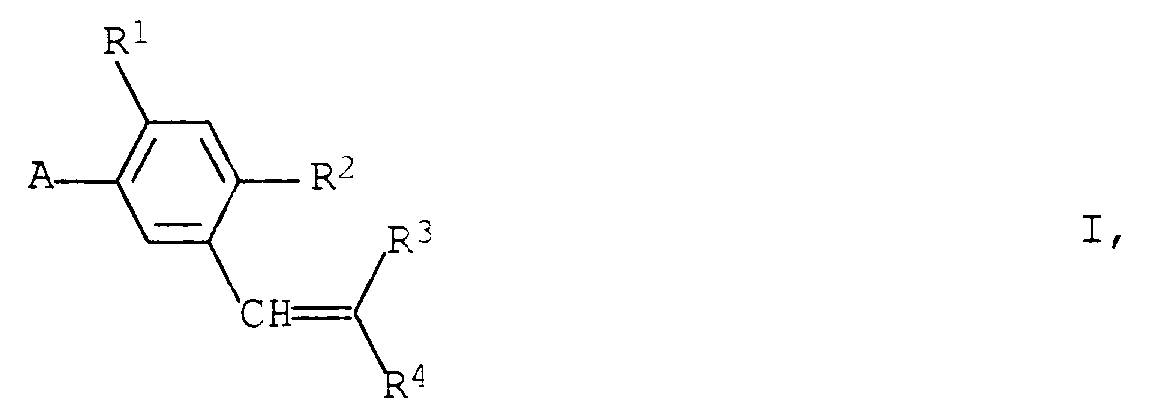EP0493721B1 - Styrene derivatives - Google Patents
Styrene derivatives Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0493721B1 EP0493721B1 EP91121314A EP91121314A EP0493721B1 EP 0493721 B1 EP0493721 B1 EP 0493721B1 EP 91121314 A EP91121314 A EP 91121314A EP 91121314 A EP91121314 A EP 91121314A EP 0493721 B1 EP0493721 B1 EP 0493721B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- formula
- halogen
- weight
- compounds
- hydrogen
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 125000003011 styrenyl group Chemical class [H]\C(*)=C(/[H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 title claims abstract 8
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 125000004916 (C1-C6) alkylcarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 239000004009 herbicide Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 125000004178 (C1-C4) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical group [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical group [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 17
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 230000002363 herbicidal effect Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 150000003935 benzaldehydes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 229920000742 Cotton Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 241000219146 Gossypium Species 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000035613 defoliation Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 240000002024 Gossypium herbaceum Species 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000004341 Gossypium herbaceum Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- XYFCBTPGUUZFHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphine Chemical compound P XYFCBTPGUUZFHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052717 sulfur Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000011593 sulfur Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims 1
- 125000001309 chloro group Chemical group Cl* 0.000 claims 1
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 claims 1
- 230000008635 plant growth Effects 0.000 claims 1
- -1 heterocyclic radical Chemical class 0.000 abstract description 40
- 239000005864 Sulphur Chemical group 0.000 abstract 1
- 125000005157 alkyl carboxy group Chemical group 0.000 abstract 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 28
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 27
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 22
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 17
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 16
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 14
- 150000003440 styrenes Chemical class 0.000 description 13
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 9
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 8
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 7
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 7
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 7
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylselenoniopropionate Natural products CCC(O)=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 125000004123 n-propyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 6
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 5
- WBIQQQGBSDOWNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC=C1S(O)(=O)=O WBIQQQGBSDOWNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene oxide Chemical compound C1CO1 IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Naphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CIUQDSCDWFSTQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N [C]1=CC=CC=C1 Chemical compound [C]1=CC=CC=C1 CIUQDSCDWFSTQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000002191 fatty alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 125000000959 isobutyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 4
- 125000004108 n-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 4
- 239000006072 paste Substances 0.000 description 4
- VBQCHPIMZGQLAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphorane Chemical class [PH5] VBQCHPIMZGQLAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000002798 polar solvent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000002914 sec-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 4
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 4
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 4
- ZWZVWGITAAIFPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiophosgene Chemical compound ClC(Cl)=S ZWZVWGITAAIFPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiourea Chemical compound NC(N)=S UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 4
- BQVOQZZFZKJDIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[2-chloro-3-[methylidene(diphenyl)-lambda5-phosphanyl]phenyl]ethanone Chemical compound C(C)(=O)C=1C(=C(C=CC=1)P(C1=CC=CC=C1)(C1=CC=CC=C1)=C)Cl BQVOQZZFZKJDIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000005995 Aluminium silicate Substances 0.000 description 3
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004721 Polyphenylene oxide Substances 0.000 description 3
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 244000098338 Triticum aestivum Species 0.000 description 3
- 229960000583 acetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000013543 active substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000012211 aluminium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 150000001448 anilines Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 244000038559 crop plants Species 0.000 description 3
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000002540 isothiocyanates Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N kaolin Chemical compound O.O.O=[Al]O[Si](=O)O[Si](=O)O[Al]=O NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000010755 mineral Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920000570 polyether Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000019260 propionic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- IUVKMZGDUIUOCP-BTNSXGMBSA-N quinbolone Chemical compound O([C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@]4(C=CC(=O)C=C4CC3)C)CC[C@@]21C)C1=CCCC1 IUVKMZGDUIUOCP-BTNSXGMBSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 159000000000 sodium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000005919 1,2,2-trimethylpropyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000005918 1,2-dimethylbutyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000006218 1-ethylbutyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- KBLAMUYRMZPYLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-bis(2-methylpropyl)naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(S(O)(=O)=O)=C(CC(C)C)C(CC(C)C)=CC2=C1 KBLAMUYRMZPYLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ABRKONSNRDSBKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-5-(3,4-dimethyl-2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)benzaldehyde Chemical compound O=C1C(C)=C(C)C(=O)N1C1=CC=C(Cl)C(C=O)=C1 ABRKONSNRDSBKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000006176 2-ethylbutyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])*)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 125000004493 2-methylbut-1-yl group Chemical group CC(C*)CC 0.000 description 2
- 125000005916 2-methylpentyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000003542 3-methylbutan-2-yl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 125000005917 3-methylpentyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- PAYRUJLWNCNPSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Aniline Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC=C1 PAYRUJLWNCNPSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 0 CN(C(C1=C2CCC(*)CC1)=O)C2=O Chemical compound CN(C(C1=C2CCC(*)CC1)=O)C2=O 0.000 description 2
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethoxyethane Chemical compound COCCOC XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium sulfate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 240000007594 Oryza sativa Species 0.000 description 2
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperazine Chemical compound C1CNCCN1 GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DKGAVHZHDRPRBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tert-Butanol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)O DKGAVHZHDRPRBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000021307 Triticum Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Natural products NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000007239 Wittig reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000011054 acetic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000001299 aldehydes Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000003863 ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 159000000007 calcium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000013877 carbamide Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- MVPPADPHJFYWMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N chlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC=C1 MVPPADPHJFYWMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007859 condensation product Substances 0.000 description 2
- JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanone Chemical compound O=C1CCCCC1 JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940060296 dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000002170 ethers Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000013312 flour Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000008282 halocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000002484 inorganic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodine Chemical compound II PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N isobutanol Chemical compound CC(C)CO ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KQNPFQTWMSNSAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N isobutyric acid Chemical compound CC(C)C(O)=O KQNPFQTWMSNSAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000004491 isohexyl group Chemical group C(CCC(C)C)* 0.000 description 2
- 125000001972 isopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- HJOVHMDZYOCNQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N isophorone Chemical compound CC1=CC(=O)CC(C)(C)C1 HJOVHMDZYOCNQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920005610 lignin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanoic acid Natural products OC=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-NJFSPNSNSA-N methanone Chemical compound O=[14CH2] WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-NJFSPNSNSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002480 mineral oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010446 mineral oil Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 125000001280 n-hexyl group Chemical group C(CCCCC)* 0.000 description 2
- 125000000740 n-pentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 150000002790 naphthalenes Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 125000001971 neopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 125000003538 pentan-3-yl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920000151 polyglycol Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000010695 polyglycol Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 2
- BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCO BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000003548 sec-pentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 2
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000001973 tert-pentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 150000003512 tertiary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000003672 ureas Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000013311 vegetables Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000080 wetting agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000000229 (C1-C4)alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- DYLIWHYUXAJDOJ-OWOJBTEDSA-N (e)-4-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)but-2-en-1-ol Chemical compound NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2C\C=C\CO DYLIWHYUXAJDOJ-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YFVHMZIBVSNMOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[4-chloro-3-(2-chloro-3-oxobut-1-enyl)phenyl]-3,4-dimethylpyrrole-2,5-dione Chemical compound C1=C(Cl)C(C=C(Cl)C(=O)C)=CC(N2C(C(C)=C(C)C2=O)=O)=C1 YFVHMZIBVSNMOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CMCBDXRRFKYBDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-dodecoxydodecane Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCOCCCCCCCCCCCC CMCBDXRRFKYBDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XUJLWPFSUCHPQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 11-methyldodecan-1-ol Chemical compound CC(C)CCCCCCCCCCO XUJLWPFSUCHPQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QFUSCYRJMXLNRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dinitroaniline Chemical class NC1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=CC=C1[N+]([O-])=O QFUSCYRJMXLNRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PAWQVTBBRAZDMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(3-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)acetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC1=CC=CC(Br)=C1F PAWQVTBBRAZDMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BWMOUYGOKKZWFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-3-[2-chloro-5-(3,4-dimethyl-2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)phenyl]prop-2-enenitrile Chemical compound O=C1C(C)=C(C)C(=O)N1C1=CC=C(Cl)C(C=C(Cl)C#N)=C1 BWMOUYGOKKZWFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CBSBKANZWBSEPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-6-[methylidene(diphenyl)-lambda5-phosphanyl]benzonitrile Chemical compound ClC=1C(=C(C=CC=1)P(C1=CC=CC=C1)(C1=CC=CC=C1)=C)C#N CBSBKANZWBSEPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CMWKITSNTDAEDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-nitrobenzaldehyde Chemical class [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C=O CMWKITSNTDAEDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PIAOLBVUVDXHHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-nitroethenylbenzene Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PIAOLBVUVDXHHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QBGQIMOGHUXVKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoindole-1,3-dione Chemical class O=C1C(CCCC2)=C2C(=O)N1C1=CC=CC=C1 QBGQIMOGHUXVKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- REEXLQXWNOSJKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2h-1$l^{4},2,3-benzothiadiazine 1-oxide Chemical class C1=CC=C2S(=O)NN=CC2=C1 REEXLQXWNOSJKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FOGYNLXERPKEGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-[2-methoxy-4-(3-sulfopropyl)phenoxy]propane-1-sulfonic acid Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(CC(CS(O)(=O)=O)OC=2C(=CC(CCCS(O)(=O)=O)=CC=2)OC)=C1O FOGYNLXERPKEGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)aniline Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC(N)=CC=2)=C1 OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XAZNOOMRYLFDQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4h-3,1-benzoxazine Chemical class C1=CC=C2COC=NC2=C1 XAZNOOMRYLFDQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XVMSFILGAMDHEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-(4-aminophenyl)sulfonylpyridin-3-amine Chemical compound C1=CC(N)=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=N1 XVMSFILGAMDHEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 240000006995 Abutilon theophrasti Species 0.000 description 1
- 240000001592 Amaranthus caudatus Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000009328 Amaranthus caudatus Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 244000237956 Amaranthus retroflexus Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000013479 Amaranthus retroflexus Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 239000004254 Ammonium phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 description 1
- LPBXJWRZMSPEAB-CLFYSBASSA-N C/N=C(/N1N2C=CCC1)\SC2=[IH] Chemical compound C/N=C(/N1N2C=CCC1)\SC2=[IH] LPBXJWRZMSPEAB-CLFYSBASSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000025254 Cannabis sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000012766 Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000012765 Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. spontanea Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000008733 Citrus aurantifolia Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dioxygen Chemical compound O=O MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000233866 Fungi Species 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000021506 Ipomoea Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 241000207783 Ipomoea Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000005909 Kieselgur Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019738 Limestone Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000002720 Malnutrition Diseases 0.000 description 1
- IGFHQQFPSIBGKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nonylphenol Natural products CCCCCCCCCC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 IGFHQQFPSIBGKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000007164 Oryza sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000005662 Paraffin oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- YGYAWVDWMABLBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosgene Chemical compound ClC(Cl)=O YGYAWVDWMABLBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007868 Raney catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000564 Raney nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- NPXOKRUENSOPAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Raney nickel Chemical compound [Al].[Ni] NPXOKRUENSOPAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000061457 Solanum nigrum Species 0.000 description 1
- 229940100389 Sulfonylurea Drugs 0.000 description 1
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfurous acid Chemical compound OS(O)=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000011941 Tilia x europaea Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010044278 Trace element deficiency Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229920001807 Urea-formaldehyde Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000007295 Wittig olefination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 241000607479 Yersinia pestis Species 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004036 acetal group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000003342 alkenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002877 alkyl aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000008055 alkyl aryl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000005037 alkyl phenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910000148 ammonium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000019289 ammonium phosphates Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- BFNBIHQBYMNNAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N ammonium sulfate Chemical compound N.N.OS(O)(=O)=O BFNBIHQBYMNNAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052921 ammonium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011130 ammonium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000008064 anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000010 aprotic solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004945 aromatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000004104 aryloxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 159000000009 barium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-KWCOIAHCSA-N benzaldehyde Chemical group O=[11CH]C1=CC=CC=C1 HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-KWCOIAHCSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzenecarboxaldehyde Natural products O=CC1=CC=CC=C1 HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- OSGAYBCDTDRGGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium sulfate Inorganic materials [Ca+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O OSGAYBCDTDRGGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 235000009120 camo Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004359 castor oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019438 castor oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009903 catalytic hydrogenation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005119 centrifugation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000013339 cereals Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000005607 chanvre indien Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001851 cinnamic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000004927 clay Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003776 cleavage reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011280 coal tar Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940125782 compound 2 Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001907 coumarones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- HJSLFCCWAKVHIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexane-1,3-dione Chemical class O=C1CCCC(=O)C1 HJSLFCCWAKVHIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HPXRVTGHNJAIIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanol Chemical compound OC1CCCCC1 HPXRVTGHNJAIIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MNNHAPBLZZVQHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N diammonium hydrogen phosphate Chemical compound [NH4+].[NH4+].OP([O-])([O-])=O MNNHAPBLZZVQHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HTFFABIIOAKIBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N diazinane Chemical class C1CCNNC1 HTFFABIIOAKIBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004891 diazines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002283 diesel fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 1
- USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl ether Chemical class C=1C=CC=CC=1OC1=CC=CC=C1 USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HCUYBXPSSCRKRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphosgene Chemical compound ClC(=O)OC(Cl)(Cl)Cl HCUYBXPSSCRKRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010459 dolomite Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000514 dolomite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010410 dusting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethylene glycol Natural products OCCO LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003337 fertilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000019253 formic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035784 germination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012362 glacial acetic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N glycerol triricinoleate Natural products CCCCCC[C@@H](O)CC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](COC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@@H](O)CCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@H](O)CCCCCC ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940093915 gynecological organic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003977 halocarboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000003306 harvesting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011487 hemp Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003864 humus Substances 0.000 description 1
- WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxyacetaldehyde Natural products OCC=O WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002505 iron Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003350 kerosene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004571 lime Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006028 limestone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000395 magnesium oxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium oxide Inorganic materials [Mg]=O CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052943 magnesium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000019341 magnesium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium;oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[Mg+2] AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WPBNNNQJVZRUHP-UHFFFAOYSA-L manganese(2+);methyl n-[[2-(methoxycarbonylcarbamothioylamino)phenyl]carbamothioyl]carbamate;n-[2-(sulfidocarbothioylamino)ethyl]carbamodithioate Chemical compound [Mn+2].[S-]C(=S)NCCNC([S-])=S.COC(=O)NC(=S)NC1=CC=CC=C1NC(=S)NC(=O)OC WPBNNNQJVZRUHP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000956 methoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])O* 0.000 description 1
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010981 methylcellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012452 mother liquor Substances 0.000 description 1
- PSZYNBSKGUBXEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid Chemical class C1=CC=C2C(S(=O)(=O)O)=CC=CC2=C1 PSZYNBSKGUBXEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002663 nebulization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002828 nitro derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 231100001184 nonphytotoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- SNQQPOLDUKLAAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N nonylphenol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC=C1O SNQQPOLDUKLAAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000000655 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000016709 nutrition Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000002347 octyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleic acid group Chemical group C(CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC)(=O)O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- QNGNSVIICDLXHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N para-ethylbenzaldehyde Natural products CCC1=CC=C(C=O)C=C1 QNGNSVIICDLXHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012188 paraffin wax Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- XYFCBTPGUUZFHI-UHFFFAOYSA-O phosphonium Chemical compound [PH4+] XYFCBTPGUUZFHI-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003032 phytopathogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000004885 piperazines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003495 polar organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium benzoate Chemical compound [K+].[O-]C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001436 propyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000004805 propylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 description 1
- 239000011814 protection agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- LOAUVZALPPNFOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinaldic acid Chemical class C1=CC=CC2=NC(C(=O)O)=CC=C21 LOAUVZALPPNFOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000376 reactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000009566 rice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000007363 ring formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012266 salt solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004576 sand Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007017 scission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004760 silicates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011877 solvent mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009331 sowing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000003107 substituted aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- RWSOTUBLDIXVET-UHFFFAOYSA-O sulfonium Chemical compound [SH3+] RWSOTUBLDIXVET-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 125000005537 sulfoxonium group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000002195 synergetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000012222 talc Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000005621 tetraalkylammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- CXWXQJXEFPUFDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetralin Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CCCCC2=C1 CXWXQJXEFPUFDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004809 thin layer chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003585 thioureas Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003918 triazines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004562 water dispersible granule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/44—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D207/444—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having two doubly-bound oxygen atoms directly attached in positions 2 and 5
- C07D207/448—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having two doubly-bound oxygen atoms directly attached in positions 2 and 5 with only hydrogen atoms or radicals containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms directly attached to other ring carbon atoms, e.g. maleimide
- C07D207/452—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having two doubly-bound oxygen atoms directly attached in positions 2 and 5 with only hydrogen atoms or radicals containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms directly attached to other ring carbon atoms, e.g. maleimide with hydrocarbon radicals, substituted by hetero atoms, directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/30—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D207/34—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D207/36—Oxygen or sulfur atoms
- C07D207/40—2,5-Pyrrolidine-diones
- C07D207/404—2,5-Pyrrolidine-diones with only hydrogen atoms or radicals containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms directly attached to other ring carbon atoms, e.g. succinimide
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N37/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids
- A01N37/18—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing the group —CO—N<, e.g. carboxylic acid amides or imides; Thio analogues thereof
- A01N37/32—Cyclic imides of polybasic carboxylic acids or thio analogues thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N37/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids
- A01N37/44—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing at least one carboxylic group or a thio analogue, or a derivative thereof, and a nitrogen atom attached to the same carbon skeleton by a single or double bond, this nitrogen atom not being a member of a derivative or of a thio analogue of a carboxylic group, e.g. amino-carboxylic acids
- A01N37/46—N-acyl derivatives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/48—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with two nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- A01N43/56—1,2-Diazoles; Hydrogenated 1,2-diazoles
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/90—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having two or more relevant hetero rings, condensed among themselves or with a common carbocyclic ring system
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D209/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D209/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom condensed with one carbocyclic ring
- C07D209/44—Iso-indoles; Hydrogenated iso-indoles
- C07D209/48—Iso-indoles; Hydrogenated iso-indoles with oxygen atoms in positions 1 and 3, e.g. phthalimide
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D231/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings
- C07D231/54—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D231/56—Benzopyrazoles; Hydrogenated benzopyrazoles
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D513/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for in groups C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D499/00 - C07D507/00
- C07D513/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for in groups C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D499/00 - C07D507/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D513/04—Ortho-condensed systems
Definitions
- the invention further relates to processes for the preparation of these compounds and herbicidal compositions and processes for defoliation (desiccation) of cotton.
- the object of the invention was to provide compounds which are particularly effective as herbicides. Furthermore, the compounds should be usable as bioregulators, in particular for the defoliation of cotton.
- the compounds of the formula I are obtained by reacting a suitably substituted benzaldehyde of the formula II with a phosphorane of the formula III in a manner known per se, for example analogously to the conditions described in Synthesis 10 (1984) 862, in a solvent at temperatures between 0 ° C and the boiling point of the solvent:
- Ar in formula III means an unsubstituted or substituted aryl radical, with the phenyl radical generally being preferred.
- phosphoranes III required for the preparation of the styrene derivatives I which are also referred to as phosphorus ylides, are based on methods known from the literature (for example Houben-Weyl, Methods of Organic Chemistry, Vol. E1, pp. 636-639, Georg-Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1982 or Chem. Ber. 95 , 1962, page 3993).
- the Ar groups of these phosphoranes can be unsubstituted or substituted phenyl radicals.
- the number of substituents per phenyl radical and the substitution pattern of the phenyl radicals are generally not critical for the success of the process, but in general a phenyl radical carries no more than 3 substituents.
- Preferred substituents for the phenyl radicals are those which are inert under the conditions of the process, for example the halides fluorine, chlorine and bromine, alkyl groups, preferably C 1 to C 4 alkyl groups, in particular the methyl group, or C 1 to C 4 -Alkoxy groups, especially the methoxy group.
- triarylphosphoranes III with an unsubstituted phenyl radical are generally preferred.
- the reaction of the starting compounds II and III is generally carried out advantageously in the presence of a solvent.
- solvents all can usually be carried out solvents used by Wittig reactions are used, for example halogenated solvents such as chloroform, or ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether.
- Preferred solvents are alcohols, especially C 1 to C 4 alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, propanol, isopropanol, butanol, isobutanol and tert-butanol.
- the solvents can also be used in the form of solvent mixtures, but the pure solvents are generally preferred.
- reaction is carried out at temperatures between 0 ° C and 100 ° C.
- the optimum reaction temperature depends on the starting compounds II and III to be reacted in each case and on the solvent used.
- the starting compounds II and III can be reacted with one another in stoichiometric amounts. However, it may prove advantageous if one of the two reactants, II or III, is used in a 0.05-5-fold molar excess in the reaction.
- the course of the Wittig reaction can be followed using conventional analytical methods such as thin layer chromatography and high pressure liquid chromatography.
- the product I can be isolated by conventional methods such as filtration, centrifugation or by adding water with subsequent extraction. If desired, the styrene derivatives I thus obtained can be purified further, for example by recrystallization or by means of chromatographic methods.
- the styrene derivatives I are generally obtained as cis-trans isomer mixtures with respect to the alkenyl side chain, the trans isomer generally predominating.
- the process for the preparation of the styrene derivatives of the formula I also includes the possibility of interchanging the sequence in the synthesis of the benzaldehydes of the general formula II and the Wittig olefination.
- benzaldehydes of the general formula II used as starting material are easily accessible by the methods of DE-A 38 15 042 ( ⁇ EP-A 340 708) or can be prepared, for example, as described below.
- the benzaldehydes of the formula IIc are obtained, if an aniline derivative of the formula IV is first converted into the corresponding isothiocyanate V using thiophosgene in accordance with the conditions described for IX, V is added to a piperazine VI, and the thiourea derivative VII thus obtained is added with acidic cleavage of the acetal group Aldehyde function with a phosgenating agent or cyclized to aldehyde IIc, d:
- V, VII, VIII, B denotes an ethylene or propylene unit which can carry one to three alkyl groups such as methyl, ethyl, propyl and 1-methylethyl, preferably methyl.
- the dotted line in the formulas VI, VII, VIII and IIc, d stands for a ⁇ bond that may be present.
- the acetal group in compound VIII is converted into the aldehyde function under acidic conditions, for example in the presence of mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid or organic acids such as p-toluenesulfonic acid.
- the compounds I with the radicals A 1 and A 2 are also obtained, for example, by condensing an aniline of the general formula IX with anhydrides of the general formula Xa or Xb:
- Inert organic solvents such as lower alkanoic acids such as acetic acid, propionic acid and isobutyric acid and the esters of these acids such as ethyl acetate, higher-boiling hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene and / or dimethylformamide are used for the condensation.
- the reaction is usually carried out at temperatures between 25 ° C. and the boiling point of the respective reaction mixture, preferably between 50 and 140 ° C. When using an aprotic solvent, it is advisable to remove the water continuously.
- Anilines IX are obtained, for example, by reduction from the corresponding nitroderivatives in analogy to known methods (DE-A 37 24 399, DE-A 36 03 789):
- a nitrostyrene XII is converted to aniline derivative IX in a manner known per se using inorganic compounds such as tin-II salts or iron or tin or by catalytic hydrogenation on metal contacts such as Raney nickel, palladium and platinum in an inert organic solvent reduced.
- Suitable solvents for the reaction with inorganic compounds are, for example, alcohols such as methanol, ethanol and isopropanol and lower alkanoic acids such as formic acid, acetic acid and propionic acid and corresponding mixtures.
- the reaction temperatures are 25 ° C to 150 ° C, preferably 25 ° C to 100 ° C.
- solvents such as methanol or other alcohols, dimethylformamide, propionic acid, tetrahydrofuran and glacial acetic acid and corresponding mixtures at a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 150 bar, preferably 1 to 50 bar and temperatures of 25 ° C. to 100 ° C, preferably 25 to 70 ° C.
- the compounds Ic, d are also obtained, for example, by reacting a derivative of the general formula IX in a manner known per se (Houben-Weyl, Vol. IX, pp. 867 f. (1955)) in an inert organic solvent with thiophosgene converted into the corresponding isothiocyanate XIII, XIII then added in an aprotic polar solvent to a tetrahydro or perhydrodiazine derivative VI and the thiourea thus obtained XIV cyclized with a phosgenating agent or thiophosgenating agent (Phos.)
- a phosgenating agent or thiophosgenating agent Phos.
- reaction of derivative IX with thiophosgene generally takes place at temperatures from (-50) ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 50 ° C.
- This reaction can be carried out both in a two-phase solvent system such as methylene chloride / water and in the presence of a base in an aprotic polar organic solvent.
- toluene in the presence of an organic base, preferably a tertiary amine such as triethylamine.
- the reaction of the isothiocyanates XIII with the piperazines VI is preferably carried out in aprotic polar solvents such as preferably ethers, in particular tetrahydrofuran at temperatures from (-50) ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 50 ° C.
- aprotic polar solvents such as preferably ethers, in particular tetrahydrofuran at temperatures from (-50) ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 50 ° C.
- the subsequent cyclization of thiourea XIV with a phosgenating agent or thiophosgenating agent is usually carried out at temperatures from 0 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 20 ° C. to 70 ° C. in an aprotic polar solvent in the presence of a base.
- Particularly suitable phosgenating agents and thiophosgenating agents are phosgene, thiophosgene and trichloromethyl chloroformate.
- halogenated hydrocarbons and hydrocarbons are preferably used as solvents.
- Suitable bases are tertiary amines such as pyridine in particular.
- the styrene derivatives I can be obtained in the preparation as isomer mixtures, enantiomer or diastereomer mixtures and in particular E / Z isomer mixtures being possible. If desired, the isomer mixtures can be prepared by the usual methods, e.g. be separated by chromatography or by crystallization.
- the styrene derivatives I can be in the form of their agriculturally useful salts.
- the salts of acids which do not impair the herbicidal activity of I are generally suitable, for example alkali metal salts, in particular the sodium or potassium salt, alkaline earth metal salts, in particular the calcium, magnesium or barium salt, manganese, copper, zinc or iron salt and also ammonium, phosphonium, sulfonium or sulfoxonium salts, for example ammonium salts, tetraalkylammonium salts, benzyltrialkylammonium salts, trialkylsulfonium salts or trialkylsulfoxonium salts.
- the styrene derivatives I are suitable, both as isomer mixtures and in the form of the pure isomers, as herbicides.
- the compounds I or the herbicidal and defolianting compositions comprising them can be sprayed, for example in the form of directly sprayable solutions, powders, suspensions, including high-strength aqueous, oily or other suspensions or dispersions, emulsions, oil dispersions, pastes, dusts, sprays or granules. Nebulization, dusting, scattering or pouring can be used.
- the application forms depend on the purposes; in any case, they should ensure the finest possible distribution of the active compounds according to the invention.
- the styrene derivatives I are generally suitable for the preparation of directly sprayable solutions, emulsions, pastes or oil dispersions.
- Mineral oil fractions of medium to high boiling point such as kerosene or diesel oil, furthermore coal tar oils as well as oils of vegetable or animal origin, aliphatic, cyclic and aromatic hydrocarbons, e.g.
- strongly polar solvents such as N, N-dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, N-methylpyrrolidone or water .
- Aqueous use forms can be prepared from emulsion concentrates, dispersions, pastes, wettable powders or water-dispersible granules by adding water.
- emulsions, pastes or oil dispersions the substrates as such or dissolved in an oil or solvent can be homogenized in water by means of wetting agents, adhesives, dispersants or emulsifiers.
- concentrates consisting of an active substance, wetting agent, tackifier, dispersant or emulsifier and possibly solvent or oil, which are suitable for dilution with water.
- alkali, alkaline earth, ammonium salts of aromatic sulfonic acids e.g. Lignin, phenol, naphthalene and dibutylnaphthalenesulfonic acid, as well as of fatty acids, alkyl and alkylarylsulfonates, alkyl, lauryl ether and fatty alcohol sulfates, and salts of sulfated hexa-, hepta- and octadecanols, as well as fatty alcohol glycol ethers, condensation products of sulfonated naphthalene and its derivatives with formaldehyde, condensation products of naphthalene or naphthalenesulfonic acids with phenol and formaldehyde, polyoxyethylene octylphenol ether, ethoxylated isooctyl, octyl or nonylphenol, alkylphenyl, tributylphenyl poly
- Powders, materials for broadcasting and dusts can be prepared by mixing or grinding the active substances together with a solid carrier.
- Granules e.g. Coated, impregnated and homogeneous granules can be produced by binding the active ingredients to solid carriers.
- Solid carriers are mineral earths like. Silicas, silica gels, silicates, talc, kaolin, limestone, lime, chalk, bolus, loess, clay, dolomite, diatomaceous earth, calcium and magnesium sulfate, magnesium oxide, ground plastics, fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium nitrate, ureas and vegetable products such as cereal flour , Tree bark, wood and nutshell flour, cellulose powder or other solid carriers.
- the formulations contain between 0.01 and 95% by weight, preferably between 0.5 and 90% by weight, of active ingredient.
- the active ingredients are used in a purity of 90% to 100%, preferably 95% to 100% (according to the NMR spectrum).
- the herbicidal compositions or the active compounds can be applied pre- or post-emergence. If the active ingredients are less compatible with certain crop plants, application techniques can be used in which the herbicidal compositions are sprayed with the aid of sprayers in such a way that the leaves of the sensitive crop plants are not hit as far as possible, while the active ingredients are applied to the leaves of undesirable plants growing below them or the uncovered floor area (post-directed, lay-by).
- the application rates of active ingredient are 0.001 to 3, preferably 0.01 to 1 kg / ha of active substance (a.S.).
- the compounds I can also be used for the desiccation of cotton, since they promote the formation of separating tissue between the leaf and shoot part of the plant.
- the compounds according to the invention or compositions containing them can also be used in a further number of crop plants for eliminating unwanted plants.
- the following crops are considered, for example:
- the styrene derivatives I can be mixed with numerous representatives of other herbicidal or growth-regulating active compound groups and applied together.
- Plastic flower pots with loamy sand with about 3.0% humus as substrate served as culture vessels.
- the seeds of the test plants were sown separately according to species.
- the active ingredients suspended or emulsified in water were applied directly after sowing using finely distributing nozzles.
- the tubes were lightly sprinkled to promote germination and growth and then covered with clear plastic hoods until the plants had grown. This cover causes the test plants to germinate evenly, unless this was affected by the active ingredients.
- test plants were treated with the active ingredients suspended or emulsified in water only at a growth height of 3 to 15 cm, depending on the growth habit.
- the application rate for post-emergence treatment was 0.03 kg / ha as
- the plants were kept at 10-25 ° C and 20-35 ° C depending on the species.
- the trial period lasted 2 to 4 weeks. During this time, the plants were cared for and their response to the individual treatments was evaluated.
- Evaluation was carried out on a scale from 0 to 100. 100 means no emergence of the plants or complete destruction of at least the aerial parts and 0 means no damage or normal growth.
- the plants used in the greenhouse experiments are composed of the following types: Latin name German name Abutilon theophrasti Chinese hemp Amaranthus retroflexus Curved foxtail Oryza sativa rice Solanum nigrum Black nightshade Ipomoea subspecies Magnificent wind species Triticum aestivum Summer wheat
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Agronomy & Crop Science (AREA)
- Pest Control & Pesticides (AREA)
- Plant Pathology (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Agricultural Chemicals And Associated Chemicals (AREA)
- Pyrrole Compounds (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
- Nitrogen And Oxygen Or Sulfur-Condensed Heterocyclic Ring Systems (AREA)
- Indole Compounds (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
- Preparation Of Compounds By Using Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Saccharide Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft neue Styrolderivate der allgemeinen Formel I
- R1
- Wasserstoff oder Halogen;
- R2
- Halogen;
- R3
- Wasserstoff, Halogen oder C1-C4-Alkyl;
- R4
- Cyano oder C1-C6-Alkylcarbonyl;
- A
- einen heterocyclischen Rest, ausgewählt aus der Gruppe A1 bis A4
sowie deren landwirtschaftlich brauchbaren Salze, wobei die Formel I sämtliche isomere Formen dieser Verbindungen umfaßt.The present invention relates to new styrene derivatives of the general formula I.
- R 1
- Hydrogen or halogen;
- R 2
- Halogen;
- R 3
- Hydrogen, halogen or C 1 -C 4 alkyl;
- R 4
- Cyano or C 1 -C 6 alkylcarbonyl;
- A
- a heterocyclic radical selected from the group A 1 to A 4
and their agriculturally useful salts, the formula I encompassing all isomeric forms of these compounds.
Des weiteren betrifft die Erfindung Verfahren zur Herstellung dieser Verbindungen sowie herbizide Mittel und Verfahren zur Entblätterung (Desikkation) von Baumwolle.The invention further relates to processes for the preparation of these compounds and herbicidal compositions and processes for defoliation (desiccation) of cotton.
Aus der japanischen Offenlegungsschrift JP-A Kokai 27962/1986 und der DE-A 37 24 399 sind Zimtsäureester der Struktur I' bekannt
Außerdem fallen diejenigen Verbindungen I mit A = A2, n = 0, R1 = Wasserstoff und R3 = Wasserstoff, Chlor, Brom oder C1-C4-Alkyl unter die allgemeine Lehre der DE-A 36 03 789, diejenigen mit A = A2, n = 1 und R1 = H oder Fluor unter die allgemeine Lehre der DE-A 39 17 676.In addition, those compounds I with A = A 2 , n = 0, R 1 = hydrogen and R 3 = hydrogen, chlorine, bromine or C 1 -C 4 alkyl fall under the general teaching of DE-A 36 03 789, those with A = A 2 , n = 1 and R 1 = H or fluorine under the general teaching of DE-A 39 17 676.
Da die Verbindungen des o.g. Standes der Technik entweder nicht ausreichende Selektivität aufweisen oder hinsichtlich der benötigten Aufwandmengen zu wünschen übrig lassen, lag der Erfindung die Aufgabe zugrunde, Verbindungen zur Verfügung zu stellen, die herbizid besonders gut wirksam sind. Weiterhin sollten die Verbindungen als Bioregulatoren, insbesondere zur Entblätterung von Baumwolle, verwendbar sein.Since the compounds of the abovementioned prior art either do not have sufficient selectivity or leave anything to be desired in terms of the application rates required, the object of the invention was to provide compounds which are particularly effective as herbicides. Furthermore, the compounds should be usable as bioregulators, in particular for the defoliation of cotton.
Es wurde nun gefunden, daß die eingangs definierten Styrolderivate I auch bei geringen Aufwandmengen eine gute herbizide Wirksamkeit besitzen und sehr gut zur Entblätterung von Baumwolle geeignet sind.It has now been found that the styrene derivatives I defined at the outset have good herbicidal activity even at low application rates and are very suitable for defoliation of cotton.
Man erhält die Verbindungen der Formel I, indem man einen geeignet substituierten Benzaldehyd der Formel II mit einem Phosphoran der Formel III in an sich bekannter Weise, z.B. analog den in Synthesis 10 (1984) 862 beschriebenen Bedingungen, in einem Lösungsmittel bei Temperaturen zwischen 0°C und dem Siedepunkt des Lösungsmittels umsetzt:
Ar in Formel III bedeutet einen unsubstituierten oder substituierten Arylrest, wobei im allgemeinen der Phenylrest bevorzugt wird.Ar in formula III means an unsubstituted or substituted aryl radical, with the phenyl radical generally being preferred.
Die zur Herstellung der Styrolderivate I benötigten Phosphorane III, welche auch als Phosphor-Ylide bezeichnet werden, sind nach literaturbekannten Methoden (z.B. Houben-Weyl, Methoden der Organischen Chemie, Bd. E1, S. 636-639, Georg-Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1982 oder Chem. Ber. 95, 1962, Seite 3993) erhältlich.The phosphoranes III required for the preparation of the styrene derivatives I, which are also referred to as phosphorus ylides, are based on methods known from the literature (for example Houben-Weyl, Methods of Organic Chemistry, Vol. E1, pp. 636-639, Georg-Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1982 or Chem. Ber. 95 , 1962, page 3993).
Die Gruppen Ar dieser Phosphorane können unsubstituierte oder substituierte Phenylreste sein. Die Zahl der Substituenten pro Phenylrest sowie das Substitutionsmuster der Phenylreste sind in der Regel für das Gelingen des Verfahrens nicht kritisch, im allgemeinen trägt ein Phenylrest aber nicht mehr als 3 Substituenten. Als Substituenten der Phenylreste sind solche bevorzugt, welche sich unter den Bedingungen des Verfahrens inert verhalten, z.B. die Halogenide Fluor, Chlor und Brom, Alkylgruppen, bevorzugt C1- bis C4-Alkylgruppen, insbesondere die Methylgruppe, oder C1- bis C4-Alkoxygruppen, insbesondere die Methoxygruppe. Allerdings werden in der Regel Triarylphosphorane III mit unsubstituiertem Phenylrest bevorzugt.The Ar groups of these phosphoranes can be unsubstituted or substituted phenyl radicals. The number of substituents per phenyl radical and the substitution pattern of the phenyl radicals are generally not critical for the success of the process, but in general a phenyl radical carries no more than 3 substituents. Preferred substituents for the phenyl radicals are those which are inert under the conditions of the process, for example the halides fluorine, chlorine and bromine, alkyl groups, preferably C 1 to C 4 alkyl groups, in particular the methyl group, or C 1 to C 4 -Alkoxy groups, especially the methoxy group. However, triarylphosphoranes III with an unsubstituted phenyl radical are generally preferred.
Die Umsetzung der Ausgangsverbindungen II und III wird im allgemeinen vorteilhaft in Gegenwart eines Lösungsmittels durchgeführt. Als Lösungsmittel können alle üblicherweise bei der Durchführung von Wittig-Reaktionen verwendeten Lösungsmittel Anwendung finden, beispielsweise halogenierte Lösungsmittel wie Chloroform, oder Ether wie Tetrahydrofuran, Dioxan und Ethylenglykoldimethylether. Bevorzugte Lösungsmittel sind Alkohole, insbesondere C1- bis C4-Alkohole wie Methanol, Ethanol, Propanol, Isopropanol, Butanol, Isobutanol und tert.-Butanol. Die Lösungsmittel können auch in Form von Lösungsmittelgemischen eingesetzt werden, in der Regel werden jedoch bevorzugt die reinen Lösungsmittel verwendet.The reaction of the starting compounds II and III is generally carried out advantageously in the presence of a solvent. As solvents, all can usually be carried out solvents used by Wittig reactions are used, for example halogenated solvents such as chloroform, or ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether. Preferred solvents are alcohols, especially C 1 to C 4 alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, propanol, isopropanol, butanol, isobutanol and tert-butanol. The solvents can also be used in the form of solvent mixtures, but the pure solvents are generally preferred.
Im allgemeinen wird die Reaktion bei Temperaturen zwischen 0°C und 100°C ausgeführt. Es versteht sich jedoch von selbst, daß die optimale Reaktionstemperatur von den jeweils umzusetzenden Ausgangsverbindungen II und III sowie dem verwendeten Lösungsmittel abhängig ist.In general, the reaction is carried out at temperatures between 0 ° C and 100 ° C. However, it goes without saying that the optimum reaction temperature depends on the starting compounds II and III to be reacted in each case and on the solvent used.
Die Ausgangsverbindungen II und III können in stöchiometrischen Mengen miteinander umgesetzt werden. Es kann sich jedoch als vorteilhaft erweisen, wenn einer der beiden Reaktanden, II oder III, in einem 0,05-5fachen molaren Überschuß in die Reaktion eingesetzt wird.The starting compounds II and III can be reacted with one another in stoichiometric amounts. However, it may prove advantageous if one of the two reactants, II or III, is used in a 0.05-5-fold molar excess in the reaction.
Der Verlauf der Wittig-Reaktion kann mittels üblicher analytischer Methoden, wie Dünnschichtchromatographie und Hochdruckflüssigkeitschromatographie, verfolgt werden. Nach beendeter Reaktion kann das Produkt I nach herkömmlichen Verfahren wie Filtration, Zentrifugation oder durch Zugabe von Wasser mit anschließender Extraktion isoliert werden. Gewünschtenfalls können die so erhaltenen Styrolderivate I beispielsweise durch Umkristallisation oder mittels chromatographischer Methoden weiter gereinigt werden.The course of the Wittig reaction can be followed using conventional analytical methods such as thin layer chromatography and high pressure liquid chromatography. After the reaction has ended, the product I can be isolated by conventional methods such as filtration, centrifugation or by adding water with subsequent extraction. If desired, the styrene derivatives I thus obtained can be purified further, for example by recrystallization or by means of chromatographic methods.
Nach vorstehendem Verfahren werden die Styrolderivate I hinsichtlich der Alkenylseitenkette im allgemeinen als cis-trans-Isomerengemische erhalten, wobei in der Regel das trans-Isomere überwiegt.According to the above process, the styrene derivatives I are generally obtained as cis-trans isomer mixtures with respect to the alkenyl side chain, the trans isomer generally predominating.
Das Verfahren zur Herstellung der Styrolderivate der Formel I beinhaltet weiterhin die Möglichkeit, die Reihenfolge in der Synthese der Benzaldehyde der allgemeinen Formel II und die Wittig-Olefinierung zu vertauschen.The process for the preparation of the styrene derivatives of the formula I also includes the possibility of interchanging the sequence in the synthesis of the benzaldehydes of the general formula II and the Wittig olefination.
Es besteht insbesondere die Möglichkeit geeignete Vorstufen der Benzaldehyde II mit den Phosphoranen III umzusetzen, und erst dann die entsprechenden Substituenten im Benzaldehydteil zu der Struktur der allgemeinen Formel I zu ergänzen (wie weiter unten beschrieben).In particular, it is possible to implement suitable precursors of the benzaldehydes II with the phosphoranes III and only then to add the corresponding substituents in the benzaldehyde part to the structure of the general formula I (as described below).
Die als Ausgangsmaterial verwendeten Benzaldehyde der allgemeinen Formel II sind nach den Methoden der DE-A 38 15 042 (≙ EP-A 340 708) auf einfache Weise zugänglich oder können beispielsweise wie nachfolgend beschrieben hergestellt werden.The benzaldehydes of the general formula II used as starting material are easily accessible by the methods of DE-A 38 15 042 (≙ EP-A 340 708) or can be prepared, for example, as described below.
Man erhält die Benzaldehyde der Formel IIc, d wenn man ein Anilinderivat der Formel IV entsprechend den für IX geschilderten Bedingungen zuerst mit Thiophosgen in das entsprechende Isothiocyanat V überführt, V an ein Piperazin VI addiert, das so erhaltene Thioharnstoffderivat VII unter saurer Spaltung der Acetalgruppe zur Aldehydfunktion mit einem Phosgenierungsmittel oder zum Aldehyd IIc, d cyclisiert:
In den Formeln IV, V, VII, VIII bedeutet B eine Ethylen- oder Propyleneinheit, welche ein bis drei Alkylgruppen wie Methyl, Ethyl, Propyl und 1-Methylethyl, vorzugsweise Methyl, tragen kann. Die gepunktete Linie in den Formeln VI, VII, VIII und IIc, d steht für eine ggf. vorhandene π-Bindung.In the formulas IV, V, VII, VIII, B denotes an ethylene or propylene unit which can carry one to three alkyl groups such as methyl, ethyl, propyl and 1-methylethyl, preferably methyl. The dotted line in the formulas VI, VII, VIII and IIc, d stands for a π bond that may be present.
Die Umsetzungen von IV zu V, von V zu VII und von VII zu VIII verlaufen unter den nachstehend geschilderten Bedingungen analog zur zweiten Synthesevariante von Ic, d.The reactions from IV to V, from V to VII and from VII to VIII proceed under the conditions described below analogously to the second synthesis variant of Ic, i.
Die Acetalgruppe in Verbindung VIII wird unter sauren Bedingungen beispielsweise in Gegenwart von Mineralsäuren wie Salzsäure und Schwefelsäure oder organischen Säuren wie p-Toluolsulfonsäure in die Aldehydfunktion übergeführt.The acetal group in compound VIII is converted into the aldehyde function under acidic conditions, for example in the presence of mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid or organic acids such as p-toluenesulfonic acid.
Man erhält die Verbindungen I mit den Resten A1 und A2 aber beispielsweise auch dadurch, daß man ein Anilin der allgemeinen Formel IX mit Anhydriden der allgemeinen Formel Xa oder Xb kondensiert:
Für die Kondensation dienen inerte organische Lösungsmittel wie niedere Alkansäuren wie Essigsäure, Propionsäure und Isobuttersäure, sowie die Ester dieser Säuren wie Essigsäureethylester, höhersiedende Kohlenwasserstoffe wie Toluol und Xylol und/oder Dimethylformamid. Die Umsetzung erfolgt in der Regel bei Temperaturen zwischen 25°C und dem Siedepunkt der jeweiligen Reaktionsmischung, vorzugsweise zwischen 50 und 140°C. Bei Verwendung eines aprotischen Lösungsmittels empfiehlt es sich, das Wasser fortlaufend zu entfernen.Inert organic solvents such as lower alkanoic acids such as acetic acid, propionic acid and isobutyric acid and the esters of these acids such as ethyl acetate, higher-boiling hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene and / or dimethylformamide are used for the condensation. The reaction is usually carried out at temperatures between 25 ° C. and the boiling point of the respective reaction mixture, preferably between 50 and 140 ° C. When using an aprotic solvent, it is advisable to remove the water continuously.
Die Aniline IX erhält man beispielsweise durch Reduktion aus den entsprechenden Nitroderivaten analog bekannter Methoden (DE-A 37 24 399, DE-A 36 03 789):
Die Umsetzung der Nitrobenzaldehyde XI mit den Phosphoranen III erfolgt analog zu den oben beschriebenen Methoden.The reaction of the nitrobenzaldehydes XI with the phosphoranes III is carried out analogously to the methods described above.
In der zweiten Stufe der Reaktionsfolge wird ein Nitrostyrol XII in an sich bekannter Weise mit anorganischen Verbindungen wie Zinn-II-salzen oder Eisen oder Zinn oder durch katalytische Hydrierung an Metallkontakten wie Raney-Nickel, Palladium und Platin in einem inerten organischen Lösungsmittel zum Anilinderivat IX reduziert.In the second stage of the reaction sequence, a nitrostyrene XII is converted to aniline derivative IX in a manner known per se using inorganic compounds such as tin-II salts or iron or tin or by catalytic hydrogenation on metal contacts such as Raney nickel, palladium and platinum in an inert organic solvent reduced.
Geeignete Lösungsmittel für die Reaktion mit anorganischen Verbindungen sind beispielsweise Alkohole wie Methanol, Ethanol und Isopropanol und niedere Alkansäuren wie Ameisensäure, Essigsäure und Propionsäure sowie entsprechende Gemische. Die Reaktionstemperaturen liegen bei 25°C bis 150°C, vorzugsweise bei 25°C bis 100°C.Suitable solvents for the reaction with inorganic compounds are, for example, alcohols such as methanol, ethanol and isopropanol and lower alkanoic acids such as formic acid, acetic acid and propionic acid and corresponding mixtures. The reaction temperatures are 25 ° C to 150 ° C, preferably 25 ° C to 100 ° C.
Sofern man die Reduktion an Metallkontakten mit Wasserstoff durchführt, eignen sich Lösungsmittel wie Methanol oder andere Alkohole, Dimethylformamid, Propionsäure, Tetrahydrofuran und Eisessig und entsprechende Gemische bei einem Wasserstoffdruck von 1 bis 150 bar, vorzugsweise 1 bis 50 bar und Temperaturen von 25°C bis 100°C, vorzugsweise 25 bis 70°C.If the reduction is carried out on metal contacts with hydrogen, solvents such as methanol or other alcohols, dimethylformamide, propionic acid, tetrahydrofuran and glacial acetic acid and corresponding mixtures at a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 150 bar, preferably 1 to 50 bar and temperatures of 25 ° C. to 100 ° C, preferably 25 to 70 ° C.
Man erhält die Verbindungen Ic, d beispielsweise aber auch dadurch, daß man ein Derivat der allgemeinen Formel IX in an sich bekannter Weise (Houben-Weyl, Bd. IX, S. 867 f. (1955)) in einem inerten organischen Lösungsmittel mit Thiophosgen in das entsprechende Isothiocyanat XIII überführt, XIII anschließend in einem aprotisch polaren Lösungsmittel an ein Tetrahydro- oder Perhydrodiazinderivat VI addiert und den so erhaltenen Thioharnstoff XIV mit einem Phosgenierungsmittel oder Thiophosgenierungsmittel (Phos.) zu Ic, d cyclisiert:
Die Umsetzung des Derivats IX mit Thiophosgen erfolgt in der Regel bei Temperaturen von (-50)°C bis 100°C, vorzugsweise 0°C bis 50°C.The reaction of derivative IX with thiophosgene generally takes place at temperatures from (-50) ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 50 ° C.
Diese Umsetzung kann sowohl in einem Zweiphasen-Lösungsmittelsystem wie Methylenchlorid/Wasser als auch in Gegenwart einer Base in einem aprotisch polaren organischen Lösungsmittel durchgeführt werden.This reaction can be carried out both in a two-phase solvent system such as methylene chloride / water and in the presence of a base in an aprotic polar organic solvent.
Im letztgenannten Fall arbeitet man bevorzugt in Toluol in Gegenwart einer organischen Base, vorzugsweise eines tertiären Amins wie Triethylamin.In the latter case, it is preferred to work in toluene in the presence of an organic base, preferably a tertiary amine such as triethylamine.
Die Umsetzung der Isothiocyanate XIII mit den Piperazinen VI erfolgt bevorzugt in aprotisch polaren Lösungsmitteln wie vorzugsweise Ethern, insbesondere Tetrahydrofuran bei Temperaturen von (-50)°C bis 100°C, vorzugsweise 0°C bis 50°C.The reaction of the isothiocyanates XIII with the piperazines VI is preferably carried out in aprotic polar solvents such as preferably ethers, in particular tetrahydrofuran at temperatures from (-50) ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 50 ° C.
Die anschließende Cyclisierung des Thioharnstoffs XIV mit einem Phosgenierungsmittel oder Thiophosgenierungsmittel geschieht in der Regel bei Temperaturen von 0°C bis 100°C, vorzugsweise 20°C bis 70°C in einem aprotisch polaren Lösungsmittel in Gegenwart einer Base.The subsequent cyclization of thiourea XIV with a phosgenating agent or thiophosgenating agent is usually carried out at temperatures from 0 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 20 ° C. to 70 ° C. in an aprotic polar solvent in the presence of a base.
Als Phosgenierungsmittel und Thiophosgenierungsmittel eignen sich insbesondere Phosgen, Thiophosgen und Chlorameisensäuretrichlormethylester.Particularly suitable phosgenating agents and thiophosgenating agents are phosgene, thiophosgene and trichloromethyl chloroformate.
Als Lösungsmittel dienen vorzugsweise Ether, Halogenkohlenwasserstoffe und Kohlenwasserstoffe, insbesondere Halogenkohlenwasserstoffe wie Methylenchlorid.Ether, halogenated hydrocarbons and hydrocarbons, in particular halogenated hydrocarbons such as methylene chloride, are preferably used as solvents.
Geeignete Basen Sind tertiäre Amine wie insbesondere Pyridin.Suitable bases are tertiary amines such as pyridine in particular.
Die Styrolderivate I können bei der Herstellung als Isomerengemische anfallen, wobei Enantiomeren- oder Diastereomerengemische und insbesondere E-/Z-Isomerengemische möglich sind. Die Isomerengemische können gewünschtenfalls nach den hierfür üblichen Methoden, z.B. durch Chromatographie oder durch Kristallisation, getrennt werden.The styrene derivatives I can be obtained in the preparation as isomer mixtures, enantiomer or diastereomer mixtures and in particular E / Z isomer mixtures being possible. If desired, the isomer mixtures can be prepared by the usual methods, e.g. be separated by chromatography or by crystallization.
Im Hinblick auf die bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung der Verbindungen I als Herbizide kommen als Substituenten vorzugsweise folgende Reste in Betracht:
- R1
- Wasserstoff oder Halogen, wie Fluor, Chlor und Brom, insbesondere Wasserstoff oder Fluor;
- R2
- Halogen wie Fluor, Chlor und Brom, insbesondere Chlor;
- R3
- Wasserstoff; ein Halogenatom wie unter R2 genannt, aber auch Jod, insbesondere Chlor und Brom; eine verzweigte oder unverzweigte C1-C4-Alkylgruppe wie Methyl, Ethyl, n-Propyl, Isopropyl, n-Butyl, 1-Methylpropyl, 2-Methylpropyl und 1,1-Dimethylethyl, insbesondere Methyl und Ethyl;
- R4
- Cyano; C1-C6-Alkylcarbonyl, wobei als Alkylreste Methyl, Ethyl, n-Propyl, Isopropyl, n-Butyl, 1-Methylpropyl, 2-Methylpropyl, 1,1-Dimethylethyl, n-Pentyl, 1-Methylbutyl, 2-Methylbutyl, 3-Methylbutyl, 1,2-Dimethylpropyl, 1,1-Dimethylpropyl, 2,2-Dimethylpropyl, 1-Ethylpropyl, n-Hexyl, 1-Methylpentyl, 2-Methylpentyl, 3-Methylpentyl, 4-Methylpentyl, 1,2-Dimethylbutyl, 1,3-Dimethylbutyl, 2,3-Dimethylbutyl, 1,1-Dimethylbutyl, 2,2-Dimethylbutyl, 3,3-Dimethylbutyl, 1,1,2-Trimethylpropyl, 1,2,2-Trimethylpropyl, 1-Ethylbutyl, 2-Ethylbutyl und 1-Ethyl-2-methylpropyl, insbesondere Methyl, Ethyl, n-Propyl und Isopropyl in Betracht kommen;
- R5 und R6
- Wasserstoff, Methyl und Ethyl.
- R 1
- Hydrogen or halogen, such as fluorine, chlorine and bromine, in particular hydrogen or fluorine;
- R 2
- Halogen such as fluorine, chlorine and bromine, especially chlorine;
- R 3
- Hydrogen; a halogen atom as mentioned under R 2 , but also iodine, especially chlorine and bromine; a branched or unbranched C 1 -C 4 alkyl group such as methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, 1-methylpropyl, 2-methylpropyl and 1,1-dimethylethyl, in particular methyl and ethyl;
- R 4
- Cyano; C 1 -C 6 -alkylcarbonyl, where as alkyl radicals are methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, 1-methylpropyl, 2-methylpropyl, 1,1-dimethylethyl, n-pentyl, 1-methylbutyl, 2-methylbutyl , 3-methylbutyl, 1,2-dimethylpropyl, 1,1-dimethylpropyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl, 1-ethylpropyl, n-hexyl, 1-methylpentyl, 2-methylpentyl, 3-methylpentyl, 4-methylpentyl, 1,2 -Dimethylbutyl, 1,3-dimethylbutyl, 2,3-dimethylbutyl, 1,1-dimethylbutyl, 2,2-dimethylbutyl, 3,3-dimethylbutyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropyl, 1,2,2-trimethylpropyl, 1-ethylbutyl, 2-ethylbutyl and 1-ethyl-2-methylpropyl, in particular methyl, ethyl, n-propyl and isopropyl;
- R 5 and R 6
- Hydrogen, methyl and ethyl.
Die Styrolderivate I können in Form ihrer landwirtschaftlich brauchbaren Salze vorliegen. Allgemein eignen sich die Salze von solchen Säuren, welche die herbizide Wirkung von I nicht beeinträchtigen, beispielsweise Alkalimetallsalze, insbesondere das Natrium- oder Kaliumsalz, Erdalkalisalze, insbesondere das Calcium-, Magnesium- oder Bariumsalz, Mangan-, Kupfer-, Zink- oder Eisensalz sowie Ammonium-, Phosphonium-, Sulfonium- oder Sulfoxoniumsalze, beispielsweise Ammoniumsalze, Tetraalkylammoniumsalze, Benzyltrialkylammoniumsalze, Trialkylsulfoniumsalze oder Trialkylsulfoxoniumslaze.The styrene derivatives I can be in the form of their agriculturally useful salts. The salts of acids which do not impair the herbicidal activity of I are generally suitable, for example alkali metal salts, in particular the sodium or potassium salt, alkaline earth metal salts, in particular the calcium, magnesium or barium salt, manganese, copper, zinc or iron salt and also ammonium, phosphonium, sulfonium or sulfoxonium salts, for example ammonium salts, tetraalkylammonium salts, benzyltrialkylammonium salts, trialkylsulfonium salts or trialkylsulfoxonium salts.
Beispielsweise seien die in den nachstehenden Tabellen 1 bis 5 aufgeführten Verbindungen I genannt.
Die Styrolderivate I eignen sich, sowohl als Isomerengemische als auch in Form der reinen Isomeren, als Herbizide. Die Verbindungen I bzw. die sie enthaltenden herbiziden und entblätternden Mittel können beispielsweise in Form von direkt versprühbaren Lösungen, Pulvern, Suspensionen, auch hochprozentigen wäßrigen, öligen oder sonstigen Suspensionen oder Dispersionen, Emulsionen, Öldispersionen, Pasten, Stäubemitteln, Streumitteln oder Granulaten durch Versprühen, Vernebeln, Verstäuben, Verstreuen oder Gießen angewendet werden. Die Anwendungsformen richten sich nach den Verwendungszwecken; sie sollten in jedem Fall möglichst die feinste Verteilung der erfindungsgemäßen Wirkstoffe gewährleisten.The styrene derivatives I are suitable, both as isomer mixtures and in the form of the pure isomers, as herbicides. The compounds I or the herbicidal and defolianting compositions comprising them can be sprayed, for example in the form of directly sprayable solutions, powders, suspensions, including high-strength aqueous, oily or other suspensions or dispersions, emulsions, oil dispersions, pastes, dusts, sprays or granules. Nebulization, dusting, scattering or pouring can be used. The application forms depend on the purposes; in any case, they should ensure the finest possible distribution of the active compounds according to the invention.
Die Styrolderivate I eignen sich allgemein zur Herstellung von direkt versprühbaren Lösungen, Emulsionen, Pasten oder Öldispersionen. Als inerte Zusatzstoffe kommen Mineralölfraktionen von mittlerem bis hohem Siedepunkt, wie Kerosin oder Dieselöl, ferner Kohlenteeröle sowie Öle pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs, aliphatische, cyclische und aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffe, z.B. Toluol, Xylol, Paraffin, Tetrahydronaphthalin, alkylierte Naphthaline oder deren Derivate, Methanol, Ethanol, Propanol, Butanol, Cyclohexanol, Cyclohexanon, Chlorbenzol, Isophoron oder stark polare Lösungsmittel, wie N,N-Dimethylformamid, Dimethylsulfoxid, N-Methylpyrrolidon oder Wasser in Betracht.The styrene derivatives I are generally suitable for the preparation of directly sprayable solutions, emulsions, pastes or oil dispersions. Mineral oil fractions of medium to high boiling point, such as kerosene or diesel oil, furthermore coal tar oils as well as oils of vegetable or animal origin, aliphatic, cyclic and aromatic hydrocarbons, e.g. Toluene, xylene, paraffin, tetrahydronaphthalene, alkylated naphthalenes or their derivatives, methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone, chlorobenzene, isophorone or strongly polar solvents, such as N, N-dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, N-methylpyrrolidone or water .
Wäßrige Anwendungsformen können aus Emulsionskonzentraten, Dispersionen, Pasten, netzbaren Pulvern oder wasserdispergierbaren Granulaten durch Zusatz von Wasser bereitet werden. Zur Herstellung von Emulsionen, Pasten oder Öldispersionen können die Substrate als solche oder in einem Öl oder Lösungsmittel gelöst, mittels Netz-, Haft-, Dispergier- oder Emulgiermittel in Wasser homogenisiert werden. Es können aber auch aus wirksamer Substanz, Netz-, Haft-, Dispergier- oder Emulgiermittel und eventuell Lösungsmittel oder Öl bestehende Konzentrate hergestellt werden, die zur Verdünnung mit Wasser geeignet sind.Aqueous use forms can be prepared from emulsion concentrates, dispersions, pastes, wettable powders or water-dispersible granules by adding water. To prepare emulsions, pastes or oil dispersions, the substrates as such or dissolved in an oil or solvent can be homogenized in water by means of wetting agents, adhesives, dispersants or emulsifiers. However, it is also possible to prepare concentrates consisting of an active substance, wetting agent, tackifier, dispersant or emulsifier and possibly solvent or oil, which are suitable for dilution with water.
Als oberflächenaktive Stoffe kommen die Alkali-, Erdalkali-, Ammoniumsalze von aromatischen Sulfonsäuren, z.B. Lignin-, Phenol-, Naphthalin- und Dibutylnaphthalinsulfonsäure, sowie von Fettsäuren, Alkyl- und Alkylarylsulfonaten, Alkyl-, Laurylether- und Fettalkoholsulfaten, sowie Salze sulfatierter Hexa-, Hepta- und Octadecanolen, sowie von Fettalkoholglykolether, Kondensationsprodukte von sulfoniertem Naphthalin und seiner Derivate mit Formaldehyd, Kondensationsprodukte des Naphthalins bzw. der Naphthalinsulfonsäuren mit Phenol und Formaldehyd, Polyoxyethylenoctylphenolether, ethoxyliertes Isooctyl-, Octyl- oder Nonylphenol, Alkylphenyl-, Tributylphenylpolyglykolether, Alkylarylpolyetheralkohole, Isotridecylalkohol, Fettalkoholethylenoxid-Kondensate, ethoxyliertes Rizinusöl, Polyoxyethylenalkylether oder Polyoxypropylenalkylether, Laurylalkoholpolyglykoletheracetat, Sorbitester, Lignin-Sulfitablaugen oder Methylcellulose in Betracht.The alkali, alkaline earth, ammonium salts of aromatic sulfonic acids, e.g. Lignin, phenol, naphthalene and dibutylnaphthalenesulfonic acid, as well as of fatty acids, alkyl and alkylarylsulfonates, alkyl, lauryl ether and fatty alcohol sulfates, and salts of sulfated hexa-, hepta- and octadecanols, as well as fatty alcohol glycol ethers, condensation products of sulfonated naphthalene and its derivatives with formaldehyde, condensation products of naphthalene or naphthalenesulfonic acids with phenol and formaldehyde, polyoxyethylene octylphenol ether, ethoxylated isooctyl, octyl or nonylphenol, alkylphenyl, tributylphenyl polyglycol ether, alkylaryl polyether alcohols, isotridecyl alcohol, polyether ethoxylate, fatty alcohol, ethoxylated ethoxylated ethoxylated alcohol, fatty alcohol ethoxylated ethoxylated ethoxylated alcohol, fatty alcohol ethoxylated ethoxylated polyether Lignin liquor or methyl cellulose into consideration.
Pulver-, Streu- und Stäubemittel können durch Mischen oder gemeinsames Vermahlen der wirksamen Substanzen mit einem festen Trägerstoff hergestellt werden.Powders, materials for broadcasting and dusts can be prepared by mixing or grinding the active substances together with a solid carrier.
Granulate, z.B. Umhüllungs-, Imprägnierungs- und Homogengranulate können durch Bindung der Wirkstoffe an feste Trägerstoffe hergestellt werden. Feste Trägerstoffe sind Mineralerden wie . Kieselsäuren, Kieselgele, Silikate, Talkum, Kaolin, Kalkstein, Kalk, Kreide, Bolus, Löß, Ton, Dolomit, Diatomeenerde, Calcium- und Magnesiumsulfat, Magnesiumoxid, gemahlene Kunststoffe, Düngemittel wie Ammoniumsulfat, Ammoniumphosphat, Ammoniumnitrat, Harnstoffe und pflanzliche Produkte wie Getreidemehl, Baumrinden-, Holz- und Nußschalenmehl, Cellulosepulver oder andere feste Trägerstoffe.Granules, e.g. Coated, impregnated and homogeneous granules can be produced by binding the active ingredients to solid carriers. Solid carriers are mineral earths like. Silicas, silica gels, silicates, talc, kaolin, limestone, lime, chalk, bolus, loess, clay, dolomite, diatomaceous earth, calcium and magnesium sulfate, magnesium oxide, ground plastics, fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium nitrate, ureas and vegetable products such as cereal flour , Tree bark, wood and nutshell flour, cellulose powder or other solid carriers.
Die Formulierungen enthalten zwischen 0,01 und 95 Gew.%, vorzugsweise zwischen 0,5 und 90 Gew.%, Wirkstoff. Die Wirkstoffe werden dabei in einer Reinheit von 90 % bis 100 %, vorzugsweise 95 % bis 100 % (nach NMR-Spektrum) eingesetzt.The formulations contain between 0.01 and 95% by weight, preferably between 0.5 and 90% by weight, of active ingredient. The active ingredients are used in a purity of 90% to 100%, preferably 95% to 100% (according to the NMR spectrum).
Die erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen I können beispielsweise wie folgt formuliert werden:
- I. Man vermischt 90 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung Nr. 2 mit 10 Gewichtsteilen N-Methyl-α-pyrrolidon und erhält eine Lösung, die zur Anwendung in Form kleinster Tropfen geeignet ist.
- II. 20 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung Nr. 3 werden in einer Mischung gelöst, die aus 80 Gewichtsteilen Xylol, 10 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 8 bis 10 Mol Ethylenoxid an 1 Mol Ölsäure-N-monoethanolamid, 5 Gewichtsteilen Calciumsalz der Dodecylbenzolsulfonsäure und 5 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 40 Mol Ethylenoxid an 1 Mol Ricinusöl besteht. Durch Ausgießen und feines Verteilen der Lösung in 100 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,02 Gew.% des Wirkstoffs enthält.
- III. 20 Gewichtsteile des Wirkstoffs Nr. 4 werden mit 3 Gewichtsteilen des Natriumsalzes der Diisobutylnaphthalin-α-sulfonsäure, 17 Gewichtsteilen des Natriumsalzes einer Ligninsulfonsäure aus einer Sulfit-Ablauge und 60 Gewichtsteilen pulverförmigem Kieselsäuregel gut vermischt und in einer Hammermühle vermahlen. Durch feines Verteilen der Mischung in 20 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine Spritzbrühe, die 0,1 Gew.% des Wirkstoffs enthält.
- IV. 3 Gewichtsteile des Wirkstoffs Nr. 6 werden mit 97 Gewichtsteilen feinteiligem Kaolin vermischt. Man erhält auf diese Weise ein Stäubemittel, das 3 Gew.% des Wirkstoffs enthält.
- V. 30 Gewichtsteile des Wirkstoffs Nr. 7 werden mit einer Mischung aus 92 Gewichtsteilen pulverförmigem Kieselsäuregel und 8 Gewichtsteilen Paraffinöl, das auf die Oberfläche dieses Kieselsäuregels gesprüht wurde, innig vermischt. Man erhält auf diese Weise eine Aufbereitung des Wirkstoffs mit guter Haftfähigkeit.
- VI. 20 Gewichtsteile des Wirkstoffs Nr. 9 werden mit 2 Gewichtsteilen Calciumsalz der Dodecylbenzolsulfonsäure, 8 Gewichtsteilen Fettalkohol-polyglykolether, 2 Gewichtsteilen Natriumsalz eines Phenol-Harnstoff-Formaldehyd-Kondensates und 68 Gewichtsteilen eines paraffinischen Mineralöls innig vermischt. Man erhält eine stabile ölige Dispersion.
- I. 90 parts by weight of compound no. 2 are mixed with 10 parts by weight of N-methyl-α-pyrrolidone and a solution is obtained which is suitable for use in the form of tiny drops.
- II. 20 parts by weight of compound no. 3 are dissolved in a mixture consisting of 80 parts by weight of xylene, 10 parts by weight of the adduct of 8 to 10 moles of ethylene oxide and 1 mole of oleic acid-N-monoethanolamide, 5 parts by weight of calcium salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid and 5 parts by weight of the adduct of 40 moles of ethylene oxide with 1 mole of castor oil. By pouring the solution into 100,000 parts by weight of water and finely distributing it therein, an aqueous dispersion is obtained which contains 0.02% by weight of the active ingredient.
- III. 20 parts by weight of active ingredient No. 4 are mixed well with 3 parts by weight of the sodium salt of diisobutylnaphthalene-α-sulfonic acid, 17 parts by weight of the sodium salt of lignosulfonic acid from a sulfite waste liquor and 60 parts by weight of powdered silica gel and ground in a hammer mill. By finely distributing the mixture in 20,000 parts by weight of water, a spray liquor is obtained which contains 0.1% by weight of the active ingredient.
- IV. 3 parts by weight of active ingredient No. 6 are mixed with 97 parts by weight of finely divided kaolin. In this way a dust is obtained which contains 3% by weight of the active ingredient.
- V. 30 parts by weight of active ingredient No. 7 are intimately mixed with a mixture of 92 parts by weight of powdered silica gel and 8 parts by weight of paraffin oil which has been sprayed onto the surface of this silica gel. In this way, a preparation of the active ingredient with good adhesiveness is obtained.
- VI. 20 parts by weight of active ingredient No. 9 are intimately mixed with 2 parts by weight of calcium salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 8 parts by weight of fatty alcohol polyglycol ether, 2 parts by weight of sodium salt of a phenol-urea-formaldehyde condensate and 68 parts by weight of a paraffinic mineral oil. A stable oily dispersion is obtained.
Die Applikation der herbiziden Mittel bzw. der Wirkstoffe kann im Vorauflauf- oder im Nachauflaufverfahren erfolgen. Sind die Wirkstoffe für gewisse Kulturpflanzen weniger verträglich, so können Ausbringungstechniken angewandt werden, bei welchen die herbiziden Mittel mit Hilfe der Spritzgeräte so gespritzt werden, daß die Blätter der empfindlichen Kulturpflanzen nach Möglichkeit nicht getroffen werden, während die Wirkstoffe auf die Blätter darunter wachsender unerwünschter Pflanzen oder die unbedeckte Bodenfläche gelangen (post-directed, lay-by).The herbicidal compositions or the active compounds can be applied pre- or post-emergence. If the active ingredients are less compatible with certain crop plants, application techniques can be used in which the herbicidal compositions are sprayed with the aid of sprayers in such a way that the leaves of the sensitive crop plants are not hit as far as possible, while the active ingredients are applied to the leaves of undesirable plants growing below them or the uncovered floor area (post-directed, lay-by).
Die Aufwandmengen an Wirkstoff betragen je nach Bekämpfungsziel, Jahreszeit, Zielpflanzen und Wachstumsstadium 0,001 bis 3, vorzugsweise 0,01 bis 1 kg/ha aktive Substanz (a.S.).Depending on the control target, the season, the target plants and the growth stage, the application rates of active ingredient are 0.001 to 3, preferably 0.01 to 1 kg / ha of active substance (a.S.).
Die Verbindungen I können daneben zur Dessikation von Baumwolle eingesetzt werden, da sie die Ausbildung von Trenngewebe zwischen Blatt- und Sproßteil der Pflanze fördern.The compounds I can also be used for the desiccation of cotton, since they promote the formation of separating tissue between the leaf and shoot part of the plant.
Außerdem führt die Verkürzung des Zeitintervalls, in dem die einzelnen Baumwollpflanzen reif werden, zu einer erhöhten Faserqualität nach der Ernte.In addition, the shortening of the time interval in which the individual cotton plants ripen leads to increased fiber quality after the harvest.
In Anbetracht der Vielseitigkeit der Applikationsmethoden können die erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen bzw. sie enthaltende Mittel noch in einer weiteren Zahl von Kulturplfanzen zur Beseitigung unerwünschter Pflanzen eingesetzt werden. In Betracht kommen beispielsweise folgende Kulturen:
Zur Verbreiterung des Wirkungsspektrums und zur Erzielung synergistischer Effekte können die Styrolderivate I mit zahlreichen Vertretern anderer herbizider oder wachstumsregulierender Wirkstoffgruppen gemischt und gemeinsam ausgebracht werden. Beispielsweise kommen als Mischungspartner Diazine, 4H-3,1-Benzoxazinderivate, Benzothiadiazinone, 2,6-Dinitroaniline, N-Phenylcarbamate, Thiolcarbamate, Halogencarbonsäuren, Triazine, Amide, Harnstoffe, Diphenylether, Triazinone, Uracile, Benzofuranderivate, Cyclohexan-1,3-dionderivate, Chinolincarbonsäurederivate, Sulfonylharnstoffe, Aryloxy-, Heteroaryloxyphenoxypropionsäuren sowie deren Salze, Ester und Amide und andere in Betracht.To widen the spectrum of activity and to achieve synergistic effects, the styrene derivatives I can be mixed with numerous representatives of other herbicidal or growth-regulating active compound groups and applied together. For example, diazines, 4H-3,1-benzoxazine derivatives, benzothiadiazinones, 2,6-dinitroanilines, N-phenyl carbamates, thiol carbamates, halocarboxylic acids, triazines, amides, ureas, diphenyl ethers, triazinones, uracils, benzofuran derivatives, cyclohexane-1,3- dione derivatives, quinoline carboxylic acid derivatives, sulfonylureas, aryloxy, heteroaryloxyphenoxypropionic acids and their salts, esters and amides and others into consideration.
Außerdem kann es von Nutzen sein, die neuen Verbindungen I allein oder in Kombination mit anderen Herbiziden auch noch mit weiteren Pflanzenschutzmitteln gemischt gemeinsam auszubringen, beispielsweise mit Mitteln zur Bekämpfung von Schädlingen oder phytopathogenen Pilzen bzw. Bakterien. Von Interesse ist ferner die Mischbarkeit mit Mineralsalzlösungen, welche zur Behebung von Ernährungs- und Spurenelementmängeln eingesetzt werden. Es können auch nichtphytotoxische Öle und Ölkonzentrate zugesetzt werden.It may also be useful to apply the new compounds I, alone or in combination with other herbicides, mixed with other crop protection agents, for example with agents for controlling pests or phytopathogenic fungi or bacteria. Also of interest is the miscibility with mineral salt solutions, which are used to remedy nutritional and trace element deficiencies. Non-phytotoxic oils and oil concentrates can also be added.
70 ml einer Lösung aus 12,3 g (35 mmol) Acetyl-(chlor)-methylentriphenylphosphoran in Ethanol wurden bei Raumtemperatur vorgelegt und 2,1 g (8 mmol) N-(4-Chlor-3-formylphenyl)-dimethylmaleinsäureimid zugegeben. Nach 4 Stunden Rühren bei ca. 20 bis 25°C kühlte man den Ansatz auf (-10)°C, wonach der Feststoffanteil abgetrennt, mit wenig kaltem Ethanol gewaschen und unter reduziertem Druck bei 40°C getrocknet wurde. Ausbeute: 89 %; Fp.: 173-179°C.70 ml of a solution of 12.3 g (35 mmol) of acetyl- (chloro) methylenetriphenylphosphorane in ethanol were initially introduced at room temperature and 2.1 g (8 mmol) of N- (4-chloro-3-formylphenyl) dimethylmaleimide were added. After 4 hours of stirring at about 20 to 25 ° C, the mixture was cooled to (-10) ° C, after which the solids content was separated off, washed with a little cold ethanol and dried at 40 ° C under reduced pressure. Yield: 89%; Mp: 173-179 ° C.
12,3 g (35 mmol) Acetyl-(chlor)-methylentriphenylphosphoran wurden in 70 ml Ethanol vorgelegt und 2,15 g (7 mmol) N-(4-Chlor-2-fluor-5-formylphenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrophthalsäureimid zugegeben. Man rührte 1 Stunde bei etwa 20°C, kühlte auf (-10)°C ab, saugte ab und wusch mit wenig kaltem Ethanol nach. Durch Einengen der Mutterlauge konnte weiterer Feststoff isoliert werden. Das Rohprodukt wurde unter reduziertem Druck bei 40°C getrocknet. Ausbeute: 67 %; Fp.: 141-142,5°C.12.3 g (35 mmol) of acetyl- (chloro) methylenetriphenylphosphorane were placed in 70 ml of ethanol and 2.15 g (7 mmol) of N- (4-chloro-2-fluoro-5-formylphenyl) -4.5, 6,7-tetrahydrophthalimide added. The mixture was stirred at about 20 ° C for 1 hour, cooled to (-10) ° C, suction filtered and washed with a little cold ethanol. Further solids could be isolated by concentrating the mother liquor. The crude product was dried at 40 ° C under reduced pressure. Yield: 67%; Mp: 141-142.5 ° C.
12,3 g (35 mmol) Acetyl-(chlor)-methylentriphenylphosphoran wurden in 70 ml Ethanol vorgelegt und 2,3 g (8 mmol) N-(2,4-Difluor-5-formylphenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrophthalsäureimid zugegeben. Man rührte 1 Stunde bei 20 bis 25°C, kühlte auf (-10)°C ab, saugte ab und wusch mit wenig kaltem Ethanol nach. Der Rückstand wurde bei 35°C unter reduziertem Druck getrocknet. Ausbeute: 82 %; Fp.: 170-172°C.12.3 g (35 mmol) of acetyl- (chloro) methylenetriphenylphosphorane were placed in 70 ml of ethanol and 2.3 g (8 mmol) of N- (2,4-difluoro-5-formylphenyl) -4,5,6, 7-tetrahydrophthalimide added. The mixture was stirred at 20 to 25 ° C for 1 hour, cooled to (-10) ° C, suction filtered and washed with a little cold ethanol. The residue was dried at 35 ° C under reduced pressure. Yield: 82%; Mp .: 170-172 ° C.
Analog den Beispielen 2 bis 4 wurden unter entsprechender Abwandlung der Ausgangsverbindungen die in Tabelle 5 aufgelisteten Styrolderivate I hergestellt:
Zu einer Mischung aus 8,4 g (25 mmol) Chlor-(cyano)-methylentriphenylphosphoran in 40 ml Methanol wurden 2,6 g (10 mmol) N-(4-Chlor-3-formylphenyl)-dimethylmaleinsäureimid gegeben. Man rührte 4 Stunden bei etwa 20 bis 25°C und kühlte dann auf (-10)°C ab, wonach der Feststoffanteil abgetrennt und mit wenig kaltem Methanol nachgewaschen wurde. Der Rückstand wurde unter reduziertem Druck bei 30°C getrocknet. Ausbeute: 69 %; Fp.: 139-140,5°C.2.6 g (10 mmol) of N- (4-chloro-3-formylphenyl) dimethylmaleimide were added to a mixture of 8.4 g (25 mmol) of chloro (cyano) methylene triphenylphosphorane in 40 ml of methanol. The mixture was stirred for 4 hours at about 20 to 25 ° C and then cooled to (-10) ° C, after which the solids content was separated and washed with a little cold methanol. The residue was dried at 30 ° C under reduced pressure. Yield: 69%; Mp .: 139-140.5 ° C.
Analog zu Beispiel 4 wurden die Verbindungen der Tabelle 6 hergestellt:
Die herbizide Wirkung der Styrolderivate I ließ sich durch Gewächshausversuche zeigen:The herbicidal activity of the styrene derivatives I was demonstrated by greenhouse tests:
Als Kulturgefäße dienten Plastikblumentöpfe mit lehmigem Sand mit etwa 3,0 % Humus als Substrat. Die Samen der Testpflanzen wurden nach Arten getrennt eingesät.Plastic flower pots with loamy sand with about 3.0% humus as substrate served as culture vessels. The seeds of the test plants were sown separately according to species.
Bei Vorauflaufbehandlung wurden die in Wasser suspendierten oder emulgierten Wirkstoffe direkt nach Einsaat mittels fein verteilender Düsen aufgebracht. Die Gefäße wurden leicht beregnet, um Keimung und Wachstum zu fördern und anschließend mit durchsichtigen Plastikhauben abgedeckt, bis die Pflanzen angewachsen waren. Diese Abdeckung bewirkt ein gleichmäßiges Keimen der Testpflanzen, sofern dies nicht durch die Wirkstoffe beeinträchtigt wurde.In pre-emergence treatment, the active ingredients suspended or emulsified in water were applied directly after sowing using finely distributing nozzles. The tubes were lightly sprinkled to promote germination and growth and then covered with clear plastic hoods until the plants had grown. This cover causes the test plants to germinate evenly, unless this was affected by the active ingredients.
Zum Zwecke der Nachauflaufbehandlung wurden die Testpflanzen je nach Wuchs form erst bei einer Wuchshöhe von 3 bis 15 cm mit den in Wasser suspendierten oder emulgierten Wirkstoffen behandelt. Die Aufwandmenge für die Nachauflaufbehandlung betrug 0,03 kg/ha a.S.For the purpose of post-emergence treatment, the test plants were treated with the active ingredients suspended or emulsified in water only at a growth height of 3 to 15 cm, depending on the growth habit. The application rate for post-emergence treatment was 0.03 kg / ha as
Die Pflanzen wurden artenspezifisch bei Temperaturen von 10-25°C bzw. 20-35°C gehalten. Die Versuchsperiode erstreckte sich über 2 bis 4 Wochen. Während dieser Zeit wurden die Pflanzen gepflegt und ihre Reaktion auf die einzelnen Behandlungen wurde ausgewertet.The plants were kept at 10-25 ° C and 20-35 ° C depending on the species. The trial period lasted 2 to 4 weeks. During this time, the plants were cared for and their response to the individual treatments was evaluated.
Bewertet wurde nach einer Skala von 0 bis 100. Dabei bedeutet 100 kein Aufgang der Pflanzen bzw. völlige Zerstörung zumindest der oberirdischen Teile und 0 keine Schädigung oder normaler Wachstumsverlauf.Evaluation was carried out on a scale from 0 to 100. 100 means no emergence of the plants or complete destruction of at least the aerial parts and 0 means no damage or normal growth.
Die in den Gewächshausversuchen verwendeten Pflanzen setzten sich aus folgenden Arten zusammen:
Mit 0,03 und 0,015 kg/ha a.S. im Nachauflaufverfahren eingesetzt, lassen sich mit dem Beispiel 2 breitblättrige unerwünschte Pflanzen sehr gut bekämpfen. Gleichzeitig ist die Verbindung 2 verträglich für die Kulturpflanzen Sommerweizen und Reis.With 0.03 and 0.015 kg / ha a.S. used in the post-emergence process, 2 broad-leaved unwanted plants can be combated very well with Example. At the same time, compound 2 is compatible with the summer wheat and rice crops.
Claims (6)
- A herbicide containing conventional inert additives and at least one styrene derivative of the formula I
- A method for controlling undesirable plant growth, wherein the undesirable plants and/or their habitat are or is treated with a herbicidal amount of a styrene derivative of the formula I as claimed in claim 1.
- A method for the defoliation of cotton, wherein the cotton plants are treated with an effective amount of a styrene derivative of the formula I as claimed in claim 1.
- Use of a styrene derivative of the formula I as claimed in claim 1 as a herbicide or bioregulator.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE4042194 | 1990-12-29 | ||
| DE4042194A DE4042194A1 (en) | 1990-12-29 | 1990-12-29 | STYRENE DERIVATIVES |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0493721A1 EP0493721A1 (en) | 1992-07-08 |
| EP0493721B1 true EP0493721B1 (en) | 1997-05-14 |
Family
ID=6421662
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP91121314A Expired - Lifetime EP0493721B1 (en) | 1990-12-29 | 1991-12-12 | Styrene derivatives |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5356860A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0493721B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPH04308568A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR920012028A (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE153017T1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2058469A1 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE4042194A1 (en) |
| HU (1) | HU210729B (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU2274795A (en) * | 1994-04-08 | 1995-10-30 | Degussa A.G. | Herbicidal bicyclic and tricyclic imides |
| DE4438578A1 (en) * | 1994-10-28 | 1996-05-02 | Basf Ag | Substituted phthalimido-cinnamic acid derivatives and intermediates for their preparation |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3724399A1 (en) * | 1987-07-23 | 1989-02-02 | Basf Ag | PHENYL ALKENYLCARBONSAEURES AND THEIR ESTERS |
| DE3901705A1 (en) * | 1989-01-21 | 1990-07-26 | Basf Ag | N-PHENYLTETRAHYDROINDAZOLE DERIVATIVES OF GENERAL FORMULAS IA AND IB |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2714653C3 (en) * | 1977-04-01 | 1980-10-30 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | Styryl cationic dyes and methods of dyeing with these dyes |
| JPS60194189A (en) * | 1984-03-07 | 1985-10-02 | 三菱化学株式会社 | Vinyl tricianide dye for alkali resist and discharge style |
| DE3603789A1 (en) * | 1986-02-07 | 1987-08-13 | Basf Ag | N-SUBSTITUTED 3,4,5,6-TETRAHYDROPHTHALIMIDES |
| GB8620251D0 (en) * | 1986-08-20 | 1986-10-01 | Ici Plc | Fungicides |
| US4914190A (en) * | 1987-03-19 | 1990-04-03 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Tricyanovinyl-N,N-disubstituted anilines as disperse dyes |
| DE3714373A1 (en) * | 1987-04-30 | 1988-11-10 | Hoechst Ag | SUBSTITUTED TETRAHYDROPHTHALIMIDES, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THEIR USE AS HERBICIDES |
| US4958043A (en) * | 1988-04-18 | 1990-09-18 | Eastman Kodak Company | Novel methine compounds, polymers containing them and formed articles therefrom |
| DE3901550A1 (en) * | 1989-01-20 | 1990-07-26 | Basf Ag | NEW TETRAHYDROINDAZOLE WITH PHENYL ETHER STRUCTURE |
| DE3917676A1 (en) * | 1989-05-31 | 1990-12-06 | Basf Ag | 5-Tetra:hydro:phthalimido-cinnamic acid derivs. |
| DE3924719A1 (en) * | 1989-07-26 | 1991-01-31 | Basf Ag | cinnamic |
-
1990
- 1990-12-29 DE DE4042194A patent/DE4042194A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
1991
- 1991-12-12 EP EP91121314A patent/EP0493721B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-12-12 DE DE59108703T patent/DE59108703D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-12-12 AT AT91121314T patent/ATE153017T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1991-12-25 JP JP3343342A patent/JPH04308568A/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1991-12-27 CA CA002058469A patent/CA2058469A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 1991-12-27 HU HU914126A patent/HU210729B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1991-12-30 KR KR1019910025360A patent/KR920012028A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
-
1993
- 1993-05-14 US US08/061,535 patent/US5356860A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3724399A1 (en) * | 1987-07-23 | 1989-02-02 | Basf Ag | PHENYL ALKENYLCARBONSAEURES AND THEIR ESTERS |
| DE3901705A1 (en) * | 1989-01-21 | 1990-07-26 | Basf Ag | N-PHENYLTETRAHYDROINDAZOLE DERIVATIVES OF GENERAL FORMULAS IA AND IB |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH04308568A (en) | 1992-10-30 |
| DE59108703D1 (en) | 1997-06-19 |
| ATE153017T1 (en) | 1997-05-15 |
| HUT59561A (en) | 1992-06-29 |
| CA2058469A1 (en) | 1992-06-30 |
| EP0493721A1 (en) | 1992-07-08 |
| DE4042194A1 (en) | 1992-07-02 |
| KR920012028A (en) | 1992-07-25 |
| HU914126D0 (en) | 1992-03-30 |
| US5356860A (en) | 1994-10-18 |
| HU210729B (en) | 1995-07-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0084893A2 (en) | 4H-3,1-Benzoxazin derivatives, methods for their preparation, and their use for combatting undesirable vegetation | |
| EP0136702B1 (en) | Cyclohexenol derivatives, process for their preparation and their use in combating undesirable plant growth | |
| EP0640597B1 (en) | Acylamino substituted isoxazoles and/or isothiazols, process for their preparation and their use | |
| EP0066195B1 (en) | Derivatives of cyclohexane-1,3-dione, process for their preparation and their use to combat undesired growth of plants | |
| EP0332009B1 (en) | N-aryl-tetrahydrophthalimide compounds | |
| EP0136647A2 (en) | Cyclohexenon derivatives, process for their preparation and their use in combating undesirable plant growth | |
| EP0218233B1 (en) | Cyclohexenon derivatives, process for their preparation and their use in combating the growth of undesirable plants | |
| EP0135838B1 (en) | 3-phenyl-4-methoxycarbonyl pyrazoles, process for their preparation and their use against plant growth | |
| EP0137174B1 (en) | Cyclohexane-1,3-dione derivatives, process for their preparation and their use as herbicides | |
| EP0493721B1 (en) | Styrene derivatives | |
| EP0419917B1 (en) | Pyrazol-3-carboxylic acid amides | |
| EP0456089B1 (en) | Cyclohexenonoximethers, process for their production and their application as herbicides | |
| EP0169521B1 (en) | Cyclohexenone derivatives, their preparation and their use against the growth of undesired plants | |
| EP0410265B1 (en) | Cinnamic acid esters | |
| EP0358108B1 (en) | 5-(n-3,4,5,6-tetrahydrophthalimido)-cinnamic-acid derivatives | |
| DE2846625A1 (en) | M-ANILIDURETHANE | |
| EP0107123B1 (en) | Aniline derivatives, process for their preparation and their use in combating undesired plant growth | |
| EP0192998B1 (en) | Thiazolyl amides, process for their preparation and their use in combating non-desired plant growth | |
| EP0098440B1 (en) | 3,7-dichloroquinoline derivatives, process for their preparation and their use to prevent undesired plant growth | |
| EP0120448A1 (en) | Derivatives of cyclohexane-1,3-dione, methods for their preparation and their use in combating non desired plants | |
| EP0144052A2 (en) | Quinolinoxyphenyl ureas, process for their preparation and their use to combat unwanted plant growth | |
| EP0400427B1 (en) | Herbicidal 5-(N-3,4,5,6-tetrahydrophthalimido)-cinnamic acid esters, process for their preparation and their use | |
| EP0456125B1 (en) | N-aryltetrahydrophthalimides and their use as herbicides | |
| EP0136703A2 (en) | Cyclohexenone derivatives, process for their preparation and use in controlling the growth of undesired plants | |
| EP0084671B1 (en) | Aniline derivatives, process for their preparation and their use in combating undesired plant growth, and intermediates for their preparation |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19920401 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19940929 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 19970514 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19970514 Ref country code: ES Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19970514 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 153017 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19970515 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59108703 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19970619 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19970616 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19970814 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19971212 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19971231 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: BASF A.G. Effective date: 19971231 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20001117 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20001124 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20001201 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20001216 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20011212 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF THE APPLICANT RENOUNCES Effective date: 20011218 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20011231 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20011231 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20011212 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020830 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |