abstand C zwischen der Nasenwalze und der Umlenkungswalze zweckmäßigerweise beim Verfahren bzw. Teleskopieren vergrößert und beim Zurückfahren der Nasenwalze verkleinert. Gemäß besonders bevorzugter Ausführungsform ist die Nasenwalze in horizontaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. teleskopierbar und in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. absenkbar. Dieser Ausführungsform liegt die Erkenntnis zugrunde, dass verschiedenste Positionen der Nasenwalze eingestellt werden können. Beispielsweise kann ein zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund hin orientiertes Ablagesiebband realisiert werden und zugleich kann die Nasenwalze nah an die Folgevorrichtung herangefahren werden. Wenn die Nasenwalze bereits in vertikaler Richtung verfahren bzw. abgesenkt ist, meint horizontale Verfahrbarkeit bzw. Teleskopierbarkeit im Übrigen zweckmäßigerweise auch die Verfahrbarkeit bzw. Teleskopierbarkeit der Nasenwalze in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes, also entsprechend dem eingestellten Gefälle des Ablagesiebbandes bzw. des Übergabetisches zwischen der Umlenkungswalze und der Nasenwalze.A further preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention is characterized in that the nose roller can be moved or telescoped in a horizontal direction. In this context, horizontal direction means in particular in a direction parallel to the device base. Due to the horizontal moveability or telescoping of the nose roller, the nose roller can thus be moved closer to the following device, for example. Furthermore, the distance C between the nose roller and the deflection roller is expediently increased when moving or telescoping and reduced when the nose roller is retracted. According to a particularly preferred embodiment, the nose roller can be moved or telescoped in a horizontal direction and can be moved or lowered in a vertical direction. This embodiment is based on the knowledge that the nose roller can be set to a wide variety of positions. For example, a deposit screen belt oriented towards the device base can be realized and at the same time the nose roller can be moved close to the following device. If the nose roller has already been moved or lowered in the vertical direction, horizontal movability or telescoping also expediently means the movability or telescoping of the nose roller in the transport direction of the deposit screen belt, i.e. in accordance with the set gradient of the deposit screen belt or the transfer table between the deflection roller and the nose roller.
Wenn gemäß besonders bevorzugter Ausführungsform der Erfindung die Nasenwalze in horizontaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. teleskopierbar und in vertikaler Richtung absenkbar bzw. verfahrbar ist und zusätzlich die Abhebewalze bzw. die Abhebewalzen in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar sind, können verschiedene Positionen der Nasenwalze eingestellt werden und die Abhebewalzen können in ihren Abhebepositionen derart angeordnet werden, dass die vorstehend beschriebenen Abstände der Walzen untereinander und des Ablösebereiches A von der Nasenwalze realisiert werden. Diese Abstände und Positionen beziehen sich somit auf den Betriebszustand der Vorrichtung.If, according to a particularly preferred embodiment of the invention, the nose roller can be moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction and lowered or moved in the vertical direction and, in addition, the lifting roller or the lifting rollers can be moved in the vertical direction, different positions of the nose roller can be set and the lifting rollers can be arranged in their lifting positions in such a way that the above-described distances between the rollers and between the detachment area A and the nose roller are achieved. These distances and positions therefore relate to the operating state of the device.
Es liegt im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass der Abstand A des Ablösebereiches von der Nasenwalze (auch) durch die vertikale Verfahrbarkeit und/oder die horizontale Verfahrbarkeit bzw. Teleskopierbarkeit der Nasenwalze einstellbar ist.It is within the scope of the invention that the distance A of the detachment area from the nose roller can be adjusted (also) by the vertical mobility and/or the horizontal mobility or telescoping of the nose roller.
Gemäß einer Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung ist die Nasenwalze lediglich in horizontaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. teleskopierbar und nicht in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. absenkbar. In dieser Ausführungsform ist das Ablagesiebband parallel bzw. im Wesentlichen parallel zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund bzw. zum Erdboden angeordnet und die Nasenwalze ist in horizontaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. teleskopierbar. Gemäß einer weiteren Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung ist die Nasenwalze weder in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. absenkbar, noch in horizontaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. teleskopierbar, sodass gleichsam ein starres Ablagesiebband vorliegt, das parallel bzw. im Wesentlichen parallel zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund bzw. zum Erdboden angeordnet ist. Im Rahmen dieser vorstehend beschriebenen Ausführungsformen ist es möglich, dass die Vorrichtung keine Umlenkungswalze aufweist. Gemäß einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform der Erfindung ist der Abstand A zwischen dem Ablösebereich bzw. der Ablöselinie und der Nasenwalze kleiner als der Abstand E zwischen der Nasenwalze und dem Ablagebereich des Ablagesiebbandes. Der Abstand E wird im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere zwischen einer Projektion der Drehachse der Nasenwalze auf das Ablagesiebband und dem Ablagebereich, insbesondere der Mitte des Ablagebereiches, gemessen, wobei die Projektion der Drehachse der Nasenwalze senkrecht zu der Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes im Bereich des Abstandes E erfolgt. Es ist bevorzugt, dass der Abstand A maximal 50 %, vorzugsweise maximal 25 %, bevorzugt maximal 10 %, besonders bevorzugt maximal 5 %, ganz besonders bevorzugt maximal 2,5 %, beispielsweise 1 % von dem Abstand E beträgt. Der Abstand E bezieht sich zweckmäßigerweise auf einen Zustand der Vorrichtung, in dem das Ablagesiebband parallel bzw. im Wesentlichen parallel zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund bzw. zum Erdboden angeordnet ist und insbesondere auf eine Ausführungsform, bei der die Vorrichtung keine Umlenkungswalze aufweist und/oder bei der die Nasenwalze nicht in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. absenkbar ist und/oder nicht in horizontaler Richtung verfahrbar bzw. teleskopierbar ist.According to one embodiment of the device according to the invention, the nose roller can only be moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction and not moved or lowered in the vertical direction. In this embodiment, the depositing sieve belt is arranged parallel or substantially parallel to the device base or the ground and the nose roller can be moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction. According to another embodiment of the device according to the invention, the nose roller can neither be moved or lowered in the vertical direction nor moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction, so that there is a rigid depositing sieve belt that is arranged parallel or substantially parallel to the device base or the ground. Within the scope of these embodiments described above, it is possible for the device not to have a deflection roller. According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, the distance A between the detachment area or the detachment line and the nose roller is smaller than the distance E between the nose roller and the deposit area of the deposit screen belt. The distance E is measured in the context of the invention in particular between a projection of the axis of rotation of the nose roller onto the deposit screen belt and the deposit area, in particular the middle of the deposit area, wherein the projection of the axis of rotation of the nose roller is perpendicular to the longitudinal extent of the deposit screen belt in the region of the distance E. It is preferred that the distance A is a maximum of 50%, preferably a maximum of 25%, preferably a maximum of 10%, particularly preferably a maximum of 5%, very particularly preferably a maximum of 2.5%, for example 1% of the distance E. The distance E expediently refers to a state of the device in which the deposit screen belt is arranged parallel or essentially parallel to the device base or to the ground and in particular to an embodiment in which the device does not have a deflection roller and/or in which the nose roller cannot be moved or lowered in the vertical direction and/or cannot be moved or telescoped in the horizontal direction.
Eine Ausführungsform, der im Rahmen der Erfindung ganz besondere Bedeutung zukommt ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Folgevorrichtung eine Verfestigungsvorrichtung, insbesondere ein Heißluftbondierer, beispielsweise ein Ofen, und/oder ein Kalander ist und/oder dass die Folgevorrichtung ein Wickler ist. Es ist möglich, dass die Vorrichtung zumindest zwei Folgevorrichtungen, beispielsweise eine Verfestigungsvorrichtung, insbesondere einen Kalander und einen Wickler aufweist. Zweckmäßigerweise ist in Förderrichtung der Vliesbahn dann zunächst die Verfestigungsvorrichtung bzw. der Kalander angeordnet und hinter der Verfestigungsvorrichtung bzw. dem Kalander ist der Wickler vorgesehen. Die Verfestigungsvorrichtung bzw. der Kalander dient insbesondere zur Verfestigung bzw. Endverfestigung der Vliesbahn. Zweckmäßigerweise wird die Vliesbahn nach dem Ablösevorgang im Ablösebereich an die Verfestigungsvorrichtung bzw. den Kalander übergeben.An embodiment which is of particular importance within the scope of the invention is characterized in that the downstream device is a consolidation device, in particular a hot-air bonder, for example an oven, and/or a calender and/or that the downstream device is a winder. It is possible for the device to have at least two downstream devices, for example a consolidation device, in particular a calender and a winder. The consolidation device or calender is then expediently arranged first in the conveying direction of the nonwoven web and the winder is provided behind the consolidation device or calender. The consolidation device or calender serves in particular for the consolidation or final consolidation of the Nonwoven web. After the detachment process, the nonwoven web is conveniently transferred to the bonding device or calender in the detachment area.
Es liegt im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die Verfestigungsvorrichtung bzw. der Kalander zumindest eine Kalanderwalze, insbesondere zumindest ein Kalanderwalzenpaar aufweist, wobei zumindest eine Kalanderwalze vorzugsweise in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar ist. Die Vliesbahn wird insbesondere durch den Spalt bzw. Nip zwischen den zumindest zwei - bevorzugt übereinander angeordneten - Kalanderwalzen des zumindest einen Kalanderwalzenpaares geführt. Dabei kann die Vliesbahn entweder derart geführt werden, dass sie keine der Kalanderwalzen berührt, da der Kalander bzw. das zumindest eine Kalanderwalzenpaar offen ist oder derart geführt werden, dass sie lediglich eine der Kalanderwalzen berührt, um etwa die Eigenschaften der entsprechenden Seite der Vliesbahn zu beeinflussen oder derart geführt werden, dass sie beide Kalanderwalzen berührt, da der Kalander bzw. das zumindest eine Kalanderwalzenpaar geschlossen ist. Es liegt weiterhin im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die Vliesbahn beim Durchführen zwischen den beiden Kalanderwalzen - insbesondere durch Thermobondieren - verfestigt wird. Besonders bevorzugt sind für die Verfestigungsvorrichtung bzw. für den Kalander zumindest drei Kalanderwalzen vorgesehen, wobei vorzugsweise zumindest eine Kalanderwalze in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar ist und wobei die zumindest drei Kalanderwalzen besonders bevorzugt übereinander angeordnet sind. Durch diese Anordnung ergeben sich jeweils zwei Kalanderwalzenpaare aus der obersten Kalanderwalze und der mittleren Kalanderwalze und aus der untersten Kalanderwalze und der mittleren Kalanderwalze. Die Vliesbahn wird zur Verfestigung bzw. Endverfestigung zweckmäßigerweise durch einen der sich ergebenden Spalte geführt. Es liegt in diesem Zusammenhang im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die Position der Nasenwalze und/oder der Abhebewalzen in Abhängigkeit von dem Betriebsmodus des Kalanders einstellbar ist bzw. eingestellt wird. Die Verfestigungsvorrichtung bzw. der Kalander weist empfohlenermaßen zumindest einen Verfestigungsbereich auf, in dem die Vliesbahn verfestigt bzw. endverfestigt wird. Verfestigungsbereich meint in diesem Zusammenhang den Bereich, in dem die Vliesbahn durch die Wechselwirkung bzw. den Kontakt zu zumindest einer Kalanderwalze verfestigt bzw. endverfestigt oder anderweitig behandelt wird. Es empfiehlt sich, dass der Verfestigungsbereich der Verfestigungsvorrichtung bzw. des Kalanders oberhalb der Nasenwalze und/oder oberhalb des Ablagesiebbandes angeordnet ist. Die Anordnung des Verfestigungsbereiches bezieht sich dabei auf die Betriebsposition bzw. den Betriebszustand der Vorrichtung.It is within the scope of the invention that the consolidation device or the calender has at least one calender roller, in particular at least one pair of calender rollers, with at least one calender roller preferably being movable in the vertical direction. The nonwoven web is guided in particular through the gap or nip between the at least two - preferably arranged one above the other - calender rollers of the at least one pair of calender rollers. The nonwoven web can either be guided in such a way that it does not touch any of the calender rollers, since the calender or the at least one pair of calender rollers is open, or it can be guided in such a way that it only touches one of the calender rollers in order to influence the properties of the corresponding side of the nonwoven web, or it can be guided in such a way that it touches both calender rollers, since the calender or the at least one pair of calender rollers is closed. It is also within the scope of the invention that the nonwoven web is consolidated as it passes between the two calender rollers - in particular by thermal bonding. Particularly preferably, at least three calender rolls are provided for the consolidation device or for the calender, whereby preferably at least one calender roll is movable in the vertical direction and whereby the at least three calender rolls are particularly preferably arranged one above the other. This arrangement results in two calender roll pairs each consisting of the uppermost calender roll and the middle calender roll and of the lowermost calender roll and the middle calender roll. The nonwoven web is expediently guided through one of the resulting gaps for consolidation or final consolidation. In this context, it is within the scope of the invention that the position of the nose roll and/or the lifting rolls is dependent on the The operating mode of the calender is adjustable or is set. The consolidation device or the calender is recommended to have at least one consolidation area in which the nonwoven web is consolidated or finally consolidated. In this context, consolidation area means the area in which the nonwoven web is consolidated or finally consolidated or otherwise treated by interaction or contact with at least one calender roller. It is recommended that the consolidation area of the consolidation device or the calender is arranged above the nose roller and/or above the deposit screen belt. The arrangement of the consolidation area relates to the operating position or the operating state of the device.
Es liegt im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass der Kalander ein Verfestigungskalander und/oder ein Beschichtungskalander und/oder ein Kalibrierkalander und/oder ein Laminierkalander und/oder ein Aktivierungskalander ist.It is within the scope of the invention that the calender is a consolidation calender and/or a coating calender and/or a calibration calender and/or a laminating calender and/or an activation calender.
Es empfiehlt sich, dass das Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband nach einer Vorverfestigung der Vliesbahn erfolgt. Die Vliesbahn wird somit empfohlenermaßen vor der Ablösung von dem Ablagesiebband vorverfestigt. Dazu weist die Vorrichtung zweckmäßigerweise eine Vorverfestigungsvorrichtung auf, die bevorzugt in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes vor dem Ablösebereich angeordnet ist. Es ist möglich, dass das Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband vor einer Endverfestigung der Vliesbahn erfolgt. Grundsätzlich ist es aber auch möglich, dass die Vorrichtung derart eingerichtet ist, dass die Endverfestigung der Vliesbahn vor dem Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband erfolgt. Eine solche Ausführungsform, bei der die Endverfestigung der Vliesbahn vor dem Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband erfolgt, ist besonders bevorzugt, wenn die Vliesbahn im Anschluss unmittelbar einem Beschichtungskalander und/oder einem Kalibrierkalander und/oder einem Laminierkalander und/oder einem Aktivierungskalander und/oder einem Heißluftbondierer, beispielsweise einem Ofen, zugeführt wird.It is recommended that the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt after a pre-consolidation of the nonwoven web. The nonwoven web is therefore recommended to be pre-consolidated before it is detached from the depositing screen belt. For this purpose, the device expediently has a pre-consolidation device, which is preferably arranged in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt in front of the detachment area. It is possible that the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt before the nonwoven web is finally consolidated. In principle, however, it is also possible for the device to be set up in such a way that the nonwoven web is finally consolidated before the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt. Such an embodiment, in which the nonwoven web is finally consolidated before the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt, is particularly preferred if the nonwoven web is immediately subjected to a coating calender and/or a calibration calender and/or a laminating calender and/or an activation calender and/or a hot air bonder, for example an oven.
Es liegt fernerhin im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die zumindest eine Abhebewalze und/oder die zweite Abhebewalze einen Abstand U von der Nasenwalze aufweist, der zumindest 50 % des Durchmessers der jeweiligen Abhebewalze beträgt. Der Abstand U wird zweckmäßigerweise zwischen den Projektionen der Drehachsen der Abhebewalze und der Nasenwalze auf das Ablagesiebband gemessen, wobei die Projektionen der Drehachsen senkrecht zur Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes bzw. zu der imaginären Verlängerung dieser Längserstreckung im Bereich des Abstandes U erfolgen. Wenn gemäß bevorzugter Ausführungsform zumindest zwei, insbesondere zwei Abhebewalzen vorgesehen sind, weisen bevorzugt beide Abhebewalzen einen Abstand U1 und U2 von der Nasenwalze auf, der zumindest 50 % des Durchmessers der jeweiligen Abhebewalze beträgt.It is further within the scope of the invention that the at least one lifting roller and/or the second lifting roller has a distance U from the nose roller that is at least 50% of the diameter of the respective lifting roller. The distance U is expediently measured between the projections of the axes of rotation of the lifting roller and the nose roller onto the depositing screen belt, wherein the projections of the axes of rotation are perpendicular to the longitudinal extension of the depositing screen belt or to the imaginary extension of this longitudinal extension in the region of the distance U. If, according to a preferred embodiment, at least two, in particular two lifting rollers are provided, both lifting rollers preferably have a distance U 1 and U 2 from the nose roller that is at least 50% of the diameter of the respective lifting roller.
Zur Lösung des technischen Problems lehrt die Erfindung weiterhin ein Verfahren zum Transport und zur Behandlung einer Vliesbahn aus Endlosfilamenten, insbesondere mit einer vorstehend beschriebenen Vorrichtung, wobei die Vliesbahn über ein in einem Umlenkungsbereich durch eine Nasenwalze aus seiner Transportrichtung ablenkbares Ablagesiebband geführt wird, wobei die Vliesbahn an eine nachgeschaltete Folgevorrichtung übergeben wird, wobei die Vliesbahn vor dem Umlenkungsbereich von dem Ablagesiebband abgelöst wird. Das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Vliesbahn zur Ablösung von dem Ablagesiebband über zumindest eine Abhebewalze geführt wird, die oberhalb des Ablagesiebbandes angeordnet ist, wobei die zumindest eine Abhebewalze in Bezug auf das Ablagesiebband höhenverstellbar ist und dazu vorzugsweise in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar ist, wobei die Vliesbahn mittels der zumindest einen Abhebewalze in einem Ablösebereich von dem Ablagesiebband abgelöst wird, der mit einem Abstand A zu der Nasenwalze angeordnet ist und wobei die Vliesbahn anschließend der Folgevorrichtung zugeführt wird.To solve the technical problem, the invention further teaches a method for transporting and treating a nonwoven web made of continuous filaments, in particular with a device described above, wherein the nonwoven web is guided over a depositing screen belt that can be deflected from its transport direction in a deflection area by a nose roller, wherein the nonwoven web is transferred to a downstream device, wherein the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt before the deflection area. The method according to the invention is characterized in that the nonwoven web is guided over at least one lifting roller for detachment from the depositing screen belt, which is arranged above the depositing screen belt, wherein the at least one lifting roller is height-adjustable in relation to the depositing screen belt and is preferably movable in the vertical direction for this purpose, wherein the nonwoven web is detached from the depositing screen belt by means of the at least one lifting roller in a detachment region which is arranged at a distance A from the nose roller and wherein the nonwoven web is subsequently fed to the subsequent device.
Gemäß bevorzugter Ausführungsform wird die Vliesbahn in der Folgevorrichtung bzw. in den Folgevorrichtungen anschließend gewickelt und/oder beschichtet und/oder kalibriert und/oder aktiviert und/oder verfestigt.According to a preferred embodiment, the nonwoven web is subsequently wound and/or coated and/or calibrated and/or activated and/or consolidated in the subsequent device(s).
Der Erfindung liegt die Erkenntnis zugrunde, dass mit der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung ein funktionssicheres und einfaches Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband möglich ist und dass insbesondere der Kraftaufwand für das Ablösen der Vliesbahn im Vergleich zu bekannten Maßnahmen reduziert werden kann. Dies wird durch die Ablösung der Vliesbahn mittels zumindest einer Abhebewalze in einem Ablösebereich, der in Transportrichtung des Ablagesiebbandes vor dem Umlenkungsbereich angeordnet ist, erreicht. Das Ablösen der Vliesbahn kann durch die erfindungsgemäßen Maßnahmen insbesondere ohne Beschädigung der Vliesbahn beispielsweise durch Herausreißen von Filamenten erfolgen, sodass auch keine unerwünschten Filamentreste an dem Ablagesiebband verbleiben. Zu betonen ist weiterhin, dass die erfindungsgemäßen Maßnahmen relativ einfach und ohne nennenswerten Aufwand bzw. Kostenaufwand realisiert werden können. Wenn gemäß bevorzugter Ausführungsform der Erfindung zumindest zwei, insbesondere zwei Abhebewalzen vorgesehen sind, lässt sich der Ablösebereich bzw. die Ablöselinie und somit der Abstand A von der Nasenwalze sehr präzise einstellen. Durch die bevorzugte vertikale Verfahrbarkeit der Abhebewalze bzw. der Abhebewalzen und/oder durch die horizontale Verfahrbarkeit bzw. Teleskopierbarkeit der Nasenwalze und/oder die vertikale Verfahrbarkeit der Nasenwalze können verschiedene Betriebszustände der Vorrichtung eingestellt werden und insbesondere kann der Abstand der Nasenwalze zu einer Folgevorrichtung, beispielsweise zu einem Kalander, eingestellt und/oder ein Gefälle des Ablagesiebbandes realisiert werden, wobei nichtsdestoweniger die Abhebewalze bzw. die Abhebewalzen so zu dem Ablagesiebband angeordnet werden können, dass das Ablösen der Vliesbahn in einem Ablösebereich bzw. an einer Ablöselinie vor dem Umlenkungsbereich erfolgt bzw. erfolgen kann. Die erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung bzw. das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren ist somit sehr flexibel einsetzbar, wobei in den verschiedenen Betriebspositionen jeweils ein einfaches und funktionssicheres Ablösen der Vliesbahn von dem Ablagesiebband möglich ist, für das ein verhältnismäßig geringer Kraftaufwand erforderlich ist und das insbesondere ohne Beschädigungen der Vliesbahn erfolgen kann.The invention is based on the finding that the device according to the invention enables the nonwoven web to be detached from the depositing screen belt in a functionally reliable and simple manner and that, in particular, the amount of force required to detach the nonwoven web can be reduced compared to known measures. This is achieved by detaching the nonwoven web by means of at least one lifting roller in a detachment area that is arranged in the transport direction of the depositing screen belt in front of the deflection area. The nonwoven web can be detached by the measures according to the invention in particular without damaging the nonwoven web, for example by tearing out filaments, so that no unwanted filament residues remain on the depositing screen belt. It should also be emphasized that the measures according to the invention can be implemented relatively easily and without any significant effort or cost. If, according to a preferred embodiment of the invention, at least two, in particular two lifting rollers are provided, the detachment area or the detachment line and thus the distance A from the nose roller can be set very precisely. Due to the preferred vertical mobility of the lifting roller(s) and/or the horizontal mobility or telescopicity of the nose roller and/or the vertical mobility of the nose roller, different operating states of the device can be set and in particular the distance of the nose roller to a subsequent device, for example to a calender, can be adjusted and/or a gradient of the depositing screen belt can be realized, whereby the lifting roller or the lifting rollers can nevertheless be arranged in relation to the depositing screen belt such that the detachment of the nonwoven web takes place or can take place in a detachment area or on a detachment line in front of the deflection area. The device or the method according to the invention can therefore be used very flexibly, whereby in the various operating positions a simple and functionally reliable detachment of the nonwoven web from the depositing screen belt is possible, for which a relatively small amount of force is required and which can take place in particular without damaging the nonwoven web.
Nachfolgend wird die Erfindung anhand einer lediglich ein Ausführungsbeispiel darstellenden Zeichnung näher erläutert. Es zeigen in schematischer Darstellung:
- Fig. 1
- einen Vertikalschnitt durch eine erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung mit zwei Abhebewalzen in ihrem Grundzustand,
- Fig. 2
- die Vorrichtung nach
Fig. 1 in einem ersten Betriebszustand bzw. in einer ersten Betriebsposition, - Fig. 3
- die Vorrichtung nach
Fig. 1 in einem zweiten Betriebszustand bzw. in einer zweiten Betriebsposition, - Fig. 4
- eine vergrößerte Darstellung der Nasenwalze und der Abhebewalzen der Vorrichtung im Zustand gemäß
Fig. 2 .
- Fig.1
- a vertical section through a device according to the invention with two lifting rollers in its basic state,
- Fig.2
- the device according to
Fig.1 in a first operating state or in a first operating position, - Fig.3
- the device according to
Fig.1 in a second operating state or in a second operating position, - Fig.4
- an enlarged view of the nose roller and the lifting rollers of the device in the state according to
Fig. 2 .
Die Figuren zeigen eine Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Vliesstoffen aus Endlosfilamenten, wobei eine als Spinnerette ausgebildete Spinneinrichtung 1 zum Erspinnen der Filamente und eine Kühleinrichtung 2 zum Kühlen der Filamente vorhanden ist. Weiterhin ist ein Ablagesiebband 3 vorgesehen, auf dem die Filamente in einem Ablagebereich 4 zur Vliesbahn 5 ablegbar sind. Zweckmäßigerweise und im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß den Figuren handelt es sich bei der Vorrichtung um eine Spunbond-Vorrichtung, wobei eine Verstreckeinrichtung 17 zum Verstrecken der Filamente vorgesehen ist. Bei den Endlosfilamenten kann es sich zweckmäßigerweise um Monokomponentenfilamente aus zumindest einem thermoplastischen Kunststoff handeln. Die Kühleinrichtung 2 weist empfohlenermaßen und im Ausführungsbeispiel eine Kühlkammer 18 auf, durch die die Endlosfilamente zur Kühlung geführt werden. Bevorzugt und im Ausführungsbeispiel sind an zwei gegenüberliegenden Seiten der Kühlkammer 18 zwei übereinander angeordnete Luftzufuhrkabinen 19, 20 angeordnet, aus denen bevorzugt Luft unterschiedlicher Temperatur in die Kühlkammer 18 eingeführt wird. Weiterhin bevorzugt und im Ausführungsbeispiel ist zwischen der Spinneinrichtung 1 und der Kühleinrichtung 2 eine Monomer-Absaugungseinrichtung 21 vorgesehen, mit der störende Gase, die beim Spinnprozess auftreten aus der Vorrichtung bzw. der Spunbond-Vorrichtung entfernt werden können. Bei den störenden Gasen kann es sich etwa um Monomere, Oligomere und dergleichen Substanzen handeln.The figures show a device for producing nonwovens from continuous filaments, with a spinning device 1 designed as a spinneret for spinning the filaments and a
Zweckmäßigerweise und im Ausführungsbeispiel ist der Kühleinrichtung 2 in Filamentströmungsrichtung FS die Verstreckeinrichtung 17 zum Verstrecken der Filamente nachgeschaltet. Gemäß sehr empfohlener Ausführungsform und im Ausführungsbeispiel ist das Aggregat aus der Kühleinrichtung 2 und der Verstreckeinrichtung 17 als geschlossenes Aggregat ausgebildet, bei dem außer der Zufuhr der Kühlluft in der Kühleinrichtung 2 keine weitere Luftzufuhr in das geschlossene Aggregat stattfindet.Appropriately and in the exemplary embodiment, the stretching
Im Rahmen der Erfindung und im Ausführungsbeispiel ist zwischen der Verstreckeinrichtung 17 und dem Ablagesiebband 3 ein Diffusor 23 angeordnet, durch den die Endlosfilamente geführt werden. Gemäß einer empfohlenen Ausführungsform und im Ausführungsbeispiel sind zwischen der Verstreckeinrichtung 17 und dem Diffusor 23 Sekundärluft-Eintrittsspalte 24 für die Einführung von Sekundärluft in den Diffusor 23 vorgesehen. Nach dem Durchlaufen des Diffusors 23 werden die Endlosfilamente auf dem Ablagesiebband 3 in dem Ablagebereich 4 zur Vliesbahn 5 abgelegt und dann zweckmäßigerweise mit dem Ablagesiebband 3 in Transportrichtung T des Ablagesiebbandes 3 abtransportiert. Empfohlenermaßen und im Ausführungsbeispiel ist unter dem Ablagesiebband 3 eine Absaugungseinrichtung 22 zum Absaugen von Luft bzw. Prozessluft durch das Ablagesiebband 3 vorgesehen.Within the scope of the invention and in the exemplary embodiment, a
Erfindungsgemäß ist das Ablagesiebband 3 in einem Umlenkungsbereich 6 durch zumindest eine Nasenwalze 7 aus seiner Transportrichtung T ablenkbar. Die Vliesbahn 5 ist im Betriebszustand der Vorrichtung (
Zur Ablösung der Vliesbahn 5 von dem Ablagesiebband 3 sind bevorzugt und im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß den Figuren zwei Abhebewalzen 9, 14 vorhanden. Empfohlenermaßen und im Ausführungsbeispiel sind die Abhebewalzen 9, 14 in Bezug auf das Ablagesiebband 3 höhenverstellbar ausgebildet und vorzugsweise und im Ausführungsbeispiel in vertikaler Richtung verfahrbar. Dies ist insbesondere in der
Empfohlenermaßen und im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß den Figuren ist im Betriebszustand der Vorrichtung die erste Abhebewalze 9 in Transportrichtung T des Ablagesiebbandes 3 hinter der Nasenwalze 7 angeordnet (
Gemäß besonders bevorzugter Ausführungsform der Erfindung und im Ausführungsbeispiel ist der Abstand A kleiner als der Abstand C zwischen der Nasenwalze 7 und einer Umlenkungswalze 15. Die Umlenkungswalze 15 ist zweckmäßigerweise eine zusätzlich zu der Nasenwalze 7 zum Transport des Ablagesiebbandes 3 eingerichtete Walze, die in Transportrichtung T des Ablagesiebbandes 3 vor der Nasenwalze 7 angeordnet ist. Die Umlenkungswalze 15 ist empfohlenermaßen und im Ausführungsbeispiel zwischen dem Ablagebereich 4 und dem Umlenkungsbereich 6 vorgesehen. An der Umlenkungswalze 15 kann das Ablagesiebband 3 entweder ohne Ablenkung aus seiner Transportrichtung entlang geführt werden (
Abstand C zwischen der Nasenwalze 7 und der Umlenkungswalze 15 meint im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere den Abstand der Drehachsen der Nasenwalze 7 und der Umlenkungswalze 15, der zweckmäßigerweise zwischen den Projektionen der Drehachsen auf das Ablagesiebband 3 gemessen wird, wobei die Projektionen der Drehachsen senkrecht zur Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes 3 im Bereich des Abstandes C erfolgen. Es empfiehlt sich, dass der Abstand A maximal 30 %, bevorzugt maximal 20 % von dem Abstand C beträgt. Im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß der
Empfohlenermaßen und im Ausführungsbeispiel sind die Abhebewalzen 9, 14 als rotierende Abhebewalzen ausgebildet. Der Durchmesser d der Abhebewalzen 9, 14 beträgt bevorzugt 25 bis 400 mm, besonders bevorzugt 100 bis 250 mm. Im Rahmen der Erfindung und im Ausführungsbeispiel weisen die erste Abhebewalze 9 und die zweite Abhebewalze 14 den gleichen Durchmesser d bzw. im Wesentlichen den gleichen Durchmesser d auf. Besonders bevorzugt und im Ausführungsbeispiel (insbesondere
Zweckmäßigerweise und im Ausführungsbeispiel sind die Abhebewalzen 9, 14 in Bezug auf das Ablagesiebband 3 mit einem Abstand D angeordnet. Abstand D meint in diesem Zusammenhang insbesondere den Abstand der Drehachse der jeweiligen Abhebewalze 9, 14 zu dem Ablagesiebband 3. Der Abstand D zu dem Ablagesiebband 3 wird dabei zweckmäßigerweise senkrecht zu der Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes 3 im Bereich der Abhebewalzen 9, 14 bzw. zu der imaginären Verlängerung dieser Längserstreckung gemessen bzw. bestimmt. Im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß den Figuren (insbesondere
Weiterhin bevorzugt und im Ausführungsbeispiel (insbesondere
Gemäß sehr bevorzugter Ausführungsform und im Ausführungsbeispiel ist die Nasenwalze 7 in vertikaler Richtung derart verfahrbar bzw. absenkbar, dass das Ablagesiebband 3 zwischen der Umlenkungswalze 15 und der Nasenwalze 7 in Transportrichtung T zum Vorrichtungsuntergrund 11 hin orientiert ist. Zweckmäßigerweise und im Ausführungsbeispiel weist das Ablagesiebband in diesem Bereich ein Gefälle von 3° bis 20° auf. Im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß der
Im Rahmen der Erfindung und im Ausführungsbeispiel ist eine Folgevorrichtung 8 als Kalander 16 ausgestaltet. Im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß der
Weiter bevorzugt und im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß den Figuren erfolgt das Ablösen der Vliesbahn 5 von dem Ablagesiebband 3 nach einer Vorverfestigung der Vliesbahn 5. Die Vliesbahn wird somit empfohlenermaßen und im Ausführungsbeispiel vor der Ablösung von dem Ablagesiebband 3 mittels einer Vorverfestigungsvorrichtung 25 vorverfestigt. Dies ist insbesondere in der
Es liegt fernerhin im Rahmen der Erfindung, dass die erste Abhebewalze 9 und/oder die zweite Abhebewalze 14 einen Abstand U von der Nasenwalze 7 aufweist, der zumindest 50 % des Durchmessers der jeweiligen Abhebewalze 9, 14 beträgt. Abstand U meint in diesem Zusammenhang insbesondere den Abstand der Drehachse der zumindest einen Abhebewalze 9, 14 von der Drehachse der Nasenwalze 7, wobei der Abstand U zweckmäßigerweise zwischen den Projektionen der Drehachsen der Abhebewalze 9, 14 und der Nasenwalze 7 auf das Ablagesiebband 3 gemessen wird, wobei die Projektionen der Drehachsen senkrecht zur Längserstreckung des Ablagesiebbandes 3 bzw. zu der imaginären Verlängerung dieser Längserstreckung im Bereich des Abstandes U erfolgen. Im Ausführungsbeispiel gemäß den Figuren weisen beide Abhebewalzen 9, 14 jeweils einen Mittelpunktsabstand U1 und U2 von der Nasenwalze 7 auf, der zumindest 50 % des Durchmessers d der jeweiligen Abhebewalze 9, 14 beträgt (
Claims (17)
- Apparatus for making nonwoven from continuous filaments, the apparatus comprising a spinner (1) for spinning the filaments, a cooler (2) for cooling the filaments, a deposition mesh belt (3) on which the filaments can be deposited in a deposition area (4) to form a nonwoven web (5), at least one nose roller (7) over which the deposition mesh belt (3) is deflected in a deflection zone (6) from its travel direction, and at least one downstream treatment device (8) for the nonwoven web (5) downstream of the deposition mesh belt (3) in the travel direction of the nonwoven web (5), the nonwoven web (5) being separable from the deposition mesh belt (3) upstream of the deflection zone (6) and then transferable to the downstream treatment device (8), wherein at least one lift roller (9) is provided for separating the nonwoven web (5) from the deposition mesh belt (3), wherein the lift roller (9) is set or positionable above the deposition mesh belt (3), wherein the nonwoven web (5) is separable from the deposition mesh belt (3) with the at least one lift roller (9) at a separation location (10) at a spacing A from the nose roller (7), characterized in, that
the at least one lift roller (9) is adjustable with respect to height relative to the deposition mesh belt (3) and, for this purpose, preferably is vertically movable. - The apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the at least one lift roller (9) is set or positionable relative to the nose roller (7) such that the separation location (10) is spaced or orientable in the travel direction of the deposition mesh belt (3) upstream of the deflection zone (6), the at least one lift roller (9) preferably being upstream or downstream of the nose roller (7) in the travel direction of the deposition mesh belt (3).
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 or 2, wherein the spacing A is smaller than the spacing C between the nose roller (7) and a deflection roller (15) and in particular is a maximum of 50%, preferably a maximum of 25%, preferably a maximum of 10%, especially preferably a maximum of 5%, very particularly preferably a maximum of 2.5%, for example 1% of the spacing C.
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the at least one lift roller (9) is rotatable and in particular driven.
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 4, wherein the at least one lift roller (9) is set or positionable at a spacing D from the deposition mesh belt (3) and this spacing D is greater than 50% of the diameter d of the lift roller (9) and preferably at least 55%, particularly preferably at least 60% of the diameter d of the lift roller (9) .
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 5, wherein the diameter d of the at least one lift roller (9) is 10 to 500 mm, preferably 25 to 400 mm, preferably 50 to 300 mm, and especially preferably 100 to 250 mm.
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 6, wherein at least two, in particular two, lift rollers (9, 14) are provided of which a second lift roller (14) is preferably set or positionable in the travel direction of the deposition mesh belt (3) upstream of the nose roller (7) and a first lift roller (9) is preferably set or positionable in the travel direction of the deposition mesh belt (3) between the second lift roller (14) and the nose roller (7) or downstream of the nose roller (7).
- The apparatus according to claim 7, wherein the first lift roller (9) and the second lift roller (14) have the same or substantially the same diameter d and preferably the spacing m between the axes of rotation of the two lift rollers (9, 14) is at least 105%, preferably at least 110%, especially preferably at least 115% of the diameter d of the lift rollers (9, 14).
- The apparatus according to one of claims 7 or 8, wherein the nonwoven web (5) can be guided under the second lift roller (14) and over the first lift roller (9).
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 9, wherein the nose roller (7) can be moved or lowered vertically to angle the deposition mesh belt (3) at least between the deflection roller (15) and the nose roller (7) in the travel direction toward the device base (11) and preferably at a downward slope from 3° to 20°, preferably from 4° to 18°, particularly preferably from 5° to 16°.
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 11, wherein the nose roller (7) can be moved or telescopically moved horizontally.
- The apparatus according to one of claims 10 or 11, wherein the spacing A of the separation location (10) from the nose roller (7) is adjusted by the vertical movability and/or the horizontal movability or telescoping of the nose roller (7).
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 12, wherein the downstream treatment device (8) is a consolidator, in particular a hot-air bonder, for example an oven, and/or a calender (16), and/or the downstream treatment device (8) is a winder.
- The apparatus of claim 13, wherein the consolidator or the calender (16) has at least one calender roll (12), in particular at least one pair of calender rolls, and at least one calender roll (12) preferably is movable vertically.
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 14, wherein separation of the nonwoven web (5) from the deposition mesh belt takes place (3) after preconsolidation of the nonwoven web (5).
- The apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 15, wherein the at least one lift roller (9) and/or the second lift roller (14) has a spacing U from the nose roller (7) that is at least 50% of the diameter d of the respective lift roller (9, 14).
- A method of transporting and treating a nonwoven web made of continuous filaments with an apparatus according to one of claims 1 to 16, wherein the nonwoven web (5) is guided over a deposition mesh belt (3) deflectable in a deflection zone (6) from its travel direction by a nose roller (7), the nonwoven web (5) passing to a downstream treatment device (8), the nonwoven web (5) being separated from the deposition mesh belt (3) upstream of the deflection zone (6), characterized in, that
at least one lift roller (9) is arranged above the deposition mesh belt (3) and over which the nonwoven web (5) is guided for separation of the nonwoven web (5) from the deposition mesh belt (3), the at least one lift roller (9) is adjustable with respect to height relative to the deposition mesh belt (3) and, for this purpose, preferably is vertically movable, the lift roller (9) separating the nonwoven web (5) in a separation location (10) from the deposition mesh belt (3), the separation location (10) being at a spacing A from the nose roller (7) and the nonwoven web (5) is then fed to the downstream treatment device (8).
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL20208671.6T PL4001488T3 (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2020-11-19 | Device for the manufacture of non-woven fabrics from continuous filaments |
| EP20208671.6A EP4001488B1 (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2020-11-19 | Device for the manufacture of non-woven fabrics from continuous filaments |
| ES20208671T ES2980459T3 (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2020-11-19 | Device for manufacturing nonwoven fabrics from continuous filaments |
| JP2021175253A JP2022081417A (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2021-10-27 | Apparatus for producing nonwoven fabric comprising continuous filament |
| KR1020210159418A KR20220068941A (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2021-11-18 | Method of making nonwoven from continuous filament |
| US17/530,509 US11598035B2 (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2021-11-19 | Method and apparatus for making a nonwoven from continuous filaments |
| CN202111374384.XA CN114541044A (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2021-11-19 | Apparatus for making nonwoven articles from continuous filaments |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20208671.6A EP4001488B1 (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2020-11-19 | Device for the manufacture of non-woven fabrics from continuous filaments |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP4001488A1 EP4001488A1 (en) | 2022-05-25 |
| EP4001488B1 true EP4001488B1 (en) | 2024-04-24 |
| EP4001488C0 EP4001488C0 (en) | 2024-04-24 |
Family
ID=73497630
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20208671.6A Active EP4001488B1 (en) | 2020-11-19 | 2020-11-19 | Device for the manufacture of non-woven fabrics from continuous filaments |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP4001488B1 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2980459T3 (en) |
| PL (1) | PL4001488T3 (en) |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5667749A (en) * | 1995-08-02 | 1997-09-16 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Method for the production of fibers and materials having enhanced characteristics |
| WO2000046434A1 (en) * | 1999-02-02 | 2000-08-10 | Hills, Inc. | Spunbond web formation |
| FR2861751B1 (en) * | 2003-10-31 | 2006-01-06 | Rieter Perfojet | MACHINE FOR THE PRODUCTION OF MULTIPLE QUALITY NUTS. |
| DE102017129300A1 (en) * | 2017-12-08 | 2019-06-13 | Trützschler GmbH & Co Kommanditgesellschaft | Plant and method for producing a spunbonded nonwoven |
-
2020
- 2020-11-19 EP EP20208671.6A patent/EP4001488B1/en active Active
- 2020-11-19 ES ES20208671T patent/ES2980459T3/en active Active
- 2020-11-19 PL PL20208671.6T patent/PL4001488T3/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP4001488A1 (en) | 2022-05-25 |
| EP4001488C0 (en) | 2024-04-24 |
| ES2980459T3 (en) | 2024-10-01 |
| PL4001488T3 (en) | 2024-08-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3239378B1 (en) | Device and method for the manufacture of material from continuous filaments | |
| DE60019956T2 (en) | IMPROVED NONWOVEN FABRIC WITH HIGH STRENGTH IN THE CROSS-REFERENCE AND METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF | |
| EP3088585B1 (en) | Method and device for manufacturing a spunbonding fabric made of filaments and spun fabric | |
| DE60309653T2 (en) | DEVICE FOR PRODUCING THERMOPLASTIC NONWOVENS AND COMPOUNDS | |
| EP1967628B1 (en) | Method and device for producing spinning fleece | |
| DE3728002C2 (en) | ||
| EP3771763B1 (en) | Device and method for producing nonwoven fabric from crimped fibers | |
| DE69409648T3 (en) | Dispositif pour detacher et transporter à grande vitesse un voile fibreux en sortie de carde | |
| WO2003004229A1 (en) | Non-woven fabric perforating device and method therefor | |
| EP2128320B1 (en) | Method and device for the manufacture of nonwoven material from filaments | |
| WO2017129313A1 (en) | Device and method for producing spun nonwoven fabrics made of continuous filaments | |
| DE60036994T2 (en) | Nonwoven fabric of polypropylene fiber and process for its production | |
| DE2525819C2 (en) | Device for producing a filament fleece | |
| DE60014900T2 (en) | DEVICE FOR MANUFACTURING A FIBER TRAY AND METHOD FOR CARRYING OUT THIS DEVICE | |
| EP0598463A1 (en) | Process and apparatus for conveying and for laying continuos filaments bundle with air force | |
| DE102008008549A1 (en) | Apparatus for producing and solidifying a pure spunbonded nonwoven | |
| EP3495543B1 (en) | System and method for creating a spunbonded fabric | |
| EP3771764B1 (en) | Method and device for producing a nonwoven fabric | |
| EP4001488B1 (en) | Device for the manufacture of non-woven fabrics from continuous filaments | |
| EP4067548B1 (en) | System for consolidating layers comprising fibres to a nonwoven web | |
| EP3199671B1 (en) | Device for manufacturing non-woven material | |
| EP0480550B1 (en) | Process and apparatus for producing spunbonded nonwoven | |
| DE102020130593A1 (en) | Device for producing non-woven fabrics from continuous filaments | |
| DE2644961A1 (en) | Felting thermal bonding process - uses only air pressure loss at the back cloth to prevent shrinkage | |
| DE19956368A1 (en) | Melt blown thermoplastic plastic fiber fleece production involves blowing fiber flow leaving nozzle to form angle with nozzle axis |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20211006 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R079 Ref document number: 502020007741 Country of ref document: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: D04H0003020000 Ipc: B65H0027000000 Ref country code: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: D04H0003020000 Ipc: B65H0027000000 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: D04H 3/16 20060101ALI20231218BHEP Ipc: D04H 3/14 20120101ALI20231218BHEP Ipc: D01D 5/088 20060101ALI20231218BHEP Ipc: D04H 3/02 20060101ALI20231218BHEP Ipc: B65H 27/00 20060101AFI20231218BHEP |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20240111 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502020007741 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| U01 | Request for unitary effect filed |
Effective date: 20240510 |
|
| U07 | Unitary effect registered |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG DE DK EE FI FR IT LT LU LV MT NL PT SE SI Effective date: 20240523 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2980459 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20241001 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240824 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240424 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240725 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240724 |