EP1050388B1 - Machine for machining edges with a workpiece conveyor chain - Google Patents
Machine for machining edges with a workpiece conveyor chain Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1050388B1 EP1050388B1 EP00106890A EP00106890A EP1050388B1 EP 1050388 B1 EP1050388 B1 EP 1050388B1 EP 00106890 A EP00106890 A EP 00106890A EP 00106890 A EP00106890 A EP 00106890A EP 1050388 B1 EP1050388 B1 EP 1050388B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- entrainment
- workpieces
- conveyor
- machine
- point
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B27—WORKING OR PRESERVING WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL; NAILING OR STAPLING MACHINES IN GENERAL
- B27C—PLANING, DRILLING, MILLING, TURNING OR UNIVERSAL MACHINES FOR WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL
- B27C5/00—Machines designed for producing special profiles or shaped work, e.g. by rotary cutters; Equipment therefor
- B27C5/02—Machines with table
- B27C5/06—Arrangements for clamping or feeding work
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B27—WORKING OR PRESERVING WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL; NAILING OR STAPLING MACHINES IN GENERAL
- B27B—SAWS FOR WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL; COMPONENTS OR ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- B27B25/00—Feeding devices for timber in saw mills or sawing machines; Feeding devices for trees
- B27B25/04—Feeding devices for timber in saw mills or sawing machines; Feeding devices for trees with feed chains or belts
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B27—WORKING OR PRESERVING WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL; NAILING OR STAPLING MACHINES IN GENERAL
- B27B—SAWS FOR WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL; COMPONENTS OR ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- B27B31/00—Arrangements for conveying, loading, turning, adjusting, or discharging the log or timber, specially designed for saw mills or sawing machines
- B27B31/06—Adjusting equipment, e.g. using optical projection
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B27—WORKING OR PRESERVING WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL; NAILING OR STAPLING MACHINES IN GENERAL
- B27B—SAWS FOR WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL; COMPONENTS OR ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- B27B5/00—Sawing machines working with circular or cylindrical saw blades; Components or equipment therefor
- B27B5/02—Sawing machines working with circular or cylindrical saw blades; Components or equipment therefor characterised by a special purpose only
- B27B5/04—Sawing machines working with circular or cylindrical saw blades; Components or equipment therefor characterised by a special purpose only for edge trimming
Definitions
- the invention relates to an edge processing machine of the type specified in the preamble of claim 1 in more detail.
- a driver device which detects the workpieces is present on the inlet side of one of the two transport chains.
- This driver device is not used to introduce the workpieces between the top pressure and the transport chain. Rather, the driver device is only used, when elongated workpieces are to be transported in their longitudinal direction on the only one of the two transport chains and these workpieces are first approached for processing on one of its longitudinal sides transversely to the transport direction against a lying in the conveying direction guide ruler.
- the driving device can be lowered onto the workpieces and has the workpieces acting on rollers, which are inclined relative to the conveying direction of the conveyor chain to exert on the workpieces a conveying component transverse to the transport direction.
- the transport of the workpieces is also carried out on arranged on the transport chain driving cams over which the introduction of the workpieces between top pressure and transport chain.
- the document EP 0 504 442 A1 discloses an edge processing machine of the type mentioned in the introduction, which has a driver device with cams in the manner of cams, which are reciprocated between the feed point for the workpieces and the point of introduction between the transport chains and the top pressure.
- a driver device with cams in the manner of cams, which are reciprocated between the feed point for the workpieces and the point of introduction between the transport chains and the top pressure.
- the entrainment devices are part of a pre-built before the intake point of the processing machine machine device, which is provided with its own conveyor belts for transporting the workpieces. On these conveyor belts, the workpieces are held down by pressure rollers arranged on pressure rollers.
- the invention has for its object to provide an edge processing machine of the type mentioned, in which the workpiece feed point and the entrainment devices interact with the driving cams directly with the machine's own workpiece transport system.
- For the invention is essential that it no longer needs follower cams on the transport chain, because the clamping forces that can be built between the lower strand of the upper pressure and the upper strand of the transport chain, sufficient to workpieces without the rear Stop at cams to fix sufficiently for the respective processing. Even if one is no longer bound to a predetermined pitch of the driving cams along the transport chain, the workpieces to be processed one after another can be conveyed through the edge processing machine even with the smallest possible gaps, which increases the machine throughput.
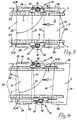
- Figures 1 and 2 show those front end portion of an edge processing machine, on which workpieces 5 are placed on two parallel and transversely congruent transport chains 1, which successively pass through different processing stations in the edge processing machine, which are not shown in the drawing.
- the transport chains 1 are each guided over an end-side deflection wheel 2 and have from there to a corresponding end-side deflection on the outlet side of the machine a horizontally guided upper strand 4. Where the deflection of the transport chains 1 is completed and accordingly the respective upper strand 4 begins, There is a support point 3, at which the workpieces 5 are placed on the two transport chains 1 so that they protrude with the edges to be machined or edges on both sides of the transport chains 1.
- each an associated upper pressure 7 is arranged, which consists essentially of a rotating Band exists, which rotates in a vertical plane over a front guide wheel 8 away, this vertical plane is usually aligned with that vertical plane in which the underlying transport chain 1 rotates.
- the workpieces 5 are thus detected between the lower run 9 of the upper pressure 7 and the upper run 4 of the associated transport chain 1, the lower run 9 of the upper pressure 7 the detected workpieces 5 clamped against the upper strand of the transport chain 1. Therefore, the lower run 9 of the upper pressure 7 is supported upward on the entire conveying length.
- the transport chains 1 are thus extended at the end of the edge processing machine on the top pressure 7 against the conveying direction addition.
- This area is not only used to support the workpieces 5 on the upper run 4 of the transport chains 1, but also to detect the individual workpieces 5 in the correct position and at the entry point 6 in this orientation between the lower run 9 of the upper pressure 7 and the respective upper run 4 of Introduce transport chains 1.
- a driver device 10 which is movable between the feed point 3 and 6 Einzugstelle.
- Each of the transport chains 1 is associated with such a driver device 10, which is arranged on the opposite sides of the transport chains 1.
- a linear guide 11 is arranged in each case, which is in the length of a Place below theanistelle 3 extends to a point below the Einzugstelle 6 away, this projecting in the conveying direction of the transport chain 1, the respective linear guide 11 still on the task-side end of the upper pressure 7 also.
- a carriage 12 On each of the linear guides 11, a carriage 12 is mounted reciprocable, on which an electric drive motor 13 is arranged, which engages with a pinion 14 in a rack 15 fixed to the machine frame.
- These drive motors 13 are speed-controllable motors, expediently frequency-controlled induction machines are used for this purpose.
- a lifting cylinder 16 which carries in each case a driving cam 17, which can be raised from a position below the conveying plane of the associated transport chain 1 to at least one further position by projecting over the conveying plane of the transport chain 1 upwards.
- This driving cam 17 is intended to detect the workpieces 5 to be transported from the feeding point 3 to the draw-in point 6, depending on the height of these workpieces 5, the driving cam 17 can be extended more or less far upwards and therefore occupy different extended positions.
- the driving cams 17 are then in the upper extended position, when the respectively associated carriage 12 moves from the feeding point 3 to the insertion point 6.
- the driving cams 17 have the task of applying the workpieces 5 either on their in the conveying direction of the transport chains 1 rear edge 21 to introduce them at the Einzugstelle 6 between the upper run 4 of the transport chains 1 and 9 Untertrum the top pressure 7.
- the driver devices 10 represent a slide-in system.
- the speed of the carriage 12 and thus the speed of the driving cam 17 is selected so that the feed of the transport chains 1 already taken along with the feed to the draw-in point 6 5 and then with the Feed rate of the transport chains 1 are pushed at the intake point 6 under the upper pressure 7. Accordingly, the carriages 12 on a portion of the feed path then have a higher speed than the transport chains 1 in the conveying direction.
- the workpieces 5, which have been placed on the transport chains 1 at the feed point 3 can be aligned via the driving cams 17 of the entrainment devices 10. If the workpiece trailing edge 21 or the workpiece front edge 22 of the workpieces 5 is the reference edge at which the angularity of the other edges has to be oriented, the carriages 12 and thus the driving cams 17 can be moved synchronously along the feed path, their connecting line being exactly perpendicular to the feed path the conveying direction of the transport chains 1 and accordingly also to the feed direction of the driving devices 10 is.
- FIG. 3 shows an example in which the driving cams 17 of the entrainment device 10 grasp the workpieces 5 at the workpiece trailing edges 21, which are aligned exactly at right angles to processing lines 23 which extend parallel to the conveying direction of the transport chains 1.
- a skewness of the further workpiece edges 24 can be compensated for by firstly passing the workpieces 5 through a milling station in which the lateral workpiece edges 24 are cut at right angles to the workpiece trailing edge 21.
- the workpieces 5 can be aligned by means of the driver devices 10 and fitting. This is shown in Fig. 4.
- the driving cam 17 is raised and set the slide 12 in the feed direction in motion, until the driving cam 17 abuts the workpiece trailing edge 21.
- the workpieces 5 must be aligned why the past in the conveying direction carriage 12 is accelerated until it is seen in the conveying direction at the same height with the second carriage 12, after which then the line connecting the driving cam 17 runs exactly perpendicular to the conveying direction.
- the workpiece 5 shown on the left in Figure 4 has changed its original position shown in solid lines in the final, aligned position, which is represented by dotted lines.
- the different control of the carriage 12 via the electric drive motors 13, which - as I said - are preferably designed as a frequency-controllable induction machines.
- the dependence of the control of one drive motor 13 on that of the other drive motor 13 can be provided here.
- an electric or electronic wave can be realized, with the synchronization between the two drive motors 13 and thus synchronization between the carriage 12 can be achieved.
- the one drive motor 13 and thus the relevant carriage 12 can be accelerated or decelerated relative to the other.
- the caster of one carriage 12 shown in FIG. 4 can be stabilized with respect to the other in order to maintain the inclined position of the workpieces 5 relative to the conveying direction. Then namely the workpieces 5 are drawn in this inclined position between the upper pressure 7 and the upper run 4 of the transport chains 1 and held in this position, after which processing and trimming the lateral, opposite workpiece edges 24 along the processing lines 23, whereby the workpieces. 5 can receive a deviating from the rectangular shape angularity. So it is specifically possible to give the workpieces 5, the basic shape of a parallelogram.
- Both in the loading of the workpieces 5 at the feed point 3 by hand and in a machine manner can be due to the flexible entrainment devices 10 a minimum distance between the successively machined workpieces 5 comply.
- the Lükken between the workpieces 5 can be kept very small even if the workpieces 5 seen in the conveying direction have different widths.
- the insertion or introduction system can also be realized on a single-sided edge processing machine.
- a ruler 18 can occur, which is height-adjustable in the same manner as the driving cam 17 via lifting cylinder 16 to the carriage 12 and which corresponds in its transverse direction of the connecting line of the opposite driving cam 17.
- the cam device 10 may be configured in the same manner as in the above-described double-sided workpiece machining machine.
- the supernatant of the workpieces 5 transversely to the conveying direction of the conveyor chain 1 on the side remote from the driver 10 side is determined here by a guide rule 26 which projects upwardly at a level with the conveying level of the conveyor chain 1 support table 25.
- This guide ruler 26, which extends parallel to the conveying direction, serves as a transverse stop for the lateral workpiece edges 24, being ensured by a feed device 28 that the workpieces 5 are applied not only in the conveying direction of the transport chain 1, but also transversely thereto.
- the feed direction 28 consists of a plurality of feed rollers 27, whose axes are set slightly inclined relative to the perpendicular to the conveying direction.
- the workpieces 5 a conveyor component exerted transversely to the main conveying direction of the transport chain 1, whereby the workpieces 5 come with their lateral workpiece edges 24 for abutment with the guide bar 26 and then inserted or inserted in the same manner at the entry point 6 between the upper pressure 7 and the upper run 4 of the transport chain 1, as has been described above with reference to the double-sided machine with two parallel opposite transport chains 1.
- an oblique section of the workpieces 5 can be provided, an angular error between the workpiece trailing edge 21 or the leading edge 22 and the lateral workpiece edge 24 can be compensated and it is also the straightening of the workpieces 5 via the differently controllable carriages 12 on the linear guides 11 Driver device 10 possible, as indicated in Figure 7.
- the feed device 28 can also be dispensed with when the workpieces 5 are pushed open.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Forests & Forestry (AREA)
- Feeding Of Workpieces (AREA)
- Control Of Conveyors (AREA)
- Attitude Control For Articles On Conveyors (AREA)
- Multi-Process Working Machines And Systems (AREA)
Description
Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf eine Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine der im Oberbegriff des Patentanspruchs 1 näher bezeichneten Art.The invention relates to an edge processing machine of the type specified in the preamble of
Aus dem IMA-Prospekt "COMBIMA" sind als "COMBIMA I/II" Kantenbearbeitungsmaschinen bekannt, die je nachdem, ob die plattenförmigen Werkstücke einseitig oder beidseitig bearbeitet werden, eine oder zwei Transportketten aufweisen, an denen Mitnahmenocken angeordnet sind. An den betreffenden Kettengliedern sind die Mitnahmenocken zwischen einer an deren Oberseite einliegenden und einer ausgefahrenen Position verstellbar, um bei Werkstücken mit in Durchlaufrichtung unterschiedlicher Breite auch bei den kleineren Breiten möglichst geringe Abstände zwischen den nacheinander zu bearbeitenden Werkstücken zu erzielen. Die Einrichtungen zur Verstellung der Mitnahmenocken an den Ketten sind sehr aufwendig, hierfür wird wiederum eine verstellbare Steuerkurve oder Kulisse benötigt, des weiteren müssen die Mitnahmenocken in ihren beiden Endpositionen fixiert werden. Der vorhandene Oberdruck hat die Aufgabe, bei den Bearbeitungsvorgängen die Werkstücke auf dem Obertrum der Transportketten niederzuhalten, zugleich wird dadurch auch eine Verschiebung der Werkstücke von den Mitnahmenocken der Ketten weg verhindert.From the IMA brochure "COMBIMA" edge processing machines are known as "COMBIMA I / II", which, depending on whether the plate-shaped workpieces are processed on one side or both sides, have one or two transport chains on which driving cams are arranged. At the relevant chain links, the driving cams between one at the top and in an extended position are adjustable to achieve the smallest possible distances between the workpieces to be machined successively in workpieces with different width in the passage direction even at the smaller widths. The means for adjusting the driving cams on the chains are very expensive, this in turn requires an adjustable cam or link, further, the driving cams must be fixed in its two end positions. The existing upper pressure has the task to suppress the workpieces on the upper run of the transport chains during the machining operations, at the same time thereby also a displacement of the workpieces is prevented by the driving cams of the chains away.
Bei der bekanten Maschine IMA-COMBIMA I/II ist an der Einlaufseite einer der beiden Transportketten eine die Werkstücke erfassende Mitnehmervorrichtung vorhanden. Diese Mitnehmervorrichtung dient nicht dazu, die Werkstücke zwischen den Oberdruck und die Transportkette einzuführen. Vielmehr kommt die Mitnehmervorrichtung nur dann zum Einsatz, wenn längliche Werkstücke in ihrer Längsrichtung auf der nur einen der beiden Transportketten befördert werden sollen und diese Werkstücke zwecks Bearbeitung an einer ihrer Längsseiten zunächst quer zur Transportrichtung gegen ein in der Förderrichtung liegendes Führungslineal angefahren werden. Dazu ist die Mitnehmervorrichtung an die Werkstücke absenkbar und hat die Werkstücke beaufschlagende Rollen, die gegenüber der Förderrichtung der Transportkette schräg gestellt sind, um auf die Werkstücke eine Förderkomponente quer zur Transportrichtung auszuüben. Die Beförderung der Werkstücke erfolgt auch hierbei über an der Transportkette angeordnete Mitnahmenocken, über welche die Einführung der Werkstücke zwischen Oberdruck und Transportkette erfolgt.In the case of the known IMA-COMBIMA I / II machine, a driver device which detects the workpieces is present on the inlet side of one of the two transport chains. This driver device is not used to introduce the workpieces between the top pressure and the transport chain. Rather, the driver device is only used, when elongated workpieces are to be transported in their longitudinal direction on the only one of the two transport chains and these workpieces are first approached for processing on one of its longitudinal sides transversely to the transport direction against a lying in the conveying direction guide ruler. For this purpose, the driving device can be lowered onto the workpieces and has the workpieces acting on rollers, which are inclined relative to the conveying direction of the conveyor chain to exert on the workpieces a conveying component transverse to the transport direction. The transport of the workpieces is also carried out on arranged on the transport chain driving cams over which the introduction of the workpieces between top pressure and transport chain.
Aus dem Dokument EP 0 504 442 Al ist eine Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine der eingangs genannten Art bekannt, die eine Mitnehmervorrichtung mit Mitnehmern nach Art von Nocken aufweist, die zwischen der Aufgabestelle für die Werkstücke und der Einzugstelle zwischen den Transportketten und dem Oberdruck hin- und herverfahren werden. Auf dem Weg zu der Einzugstelle hin stehen die Mitnehmer über die Förderebene der Transportketten vor, auf dem Rückweg zu der Aufgabestelle hin sind sie unter diese Förderebene abgesenkt. Die Mitnehmervorrichtungen sind Teil einer vor die Einzugstelle der Bearbeitungsmaschine vorgebauten maschinellen Vorrichtung, die mit eigenen Förderbändern zum Transport der Werkstücke versehen ist. Auf diesen Förderbändern werden die Werkstücke mittels an Druckbalken angeordneten Druckrollen niedergehalten.The document EP 0 504 442 A1 discloses an edge processing machine of the type mentioned in the introduction, which has a driver device with cams in the manner of cams, which are reciprocated between the feed point for the workpieces and the point of introduction between the transport chains and the top pressure. On the way to the Einzugstelle towards the carriers on the conveying plane of the transport chains, on the way back to the Aufgabestelle they are lowered below this conveying level. The entrainment devices are part of a pre-built before the intake point of the processing machine machine device, which is provided with its own conveyor belts for transporting the workpieces. On these conveyor belts, the workpieces are held down by pressure rollers arranged on pressure rollers.
Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine der genannten Art zu schaffen, bei der die Werkstückaufgabestelle und die Mitnehmervorrichtungen mit den Mitnahmenocken unmittelbar mit dem maschineneigenen Werkstücktransportsystem zusammenwirken.The invention has for its object to provide an edge processing machine of the type mentioned, in which the workpiece feed point and the entrainment devices interact with the driving cams directly with the machine's own workpiece transport system.
Diese Aufgabe wird durch die Merkmale des Patentanspruchs 1 gelöst.This object is solved by the features of
Für die Erfindung ist wesentlich, daß es mitlaufender Mitnahmenocken an der Transportkette nicht mehr bedarf, denn die Spannkräfte, die zwischen dem Untertrum des Oberdrucks und dem Obertrum der Transportkette aufgebaut werden können, reichen aus, um die Werkstücke auch ohne den rückwärtigen Anschlag an Nocken ausreichend für die jeweilige Bearbeitung zu fixieren. Auch ist man an eine vorgegebene Teilung der Mitnahmenocken entlang der Transportkette nicht mehr gebunden, so lassen sich die nacheinander zu bearbeitenden Werkstücke auch mit kleinstmöglichen Lücken durch die Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine hindurchbefördern, was den Maschinendurchsatz erhöht.For the invention is essential that it no longer needs follower cams on the transport chain, because the clamping forces that can be built between the lower strand of the upper pressure and the upper strand of the transport chain, sufficient to workpieces without the rear Stop at cams to fix sufficiently for the respective processing. Even if one is no longer bound to a predetermined pitch of the driving cams along the transport chain, the workpieces to be processed one after another can be conveyed through the edge processing machine even with the smallest possible gaps, which increases the machine throughput.
Vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungsmerkmale der Erfindung ergeben sich aus den Unteransprüchen.Advantageous design features of the invention will become apparent from the dependent claims.
Die Erfindung wird nachfolgend anhand der Zeichnung an Ausführungsbeispielen noch näher erläutert. Dabei zeigen:
- Fig. 1
- die Draufsicht auf den einlaufseitigen Bereich einer Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine,
- Fig. 2
- die Seitansicht des Bereichs der Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine nach Fig. 1 unter Weglassung des Oberdrucks,
- Fig. 3
- eine der
Figur 2 entsprechende Draufsicht zur Veranschaulichung des Ausgleichs von Winkelfehlern an den Werkstücken, - Fig. 4
- eine den
Figuren 2 und 3 entsprechende Draufsicht zur Veranschaulichung des Geraderichtens von Werkstücken, - Fig. 5
- die Seitansicht des Einlaufbereichs einer einseitig bearbeitenden Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine,
- Fig. 6
- die Draufsicht auf den Einlaufbereich der Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine nach
Figur 5 und - Fig. 7
- eine der
Figur 6 entsprechende Draufsicht zur Veranschaulichung des Ausgleichs von Winkelfehlern an den Werkstücken.
- Fig. 1
- the plan view of the inlet side region of an edge processing machine,
- Fig. 2
- the side view of the area of the edge processing machine of FIG. 1 with the omission of the upper pressure,
- Fig. 3
- 2 is a plan view corresponding to FIG. 2 for illustrating the compensation of angular errors on the workpieces;
- Fig. 4
- a plan view corresponding to Figures 2 and 3 illustrating the straightening of workpieces,
- Fig. 5
- the side view of the inlet area of a single-sided edge processing machine,
- Fig. 6
- the top view of the inlet region of the edge processing machine of Figure 5 and
- Fig. 7
- a plan view corresponding to Figure 6 to illustrate the compensation of angular errors on the workpieces.
Im einzelnen zeigen die Figuren 1 und 2 denjenigen vorderen Endbereich einer Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine, an welchem Werkstücke 5 auf zwei miteinander parallele und in Querrichtung gesehen deckungsgleiche Transportketten 1 aufgegeben werden, die in der Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine nacheinander verschiedene Bearbeitungsstationen durchlaufen, die in der Zeichnung nicht dargestellt sind. Die Transportketten 1 sind jeweils über ein endseitiges Umlenkrad 2 geführt und haben von da ab bis zu einem entsprechenden endseitigen Umlenkrad an der Auslaufseite der Maschine ein horizontal geführtes Obertrum 4. Dort wo die Umlenkung der Transportketten 1 beendet ist und entsprechend das jeweilige Obertrum 4 beginnt, befindet sich eine Auflagestelle 3, an der die Werkstücke 5 auf die beiden Transportketten 1 so aufgelegt werden, daß sie mit den zu bearbeitenden Rändern oder Kanten beidseits über die Transportketten 1 überstehen.In detail, Figures 1 and 2 show those front end portion of an edge processing machine, on which
Bis zu einer Einzugstelle 6 sind die Obertrume 4 der Transportketten 1 nicht überdeckt, von der Einzugstelle 6 ab ist oberhalb der Transportketten 1 jeweils ein zugehöriger Oberdruck 7 angeordnet, der im wesentlichen aus einem umlaufenden Band besteht, welches in einer Vertikalebene über ein vorderes Umlenkrad 8 hinweg umläuft, wobei diese Vertikalebene in der Regel mit derjenigen Vertikalebene fluchtet, in der die darunter angeordnete Transportkette 1 umläuft. So liegt das Untertrum 9 des Oberdrucks 7 unmittelbar mit geringem Abstand oberhalb des Obertrums 4 der Transportketten 1. Die Werkstücke 5 werden somit zwischen dem Untertrum 9 des Oberdrucks 7 und dem Obertrum 4 der zugehörigen Transportkette 1 erfaßt, wobei das Untertrum 9 des Oberdrucks 7 die erfaßten Werkstücke 5 gegen das Obertrum der Transportkette 1 verspannt. Deshalb ist das Untertrum 9 des Oberdrucks 7 nach oben hin auf der gesamten Förderlänge abgestützt. Um den Bereich, der zwischen der Einzugstelle 6 und der endseitigen Aufgabestelle 3 liegt, sind die Transportketten 1 somit am Aufgabeende der Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine über den Oberdruck 7 entgegen der Förderrichtung hinaus verlängert. Dieser Bereich dient nicht nur zur Auflage der Werkstücke 5 auf das Obertrum 4 der Transportketten 1, sondern auch dazu, die einzelnen Werkstücke 5 lagerichtig zu erfassen und an der Einzugstelle 6 in dieser Ausrichtung zwischen das Untertrum 9 des Oberdrucks 7 und das jeweilige Obertrum 4 der Transportketten 1 einzuführen.Up to a
Dazu dient eine Mitnehmervorrichtung 10, die zwischen der Aufgabestelle 3 und der Einzugstelle 6 verfahrbar ist. Jeder der Transportketten 1 ist eine solche Mitnehmervorrichtung 10 zugeordnet, die an den voneinander abliegenden Seiten der Transportketten 1 angeordnet ist. Seitlich am Maschinengestell, welche die Verlängerung der Transportketten 1 über den Oberdruck 7 hinaus trägt, ist jeweils eine Linearführung 11 angeordnet, die sich in der Länge von einem Ort unterhalb der Aufgabestelle 3 bis zu einer Stelle unterhalb der Einzugstelle 6 weg erstreckt, hierbei ragt in Förderrichtung der Transportkette 1 die jeweilige Linearführung 11 noch über das aufgabeseitige Ende des Oberdrucks 7 hinaus. Auf jeder der Linearführungen 11 ist ein Schlitten 12 hin- und herverfahrbar gelagert, auf dem ein elektrischer Antriebsmotor 13 angeordnet ist, welcher mit einem Ritzel 14 in eine am Maschinengestell feste Zahnstange 15 eingreift. Bei diesen Antriebsmotoren 13 handelt es sich um drehzahlsteuerbare Motoren, zweckmäßig werden hierfür frequenzgesteuerte Drehfeldmaschinen verwendet.The purpose of a
An jedem Schlitten 12 sitzt ein Hubzylinder 16, der jeweils einen Mitnahmenocken 17 trägt, welcher von einer Position unterhalb der Förderebene der zugehörigen Transportkette 1 bis in zumindest eine weitere Position hochfahrbar ist, indem er über die Förderebene der Transportkette 1 nach oben hin vorsteht. Dieser Mitnahmenocken 17 ist dazu bestimmt, die von der Aufgabestelle 3 zu der Einzugstelle 6 hin zu transportierenden Werkstücke 5 zu erfassen, je nach Höhe dieser Werkstücke 5 kann der Mitnahmenocken 17 mehr oder weniger weit nach oben ausgefahren werden und deshalb unterschiedliche ausgefahrene Positionen einnehmen. Die Mitnahmenocken 17 befinden sich dann in der oberen ausgefahrenen Position, wenn sich der jeweils zugehörige Schlitten 12 von der Aufgabestelle 3 hin zur Einzugstelle 6 bewegt. Beim Rückzug von der Einzugstelle 6 zur Aufgabestelle 3 hin sind die Mitnahmenocken 17 in die Position unterhalb der Förderebene der Transportketten 1 zurückgezogen, die Schlitten 12 können daher kollisionsfrei unter den Werkstücken 5 hindurch zur Aufgabestelle 3 zurückgefahren werden, die sich an der Aufgabestelle 3 noch befinden oder bereits ein Wegstück zur Einzugstelle 6 auf dem Transportketten 1 zurückgelegt haben.At each
Die Mitnahmenocken 17 haben die Aufgabe, die Werkstücke 5 entweder an ihrer in Förderrichtung der Transportketten 1 hintenliegenden Kante 21 zu beaufschlagen, um sie an der Einzugstelle 6 zwischen dem Obertrum 4 der Transportketten 1 und dem Untertrum 9 der Oberdruck 7 einzuführen. In diesem Fall stellen die Mitnehmervorrichtungen 10 ein Einschubsystem dar. Hierbei wird die Geschwindigkeit der Schlitten 12 und damit die Geschwindigkeit der Mitnahmenocken 17 so gewählt, daß beim Vorschub zu der Einzugstelle 6 hin die von den Transportketten 1 bereits mitgenommenen Werkstücke 5 eingeholt und dann mit der Vorschubgeschwindigkeit der Transportketten 1 an der Einzugstelle 6 unter den Oberdruck 7 geschoben werden. Entsprechend haben die Schlitten 12 auf einem Teilstück des Vorschubweges dann eine höhere Geschwindigkeit als die Transportketten 1 in der Förderrichtung. Zum anderen kann auch umgekehrt vorgegangen werden, indem die Fördergeschwindigkeit der Transportketten 1 in Förderrichtung größer als die Vorschubgeschwindigkeit der Schlitten 12 auf einem Teil des Vorschubweges ist. Dann holen die an der Aufgabestelle 3 aufgegebenen Werkstücke 5 die über die Förderebene vorstehenden Mitnahmenocken 17 ein, sie schlagen mit ihren in Förderrichtung vornliegenden Vorderkanten 22 an die Mitnahmenocken 17 an und laufen zusammen mit diesen an der Einzugstelle 6 unter die Oberdrukke 7 ein.The driving
In beiden vorstehend beschriebenen Fällen können über die Mitnehmernocken 17 der Mitnehmervorrichtungen 10 die Werkstücke 5, die auf die Transportketten 1 an der Aufgabestelle 3 aufgelegt worden sind, passend ausgerichtet werden. Sofern die Werkstückhinterkante 21 oder die Werkstückvorderkante 22 der Werkstücke 5 diejenige Bezugskante ist, an der sich die Winkligkeit der übrigen Kanten zu orientieren hat, können die Schlitten 12 und damit die Mitnahmenocken 17 synchron miteinander entlang dem Vorschubweg verfahren werden, wobei ihre Verbindungslinie exakt lotrecht zur der Förderrichtung der Transportketten 1 und entsprechend auch zu der Vorschubrichtung der Mitnehmervorrichtungen 10 steht.In both cases described above, the
Fig. 3 zeigt an einem Beispiel, bei dem die Mitnahmenocken 17 der Mitnehmervorrichtung 10 die Werkstücke 5 an den Werkstückhinterkanten 21 erfassen, die exakt rechtwinklig zu Bearbeitungslinien 23 ausgerichtet sind, die sich parallel zu der Förderrichtung der Transportketten 1 erstrecken. So kann eine Schiefwinkligkeit der weiteren Werkstückkanten 24 ausgeglichen werden, indem die Werkstücke 5 zunächst durch eine Frässtation laufen, in welcher die seitlichen Werkstückkanten 24 rechtwinklig zu der Werkstückhinterkante 21 geschnitten werden.FIG. 3 shows an example in which the driving
Darüber hinaus können die Werkstücke 5 mittels der Mitnehmervorrichtungen 10 auch passend ausgerichtet werden. Dies zeigt Fig. 4. In diesem Fall wird der Vorschub der Schlitten 12, die sich in einer Position nahe der Aufgabestelle 3 befinden, dann erst aktiviert, wenn die jeweilige Werkstückhinterkante 21 des betreffenden Werkstücks 5 den Mitnahmepocken 17 an diesem Schlitten 12 überfahren hat, was durch einen entsprechenden Sensor am Schlitten 12 ermittelt werden kann. Danach wird der Mitnahmenocken 17 hochgefahren und der Schlitten 12 in Vorschubrichtung in Gang gesetzt, bis der Mitnahmenocken 17 an der Werkstückhinterkante 21 anschlägt. Sind auf diese Weise beide Mitnahmenocken 17 der zwei Schlitten 12 in Anlage an der Werkstückhinterkante 21 gebracht, dann verläuft zunächst deren Verbindungslinie unter einem Winkel zur Lotrechten auf die Förderrichtung der Transportketten 1 bzw. der Mitnehmervorrichtung 10. Um diesen Winkel müssen die Werkstücke 5 ausgerichtet werden, weshalb der in Förderrichtung zurückliegende Schlitten 12 solange beschleunigt wird, bis er in Förderrichtung gesehen auf gleicher Höhe mit dem zweiten Schlitten 12 liegt, wonach dann die Verbindungslinie der Mitnahmenocken 17 exakt senkrecht zur Förderrichtung verläuft. Hierdurch hat das in Figur 4 links dargestellte Werkstück 5 seine ursprüngliche mit ausgezogenen Linien dargestellte Lage in die endgültige, ausgerichtete Lage geändert, die durch gestrichte Linien wiedergegeben ist.In addition, the
Die unterschiedliche Steuerung der Schlitten 12 erfolgt über die elektrischen Antriebsmotore 13, die - wie gesagt - vorzugsweise als frequenzsteuerbare Drehfeldmaschinen ausgelegt sind. Nach dem Master & Slave-Prinzip kann hier die Abhängigkeit der Steuerung des einen Antriebsmotors 13 von der des anderen Antriebsmotors 13 vorgesehen werden. Auf diese Weise läßt sich eine elektrische bzw. elektronische Welle realisieren, mit der ein Gleichlauf zwischen den beiden Antriebsmotoren 13 und damit eine Synchronisation zwischen den Schlitten 12 erzielt werden kann. Durch Aufschalten einer Frequenzdifferenz, läßt sich der eine Antriebsmotor 13 und damit der betreffende Schlitten 12 gegenüber dem anderen beschleunigen oder verzögern.The different control of the
Es kann aber auch der in Figur 4 dargestellte Nachlauf des einen Schlittens 12 gegenüber dem anderen stabilisiert beibehalten werden, um die Schräglage der Werkstücke 5 bezogen auf die Förderrichtung beizubehalten. Dann nämlich werden die Werkstücke 5 in dieser Schräglage zwischen dem Oberdruck 7 und dem Obertrum 4 der Transportketten 1 eingezogen und in dieser Position festgehalten, wonach dann eine Bearbeitung und Beschneidung der seitlichen, einander gegenüberliegenden Werkstückkanten 24 entlang der Bearbeitungslinien 23 erfolgt, wodurch die Werkstücke 5 eine von der rechtwinkligen Gestalt abweichende Winkligkeit erhalten können. So ist es gezielt möglich, den Werkstücken 5 die Grundform eines Parallelogramms zu geben.However, it is also possible for the caster of one
Sowohl bei der Beschickung der Werkstücke 5 an der Aufgabestelle 3 von Hand als auch auf maschinelle Weise läßt sich aufgrund der flexiblen Mitnehmervorrichtungen 10 ein minimaler Abstand zwischen den nacheinander zu bearbeitenden Werkstücken 5 einhalten. Mit anderen Worten können die Lükken zwischen den Werkstücken 5 auch dann sehr klein gehalten werden, wenn die Werkstücke 5 in Förderrichtung gesehen unterschiedliche Breiten haben.Both in the loading of the
Zudem läßt sich das Einschub- oder Einführungssystem auch an einer einseitig bearbeitenden Kantenbearbeitungsmaschine verwirklichen. Dies zeigen die Figuren 5 und 6. Darüber hinaus ist hier zu erkennen, daß anstelle der beschriebenen Mitnahmenocken 17 auch ein Lineal 18 treten kann, welches in gleicher Weise wie die Mitnahmenocken 17 über Hubzylinder 16 an den Schlitten 12 höhenverstellbar ist und welches in seiner Querrichtung der Richtung der Verbindungslinie der einander gegenüberliegenden Mitnahmenocken 17 entspricht. Dies wird auch hier durch eine synchrone Bewegung der beiden das Lineal 18 tragenden Schlitten 12 entweder in Querausrichtung oder in Schrägausrichtung zueinander bezogen auf die Förderrichtung oder auch durch einen unterschiedlich beschleunigten Antrieb erreicht.In addition, the insertion or introduction system can also be realized on a single-sided edge processing machine. This show the figures 5 and 6. In addition, it can be seen here that instead of the described
Bei der einseitig bearbeitenden Maschine wird lediglich eine einzige Transportkette 1 und entsprechend ein einziger darüber angeordneter Oberdruck 7 benötigt. Die Mitnehmervorrichtung 10 kann im übrigen in gleicher Weise wie bei der vorstehend beschriebenen Maschine für die doppelseitige Werkstückbearbeitung ausgeführt sein. Der Überstand der Werkstücke 5 quer zur Förderrichtung der Transportkette 1 an der von der Mitnehmervorrichtung 10 abliegenden Seite wird hier durch ein Führungslineal 26 bestimmt, das an einem mit dem Förderniveau der Transportkette 1 höhengleichen Auflagetisch 25 nach oben vorsteht. Dieses Führungslineal 26, welches sich parallel zur Förderrichtung erstreckt, dient als Queranschlag für die seitlichen Werkstückkanten 24, wobei durch eine Vorschubvorrichtung 28 dafür gesorgt ist, daß die Werkstücke 5 nicht nur in der Förderrichtung der Transportkette 1, sondern auch quer dazu beaufschlagt werden. Dazu besteht die Vorschubrichtung 28 aus einer Mehrzahl von Einzugrollen 27, deren Achsen relativ zur Senkrechten auf die Förderrichtung etwas schrägt gestellt sind. Dadurch wird auf die Werkstücke 5 eine Förderkomponente quer zur Hauptförderrichtung der Transportkette 1 ausgeübt, wodurch die Werkstücke 5 mit ihren seitlichen Werkstückkanten 24 zur Anlage an dem Führungslineal 26 kommen und danach in gleicher Weise an der Einzugstelle 6 zwischen dem Oberdruck 7 und dem Obertrum 4 der Transportkette 1 eingeschoben oder eingeführt werden können, wie es zuvor anhand der doppelseitig bearbeitenden Maschine mit zwei einander parallel gegenüberliegenden Transportketten 1 beschrieben worden ist. Auch hierbei kann ein Schrägschnitt der Werkstücke 5 vorgesehen werden, es kann ein Winkelfehler zwischen der Werkstückhinterkante 21 oder der Vorderkante 22 und der seitlichen Werkstückkante 24 ausgeglichen werden und es ist gleichfalls das Geraderichten der Werkstücke 5 über die unterschiedlich steuerbaren Schlitten 12 an den Linearführungen 11 der Mitnehmervorrichtung 10 möglich, wie es in Figur 7 angedeutet ist. Grundsätzlich kann bei schiebender Beaufschlagung der Werkstücke 5 die Vorschubvorrichtung 28 auch entfallen.In the single-sided machining machine only a
Claims (10)
- Machine for machining edges for panel-type workpieces (5) of wood or wood substitutes, such as parts for the furniture industry or internal fittings, with conveyor chains (1) receiving the workpieces (5) on their upper side troughs (4) and moving them in continuous flow along from machining stations, and with an upper press (7) which revolves over the conveyor chains (1) and which has lower sides (9) supported upwards which are arranged extending in the conveyor direction above the upper side troughs (4) of the conveyor chains (1) and moving synchronously with same, tensioning the workpieces (5) by applying pressure against the upper sides (4) of the conveyor chains (1) whereby at the inlet side of the conveyor chains (1) there is an entrainment device (10) which seizes the workpieces (5) and runs in at an entry point between the upper press (7) and the conveyor chains (1) and which has at least one entrainment cam (17) which can move to and fro between a pick-up point (3) for the workpieces (5) and the entry point (6) between the conveyor chains (1) and the upper press (7) and which protrudes on the way to the entry point (6) beyond the conveyor plane of the conveyor chains (1),
characterised in that
the conveyor chains (1) are extended opposite the conveying direction beyond the upper press (7) and form the pick-up point (3) for the workpieces and that each relevant conveyor chain is assigned one of the entrainment devices (10) each with an entrainment cam (17). - Machine for machining edges according to claim 1,
characterised in that
the entrainment devices (10) have slide carriages (12) fitted with entrainment cams (17) and movable to and fro on linear guides (11) between the pick up point (3) and the entry point (6). - Machine for machining edges according to claim 2,
characterised in that
the entrainment cams (17) are displaceable on the slide carriage (12) between a first position in which they are mounted underneath the conveyor plane during the return path from the entry point (6) to the pick-up point (3), and at least a further position for the way to the entry point (6) in which they protrude up beyond the conveyor plane of the conveyor chains (1). - Machine for machining edges according to one of claims 2 or 3,
characterised in that
along each linear guide (11) there is a toothed rack (15) in which a pinion (14) engages which is mounted on the slide carriage (12) and is coupled to an electric drive motor (13). - Machine for machining edges according to one of claims 2 to 4,
characterised in that
in place of the entrainment cams (17) the entrainment devices (10) have a straight edge ruler (18) extending between the slide carriages (12). - Machine for machining edges according to one of claims 2 to 5,
characterised in that
the conveyor chains (1) move at a faster speed than the slide carriages (12) of the entrainment devices (10) over a part of the entrainment path between the pick-up point (3) and the entry point (6) and the entrainment cams (17) or the straight edged ruler (18) of the entrainment devices (10) seize the workpieces (5) abutting same by the edges which lie at the front in the conveyor direction. - Machine for machining edges according to one of claims 2 to 5,
characterised in that
the slide carriages (12) of the entrainment devices (10) move over a part of the entrainment path between the pick-up point (3) and the entry point (6) for the workpieces (5) at a faster speed than the conveyor chains (1) and seize the workpieces (5) through impact by the edges which lie at the back in the conveyor direction. - Machine for machining edges according to claim 7,
characterised in that
at the side next to the upper side (4) of one of the conveyor chains (1) on the side away from the entrainment device (10) there is a straight edged guide ruler (26) which is parallel to the conveyor chain (1) and between this conveyor chain (1) and this straight edge guide ruler (26) there is a feed device (20) which bears on the workpieces (5) with a transversal component across the conveyor direction of the conveyor chain (1), and that each of the slide carriages (12) is then set in motion in a direction towards the entry point (6) when the entrainment cam (17) located on same has been overrun by the rear edge of the relevant workpiece (5) in the conveyor direction. - Machine for machining edges according to one of claims 6 to 8,
characterised in that
the slide carriages (12) of the entrainment devices (10) can be set along the entrainment path with the connecting line of their entrainment cams (17) or with the straight-edged ruler (18) at an angle deviating from a right angle with the conveyor direction of the conveyor chains (1). - Machine for machining edges according to one of claims 2 to 9,
characterised in that
the drive motors (13) of the slide carriages (12) of the entrainment devices (10) are frequency-controlled induction machines and are coupled to one another by means of an electric or electronic wave on the master and slave principle.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19921058A DE19921058C1 (en) | 1999-05-07 | 1999-05-07 | Chain transport machine with tools for working edges and faces of workpieces has band arranged above transport chain |
| DE19921058 | 1999-05-07 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1050388A2 EP1050388A2 (en) | 2000-11-08 |
| EP1050388A3 EP1050388A3 (en) | 2004-05-26 |
| EP1050388B1 true EP1050388B1 (en) | 2006-07-05 |
Family
ID=7907289
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00106890A Expired - Lifetime EP1050388B1 (en) | 1999-05-07 | 2000-03-31 | Machine for machining edges with a workpiece conveyor chain |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1050388B1 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE19921058C1 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2264656T3 (en) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10105960B4 (en) * | 2000-09-25 | 2004-07-01 | Homag Maschinenbau Ag | Method and device for machining continuously moving workpieces |
| DE10323267B4 (en) * | 2003-05-23 | 2005-04-14 | Ima Klessmann Gmbh Holzbearbeitungssysteme | Continuous machine for plate processing with inlet side support device |
| DE102006019298A1 (en) * | 2006-04-26 | 2007-10-31 | Wemhöner Anlagen GmbH & Co. KG | Transport system for boards at a woodworking machine, to cut profiles at both ends, has an upper pressure belt with an inflatable hose to press down on the workpiece and prevent vibration |
| DE102009045731A1 (en) * | 2009-10-15 | 2011-04-21 | Homag Holzbearbeitungssysteme Ag | Device for processing workpieces |
| CN103802172B (en) * | 2012-11-13 | 2016-08-03 | 佛山市顺德区一涵机械制造有限公司 | Double-end milling workpiece lateral processing feeding mechanism |
| NL1040638C2 (en) * | 2014-01-29 | 2015-08-06 | Gmv Gyártó-Szolgáltató És Forgalmazó Kft | DEVICE FOR CUTTING A STONE STRIP FROM A STONE, METHOD FOR CUTTING A STONE STRIP FROM A STONE. |
| ITUB20156072A1 (en) * | 2015-12-02 | 2017-06-02 | Scm Group Spa | Improved wood processing machine and its method of operation. |
| DE102021122721A1 (en) * | 2021-09-02 | 2023-03-02 | Homag Gmbh | Conveyor with independently moveable cams for feeding and/or aligning workpieces |
| DE102021131764A1 (en) * | 2021-12-02 | 2023-06-07 | Homag Gmbh | Process for processing continuously moving workpieces |
| DE102022129234A1 (en) | 2022-11-04 | 2024-05-08 | Ima Schelling Deutschland Gmbh | Woodworking device and method for machining plate-shaped workpieces |
| DE102022132505A1 (en) * | 2022-12-07 | 2024-06-13 | Homag Gmbh | Processing machine and method for processing workpieces |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3890509A (en) * | 1972-05-09 | 1975-06-17 | Black Clawson Co | Automatic edger set works method and apparatus |
| DE8114121U1 (en) * | 1981-05-13 | 1981-12-10 | Hornberger Maschinenbaugesellschaft mbH & Co KG, 7294 Schopfloch | FEEDER DEVICE FOR A FORMAT AND / OR EDGE BANDING MACHINE FOR EDGE PROCESSING WORKPIECES |
| DE59107976D1 (en) * | 1991-03-18 | 1996-08-08 | Homag Maschinenbau Ag | Device for feeding workpieces to a processing machine |
| DE4234681C2 (en) * | 1992-10-14 | 1997-01-09 | Klessmann Ima Norte Maschfab | Transfer device for plate-shaped workpieces, such as furniture parts |
-
1999
- 1999-05-07 DE DE19921058A patent/DE19921058C1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2000
- 2000-03-31 DE DE50013107T patent/DE50013107D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-03-31 ES ES00106890T patent/ES2264656T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-03-31 EP EP00106890A patent/EP1050388B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1050388A2 (en) | 2000-11-08 |
| DE50013107D1 (en) | 2006-08-17 |
| ES2264656T3 (en) | 2007-01-16 |
| DE19921058C1 (en) | 2000-06-15 |
| EP1050388A3 (en) | 2004-05-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0399264B1 (en) | Method of and apparatus for changing the relative position of packs, especially of parallelepipedic cigarette packs of the flip-top type (hinge-lid pack) | |
| EP3202673B1 (en) | Deep draw packaging machine | |
| EP3652096B1 (en) | Conveying storage device and method for operating the conveying storage device | |
| EP1522508B2 (en) | Separating, synchronising and accumulating device | |
| EP0222349A2 (en) | Device for the skidless transport of two panels, particularly glazing panes | |
| EP2792623A1 (en) | Device and method for forming a predefined formation on a conveyor belt | |
| EP2110348A1 (en) | Intake station and packet grabber of a palletising device and method for transferring packets from an intake station to a packet grabber | |
| EP1050388B1 (en) | Machine for machining edges with a workpiece conveyor chain | |
| CH680509A5 (en) | ||
| WO2003070420A1 (en) | Feeder device for delivering workpiece supports to a work station in the longitudinal direction of a belt conveyor | |
| EP2186756B1 (en) | Horizontal transporter for transporting piece goods | |
| DE2058606A1 (en) | Method and device for the lateral alignment of sheets, in particular in a printing press | |
| EP0504442B1 (en) | Device for feeding workpieces to a production machine | |
| DE3147590C2 (en) | Device for forming gaps in a series of piece goods, in particular of moldings cut from a clay strand | |
| WO2002090044A1 (en) | Device for returning workpieces | |
| DE69607698T2 (en) | Device for loading and / or unloading a container with stacks of packs, in particular egg boxes | |
| DE102008048831A1 (en) | Conveying device for packaging machine, has buffer conveyor, on which containers are conveyed, and collecting conveyor, through which containers are brought in predetermined distance to each other | |
| DE10059312C2 (en) | Centering device for conveyed goods | |
| EP1401611A1 (en) | Assembly line | |
| EP3369663B1 (en) | Collar forming device for elongated workpieces and method for bundling elongated workpieces | |
| EP3395696B1 (en) | Packaging of food products | |
| DE19821108C2 (en) | Grouping device for packs | |
| DE10323267B4 (en) | Continuous machine for plate processing with inlet side support device | |
| DE29521082U1 (en) | Grouping and buffering device | |
| DE3931673C2 (en) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK RO SI |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: 7B 23Q 7/06 B Ipc: 7B 23Q 7/18 B Ipc: 7B 27C 5/06 A Ipc: 7B 27B 31/06 B |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20041118 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): DE ES IT |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20050601 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE ES IT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20060705 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: IMA KLESSMANN GMBH HOLZBEARBEITUNGSSYSTEME |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50013107 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20060817 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2264656 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20070410 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20090304 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20110415 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110404 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100401 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20170323 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20170328 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50013107 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180331 |