EP2811099A1 - Exterior door or window with exposed wood and method for the production thereof - Google Patents
Exterior door or window with exposed wood and method for the production thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2811099A1 EP2811099A1 EP14163937.7A EP14163937A EP2811099A1 EP 2811099 A1 EP2811099 A1 EP 2811099A1 EP 14163937 A EP14163937 A EP 14163937A EP 2811099 A1 EP2811099 A1 EP 2811099A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- planks
- support cell
- window
- exterior door
- fixed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E06—DOORS, WINDOWS, SHUTTERS, OR ROLLER BLINDS IN GENERAL; LADDERS
- E06B—FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES
- E06B3/00—Window sashes, door leaves, or like elements for closing wall or like openings; Layout of fixed or moving closures, e.g. windows in wall or like openings; Features of rigidly-mounted outer frames relating to the mounting of wing frames
- E06B3/30—Coverings, e.g. protecting against weather, for decorative purposes
- E06B3/301—Coverings, e.g. protecting against weather, for decorative purposes consisting of prefabricated profiled members or glass
- E06B3/302—Covering wooden frames with metal or plastic profiled members
Definitions
- the present invention refers to an exterior door or window with exposed wood and to a method for the production thereof, according to the preamble of the respective independent claims.
- the present door or window and method are inserted in general in the field of production of windows, doors, French doors i.e. doors or windows variously composed also by top frame pane or bottom frame pane units combined together with each other on a same frame.
- the exterior doors or windows have a fixed frame rigidly anchored to the wall of a building, which supports a wing of fixed type or movable type, provided with a usually multi-pane glass panel separated by double glazing.
- the fixed frame performs a double function, i.e. the function of fixing to the wall, usually for example by means of brackets with projections inserted in the wall and fixed with screws to the frame, and the function of facing the wing by means of suitable shaped parts thereof.
- the frame has a projecting shaped portion intended to receive in abutment, with the interposition of a seal, the support frame of the glass panel of the movable wing.
- the frame has a shaped portion, usually for example step-like for defining a seat adapted to receive the fixed wing, obtained for example with the single glass panel.
- the fittings must be arranged on the frame for the support of the wing, i.e. for its movement for example with tilt/turn hinges, balanced hinges, top-hung hinges in accordance with the known technical terminology (hereinbelow indicated with the expression “window hinged at the upper part”), and the strikers for the closure bolts must be arranged.
- the aforesaid multiple functions, to which the frame must be subjected, oblige the latter to have a high mechanical strength for fixing to the wall and for supporting the fittings for the movement and closure of the wing, to arrange an internal part in exposed wood for aesthetic reasons, as well as arrange wood that is easily workable for obtaining all the necessary grooves aimed to obtain the coupling of the frame thus shaped with the wing, whether this is of movable or fixed type, with limited production costs.
- the doors or windows of known type are in practice unable to optimize all the different requirements and generally provide for the production of frames made of materials with mechanical strength that is not particularly high, shaped in order to simultaneously act as structural elements and abutments for the wings. Such frames are also provided with sufficiently wide sections in order to compensate for the aforesaid poor mechanical characteristics.
- the door or window comprises a frame formed by a shaped frame susceptible to be fixed to the wall of a building and provided with four or more shaped planks of wood, not particularly mechanically strong, connected together at the ends by means of first fastening means.
- the aforesaid door or window comprises a finishing frame formed by multiple profiles of wood of the same type as those that make up the shaped frame, each fixed on a corresponding plank of the shaped frame, and at least one fixed and/or movable wing mounted on the shaped frame and mechanically associated with the finishing frame.
- a further drawback of the aforesaid door or window of known type consists of the fact that the shaped frame is a costly component to be produced and that it requires milling processing, since its wood planks must be shaped to abut against a support frame of the movable wing.
- a further drawback of the aforesaid door or window of known type consists of the fact that the shaped frame is a component that cannot be standardized, since its planks must be shaped by means of the milling operations in order to be mechanically coupled with different types of wings.
- Such reinforcement portion is usually obtained with an aluminum profile, or a polyamide or polyurethane profile, fixed to the wood portion with screws, clips or glue.
- Such frame involves high production costs, and to the extent that the reinforcement portion results visible, it is not particularly appreciated by the market from an aesthetic standpoint.
- FIG. 1 One example of a door or window of known type is illustrated in the section view of figure A with the darkest part constituted by the external reinforcement portion indicated with 100 and with the lightest part constituted by the internal wood portion indicated with 200.
- the problem underlying the present invention is therefore to overcome the drawbacks manifested by the solutions of known type, by providing an exterior door or window with exposed wood which optimizes both the aesthetic and mechanical strength requirements.
- Further object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which allows mounting a movable wing in a very versatile manner.
- Further object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which has a frame provided with high mechanical strength in order to precisely support the wing over time.
- Further object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which overall is not very bulky and in particular has an overall frame formed by the fixed frame and by the wing with particularly reduced section.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which resists, in an optimal manner, stresses transmitted thereto by the wing and by the fittings.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which has a high thermal insulation value.
- Further object of the present invention is to provide a method for the production of an exterior door or window with exposed wood which is inexpensive and easy to produce.
- reference number 1 indicates overall the exterior door or window with exposed wood, object of the present invention.
- an exterior door or window 1 in particular constituted by a window, a door, a French door, a skylight or a different item, or any combination thereof that can comprise a top frame pane, a bottom frame pane, wings of movable type on hinges or of movable type with tilt and turn, or of top hinge type, it being intended that the invention can therefore refer to any other type of door or window, without departing from the protective scope of the present patent.
- the exterior door or window 1, object of the present invention comprises at least one support cell 2, obtained with four or more planks 3 of structural plywood fixed together and it is susceptible to be fixed securely to the wall of a building, as will be specified hereinbelow.
- Such support cell 2 is a bare support substructure that must then be fit with a dedicated frame at the wing of the door or window, as well as with the same wing as specified hereinbelow.
- each plank 3 is a board that is extended in a main longitudinal extension direction Y and preferably has a width L of 80-160 mm and a thickness S of 20-40 mm.
- the gluing of the layers is preferably carried out in class 3 (EN 314) Type M 100 (UNI 6478/69) and advantageously with glues of phenol or melamine type, thus suitable for uses in outdoor settings.
- the section S of the plank 3 is substantially quadrangular and preferably rectangular, with at least two substantially flat main faces A, A' spaced from each other by the thickness S, with smaller extension than the width of the faces A, A'.
- the two main faces A, A' are connected by perimeter faces P (with smaller extension) that are extended over four sides for the thickness S of the plank 3.
- the main faces A, A' of the planks 3 are parallel to the layers of the plywood.
- the main faces A, A' of the planks 3 are orthogonal to the overall lying plane of the door or window, hence with the main external perimeter face A of the main faces, of the non-internal planks 3, fixed to the wall 16 of the building, as explained hereinbelow.
- substantially quadrangular also geometries that are not perfectly square or rectangular should be deemed to be comprised; such imperfections may be due for example to the presence of grooves 13" for fixing to the brackets 13 as provided for in figure 3A , 4A and 8A .
- planks 3 are connected together at the ends by means of first fastening means 4 in order to form the support cell 2.
- planks 3 of the support cell 2 are rigidly fixed to each other at the four vertices through the first fastening means 4, per se of conventional type, such as brackets, screws, tenons and pins etc., not described in detail since per se known to the man skilled in the art.
- Crosspieces and uprights can also be present within the external perimeter of the support cell 2, in order to divide the support cell 2 into substructures to which wings of movable type can be associated.
- the support cell 2 therefore assumes the original geometric form of a rigid frame, whose structure is dedicated to the static mechanical strength for support of the wings, and at the same time is quite thin (narrow) since it is substantially formed by planks with substantially flat main faces A, A' that define at least one closed external perimeter extension - usually defined by four profiles orthogonally joined together at their ends - as well as possibly other closed extensions defined by internal uprights and crosspieces of intermediate planks.
- planks 3 of the cell are therefore advantageously provided with substantially flat main faces A, A' that lack processing in order to allow optimizing the mechanical strength thereof, obtaining a standardized manufactured product then susceptible to be fitted (as will be explained below) with shaped frames easily formed on softer material. Indeed, due to the very high mechanical strength of the material with which they are obtained, they are substantially intended only to support the door or window on the wall, whereas the shape intended for the connection with the wing is obtained, as indicated hereinbelow, by the shaped frame made of material that is less mechanically strong and hence more easily workable.
- planks with flat main faces A, A' in accordance with the first preferred embodiment of figures 3 , 4 and 8 , or, also preferably, planks in accordance with the second embodiment of figures 3A , 4A and 8A with at least one external main face A of the main faces with a little processing in order to improve its fastening to the wall, as is better explained below.
- the closed extension of the support cell 2 delimits at least one opening which is engaged by a wing, in particular glass, of movable type 8'.
- the closed extension from the support cell 2 delimits a plurality of openings, each of which engaged with a corresponding movable glass wing 8'.
- the closed extension of the support cell 2 delimits a plurality of openings, of which at least one opening is advantageously engaged by a corresponding movable glass wing 8' and the remaining openings of the plurality of openings are each engaged by an optional corresponding wing, in particular glass, that is fixed 8.
- the fixed glass wing 8 can be obtained substantially with only one glass panel, for example with multiple panes separated by a double glazing.
- plank made of structural plywood it is intended, as is known to the man skilled in the art, a plank 3 formed by multiple layers of superimposed wood, joined together by glue in order to confer high mechanical characteristics to the plan thus assembled, as well as perfect flatness, torsional strength, and resistance to water, humidity and inclement outdoor weather.
- plank 3 made of structural plywood with thickness comprised between 20 and 40 mm, with a number of layers comprised between 9 and 15 and with glue of phenol or melamine type, has longitudinal and transverse bending strength according to regulations EN 310 comprised between 30 and 39 Mpa.
- the same plank 3 also has longitudinal and transverse modulus of elasticity according to regulations EN 310 comprised between 4100 and 4700 MPa.
- the same plank 3 also has longitudinal and transverse bending strength according to regulations EN 789 comprised between 25 and 27 MPa.
- the same plank 3 also has longitudinal and transverse modulus of elasticity according to regulations EN 789 MPa ranging from 4620 to 4660.
- the plank 3 is made of Okoume plywood with phenol or melamine gluing. This wood came to be the preferred selection of the invention because the plywood plank thus obtained is distinguished by good durability characteristics and high mechanical strength performances, while having a limited weight.
- plank made of structural plywood is a multilayer marine wood or marine plywood better known with the term "Marine Plywood”, well-known to be used for its mechanical strength, resistance to humidity and to the most challenging weathering agents, in the construction of ship parts.
- Marine Plywood well-known to be used for its mechanical strength, resistance to humidity and to the most challenging weathering agents, in the construction of ship parts.
- the exterior door or window 1 further comprises at least one shaped frame 5, 5', formed by multiple profiles 6, 6' fixed by means of second fastening means 7 on at least one main face A' of the planks 3 of the support cell 2 or also both main faces A and A' for the planks 3 which form intermediate uprights and crosspieces of the support cell 2.
- the exterior door or window 1 comprises at least one movable glass wing 8' and a corresponding shaped frame 5' formed by multiple profiles 6'.
- the exterior door or window 1 comprises multiple movable glass wings 8' with the corresponding shaped frames 5', multiple fixed glass wings 8 and the corresponding shaped frames 5 each formed by respective profiles 6.
- the intermediate uprights and crosspieces of the cells 2 are fixed together at the points of intersection by means of fifth fixing means 60 for example constituted by metal pins 61 which are inserted in longitudinal holes obtained in the opposite ends of two horizontal intermediate crosspieces 3, aligned to be joined (see drawing of figure 9 ), and in through holes 63 obtained in a central vertical upright 3 and (upright in figure 9 ) orthogonally interposed between the aforesaid two aligned planks.
- fifth fixing means 60 for example constituted by metal pins 61 which are inserted in longitudinal holes obtained in the opposite ends of two horizontal intermediate crosspieces 3, aligned to be joined (see drawing of figure 9 ), and in through holes 63 obtained in a central vertical upright 3 and (upright in figure 9 ) orthogonally interposed between the aforesaid two aligned planks.
- Such pins 61 are engaged at one end in a bushing 64 inserted in a transverse seat 66 obtained in an aforesaid intermediate plank at one end thereof and are made integral with such bushings 64 by means of grub screws 65, and at the other end via screwing in threaded bushings 67 pre-inserted in the thickness of the transverse plank, as schematically exemplified in figure 9 .
- the crosspieces of the planks 3 are instead fixed to the lateral uprights of the planks 3 by means of screws and bolts.
- the profiles 6, 6', in particular made of wood, are fixed to the planks of the support cell 2 in a continuous manner with respect to each other and generally orthogonally with respect to each other, along closed trajectories in order to obtain the aforesaid shaped frames 5, 5'.
- Such shaped frames 5, 5' are preferably made of a material that is softer and has lower mechanical performance than the planks 3.
- they can be made of wood that is softer and has lower mechanical performance than the planks 3. Therefore, the structural plywood of the planks 3 of the support cell 2 is provided with mechanical strength that is greater than the wood of the profiles 6, 6' of the aforesaid shaped frames 5, 5'. In particular, by mechanical strength it is intended the bending strength.
- the structural plywood of the planks 3 of the support cell 2 is provided with rigidity (modulus of elasticity) and hardness that are greater than that of the wood of the profiles 6, 6' of the aforesaid shaped frames 5, 5'.
- the exterior door or window 1 in accordance with the idea underlying the present invention thus comprises at least one glass wing 8' mounted in a movable manner on the support cell 2 between an open position, in which the movable glass wing 8' is arranged separated from the corresponding shaped frame 5' and a closed position, in which the movable glass wing 8' is susceptible to abut against the corresponding shaped frame 5'.
- the movable glass wing 8' is susceptible to abut against a seal portion 50 of the corresponding shaped frame 5' with interposition of at least one seal 82.
- the support cell 2 as defined above has functionality dedicated to the structural mechanical strength, i.e. for fixing to the wall and for supporting fittings. It does not have the typical shapes of the abutment frames of the wings and consequently has very limited section (thickness) in the direction orthogonal to the wall.
- the support cell 2 can be installed in the wall of the building even when work-site operations are still underway, such as during the construction of the building or the arrangement of the installations. Due to the high mechanical strength and to the small projection from the wall, the support cell 2 is not susceptible to be damaged in open construction sites. In this step, it can also be covered by a removable protection film 70 which will be removed when the work has been completed or nearly completed, or in any case when the doors or windows are no longer at risk for being deteriorated by the works of the work-site. Such film 70 will advantageously be arranged on the first lateral edge 17 directed towards the internal environment of the building 17 and on the exposed contiguous surface of the plank 3. Such film is exemplifyingly and schematically illustrated with a net-like surface in the single lower portion of figure 2 .
- the main internal perimeter face A' (of the main faces) of the planks opposite the main external perimeter face A (of the main faces), fixed to the wall, is substantially flat so as to facilitate the covering with the protection film 70 and thus to reduce the bulk projecting from the wall, limiting the risk of interfering with the work tools during the work-site operations.
- Such face A' is susceptible to be fit with the frame 5, 5' intended to mechanically collaborate with the wing.
- the frame 5, 5' can nevertheless be mounted when the main works of the work-site have been completed, so as to not risk being ruined.
- the second fastening means 7 mentioned above are for example obtained with simple screws that engage the profiles 6, 6' of the shaped frame 5, 5' to the planks 3 of the support cell 2.
- the aforesaid screws of the second fastening means 7 are mounted in engagement on the shaped frame 5, 5' in order to allow a facilitated removal thereof in case of substitution of movable glass wings 8' with other new wings.
- the aforesaid screws of the second fastening means 7 are preferably mounted with the head in engagement on a preferably oblique portion directed towards the external environment of the profile 6' of the shaped frame 5'.
- the aforesaid screws of the second fastening means 7 are preferably mounted with the head in engagement on the main external perimeter face A of the main faces and with the shank that, having traversed the thickness of the plank 3, is inserted in the profile 6' of the shaped frame 5'. In this manner, the screw remains hidden from view.
- the fastening screws of the movable profiles 6' are fixed on the main external perimeter face A of the main faces, and only afterward will the fixed profiles 6 be mounted on the latter face, to cover the fastening screws 7 of the movable profiles 6'.
- brackets 10 fittingly inserted in grooves 11 obtained in a substantially counter-shaped manner on the profiles 6 of the shaped frame 5.
- brackets 10 are angularly shaped in order to also cover the external edge of the profiles 6 of the shaped frame 5 in a manner so as to act as abutment for the glass panel 80.
- a layer of structural sealant glue is interposed between the glass panel 80 and the external edge of the profiles 6 of the shaped frame 5; i.e. a structural double-sided tape 9.
- At least one of its constituent planks 3, and normally all the planks 3 that form the external perimeter (usually four planks) of the support cell 2 each comprise at least one main external face A of the main faces, which is susceptible to be fixed to the wall of a building by means of third fastening means 12.
- both the main faces A, A' of the planks are covered by shaped frames 5, 5'.
- the bracket 13 can advantageously provide for ribs 13' susceptible to be inserted in counter-shaped surface grooves 13" obtained along the planks 3 in order to improve the mechanical engagement.
- a layer of insulating material 130 can be partially interposed between the main external face A of the main faces of the planks 3 that form the external perimeter of the support cell 2 and the wall 16.
- the wall 16 will for example comprise an external covering 160 (for example comprising a plaster layer) and an internal body obtained with two brick walls 161 separated by an insulating layer 162.
- an external covering 160 for example comprising a plaster layer
- the main external face A of the main faces, of the planks 3, intended to be engaged with the brackets 13, is provided with longitudinal grooves adapted to receive, in form engagement, counter-shaped portions of the brackets.
- planks 3 of the support cell 2 are placed projecting from the wall 16 even if substantially hidden from view by the shaped frame 5, 5' and by the movable glass wing 8' or by the optional fixed glass wing 8.
- planks 3 of the support cell 2 are extended with their width L into the thickness of the wall and therefore delimit a first lateral edge 17, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figure is oriented towards the internal setting of the building, and a second lateral edge 18, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figures is oriented towards the external setting of the building.
- lateral edge 18 of the plank 3 which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figures is oriented towards the outside environment, is covered by a protection profile 23 made of aluminum fixed by means of clips 24 with screw shank, to the same plank 3, or, in accordance with a non-illustrated embodiment, by means of forced fitting of projecting portions of the protection profile in grooves of the plank 3.
- the shaped frame 5, 5' is fixed to a main face A' (or even to both the main faces A and A' for the planks 3 that form intermediate uprights and crosspieces of the support cell 2) of the planks 3 of the support cell 2, in particular substantially starting from the aforesaid first lateral edge 17 of the planks 3, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figures is oriented towards the internal environment.
- the movable glass wing 8' in closed position, or the optional fixed glass wing 8 substantially faces a main face A' (or even both the main faces A and A' for the planks 3 which form intermediate uprights and crosspieces of the support cell 2) of the planks 3 of the support cell 2, in particular substantially starting from the aforesaid second lateral edge 18 of the planks 3, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figures is directed oriented towards the external environment.
- the support cell 2 mounts part of the fittings of the movable glass wing 8', constituted by mechanisms per se known to the man skilled in the art and for this reason not described in detail hereinbelow, in particular formed by support hinges for the movable glass wing 8' (as indicated with 20 in figure 8 ), by compass hinges for the movable glass wing 8' (as indicated with 21 in figures 3 and 5 ), by lock bolt strikers, also perimeter, or by top-hung upper hinge systems (as indicated with 22 in figures 4 and 6 with reference to engagement mechanisms).
- the movable glass wing 8' is rotatingly supported by the support cell 2 and comprises a glass panel 80 and a support frame 81, which is perimetrically extended around the glass panel 80 and mounts the complements of the hinges or tilt and turn mechanisms provided on the support cell 2 in order to allow the support cell 2 to rotatably support the wing 8' itself.
- the movable glass wing 8' has, externally associated on its external surface of the support frame 81 directed towards the outside environment, a protection profile 23', it too preferably obtained with an extruded aluminum profile fixed to the aforesaid external surface by means of clips 24 provided with head 24' inserted in engagement in longitudinal grooves 25 of the extruded aluminum profile 23' and with threaded shank 24" engaged for screwing into the aforesaid external surface of the support frame 81 of the wing 8'.
- Such protection profile 23' performs the function of externally fixing the glass panel 80 to the movable wing 8'.
- These fourth fixing means 90 preferably comprise one or multiple profiles, for example constituted by one or more aluminum extrusions fixed to the planks 3 of the support cell 2 at their second lateral edge 18 by means of screws or clips 24 and/or by means of male-female portions engaged with each other (solution non illustrated).
- a protection profile 23 and a retention profile 23" can be provided.
- the protection profile 23 is placed to cover the second lateral edge 18 of the planks 3 of the support cell 2.
- the retention profile 23" acts on the external edge of the glass panel 80 and is fixed to at least one main face A, A' of the plank 3 of the support cell 2.
- the protection profile 23 is fixed on the second lateral edge 18 of the planks 3 of the support cell 2 by means of clips 24 provided with head 24' inserted in engagement in longitudinal grooves 25 of the protection profile 23 and with threaded shank 24" engaged via screwing on the external surface of the plank 3.
- the retention profile 23" is fixed to at least one main face A, A' of the plank 3 of the support cell 2 by means of screws.
- the protection profile 23 fixed on the second lateral edge 18 of the planks 3 of the support cell 2 is also extended to cover the perimeter edge of the glass panel 80, also performing the simultaneous function of fixing the same glass panel 80 to the shaped frame 5.
- Such extruded aluminum profile 23 therefore performs both the function of fixing and that of external protection covering indicated above.
- the protection profile 23 defines at the front part of the lower edge of the glass panel, a channel 231 for the drainage of the water.
- the latter advantageously receives the water from a channel profile 230 that hits the main internal perimeter face A' of the plank 3, which is advantageously extended starting from the profile 6' of the shaped frame 5' of the movable glass wing 8' and has at least one portion tilted outward for the drainage of the water towards the channel 231.
- the glass panel 80 for both types of glass wing 8, 8', advantageously comprises, in a manner per se entirely conventional, an internal sheet and an external sheet, fixed to each other by a perimeter cord made of sealant material (e.g. of structural silicone) as well as spaced from the same internal sheet by means of a channel defining at least one double glazing together with the glass sheets.
- sealant material e.g. of structural silicone
- the lower perimeter edge of the glass panel 80 is inserted in a step defined between the plank 3 and the frame 5 in the case of the optional fixed glass wing 8 and in a step defined in the support frame 81 in the case of movable wing 8'.
- plastic support brackets 232 e.g. with 6-9 cm length fixed with screws and shaped for compensating for such tilt and maintaining the glass panel 80 vertical.
- a perimeter channel 15 is preferably provided, fixed by means of screws 15' to the internal face 81' of the support frame 81 of the movable glass wing 8' which is opposed to the main face A' of the main faces of the planks 3 of the support cell 2, in order to convey the humidity that condenses and the water that filters towards the outside of the door or window.
- Preferably such channel 15 is obtained with linear sections joined together at 90 degrees and suitably undercut in the superimposed parts.
- Also forming an object of the present invention is a method for the production of an exterior door or window with exposed wood, in particular of the type described above in the different embodiments; in order to simplify the description, the same reference numbers and nomenclature will be maintained hereinbelow.
- planks of structural plywood 3 by means of a first operation of cutting a panel of structural plywood with parallel cuts of predefined width L, obtaining planks of structural plywood 3 having substantially quadrangular section with at least two substantially flat main faces A, A', spaced by the thickness S of the same planks 3, and parallel to the layers of the plywood.
- the production of the planks of structural plywood 3 also provides for a second operation of cutting the planks of structural plywood 3 to the required length L, in order to obtain the door or window with the desired size.
- an operation is provided for mounting at least one fixed wing 8 mechanically constrained to the corresponding shaped frame 5 by means of a mechanical retention collaboration relation.
- the fixing of the shaped frame 5, 5' to the support cell 2 occurs with screws having the head in engagement on the shaped frame 5, 5', in order to allow an easy removal thereof in case of substitution of glass wings of movable type 8' with other new wings.
- a step is advantageously provided for provisionally covering the main faces A, A' of the planks 3 of the cell 2, not intended for coupling to the wall, with a protection film 70 in order to allow the cell 2 to be installed in the presence of a work-site of a building (e.g. for fabrication, restoration, renovation or maintenance of the building), entirely free of projecting frames 5, 5' as well as glass wings 8' that could be damaged during the work-site activity. Due to the covering 70 and to the hardness of the cell 2, the latter is correctly protected from accidental damage, to which it could be subjected during normal work-site operations, and which could be due both to the dirtying with liquid substances (corrosive substances, lime, solvent paints or other items) and to mechanical impact, e.g. during the movement of normal equipment used in work-sites.
- a protection film 70 in order to allow the cell 2 to be installed in the presence of a work-site of a building (e.g. for fabrication, restoration, renovation or maintenance of the building), entirely free of projecting frames 5, 5'
- a step is provided for removing the protection film 70 such that the aforesaid step can take place for fixing the shaped frame 5, 5' as well as the step for mounting the glass wings 8'.
- the exterior door or window 1 thus obtained comprises the support cell 2, whose structure is dedicated to the static mechanical strength, the shaped frames 5, 5' and the at least one movable glass wing 8' susceptible to abut against the corresponding shaped frame 5'.
- the support cell 2 is made with planks 3 of structural plywood having the main faces A, A' substantially flat and lacking processing and adapted to sustain mechanical stresses (derived from the stresses for supporting the door or window on the wall, from the stresses transmitted to the support cell 2 by the wing, etc.), while the shaped frames 5, 5' are made of a softer material, mechanically less performing than the structural plywood of the planks 3 and adapted to be processed in order to define the abutment with the corresponding wing and the mounting seats of the seals.
- the finding thus conceived therefore attains the pre-established objects.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Closures For Containers (AREA)
- Securing Of Glass Panes Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Exterior door or window with exposed wood, which comprises at least one support cell (2) susceptible to be fixed securely to the wall (16) of a building, provided with four or more planks (3) of structural plywood, a substantially quadrangular section with at least two substantially flat main faces (A, A'), parallel to the layers of said plywood, and connected together at least at the ends by means of first fastening means (4) in order to form said support cell (2). The door or window also comprises a shaped frame (5,5'), formed by multiple profiles (6, 6') fixed together in a continuous manner by means of second fastening means (7) on at least one substantially flat main face (A, A') of the planks (3) of said support cell (2), and at least one movable wing (8') mounted on the support cell (2) and susceptible to abut against the corresponding shaped frame (5').
Description
- The present invention refers to an exterior door or window with exposed wood and to a method for the production thereof, according to the preamble of the respective independent claims.
- The present door or window and method are inserted in general in the field of production of windows, doors, French doors i.e. doors or windows variously composed also by top frame pane or bottom frame pane units combined together with each other on a same frame.
- According to the conventional technique closest to the present invention, the exterior doors or windows have a fixed frame rigidly anchored to the wall of a building, which supports a wing of fixed type or movable type, provided with a usually multi-pane glass panel separated by double glazing.
- The fixed frame performs a double function, i.e. the function of fixing to the wall, usually for example by means of brackets with projections inserted in the wall and fixed with screws to the frame, and the function of facing the wing by means of suitable shaped parts thereof. For example, in the case of movable wing, the frame has a projecting shaped portion intended to receive in abutment, with the interposition of a seal, the support frame of the glass panel of the movable wing. In the case of fixed wing, the frame has a shaped portion, usually for example step-like for defining a seat adapted to receive the fixed wing, obtained for example with the single glass panel.
- In the frequent movable wing case, also the fittings must be arranged on the frame for the support of the wing, i.e. for its movement for example with tilt/turn hinges, balanced hinges, top-hung hinges in accordance with the known technical terminology (hereinbelow indicated with the expression "window hinged at the upper part"), and the strikers for the closure bolts must be arranged.
- In addition, the frame at the wing must resist the stresses transmitted by the latter.
- At the same time the frame must resist the thermal stresses and the moisture transmitted by the outside environment.
- The aforesaid multiple functions, to which the frame must be subjected, oblige the latter to have a high mechanical strength for fixing to the wall and for supporting the fittings for the movement and closure of the wing, to arrange an internal part in exposed wood for aesthetic reasons, as well as arrange wood that is easily workable for obtaining all the necessary grooves aimed to obtain the coupling of the frame thus shaped with the wing, whether this is of movable or fixed type, with limited production costs.
- Given the different needs, the doors or windows of known type are in practice unable to optimize all the different requirements and generally provide for the production of frames made of materials with mechanical strength that is not particularly high, shaped in order to simultaneously act as structural elements and abutments for the wings. Such frames are also provided with sufficiently wide sections in order to compensate for the aforesaid poor mechanical characteristics.
- One example of an exterior door or window of known type, which has the aforesaid drawbacks, is described in the German utility model
DE 202004014618 ; here, the door or window comprises a frame formed by a shaped frame susceptible to be fixed to the wall of a building and provided with four or more shaped planks of wood, not particularly mechanically strong, connected together at the ends by means of first fastening means. In addition, the aforesaid door or window comprises a finishing frame formed by multiple profiles of wood of the same type as those that make up the shaped frame, each fixed on a corresponding plank of the shaped frame, and at least one fixed and/or movable wing mounted on the shaped frame and mechanically associated with the finishing frame. - The door or window of known type described in this utility model
DE 202004014618 in practice has further drawbacks in addition to those mentioned above. - A further drawback of the aforesaid door or window of known type consists of the fact that the shaped frame is a costly component to be produced and that it requires milling processing, since its wood planks must be shaped to abut against a support frame of the movable wing.
- A further drawback of the aforesaid door or window of known type consists of the fact that the shaped frame is a component that cannot be standardized, since its planks must be shaped by means of the milling operations in order to be mechanically coupled with different types of wings.
- In order to remedy the problem constituted by shaped support frames provided with sections sufficiently wide to compensate for the aforesaid poor mechanical characteristics deriving from the need to be able to mill them for the coupling with the wings (such that they cannot be made of particularly strong materials), recently fixed frames have been developed that are provided with an internal wood portion, and with an external reinforcement portion, fixed to the internal wood portion, intended to obtain the coupling with the wing as well as support the mounting of the relative fittings.
- Such reinforcement portion is usually obtained with an aluminum profile, or a polyamide or polyurethane profile, fixed to the wood portion with screws, clips or glue.
- Such frame involves high production costs, and to the extent that the reinforcement portion results visible, it is not particularly appreciated by the market from an aesthetic standpoint.
- One example of a door or window of known type is illustrated in the section view of figure A with the darkest part constituted by the external reinforcement portion indicated with 100 and with the lightest part constituted by the internal wood portion indicated with 200.
- In this situation, the problem underlying the present invention is therefore to overcome the drawbacks manifested by the solutions of known type, by providing an exterior door or window with exposed wood which optimizes both the aesthetic and mechanical strength requirements.
- Further object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which allows mounting a movable wing in a very versatile manner.
- Further object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which has a frame provided with high mechanical strength in order to precisely support the wing over time.
- Further object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which overall is not very bulky and in particular has an overall frame formed by the fixed frame and by the wing with particularly reduced section.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which resists, in an optimal manner, stresses transmitted thereto by the wing and by the fittings.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide an exterior door or window with exposed wood which has a high thermal insulation value.
- Further object of the present invention is to provide a method for the production of an exterior door or window with exposed wood which is inexpensive and easy to produce.
- The technical characteristics of the finding, according to the aforesaid objects, can be clearly seen in the contents of the below-reported claims, and the advantages thereof will be more evident in the following detailed description, made with reference to the enclosed drawings, which represent several merely exemplifying and non-limiting embodiments of the invention, in which:
-
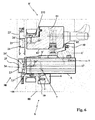
figure 1 shows a perspective view of an exterior door or window, object of the present invention, with at least one movable wing, some parts having been removed in order to better illustrate others; -
figure 2 shows a perspective view of a detail offigure 1 relative to a support cell made of structural plywood; -
figure 3 shows a section view of the upright of a movable wing hinged on the upper part, with the means for fixing to the wall indicated, according to a first embodiment of the exterior door or window, object of the present invention; -
figure 3A shows a section view of the upright of a movable wing hinged on the upper part, with the means for fixing to the wall indicated, according to a second embodiment of the exterior door or window, object of the present invention; -
figure 3B shows a section view of a portion of the door or window offigure 1 regarding the upright of an optional fixed wing, with the means for fixing to the wall indicated, according to the first embodiment of the exterior door or window, object of the present invention; -
figure 4 shows a section view of the crosspiece of a wing hinged at the upper part, according to the first embodiment of the exterior door or window, object of the present invention; -
figure 4A shows a section view of the crosspiece of a wing hinged on the upper part, according to the second embodiment of the exterior door or window, object of the present invention; -
figure 5 shows a section view of the crosspiece of a door or window provided with an optional top frame pane fixed above a wing hinged on the upper part, according to the first embodiment of the exterior door or window, object of the present invention; -
figure 6 shows a section view of the crosspiece of a door or window provided with an optional bottom frame pane fixed below a wing hinged on the upper part, according to the first embodiment of the exterior door or window, object of the present invention; -
figure 7 shows a section view of the crosspiece of an exterior door or window which separates two optional fixed wings; -
figure 8 shows a section view of the upright of a door, according to the first embodiment of the exterior door or window, object of the present invention; -
figure 8A shows a section view of the upright of a door, according to the second embodiment of the exterior door or window object of the present invention; -
figure 9 shows a perspective view of a detail of an exterior door or window, object of the present invention, relative to fifth fixing means for connecting together crosspieces and uprights inside said cell. - With reference to the enclosed drawings, reference number 1 indicates overall the exterior door or window with exposed wood, object of the present invention.
- Hereinbelow in the present description, reference will be made to an exterior door or window 1, in particular constituted by a window, a door, a French door, a skylight or a different item, or any combination thereof that can comprise a top frame pane, a bottom frame pane, wings of movable type on hinges or of movable type with tilt and turn, or of top hinge type, it being intended that the invention can therefore refer to any other type of door or window, without departing from the protective scope of the present patent.
- The exterior door or window 1, object of the present invention, comprises at least one
support cell 2, obtained with four ormore planks 3 of structural plywood fixed together and it is susceptible to be fixed securely to the wall of a building, as will be specified hereinbelow. -
Such support cell 2 is a bare support substructure that must then be fit with a dedicated frame at the wing of the door or window, as well as with the same wing as specified hereinbelow. - More clearly, each
plank 3 is a board that is extended in a main longitudinal extension direction Y and preferably has a width L of 80-160 mm and a thickness S of 20-40 mm. - Advantageously, in the range of 20 - 40 mm, between 9 and 15 layers are provided.
- The gluing of the layers is preferably carried out in class 3 (EN 314) Type M 100 (UNI 6478/69) and advantageously with glues of phenol or melamine type, thus suitable for uses in outdoor settings.
- The section S of the
plank 3 is substantially quadrangular and preferably rectangular, with at least two substantially flat main faces A, A' spaced from each other by the thickness S, with smaller extension than the width of the faces A, A'. The two main faces A, A' are connected by perimeter faces P (with smaller extension) that are extended over four sides for the thickness S of theplank 3. - The main faces A, A' of the
planks 3 are parallel to the layers of the plywood. - Preferably, moreover, the main faces A, A' of the
planks 3 are orthogonal to the overall lying plane of the door or window, hence with the main external perimeter face A of the main faces, of thenon-internal planks 3, fixed to thewall 16 of the building, as explained hereinbelow. - With the term "substantially quadrangular", also geometries that are not perfectly square or rectangular should be deemed to be comprised; such imperfections may be due for example to the presence of
grooves 13" for fixing to thebrackets 13 as provided for infigure 3A ,4A and8A . - The
planks 3 are connected together at the ends by means of first fastening means 4 in order to form thesupport cell 2. - More in detail, at least four
planks 3 of thesupport cell 2 are rigidly fixed to each other at the four vertices through the first fastening means 4, per se of conventional type, such as brackets, screws, tenons and pins etc., not described in detail since per se known to the man skilled in the art. Crosspieces and uprights can also be present within the external perimeter of thesupport cell 2, in order to divide thesupport cell 2 into substructures to which wings of movable type can be associated. - The
support cell 2 therefore assumes the original geometric form of a rigid frame, whose structure is dedicated to the static mechanical strength for support of the wings, and at the same time is quite thin (narrow) since it is substantially formed by planks with substantially flat main faces A, A' that define at least one closed external perimeter extension - usually defined by four profiles orthogonally joined together at their ends - as well as possibly other closed extensions defined by internal uprights and crosspieces of intermediate planks. - The
planks 3 of the cell are therefore advantageously provided with substantially flat main faces A, A' that lack processing in order to allow optimizing the mechanical strength thereof, obtaining a standardized manufactured product then susceptible to be fitted (as will be explained below) with shaped frames easily formed on softer material. Indeed, due to the very high mechanical strength of the material with which they are obtained, they are substantially intended only to support the door or window on the wall, whereas the shape intended for the connection with the wing is obtained, as indicated hereinbelow, by the shaped frame made of material that is less mechanically strong and hence more easily workable. - With the expression "substantially flat" referred to at least the main faces A, A' of the planks and preferably to all the faces of the planks, the following will have to be considered as comprised: planks with flat main faces A, A', in accordance with the first preferred embodiment of
figures 3 ,4 and8 , or, also preferably, planks in accordance with the second embodiment offigures 3A ,4A and8A with at least one external main face A of the main faces with a little processing in order to improve its fastening to the wall, as is better explained below. - The closed extension of the
support cell 2 delimits at least one opening which is engaged by a wing, in particular glass, of movable type 8'. Advantageously, the closed extension from thesupport cell 2 delimits a plurality of openings, each of which engaged with a corresponding movable glass wing 8'. Preferably, the closed extension of thesupport cell 2 delimits a plurality of openings, of which at least one opening is advantageously engaged by a corresponding movable glass wing 8' and the remaining openings of the plurality of openings are each engaged by an optional corresponding wing, in particular glass, that is fixed 8. - In particular the fixed
glass wing 8 can be obtained substantially with only one glass panel, for example with multiple panes separated by a double glazing. - With the term "plank made of structural plywood" it is intended, as is known to the man skilled in the art, a
plank 3 formed by multiple layers of superimposed wood, joined together by glue in order to confer high mechanical characteristics to the plan thus assembled, as well as perfect flatness, torsional strength, and resistance to water, humidity and inclement outdoor weather. - The man skilled in the art, based on such definition, is able to easily identify the plywood on the market.
-
Such plank 3 made of structural plywood with thickness comprised between 20 and 40 mm, with a number of layers comprised between 9 and 15 and with glue of phenol or melamine type, has longitudinal and transverse bending strength according to regulations EN 310 comprised between 30 and 39 Mpa. - Preferably the
same plank 3 also has longitudinal and transverse modulus of elasticity according to regulations EN 310 comprised between 4100 and 4700 MPa. - Preferably the
same plank 3 also has longitudinal and transverse bending strength according to regulations EN 789 comprised between 25 and 27 MPa. - Preferably the
same plank 3 also has longitudinal and transverse modulus of elasticity according to regulations EN 789 MPa ranging from 4620 to 4660. - Advantageously, such characteristics are derived from multiple superimposed layers of wood, in particular high-quality wood with considerable hardness such as mahogany, Okoume, Iroko, maple, preferably glued together with melamine or phenol resins.
- Preferably the
plank 3 is made of Okoume plywood with phenol or melamine gluing. This wood came to be the preferred selection of the invention because the plywood plank thus obtained is distinguished by good durability characteristics and high mechanical strength performances, while having a limited weight. - Preferably, the plank made of structural plywood is a multilayer marine wood or marine plywood better known with the term "Marine Plywood", well-known to be used for its mechanical strength, resistance to humidity and to the most challenging weathering agents, in the construction of ship parts.
- It is for example defined in a manner in accordance with the English regulations BS 1088, which considers marine plywood to be a plywood plank of untreated hard woods, of tropical origin, having a high capacity of resistance even to fungal attacks. The glue, according to such regulations, must prove to be highly resistant to the outside environment, to microorganisms, to hot water and boiling water, to steam and dry heat by passing the tests provided by the English regulations BS 1088.
- According to the present invention the exterior door or window 1 further comprises at least one
shaped frame 5, 5', formed bymultiple profiles 6, 6' fixed by means of second fastening means 7 on at least one main face A' of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2 or also both main faces A and A' for theplanks 3 which form intermediate uprights and crosspieces of thesupport cell 2. - The exterior door or window 1 comprises at least one movable glass wing 8' and a corresponding shaped frame 5' formed by multiple profiles 6'. Advantageously, in accordance with
figure 1 , the exterior door or window 1 comprises multiple movable glass wings 8' with the corresponding shaped frames 5', multiple fixedglass wings 8 and the corresponding shapedframes 5 each formed byrespective profiles 6. - Advantageously, the intermediate uprights and crosspieces of the
cells 2 are fixed together at the points of intersection by means of fifth fixing means 60 for example constituted bymetal pins 61 which are inserted in longitudinal holes obtained in the opposite ends of two horizontalintermediate crosspieces 3, aligned to be joined (see drawing offigure 9 ), and in throughholes 63 obtained in a centralvertical upright 3 and (upright infigure 9 ) orthogonally interposed between the aforesaid two aligned planks.Such pins 61 are engaged at one end in abushing 64 inserted in a transverse seat 66 obtained in an aforesaid intermediate plank at one end thereof and are made integral withsuch bushings 64 by means ofgrub screws 65, and at the other end via screwing in threadedbushings 67 pre-inserted in the thickness of the transverse plank, as schematically exemplified infigure 9 . - The crosspieces of the
planks 3 are instead fixed to the lateral uprights of theplanks 3 by means of screws and bolts. Theprofiles 6, 6', in particular made of wood, are fixed to the planks of thesupport cell 2 in a continuous manner with respect to each other and generally orthogonally with respect to each other, along closed trajectories in order to obtain the aforesaid shapedframes 5, 5'. - Such shaped
frames 5, 5' are preferably made of a material that is softer and has lower mechanical performance than theplanks 3. Advantageously they can be made of wood that is softer and has lower mechanical performance than theplanks 3. Therefore, the structural plywood of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2 is provided with mechanical strength that is greater than the wood of theprofiles 6, 6' of the aforesaid shapedframes 5, 5'. In particular, by mechanical strength it is intended the bending strength. In addition, the structural plywood of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2 is provided with rigidity (modulus of elasticity) and hardness that are greater than that of the wood of theprofiles 6, 6' of the aforesaid shapedframes 5, 5'. - The exterior door or window 1 in accordance with the idea underlying the present invention thus comprises at least one glass wing 8' mounted in a movable manner on the
support cell 2 between an open position, in which the movable glass wing 8' is arranged separated from the corresponding shaped frame 5' and a closed position, in which the movable glass wing 8' is susceptible to abut against the corresponding shaped frame 5'. - In particular, the movable glass wing 8' is susceptible to abut against a
seal portion 50 of the corresponding shaped frame 5' with interposition of at least oneseal 82. - The
support cell 2 as defined above has functionality dedicated to the structural mechanical strength, i.e. for fixing to the wall and for supporting fittings. It does not have the typical shapes of the abutment frames of the wings and consequently has very limited section (thickness) in the direction orthogonal to the wall. - Such circumstance allows the
support cell 2 to be installed in the wall of the building even when work-site operations are still underway, such as during the construction of the building or the arrangement of the installations. Due to the high mechanical strength and to the small projection from the wall, thesupport cell 2 is not susceptible to be damaged in open construction sites. In this step, it can also be covered by a removable protection film 70 which will be removed when the work has been completed or nearly completed, or in any case when the doors or windows are no longer at risk for being deteriorated by the works of the work-site. Such film 70 will advantageously be arranged on the firstlateral edge 17 directed towards the internal environment of thebuilding 17 and on the exposed contiguous surface of theplank 3. Such film is exemplifyingly and schematically illustrated with a net-like surface in the single lower portion offigure 2 . - The main internal perimeter face A' (of the main faces) of the planks opposite the main external perimeter face A (of the main faces), fixed to the wall, is substantially flat so as to facilitate the covering with the protection film 70 and thus to reduce the bulk projecting from the wall, limiting the risk of interfering with the work tools during the work-site operations.
- Such face A', as explained below, is susceptible to be fit with the
frame 5, 5' intended to mechanically collaborate with the wing. Theframe 5, 5' can nevertheless be mounted when the main works of the work-site have been completed, so as to not risk being ruined. - The second fastening means 7 mentioned above are for example obtained with simple screws that engage the
profiles 6, 6' of the shapedframe 5, 5' to theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2. - The aforesaid screws of the second fastening means 7 are mounted in engagement on the shaped
frame 5, 5' in order to allow a facilitated removal thereof in case of substitution of movable glass wings 8' with other new wings. - Advantageously, in accordance with the first embodiment illustrated in
figures 3 ,4 and8 , in the case of movable glass wing 8', the aforesaid screws of the second fastening means 7 are preferably mounted with the head in engagement on a preferably oblique portion directed towards the external environment of the profile 6' of the shaped frame 5'. - Otherwise, in accordance with the second embodiment illustrated in
figures 3A ,4A and8A , the aforesaid screws of the second fastening means 7 are preferably mounted with the head in engagement on the main external perimeter face A of the main faces and with the shank that, having traversed the thickness of theplank 3, is inserted in the profile 6' of the shaped frame 5'. In this manner, the screw remains hidden from view. In the case of the presence of an optional top frame pane or an optional bottom frame pane, first the fastening screws of the movable profiles 6' are fixed on the main external perimeter face A of the main faces, and only afterward will the fixedprofiles 6 be mounted on the latter face, to cover the fastening screws 7 of the movable profiles 6'. - In the case of an optional fixed
glass wing 8, the aforesaid screws of the second fastening means 7 are preferably mounted with the heads in engagement onbrackets 10 fittingly inserted ingrooves 11 obtained in a substantially counter-shaped manner on theprofiles 6 of the shapedframe 5.Such brackets 10 are angularly shaped in order to also cover the external edge of theprofiles 6 of the shapedframe 5 in a manner so as to act as abutment for theglass panel 80. - Advantageously, in one embodiment of the optional fixed
glass wing 8 not illustrated in the enclosed figures, a layer of structural sealant glue is interposed between theglass panel 80 and the external edge of theprofiles 6 of the shapedframe 5; i.e. a structural double-sided tape 9. - In order to allow the firm fixing of the
support cell 2 to thewall 16, at least one of itsconstituent planks 3, and normally all theplanks 3 that form the external perimeter (usually four planks) of thesupport cell 2, each comprise at least one main external face A of the main faces, which is susceptible to be fixed to the wall of a building by means of third fastening means 12. - The remaining face of the main faces of the
planks 3 to be considered internal, i.e. directed towards the opening delimited by thesupport cell 2, indicated with A' in the enclosed figures, bears, fixed, the shapedframe 5, 5' by means of the aforesaid second fastening means7. - Of course, in the case of planks of uprights and crosspieces within the external perimeter of the
support cell 2, in order to divide the support structure of thesupport cell 2 into substructures to which glass wings are associated, both the main faces A, A' of the planks are covered by shapedframes 5, 5'. - More in detail, the third fastening means 12 can be obtained with
brackets 13 per se entirely conventional and known to the man skilled in the art, and for this reason only indicated schematically in the single enclosedfigure 3 , relative to an upright of the exterior door or window 1 in a section view.Such brackets 13 rigidly connected theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2 to thewall 16. For such purpose, first screws 14 are provided for fixing the brackets to the wall. Advantageously, in accordance with the second embodiment illustrated infigure 3A , second screws 14' are provided for fixing thebrackets 13 to theplanks 3. - Advantageously, in accordance with the second embodiment illustrated in
figure 3A , thebracket 13 can advantageously provide for ribs 13' susceptible to be inserted incounter-shaped surface grooves 13" obtained along theplanks 3 in order to improve the mechanical engagement. Advantageously, between the main external face A of the main faces of theplanks 3 that form the external perimeter of thesupport cell 2 and thewall 16, a layer of insulatingmaterial 130 can be partially interposed. - The
wall 16 will for example comprise an external covering 160 (for example comprising a plaster layer) and an internal body obtained with twobrick walls 161 separated by an insulatinglayer 162. - Preferably, in accordance with the second embodiment illustrated in
figure 3A , the main external face A of the main faces, of theplanks 3, intended to be engaged with thebrackets 13, is provided with longitudinal grooves adapted to receive, in form engagement, counter-shaped portions of the brackets. - Advantageously, the
planks 3 of thesupport cell 2 are placed projecting from thewall 16 even if substantially hidden from view by the shapedframe 5, 5' and by the movable glass wing 8' or by the optional fixedglass wing 8. - The
planks 3 of thesupport cell 2 are extended with their width L into the thickness of the wall and therefore delimit a firstlateral edge 17, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figure is oriented towards the internal setting of the building, and a secondlateral edge 18, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figures is oriented towards the external setting of the building. - The latter
lateral edge 18 of theplank 3, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figures is oriented towards the outside environment, is covered by aprotection profile 23 made of aluminum fixed by means ofclips 24 with screw shank, to thesame plank 3, or, in accordance with a non-illustrated embodiment, by means of forced fitting of projecting portions of the protection profile in grooves of theplank 3. - The shaped
frame 5, 5' is fixed to a main face A' (or even to both the main faces A and A' for theplanks 3 that form intermediate uprights and crosspieces of the support cell 2) of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2, in particular substantially starting from the aforesaid firstlateral edge 17 of theplanks 3, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figures is oriented towards the internal environment. - The movable glass wing 8', in closed position, or the optional fixed
glass wing 8 substantially faces a main face A' (or even both the main faces A and A' for theplanks 3 which form intermediate uprights and crosspieces of the support cell 2) of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2, in particular substantially starting from the aforesaid secondlateral edge 18 of theplanks 3, which in particular in accordance with the enclosed figures is directed oriented towards the external environment. - The
support cell 2 mounts part of the fittings of the movable glass wing 8', constituted by mechanisms per se known to the man skilled in the art and for this reason not described in detail hereinbelow, in particular formed by support hinges for the movable glass wing 8' (as indicated with 20 infigure 8 ), by compass hinges for the movable glass wing 8' (as indicated with 21 infigures 3 and5 ), by lock bolt strikers, also perimeter, or by top-hung upper hinge systems (as indicated with 22 infigures 4 and6 with reference to engagement mechanisms). - The movable glass wing 8' is rotatingly supported by the
support cell 2 and comprises aglass panel 80 and asupport frame 81, which is perimetrically extended around theglass panel 80 and mounts the complements of the hinges or tilt and turn mechanisms provided on thesupport cell 2 in order to allow thesupport cell 2 to rotatably support the wing 8' itself. - Advantageously, the movable glass wing 8' has, externally associated on its external surface of the
support frame 81 directed towards the outside environment, a protection profile 23', it too preferably obtained with an extruded aluminum profile fixed to the aforesaid external surface by means ofclips 24 provided withhead 24' inserted in engagement inlongitudinal grooves 25 of the extruded aluminum profile 23' and with threadedshank 24" engaged for screwing into the aforesaid external surface of thesupport frame 81 of the wing 8'. Such protection profile 23' performs the function of externally fixing theglass panel 80 to the movable wing 8'. - As stated, the exterior door or window 1 optionally comprises the fixed
glass wing 8 and in this case it is advantageously rigidly fixed in abutment against the corresponding shapedframe 5 by means of fourth fixing means 90 and it can be obtained in a simple manner, only by aglass panel 80. - These fourth fixing means 90 preferably comprise one or multiple profiles, for example constituted by one or more aluminum extrusions fixed to the
planks 3 of thesupport cell 2 at their secondlateral edge 18 by means of screws orclips 24 and/or by means of male-female portions engaged with each other (solution non illustrated). - In accordance with one embodiment of the optional fixed
glass wing 8 illustrated in the enclosedfigures 3B ,5 ,6 and7 , aprotection profile 23 and aretention profile 23" can be provided. In particular, theprotection profile 23 is placed to cover the secondlateral edge 18 of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2. In particular, theretention profile 23" acts on the external edge of theglass panel 80 and is fixed to at least one main face A, A' of theplank 3 of thesupport cell 2. - Suitably, the
protection profile 23 is fixed on the secondlateral edge 18 of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2 by means ofclips 24 provided withhead 24' inserted in engagement inlongitudinal grooves 25 of theprotection profile 23 and with threadedshank 24" engaged via screwing on the external surface of theplank 3. In addition, theretention profile 23" is fixed to at least one main face A, A' of theplank 3 of thesupport cell 2 by means of screws. - In accordance with one embodiment of the optional fixed
glass wing 8 not illustrated in the enclosed figures, theprotection profile 23 fixed on the secondlateral edge 18 of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2 is also extended to cover the perimeter edge of theglass panel 80, also performing the simultaneous function of fixing thesame glass panel 80 to the shapedframe 5. Such extrudedaluminum profile 23 therefore performs both the function of fixing and that of external protection covering indicated above. - Advantageously, according to one embodiment of the present invention, in the case in which the
plank 3 is relative to a lower crosspiece of the exterior door or window 1, theprotection profile 23 defines at the front part of the lower edge of the glass panel, achannel 231 for the drainage of the water. - The latter advantageously receives the water from a
channel profile 230 that hits the main internal perimeter face A' of theplank 3, which is advantageously extended starting from the profile 6' of the shaped frame 5' of the movable glass wing 8' and has at least one portion tilted outward for the drainage of the water towards thechannel 231. - The
glass panel 80, for both types ofglass wing 8, 8', advantageously comprises, in a manner per se entirely conventional, an internal sheet and an external sheet, fixed to each other by a perimeter cord made of sealant material (e.g. of structural silicone) as well as spaced from the same internal sheet by means of a channel defining at least one double glazing together with the glass sheets. - The lower perimeter edge of the
glass panel 80 is inserted in a step defined between theplank 3 and theframe 5 in the case of the optional fixedglass wing 8 and in a step defined in thesupport frame 81 in the case of movable wing 8'. In the latter case, given that preferably the base of the step is externally tilted, on the profile of the support crosspiece it is provided to useplastic support brackets 232, e.g. with 6-9 cm length fixed with screws and shaped for compensating for such tilt and maintaining theglass panel 80 vertical. - A
perimeter channel 15 is preferably provided, fixed by means of screws 15' to the internal face 81' of thesupport frame 81 of the movable glass wing 8' which is opposed to the main face A' of the main faces of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2, in order to convey the humidity that condenses and the water that filters towards the outside of the door or window. Preferablysuch channel 15 is obtained with linear sections joined together at 90 degrees and suitably undercut in the superimposed parts. - Also forming an object of the present invention is a method for the production of an exterior door or window with exposed wood, in particular of the type described above in the different embodiments; in order to simplify the description, the same reference numbers and nomenclature will be maintained hereinbelow.
- The aforesaid method, according to the idea underlying the present invention, provides for the following operative steps.
- It is provided to produce planks of
structural plywood 3 by means of a first operation of cutting a panel of structural plywood with parallel cuts of predefined width L, obtaining planks ofstructural plywood 3 having substantially quadrangular section with at least two substantially flat main faces A, A', spaced by the thickness S of thesame planks 3, and parallel to the layers of the plywood. - The production of the planks of
structural plywood 3 also provides for a second operation of cutting the planks ofstructural plywood 3 to the required length L, in order to obtain the door or window with the desired size. - Then there is the operation of fixing together the ends of at least four planks
structural plywood 3 obtained with the above-specified cutting operations, by means of first fastening means 4. In this manner, asupport cell 2 is formed that is susceptible to be fixed securely to thewall 16 of a building. - Then there is an operation for fixing
profiles 6, 6' on at least one main face A, A' of theplanks 3 of thesupport cell 2 by means of second fastening means 7, fitting theprofiles 6, 6' to form a trajectory closed without interruption in order to obtain ashaped frame 5, 5'. - Then there is an operation for mounting at least one movable glass wing 8' on the
support cell 2 by means of fittings susceptible to movably support the movable wing 8' with respect to thesupport cell 2 between an open position, in which the movable wing 8' is arranged separated from the corresponding shaped frame 5' and a closed position, in which the movable wing 8' is arranged in abutment against the corresponding shaped frame 5'. - Optionally, an operation is provided for mounting at least one
fixed wing 8 mechanically constrained to the corresponding shapedframe 5 by means of a mechanical retention collaboration relation. - Preferably, the fixing of the shaped
frame 5, 5' to thesupport cell 2 occurs with screws having the head in engagement on the shapedframe 5, 5', in order to allow an easy removal thereof in case of substitution of glass wings of movable type 8' with other new wings. - A step is advantageously provided for provisionally covering the main faces A, A' of the
planks 3 of thecell 2, not intended for coupling to the wall, with a protection film 70 in order to allow thecell 2 to be installed in the presence of a work-site of a building (e.g. for fabrication, restoration, renovation or maintenance of the building), entirely free of projectingframes 5, 5' as well as glass wings 8' that could be damaged during the work-site activity. Due to the covering 70 and to the hardness of thecell 2, the latter is correctly protected from accidental damage, to which it could be subjected during normal work-site operations, and which could be due both to the dirtying with liquid substances (corrosive substances, lime, solvent paints or other items) and to mechanical impact, e.g. during the movement of normal equipment used in work-sites. - Once the most problematic work-site operations, with regard to the safety of the
cell 2, have been completed, a step is provided for removing the protection film 70 such that the aforesaid step can take place for fixing the shapedframe 5, 5' as well as the step for mounting the glass wings 8'. - Suitably, the exterior door or window 1 thus obtained comprises the
support cell 2, whose structure is dedicated to the static mechanical strength, the shapedframes 5, 5' and the at least one movable glass wing 8' susceptible to abut against the corresponding shaped frame 5'. Therefore, thesupport cell 2 is made withplanks 3 of structural plywood having the main faces A, A' substantially flat and lacking processing and adapted to sustain mechanical stresses (derived from the stresses for supporting the door or window on the wall, from the stresses transmitted to thesupport cell 2 by the wing, etc.), while the shapedframes 5, 5' are made of a softer material, mechanically less performing than the structural plywood of theplanks 3 and adapted to be processed in order to define the abutment with the corresponding wing and the mounting seats of the seals. - The finding thus conceived therefore attains the pre-established objects.
- Of course, in the practical attainment thereof, it can also assume forms and configurations that are different from that illustrated above, without departing from the present protective scope.
- In addition, all details can be substituted by technically equivalent elements and the size, shapes and materials employed can be of any type according to the needs.
Claims (13)
- Exterior door or window with exposed wood characterized in that it comprises:- at least one support cell (2) susceptible to be fixed securely to the wall (16) of a building, provided with four or more planks (3) of structural plywood, having a substantially quadrangular section with two substantially flat main faces (A, A') spaced from each other by the thickness (S) of said planks (3), parallel to the layers of said plywood, and connected together at least at the ends by means of first fastening means (4) in order to form said support cell (2);at least one shaped frame (5, 5'), formed by multiple profiles (6, 6') fixed together in a continuous manner by means of second fastening means (7) on at least one substantially flat main face (A, A') of said planks (3) of said support cell (2);
at least one wing (8') movable between a closed position and an open position, mounted on said support cell (2) and susceptible to abut against the corresponding shaped frame (5') in closed position. - Exterior door or window as claimed in claim 1, characterized in that at least one plank (3) of said support cell (2) comprises at least one main internal face (A'), on which said shaped frame (5, 5') is fixed by means of said second fastening means (7), and at least one main external face (A), which is suitable to be fixed to the wall (16) of a building by means of third fastening means (12).
- Exterior door or window as claimed in claim 1, characterized in that said shaped frame (5, 5') is fixed to at least one said main face (A, A') of the planks (3) of said support cell (2), in particular substantially starting from a first lateral edge (17) of said planks (3), said movable wing (8, 8') in closed position substantially facing said main face (A, A') starting from a second lateral edge (18) of said planks (3).
- Exterior door or window as claimed in claim 1, characterized in that said second fastening means (7) consist of screws, the head of which being engaged in said shaped frame (5, 5').
- Exterior door or window as claimed in claim 1, characterized in that at least some of the fittings of said movable wing (8, 8') are mounted on said support cell (2), in particular fittings of the type comprising: support hinges for said mobile wing (8'); compass hinges for said mobile wing (8'); lock bolt strikers; tilt and turn systems; top-hung hinge systems, perimeter protection systems.
- Exterior door or window as claimed in claim 1, characterized in that said movable wing (8') is rotatingly supported by said support cell (2) and comprises a glass panel (80) and a support frame (81) of said glass panel (80) susceptible to abut against the corresponding shaped frame (5') with the interposition of at least a seal (82).
- Exterior door or window as claimed in claim 1, characterized in that it comprises at least one fixed wing (8), rigidly fixed in abutment against the corresponding frame (5) by fourth fastening means (90), in particular comprising at least one retention profile (23) fixed to the planks (3) of said support cell (2) at their second lateral edge (18).
- Exterior door or window as claimed in any of the preceding claims, characterized in that said planks (3) of structural plywood are made of marine plywood.
- Exterior door or window as claimed in any of the preceding claims, characterized in that the structural plywood of the planks (3) of said support cell (2) is provided with greater mechanical strength than the wood of said profiles (6, 6') of said shaped frame (5, 5').
- Method of production of an exterior door or window with exposed wood, comprising the following steps:production of planks of structural plywood (3) by means of:- cutting a panel of structural plywood by means of parallel cuts having a predefined width (L) to obtain planks of structural plywood (3) having a substantially quadrangular section with at least two substantially flat main faces (A, A') spaced by the thickness (S) of said planks themselves, and parallel to the layers of said plywood;- cutting of said structural plywood (3) to the required length;fixing together the ends of four or more planks of structural plywood (3) thus obtained by means of first fastening means (4) in order to form a support cell (2) susceptible to be fixed securely to the wall (16) of a building,- by means of second fastening means (7), fixing profiles (6, 6') on at least one substantially flat main face (A, A') of the planks (3) of said support cell (2), fitting them in a continuous manner to obtain a shaped frame (5, 5');- mounting at least one movable wing (8') on said support cell (2), by means of fittings susceptible to movably support said movable wing (8') with respect to said support cell (2) between an open position and a closed position, wherein said movable wing (8') is in abutment against said shaped frame (5').
- Method of production of an exterior door or window as claimed in claim 10, wherein said shaped frame (5, 5') is fixed to said support cell (2) by means of said second fastening means (7) comprising screws, the head of which being engaged in said shaped frame (5, 5').
- Method of production of an exterior door or window as claimed in claim 10 or 11, wherein said step of fastening said planks of structural plywood (3) to form one said support cell (2) is followed by a step in which said support cell (2) is installed in the wall of a building and a subsequent step of provisionally covering the substantially flat main surfaces (A, A') of the planks (3) of said support cell (2) to which said profiles (6, 6') are to be fixed, in order to prevent them from being damaged during activities at the work-site.
- Method of production of an exterior door or window as claimed in claim 12, wherein said step of fixing said profiles (6, 6') on at least one of said main faces (A, A') of said support cell (2) is preceded by a step in which said protective covering (70) is removed.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT000163A ITPD20130163A1 (en) | 2013-06-05 | 2013-06-05 | CLOSURE WITH VIEW WOOD AND METHOD FOR ITS REALIZATION |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2811099A1 true EP2811099A1 (en) | 2014-12-10 |
Family
ID=49000556
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14163937.7A Withdrawn EP2811099A1 (en) | 2013-06-05 | 2014-04-08 | Exterior door or window with exposed wood and method for the production thereof |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2811099A1 (en) |
| IT (1) | ITPD20130163A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104879038A (en) * | 2015-03-19 | 2015-09-02 | 陈金大 | Wood door leaf component, wood door leaf and manufacturing method of wood door leaf |
| IT201800001548A1 (en) * | 2018-01-19 | 2019-07-19 | Uniform S P A | WINDOW FOR EXTERIORS |
| CN114986627A (en) * | 2022-06-27 | 2022-09-02 | 福建茂增木业有限公司 | Anti-fracture aldehyde-free plywood and process thereof |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE202004014618U1 (en) | 2004-09-20 | 2004-11-18 | Holzbau Schmid Gmbh & Co. Kg | Fire-resistant glazing |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE8701724U1 (en) * | 1987-02-05 | 1987-04-02 | Winkler, Klaus Dieter, 71229 Leonberg | Bullet-proof door element |
-
2013
- 2013-06-05 IT IT000163A patent/ITPD20130163A1/en unknown
-
2014
- 2014-04-08 EP EP14163937.7A patent/EP2811099A1/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE202004014618U1 (en) | 2004-09-20 | 2004-11-18 | Holzbau Schmid Gmbh & Co. Kg | Fire-resistant glazing |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104879038A (en) * | 2015-03-19 | 2015-09-02 | 陈金大 | Wood door leaf component, wood door leaf and manufacturing method of wood door leaf |
| IT201800001548A1 (en) * | 2018-01-19 | 2019-07-19 | Uniform S P A | WINDOW FOR EXTERIORS |
| EP3514309A1 (en) * | 2018-01-19 | 2019-07-24 | Uniform S.p.A. | Outdoor window |
| US10995542B2 (en) | 2018-01-19 | 2021-05-04 | Uniform S.P.A. | Outdoor window |
| CN114986627A (en) * | 2022-06-27 | 2022-09-02 | 福建茂增木业有限公司 | Anti-fracture aldehyde-free plywood and process thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ITPD20130163A1 (en) | 2014-12-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10718151B2 (en) | Door assembly | |
| US9766045B2 (en) | Security door | |
| CA2691116C (en) | Reinforced mull post assembly | |
| US10801248B2 (en) | Door assembly | |
| EP2594720B1 (en) | Window and door frames that can be covered with various materials made of thermoplastic, weldable material | |
| EA018965B1 (en) | Profile system for a sliding door | |
| EP2811099A1 (en) | Exterior door or window with exposed wood and method for the production thereof | |
| US7836643B2 (en) | Window | |
| US20140130448A1 (en) | Door with assembly of stiles and rails | |
| US10648226B2 (en) | Main-frame bar and/or wing-frame bar, and door, window, or façade element | |
| AU2015101579A4 (en) | Lightweight High Tech Door | |
| NO309057B1 (en) | window Construction | |
| CA3081504A1 (en) | Exterior door and methods for forming exterior doors | |
| HRP20100129A2 (en) | Casement for a glass window or leaf for a glass door, window or door frame and window system | |
| US10590696B2 (en) | Sill track seal for a window frame | |
| US20200032575A1 (en) | Male and female gasket coupling for a window frame | |
| CN211173810U (en) | Three-layer composite heat insulation window | |
| KR101218930B1 (en) | System doorframe assembly | |
| US10731402B2 (en) | Jacking screw for adjusting a window frame | |
| US20070193704A1 (en) | Overhead Wood Door With Inset Strut, and Methods | |
| US10844651B2 (en) | Compression gasket for sealing a window in a window frame | |
| US20080141600A1 (en) | Molding system for accordion hurricane shutters | |
| US6301852B1 (en) | Window glazing assembly | |
| US11634941B2 (en) | Window/shutter/door for outdoor settings | |
| US20230248149A1 (en) | Cabinet enclosure and cabinet door with expansion gaps and related methods |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20140408 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20150611 |