CN115285214A - Vehicle control method and device based on steering system and storage medium - Google Patents
Vehicle control method and device based on steering system and storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115285214A CN115285214A CN202211051496.6A CN202211051496A CN115285214A CN 115285214 A CN115285214 A CN 115285214A CN 202211051496 A CN202211051496 A CN 202211051496A CN 115285214 A CN115285214 A CN 115285214A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- temperature
- motor
- steering
- steering system
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 54
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 12
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 18
- 230000017525 heat dissipation Effects 0.000 claims description 39
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000013021 overheating Methods 0.000 abstract description 36
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000020169 heat generation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000011065 in-situ storage Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B62—LAND VEHICLES FOR TRAVELLING OTHERWISE THAN ON RAILS
- B62D—MOTOR VEHICLES; TRAILERS
- B62D5/00—Power-assisted or power-driven steering
- B62D5/04—Power-assisted or power-driven steering electrical, e.g. using an electric servo-motor connected to, or forming part of, the steering gear
- B62D5/0457—Power-assisted or power-driven steering electrical, e.g. using an electric servo-motor connected to, or forming part of, the steering gear characterised by control features of the drive means as such
- B62D5/0481—Power-assisted or power-driven steering electrical, e.g. using an electric servo-motor connected to, or forming part of, the steering gear characterised by control features of the drive means as such monitoring the steering system, e.g. failures
- B62D5/0496—Power-assisted or power-driven steering electrical, e.g. using an electric servo-motor connected to, or forming part of, the steering gear characterised by control features of the drive means as such monitoring the steering system, e.g. failures by using a temperature sensor
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B62—LAND VEHICLES FOR TRAVELLING OTHERWISE THAN ON RAILS
- B62D—MOTOR VEHICLES; TRAILERS
- B62D5/00—Power-assisted or power-driven steering
- B62D5/04—Power-assisted or power-driven steering electrical, e.g. using an electric servo-motor connected to, or forming part of, the steering gear
- B62D5/0457—Power-assisted or power-driven steering electrical, e.g. using an electric servo-motor connected to, or forming part of, the steering gear characterised by control features of the drive means as such
- B62D5/0481—Power-assisted or power-driven steering electrical, e.g. using an electric servo-motor connected to, or forming part of, the steering gear characterised by control features of the drive means as such monitoring the steering system, e.g. failures
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/72—Electric energy management in electromobility
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Steering Control In Accordance With Driving Conditions (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a vehicle control method, a vehicle control device and a storage medium based on a steering system, wherein the method comprises the following steps: acquiring the temperature of a vehicle steering system and the running state of a vehicle; when the temperature is greater than the first temperature threshold value and the vehicle running state is the vehicle static state or the low-speed state, exiting the transverse driving control; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained. By the embodiment of the invention, the EPS temperature is monitored in real time, the EPS overheating early warning is carried out when the EPS temperature is overheated, and safe parking and other operations are carried out before the EPS is out of control. The invention can effectively reduce the frequency of EPS overheating, and can give an early warning before the EPS overheating, thereby achieving the purpose of safe parking.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of vehicles, in particular to a vehicle control method and device based on a steering system and a storage medium.
Background
In the process of driving of a vehicle, especially in low-speed and large-angle turning scenes (such as urban village driving and other scenes), the EPS assistance is increased, and further, the EPS ECU and the motor are overheated to cause EPS error reporting failure. After the EPS is overheated to cause system failure, the transverse direction of the vehicle can be uncontrollable, and therefore the running danger of the vehicle can be generated.
Disclosure of Invention
The invention mainly aims to provide a vehicle control method, a vehicle control device and a storage medium based on a steering system, and aims to solve the problem that in the prior art, after the EPS is overheated to cause system failure, the transverse direction of a vehicle can be uncontrollable, so that the vehicle can run dangerously.
In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a vehicle control method based on a steering system, the method comprising the steps of:
acquiring the temperature of a vehicle steering system and the running state of a vehicle;
when the temperature is greater than a first temperature threshold value and the vehicle running state is a vehicle static state or a low-speed state, exiting the transverse driving control; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained.
Optionally, the obtaining the temperature of the vehicle steering system includes:
calibrating the motor temperature of a vehicle steering system of each type of vehicle within a specified temperature range to obtain a calibration relation between the temperature range and/or the motor current and the motor temperature;
and acquiring the ambient temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current of a vehicle steering system, and acquiring the temperature of the motor from the calibration relation according to the ambient temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current.
Optionally, the calibrating the motor temperature of the vehicle steering system in the specified temperature range for each type of vehicle comprises the following steps:
acquiring the environmental temperature of a vehicle of a specified type;
acquiring an input current value of a motor of a vehicle steering system, and integrating the current value within a specified time range to obtain the maximum heat productivity of the motor;
obtaining the maximum heat dissipation capacity of the motor within the appointed time range according to the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor;
subtracting the maximum heat dissipation amount from the maximum heat dissipation amount to obtain the actual heat dissipation amount of the motor;
and acquiring the temperature of the motor according to the environment temperature and the actual heating value of the motor.
Optionally, the obtaining the temperature of the vehicle steering system includes:
the temperature of an electronic control unit of the vehicle steering system is acquired.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
and after the vehicle issues the brake instruction and exits the transverse control, when the vehicle running state is not the vehicle static state or the low-speed state, stopping braking and entering the transverse control again.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
and after the vehicle exits the transverse control, when the temperature is greater than a second temperature threshold value, the vehicle executes an edge-approaching parking operation.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
limiting the input steering angular speed, and only allowing the input steering angular speed smaller than a first threshold value; or the like, or, alternatively,
prohibiting pivot steering operation of the vehicle when the vehicle is static, and allowing vehicle steering after the running speed of the vehicle reaches a first speed; or
When the vehicle is subjected to pivot steering operation, the input steering angle is a fixed value; or the like, or a combination thereof,
the vehicle running speed is less than the second speed, and the steering angle speed input to the vehicle is less than a second threshold value.
In order to achieve the above object, the present invention further provides a steering system-based vehicle control device, including:
a temperature acquisition unit for acquiring a temperature of a steering system of a vehicle;
a state acquisition unit for acquiring a vehicle state;
a safety operation unit for exiting the lateral driving control when the temperature is greater than a first temperature threshold and the vehicle running state is a vehicle stationary state or a low speed state; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained.
Further, to achieve the above object, the present invention also proposes a vehicle comprising: a memory, a processor, and a steering-system based vehicle control program stored on the memory and executable on the processor, the steering-system based vehicle control program configured to implement the steps of the steering-system based vehicle control method as described above.
Furthermore, to achieve the above object, the present invention also proposes a computer-readable storage medium having stored thereon a computer program which, when executed by a processor, implements the steps of the steering-system-based vehicle control method as described above.
By the embodiment of the invention, the EPS temperature is monitored in real time, and the EPS overheating early warning is carried out when the EPS temperature is overheated. When the vehicle is stopped, the transverse control is directly withdrawn, so that the current of the EPS is reduced, and the overheating frequency of the EPS is greatly reduced; and carrying out safe parking and other operations before the EPS is out of control. The invention can effectively reduce the frequency of EPS overheating, and can early warn before the EPS overheating, thereby achieving the purpose of safe parking.
Drawings
Fig. 1 is a schematic flow chart of a steering system-based vehicle control method provided by the invention.
Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of a process for obtaining a motor temperature according to the present invention.
Fig. 3 is a schematic flow chart of the motor temperature calibration provided by the present invention.
Fig. 4 is a schematic flow chart of acquiring the temperature of the electronic control unit according to the present invention.
Fig. 5 is another schematic flow chart of a steering system-based vehicle control method provided by the invention.
Fig. 6 is a schematic flow chart of the vehicle safety operation provided by the present invention.
Fig. 7 is a block diagram showing the structure of an embodiment of a vehicle control device based on a steering system according to the present invention.
Fig. 8 is a vehicle structure diagram of a hardware operating environment according to an embodiment of the present invention.
The implementation, functional features and advantages of the objects of the present invention will be further explained with reference to the accompanying drawings.
Detailed Description
In order to make the technical problems, technical solutions and advantageous effects of the present invention more clear and obvious, the present invention is further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are merely illustrative of the invention and are not intended to limit the invention.
In the following description, suffixes such as "module", "component", or "unit" used to denote elements are used only for facilitating the explanation of the present invention, and have no specific meaning in itself. Thus, "module", "component" or "unit" may be used mixedly.
It should be noted that the terms "first," "second," and the like in the description and claims of the present invention and in the drawings described above are used for distinguishing between similar elements and not necessarily for describing a particular sequential or chronological order.
In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, the present invention provides a steering system based vehicle control method, the method comprising:
and step S101, acquiring the temperature of a vehicle steering system and the vehicle running state.
The method comprises the steps of obtaining the current temperature of the vehicle steering system, wherein the temperature of the vehicle steering system comprises the temperature of an electronic control unit of the vehicle steering system and the temperature of a motor of the vehicle steering system.
The temperature of the motor of the vehicle steering system is obtained, see the flow chart shown in fig. 2.
Step S201, calibrating the motor temperature of the vehicle steering system in a specified temperature range for each type of vehicle to obtain the temperature range and/or the calibration relation between the motor current and the motor temperature.
In the motor of the steering system of the vehicle, the temperature inside the motor cannot be obtained by installing a temperature sensor due to a construction problem. It is necessary to estimate the temperature inside the motor based on the current input to the motor, which is estimated based on the ambient temperature and the type of vehicle. Therefore, the calibration of the ambient temperature and the motor temperature needs to be performed for each vehicle type, and a specific calibration process is shown in fig. 3:
step S301, the environmental temperature of the vehicle of the specified type is obtained.
When calibrating the corresponding relation between the environment temperature and the motor temperature, each vehicle type needs to be calibrated one by one. Each vehicle type is calibrated at different ambient temperatures, for example, a plurality of temperature ranges are divided for the ambient temperature range of-40 ℃ to 40 ℃, as shown in the following table:
| serial number | Range of ambient temperature |
| 1 | -40℃~-35℃ |
| 2 | -35℃~-30℃ |
| -30℃~-25℃ | |
| … | |
| 30℃~35℃ | |
| 35℃~40℃ |
The ambient temperature can be realized by a third-party device, such as a vehicle is prevented from being in a cold storage to realize that the ambient temperature of the vehicle is a low-temperature environment. The environment temperature of the environment where the vehicle is located is specifically constructed, and the technical scheme is not carried out at present by using the equipment.
The vehicle is calibrated once in each divided temperature range, and the current ambient temperature of the vehicle is obtained, for example, the ambient temperature is 25 ℃.
Step S302, obtaining an input current value of a motor of a vehicle steering system, and integrating the current value in a specified time range to obtain the maximum heat productivity of the motor.
In a specified time range, such as 10. Then using the formula:and (4) integrating, wherein I is the current value of the input motor, R is the resistance equivalent value of the motor, and t1 and t2 are the integration starting time and the integration ending time. And obtaining the maximum heat productivity of the motor through integration.
And step S303, obtaining the maximum heat dissipation capacity of the motor within the appointed time range according to the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor.
The heat dissipation efficiency of the motor of the vehicle steering system of each vehicle type is different, and the heat dissipation amount within a specified time length range needs to be obtained according to the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor. And calculating the heat dissipation capacity of the motor by using a formula w (t 2-t 1), wherein w is the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor, and the heat dissipation starting time and the heat dissipation finishing time of t1 and t 2. By the above formula, the heat dissipation amount in the time range of 10.
And S304, subtracting the maximum heat dissipation capacity from the maximum heat generation capacity to obtain the actual heat generation capacity of the motor.
The motor obtains the maximum heating value (such as the heating value a 1) of the motor by subtracting the maximum heat dissipation value (such as the heat dissipation value b 1) of the motor through current integration, and obtains the actual heating value (such as the actual heating value c 1) of the motor.
And S305, estimating the temperature of the motor according to the environment temperature and the actual heating value of the motor.
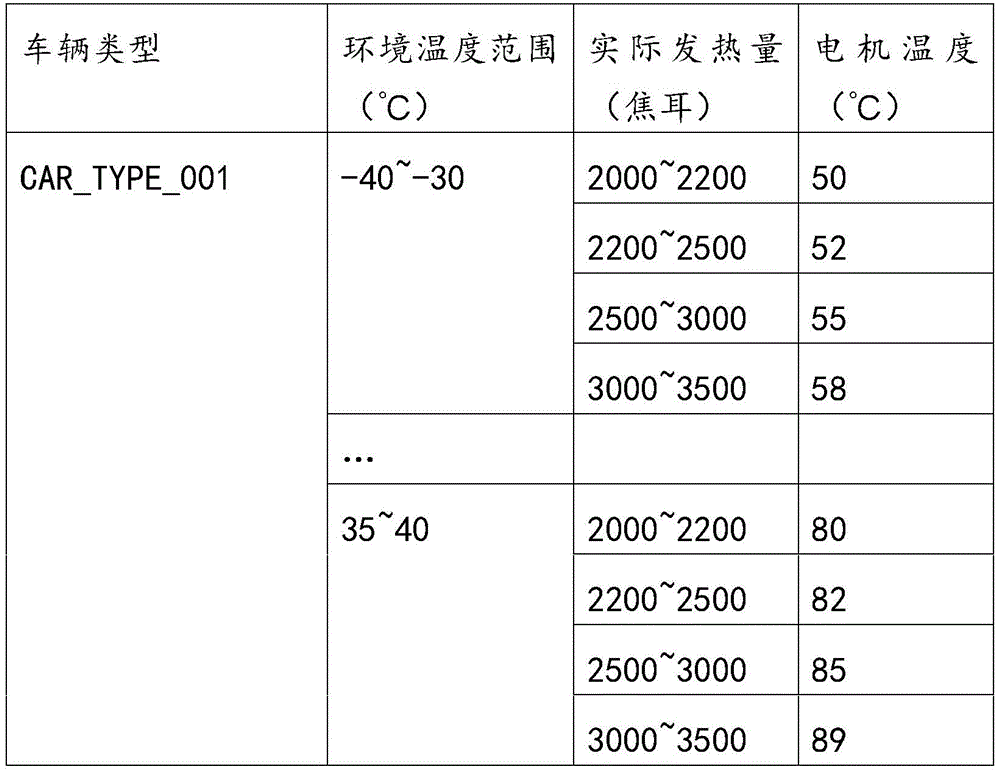
And acquiring the actual heat productivity of the motor in each divided environment temperature range, and estimating the temperature inside the motor according to the current environment temperature and the actual heat productivity of the motor. Under the same environment temperature, the estimated values of the motor temperature obtained by different actual heating values are different. The estimation process can be estimated according to the motor model and empirical values, and the specific estimation method is not limited by the technical scheme. The estimated motor temperature, as shown in the following table:
| serial number | Ambient temperature | Actual heat generation | Temperature of the motor |
| 1 | -40℃ | 2000 Joule | 50℃ |
| 2 | -30℃ | 2100 Joule | 55℃ |
| 3 | -20℃ | 2100 joules of | 60℃ |
| 4 | 0℃ | 2200 joules | 68℃ |
| 5 | 5℃ | 2200 joules | 72℃ |
| 35℃ | 2300J | 80℃ |
Through the estimation, the motor temperature of the motor of the vehicle steering system of the vehicle can be obtained, and the corresponding motor temperature in each environment temperature range is shown in the following table:
and estimating the motor temperature of each vehicle type, and then obtaining the corresponding relation between each vehicle type and the ambient temperature and the motor temperature. And storing the corresponding relation in a database table to obtain the calibration relation between the temperature range and the motor temperature. As shown in the following table:
step S202, obtaining the environment temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current of a vehicle steering system, and obtaining the temperature of the motor from the calibration relation according to the environment temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current.
The ambient temperature of the vehicle is obtained at intervals (e.g., at intervals of 5 minutes), or the ambient temperature of the vehicle may be obtained in real time. Such as to obtain an ambient temperature of 25 c for the vehicle. Then, the current input into the motor of the steering system of the vehicle is obtained in real time, and then a formula is used for the input current:and (4) integrating, wherein I is the current value of the input motor, R is the resistance equivalent value of the motor, and t1 and t2 are the integration starting time and the integration ending time. And obtaining the maximum heat productivity of the motor through integration.
The heat dissipation efficiency of the motor of the vehicle steering system of each vehicle type is different, and the heat dissipation amount within a specified time length range needs to be obtained according to the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor. And calculating the heat dissipation capacity of the motor by using a formula w (t 2-t 1), wherein w is the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor, and the heat dissipation starting time and the heat dissipation finishing time of t1 and t 2. By the above formula, the heat dissipation amount in the time range of 10.
The motor obtains the maximum heating value (such as heating value a 2) of the motor by subtracting the maximum heat dissipation value (such as heat dissipation value b 2) of the motor through current integration, and obtains the actual heating value (such as actual heating value c 2) of the motor. And then obtaining the type of the vehicle to which the current vehicle belongs.
Finally, the parameters of the vehicle type, the ambient temperature and the actual heating value are obtained, and are shown in the following table:
| type of vehicle | Ambient temperature | Actual heat generation |
| CAR_TYPE_001 | 25℃ | 2300J |
And querying a table corresponding to the calibration relation between the temperature range and the motor temperature in the database by using the vehicle type, the environment temperature and the actual heating value to obtain the estimated temperature of the current motor, namely the motor temperature. The motor temperature as queried was 75 ℃.
The temperature of the electronic control unit of the vehicle steering system is acquired, see the flow chart shown in fig. 4.
And S401, acquiring the temperature of an electronic control unit of the vehicle steering system.
A temperature sensor is installed at a main chip of a PCB board of an ECU of a vehicle steering system (EPS) to detect the temperature of the ECU in real time.
Acquiring a vehicle driving state, wherein the vehicle driving state comprises the following steps: vehicle stationary state, vehicle low speed state. If the vehicle is in traffic jam or stops at a traffic light, the running state of the vehicle is the static state of the vehicle.
When the vehicle meets the following conditions, the vehicle running state is a vehicle low-speed state:
when the current speed of the vehicle is less than the first speed, the speed of the whole track issued by the automatic driving plan of the vehicle is less than the second speed, the distance between the current position of the vehicle and the track end point of the automatic driving plan is less than the specified distance, and the acceleration of the vehicle is less than or equal to 0.
The first speed, the second speed and the designated distance can be set according to actual conditions. If the first speed is 0.5m/s, the second speed is 0.5m/s, and the specified distance is 1m.
Step S102, when the temperature is greater than a first temperature threshold value and the vehicle running state is a vehicle static state or a low-speed state, exiting the transverse driving control; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained.
And judging whether the motor temperature and the electronic control unit temperature are greater than specified temperature thresholds.
If the motor temperature threshold can be set according to the time condition, if the maximum working temperatures of the motors corresponding to different types of vehicles are different, the motor temperature threshold can be set to be the maximum working temperature of the motor corresponding to the type of the vehicle. If the motor temperature threshold is 70 ℃, the inquired motor temperature is 75 ℃. And judging that the current motor temperature (75 ℃) is greater than a motor temperature threshold (70 ℃).
When the motor temperature is higher than the motor temperature threshold value, the motor temperature overheating early warning information of the vehicle steering system needs to be sent to a vehicle control system, such as an ECU; or to the control unit of the autopilot system. And sending the data to the equipment, and setting according to actual requirements.
It is determined whether the temperature of the ECU is greater than a specified ECU temperature threshold. The ECU temperature threshold may be set according to actual conditions, and if the maximum operating temperatures of the ECUs corresponding to different types of vehicles are different, the ECU temperature threshold may be set to the maximum operating temperature of the ECU corresponding to the type of the vehicle. If the ECU temperature threshold is 70 ℃, the real-time detected ECU temperature is 75 ℃. It is determined that the current temperature of the ECU (75 deg.c) is greater than the ECU temperature threshold (70 deg.c).
When the temperature of the ECU is greater than the temperature threshold of the ECU, the overheating early warning information of the temperature of the electronic control unit needs to be sent to a vehicle control system; or to the control unit of the autopilot system. And sending the data to the equipment, and setting according to actual requirements.
And after receiving the motor temperature overheating early warning information or the electronic control unit temperature overheating early warning information of the vehicle steering system, the vehicle judges whether the current vehicle running state is in a static state or a low-speed state. When the vehicle is in a static state or a low-speed state in a running state, the automatic driving system of the vehicle sends a braking instruction, and the automatic driving system quits the transverse control of the vehicle. Thereby reducing the current output of the electric resistance steering motor and achieving the purpose of slowing down the heating of the motor.
According to the embodiment of the invention, the temperature of the EPS motor is monitored in real time, and when the temperature of the EPS motor is overheated, the overheating of the EPS motor is early warned. When the vehicle is stopped, the transverse control is directly withdrawn, so that the current of the EPS is reduced, and the overheating frequency of the EPS is greatly reduced; and carrying out safe parking and other operations before the EPS is out of control. The invention can effectively reduce the frequency of EPS overheating, and can early warn before the EPS overheating, thereby achieving the purpose of safe parking.
In one embodiment, the present invention provides a steering system based vehicle control method, as shown in FIG. 5. On the basis of the method shown in fig. 1, the method further comprises the following steps:
and step S103, when the vehicle issues the brake instruction and exits the transverse control and the running state of the vehicle is not the vehicle static state or the low-speed state, stopping braking of the vehicle and entering the transverse control again.
When the vehicle issues a braking instruction, the vehicle can quit the transverse control, so that the output of the EPS current is reduced, and the purpose of reducing heating is achieved. And when the running state of the vehicle does not satisfy the static state any more and also does not satisfy the low-speed state, the automatic driving system of the vehicle issues a braking stopping instruction. The DBW (drive by wire) can enable the vehicle to reenter the transverse control, and when the vehicle transversely reenters automatically, the longitudinal direction of the vehicle can give an instruction to enable the vehicle to start.
And step S104, after the vehicle issues a braking instruction and quits the transverse control, if the temperature is higher than a second temperature threshold value, the vehicle executes the side-approaching parking operation.
When the temperature of an electronic control unit of a vehicle steering system reaches an ECU temperature threshold value, or the temperature of a motor of the steering system reaches a motor temperature threshold value, after the vehicle issues a braking instruction and exits from transverse control, if the temperature of the electronic control unit of the vehicle steering system or the temperature of the motor still continuously rises and reaches a preset second temperature (such as 80 ℃), level3 alarm information is sent out, and when an automatic vehicle driving system receives the Level3 alarm information, the vehicle stops while keeping to avoid the problem of transverse control failure caused by continuous driving of the vehicle.
According to the embodiment of the invention, the temperature of the electronic control unit of the EPS is monitored in real time, and when the temperature of the EPS is too hot, the warning of the EPS overheating is carried out. When the vehicle is stopped, the transverse control is directly withdrawn, so that the current of the EPS is reduced, and the overheating frequency of the EPS is greatly reduced; and performing safe parking and other operations before the EPS is out of control. The invention can effectively reduce the frequency of EPS overheating, and can early warn before the EPS overheating, thereby achieving the purpose of safe parking.
In one embodiment, the present invention provides a steering system based vehicle control method, as shown in FIG. 6. The method further comprises the following steps:
step S501, limiting the input steering angular speed, and only allowing the input steering angular speed smaller than a first threshold value;
step S502, prohibiting pivot steering operation of the vehicle when the vehicle is static, and allowing vehicle steering when the running speed of the vehicle reaches a first speed;
step S503, when the vehicle is subjected to pivot steering operation, the input steering angle is a fixed value;
and step S504, when the running speed of the vehicle is less than the second speed, inputting that the steering angle speed of the vehicle is less than a second threshold value.
After the vehicle receives the EPS overheating early warning information (such as the motor temperature overheating early warning information of the vehicle steering system or the electronic control unit temperature overheating early warning information of the vehicle steering system), the vehicle steering system (EPS) needs to avoid the following operations:
1. when the vehicle turns around, the steering angular speed needs to be limited (if the steering angular speed does not exceed 100 deg/s), the steering is not required to be performed on site, and the steering is started when the vehicle speed reaches more than 2 km/h;
2. if the vehicle has no higher precision requirement on the angle during the in-situ large-angle steering, the automatic driving system sends a fixed angle value instead of a floating value (the angle control precision can be relaxed to 3deg during in-situ).
3. When the vehicle speed is less than 10km/h, the steering wheel angular velocity value during running is reduced.
According to the embodiment of the invention, when the temperature of the EPS is overheated, the EPS overheating is early warned, and an automatic driving system is prompted to avoid operations such as in-situ large-angle steering, so that the frequency of the EPS overheating is greatly reduced.
In addition, an embodiment of the present invention further provides a vehicle control device based on a steering system, and with reference to fig. 7, the vehicle control device based on the steering system includes:
a temperature acquisition unit 10 for acquiring a temperature of a steering system of a vehicle;
a state acquisition unit 20 for acquiring a vehicle state;
a safety operation unit 30 for exiting the lateral driving control when the temperature is greater than a first temperature threshold value and the vehicle running state is a vehicle stationary state or a low speed state; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained.
By the embodiment of the invention, the EPS temperature is monitored in real time, and the EPS overheating early warning is carried out when the EPS temperature is overheated. When the vehicle is stopped, the transverse control is directly withdrawn, so that the current of the EPS is reduced, and the overheating frequency of the EPS is greatly reduced; and carrying out safe parking and other operations before the EPS is out of control. The invention can effectively reduce the frequency of EPS overheating, and can early warn before the EPS overheating, thereby achieving the purpose of safe parking.
It should be noted that each unit in the apparatus may be configured to implement each step in the method, and achieve the corresponding technical effect, which is not described herein again.
Referring to fig. 8, fig. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of a vehicle in a hardware operating environment according to an embodiment of the present invention.
As shown in fig. 8, the vehicle may include: a processor 1001, e.g. a CPU, a communication bus 1002, a user interface 1003, a network interface 1004, a memory 1005. Wherein a communication bus 1002 is used to enable connective communication between these components. The user interface 1003 may include a Display (Display), an input unit such as a Keyboard (Keyboard), and the optional user interface 1003 may also include a standard wired interface, a wireless interface. The network interface 1004 may optionally include standard wired interfaces, wireless interfaces (e.g., WI-FI, 4G, 5G interfaces). The memory 1005 may be a high-speed RAM memory or a non-volatile memory (e.g., a magnetic disk memory). The memory 1005 may alternatively be a storage device separate from the processor 1001.
Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the configuration shown in fig. 8 does not constitute a limitation of the vehicle and may include more or fewer components than those shown, or some components may be combined, or a different arrangement of components.
As shown in fig. 8, an operating system, a network communication module, a user interface module, and a steering system-based vehicle control program may be included in the memory 1005, which is one type of computer storage medium.
In the vehicle shown in fig. 8, the network interface 1004 is mainly used for data communication with an external network; the user interface 1003 is mainly used for receiving an input instruction of a user; the vehicle invokes a steering system based vehicle control program stored in the memory 1005 via the processor 1001 and performs the following operations:
acquiring the temperature of a vehicle steering system and the running state of a vehicle;
when the temperature is greater than a first temperature threshold value and the vehicle running state is a vehicle static state or a low-speed state, exiting the transverse driving control; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained.
Optionally, the obtaining the temperature of the vehicle steering system includes:
calibrating the motor temperature of a vehicle steering system of each type of vehicle within a specified temperature range to obtain a calibration relation between the temperature range and/or the motor current and the motor temperature;
and acquiring the environment temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current of a vehicle steering system, and acquiring the temperature of the motor from the calibration relation according to the environment temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current.
Optionally, the calibrating the motor temperature of the vehicle steering system in the specified temperature range for each type of vehicle includes the following steps:
acquiring the environmental temperature of a vehicle of a specified type;
acquiring an input current value of a motor of a vehicle steering system, and integrating the current value in a specified time range to obtain the maximum heat productivity of the motor;
obtaining the maximum heat dissipation capacity of the motor within the specified time range according to the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor;
subtracting the maximum heat dissipation amount from the maximum heat productivity to obtain the actual heat productivity of the motor;
and acquiring the temperature of the motor according to the environment temperature and the actual heating value of the motor.
Optionally, the obtaining the temperature of the vehicle steering system includes:
the temperature of an electronic control unit of the vehicle steering system is obtained.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
and after the vehicle issues the brake instruction and exits the transverse control, when the vehicle running state is not the vehicle static state or the low-speed state, stopping braking and entering the transverse control again.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
and after the vehicle exits the transverse control, when the temperature is greater than a second temperature threshold value, the vehicle executes an edge-approaching parking operation.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
limiting the input steering angular speed, and only allowing the input steering angular speed smaller than a first threshold value; or the like, or, alternatively,
prohibiting pivot steering operation of the vehicle when the vehicle is static, and allowing vehicle steering after the running speed of the vehicle reaches a first speed; or
When the vehicle is subjected to pivot steering operation, the input steering angle is a fixed value; or the like, or a combination thereof,
the vehicle running speed is less than the second speed, and the steering angle speed input into the vehicle is less than a second threshold value.
By the embodiment of the invention, the EPS temperature is monitored in real time, and the EPS overheating early warning is carried out when the EPS temperature is overheated. When the vehicle is stopped, the transverse control is directly withdrawn, so that the current of the EPS is reduced, and the overheating frequency of the EPS is greatly reduced; and carrying out safe parking and other operations before the EPS is out of control. The invention can effectively reduce the frequency of EPS overheating, and can early warn before the EPS overheating, thereby achieving the purpose of safe parking.
Furthermore, an embodiment of the present invention further provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a steering-system-based vehicle control program is stored, where the steering-system-based vehicle control program, when executed by a processor, implements the following operations:
acquiring the temperature of a vehicle steering system and the vehicle running state;
when the temperature is greater than a first temperature threshold value and the vehicle running state is a vehicle static state or a low-speed state, exiting the transverse driving control; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained.
Optionally, the obtaining the temperature of the vehicle steering system includes:
calibrating the motor temperature of a vehicle steering system of each type of vehicle within a specified temperature range to obtain a temperature range and/or a calibration relation between the motor current and the motor temperature;
and acquiring the ambient temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current of a vehicle steering system, and acquiring the temperature of the motor from the calibration relation according to the ambient temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current.
Optionally, the calibrating the motor temperature of the vehicle steering system in the specified temperature range for each type of vehicle includes the following steps:
acquiring the environmental temperature of a vehicle of a specified type;
acquiring an input current value of a motor of a vehicle steering system, and integrating the current value in a specified time range to obtain the maximum heat productivity of the motor;
obtaining the maximum heat dissipation capacity of the motor within the specified time range according to the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor;
subtracting the maximum heat dissipation amount from the maximum heat productivity to obtain the actual heat productivity of the motor;
and acquiring the temperature of the motor according to the environment temperature and the actual heating value of the motor.
Optionally, the obtaining the temperature of the vehicle steering system includes:
the temperature of an electronic control unit of the vehicle steering system is acquired.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
and after the vehicle issues the brake instruction and exits the transverse control, when the running state of the vehicle is not the vehicle static state or the low-speed state, stopping braking of the vehicle and entering the transverse control again.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
and after the vehicle exits the transverse control, when the temperature is greater than a second temperature threshold value, the vehicle executes an edge-approaching parking operation.
Optionally, the method further comprises the steps of:
limiting the input steering angular speed, and only allowing the input steering angular speed smaller than a first threshold value; or the like, or, alternatively,
prohibiting pivot steering operation of the vehicle when the vehicle is stationary, and permitting vehicle steering only when the running speed of the vehicle reaches a first speed; or
When the vehicle is subjected to pivot steering operation, the input steering angle is a fixed value; or the like, or, alternatively,
the vehicle running speed is less than the second speed, and the steering angle speed input to the vehicle is less than a second threshold value.
By the embodiment of the invention, the EPS temperature is monitored in real time, and the EPS overheating early warning is carried out when the EPS temperature is overheated. When the vehicle is stopped, the transverse control is directly withdrawn, so that the current of the EPS is reduced, and the overheating frequency of the EPS is greatly reduced; and carrying out safe parking and other operations before the EPS is out of control. The invention can effectively reduce the frequency of EPS overheating, and can early warn before the EPS overheating, thereby achieving the purpose of safe parking.
It should be noted that, in this document, the terms "comprises," "comprising," or any other variation thereof, are intended to cover a non-exclusive inclusion, such that a process, method, article, or system that comprises a list of elements does not include only those elements but may include other elements not expressly listed or inherent to such process, method, article, or system. Without further limitation, an element defined by the phrases "comprising a," "8230," "8230," or "comprising" does not exclude the presence of other like elements in a process, method, article, or system comprising the element.
The above-mentioned serial numbers of the embodiments of the present invention are merely for description and do not represent the merits of the embodiments.
Through the description of the foregoing embodiments, it is clear to those skilled in the art that the method of the foregoing embodiments may be implemented by software plus a necessary general hardware platform, and certainly may also be implemented by hardware, but in many cases, the former is a better implementation. Based on such understanding, the technical solution of the present invention may be embodied in the form of a software product, which is stored in a storage medium (e.g., ROM/RAM, magnetic disk, optical disk) as described above and includes instructions for enabling a terminal device (e.g., a mobile phone, a computer, a server, a controller, or a network device) to execute the method according to the embodiments of the present invention.
The above description is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, and all modifications of equivalent structures and equivalent processes, which are made by using the contents of the present specification and the accompanying drawings, or directly or indirectly applied to other related technical fields, are included in the scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
1. A steering system based vehicle control method, characterized in that the method comprises the steps of:
acquiring the temperature of a vehicle steering system and the running state of a vehicle;
when the temperature is greater than a first temperature threshold value and the vehicle running state is a vehicle static state or a low-speed state, exiting the transverse driving control; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein said obtaining a temperature of a vehicle steering system comprises the steps of:
calibrating the motor temperature of a vehicle steering system of each type of vehicle within a specified temperature range to obtain a calibration relation between the temperature range and/or the motor current and the motor temperature;
and acquiring the environment temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current of a vehicle steering system, and acquiring the temperature of the motor from the calibration relation according to the environment temperature of the vehicle and/or the motor current.
3. The method of claim 2, wherein calibrating the motor temperature of the vehicle steering system for each type of vehicle within a specified temperature range comprises the steps of:
acquiring the environmental temperature of a vehicle of a specified type;
acquiring an input current value of a motor of a vehicle steering system, and integrating the current value within a specified time range to obtain the maximum heat productivity of the motor;
obtaining the maximum heat dissipation capacity of the motor within the specified time range according to the heat dissipation efficiency of the motor;
subtracting the maximum heat dissipation amount from the maximum heat dissipation amount to obtain the actual heat dissipation amount of the motor;
and acquiring the temperature of the motor according to the environment temperature and the actual heating value of the motor.
4. The method of claim 1, wherein said obtaining a temperature of a vehicle steering system comprises the steps of:
the temperature of an electronic control unit of the vehicle steering system is acquired.
5. The method of claim 1, further comprising the steps of:
and after the vehicle issues the brake instruction and exits the transverse control, when the running state of the vehicle is not the vehicle static state or the low-speed state, stopping braking of the vehicle and entering the transverse control again.
6. The method of claim 1, further comprising the steps of:
and after the vehicle exits the transverse control, when the temperature is greater than a second temperature threshold value, the vehicle executes an edge-approaching parking operation.
7. The method of claim 1, further comprising the steps of:
limiting the input steering angular speed, and only allowing the input steering angular speed smaller than a first threshold value; or the like, or, alternatively,
prohibiting pivot steering operation of the vehicle when the vehicle is stationary, and permitting vehicle steering only when the running speed of the vehicle reaches a first speed; or
When the vehicle is subjected to pivot steering operation, the input steering angle is a fixed value; or the like, or, alternatively,
the vehicle running speed is less than the second speed, and the steering angle speed input to the vehicle is less than a second threshold value.
8. A steering-system-based vehicle control apparatus, characterized by comprising:
a temperature acquisition unit for acquiring a temperature of a steering system of a vehicle;
a state acquisition unit for acquiring a vehicle state;
a safety operation unit for exiting the lateral driving control when the temperature is greater than a first temperature threshold and the vehicle running state is a vehicle stationary state or a low speed state; otherwise, the vehicle lateral driving control is maintained.
9. A vehicle, characterized in that it comprises: a memory, a processor, and a steering-system based vehicle control program stored on the memory and executable on the processor, the steering-system based vehicle control program configured to implement the steps of the steering-system based vehicle control method according to any one of claims 1 to 7.
10. A computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, which, when being executed by a processor, carries out the steps of the steering-system-based vehicle control method according to any one of claims 1 to 7.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211051496.6A CN115285214A (en) | 2022-08-31 | 2022-08-31 | Vehicle control method and device based on steering system and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211051496.6A CN115285214A (en) | 2022-08-31 | 2022-08-31 | Vehicle control method and device based on steering system and storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115285214A true CN115285214A (en) | 2022-11-04 |
Family
ID=83831182
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211051496.6A Pending CN115285214A (en) | 2022-08-31 | 2022-08-31 | Vehicle control method and device based on steering system and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115285214A (en) |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1721251A (en) * | 2004-05-31 | 2006-01-18 | 日产自动车株式会社 | The steering hardware and the turning rate control method that are used for power actuated vehicle |
| JP2006151391A (en) * | 2006-03-13 | 2006-06-15 | Jtekt Corp | Steering device of vehicle |
| CN102566434A (en) * | 2012-02-13 | 2012-07-11 | 范示德汽车技术(上海)有限公司 | Motor thermodynamic model-based over-temperature protection method for electric power-assisted steering system |
| CN105584519A (en) * | 2014-11-12 | 2016-05-18 | 上海航天汽车机电股份有限公司 | Heat management method and system for electric power steering system |
| CN106627741A (en) * | 2016-09-14 | 2017-05-10 | 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司 | Motor thermal protection system and method based on motor and ECU separated type electric power steering system |
| CN108248679A (en) * | 2018-01-16 | 2018-07-06 | 北京汽车股份有限公司 | The control method for over-heating protection of vehicle and its electric boosting steering system, device |
| CN110539737A (en) * | 2018-05-28 | 2019-12-06 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | Vehicle parking method and device, storage medium, electronic device and vehicle |
| CN110937019A (en) * | 2019-11-12 | 2020-03-31 | 南京航空航天大学 | Motor thermodynamic protection strategy based on dual-motor steer-by-wire system control |
| CN113492834A (en) * | 2020-03-18 | 2021-10-12 | 本田技研工业株式会社 | Vehicle control device |
| CN113928414A (en) * | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-14 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | Method and device for controlling steering motor of vehicle and vehicle |
| CN114620117A (en) * | 2020-12-11 | 2022-06-14 | 上海海拉电子有限公司 | Electronic controller for electric power steering control system and working method thereof |
-
2022
- 2022-08-31 CN CN202211051496.6A patent/CN115285214A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1721251A (en) * | 2004-05-31 | 2006-01-18 | 日产自动车株式会社 | The steering hardware and the turning rate control method that are used for power actuated vehicle |
| JP2006151391A (en) * | 2006-03-13 | 2006-06-15 | Jtekt Corp | Steering device of vehicle |
| CN102566434A (en) * | 2012-02-13 | 2012-07-11 | 范示德汽车技术(上海)有限公司 | Motor thermodynamic model-based over-temperature protection method for electric power-assisted steering system |
| CN105584519A (en) * | 2014-11-12 | 2016-05-18 | 上海航天汽车机电股份有限公司 | Heat management method and system for electric power steering system |
| CN106627741A (en) * | 2016-09-14 | 2017-05-10 | 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司 | Motor thermal protection system and method based on motor and ECU separated type electric power steering system |
| CN108248679A (en) * | 2018-01-16 | 2018-07-06 | 北京汽车股份有限公司 | The control method for over-heating protection of vehicle and its electric boosting steering system, device |
| CN110539737A (en) * | 2018-05-28 | 2019-12-06 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | Vehicle parking method and device, storage medium, electronic device and vehicle |
| CN110937019A (en) * | 2019-11-12 | 2020-03-31 | 南京航空航天大学 | Motor thermodynamic protection strategy based on dual-motor steer-by-wire system control |
| CN113492834A (en) * | 2020-03-18 | 2021-10-12 | 本田技研工业株式会社 | Vehicle control device |
| CN113928414A (en) * | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-14 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | Method and device for controlling steering motor of vehicle and vehicle |
| CN114620117A (en) * | 2020-12-11 | 2022-06-14 | 上海海拉电子有限公司 | Electronic controller for electric power steering control system and working method thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101936891B1 (en) | Method and device for generating driving behavior guidance information | |
| JP6079596B2 (en) | Parking assistance device | |
| CN110696829B (en) | Method and device for processing vehicle soaring and slipping, electric vehicle and storage medium | |
| KR101735846B1 (en) | Method for reducing the drive power of a vehicle drive | |
| CN109305115B (en) | Automobile control method, electric automobile and computer readable storage medium | |
| US20110160965A1 (en) | Method of protecting motor-driven power steering system from overheat | |
| CN108333518B (en) | Battery health assessment | |
| US20190243363A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for controlling vehicle based on redundant architecture | |
| CN106240372B (en) | Control device for electric vehicle | |
| US11091106B2 (en) | Hybrid power network for a vehicle | |
| CN115675430B (en) | System and method for predicting braking thermal failure and actively intervening of long downhill road section automobile | |
| CN111469917A (en) | Vehicle steering control method and device | |
| CN113291307B (en) | Automobile power control method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN115285214A (en) | Vehicle control method and device based on steering system and storage medium | |
| CN111572561B (en) | Speed control method, device and equipment for automatic driving automobile and storage medium | |
| US10266132B2 (en) | Method for operating driver assistance systems in a motor vehicle, and motor vehicle | |
| JP2015077963A (en) | Method to control internal combustion engine and electric machines in hybrid vehicle | |
| US8364341B2 (en) | Method for controlling a driver assistance system | |
| SE1650726A1 (en) | A wheeled motor vehicle and a method for controlling the flow of electric power of an electric system of such a vehicle | |
| CN113002530B (en) | Automatic parking method, device, equipment and storage medium based on uneven road surface | |
| US11279203B2 (en) | Air conditioning control device | |
| CN112389275B (en) | Safety control method and device based on electric drive active heating mode | |
| CN112995061B (en) | Vehicle data transmission method, device and system and storage medium | |
| CN117445922B (en) | Method and device for controlling abnormal working conditions of unmanned mine car | |
| KR101509907B1 (en) | Method for diagnosing status of vehicle controller and system thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |