EP1201594A1 - Telekopiersystem eines Kranauslegers - Google Patents
Telekopiersystem eines Kranauslegers Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1201594A1 EP1201594A1 EP00420221A EP00420221A EP1201594A1 EP 1201594 A1 EP1201594 A1 EP 1201594A1 EP 00420221 A EP00420221 A EP 00420221A EP 00420221 A EP00420221 A EP 00420221A EP 1201594 A1 EP1201594 A1 EP 1201594A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- actuator
- block
- locking
- telescoping
- immobilizing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66C—CRANES; LOAD-ENGAGING ELEMENTS OR DEVICES FOR CRANES, CAPSTANS, WINCHES, OR TACKLES
- B66C23/00—Cranes comprising essentially a beam, boom, or triangular structure acting as a cantilever and mounted for translatory of swinging movements in vertical or horizontal planes or a combination of such movements, e.g. jib-cranes, derricks, tower cranes
- B66C23/62—Constructional features or details
- B66C23/64—Jibs
- B66C23/70—Jibs constructed of sections adapted to be assembled to form jibs or various lengths
- B66C23/701—Jibs constructed of sections adapted to be assembled to form jibs or various lengths telescopic
- B66C23/708—Jibs constructed of sections adapted to be assembled to form jibs or various lengths telescopic locking devices for telescopic jibs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66C—CRANES; LOAD-ENGAGING ELEMENTS OR DEVICES FOR CRANES, CAPSTANS, WINCHES, OR TACKLES
- B66C23/00—Cranes comprising essentially a beam, boom, or triangular structure acting as a cantilever and mounted for translatory of swinging movements in vertical or horizontal planes or a combination of such movements, e.g. jib-cranes, derricks, tower cranes
- B66C23/62—Constructional features or details
- B66C23/64—Jibs
- B66C23/70—Jibs constructed of sections adapted to be assembled to form jibs or various lengths
- B66C23/701—Jibs constructed of sections adapted to be assembled to form jibs or various lengths telescopic
- B66C23/705—Jibs constructed of sections adapted to be assembled to form jibs or various lengths telescopic telescoped by hydraulic jacks
Definitions
- the present invention relates to the technical field of arrows telescopic cranes, whether stationary or carried by self-propelled mobile structures or not.
- the telescopic arrows are the most generally mounted on a turret swiveling in azimuth relative to a load-bearing structure and on which the turret is articulated in elevation, an arrow consisting of at least three separate telescopic elements.
- the first element is said to be basic and is generally linked to the axis of articulation in site
- the second element is said to be intermediate
- the third is said external and most often carries at least one jib head pulley.
- an arrow of the above type provided for the existence of technical means capable of making telescoping possible under load, so as to be able to offer a range of adjustment relative to plumb with a determined point in relation to which the load was to be mounted, lowered, placed or removed.
- Such means are particularly expensive, must be designed so very robust and be very carefully maintained so that the essential function first can be safely assumed.
- such means represent an important mass which strikes the functional capacities of the arrow.
- This technique consists in assessing a priori the scope to be conferred on the arrow so that it can, from its implantation site, reach the vertical pick-up or drop-off point, or even the geometric location, for example for circular part, which this point is likely to follow and then to adjust the boom length.
- a rectilinear displacement actuator inside a telescopic boom which is, for example, linked to the basic element and made relatively mobile by compared to the extreme element.
- such an actuator is constituted by a hydraulic cylinder of the double acting type with predetermined single stroke which generally corresponds the longest re-entry or exit run that any one can mobile elements, except of course the basic element considered as fixed.
- the first is that of being able to keep the elements locked telescopic to each other in the retracted or extended position.
- the second is the need to be able to selectively manage one any of the telescopic elements to ensure separation from it to the position it occupies and then drive to the new position sought to the right of which a new lock must occur.
- this technology involves sets of interlocking and supporting members which overlap and must be the subject of an energy supply based on pressurized fluid, the distribution must be perfectly synchronized to obtain the desired result which happens, for example, during a telescoping out, necessarily by respecting a sequence of taking charge of the element concerned, then unlocking this element before engaging its relative sliding until the new position where a Lock must be re-established.
- German application DE 43 44 795 can also be cited, in which between the actuator and each of the telescopic elements, means are provided for support of the same order as the previous request and means of locks which consist of the engagement of pins to be controlled separately during erasure or withdrawal to free an element from another.
- Such technology which may appear lighter technically than that of the previous request, however, involves always implementing two types of actuators capable of selectively performing the linkage function between the actuator and any of the elements to be moved and the separation of said element to be moved relative to the next.
- the object of the invention is to propose a new telescoping technique and new means of implementation, in order to be able to carry out in all safety the above functions from a reduced weight equipment.
- An object of the invention is to be able to transfer, for the benefit of the realization of the arrow, the gain of weight thus obtained in order to reinforce the effectiveness of the latter without in total the overall mass can be considered changed to the point of reducing capacity functional.
- the object of the invention is to propose a new technique and new means of implementation which make it possible, from the combination of two technical means cooperating with each other, the two functions which, hand, are the takeover or temporary coupling between the actuator and one telescopic elements to be moved and, on the other hand, unlocking the latter relative to the element that surrounds it to allow its relative displacement and, conversely, the opposite functions when it is appropriate to immobilize in the new position sought any of the elements moved in order to then authorize its uncoupling from the actuator.
- the subject of the invention is also an arrow making use of the means precedents.
- Fig. 1 is a schematic view illustrating an example of an arrow concerned by the means according to the invention.
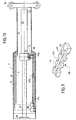
- Fig. 2 is a schematic sectional elevation of a telescopic boom according to the invention.
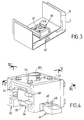
- Fig. 3 is a partial perspective, on a larger scale, illustrating a constructive detail.
- Fig. 4 is a perspective showing more detail in FIG. 3.
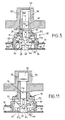
- Fig. 5 is a partial sectional elevation taken, on a different scale, along the plane VV of FIG. 4.
- Fig. 6 is a partial perspective similar to FIG. 4 .
- Fig. 7 is a partial perspective even more stripped down, according to FIG. 6.
- Fig. 8 is a schematic, partial cross-section showing, on a larger scale, certain characteristic details.
- Fig. 9 is a perspective showing, on a different scale, a constructive detail.
- Fig. 10 is a schematic elevation, on a smaller scale, illustrating a functional position.
- Fig. 11 is a sectional elevation corresponding to FIG. 5 but showing another characteristic position.
- Fig. 12 is a sectional elevation taken substantially along the plane XII-XII of FIG. 4.
- Fig. 13 is a partial perspective of an organ of a constructive variant.
- FIG. 14 and 15 are schematic sectional elevations similar to FIG. 2 but illustrating two alternative embodiments.
- Fig. 16 is a partial sectional elevation showing, on a different scale, an alternative embodiment of one of the constituent elements of the device of the invention.
- Fig. 1 shows an example of application of the object of the invention to a crane of the mobile and self-propelled type. Such an example is provided for illustrative purposes only, because the object of the invention could be implemented just as well on a crane installed at a fixed station, or even on a similar installation.
- the crane according to fig. 1 comprises a platform or a chassis 1 carried by rolling bodies 2 constituted, for example in a known manner, by several power steering trains.
- the platform or chassis 1 comprises a driving cabin 3 housing one or more engine and / or propulsion units.
- Lateral stabilizers 4 are provided on the chassis 1, substantially in line with the front and rear parts, to give a stable attitude when the crane is put into service.
- the platform 1 also includes a turret 5 which is orientable in azimuth on a vertical axis x-x ' .
- This turret 5 carries, by a horizontal articulation axis 6, an arrow 7 which is orientable in elevation by means of a jack 8.
- the arrow 7 is constituted by telescopic elements, for example four in number, of which the first 9, called basic, is directly carried by the axis 6.
- the elements 10 and 11 are said to be intermediate, while the element 12 is said to be extreme and carries at least one jib head pulley 13.
- the arrow 7 is completed by at least one cable or the like 14 wound and / or unwound from a winch 15 and passing over the pulley 13 beyond which such a cable ensures the suspension of a load 16.
- the turret 5 is, moreover, equipped with a so-called boom 18 cabin which allows the actuation of the actuation means of the latter such as the jack 8, the winch 15, as well as a telescoping means 19 included in the arrow 7 and shown in dashed lines in FIG 1.
- a telescoping means such as 19 must be considered in absolute terms as pertaining to the known technique, while the means according to the invention are provided to make it possible, from such a telescoping means 19, the re-entry and the individual exit of each of the mobile telescopic elements, namely 10, 11, 12 and the immobilization of each of them in an extended position and in the retracted position.
- the means according to the invention involve a device which is able to allow the implementation of the telescoping method according to the invention as described below with reference in particular to FIG. 2 .
- Such a device comprises, first of all, the actuator 19 which is constituted so as to have, on the one hand, a fulcrum 20 in relation to the base element 9 and, on the other hand, a mobile element 21 capable of being driven by a displacement in alternative rectilinear travel parallel to the axis YY 'of the arrow.
- the actuator 19 is aligned on such an axis.
- the actuator 19 is constituted by a hydraulic cylinder of the double-acting type, with a single stage or with a single stroke, the rod 22 of which is integral with the fulcrum 20, while the body 23 is linked to the mobile element 21 and is adapted to be carried, with the possibility of relative guided movement, by the extreme element 12.
- a possibility can, for example, be ensured by means of a foot 24 provided rollers or the like 25 capable of cooperating with a guide track, not shown.
- an actuator 19 of the above type can be considered, although its position is reversed, as not posing any problem of hydraulic supply for the skilled person and this is the reason why the pipes supplying the two chambers of such a jack are not illustrated in the drawings.
- the mobile element 21 is constituted by a telescoping head which is advantageously integrated into the bearing of the jack body 23 opposite the bottom of the latter.
- the telescoping device according to the invention further comprises a part, locking members between the telescopic elements to immobilize them relatively in retracted and extended positions and, on the other hand, means carried by the actuator to control these organs.
- each locking block 30 carried by the inner end portion of each telescopic element 10, 11 , 12.
- Each locking block 30 defines, as shown in Figs. 3 and 4, a well 31 opening from the upper face 32 of the block 30 and opening into a cage 33 containing a clamping member 34 in a tight rest position constituted by two jaws 35 which are biased always towards the one from the other by elastic members 36 (Fig. 5).
- the jaws 35 are arranged opposite by opposite facing faces which are situated on either side of a longitudinal median plane PP 'passing through the axis Y-Y'.
- Each block 30 also comprises a pusher 37 intended to cooperate with the jaws 35.
- the pusher 37 comprises for this purpose a shank 37 1 guided in the well 31 and whose actuating face 37 2 is oriented in the direction of the face 32.
- the tail 37 1 is extended by a head 37 3 disposed in the cage 33 to cooperate by inclined faces 38 with ramps 39 which have the jaws 35 opposite .
- all the locking members 30, as described above, of the telescopic elements are organized so that the actuating faces 37 2 of the pushers 37 are aligned along a line or a plane such that L which is parallel to the y-y 'axis.
- the pushers 37 provided with a tail 37 1 of length such that the face 37 2 of each is established in the plane or on the line L in the clamping position of the clamp 34 as shown in the following.
- Each locking member further comprises at least one immobilizing part 40 in a fixed position which belongs to the telescopic element externally surrounding the one carrying the locking block 30 with which it must cooperate.
- Such an immobilization piece 40 is, for example, advantageously constituted by a profile segment intended to be trapped and clamped by the faces facing the jaws 35 .
- the faces facing the jaws 35 are advantageously shaped in a manner conjugate with the sides of the part 40 on which the jaws 35 are pressed by the springs 36.
- the part 40 is formed in the form of a double rack with asymmetrical teeth 41 formed in opposition on the two longitudinal edges of the part.
- the asymmetrical teeth each have a face 42 substantially orthogonal to the longitudinal axis of the part 40 and an inclined face 43 .
- the part 40 is carried by the telescopic element so that the faces 42 are oriented in the direction of the arrow head. Because of this double rack shape, the opposite faces of the jaws 35 are provided with complementary conformations 44 conjugated to the teeth 41 (FIG. 7).
- each block 30 has in its lower part a groove 45 (fig. 4).
- each part 40 is fixed to the telescopic element which corresponds to it in order to determine, when cooperating with the corresponding block 30 of the telescopic element which is internal to it, a fixed position.
- each element 9, 10 and 11 has internally two immobilizing parts 40 defining two positions of cooperation for the corresponding immobilizing block 30 of the immediately internal element, ie 10 , 11 and 12. These two positions correspond respectively to the retracted position determined by the immobilizing part 40 1 and at an exit position determined by the immobilizing part 40 2 .
- each element 9, 10 or 11 may also include other immobilizing parts such as 40 3 intended to each determine an intermediate position.
- Fig. 8 shows that according to an alternative embodiment, as illustrated in phantom, the immobilization part 40 can, in reality, be constituted by an uninterrupted profile 40 4 running over the entire useful length of each element 9, 10 or 11 or some of them, so as to define, as will be highlighted later, the extreme re-entry and exit positions, as well as n intermediate positions.
- the profile 40 4 meets the constructive arrangements described above for the part 40.
- the device according to the invention also comprises means carried by the actuator 19 for controlling the members described above.
- Such means designated as a whole by the reference 50 (fig. 2, 5 and 8), are qualified as mobile and are provided in relation to the telescoping head 21 carried by the jack body 23 in the example illustrated.
- these means 50 comprise a member 51 capable of occupying two relative positions under the action of a motorization member 52. The first of these positions is that called erasure or retraction and the the second is said to be taking over or coupling when the member 51 is able to cooperate with the locking block 30 of one of the mobile telescopic elements 10, 11 or 12.
- the member 51 is also intended to act on the clamping member 34 of each block 30 so as to neutralize, by positive action, its clamping function to release the locking block 30 relative to the part. immobilizer 40 with which it cooperates.
- the member 51 is designed to assume two functions which take place as described in the following.
- the member 51 is constituted by a pin formed for example by the piston rod of a jack constituting the driving member 52 .
- the drive member comprises a jack body 53 which is fixed to the telescoping head 21 so that the pin 51 can be engaged in the well 31 of one of the locking blocks 30 in its exit position to exert pressure on the corresponding pusher 37 .
- the device according to the invention can also advantageously involve a reading cell 60 ( fig. 2 and 8) carried by the telescoping head 21 and able to appreciate the presence of position sensors 61 adapted on the internal walls of the elements 9, 10 and 11, as illustrated in FIG. 2.
- the position of the sensors 61 is determined to correspond to the position of the immobilizing parts 40 1 as well as to a position p of maximum retraction and of deactivation of the actuator 19.
- the cell 60 is, moreover, also intended determining the presence of position sensors 62 which are provided to correspond to the immobilizing parts 40 2 .
- intermediate position sensors could be provided in relation to the parts 40 3 or with certain positions which can be defined from the part 40 4 .
- the device described above makes it possible to implement the method of telescoping which takes place according to the invention as follows.
- each movable telescopic element namely 10, 11, 12 cooperates with the corresponding immobilizing part 40 1 carried by the immediately external element, namely 9 for the element 10 respectively.
- 10 for element 11 and 11 for element 12 in a relational situation illustrated by FIG. 5 .
- the springs 36 of each block 30 press the jaws 35 on either side of the corresponding immobilizing part 40 which is trapped firmly.
- each element is immobilized axially with respect to the immediately external element surrounding it and cannot be subjected to any sliding backwards, even if the arrow is tilted in elevation, due to the shape of the teeth 41 of the double rack 40.
- the telescopic elements are all immobilized relatively in the retracted position and remain immobilized in such a state of passive safety since the clamping members 34 are of the type with a tight rest position.
- the actuator 19 occupies, for example, the out-of-service position shown in phantom and corresponding to the position sensor p in a state of maximum retraction.
- the actuator 19 is controlled so as to move the telescoping head 21 to the level of the corresponding locking block 30 which is detected by the reading of the position sensor 61 carried by the telescopic element 12.
- the supply of the jack 52 is ensured so that the extension of the spindle 51 occurs over a length such that the latter presses on the actuating face 37 2 of the pusher 37 which controls, against the opposing action of the springs 36, l spacing of the jaws 35 releasing the immobilizing part 40 .
- the spindle 51 temporarily secures the actuator 19 and the movable element to be moved, and secondly, releases the latter relative to the immediately external element relative to which it was immobilized.
- the actuator 19 is then controlled to be moved, for example, in the direction of the arrow f 1 (fig. 2) according to the sequence taken into account, so that its extension causes the movement in the same direction of the element mobile 12 which is telescoped into the extended position.
- the supply or the control of the actuator 19 intervenes until the cell 60 detects the position of the sensor 62 carried by the element 11.
- the jack 52 is supplied to cause the retraction of the spindle 51 .
- the actuator 52 may be of the single direction, as illustrated in the drawing or of the double effect. It can of course be implemented any type of engine capable of ensuring the same function.
- the retraction stroke of the spindle 51 produces, in a second step and after complete retraction, a decoupling relative to the locking block 30, so that the temporary connection between the telescoping head 21 and said block is broken.
- the telescoped element at the outlet, in this case element 12, is again immobilized with respect to the surrounding element, in this case 11, while the actuator 19 is uncoupled from it and it can be controlled in reverse to regain position p.
- the block 30 is mounted floating in or on the telescopic element which carries it.
- a floating assembly can for example be established as shown in FIGS. 3 and 5 by providing the block with grooves 63 intended to cooperate with a housing 64 formed in the corresponding telescopic element so as to leave a clearance J transverse to the longitudinal axis y-y '.
- Such a floating assembly has the advantage of admitting an adaptation of cooperation between the members 30 and 40 and 30 and 50 despite the possible lateral deflections of the telescopic elements.
- Figs. 4, 6, 7, 12 and 13 show that according to another advantageous arrangement, it can be provided to provide each block 30 with means immobilizing the jaws against any movement in opening other than that controlled by the pushers 37.
- each block 30 is provided to surround the two jaws 35 with two half-hoops 66, arranged in the block 30 with the interposition of springs 67 urging them to engage the jaws by shoulders 68 which they form opposite.
- Each half-hoop comprises at least one spur 69 offering an inclined ramp 70 placed in a relationship of vertical cooperation with at least one complementary projection 71 presented by the head 37 3 .
- the projection 71 acts on the ramp 70 which pushes the half-hoop in order to release the subsequent movement in opening the jaws 35 under the action of the head 37 3 .
- Fig. 14 shows an alternative embodiment in which the actuator 19 consists of an endless screw 80 which is linked via a geared motor group 81 to the fixed part 20 which can then advantageously constitute a bearing for the one end of the screw, the other of which is mounted in a housing 82 carried by the foot 24 .
- the telescoping head 21 then constitutes a threaded body 83 cooperating with the worm 80 and which is immobilized in rotation for example between guides 84 connecting the fixed bearing 20 to the housing 82.
- Fig. 15 shows another alternative embodiment in which the actuator 19 is constituted by an endless chain 90 carried by pinions 91 and 92 , one of which is said to be reference and the other of which is said to be drive due to its connection with a drive member 93 such as a hydraulic or electric gear motor.
- a drive member 93 such as a hydraulic or electric gear motor.
- the pinions 91 and 92 are preferably carried by a frame-beam 94 meeting the previous requirements for securing with the fixed point 20 and for guiding in relative displacement relative to the element 12 by means of the foot 24, or even of the rollers 25.
- the telescoping head 21 can then advantageously be formed only by the body 53 of the motor member actuating the spindle 51.
- each member 51 in the form of a telescopic jack with two rods, one assuming the coupling function and the other the control function of the pushers 37.
- An example of embodiment is shown in FIG. 16 according to which the body 53 delimits a cylinder 95 containing a piston 96 extended by a rod 97 responsible for penetrating into the well 31 to assume the coupling function with the block 30.
- the rod 97 delimits a cylinder 98 containing a secondary piston 99 extended by a rod 100 responsible for acting on the face 37 2 of the pusher 37.
- FIG. 16 shows by lines in thick dotted lines that the cylinders 95 and 98 can constitute double-acting cylinders.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Jib Cranes (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR9911102A FR2797862B1 (fr) | 1999-09-01 | 1999-09-01 | Procede de telescopage d'une fleche de grue, dispositif pour sa mise en oeuvre et fleche de grue en faisant application |
| EP00420221A EP1201594B1 (de) | 1999-09-01 | 2000-10-26 | Telekopiersystem eines Kranauslegers |
| DE60023506T DE60023506T2 (de) | 2000-10-26 | 2000-10-26 | Telekopiersystem eines Kranauslegers |
| US09/709,736 US6474486B1 (en) | 1999-09-01 | 2000-11-13 | Method of telescoping a crane jib, apparatus for implementing the method, and a crane jib constituting an application thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR9911102A FR2797862B1 (fr) | 1999-09-01 | 1999-09-01 | Procede de telescopage d'une fleche de grue, dispositif pour sa mise en oeuvre et fleche de grue en faisant application |
| EP00420221A EP1201594B1 (de) | 1999-09-01 | 2000-10-26 | Telekopiersystem eines Kranauslegers |
| US09/709,736 US6474486B1 (en) | 1999-09-01 | 2000-11-13 | Method of telescoping a crane jib, apparatus for implementing the method, and a crane jib constituting an application thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1201594A1 true EP1201594A1 (de) | 2002-05-02 |
| EP1201594B1 EP1201594B1 (de) | 2005-10-26 |
Family
ID=27223626
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00420221A Expired - Lifetime EP1201594B1 (de) | 1999-09-01 | 2000-10-26 | Telekopiersystem eines Kranauslegers |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6474486B1 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP1201594B1 (de) |
| FR (1) | FR2797862B1 (de) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104528541A (zh) * | 2014-12-15 | 2015-04-22 | 徐州重型机械有限公司 | 一种单缸插销式起重机油缸防过伸装置 |
| CN106185653A (zh) * | 2016-09-12 | 2016-12-07 | 周明凯 | 内置液压动力的同步伸缩臂 |
| CN109879183A (zh) * | 2019-03-13 | 2019-06-14 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 吊臂的节臂尾部滑块的定位方法、定位装置及定位套件 |
| CN113682983A (zh) * | 2021-09-09 | 2021-11-23 | 大洋泊车股份有限公司 | 一种登高平台消防车伸缩臂稳固系统 |
Families Citing this family (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2797862B1 (fr) * | 1999-09-01 | 2001-11-16 | Ppm | Procede de telescopage d'une fleche de grue, dispositif pour sa mise en oeuvre et fleche de grue en faisant application |
| DE10104310B4 (de) * | 2001-01-22 | 2005-02-03 | Terex-Demag Gmbh & Co. Kg | Fahrzeugkran mit Teleskopausleger |
| DE202004008083U1 (de) | 2004-05-19 | 2005-11-10 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh | Mobilkran |
| CN100567132C (zh) * | 2007-06-19 | 2009-12-09 | 李海青 | 轻型折臂式塔机起升-折臂机构的钢丝绳固定装置 |
| EP2268566B1 (de) * | 2008-04-22 | 2015-08-26 | Lift Systems, Inc. | Integrierte keilverriegelungsanordnung |
| DE102009009944B4 (de) * | 2009-02-20 | 2011-02-24 | Terex-Demag Gmbh | Sicherungs- und Verbolzungseinheit |
| JP5738977B2 (ja) * | 2010-04-01 | 2015-06-24 | パー システムズ, インコーポレイテッド | 張力トラスマスト |
| CN102153023B (zh) * | 2011-04-07 | 2013-09-25 | 大连理工大学 | 起重机用插销互锁装置、单缸插销式伸缩臂及起重机 |
| CN102735172B (zh) * | 2012-06-25 | 2015-04-01 | 三一重工股份有限公司 | 臂长测量装置及测量方法、伸缩臂架 |
| WO2014047449A1 (en) | 2012-09-21 | 2014-03-27 | Par Systems, Inc. | Boat deployment assembly and method |
| US10494233B2 (en) | 2013-02-06 | 2019-12-03 | Par Systems, Llc | Relocatable fine motion positioner assembly on an overhead crane |
| DE102013006259B4 (de) * | 2013-04-11 | 2024-09-12 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh | Teleskopausleger und Kran |
| DE102013011173B4 (de) * | 2013-07-04 | 2019-05-23 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh | Verfahren zur Montage eines Krans sowie Anlenkschuss, Teleskopausleger und Kran |
| JP6223071B2 (ja) * | 2013-08-30 | 2017-11-01 | 株式会社タダノ | クレーン装置のブーム伸縮機構 |
| CN105417409B (zh) * | 2015-12-29 | 2017-11-14 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 单缸插销式伸缩臂的检测方法、装置、系统及工程机械 |
| JP6668832B2 (ja) * | 2016-03-07 | 2020-03-18 | 株式会社タダノ | ブーム伸縮装置 |
| WO2017189439A1 (en) * | 2016-04-25 | 2017-11-02 | Manitowoc Crane Companies, Llc | Crane with rotary locking mechanism |
| JP7034685B2 (ja) * | 2017-11-30 | 2022-03-14 | 株式会社加藤製作所 | クレーンのブーム伸縮装置の制御装置 |
| CN108750976A (zh) * | 2018-07-02 | 2018-11-06 | 合肥市春华起重机械有限公司 | 一种新型伸缩式旋臂起重机 |
| EP3950565A4 (de) * | 2019-04-04 | 2023-01-04 | Tadano Ltd. | Arbeitsmaschine |
| US11958726B2 (en) * | 2019-04-04 | 2024-04-16 | Tadano Ltd. | Work machine |
| JP7226184B2 (ja) * | 2019-08-21 | 2023-02-21 | 株式会社タダノ | 作業機 |
| JP7279579B2 (ja) * | 2019-08-21 | 2023-05-23 | 株式会社タダノ | 作業機 |
| CN111908356B (zh) * | 2020-07-30 | 2022-06-14 | 杭州瑞林机械有限公司 | 一种可伸缩式的施工塔吊臂 |
| CN112777498B (zh) * | 2021-03-23 | 2022-07-05 | 三一汽车起重机械有限公司 | 一种伸缩臂结构及起重机 |
| CN118637490A (zh) * | 2024-08-15 | 2024-09-13 | 中铁三局集团有限公司 | 一种辙岔专用吊装设备 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2708584A1 (fr) * | 1993-08-06 | 1995-02-10 | Ppm | Dispositif de commande sélective du déplacement simultané ou télescopique synchronisé de deux éléments constitutifs d'une flèche télescopique de grue. |
| DE4344795A1 (de) * | 1993-12-28 | 1995-06-29 | Liebherr Werk Ehingen | Fahrbarer Kran mit einem Teleskopausleger |
| FR2797862A1 (fr) * | 1999-09-01 | 2001-03-02 | Ppm | Procede de telescopage d'une fleche de grue, dispositif pour sa mise en oeuvre et fleche de grue en faisant application |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE9013210U1 (de) * | 1990-09-18 | 1991-01-03 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh, 7930 Ehingen | Teleskopiersystem mit verringerter Knicklänge des Teleskopierzylinders |
| EP0488990A1 (de) * | 1992-02-01 | 1992-06-03 | Krupp Industrietechnik Gmbh | Teleskopierbarer Ausleger mit Einspindel-Antrieb |
| DE29824453U1 (de) * | 1997-05-28 | 2001-03-01 | Mannesmann AG, 40213 Düsseldorf | Kran mit einem Teleskopausleger |
| DE19811813B4 (de) * | 1998-03-18 | 2005-11-24 | Grove U.S. LLC (n.d.Ges.d.Staates Delaware) | Seitliche Auslegerverriegelung |
-
1999
- 1999-09-01 FR FR9911102A patent/FR2797862B1/fr not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2000
- 2000-10-26 EP EP00420221A patent/EP1201594B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-11-13 US US09/709,736 patent/US6474486B1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2708584A1 (fr) * | 1993-08-06 | 1995-02-10 | Ppm | Dispositif de commande sélective du déplacement simultané ou télescopique synchronisé de deux éléments constitutifs d'une flèche télescopique de grue. |
| DE4344795A1 (de) * | 1993-12-28 | 1995-06-29 | Liebherr Werk Ehingen | Fahrbarer Kran mit einem Teleskopausleger |
| FR2797862A1 (fr) * | 1999-09-01 | 2001-03-02 | Ppm | Procede de telescopage d'une fleche de grue, dispositif pour sa mise en oeuvre et fleche de grue en faisant application |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104528541A (zh) * | 2014-12-15 | 2015-04-22 | 徐州重型机械有限公司 | 一种单缸插销式起重机油缸防过伸装置 |
| CN106185653A (zh) * | 2016-09-12 | 2016-12-07 | 周明凯 | 内置液压动力的同步伸缩臂 |
| CN106185653B (zh) * | 2016-09-12 | 2017-08-29 | 周明凯 | 内置液压动力的同步伸缩臂 |
| CN109879183A (zh) * | 2019-03-13 | 2019-06-14 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 吊臂的节臂尾部滑块的定位方法、定位装置及定位套件 |
| CN109879183B (zh) * | 2019-03-13 | 2020-05-15 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 吊臂的节臂尾部滑块的定位方法、定位装置及定位套件 |
| CN113682983A (zh) * | 2021-09-09 | 2021-11-23 | 大洋泊车股份有限公司 | 一种登高平台消防车伸缩臂稳固系统 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| FR2797862B1 (fr) | 2001-11-16 |
| FR2797862A1 (fr) | 2001-03-02 |
| EP1201594B1 (de) | 2005-10-26 |
| US6474486B1 (en) | 2002-11-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1201594A1 (de) | Telekopiersystem eines Kranauslegers | |
| FR2960215A1 (fr) | Dispositif de deverrouillage d'un atterrisseur dans une position deployee et atterrisseur equipe d'un tel dispositif | |
| EP2454152B1 (de) | Bugfahrwek mit stellvorrichtung, welche sowohl das einfahren des fahrweks als auch dessen lenkung bewerkstelligt | |
| WO2006008352A2 (fr) | Dispositif de securite en cas de retournement d’un vehicule | |
| WO2016042274A1 (fr) | Chaumard destiné à coopérer avec une chaîne d'ancrage, pour un système d'ancrage au sol d'une installation flottante | |
| EP1110857B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Stabilisierung eines Schiffes, insbesondere beim Rollen | |
| FR2640208A1 (fr) | Systeme de transport et de depose d'au moins une travure d'un vehicule tel qu'un engin blinde du genie | |
| EP3070203B1 (de) | Be-, entlade- und aufsetzsystem einer schienenweiche auf ein bahngleis | |
| EP1420980B1 (de) | Verfahren zur steuerung der seitengeländer eines fahrzeugaufzugs und vorrichtung dafür | |
| EP0362065B1 (de) | Brückenverlegevorrichtung, bestehend aus mindestens zwei auf einem Chassis übereinandergelegten Brückenteilen | |
| EP0490798A2 (de) | Kran, insbesondere für die Handhabung | |
| CA1101691A (fr) | Verin de manoeuvre et de contreventement a dispositif interne de verrouillage | |
| EP1352870B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Anheben und Aufklappen von dem Mast und zum Anheben von dem Ausleger eines Kranes | |
| EP0362063A1 (de) | Brückenlegefahrzeug | |
| EP4049936A1 (de) | System mit einem beweglichen schlitten und verfahren zur anwendung eines solchen systems mit beweglichem schlitten | |
| FR2666772A1 (fr) | Systeme de transport d'au moins une travure de pontage destinee au franchissement d'une breche et de depose de la travure au-dessus de la breche a partir d'un vehicule. | |
| EP0589792B1 (de) | Handhabungseinrichtung für Rohrbündel von Wärmetauschern | |
| FR2528774A1 (fr) | Equipement d'acces et de sortie par translation et changement de niveau et de mise en place au poste de conduite, applicable notamment et en particulier a des vehicules de paralyses des membres inferieurs | |
| FR2461078A1 (fr) | Dispositif de parcage de vehicules en situation superposee | |
| EP1472132B1 (de) | Fahrzeugstruktur, und fahrzeug mit derartigen stuktur | |
| FR2719061A1 (fr) | Procédé de pose des traverses d'une voie ferrée et agencement pour la mise en Óoeuvre de ce procédé. | |
| FR2572128A1 (fr) | Dispositif de pivotement de soutenements de tailles dans des galeries souterraines | |
| EP2511450B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Befestigen einer provisorischen Dachstruktur | |
| EP3075687B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur immobilisierung eines fahrzeugs, und diese vorrichtung umfassendes system | |
| FR2494246A1 (fr) | Portique de manutention ferroviaire et procede en faisant application pour la manutention d'objets lourds tels que des tabliers de ponts |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE ES IT Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20021031 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: DE ES IT |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20040413 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE ES IT |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 60023506 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20051201 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060206 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20060727 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20161020 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20161024 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 60023506 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180501 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20171026 |