EP0385888A1 - Piezoelektrische Kapsel mit leitenden elastischen Halterungsgliedern - Google Patents
Piezoelektrische Kapsel mit leitenden elastischen Halterungsgliedern Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0385888A1 EP0385888A1 EP90420098A EP90420098A EP0385888A1 EP 0385888 A1 EP0385888 A1 EP 0385888A1 EP 90420098 A EP90420098 A EP 90420098A EP 90420098 A EP90420098 A EP 90420098A EP 0385888 A1 EP0385888 A1 EP 0385888A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- membrane
- base body
- electrical connection
- elastic
- external electrode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 52
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 claims description 50
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 23
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 abstract description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 abstract description 4
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001369 Brass Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 208000031968 Cadaver Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000010951 brass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013013 elastic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005476 soldering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04R—LOUDSPEAKERS, MICROPHONES, GRAMOPHONE PICK-UPS OR LIKE ACOUSTIC ELECTROMECHANICAL TRANSDUCERS; DEAF-AID SETS; PUBLIC ADDRESS SYSTEMS
- H04R1/00—Details of transducers, loudspeakers or microphones
- H04R1/06—Arranging circuit leads; Relieving strain on circuit leads
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04R—LOUDSPEAKERS, MICROPHONES, GRAMOPHONE PICK-UPS OR LIKE ACOUSTIC ELECTROMECHANICAL TRANSDUCERS; DEAF-AID SETS; PUBLIC ADDRESS SYSTEMS
- H04R17/00—Piezoelectric transducers; Electrostrictive transducers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04R—LOUDSPEAKERS, MICROPHONES, GRAMOPHONE PICK-UPS OR LIKE ACOUSTIC ELECTROMECHANICAL TRANSDUCERS; DEAF-AID SETS; PUBLIC ADDRESS SYSTEMS
- H04R7/00—Diaphragms for electromechanical transducers; Cones
- H04R7/16—Mounting or tensioning of diaphragms or cones
- H04R7/18—Mounting or tensioning of diaphragms or cones at the periphery
Definitions
- the present invention relates to electroacoustic transducers, the vibrating element of which consists of a membrane with a layer of piezoelectric material provided with electrodes and maintained around its periphery in a capsule housing.
- the membrane is formed of a thin disc on which a layer of piezoelectric ceramic is secured, covering the central zone of the disc, the two faces of the layer of piezoelectric ceramic being metallized to respectively constitute an internal electrode applied against the thin disk and an external electrode.
- the membrane is housed in a housing formed by a base body and a cover which adapts to one another along a closed periphery, generally circular.
- the basic body forms a first wall substantially parallel to the disc and delimiting with the disc a posterior acoustic cavity.
- the cover forms a second wall substantially parallel to the disc and delimiting with the disc an anterior acoustic cavity.
- the housing includes a surface, for example in an inner peripheral step, against which the periphery of the disc is kept applied by holding members.
- Electrical connection means provide the respective electrical connections of one and the other of the electrodes with a first and a second connection terminal outside the housing.
- the disc is also held in abutment against a peripheral bearing of the basic body, against which it is pushed by a peripheral O-ring inserted between the disc and the cover;
- the electrical connections are provided on the one hand by an electrical conductor in the form of a wire soldered to a connection terminal and to the external electrode, and on the other hand by the disc itself made of electrically conductive material which found in contact with the box also conductive of electricity through its periphery.
- the periphery of the disc is in abutment against a peripheral surface of the cover, against which it is held in abutment by a peripheral annular seal inserted between the base body and the disc; one of the electrical connections is provided by an elastic tongue, one end of which is held against the base body and the other end of which bears on the piezoelectric element of the disc.
- the periphery of the disc is embedded between the peripheries of the cover and of the base body; one of the electrical connections is provided by an elastic tongue, a first end of which is fixed by a rivet to the center of the base body and the other end of which bears on the piezoelectric element of the disc.
- the known capsules therefore have a relative complexity, and require providing first means for ensuring the mechanical strength of the membrane in the housing and second means for ensuring the electrical connection of the electrodes, and providing for the assembly of all these means during mounting the capsule.
- the object of the present invention is in particular to avoid the drawbacks of known capsules, by attempting to simplify assembly and to reduce the number of parts to be produced and assembled, without however adversely affecting the acoustic results obtained, and by improving if possible results.
- the new capsule structure makes it possible to maintain the membrane in the housing without using an O-ring seal; the inventors have in fact found that the presence of such O-rings in a capsule has drawbacks during mass production; in fact, the known seals which can be used in large series are generally of irregular dimensions, which induces defects in the flatness of the holding surfaces of the piezoelectric membrane, and dispersions in the acoustic qualities of the capsules thus obtained. Defects linked to the presence of O-rings also result from thickness dispersions of the other stacked parts constituting the capsule, in particular the base body and the cover, creating a gripping force that is difficult to control around the periphery of the disc.
- the mechanical holding means according to the invention make it possible to avoid these dispersions.
- the new capsule structure results in a substantial increase in the possibilities of deformation of the peripheral zone of the disc, so that the electroacoustic qualities of the capsule are significantly improved.
- the present invention also provides specific embodiments leading to the general improvement of the electroacoustic qualities of the capsule.
- it is sought to distribute the natural frequencies of mechanical vibration of the various members of the capsule, so as to obtain a response curve that is as flat as possible within the usual operating frequency range.
- Another desired effect is to obtain a good compromise between the acoustic effect of the capsule and its dimensional size, in particular its thickness.
- the capsule according to the invention incorporates the main elements of known capsules, namely: a membrane formed by a thin disc carrying a layer of piezoelectric ceramic covering the central area of the disc; a housing formed by a base body and a cover secured axially to each other in a closed tower; a boltier peripheral step, inside said closed periphery, and against which a first periphery face of the disc is kept applied by holding members; first and second electrical connection terminals connected to the electrodes of the piezoelectric membrane by first and second electrical connection members; elastic electrically conductive means inserted between the membrane and the housing, bearing on the one hand against a portion of membrane electrically connected to one of the internal or external electrodes, and bearing on the other hand against a portion of box electrically connected to the corresponding electrical connection terminal, so that the elastic electrically conducting means participate in the electrical connection between said internal or external electrode and the corresponding electrical connection terminal; according to the invention: - The second membrane periphery face is free, separated from the housing by
- the peripheral holding force of the membrane is made substantially invariable, independent of the dimensional dispersions of the stacked parts.
- the piezoelectric ceramic layer forms the rear face of the disc, facing the base body, so that the external electrode faces the base body, the front face of the periphery of the disc is facing said step of the housing itself formed in the cover
- the elastic electrically conducting means are inserted between the external electrode and the internal face of the base body, bearing on the one hand on the external electrode and on the other hand on a portion of the base body electrically connected to the second electrical connection terminal, to ensure the electrical connection between the second electrical connection terminal and the external electrode
- - Said elastic means conducting electricity elastically push the membrane towards the cover and by themselves perform the function of holding the periphery of the disc against the cover step.
- the inventors have found that it is particularly advantageous, in particular to obtain the widest and flattest possible frequency response curve of the capsule, to provide that the elastic electrically conductive means are supported on the electrode external in the area located in the vicinity of the nodal circle of the membrane, that is to say the area formed by the location of the nodes of the third mode of circular vibration of the membrane, said elastic conducive means teurs of electricity being supported on said external electrode at least two points distant from each other.
- the elastic electrically conducting means may comprise several elastic electrically conducting elements distinct from each other, each bearing on the one hand on the external electrode and on the other hand on the basic housing body.
- said elastic electrically conductive means can be assembled into a single element with several branches, comprising a single support zone on the base body, the ends of the branches being supported on the electrode. external.
- each fulcrum of elastic means conducting electricity on the external electrode corresponds an elastic connection with different mechanical characteristics, thus having different own vibrational modes.
- a good compromise between the acoustic efficiency of the capsule and its dimensional size is obtained according to the invention by combining a membrane whose natural frequency is around 1 kHz with an acoustic filter comprising anterior and posterior acoustic cavities whose respective heights are about 1 mm, for a diameter of about 30 mm.
- the heights of approximately 1 mm make it possible to accommodate the connection members and allow the membrane to oscillate freely.
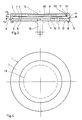
- a piezoelectric capsule according to the invention comprises a membrane 1 formed by a thin disc 2, with circular outline, on which is fixed a layer 3 of piezoelectric ceramic covering the central zone of the disc 2.
- the disc 2 is made of an electrically conductive material, for example brass, and the piezoelectric ceramic layer 3 has a concentric circular contour with respect to the disc 2, covering the central area of the disc and leaving a visible border device of the disk face 2 on which it is applied.
- the piezoelectric ceramic layer is metallized on its two faces, its internal face 4 forming an internal electrode and being pressed against the disc 2, its external face 5 forming an external electrode and being visible.
- the membrane 1 is housed in a housing 6 formed by a base body 7 and a hollow cover 8, axially secured to one another along a closed periphery 9, for example circular as shown.
- the base body 7, in the embodiment shown, consists of a flat plate of insulating material, for example a material generally used in the technique of printed circuits, the outer face 10 of which carries conductive tracks 11 and 12 shown in Figure 1.
- the cover 8 is made of an electrically conductive material, for example aluminum or aluminum alloy, and has a circular central wall 13 connected to a peripheral side wall 14.
- the peripheral wall 14 comprises a rear step 15, forming a narrowing of the interior space of the housing 6 as shown in FIG. 3 or FIG. 2, against which the periphery of the base body is supported 7.
- the edge 16 of the peripheral wall 14 is folded inwardly to come to bear on the outer face 10 of the base body 7, and crimp said base body 7 on the cover 8.
- the peripheral wall 14 of the cover 8 further comprises an anterior step 17, forming a second narrowing of the interior space of the housing 6 as shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, arranged approximately halfway between the central wall 13 and the step posterior 15.
- the first face 110 of the membrane periphery 1 is held pressed against the front step 17 of the cover 8, by elastic means which will be described below.
- the second face 111 of the membrane periphery 1 is free, that is to say separated from the base body 7 by a space 112 devoid of any seal.
- the piezoelectric ceramic layer 3 is arranged on the side of the base body 7, as shown in the figures, so that the external electrode 5 faces the base body 7.
- the base body 7 constitutes a first wall substantially parallel to the disc 2, with which it forms a posterior acoustic cavity 70, and the central wall 13 of the cover 8 is substantially parallel to the disc 2 and forms with it an anterior acoustic cavity 80.
- the central wall 13 of the cover 8 has holes 130 for the passage of sound from the anterior acoustic cavity 80 to the external atmosphere
- the base body 7 comprises a passage 71 provided with an acoustic filter connecting the posterior acoustic cavity 70 and the external atmosphere.
- the respective heights H1 and H2 of the anterior 80 and posterior 70 acoustic cavities are advantageously equal to approximately 1 mm, for example between 0.9 and 1.1 mm.
- a first electrical connection terminal 18 is fitted on the base body 7 and protrudes from the external face 10 of said base body 7 to be electrically connected to an external circuit.
- a second electrical connection terminal 19 is fitted to the base body 7 and protrudes from the outer face 10 of said base body 7 to be connected to an external electrical circuit.
- the first electrical connection terminal 18 is connected by welding to the first conductive track 11 of the base body 7, said conductive track 11 comprising a peripheral portion 20 in contact with the cover 8.
- the first electrical connection terminal 18 is electrically connected to the internal electrode 4 via the conductive disc 2, the conductive cover 8 and the conductive track 11.
- the second electrical connection terminal 19 is electrically connected by soldering to the second conductive track 12, itself in contact with a central metal rivet 21.
- the central rivet metal 21, engaged in a central hole in the base body 7, is integral with an elastic electrically conductive means 22 itself in contact with the external electrode 5.
- the second electrical connection terminal 19 is connected electrically to the external electrode 5 via the conductive track 12, the central rivet 21 and the elastic electrically conductive means 22.
- the conductive tracks 11 and 12 are electrically isolated from each other .
- the elastic electrically conductive means 22 performs the function of electrical connection between the external electrode 5 and the corresponding electrical connection terminal 19.
- the elastic electrically conductive means 22 ensures by itself holding the membrane 1 in abutment against the front step 17 of the cover 8.
- the elastic electrically conductive means 22, fixed in the center of the base body 7 by the rivet 21, has its own elasticity and a shape such that, when the capsule is assembled as shown in the figures, with the membrane 1 inserted between the cover 8 and the base body 7, and with the elastic electrically conductive means 22 inserted between said membrane 1 and the base body 7, the elastic electrically conductive means elastically pushes the membrane 1 towards the cover 8 and keeps the first face 110 of its periphery in abutment against the front step 17.
- the overall bearing force exerted by the elastic electrically conductive means 22 on the membrane 1 is advantageously between 0.3 Newton and 0.5 Newton, for a membrane whose diameter is equal to approximately 30 mm.
- the front step 17 has, in radial section, a trapezoid profile, the small base 170 of which forms a circular crown and constitutes the bearing surface of the disc 2, the said small base being separated from the peripheral wall 14 by a peripheral groove 171.
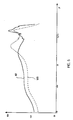
- FIG. 6 represents two comparative curves of capsules of identical dimensions, curve 100 corresponding to a capsule in which the disc is held by an O-ring bearing on a housing step, the curve 101 corresponding to a capsule according to the invention.
- the elastic electrically conductive means 22 is a metal part, made for example of a material sold under the brand Duriflex, comprising a central part 23 provided with a hole for the passage of the fastening rivet 21, and to which three branches 24, 25 and 26 are connected.
- the three branches 24, 25 and 26 each develop substantially in the form of a spiral starting from the central part 23.
- Their respective ends 27, 28 and 29 are equidistant from the center 30 of the central part 23 or center of the hole through which the fixing rivet 21 passes, and are equidistant from each other, distributed regularly at 120 ° around the center 30.
- the respective lengths of the three branches are unequal, and their widths are also uneven.
- the first branch 24 develops at an angle B of approximately 92 °
- the second branch 25 develops at an angle C of approximately 120 °
- the third branch 26 develops at an angle A of about 86 °.
- the respective widths of the branches are chosen, as shown in the figure, according to the respective lengths so that the support forces exerted by each of the ends 27, 28 and 29 of the branches against the external electrode 5 are substantially equal. Under these conditions, each of the branches has its own vibratory characteristic different from that of each of the other two branches.
- nodal circle is meant the location of the vibration nodes of the third circular mode of vibration of the membrane 1. This nodal circle can be determined empirically, by requesting a vibrating membrane according to the third mode of vibration, and by locating the position of the vibration nodes forming the nodal circle.
- the detection of the vibration nodes can be carried out by any means well known in the art, for example by observing the movement of a powder distributed over the surface of a membrane stressed in vibration.
- the part 22 can be produced by cutting and forming a plate of suitable thickness from an elastic and conductive material. electricity.
- provision may be made for using two or three separate parts, one end of which is fixed to the base body 7, and the other end of which comes to bear on an appropriate zone of the external electrode 5.
- the present invention is not limited to the embodiments which have been explicitly described, but it includes the various variants and generalizations thereof contained in the field of claims below.
- the elastic electrically conductive means consist of an elastic washer inserted axially between the conductive periphery of the disc 2 and an annular conductive support of the housing. The elastic electrically conductive means then ensure the electrical connection of the internal electrode 4 via the conductive disc 2.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Piezo-Electric Transducers For Audible Bands (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR8902930A FR2643771A1 (fr) | 1989-02-27 | 1989-02-27 | Capsule piezoelectrique a organes de maintien elastiques conducteurs |
| FR8902930 | 1989-02-27 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0385888A1 true EP0385888A1 (de) | 1990-09-05 |
Family
ID=9379420
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP90420098A Withdrawn EP0385888A1 (de) | 1989-02-27 | 1990-02-23 | Piezoelektrische Kapsel mit leitenden elastischen Halterungsgliedern |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4990816A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0385888A1 (de) |
| CA (1) | CA2010975A1 (de) |
| FR (1) | FR2643771A1 (de) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1146772A2 (de) * | 2000-04-13 | 2001-10-17 | Star Micronics Co., Ltd. | Elektroakustischer Wandler und Montagestruktur für einen elektroakustischen Wandler |
| WO2008145949A1 (en) * | 2007-05-31 | 2008-12-04 | New Transducers Limited | Audio apparatus |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07114383A (ja) * | 1993-10-15 | 1995-05-02 | Murata Mfg Co Ltd | 圧電ブザー |
| FR2755813B1 (fr) * | 1996-11-14 | 1998-12-11 | Alsthom Cge Alcatel | Combine telephonique |
| DE19712728C1 (de) * | 1997-03-26 | 1998-11-19 | Dornier Gmbh | Piezoelektrischer Lautsprecher |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2126556A1 (de) * | 1970-06-01 | 1971-12-09 | Conrac Corp | Mikrophonkapsel mit Verstärker |
| US4295009A (en) * | 1980-03-07 | 1981-10-13 | Amp Incorporated | Piezoelectric audio transducer mounting and electrical connector |
| GB2128399A (en) * | 1982-09-30 | 1984-04-26 | Emhart Ind | Piezoelectric audio signalling device |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4420706A (en) * | 1979-01-15 | 1983-12-13 | Molex Incorporated | Connector assembly for a piezoelectric transducer |
| US4429247A (en) * | 1982-01-28 | 1984-01-31 | Amp Incorporated | Piezoelectric transducer supporting and contacting means |
| JPS60199298A (ja) * | 1984-03-23 | 1985-10-08 | Murata Mfg Co Ltd | 圧電音響変換装置 |
| FR2563959B1 (fr) * | 1984-05-04 | 1990-08-10 | Lewiner Jacques | Perfectionnements aux transducteurs electro-acoustiques a electret |
| JPS6129298A (ja) * | 1984-07-19 | 1986-02-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 圧電型変換器 |
-
1989
- 1989-02-27 FR FR8902930A patent/FR2643771A1/fr not_active Withdrawn
-
1990
- 1990-02-23 EP EP90420098A patent/EP0385888A1/de not_active Withdrawn
- 1990-02-23 US US07/483,922 patent/US4990816A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1990-02-27 CA CA002010975A patent/CA2010975A1/fr not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2126556A1 (de) * | 1970-06-01 | 1971-12-09 | Conrac Corp | Mikrophonkapsel mit Verstärker |
| US4295009A (en) * | 1980-03-07 | 1981-10-13 | Amp Incorporated | Piezoelectric audio transducer mounting and electrical connector |
| GB2128399A (en) * | 1982-09-30 | 1984-04-26 | Emhart Ind | Piezoelectric audio signalling device |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| PATENT ABSTRACTS OF JAPAN, vol. 10, no. 184 (E-415)[2240], 27 juin 1986; & JP-A-61 29 298 (MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC IND. CO., LTD) 10-02-1986 * |
| PATENT ABSTRACTS OF JAPAN, vol. 10, no. 46 (E-383)[2103], 22 février 1986; & JP-A-60 199 298 (MURATA SEISAKUSHO K.K.) 08-10-1985 * |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1146772A2 (de) * | 2000-04-13 | 2001-10-17 | Star Micronics Co., Ltd. | Elektroakustischer Wandler und Montagestruktur für einen elektroakustischen Wandler |
| EP1146772A3 (de) * | 2000-04-13 | 2003-02-05 | Star Micronics Co., Ltd. | Elektroakustischer Wandler und Montagestruktur für einen elektroakustischen Wandler |
| US6577743B2 (en) | 2000-04-13 | 2003-06-10 | Star Micronics Co., Ltd. | Electroacoustic transducer and structure for mounting an electroacoustic transducer |
| WO2008145949A1 (en) * | 2007-05-31 | 2008-12-04 | New Transducers Limited | Audio apparatus |
| CN101766036B (zh) * | 2007-05-31 | 2014-07-02 | 新型转换器有限公司 | 音频设备 |
| US8842870B2 (en) | 2007-05-31 | 2014-09-23 | Nvf Tech Ltd. | Audio apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| FR2643771A1 (fr) | 1990-08-31 |
| CA2010975A1 (fr) | 1990-08-27 |
| US4990816A (en) | 1991-02-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0230336A1 (de) | Optoelektronische Vorrichtung zum oberflächigen Einbau | |
| FR2629660A1 (fr) | Capsule piezoelectrique a pinces de connection electrique laterales | |
| CH691559A5 (fr) | Micro-contacteur magnétique et son procédé de fabrication. | |
| EP0177383B1 (de) | Allseitiger Breitbandwandler elastischer Wellen und Verfahren zur Herstellung | |
| EP1158620A1 (de) | Weibliches Element eines elektrischen Verbinders | |
| FR2487619A1 (fr) | Transducteur electroacoustique bivoie, en particulier pour casques et microphones | |
| FR2698447A1 (fr) | Cellule de mesure micro-usinée. | |
| EP0505848B1 (de) | Piezoelektrischer Motor, insbesondere für Zeitmessgerät | |
| EP0385888A1 (de) | Piezoelektrische Kapsel mit leitenden elastischen Halterungsgliedern | |
| EP0186804B1 (de) | Am Armgelenk zu tragende elektronische Vorrichtung | |
| EP0385889A1 (de) | Piezoelektrische Kapsel mit flacher Auflagefläche und elastischen Halterungsgliedern | |
| FR2479579A1 (fr) | Dispositif de fixation et de prise de contact electrique d'une pile dans une montre | |
| EP0778666A1 (de) | Piezoelektrischer Resonator | |
| EP0694824B1 (de) | Uhrwerk mit elektroakustischem Umsetzer | |
| EP0810687B1 (de) | Elektrischer Verbinder zum Verbinden von elektrischen Leitungen | |
| EP0403378B1 (de) | Kugelmembran-Rundstrahllautsprecher mit magnetostriktivem Doppelschicht-Bändchen | |
| WO1988004090A1 (fr) | Sonde d'echographe avec circuit de connexion perfectionne | |
| FR2779023A1 (fr) | Telephone mobile a couvercle articule et contacts rotatifs | |
| FR2597272A1 (fr) | Dispositif de contact electrique a balai pour moteur electrique a commutateur cylindrique | |
| EP0331591A1 (de) | Elektroakustischer Kapsel mit Piezoelektrischer Membran | |
| EP1111778B1 (de) | Piezoelektrischer Dünnfilmresonator | |
| EP0136942B1 (de) | Selbstaufgehängter Resonator mit hohem Gütefaktor | |
| CH639509A5 (en) | Adjustable capacitor and method of manufacturing a series of such adjustable capacitors | |
| FR2696586A1 (fr) | Connecteur à diode/filtre. | |
| EP1432052A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Montage von einer Energiequelle für tragbares elektronisches Gerät |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19910213 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19930322 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19930803 |