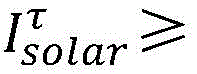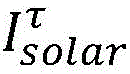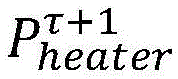CN114963284B - Household electricity heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort level and peak-valley electricity price - Google Patents
Household electricity heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort level and peak-valley electricity price Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114963284B CN114963284B CN202210613701.7A CN202210613701A CN114963284B CN 114963284 B CN114963284 B CN 114963284B CN 202210613701 A CN202210613701 A CN 202210613701A CN 114963284 B CN114963284 B CN 114963284B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- user
- electric
- electric heater
- next moment
- power
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 82
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 44
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 title abstract description 28
- 238000005485 electric heating Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 48
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 53
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 23
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000007710 freezing Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 5
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 description 14
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 7
- 244000062793 Sorghum vulgare Species 0.000 description 4
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 235000019713 millet Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004134 energy conservation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24D—DOMESTIC- OR SPACE-HEATING SYSTEMS, e.g. CENTRAL HEATING SYSTEMS; DOMESTIC HOT-WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; ELEMENTS OR COMPONENTS THEREFOR
- F24D13/00—Electric heating systems
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24D—DOMESTIC- OR SPACE-HEATING SYSTEMS, e.g. CENTRAL HEATING SYSTEMS; DOMESTIC HOT-WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; ELEMENTS OR COMPONENTS THEREFOR
- F24D19/00—Details
- F24D19/10—Arrangement or mounting of control or safety devices
- F24D19/1096—Arrangement or mounting of control or safety devices for electric heating systems
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02B—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO BUILDINGS, e.g. HOUSING, HOUSE APPLIANCES OR RELATED END-USER APPLICATIONS
- Y02B10/00—Integration of renewable energy sources in buildings
- Y02B10/20—Solar thermal
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02B—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO BUILDINGS, e.g. HOUSING, HOUSE APPLIANCES OR RELATED END-USER APPLICATIONS
- Y02B10/00—Integration of renewable energy sources in buildings
- Y02B10/70—Hybrid systems, e.g. uninterruptible or back-up power supplies integrating renewable energies
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Central Heating Systems (AREA)
Abstract
The invention provides a household electricity heating intelligent group control method with self-adaption comfort and peak-valley electricity price. The scheme comprises the steps of collecting human sensing information, solar total irradiance, wind speed and other parameters, considering the orientations of different rooms of a user, identifying the current electricity price level, and optimally adjusting the temperature set at the next moment in different rooms of the user; collecting instantaneous electric power of users and electric heater groups, identifying instantaneous electric power of other electric equipment, comparing the instantaneous electric power with a preset total power limit value, and identifying available instantaneous power at the next moment; the actual indoor temperature of different rooms of the user at the current moment is collected, the electric heating requirements of different rooms at the next moment are predicted according to the indoor temperature requirements at the next moment, and the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group is combined to intelligently adjust the electric heaters of all the rooms. This scheme is through user comfort level and relevant parameter discernment of price of electricity, combines user's electric power, carries out electric heater intelligence group control, under the prerequisite of guaranteeing that user comfort level demand and power do not transfinite, realizes energy-conserving comfortable expense of falling and subtracts carbon.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of heating control, in particular to a household electricity heating intelligent group control method with self-adaption comfort and peak-valley electricity price.
Background
Household electric heating is a free, comfortable and environment-friendly heating mode for converting clean electric energy into heat energy, and particularly in recent years, household electric heating systems for clean heating are rapidly developed.
The existing household electric heating system mainly depends on a mode of presetting temperature by a user to regulate and control equipment, and in addition, partial scheme considers heat accumulation and responds to peak-to-valley electricity price difference. However, the prior art can not identify whether a person exists in a room so as to judge the necessity of heating demand, and energy is wasted; the comfort of a user cannot be responded according to meteorological parameters in combination with the room orientation, so that the deviation between the actual room temperature and the expected room temperature is large; meanwhile, the peak-valley electricity price cannot be synchronously responded to be controlled under the condition of no capacity increase of electric power, and the operation cost is difficult to be saved as far as possible while the initial investment is reduced. In summary, the existing technology cannot guarantee higher comfort for users and the power of the electric equipment does not exceed the limit value.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above problems, the invention provides a household electric heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort and peak-valley electricity price, which performs intelligent group control on an electric heater by identifying the relevant parameters of the comfort and the electricity price of a user and combining with the electric power of the user, and realizes energy conservation, comfort, cost reduction and carbon reduction on the premise of ensuring that the comfort requirement and the power of the user are not over-limit.
According to the first aspect of the embodiment of the invention, an intelligent group control method for household electric heating with self-adaptive comfort and peak-valley electricity price is provided.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the comfort level and peak-to-valley electricity price adaptive household heating intelligent group control method includes:
acquiring human sensing information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of a user, identifying the current electricity price level, and adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next moment of the different rooms;
collecting the electric power of a user and the instantaneous electric power of an electric heater group at the current moment, identifying the instantaneous electric power of other electric equipment except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric power with a preset limit value of total power, and identifying the available instantaneous power at the next moment;
the method comprises the steps of collecting actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at the current moment, identifying preset expected indoor temperatures of the user at the next moment, predicting electric heating demands of the different rooms at the next moment according to the set temperature at the next moment, and intelligently adjusting electric heaters of the rooms by combining available instantaneous power at the next moment.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring human information, the total solar irradiance and the wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of the user, identifying the current electricity price level, adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next moment of the different rooms, further adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater by acquiring the human information, and issuing a first adjustment completion command specifically includes:
the method comprises the following steps of (1) acquiring whether a person exists in a room by using a human body sensor, and if no person exists in the room, setting the set temperature of an electric heater as the anti-freezing temperature of the room;
using a human body sensor to acquire whether a person exists in a room, and if the person exists, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater;
sending a first adjustment completion command;
in the embodiment of the invention, wherein the room anti-freezing temperature is input empirically in advance, the human body sensor generally refers to a human body proximity sensor. The human body sensor can be a human body proximity sensor, the human body proximity sensor is based on the Doppler technical principle, a microwave special microprocessor and a planar induction antenna are adopted, the detection sensitivity is high, the detection range is wide, the work is very reliable, generally, false alarm does not exist, the human body sensor can stably work within the temperature range of-15 to +60 ℃, the human body sensor is used for collecting the information whether a room is occupied or not, and if no person exists, the temperature of the electric heater is set to be the input anti-freezing temperature of the room; and if the person exists, the next judgment is carried out.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring human information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, obtaining orientations of different rooms of a user, identifying a current electricity price level, adjusting a set temperature of the user at a next moment of the different rooms, after receiving the first adjustment completion command, determining whether to adjust the set temperature of the electric heater according to the wind speed, and sending a second adjustment completion command specifically includes:
collecting the current wind speed as a wind speed parameter;
judging whether the wind speed parameter reaches a preset wind speed limit value or not by using a first calculation formula, if so, updating the set temperature of the electric heater by using a second calculation formula, and if not, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater;
sending a second adjustment completion command;
the first calculation formula is:
the second calculation formula is:
wherein,in order to judge the updated set temperature of the electric heater according to the wind speed limit value,in order to judge the set temperature of the electric heater before updating according to the wind speed limit value,is a preset temperature change value judged according to the wind speed limit value.
In the embodiment of the invention, the preset temperature change value is temperature adjustment set according to experience, the wind speed limit value is considered to be 3m/s, and the wind speed at the current moment is acquiredAnd the like, if the wind speed is lower, the wind is not consideredAdjusting the set temperature of the electric heater caused by speed; if the wind speed is high (e.g. high)) If the set temperature of the electric heater is increased
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring human information, the total solar irradiance and the wind speed, obtaining the orientation of different rooms of the user, identifying the current electricity price level, adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next time of the different rooms, and after receiving the second adjustment completion command, determining whether to send a user orientation determination command according to the total solar irradiance at the current time, specifically includes:
collecting the total solar irradiance at the current moment;
judging whether the total solar irradiance at the current moment meets a third calculation formula, if not, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater, and if so, sending a user orientation judgment command;
the third calculation formula is:
Wherein, the total solar irradiance at the current moment is collectedAnd the parameters are equal, if the total solar irradiance is lower, the adjustment of the set temperature of the electric heater caused by the solar irradiance is not considered; if it is higher (e.g. than ) Then go to the next step of judgment.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring human information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, obtaining orientations of different rooms of a user, identifying a current electricity price level, adjusting a set temperature of the user at a next moment of the different rooms, after receiving the user orientation determination command, adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater, and issuing a third adjustment completion command specifically includes:
acquiring the orientation of the user;
if the southward deviation of the user orientation distance exceeds a preset range, the adjustment of the set temperature of the electric heater caused by solar irradiance is not considered;
if the southward deviation of the user facing distance is within the preset range, adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater by using a fourth calculation formula;
sending a third adjustment completion command;
the fourth calculation formula is:
wherein,in order to judge the updated set temperature of the electric heater by the orientation of the user,in order to judge the set temperature of the electric heater before updating by the orientation of the user,the solar radiation temperature change value is preset.
In the embodiment of the invention, the orientation of the user is recognized, the preset range is within 45 ℃ of the left side and within 45 ℃ of the right side,if the facing distance deviates greatly from the south direction, the adjustment of the set temperature of the electric heater caused by the solar irradiance is not considered; if the temperature is mainly south (including 45 ℃ below south-east and 45 ℃ below south-west), the set temperature of the electric heater is reducedThe solar irradiation temperature change value is set according to experience.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the identifying a current power rate level and adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next time for different rooms specifically include:
acquiring a current electricity price level, and judging whether the electricity price is in one of a peak time period, a valley time period or a flat time period;
if the temperature is in the peak time period, the set temperature of the electric heater is reduced by a preset first adjustment amplitude within the comfort degree allowable range;
if the electric heater is in the valley period, the set temperature of the electric heater is increased by a preset second adjustment amplitude within the comfort degree allowable range;
if the time interval is flat, the set temperature of the electric heater is not adjusted.
In the embodiment of the invention, the current power price level PR is identified τ The utility model discloses a comfort level, including the electric heater, the electric heater sets for the temperature, judges that the price of electricity is in peak, millet or on-the-flat period, if in the peak period, then the electric heater sets for the temperature and reduces first adjustment amplitude in comfort level allowed band, if in the millet period, then the electric heater sets for the temperature and improves second adjustment amplitude in comfort level allowed band, if in the flat period, then the electric heater sets for the temperature and does not do the adjustment, wherein, comfort level allowed band is a preset's adjustment range, and first adjustment amplitude and second adjustment amplitude set up according to experience.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the collecting the electric power of the user and the instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment, identifying the instantaneous electric powers of other electric devices except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric powers with a preset limit value of the total power, and identifying the available instantaneous power at the next moment specifically includes:
collecting the electric power of a user and the instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment, and calculating the instantaneous electric power of other equipment by using a fifth calculation formula;
comparing the other device instantaneous electric power to the preset user total electric power limit;
when the instantaneous electric power of the other equipment is smaller than the preset user total electric power limit value, calculating the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next moment by using a sixth calculation formula, and when the instantaneous electric power of the other equipment is not smaller than the preset user total electric power limit value, the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next moment is 0;
the fifth calculation formula:
wherein,for instantaneous electric power of other apparatus, P τ For the electric power of the user at the present moment,instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment;
the sixth calculation formula:
wherein,available instantaneous power, P, for the electric heater cluster at the next time limit And the preset user total electric power limit value is obtained.
In the embodiment of the invention, the electric power P of the user at the current moment is collected τ And collecting instantaneous electric power of electric heater groupIdentifying instantaneous electric power of other devices of the user, i.e.And is compared with the preset user total electric power limit valueComparing and identifying the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next moment, i.e.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of the user at the current time, identifying a preset desired indoor temperature of the user at the next time, predicting an electric heating demand of the different rooms at the next time according to the set temperature at the next time, and intelligently adjusting the electric heaters of the rooms according to the available instantaneous power at the next time specifically includes:
identifying a user preset expected indoor temperature at the next moment;
calculating the indoor temperature set value at the next moment by using a seventh calculation formula;
the seventh calculation formula is:
wherein,is the indoor temperature set value at the next moment,a desired indoor temperature is preset for a user at the next moment,is the third adjustment amplitude.
In the embodiment of the inventionWhen the set temperature of the electric heater is increased, the seventh calculation formula is used for calculation, and the set temperature of the electric heater is required to be increasedIs arranged asThe third adjustment range is the first adjustment range; when the set temperature of the electric heater is reduced, the electric heater needs to be connected with the electric heaterIs arranged asThe third adjustment range is the second adjustment range. Recognizing a user preset desired indoor temperature at a next momentIntelligently adjusting the indoor temperature set point at the next moment, i.e.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at a current moment, identifying a preset expected indoor temperature of the user at a next moment, predicting electric heating demands of different rooms at the next moment according to a set temperature at the next moment, and intelligently adjusting each room electric heater by combining available instantaneous power at the next moment, further includes acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of the user at the current moment in real time, and predicting electric heating demands of different rooms at the next moment by using an eighth calculation formula according to a set value of the indoor temperatures at the next moment;
the eighth calculation formula is:
wherein,for the next moment of the indoor temperature set point, t τ Is the actual indoor temperature at the present moment, z is the supply power required per unit temperature change,the electric heating requirements of different rooms at the next moment are met.
In the embodiment of the invention, z is the power supply power required by unit temperature change and is an empirical value judged according to historical empirical data.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of the user at the current time, identifying a preset desired indoor temperature of the user at the next time, predicting electric heating demands of different rooms at the next time according to the set temperature at the next time, intelligently adjusting each room electric heater by combining available instantaneous power at the next time, and further combining available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next timeThe electric heaters of all rooms are pressed down to meet the electric heating requirements of different rooms at a momentAre allocated.
According to the second aspect of the embodiment of the invention, the household electric heating intelligent group control system with self-adaption comfort and peak-valley electricity price is provided.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the comfort level and peak-to-valley electricity price adaptive household heating intelligent group control system includes:
the temperature setting module is used for acquiring human sensing information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of a user, identifying the current electricity price level and adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next moment of the different rooms;
the instantaneous power identification module is used for acquiring the electric power of a user and the instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment, identifying the instantaneous electric power of other electric equipment except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric power with a preset limit value of total power, and identifying the available instantaneous power at the next moment;
and the intelligent adjusting module is used for acquiring the actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of the user at the current moment, identifying the preset expected indoor temperature of the user at the next moment, predicting the electric heating requirements of different rooms at the next moment according to the set temperature at the next moment, and intelligently adjusting the electric heaters of all the rooms by combining the available instantaneous power at the next moment.
According to a third aspect of embodiments of the present invention, there is provided a computer-readable storage medium having stored thereon computer program instructions which, when executed by a processor, implement the method according to any one of the first aspect of embodiments of the present invention.
According to a fourth aspect of embodiments of the present invention, there is provided an electronic device, comprising a memory and a processor, the memory being configured to store one or more computer program instructions, wherein the one or more computer program instructions are executed by the processor to implement the method of any one of the first aspect of embodiments of the present invention.
The technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention can have the following beneficial effects:
in the scheme of the invention, the intelligent group control of the electric heater is carried out by identifying the related parameters of the comfort level and the electricity price of the user and combining the electric power of the user, and the energy conservation, comfort, cost reduction and carbon reduction are realized on the premise of ensuring the comfort level requirement of the user and not exceeding the power limit.
According to the scheme of the invention, the user electricity heating requirements are adaptively adjusted through the identification of peak-valley electricity price, orientation and people sensing information of the power grid, and each indoor temperature set value is dynamically and quickly adjusted, so that the intelligent cooperative control of a plurality of electric heaters is realized.
Additional features and advantages of the invention will be set forth in the description which follows, and in part will be obvious from the description, or may be learned by practice of the invention. The objectives and other advantages of the invention will be realized and attained by the structure particularly pointed out in the written description and claims hereof as well as the appended drawings.
The technical solution of the present invention is further described in detail by the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
Drawings
In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention, the drawings needed to be used in the description of the embodiments will be briefly introduced below, and it is obvious that the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present invention, and it is obvious for those skilled in the art to obtain other drawings based on these drawings without creative efforts.
Fig. 1 is a flow chart of a comfort and peak-to-valley electricity price adaptive household heating intelligent group control method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 2 is a flowchart of adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater by collecting human information and issuing a first adjustment completion command in the household intelligent group control method for heating with comfort and peak-to-valley electricity prices adaptive according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 3 is a flowchart of determining whether to adjust the set temperature of the electric heater according to the wind speed and sending a second adjustment completion command after receiving the first adjustment completion command in the household intelligent group control method for heating with comfort and peak-to-valley electricity prices adaptive according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 4 is a flowchart of determining whether to issue a user orientation determination command according to the total solar irradiance at the current time after receiving the second adjustment completion command in the household electric heating intelligent group control method with adaptive comfort and peak-to-valley electricity rates according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 5 is a flowchart of adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater and issuing a third adjustment completion command after receiving the user orientation determination command in the household electric heating intelligent group control method with adaptive comfort and peak-to-valley electricity price according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 6 is a flow chart of the comfort level and peak-to-valley electricity rate adaptive household heating intelligent group control method for identifying the current electricity rate level and adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next moment for different rooms according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 7 is a flowchart of collecting the electric power of the user and the instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current time, identifying the instantaneous electric powers of other electric devices except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric powers with a preset limit value of the total power, and identifying the available instantaneous power at the next time in the household electric heating intelligent group control method with adaptive comfort and peak-to-valley electricity prices according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 8 is a block diagram of a household intelligent group control system for heating household appliances with adaptive comfort and peak-to-valley electricity prices according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 9 is a block diagram of an electronic device in one embodiment of the invention.
Detailed Description
In some of the flows described in the present specification and claims and in the above figures, a number of operations are included that occur in a particular order, but it should be clearly understood that these operations may be performed out of order or in parallel as they occur herein, with the order of the operations being indicated as 101, 102, etc. merely to distinguish between the various operations, and the order of the operations by themselves does not represent any order of performance. Additionally, the flows may include more or fewer operations, and the operations may be performed sequentially or in parallel. It should be noted that, the descriptions of "first", "second", etc. in this document are used for distinguishing different messages, devices, modules, etc., and do not represent a sequential order, nor limit the types of "first" and "second" to be different.
The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention, and it is obvious that the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present invention, and not all of the embodiments. All other embodiments, which can be derived by a person skilled in the art from the embodiments given herein without making any creative effort, shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
Household electric heating is a free, comfortable and environment-friendly heating mode for converting clean electric energy into heat energy, and particularly in recent years, household electric heating systems for clean heating are rapidly developed.
The existing household electric heating system mainly depends on a mode of presetting temperature by a user to regulate and control equipment, and in addition, partial scheme considers heat accumulation and responds to peak-to-valley electricity price difference. However, the existing technology can not identify whether a person exists in a room so as to judge the necessity of heating demand and waste energy; the comfort of the user cannot be responded according to meteorological parameters in combination with the room orientation, so that the deviation between the actual room temperature and the expected room temperature is large; meanwhile, the peak-valley electricity price cannot be synchronously responded to be controlled under the condition of no capacity increase of electric power, and the operation cost is difficult to be saved as far as possible while the initial investment is reduced. In summary, the existing technology cannot guarantee higher comfort for users and the power of the electric equipment does not exceed the limit value.
The embodiment of the invention provides a household electric heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort and peak-valley electricity price. According to the scheme, the comfort of the user and the relevant parameters of the electricity price are identified, the electric heater is intelligently controlled in a group mode by combining with the electric power of the user, and the purposes of saving energy, reducing cost and reducing carbon are achieved on the premise that the comfort requirement of the user and the power are not out of limit.
According to the first aspect of the embodiment of the invention, an intelligent group control method for household electric heating with self-adaptive comfort and peak-valley electricity price is provided.
Fig. 1 is a flow chart of a comfort and peak-to-valley electricity price adaptive household heating intelligent group control method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the comfort level and peak-to-valley electricity price adaptive household heating intelligent group control method includes:
according to the first aspect of the embodiment of the invention, an intelligent group control method for household electric heating with self-adaptive comfort and peak-to-valley electricity price is provided.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the comfort level and peak-to-valley electricity price adaptive household heating intelligent group control method includes:
s101, collecting human sensing information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of a user, identifying the current electricity price level, and adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next moment of the different rooms;
s102, collecting electric power of a user and instantaneous electric power of an electric heater group at the current moment, identifying the instantaneous electric power of other electric equipment except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric power with a preset limit value of total power, and identifying available instantaneous power at the next moment;
s103, collecting actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at the current moment, identifying a preset expected indoor temperature of the user at the next moment, predicting electric heating requirements of different rooms at the next moment according to the set temperature at the next moment, and intelligently adjusting electric heaters of all the rooms according to the available instantaneous power at the next moment.
Fig. 2 is a flowchart of adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater by collecting human information and issuing a first adjustment completion command in the household intelligent group control method for heating with comfort and peak-to-valley electricity prices adaptive according to an embodiment of the present invention.
As shown in fig. 2, in one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring human information, the total solar irradiance and the wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of the user, identifying the current electricity price level, adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next time of the different rooms, further adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater by acquiring the human information, and issuing a first adjustment completion command specifically includes:
s201, using a human body sensor to acquire whether a person exists in a room, and if no person exists in the room, setting the set temperature of the electric heater as the anti-freezing temperature of the room;
s202, using a human body sensor to acquire whether a person exists in a room, and if the person exists, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater;
s203, a first adjustment completion command is sent.
In the embodiment of the invention, wherein the room anti-freezing temperature is input empirically in advance, the human body sensor generally refers to a human body proximity sensor. The human body sensor can be a human body proximity sensor, the human body proximity sensor is based on the Doppler technical principle, a microwave special microprocessor and a planar induction antenna are adopted, the detection sensitivity is high, the detection range is wide, the work is very reliable, generally, false alarm does not exist, the human body sensor can stably work within the temperature range of-15 to +60 ℃, the human body sensor is used for collecting the information whether a room is occupied or not, and if no person exists, the temperature of the electric heater is set to be the input anti-freezing temperature of the room; and if the person exists, the next judgment is carried out.
Fig. 3 is a flowchart of determining whether to adjust the set temperature of the electric heater according to the wind speed and sending a second adjustment completion command after receiving the first adjustment completion command in the household intelligent group control method for heating with comfort and peak-to-valley electricity prices adaptive according to an embodiment of the present invention.
As shown in fig. 3, in one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring human sensing information, total solar irradiance and wind speed, acquiring orientations of different rooms of a user, identifying a current electricity price level, adjusting a set temperature of the user at a next moment of the different rooms, further determining whether to adjust the set temperature of the electric heater according to the wind speed after receiving the first adjustment completion command, and sending a second adjustment completion command specifically includes:
s301, collecting the current wind speed as a wind speed parameter;
s302, judging whether the wind speed parameter reaches a preset wind speed limit value or not by using a first calculation formula, if so, updating the set temperature of the electric heater by using a second calculation formula, and if not, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater;
and S303, sending a second adjustment completion command.
The first calculation formula is:
the second calculation formula is:
wherein,in order to judge the updated set temperature of the electric heater according to the wind speed limit value,in order to judge the set temperature of the electric heater before updating according to the wind speed limit value,is a preset temperature change value judged according to the wind speed limit value.
In the embodiment of the invention, the preset temperature change value is temperature adjustment set according to experience, the wind speed limit value is considered to be 3m/s, and the wind speed at the current moment is acquiredAnd the like, if the wind speed is low, the adjustment of the set temperature of the electric heater caused by the wind speed is not considered; if the wind speed is high (e.g. high)) If the set temperature of the electric heater is increased
Fig. 4 is a flowchart of determining whether to issue a user orientation determination command according to the total solar irradiance at the current time after receiving the second adjustment completion command in the household electric heating intelligent group control method with adaptive comfort and peak-to-valley electricity rates according to an embodiment of the present invention.
As shown in fig. 4, in one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring human information, the total solar irradiance and the wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of the user, identifying the current electricity price level, adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next time of the different rooms, and after receiving the second adjustment completion command, determining whether to issue a user orientation determination command according to the total solar irradiance at the current time includes:
s401, collecting the total solar irradiance at the current moment;
s402, judging whether the total solar irradiance at the current moment meets a third calculation formula, if not, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater, and if so, sending a user orientation judgment command.
The third calculation formula is:
Wherein, the total irradiance of the sun at the current moment is collectedAnd the parameters are equal, if the total solar irradiance is lower, the adjustment of the set temperature of the electric heater caused by the solar irradiance is not considered; if it is higher (e.g. than ) Then go to the next step.
Fig. 5 is a flowchart of adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater and issuing a third adjustment completion command after receiving the user orientation determination command in the household intelligent group heating control method with adaptive comfort level and peak-to-valley electricity price according to an embodiment of the present invention.
As shown in fig. 5, in one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring human information, total solar irradiance and wind speed, acquiring orientations of different rooms of a user, identifying a current electricity price level, adjusting a set temperature of the user at a next time of the different rooms, after receiving the user orientation determination command, adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater, and issuing a third adjustment completion command specifically includes:
s501, acquiring the orientation of the user;
s502, if the south deviation of the user facing distance exceeds a preset range, the adjustment of the set temperature of the electric heater caused by solar irradiance is not considered;
s503, if the southward deviation of the user orientation distance is within the preset range, adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater by using a fourth calculation formula;
s504, a third adjustment completion command is sent out;
the fourth calculation formula is:
wherein,in order to judge the updated set temperature of the electric heater by the orientation of the user,in order to judge the set temperature of the electric heater before updating by the orientation of the user,the solar radiation temperature change value is preset.
In the embodiment of the invention, the orientation of the user is recognized, the preset range is within 45 ℃ of the left side of the orientation and within 45 ℃ of the right side of the orientation, and if the orientation is within 45 ℃ of the left side of the orientation, the orientation is far away from the right sideIf the deviation from the south direction is large, the adjustment of the set temperature of the electric heater caused by solar irradiance is not considered; if the temperature is mainly south (including 45 ℃ in south-east and 45 ℃ in south-west), the set temperature of the electric heater is reducedThe solar irradiation temperature change value is set according to experience.
Fig. 6 is a flowchart of identifying a current electricity price level and adjusting a set temperature of a user for a different room at a next moment in the intelligent group control method for user electric heating with adaptive comfort level and peak-to-valley electricity price according to an embodiment of the present invention.
As shown in fig. 6, in one or more embodiments, preferably, the identifying the current power rate level and adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next time point of the different rooms specifically include:
s601, acquiring a current electricity price level, and judging whether the electricity price is in a peak time period, a valley time period or a flat time period;
s602, if the electric heater is in the peak time period, the set temperature of the electric heater is reduced by a preset first adjustment amplitude within a comfort degree allowable range;
s603, if the electric heater is in the valley period, the set temperature of the electric heater is increased by a preset second adjustment range within a comfort degree allowable range;
and S604, if the temperature is in the flat time period, the set temperature of the electric heater is not adjusted.
In the embodiment of the invention, the current power price level PR is identified τ The utility model discloses a comfort level, including the electric heater, the electric heater sets for the temperature, judges that the price of electricity is in peak, millet or on-the-flat period, if in the peak period, then the electric heater sets for the temperature and reduces first adjustment amplitude in comfort level allowed band, if in the millet period, then the electric heater sets for the temperature and improves second adjustment amplitude in comfort level allowed band, if in the flat period, then the electric heater sets for the temperature and does not do the adjustment, wherein, comfort level allowed band is a preset's adjustment range, and first adjustment amplitude and second adjustment amplitude set up according to experience.
Fig. 7 is a flowchart of a comfort and peak-to-valley electricity price adaptive household electric heating intelligent group control method according to an embodiment of the present invention, which collects electric power of a user at a current time and instantaneous electric power of an electric heater group, identifies instantaneous electric power of other electric devices except the electric heater, compares the instantaneous electric power with a preset total power limit value, and identifies available instantaneous power at a next time.
As shown in fig. 7, in one or more embodiments, preferably, the collecting the electric power of the user and the instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment, identifying the instantaneous electric powers of other electric devices except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric powers with a preset limit value of the total power, and identifying the available instantaneous power at the next moment specifically includes:
s701, collecting electric power of a user and instantaneous electric power of an electric heater group at the current moment, and calculating instantaneous electric power of other equipment by using a fifth calculation formula;
s702, comparing the instantaneous electric power of the other equipment with the preset user total electric power limit value;
s703, when the instantaneous electric power of the other equipment is smaller than the preset user total electric power limit value, calculating the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next moment by using a sixth calculation formula, and when the instantaneous electric power of the other equipment is not smaller than the preset user total electric power limit value, the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next moment is 0;
the fifth calculation formula:
wherein,for instantaneous electric power of other apparatus, P τ For the electric power of the user at the present moment,instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment;
the sixth calculation formula:
wherein,available instantaneous power, P, for the electric heater cluster at the next time limit And the preset user total electric power limit value is obtained.
In the embodiment of the invention, the electric power P of the user at the current moment is collected τ And collecting instantaneous electric power of electric heater groupIdentifying instantaneous electric power of other devices of the user, i.e.And is compared with the preset user total electric power limit value P limit Comparing and identifying the next instant of available instantaneous power for the electric heater cluster, i.e.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of the user at the current time, identifying a preset desired indoor temperature of the user at the next time, predicting electric heating demands of the different rooms at the next time according to the set temperature at the next time, and intelligently adjusting each room electric heater according to the available instantaneous power at the next time specifically includes:
identifying a user preset expected indoor temperature at the next moment;
calculating the indoor temperature set value at the next moment by using a seventh calculation formula;
the seventh calculation formula is:
wherein,is the indoor temperature set value at the next moment,a desired indoor temperature is preset for a user at the next moment,is the third adjustment amplitude.
In the embodiment of the present invention, when the set temperature of the electric heater is increased when the seventh calculation formula is used for calculation, it is necessary to calculate the temperature of the electric heater according to the set temperatureIs arranged asThe third adjustment range is the first adjustment range; when the set temperature of the electric heater is reduced, the electric heater needs to be connected with the electric heaterIs arranged asThe third adjustment range is the second adjustment range. Recognizing a user preset desired indoor temperature at a next momentIntelligently adjusting the indoor temperature set point at the next moment, i.e.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at a current moment, identifying a preset expected indoor temperature of the user at a next moment, predicting electric heating demands of different rooms at the next moment according to a set temperature at the next moment, and intelligently adjusting each room electric heater by combining available instantaneous power at the next moment, further includes acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of the user at the current moment in real time, and predicting electric heating demands of different rooms at the next moment by using an eighth calculation formula according to a set value of the indoor temperatures at the next moment;
the eighth calculation formula is:
wherein,for the next moment of the indoor temperature set point, t τ Is the actual indoor temperature at the present moment, z is the supply power required per unit temperature change,the electric heating requirements of different rooms at the next moment are met.
In the embodiment of the invention, z is the power supply power required by unit temperature change and is an empirical value judged according to historical empirical data.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of the user at the current time, identifying a preset desired indoor temperature of the user at the next time, predicting electric heating demands of different rooms at the next time according to the set temperature at the next time, intelligently adjusting each room electric heater by combining available instantaneous power at the next time, and further combining available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next timeThe electric heaters of all rooms are pressed down to meet the electric heating requirements of different rooms at a momentAre allocated.
According to the second aspect of the embodiment of the invention, the household electric heating intelligent group control system with self-adaption comfort and peak-valley electricity price is provided.
Fig. 8 is a block diagram of a household intelligent group control system for heating household appliances with adaptive comfort and peak-to-valley electricity prices according to an embodiment of the present invention.
In one or more embodiments, preferably, the comfort level and peak-to-valley electricity price adaptive household heating intelligent group control system includes:
the temperature setting module 801 is used for acquiring human information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of a user, identifying the current electricity price level and adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next moment of the different rooms;
an instantaneous power identification module 802, configured to collect the electric power of the user and the instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment, identify the instantaneous electric powers of other electric devices except the electric heater, compare the instantaneous electric powers with a preset limit value of the total power, and identify the available instantaneous power at the next moment;
the intelligent adjusting module 803 is configured to collect actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at the current moment, identify a preset expected indoor temperature of the user at the next moment, predict electric heating demands of the different rooms at the next moment according to the set temperature at the next moment, and intelligently adjust the electric heaters of the rooms according to the available instantaneous power at the next moment.
According to a third aspect of embodiments of the present invention, there is provided a computer-readable storage medium having stored thereon computer program instructions which, when executed by a processor, implement the method according to any one of the first aspect of embodiments of the present invention.
According to a fourth aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, there is provided an electronic apparatus. Fig. 9 is a block diagram of an electronic device in one embodiment of the invention. The electronic device shown in fig. 9 is a household intelligent group control device for electric heating with adaptive general comfort and peak-valley electricity prices. Referring to fig. 9, the electronic device may be a smart phone, a tablet computer, or the like. The electronic device 900 includes a processor 901 and memory 902. The processor 901 is electrically connected to the memory 902.
The processor 901 is a control center of the electronic device 900, connects various parts of the entire electronic device using various interfaces and lines, performs various functions of the electronic device and processes data by running or calling a computer program stored in the memory 902 and calling data stored in the memory 902, thereby integrally monitoring the electronic device.
In this embodiment, the processor 901 in the electronic device 900 loads instructions corresponding to one or more processes of the computer program into the memory 902 according to the following steps, and the processor 901 runs the computer program stored in the memory 902, so as to implement various functions, for example: acquiring human sensing information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of a user, identifying the current electricity price level, and adjusting the set temperature of the user at the next moment of the different rooms; collecting the electric power of a user and the instantaneous electric power of an electric heater group at the current moment, identifying the instantaneous electric power of other electric equipment except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric power with a preset limit value of total power, and identifying the available instantaneous power at the next moment; the method comprises the steps of collecting actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at the current moment, identifying preset expected indoor temperatures of the user at the next moment, predicting electric heating demands of the different rooms at the next moment according to the set temperature at the next moment, and intelligently adjusting electric heaters of the rooms by combining available instantaneous power at the next moment.
In some embodiments, electronic device 900 may further include: a display 903, radio frequency circuitry 904, audio circuitry 905, a wireless fidelity module 906, and a power supply 907. The display 903, the radio frequency circuit 904, the audio circuit 905, the wireless fidelity module 906 and the power supply 907 are electrically connected to the processor 901, respectively.
The display 903 may be used to display information entered by or provided to the user as well as various graphical user interfaces, which may be composed of graphics, text, icons, video, and any combination thereof. The Display 903 may include a Display panel, which may be configured in the form of a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), an Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED), or the like in some embodiments.
The rf circuit 904 may be configured to transmit and receive rf signals to establish wireless communication with a network device or other electronic devices through wireless communication, and transmit and receive signals to and from the network device or other electronic devices.
The audio circuitry 905 may be used to provide an audio interface between a user and an electronic device through a speaker, microphone.
The wi-fi module 906, which may be used for short-range wireless transmission, may assist the user in sending and receiving e-mail, browsing websites, and accessing streaming media, etc., provides wireless broadband internet access to the user.
The power supply 907 may be used to power various components of the electronic device 900. In some embodiments, power supply 907 may be logically coupled to processor 901 via a power management system, such that functions of managing charging, discharging, and power consumption are performed via the power management system.
Although not shown in fig. 9, the electronic device 900 may further include a camera, a bluetooth module, etc., which are not described in detail herein.
The technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention can have the following beneficial effects:
in the scheme of the invention, the intelligent group control of the electric heater is carried out by identifying the related parameters of the comfort level and the electricity price of the user and combining the electric power of the user, and the purposes of saving energy, reducing the cost and reducing carbon are realized on the premise of ensuring the comfort level requirement of the user and not exceeding the power limit.
According to the scheme of the invention, the user electricity heating requirements are adaptively adjusted through the identification of peak-valley electricity price, orientation and people sensing information of the power grid, and each indoor temperature set value is dynamically and quickly adjusted, so that the intelligent cooperative control of a plurality of electric heaters is realized.
As will be appreciated by one skilled in the art, embodiments of the present invention may be provided as a method, system, or computer program product. Accordingly, the present invention may take the form of an entirely hardware embodiment, an entirely software embodiment or an embodiment combining software and hardware aspects. Furthermore, the present invention may take the form of a computer program product embodied on one or more computer-usable storage media (including, but not limited to, disk storage, optical storage, and the like) having computer-usable program code embodied therein.
The present invention is described with reference to flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams of methods, apparatus (systems), and computer program products according to embodiments of the invention. It will be understood that each flow and/or block of the flow diagrams and/or block diagrams, and combinations of flows and/or blocks in the flow diagrams and/or block diagrams, can be implemented by computer program instructions. These computer program instructions may be provided to a processor of a general purpose computer, special purpose computer, embedded processor, or other programmable data processing apparatus to produce a machine, such that the instructions, which execute via the processor of the computer or other programmable data processing apparatus, create means for implementing the functions specified in the flowchart flow or flows and/or block diagram block or blocks.
These computer program instructions may also be stored in a computer-readable memory that can direct a computer or other programmable data processing apparatus to function in a particular manner, such that the instructions stored in the computer-readable memory produce an article of manufacture including instruction means which implement the function specified in the flowchart flow or flows and/or block diagram block or blocks.
These computer program instructions may also be loaded onto a computer or other programmable data processing apparatus to cause a series of operational steps to be performed on the computer or other programmable apparatus to produce a computer implemented process such that the instructions which execute on the computer or other programmable apparatus provide steps for implementing the functions specified in the flowchart flow or flows and/or block diagram block or blocks.
It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various changes and modifications may be made in the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. Thus, if such modifications and variations of the present invention fall within the scope of the claims of the present invention and their equivalents, the present invention is also intended to include such modifications and variations.
Claims (3)
1. A household electric heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort and peak-valley electricity price is characterized by comprising the following steps:
acquiring human sensing information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, acquiring the orientation of different rooms of a user, identifying the current electricity price level, and adjusting the set temperature of the user on the electric heater at the next moment of the different rooms;
collecting the electric power of a user and the instantaneous electric power of an electric heater group at the current moment, identifying the instantaneous electric power of other electric equipment except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric power with a preset limit value of total power, and identifying the available instantaneous power at the next moment;
acquiring actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at the current moment, identifying a preset expected indoor temperature of the user at the next moment, predicting electric heating demands of the different rooms at the next moment according to the set temperature of the electric heaters at the next moment, and intelligently adjusting the electric heaters of the rooms by combining with the available instantaneous power at the next moment;
wherein, gather people and feel information, the total irradiance of sun and wind speed, acquire the orientation in user's different rooms, discern current price of electricity level, the adjustment user is to the settlement temperature of the electric heater in the next moment in different rooms, still include and feel the settlement temperature adjustment that information carries out the electric heater through gathering people to send out first adjustment and accomplish the order, specifically include:
the method comprises the following steps of (1) acquiring whether a person exists in a room by using a human body sensor, and if no person exists in the room, setting the set temperature of an electric heater as the anti-freezing temperature of the room;
using a human body sensor to acquire whether a person exists in a room, and if the person exists, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater;
sending a first adjustment completion command;
wherein, gather people and feel information, solar total irradiance and wind speed, acquire the orientation in user's different rooms, discern current price of electricity level, adjust the user to the settlement temperature of the electric heater in different rooms at the next moment, still include receiving behind the first adjustment completion order, judge whether according to the wind speed adjustment the settlement temperature of electric heater sends the second adjustment and accomplishes the order, specifically includes:
collecting the current wind speed as a wind speed parameter;
judging whether the wind speed parameter reaches a preset wind speed limit value or not by using a first calculation formula, if so, updating the set temperature of the electric heater by using a second calculation formula, and if not, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater;
sending a second adjustment completion command;
the first calculation formula is:
the second calculation formula is:
wherein,in order to judge the updated set temperature of the electric heater according to the wind speed limit value,in order to judge the set temperature of the electric heater before updating according to the wind speed limit value,the preset temperature change value is judged according to the wind speed limit value;
wherein, gather people and feel information, the total irradiance of sun and wind speed, acquire the orientation in user's different rooms, discern current price level of electricity, adjust the user to the settlement temperature of the electric heater in different rooms at the next moment, still include receiving after the order is accomplished in the second adjustment, judge whether to send user orientation judgement command according to the total irradiance of sun at the present moment, specifically include:
collecting the total solar irradiance at the current moment;
judging whether the total solar irradiance at the current moment meets a third calculation formula, if not, not modifying the set temperature of the electric heater, and if so, sending a user orientation judgment command;
the third calculation formula is:
wherein, gather people and feel information, the total irradiance of sun and wind speed, acquire the orientation in user's different rooms, discern current price of electricity level, adjust the user to the settlement temperature of the electric heater in different rooms at the next moment, still include receiving after the user orientation judges the order, the adjustment the settlement temperature of electric heater sends the third adjustment and accomplishes the order, specifically includes:
acquiring the orientation of the user;
if the southward deviation of the user orientation distance exceeds a preset range, the adjustment of the set temperature of the electric heater caused by solar irradiance is not considered;
if the southward deviation of the user orientation distance is within the preset range, adjusting the set temperature of the electric heater by using a fourth calculation formula;
sending a third adjustment completion command;
the fourth calculation formula is:
wherein,in order to judge the updated set temperature of the electric heater by the orientation of the user,in order to judge the set temperature of the electric heater before updating by the orientation of the user,the value is a preset solar irradiation temperature change value;
wherein, discerning current power price level, the setting temperature of adjustment user to the electric heater of the next moment in different rooms specifically includes:
acquiring a current electricity price level, and judging whether the electricity price is in one of a peak time period, a valley time period or a flat time period;
if the temperature is in the peak time period, the set temperature of the electric heater is reduced by a preset first adjustment amplitude within the comfort degree allowable range;
if the electric heater is in the valley period, the set temperature of the electric heater is increased by a preset second adjustment amplitude within the comfort degree allowable range;
if the temperature is in the flat time interval, the set temperature of the electric heater is not adjusted;
the method includes the steps of collecting actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at a current moment, identifying a preset expected indoor temperature of the user at a next moment, predicting electric heating demands of the different rooms at the next moment according to set temperatures of the electric heaters at the next moment, and intelligently adjusting the electric heaters of the rooms by combining available instantaneous power at the next moment, and specifically includes the following steps:
identifying a user preset expected indoor temperature at the next moment;
calculating the indoor temperature set value at the next moment by using a seventh calculation formula;
the seventh calculation formula is:
wherein,is the indoor temperature set value at the next moment,a desired indoor temperature is preset for a user at the next moment,a third adjustment amplitude;
when the set temperature of the electric heater is raised, it is necessary to calculate using the seventh calculation formulaIs arranged asThe third adjustment range is the first adjustment range; when the set temperature of the electric heater is reduced, the electric heater needs to be connected with the electric heaterIs arranged asThe third adjustment amplitude is the second adjustment amplitude;
the method comprises the steps of collecting actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of a user at the current moment, identifying a preset expected indoor temperature of the user at the next moment, predicting electric heating requirements of the different rooms at the next moment according to the set temperature of the electric heater at the next moment, intelligently adjusting the electric heaters of the rooms by combining available instantaneous power at the next moment, collecting the actual indoor temperatures of the different rooms of the user at the current moment in real time, and predicting the electric heating requirements of the different rooms at the next moment by using an eighth calculation formula according to the set value of the indoor temperatures at the next moment;
the eighth calculation formula is:
2. The intelligent group control method for household electric heating with adaptive comfort and peak-to-valley electricity price according to claim 1, wherein the method comprises the steps of collecting the electric power of the user at the current moment and the instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group, identifying the instantaneous electric power of other electric devices except the electric heater, comparing the instantaneous electric power with a preset limit value of total power, and identifying the available instantaneous power at the next moment, and specifically comprises the following steps:
collecting the electric power of a user and the instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment, and calculating the instantaneous electric power of other equipment by using a fifth calculation formula;
comparing the other device instantaneous electric power to the preset user total electric power limit;
when the instantaneous electric power of the other equipment is smaller than the preset user total electric power limit value, calculating the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next moment by using a sixth calculation formula, and when the instantaneous electric power of the other equipment is not smaller than the preset user total electric power limit value, the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next moment is 0;
the fifth calculation formula:
wherein,for instantaneous electric power of other apparatus, P τ For the electric power of the user at the present moment,instantaneous electric power of the electric heater group at the current moment;
the sixth calculation formula:
3. The intelligent group control method for household electric heating with self-adaptive comfort degree and peak-valley electricity price according to claim 2, characterized in that the actual indoor temperatures of different rooms of the user at the current moment are collected, the preset expected indoor temperature of the user at the next moment is identified, the electric heating requirements of different rooms at the next moment are predicted according to the set temperature of the electric heater at the next moment, and the available instantaneous power at the next moment is combined for all the roomsThe intelligent regulation of the room electric heaters also comprises the combination of the available instantaneous power of the electric heater group at the next momentThe electric heaters of all rooms are pressed down to meet the electric heating requirements of different rooms at a momentAre allocated.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210613701.7A CN114963284B (en) | 2022-05-31 | 2022-05-31 | Household electricity heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort level and peak-valley electricity price |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210613701.7A CN114963284B (en) | 2022-05-31 | 2022-05-31 | Household electricity heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort level and peak-valley electricity price |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114963284A CN114963284A (en) | 2022-08-30 |
| CN114963284B true CN114963284B (en) | 2022-11-25 |
Family
ID=82958255
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210613701.7A Active CN114963284B (en) | 2022-05-31 | 2022-05-31 | Household electricity heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort level and peak-valley electricity price |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114963284B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115388455B (en) * | 2022-09-06 | 2024-01-02 | 中国建筑科学研究院有限公司 | Intelligent control method, system and equipment for household regenerative electric heater system |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB9006742D0 (en) * | 1989-04-03 | 1990-05-23 | Helo Tehtaat Oy | A method of controlling the supply of electric power to an electric sauna heater |
| CN105864880A (en) * | 2016-04-09 | 2016-08-17 | 上海上塔软件开发有限公司 | Building electric heating group load adjusting and dynamic distributing method |
| CN205641121U (en) * | 2016-05-26 | 2016-10-12 | 天津中德应用技术大学 | Timesharing peak valley power consumption floor heating device |
| CN206113116U (en) * | 2016-10-21 | 2017-04-19 | 天津中德应用技术大学 | Automatic intelligence electricity ground warm color tone orchestration that stops function that opens has based on WIFI |
| CN109709910A (en) * | 2018-11-30 | 2019-05-03 | 中国科学院广州能源研究所 | A kind of home energy source Optimized Operation management system and method |
| CN110332602A (en) * | 2019-05-09 | 2019-10-15 | 辽宁省鑫源温控技术有限公司 | The electric heating temperature control method of peak valley ordinary telegram valence operation function |
| CN111256201A (en) * | 2020-01-15 | 2020-06-09 | 国网冀北电力有限公司秦皇岛供电公司 | Control method and device for heat accumulating type electric heating equipment and electronic equipment |
-
2022
- 2022-05-31 CN CN202210613701.7A patent/CN114963284B/en active Active
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB9006742D0 (en) * | 1989-04-03 | 1990-05-23 | Helo Tehtaat Oy | A method of controlling the supply of electric power to an electric sauna heater |
| CN105864880A (en) * | 2016-04-09 | 2016-08-17 | 上海上塔软件开发有限公司 | Building electric heating group load adjusting and dynamic distributing method |
| CN205641121U (en) * | 2016-05-26 | 2016-10-12 | 天津中德应用技术大学 | Timesharing peak valley power consumption floor heating device |
| CN206113116U (en) * | 2016-10-21 | 2017-04-19 | 天津中德应用技术大学 | Automatic intelligence electricity ground warm color tone orchestration that stops function that opens has based on WIFI |
| CN109709910A (en) * | 2018-11-30 | 2019-05-03 | 中国科学院广州能源研究所 | A kind of home energy source Optimized Operation management system and method |
| CN110332602A (en) * | 2019-05-09 | 2019-10-15 | 辽宁省鑫源温控技术有限公司 | The electric heating temperature control method of peak valley ordinary telegram valence operation function |
| CN111256201A (en) * | 2020-01-15 | 2020-06-09 | 国网冀北电力有限公司秦皇岛供电公司 | Control method and device for heat accumulating type electric heating equipment and electronic equipment |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114963284A (en) | 2022-08-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102437569B (en) | Electronic installation, the electric power management system including electronic installation and control method thereof | |
| US20240111317A1 (en) | Optimization of energy use through model-based simulations | |
| CN104566998B (en) | A kind of reservation control method of water heater, server and system | |
| US9471070B2 (en) | Environmental control system including distributed control elements | |
| CN105588290A (en) | Control terminal, system and method for adjusting temperature of air-conditioner | |
| CN102901180A (en) | Method and system for controlling air conditioner | |
| KR20120016133A (en) | System and method for estimating and providing dispatchable operating reserve energy capacity through use of active load management | |
| CN104833038A (en) | Multi-split air conditioner centralized control method and centralized controller | |
| CN108131781A (en) | One kind is based on intelligent air condition visualization electric energy control method, system and storage medium | |
| CN110069017A (en) | A kind of equipment energy consumption control method, storage medium and its controlling terminal | |
| CN114963284B (en) | Household electricity heating intelligent group control method with self-adaptive comfort level and peak-valley electricity price | |
| KR20120065659A (en) | Air conditioning system and control method thereof | |
| CN104823120A (en) | Intelligent controller for environmental control system | |
| CN205174699U (en) | Central air conditioner centralized control device and central air conditioner micro-cloud network system | |
| CN112212475A (en) | Room temperature adjusting method and system, central control equipment and storage medium | |
| CN102055236B (en) | Intelligent power supply management system and method | |
| CN114738827A (en) | Household electric heating intelligent group control method and system based on user habits | |
| CN115560381B (en) | Intelligent group control electric heating system, method and equipment based on edge calculation | |
| CN115051374B (en) | Control method, device and storage medium for electric heating equipment to participate in electric peak regulation | |
| CN115218270B (en) | Distributed electric heating intelligent group control method and system for terminal substation level | |
| CN117872784A (en) | Device energy consumption adjusting method and device, electronic device and readable storage medium | |
| CN114992704A (en) | Man-machine interaction system and method for intelligent heat supply | |
| WO2017054331A1 (en) | Temperature control method and system, base station background, and computer storage medium | |
| CN204359444U (en) | Heating power heating temperature testing equipment | |
| CN217034535U (en) | Cold station operation control device and cold station operation system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |