CN115076820A - Air conditioner energy saving system, control method and air conditioner - Google Patents
Air conditioner energy saving system, control method and air conditioner Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115076820A CN115076820A CN202211002466.6A CN202211002466A CN115076820A CN 115076820 A CN115076820 A CN 115076820A CN 202211002466 A CN202211002466 A CN 202211002466A CN 115076820 A CN115076820 A CN 115076820A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- compressor
- temperature value
- solenoid valve
- air conditioner
- valve
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F5/00—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater
- F24F5/0007—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater cooling apparatus specially adapted for use in air-conditioning
- F24F5/001—Compression cycle type
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/30—Control or safety arrangements for purposes related to the operation of the system, e.g. for safety or monitoring
- F24F11/46—Improving electric energy efficiency or saving
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/62—Control or safety arrangements characterised by the type of control or by internal processing, e.g. using fuzzy logic, adaptive control or estimation of values
- F24F11/63—Electronic processing
- F24F11/64—Electronic processing using pre-stored data
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/62—Control or safety arrangements characterised by the type of control or by internal processing, e.g. using fuzzy logic, adaptive control or estimation of values
- F24F11/63—Electronic processing
- F24F11/65—Electronic processing for selecting an operating mode
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/70—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof
- F24F11/80—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the temperature of the supplied air
- F24F11/83—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the temperature of the supplied air by controlling the supply of heat-exchange fluids to heat-exchangers
- F24F11/84—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the temperature of the supplied air by controlling the supply of heat-exchange fluids to heat-exchangers using valves
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/70—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof
- F24F11/80—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the temperature of the supplied air
- F24F11/86—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the temperature of the supplied air by controlling compressors within refrigeration or heat pump circuits
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F5/00—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater
- F24F5/0046—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater using natural energy, e.g. solar energy, energy from the ground
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F5/00—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater
- F24F5/0046—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater using natural energy, e.g. solar energy, energy from the ground
- F24F2005/0064—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater using natural energy, e.g. solar energy, energy from the ground using solar energy
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Fuzzy Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Sustainable Energy (AREA)
- Air Conditioning Control Device (AREA)
Abstract
The invention provides an air conditioner energy-saving system, a control method and an air conditioner. The energy saving system comprises: the solar heating system comprises a solar heating unit and an air conditioning device, wherein the air conditioning device comprises an outdoor unit and an indoor unit, and the outdoor unit is provided with a spraying device and a heat exchanger; the spraying device is provided with a first nozzle inlet, a second nozzle inlet and a nozzle outlet, one end of the heat exchanger is connected to the nozzle outlet, and the other end of the heat exchanger is connected to the indoor unit through a first pipeline; the solar heating unit includes: a solar collector and a generator; the generator is provided with a first heat exchange pipeline and a second heat exchange pipeline, one end of the solar heat collector is communicated with an inlet of the first heat exchange pipeline, and the other end of the solar heat collector is communicated with an outlet of the first heat exchange pipeline; the outdoor unit further includes: and one end of the second pipeline is connected to the first nozzle inlet, and the other end of the second pipeline is connected to the indoor unit. The invention can solve the technical problem that the refrigerant reflows when the compressor is started and the solar energy is insufficient.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of air conditioners, in particular to an air conditioner energy saving system, a control method and an air conditioner.
Background
With the improvement of living standard, air conditioners become necessary in life, and the increase of the number of air conditioners brings with it the problem of large energy consumption, so that energy-saving products become the main development direction of various manufacturers. Solar energy has been paid attention to as renewable clean energy, and solar energy and power supply are complementary, so that the air conditioning system is efficient and energy-saving, and the comfort in use is improved.
In actual implementation, however, the energy output of the solar heat collecting plate changes along with the change of the sun, and the injection inlet of the injection device is connected to the solar heat collecting plate, and the injection outlet is connected to the outdoor heat exchanger; one end of the compressor is connected to the indoor heat exchanger, and the other end of the compressor is connected between the injection outlet of the injection device and the outdoor heat exchanger; the prior art has the following defects: when the solar energy is insufficient and the compressor is started, the pressure at the inlet of the compressor is higher than the pressure at the injection outlet of the injection device, so that when the compressor is started, the refrigerant in the compressor flows back, and the operating efficiency of the air conditioning system is affected.
Disclosure of Invention
The invention can solve the technical problem that the refrigerant reflows when the compressor is started and the solar energy is insufficient.
In order to solve the above problem, an embodiment of the present invention provides an energy saving system for an air conditioner, where the energy saving system includes: the solar heating system comprises a solar heating unit and an air conditioning device, wherein the air conditioning device comprises an outdoor unit and an indoor unit, and the outdoor unit is provided with a spraying device and a heat exchanger; the spraying device is provided with a first nozzle inlet, a second nozzle inlet and a nozzle outlet, one end of the heat exchanger is connected to the nozzle outlet, and the other end of the heat exchanger is connected to the indoor unit through a first pipeline; the solar heating unit includes: a solar collector and a generator; the generator is provided with a first heat exchange pipeline and a second heat exchange pipeline, one end of the solar heat collector is communicated with an inlet of the first heat exchange pipeline, and the other end of the solar heat collector is communicated with an outlet of the first heat exchange pipeline; the outdoor unit further includes: a second duct having one end connected to the first nozzle inlet and the other end connected to the indoor unit; a first solenoid valve disposed at the second pipe; a third pipe having one end connected to an inlet of the second heat exchange pipe and the other end connected to the first pipe; one end of the fourth pipeline is connected to the outlet of the second heat exchange pipeline, and the other end of the fourth pipeline is connected between the first electromagnetic valve and the inlet of the first nozzle; one end of the fifth pipeline is connected to the second nozzle inlet, and the other end of the fifth pipeline is connected between the first electromagnetic valve and the indoor unit; a compressor disposed at the fourth pipe; the refrigerant in the air conditioning device can flow to the second heat exchange pipeline from the third pipeline, the hot water in the solar heating unit can flow to the first heat exchange pipeline from the solar heat collector, and the hot water in the first heat exchange pipeline can exchange heat with the refrigerant in the second heat exchange pipeline.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: the solar collector and the generator are arranged in the solar heating unit, so that the solar collector is used for collecting solar energy and the generator is used for exchanging heat, and the circulating operation of hot water in the solar heating unit is ensured; the compressor is arranged on the fourth pipeline, so that the distance between the compressor and the solar heating unit is shortened; the phenomenon of backflow of the refrigerant is further ensured when the solar energy is insufficient, so that the problem of blockage of the refrigerant in a pipeline in the air conditioning device is avoided, and the operating efficiency of the air conditioning system is further improved; meanwhile, the purpose of saving energy when the air conditioning system heats or refrigerates is achieved.
Further, in an embodiment of the present invention, the outdoor unit further includes: one end of the sixth pipeline is connected between the injection device and the heat exchanger, and the other end of the sixth pipeline is connected between the solar heating unit and the compressor.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: through setting up the fifth pipeline, realized being in the low pressure at the refrigerant and spraying, further improved injection apparatus's suitability, avoided when refrigerant pressure is lower, injection apparatus can not spray the problem of refrigerant to the heat exchanger, further improvement air conditioning system's operating efficiency.
Further, in an embodiment of the present invention, the outdoor unit further includes: a first expansion valve disposed at the first pipe; the second expansion valve is arranged on the first pipeline and is positioned between the first expansion valve and the heat exchanger; a second solenoid valve disposed in the second conduit and between the first solenoid valve and the injection device; a third solenoid valve disposed at the fifth pipe; a fourth solenoid valve; the fourth electromagnetic valve is arranged on the sixth pipeline; the regulating valve is arranged on the fourth pipeline; and the working medium pump is arranged on the third pipeline.
Compared with the prior art, the technical effect achieved by adopting the technical scheme is as follows: by arranging the first expansion valve and the second expansion valve, the control of the refrigerant flow in the pipeline between the heat exchanger and the indoor unit is realized, and the refrigerant conveying efficiency is further improved; the arrangement of the first electromagnetic valve and the second electromagnetic valve realizes the purpose of conveying the refrigerant to the injection device, improves the efficiency of the injection device, and simultaneously ensures the operating efficiency of the air conditioning system.
Further, in an embodiment of the present invention, the control method is used for controlling the air conditioner energy saving system in the above embodiment, and the control method includes: when the air conditioner energy-saving system runs, detecting the air outlet temperature value T of the indoor unit; judging whether the energy-saving system of the air conditioner meets the starting condition of the compressor or not according to the relation between the outlet air temperature value and a preset temperature value; and if so, controlling the air conditioner energy-saving system to enter a compressor running mode.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: when solar energy is sufficient or insufficient, the heat exchange efficiency between the solar heating unit and the air conditioning device is different, and correspondingly, the refrigerating or heating effect of the air conditioning device is different; the cooling or heating effect of the air conditioner can be reflected by the air outlet temperature of the indoor unit, so that whether solar energy is sufficient or not is judged by detecting the air outlet temperature value T of the indoor unit, whether the compressor needs to be started or not is judged, and the purpose of saving energy is achieved.
Further, in an embodiment of the present invention, when the air conditioner economizer system is in cooling, whether the compressor on condition is satisfied includes: when the air outlet temperature value T is larger than a first preset temperature value T 1 When the compressor is started, the compressor is controlled to be started; and/or when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a second preset temperature value T 2 When the compressor is started, controlling the compressor to be closed; and/or at a second preset temperature value T 2 The air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to the first preset temperature value T 1 And controlling the compressor to continuously run in the current state.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: in order to improve the energy-saving efficiency of the energy-saving system of the air conditioner, when the solar energy is sufficient, the compressor is closed, and at the moment, the energy-saving system adopts a solar refrigeration or heating mode to achieve the purpose of refrigeration; when the solar energy is insufficient, the compressor is started, and at the moment, the energy-saving system adopts a mode of combining the solar energy and the compressor so as to achieve the purpose of refrigerating or heating; the outlet air temperature T is at a second preset temperature value T 2 And a first preset temperature value T 1 Meanwhile, the air conditioner is more comfortable in the current running state, so that the compressor can be controlled to run in the current state; if the compressor is in the starting state, the compressor is continuously kept started; if the compressor is in the closing state, the compressor is continuously kept closed; according to the situation whether the solar energy is sufficient or not, the opening and closing of the compressor are controlled, the refrigerating or heating effect is achieved, the user demand is met, and meanwhile the utilization rate of energy is also improved.
Further, in one embodiment of the present invention, the compressor operation mode includes: when the air outlet temperature value T is larger than the first preset temperature value T 1 When the first expansion valve, the second electromagnetic valve and the third electromagnetic valve are in an opening state; the first solenoid valve, the fourth solenoid valve, and the regulating valve are in a closed state.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: under the refrigeration mode, when the compressor is started, the opening of the electromagnetic valve and the expansion valve are adjusted, so that the purpose of refrigerant circulation in the air-conditioning system is achieved, the operating efficiency of the air conditioner is further guaranteed, and the purpose of energy conservation is achieved.
Further, in an embodiment of the present invention, the compressor operation mode further includes: when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a second preset temperature value T 2 When the first expansion valve, the second electromagnetic valve, the third electromagnetic valve and the regulating valve are in an opening state; the first solenoid valve and the fourth solenoid valve are in a closed state.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a second preset temperature value T 2 When the solar energy is enough, the compressor can be closed, the refrigeration of the air conditioner can be realized by means of the heat released by the solar energy, and the purpose of energy conservation is realized.
Further, in one embodiment of the present inventionWhen the air conditioner energy-saving system heats, whether the compressor starting condition is met or not comprises the following steps: when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a third preset temperature value T 3 When the compressor is started, the compressor is controlled to be started; and/or when the outlet air temperature value T is larger than a fourth preset temperature value T 4 When the compressor is started, controlling the compressor to be closed; and/or at a third preset temperature value T 3 The air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to the fourth preset temperature value T 4 And controlling the compressor to continuously run in the current state.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: the energy-saving efficiency of the energy-saving system of the air conditioner is improved, when the solar energy is sufficient, the compressor is closed, and the energy-saving system adopts a solar refrigeration or heating mode to achieve the purpose of heating; when the solar energy is insufficient, the compressor is started; because the air outlet temperature T is at the third preset temperature value T 3 And a fourth preset temperature value T 4 Meanwhile, the air conditioner is more comfortable in the current running state, so that the compressor can be controlled to run in the current state; if the compressor is in the starting state, the compressor is continuously kept on; if the compressor is in the off state, the compressor continues to be kept off.
Further, in one embodiment of the present invention, the compressor operation mode includes: when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to the third preset temperature value T 3 When the first expansion valve, the second expansion valve, the first electromagnetic valve and the fourth electromagnetic valve are in an open state; the second solenoid valve, the third solenoid valve, and the regulating valve are in a closed state.
Compared with the prior art, the technical effect achieved by adopting the technical scheme is as follows: in the heating mode, when the compressor is started, the opening of the electromagnetic valve and the expansion valve are adjusted, so that the purpose of refrigerant circulation in an air conditioning system is achieved, the operating efficiency of the air conditioner is further guaranteed, and the purpose of energy conservation is achieved.
Further, in an embodiment of the present invention, the compressor operation mode further includes: at the placeThe air outlet temperature value T is greater than the fourth preset temperature value T 4 When the first expansion valve, the first electromagnetic valve and the regulating valve are in an opening state; the second expansion valve, the second solenoid valve, the third solenoid valve, and the fourth solenoid valve are in a closed state.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: when the air outlet temperature value T is larger than the fourth preset temperature value T 4 When the solar energy is enough, the compressor can be closed, the air conditioner can be heated by the heat released by the solar energy, and the purpose of energy conservation is achieved.
Further, an embodiment of the present invention further provides an air conditioner, where the air conditioner is provided with the energy saving system of the air conditioner in the above embodiment; or, a processor, a memory, and a program or instructions stored on the memory and executable on the processor, wherein the program or instructions, when executed by the processor, implement the energy saving control method of the air conditioner as in the above embodiments.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme has the following technical effects: the air conditioner has all the technical features and all the beneficial effects of the energy saving system and the control method in the above embodiments after the air conditioner is provided with the energy saving system of the air conditioner in the above embodiments or the control method in the above embodiments is implemented, and details are not repeated here.
In summary, after the technical scheme of the invention is adopted, the following technical effects can be achieved:
i) the solar collector and the generator are arranged in the solar heating unit, so that the solar collector is used for collecting solar energy and the generator is used for exchanging heat, and the circulating operation of hot water in the solar heating unit is ensured; the compressor is arranged on the fourth pipeline, so that the distance between the compressor and the solar heating unit is shortened; the phenomenon of backflow of the refrigerant is further ensured when the solar energy is insufficient, so that the problems of blockage and backflow of the refrigerant in a pipeline in the air conditioning device are avoided, and the operating efficiency of the air conditioning system is further improved; meanwhile, the purpose of saving energy when the air conditioning system heats or refrigerates is achieved;
ii) the first expansion valve and the second expansion valve are arranged, so that the control of the refrigerant flow in a pipeline between the heat exchanger and the indoor unit is realized, and the refrigerant conveying efficiency is further improved; the arrangement of the first electromagnetic valve and the second electromagnetic valve realizes the purpose of conveying the refrigerant into the injection device, improves the efficiency of the injection device and simultaneously ensures the operating efficiency of the air-conditioning system;
iii) in order to improve the energy-saving efficiency of the energy-saving system of the air conditioner, when the solar energy is sufficient, the compressor is closed, and at the moment, the energy-saving system adopts a solar refrigeration or heating mode to achieve the purpose of refrigeration; when the solar energy is insufficient, the compressor is started, and at the moment, the energy-saving system adopts a mode of combining the solar energy and the compressor so as to achieve the purpose of refrigerating or heating; the outlet air temperature T is at a second preset temperature value T 2 And a first preset temperature value T 1 Meanwhile, the air conditioner is more comfortable in the current running state, so that the compressor can be controlled to run in the current state; if the compressor is in the starting state, the compressor is continuously kept on; if the compressor is in the closing state, the compressor is continuously kept closed; according to the situation whether the solar energy is sufficient or not, the opening and closing of the compressor are controlled, the refrigerating or heating effect is achieved, the user demand is met, and meanwhile the utilization rate of energy is also improved.
Description of the drawings:
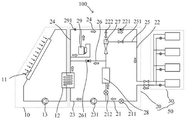
fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of an energy saving system of an air conditioner according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 2 is a cycle chart of the third embodiment of the present invention when solar energy is sufficient in the cooling mode.
Fig. 3 is a cycle chart of the third embodiment of the present invention when solar energy is insufficient in the cooling mode.
Fig. 4 is a cycle chart of the fourth embodiment of the present invention when solar energy is sufficient in the heating mode.
Fig. 5 is a cycle chart of the fourth embodiment of the present invention when the solar energy is insufficient in the heating mode.
Description of reference numerals:
100-an energy saving system; 10-a solar heating unit; 11-a solar heat collector; 12-a generator; 13-a circulation pump; 20-an outdoor unit; 21-a first conduit; 211-a first expansion valve; 212-a second expansion valve; 22-a second conduit; 221-a first solenoid valve; 222-a second solenoid valve; 23-a third conduit; 231-working medium pump; 24-a fourth conduit; 25-a fifth conduit; 251-a third solenoid valve; 26-a sixth conduit; 261-a fourth solenoid valve; 27-a spraying device; 28-a heat exchanger; 29-a compressor; 291-regulating valve; 30-indoor unit; 50-air conditioning means.
Detailed Description
In order to make the aforementioned objects, features and advantages of the present invention comprehensible, embodiments accompanied with figures are described in detail below.
[ first embodiment ] A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
Preferably, referring to fig. 1, a first embodiment of the present invention provides an energy saving system 100 for an air conditioner, where the energy saving system 100 for an air conditioner includes: the solar heating device 10 and the air conditioner 50, wherein the air conditioner 50 comprises an outdoor unit 20 and an indoor unit 30, and the outdoor unit 20 is provided with a spraying device 27 and a heat exchanger 28; the injection device 27 is provided with a first nozzle inlet, a second nozzle inlet and a nozzle outlet; one end of the heat exchanger 28 is connected to the nozzle outlet, and the other end is connected to the indoor unit 30 through the first duct 21.
Preferably, the solar heating unit 10 comprises: a solar collector 11, a generator 12 and a circulation pump 13; the generator 12 is provided with a first heat exchange pipeline and a second heat exchange pipeline, one end of the solar heat collector 11 is communicated with an inlet of the first heat exchange pipeline, and the other end of the solar heat collector is communicated with an outlet of the first heat exchange pipeline; the solar collector 11 is connected to the generator 12, the circulation pump 13 is connected between the solar collector 11 and the generator 12, and the circulation pump 13 is capable of circulating hot water between the solar collector 11 and the generator 12.
Preferably, the outdoor unit 20 further includes: a second duct 22, a third duct 23, a fourth duct 24, and a fifth duct 25; one end of the second duct 22 is connected to the first nozzle inlet, and the other end is connected to the indoor unit 30; one end of the third pipe 23 is connected to the inlet of the second heat exchange pipe, and the other end is connected to the first pipe 21; one end of the fourth pipeline 24 is connected to the outlet of the second heat exchange pipeline, and the other end is connected between the first electromagnetic valve 221 and the inlet of the first nozzle; a fifth conduit 25 has one end connected to the second nozzle inlet and the other end connected to the second conduit 22.
Further, the outdoor unit 20 further includes: a first expansion valve 211, a second expansion valve 212, a first solenoid valve 221, and a second solenoid valve 222, the first expansion valve 211 being provided in the first pipe 21; the second expansion valve 212 is disposed in the first pipe 21 and between the first expansion valve 211 and the heat exchanger 28; the first electromagnetic valve 221 is disposed in the second pipe 22; the second electromagnetic valve 222 is arranged on the second pipeline 22 and is positioned between the first electromagnetic valve 221 and the injection device 27; wherein one end of the third pipe 23 is connected to the inlet of the second heat exchange pipe, and the other end is connected between the first expansion valve 211 and the second expansion valve 212; one end of the fourth pipeline 24 is connected to the outlet of the second heat exchange pipeline, and the other end is connected between the first electromagnetic valve 221 and the second electromagnetic valve 222; one end of the fifth pipe 25 is connected to the second nozzle inlet, and the other end is connected between the first solenoid valve 221 and the indoor unit 30.
Preferably, the outdoor unit 20 further includes: compressor 29, working medium pump 231 and regulating valve 291; the compressor 29 is provided in the fourth pipe 24; a regulating valve 291 is provided in the fourth piping 24, and the regulating valve 291 is provided between the outlet and the inlet of the compressor 29; the working medium pump 231 is arranged on the third pipeline 23, and one end of the third pipeline 23 is connected to the inlet of the second heat exchange pipeline, and the other end is connected between the first expansion valve 211 and the second expansion valve 212; the regulating valve 291 and the compressor 29 are arranged in parallel on the fourth pipeline 24, that is, when the regulating valve 291 is opened, the refrigerant in the generator 12 is directly conveyed from the fourth pipeline 24 to the second pipeline 22 through the regulating valve 291, and when the regulating valve 291 is closed, the refrigerant in the generator 12 is conveyed from the fourth pipeline 24 to the second pipeline 22 through the compressor 29; the refrigerant in the air conditioning device 50 can flow to the second heat exchange pipeline through the third pipeline 23, the hot water in the solar heating unit 10 can flow to the first heat exchange pipeline through the solar heat collector 11, and the hot water in the first heat exchange pipeline can exchange heat with the refrigerant in the second heat exchange pipeline.
Preferably, the outdoor unit 20 further includes: the third solenoid valve 251 and the fourth solenoid valve 261; one end of the third solenoid valve 251 is connected to the indoor unit 30, and the other end is connected to the nozzle inlet; one end of the fourth electromagnetic valve 261 is connected to the solar heating unit 10, and the other end is connected between the injection device 27 and the heat exchanger 28; the working medium pump 231, the fourth electromagnetic valve 261 and the compressor 29 are all connected to the generator 12, namely, the third pipeline 23, the fourth pipeline 24 and the sixth pipeline 26 are all communicated to the generator 12; it should be noted that the solar heat collector 11 is used for collecting solar energy, and the generator 12 is used for exchanging heat between hot water in the solar heating unit 10 and a refrigerant in the air conditioning device 50; the circulation pump 13 then effects circulation of the hot water in the solar heating unit 10.
Specifically, the outdoor unit 20 is further provided with a fifth duct 25 and a sixth duct 26; one end of the fifth pipeline 25 is connected to a nozzle inlet of the injection device 27, and the other end is communicated to the second pipeline 22; one end of a sixth pipeline 26 is connected between the injection device 27 and the heat exchanger 28, and the other end is communicated to the fourth pipeline; wherein the third solenoid valve 251 is provided on the fifth pipe 25 and the fourth solenoid valve 261 is provided on the sixth pipe 26.
The compressor 29 is provided to compress the suction gas, the heat exchanger 28 is provided to exchange heat with the high-pressure gas output from the injection device 27, the working medium pump 231 is provided to circulate the refrigerant between the outdoor unit 20 and the indoor unit 30, and the second solenoid valve 222 is provided to circulate the refrigerant between the second pipe 22 and the injection device 27 as well as between the fourth pipe 24; the circulation of the refrigerant between the first pipe 21 and the third pipe 23 and the solar heating unit 10 can be controlled by controlling the first expansion valve 211; by controlling the second expansion valve 212, the refrigerant is circulated between the first pipe 21 and the heat exchanger 28; by arranging the third electromagnetic valve 251, the purpose of directly conveying the refrigerant in the second pipeline 22 to the injection device 27 can be achieved; further, in the present invention, in the cooling or heating mode, the opening of each expansion valve and the solenoid valve may be controlled according to the condition of whether the solar energy is sufficient, so that the comfort of the energy saving system 100 may be improved while the refrigerant circulation between the outdoor unit 20 and the indoor unit 30 is realized.
[ second embodiment ] A
In a second embodiment of the present invention, there is provided an energy saving control method for an air conditioner, the control method being used for controlling the energy saving system of the air conditioner described in the above embodiment, the control method comprising:
s10: when the air conditioner energy-saving system runs, detecting the air outlet temperature value T of the indoor unit;
s20: judging whether the air conditioner energy-saving system meets the starting condition of a compressor or not according to the relation between the air outlet temperature value and a preset temperature value;
s30: and if so, controlling the air conditioner energy-saving system to enter a compressor running mode.
Specifically, in S10, it can be understood that when solar energy is sufficient or insufficient, the heat exchange efficiency between the solar heating unit 10 and the air conditioner 50 is different, and correspondingly, the cooling or heating effect of the air conditioner 50 is different; the cooling or heating effect of the air conditioner 50 can be represented by the outlet air temperature of the indoor unit 30, so in this embodiment, whether the solar energy is sufficient is determined by detecting the outlet air temperature value T of the indoor unit 30. Further, in S20, after the outlet air temperature value T of the indoor unit 30 is detected, the outlet air temperature value T is compared with the preset temperature value T 0 The relationship between the two can be used to determine whether the economizer system 100 satisfies the compressor start condition, and further determine whether the compressor needs to be started.
It should be noted that, in the present invention, when the compressor 29 is turned on, it indicates that the solar energy is insufficient; when the compressor 29 is off, the solar energy is sufficient; or when the solar energy is sufficient, the solar energy can independently complete the cooling or heating effect, and the compressor can be controlled to be turned off at the moment for achieving the purpose of energy conservation; meanwhile, when the solar energy is insufficient, the air-conditioning energy saving system 100 is inefficient only by relying on the solar energy for heating or cooling, and therefore, the solar energy is required to be combined with the compressor 29 for cooling or heating.
Preferably, in the present invention, in order to improve the energy saving efficiency of the energy saving system 100 of the air conditioner, when the solar energy is sufficient, the compressor 29 is turned off, and at this time, the energy saving system 100 adopts a solar cooling or heating manner to achieve the purpose of cooling or heating; when the solar energy is insufficient, the compressor 29 is started, and at the moment, the energy-saving system 100 adopts a mode of combining the solar energy and the compressor to achieve the purpose of refrigerating or heating; according to the situation that whether the solar energy is sufficient or not, the opening and closing of the compressor 29 are controlled, the refrigerating or heating effect is achieved, the user demand is met, and meanwhile the energy utilization rate is improved.
[ third embodiment ]
In a third embodiment of the present invention, on the basis of the second embodiment, there is provided an energy saving control method for an air conditioner, the control method is applied to a cooling mode of an energy saving system 100, and specifically, the control method is used for controlling the energy saving system of the air conditioner described in the above embodiment, and the control method includes:
preferably, when the air conditioner energy saving system performs cooling, whether the compressor starting condition is met or not includes:
when the air outlet temperature value T is larger than a first preset temperature value T 1 When the compressor is started, the compressor is controlled to be started; and/or when the outlet air temperature value T is less than or equal to a second preset temperature value T 2 When the compressor is started, the compressor is controlled to be closed; and/or at a second preset temperature value T 2 The air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a first preset temperature value T 1 Controlling the compressor to continuously run in the current state; wherein, at a second preset temperature value T 2 The air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a first preset temperature value T 1 At the moment, the air outlet temperature T is at the second preset temperature value T 2 And a first preset temperature value T 1 Meanwhile, the air conditioner is more comfortable in the current running state, so that the compressor can be controlled to run in the current state; if the compressor 29 is in the on state, the compressor is kept on; if the compressor 29 is in the off state, the protection is continuedThe compressor is kept off.
In the embodiment of the present invention, the number of the indoor units 30 may be set to be one or multiple, and when the indoor units 30 are multiple, detecting the outlet air temperature value T of the indoor unit includes: the outlet air temperature T of all indoor units 30 is larger than a first preset temperature T 1 When the temperature is high, the compressor 29 is controlled to be started; or there are more than half of the outlet air temperature values T and the preset temperature values T of the indoor units 30 0 When the difference between the preset temperature values meets the preset temperature difference value T, the compressor 29 is controlled to be started; the preset temperature difference value T meets the following requirements: Δ T ∈ [3 deg.C, 8 deg.C]And Δ T is preferably 5 ℃; wherein, the outlet air temperature value T and the preset temperature value T of the indoor unit 30 0 The difference between them satisfies: when the outlet air temperature value T of more than half of the indoor units 30-the preset temperature value T 0 When Δ T, the compressor 29 is controlled to be started.
Specifically, the first preset temperature value T 1 Satisfies the following conditions: t is a unit of 1 ∈[15℃,18℃]Wherein, T 1 The temperature can be selected from 15 deg.C, 16 deg.C, 17 deg.C, 18 deg.C, T 1 Preferably 16 ℃; a second preset temperature value T 2 Satisfies the following conditions: t is 2 ∈[12℃,15℃]Wherein, T 2 The temperature can be 12 deg.C, 13 deg.C, 14 deg.C, 15 deg.C, T 1 Preferably 14 ℃; wherein, the first preset temperature value T 1 And a second preset temperature value T 2 Satisfies the following conditions: t is 1 >T 2 。
Preferably, referring to fig. 2, in the cooling mode, when the compressor is turned off, i.e. when the outlet air temperature value T > the first preset temperature value T 1 Meanwhile, the first expansion valve 211, the second expansion valve 212, the second solenoid valve 222, and the third solenoid valve 251 are in an open state; the first solenoid valve 221, the fourth solenoid valve 261, and the regulator valve 291 are in a closed state.
Further, the refrigerant in the air conditioner 50 flows from the indoor unit 30 to the fourth pipe 24 through the second pipe 22, and further flows from the third solenoid valve 251 to the nozzle inlet of the injection device 27, then the refrigerant in the injection device 27 flows from the nozzle outlet to the heat exchanger 28, the refrigerant after heat exchange in the heat exchanger 28 flows to the second expansion valve 212, and at this time, a part of the refrigerant passing through the second expansion valve 212 flows to the indoor unit 30 through the first expansion valve 211 on the first pipe 21 to complete circulation; the other part of the refrigerant in the second expansion valve 212 flows into the generator 12 from the working medium pump 231 on the third pipeline 23, and at this time, the refrigerant passing through the generator 12 exchanges heat with the hot water in the generator 12 and then flows into the fourth pipeline 24, and because the compressor 29 is in a closed state and the adjusting valve 291 is opened at this time, the refrigerant in the fourth pipeline 24 flows into the second electromagnetic valve 222 from the adjusting valve 291, and finally flows into the injection device 27, and finally the cycle is completed.
Preferably, referring to fig. 3, in the cooling mode, when the compressor is turned on, i.e. when the outlet air temperature value T is less than or equal to the second preset temperature value T 2 Meanwhile, the first expansion valve 211, the second expansion valve 212, the second solenoid valve 222, the third solenoid valve 251, and the regulating valve 291 are in an open state; the first solenoid valve 221 and the fourth solenoid valve 261 are in a closed state.
Further, the refrigerant in the air conditioner 50 flows from the indoor unit 30 to the fourth pipe 24 through the second pipe 22, and further flows from the third solenoid valve 251 to the nozzle inlet of the injection device 27, then the refrigerant in the injection device 27 flows from the nozzle outlet to the heat exchanger 28, the refrigerant after heat exchange in the heat exchanger 28 flows to the second expansion valve 212, and at this time, a part of the refrigerant passing through the second expansion valve 212 flows to the indoor unit 30 through the first expansion valve 211 on the first pipe 21 to complete circulation; the other part of the refrigerant in the second expansion valve 212 flows into the generator 12 from the working medium pump 231 on the third pipeline 23, and at this time, the refrigerant passing through the generator 12 exchanges heat with the hot water in the generator 12 and then flows into the fourth pipeline 24, and because the compressor 29 is in the open state and the regulating valve 291 is in the closed state at this time, the refrigerant in the fourth pipeline 24 flows from the compressor 29 to the second electromagnetic valve 222, and finally flows into the injection device 27, and finally the cycle is completed.
[ fourth example ] A
In a fourth embodiment of the present invention, on the basis of the second embodiment, there is provided an air conditioner energy saving control method, which is applied to cooling of an energy saving system 100 and is used for controlling the air conditioner energy saving system described in the above embodiment, and the control method includes:
preferably, when the air conditioner economizer system is used for heating, whether the compressor starting condition is met or not includes: when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a third preset temperature value T 3 When the compressor is started, the compressor is controlled to be started; and/or when the outlet air temperature value T is larger than a fourth preset temperature value T 4 When the compressor is started, controlling the compressor to be closed; and/or at a third preset temperature value T 3 The air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to the fourth preset temperature value T 4 When the current state of the compressor is in the normal state, controlling the compressor to continuously run in the current state; wherein, at a third preset temperature value T 3 The air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to the fourth preset temperature value T 4 At this time, the outlet air temperature T is at the third preset temperature value T 3 And a fourth preset temperature value T 4 Meanwhile, the air conditioner is more comfortable in the current running state, so that the compressor can be controlled to run in the current state; if the compressor 29 is in the on state, the compressor is kept on; if the compressor 29 is in the off state, the compressor 29 continues to be kept off.
In particular, a third preset temperature value T 3 Satisfies the following conditions: t is 3 ∈[28℃,32℃]Wherein, T 3 Can be selected from 28 deg.C, 29 deg.C, 30 deg.C, 31 deg.C, 32 deg.C, T 3 Preferably 30 ℃; a fourth preset temperature value T 4 Satisfies the following conditions: t is a unit of 4 ∈[32℃,38℃]Wherein, T 4 The temperature can be selected from 32 deg.C, 33 deg.C, 34 deg.C, 35 deg.C, 36 deg.C, 37 deg.C, 38 deg.C, T 4 Preferably 35 ℃; wherein the third preset temperature value T 3 And a fourth preset temperature value T 4 Satisfies the following conditions: t is 4 >T 3 。
In the embodiment of the present invention, the number of the indoor units 30 may be one or more, and when there are a plurality of indoor units 30, detecting the outlet air temperature value T of the indoor unit 30 includes: the outlet air temperature T of all indoor units 30 is less than or equal to a third preset temperature T 3 When the compressor is started, the compressor is controlled to be started; or there are more than half of the outlet air temperature values T and the preset temperature values T of the indoor units 30 0 When the difference between the preset temperature values meets the preset temperature difference value T, the compressor 29 is controlled to be started; the preset temperature difference value Δ T meets: the Δ T is equal to [3 ℃,8℃]and Δ T is preferably 5 ℃; wherein, the outlet air temperature value T and the preset temperature value T of the indoor unit 30 0 The difference between them satisfies: when the outlet air temperature T of more than half of the indoor units 30 is equal to the preset temperature T 0 When Δ T, the compressor 29 is controlled to be started.
Preferably, referring to fig. 4, in the heating mode, when the compressor is turned off, i.e. when the outlet air temperature value T > the fourth preset temperature value T 4 When the current is over; the first expansion valve 211, the first solenoid valve 221, and the regulating valve 291 are in an open state; the second expansion valve 212, the second solenoid valve 222, the third solenoid valve 251, and the fourth solenoid valve 261 are in a closed state.
Further, the refrigerant in the air conditioning device 50 flows from the indoor unit 30 to the third pipeline 23 through the first expansion valve 211 on the first pipeline 21, the further refrigerant is delivered to the generator 12 under the action of the working medium pump 231, the refrigerant is delivered to the fourth pipeline 24 after heat exchange with the hot water in the generator 12 is completed, at this time, since the compressor 29 is closed and the adjusting valve 291 is opened at the same time, the refrigerant in the fourth pipeline 24 flows to the second pipeline 22 after passing through the adjusting valve 291, and finally returns to the indoor unit 30 after passing through the first electromagnetic valve 221, thereby completing the circulation; however, since the second expansion valve 212, the second solenoid valve 222, the third solenoid valve 251 and the fourth solenoid valve 261 are in the closed state, when the compressor 29 is closed in the heating mode, no refrigerant flows through the compressor 29, the injection device 27 and the heat exchanger 28.
Preferably, referring to fig. 5, when the compressor is started, that is, when the outlet air temperature value T is less than or equal to the third preset temperature value T 3 When the first expansion valve 211, the second expansion valve 212, the first solenoid valve 221, and the fourth solenoid valve 261 are in the open state; the second solenoid valve 222, the third solenoid valve 251, and the regulator valve 291 are in a closed state.
Further, when the compressor 29 is turned on, the refrigerant in the air conditioning device 50 flows from the indoor unit 30 to the first expansion valve 211 through the first pipe 21, at this time, a part of the refrigerant in the first expansion valve 211 flows to the working medium pump 231 on the third pipe 23, flows to the generator 12 under the action of the working medium pump 231, further flows to the fourth pipe 24 after heat exchange with the hot water in the generator 12 is completed, at this time, because the compressor 29 is turned on and the adjusting valve 291 is turned off, the refrigerant in the fourth pipe 24 flows to the compressor 29, further, the high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant compressed by the compressor 29 flows to the second pipe 22, and finally flows to the indoor unit 30 after passing through the first electromagnetic valve 221, thereby completing the cycle; since the second expansion valve 212 is in an open state, another part of the refrigerant in the first expansion valve 211 flows into the heat exchanger 28, and since the fourth solenoid valve 261 is in an open state, the refrigerant after heat exchange by the heat exchanger 28 finally flows into the fourth pipeline 24 and further flows into the compressor 29 for compression; since the second solenoid valve 222 and the third solenoid valve 251 are in the closed state, no refrigerant flows through the injection device 27 in the heating mode and when the compressor 29 is turned on.
[ fifth embodiment ]
In a third embodiment of the present invention, there is provided an air conditioner provided with an air conditioner economizer system as described in the first embodiment; alternatively, the air conditioner is provided with a processor, a memory, and a program or instructions stored on the memory and executable on the processor, and the program or instructions, when executed by the processor, implement the air conditioner energy saving control method as in the second, third, and fourth embodiments.
Preferably, the air conditioner is provided with the energy saving system 100 of the air conditioner in the above embodiment, or after the control method in the above embodiment is implemented, the air conditioner has all technical features and all beneficial effects of the energy saving system and the control method in the above embodiment, and details are not repeated herein.
Although the present invention is disclosed above, the present invention is not limited thereto. Various changes and modifications may be effected therein by one skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined in the appended claims.
Claims (11)
1. An air conditioner economizer system, the economizer system (100) comprising: a solar heating unit (10) and an air conditioning device (50), wherein the air conditioning device (50) comprises an outdoor unit (20) and an indoor unit (30), and is characterized in that the outdoor unit (20) is provided with a spraying device (27) and a heat exchanger (28); the spraying device (27) is provided with a first nozzle inlet, a second nozzle inlet and a nozzle outlet, one end of the heat exchanger (28) is connected to the nozzle outlet, and the other end of the heat exchanger is connected to the indoor unit (30) through a first pipeline (21); the solar heating unit (10) comprises: a solar collector (11) and a generator (12); the generator (12) is provided with a first heat exchange pipeline and a second heat exchange pipeline, one end of the solar heat collector (11) is communicated with an inlet of the first heat exchange pipeline, and the other end of the solar heat collector is communicated with an outlet of the first heat exchange pipeline;
the outdoor unit (20) further comprises:
a second duct (22), one end of the second duct (22) being connected to the first nozzle inlet, and the other end being connected to the indoor unit (30);
a first solenoid valve (221), said first solenoid valve (221) being provided to said second duct (22);
a third conduit (23), said third conduit (23) being connected at one end to the inlet of said second heat exchange conduit and at the other end to said first conduit (21);
a fourth conduit (24), one end of the fourth conduit (24) being connected to the outlet of the second heat exchange conduit, the other end being connected between the first solenoid valve (221) and the first nozzle inlet;
a fifth duct (25), one end of the fifth duct (25) being connected to the second nozzle inlet, the other end being connected between the first solenoid valve (221) and the indoor unit (30);
a compressor (29), said compressor (29) being arranged in said fourth duct (24);
the refrigerant in the air conditioning device (50) can flow to the second heat exchange pipeline from the third pipeline (23), the hot water in the solar heating unit (10) can flow to the first heat exchange pipeline from the solar heat collector (11), and the hot water in the first heat exchange pipeline can exchange heat with the refrigerant in the second heat exchange pipeline.
2. The economizer system for air conditioners as claimed in claim 1, wherein the outdoor unit (20) further comprises:
a sixth conduit (26), one end of the sixth conduit (26) being connected between the injection device (27) and the heat exchanger (28), the other end being connected between the solar heating unit (10) and the compressor (29).
3. The economizer system for air conditioners as claimed in claim 2, wherein the outdoor unit (20) further comprises:
a first expansion valve (211), the first expansion valve (211) being provided to the first pipe (21);
a second expansion valve (212), the second expansion valve (212) being disposed in the first conduit (21) and being located between the first expansion valve (211) and the heat exchanger (28);
a second solenoid valve (222), said second solenoid valve (222) being arranged in said second duct (22) and being located between said first solenoid valve (221) and said injection means (27);
a third solenoid valve (251), said third solenoid valve (251) being disposed in said fifth conduit (25);
a fourth solenoid valve (261); the fourth solenoid valve (261) is provided to the sixth conduit (26);
a regulating valve (291), the regulating valve (291) being provided to the fourth piping (24);
a working medium pump (231), wherein the working medium pump (231) is arranged on the third pipeline (23).
4. An air conditioner energy saving control method for controlling the air conditioner energy saving system according to claim 3, the control method comprising:
detecting the air outlet temperature value T of an indoor unit when the air conditioner energy-saving system runs;
judging whether the air conditioner energy-saving system meets the starting condition of a compressor or not according to the relation between the air outlet temperature value and a preset temperature value;
and if so, controlling the air conditioner energy-saving system to enter a compressor running mode.
5. The energy-saving control method for the air conditioner as claimed in claim 4, wherein when the energy-saving system for the air conditioner is in cooling, whether the compressor on condition is satisfied comprises:
when the air outlet temperature value T is larger than a first preset temperature value T 1 When the compressor is started, the compressor (29) is controlled to be started;
and/or the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a second preset temperature value T 2 When the compressor (29) is controlled to be closed;
and/or at a second preset temperature value T 2 The air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to the first preset temperature value T 1 And controlling the compressor (29) to continue to operate in the current state.
6. The air conditioner energy saving control method as claimed in claim 5, wherein the compressor operation mode includes:
when the air outlet temperature value T is larger than the first preset temperature value T 1 The first expansion valve (211), the second expansion valve (212), the second solenoid valve (222), and the third solenoid valve (251) are in an open state; the first solenoid valve (221), the fourth solenoid valve (261), and the regulator valve (291) are in a closed state.
7. The air conditioner energy saving control method as set forth in claim 5, wherein the compressor operation mode further includes:
when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a second preset temperature value T 2 While the first expansion valve(211) The second expansion valve (212), the second solenoid valve (222), the third solenoid valve (251), and the regulator valve (291) are in an open state; the first solenoid valve (221) and the fourth solenoid valve (261) are in a closed state.
8. The energy-saving control method for the air conditioner according to claim 4, wherein whether the compressor on condition is satisfied when the energy-saving system for the air conditioner is heating comprises:
when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to a third preset temperature value T 3 When the compressor is started, the compressor is controlled to be started;
and/or when the outlet air temperature value T is larger than a fourth preset temperature value T 4 When the compressor is started, controlling the compressor to be closed;
and/or at a third preset temperature value T 3 The air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to the fourth preset temperature value T 4 And controlling the compressor to continuously run in the current state.
9. An energy saving control method of air conditioner according to claim 8, wherein the compressor operation mode includes:
when the air outlet temperature value T is less than or equal to the third preset temperature value T 3 When the first expansion valve (211), the second expansion valve (212), the first solenoid valve (221), and the fourth solenoid valve (261) are in an open state; the second solenoid valve (222), the third solenoid valve (251) and the regulating valve (291) are in a closed state.
10. The air conditioner energy saving control method as set forth in claim 8, wherein the compressor operation mode further includes:
when the air outlet temperature value T is larger than the fourth preset temperature value T 4 When the valve is opened, the first expansion valve (211), the first electromagnetic valve (221), and the regulating valve (291) are in an open state; the second expansion valve (212), the second solenoid valve (222), andthe third solenoid valve (251) and the fourth solenoid valve (261) are in a closed state.
11. An air conditioner, characterized in that the air conditioner comprises: the air conditioner economizer system of any one of claims 1-3; or a processor, a memory, and a program or instructions stored on the memory and executable on the processor, the program or instructions, when executed by the processor, implementing the air conditioner energy saving control method according to any one of claims 4 to 10.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211002466.6A CN115076820B (en) | 2022-08-22 | 2022-08-22 | Air conditioner energy saving system, control method and air conditioner |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211002466.6A CN115076820B (en) | 2022-08-22 | 2022-08-22 | Air conditioner energy saving system, control method and air conditioner |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115076820A true CN115076820A (en) | 2022-09-20 |
| CN115076820B CN115076820B (en) | 2022-11-25 |
Family
ID=83244572
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211002466.6A Active CN115076820B (en) | 2022-08-22 | 2022-08-22 | Air conditioner energy saving system, control method and air conditioner |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115076820B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115234976A (en) * | 2022-09-26 | 2022-10-25 | 宁波奥克斯电气股份有限公司 | Air conditioning system, control method and air conditioner |
Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB9519012D0 (en) * | 1995-09-16 | 1995-11-15 | Ward Trevor | Heat pump |
| JP2005221124A (en) * | 2004-02-04 | 2005-08-18 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Gas heat pump air conditioner and cooling water control method of gas heat pump air conditioner |
| CN101270935A (en) * | 2008-05-07 | 2008-09-24 | 中原工学院 | Solar injection electric compression heat pump combined air-conditioning unit |
| AT507218B1 (en) * | 2009-01-05 | 2010-03-15 | Richard Dipl Ing Dr Krotil | METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR COUPLED SOLAR THERMAL ELECTRICITY, HEAT AND COOLING PRODUCTION |
| CN102072541A (en) * | 2011-01-20 | 2011-05-25 | 中原工学院 | Cold storage type solar injection-compression combined refrigerator set |
| CN103398498A (en) * | 2013-07-24 | 2013-11-20 | 广东申菱空调设备有限公司 | Compact solar ejector refrigeration and heat pump integrated system and method for controlling same |
| CN105698431A (en) * | 2016-03-16 | 2016-06-22 | 北京建筑大学 | Double-heat-source efficient compressing-ejecting composite heat pump system and application |
| CN109373453A (en) * | 2018-12-17 | 2019-02-22 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Air conditioning system and control method |
| CN209197011U (en) * | 2018-12-17 | 2019-08-02 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | air conditioning system |
| WO2019231400A1 (en) * | 2018-05-30 | 2019-12-05 | National University Of Singapore | A combined cooling and power system and method |
| CN112556237A (en) * | 2020-12-23 | 2021-03-26 | 广东申菱环境系统股份有限公司 | Composite refrigeration system and control method thereof |
| CN112556230A (en) * | 2021-01-06 | 2021-03-26 | 上海海洋大学 | Ship solar vapor compression refrigeration cycle system with two-stage ejector |
-
2022
- 2022-08-22 CN CN202211002466.6A patent/CN115076820B/en active Active
Patent Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB9519012D0 (en) * | 1995-09-16 | 1995-11-15 | Ward Trevor | Heat pump |
| JP2005221124A (en) * | 2004-02-04 | 2005-08-18 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Gas heat pump air conditioner and cooling water control method of gas heat pump air conditioner |
| CN101270935A (en) * | 2008-05-07 | 2008-09-24 | 中原工学院 | Solar injection electric compression heat pump combined air-conditioning unit |
| AT507218B1 (en) * | 2009-01-05 | 2010-03-15 | Richard Dipl Ing Dr Krotil | METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR COUPLED SOLAR THERMAL ELECTRICITY, HEAT AND COOLING PRODUCTION |
| CN102072541A (en) * | 2011-01-20 | 2011-05-25 | 中原工学院 | Cold storage type solar injection-compression combined refrigerator set |
| CN103398498A (en) * | 2013-07-24 | 2013-11-20 | 广东申菱空调设备有限公司 | Compact solar ejector refrigeration and heat pump integrated system and method for controlling same |
| CN105698431A (en) * | 2016-03-16 | 2016-06-22 | 北京建筑大学 | Double-heat-source efficient compressing-ejecting composite heat pump system and application |
| WO2019231400A1 (en) * | 2018-05-30 | 2019-12-05 | National University Of Singapore | A combined cooling and power system and method |
| CN109373453A (en) * | 2018-12-17 | 2019-02-22 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Air conditioning system and control method |
| CN209197011U (en) * | 2018-12-17 | 2019-08-02 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | air conditioning system |
| CN112556237A (en) * | 2020-12-23 | 2021-03-26 | 广东申菱环境系统股份有限公司 | Composite refrigeration system and control method thereof |
| CN112556230A (en) * | 2021-01-06 | 2021-03-26 | 上海海洋大学 | Ship solar vapor compression refrigeration cycle system with two-stage ejector |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115234976A (en) * | 2022-09-26 | 2022-10-25 | 宁波奥克斯电气股份有限公司 | Air conditioning system, control method and air conditioner |
| CN115234976B (en) * | 2022-09-26 | 2023-01-10 | 宁波奥克斯电气股份有限公司 | Air conditioning system, control method and air conditioner |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115076820B (en) | 2022-11-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102425882A (en) | Heat recovery multiple heat pump air-conditioning hot water machine and floor heating system | |
| CN115076820B (en) | Air conditioner energy saving system, control method and air conditioner | |
| CN204630141U (en) | A kind of phase-changing energy-storing multiple source heat pump assembly | |
| CN201945103U (en) | Split heat pump inverter air conditioner capable of defrosting without shutdown | |
| CN103134231A (en) | Tree-joint-control system and control scheme thereof | |
| CN114909699A (en) | Defrosting control method, central controller and heating system | |
| CN102269457A (en) | Direct current heat exchange full effective hot water air conditioning system | |
| CN217303243U (en) | Multifunctional air energy cooling and heating system | |
| CN114110849B (en) | Integrated device of coupling type air conditioner, water heater and water boiler | |
| CN2716713Y (en) | Water heater utilizing heat energy of air conditioner | |
| CN201003885Y (en) | Air source thermal pump water heater unit | |
| CN213020401U (en) | Heating defrosting air source hot water pump | |
| CN115264556A (en) | Double-output refrigeration and heating hot water triple-generation air source heat pump system | |
| CN2847158Y (en) | Water heater of air conditioner | |
| CN212227291U (en) | Air energy hot water air conditioner and fluorine radiation heating system | |
| CN209639153U (en) | A kind of multi-element type recovery type heat air-conditioning system | |
| CN113803773A (en) | Double-source multi-connection heating and ventilation system and control method thereof | |
| CN115031319B (en) | Control method of water supply air conditioning system utilizing natural energy | |
| CN114763946B (en) | Air conditioner hot water system | |
| CN109654612A (en) | A kind of multi-element type recovery type heat air-conditioning system | |
| CN2540587Y (en) | Air-cooled double-temp. split air conditioner with water heating device | |
| CN202195548U (en) | Direct-current heat-exchange type full-efficiency hot-water air-conditioning system | |
| CN217654022U (en) | Air-conditioning heat pump system capable of providing domestic hot water | |
| CN218209861U (en) | Air conditioner capable of heating water | |
| CN2814224Y (en) | Air conditioner water heater |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |