CN114885384A - Data forwarding method and device and communication equipment - Google Patents
Data forwarding method and device and communication equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114885384A CN114885384A CN202110164796.4A CN202110164796A CN114885384A CN 114885384 A CN114885384 A CN 114885384A CN 202110164796 A CN202110164796 A CN 202110164796A CN 114885384 A CN114885384 A CN 114885384A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- far
- eas
- information
- instruction
- sending
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 108
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 94
- 101150119040 Nsmf gene Proteins 0.000 claims description 20
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000003550 marker Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 15
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000005012 migration Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000013508 migration Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001174 ascending effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003139 buffering effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008447 perception Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005641 tunneling Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/0005—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off
- H04W36/0011—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection
- H04W36/0016—Hand-off preparation specially adapted for end-to-end data sessions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/16—Performing reselection for specific purposes
- H04W36/18—Performing reselection for specific purposes for allowing seamless reselection, e.g. soft reselection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
- H04W40/34—Modification of an existing route
- H04W40/36—Modification of an existing route due to handover
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
The application discloses a data forwarding method, a data forwarding device and communication equipment, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The data forwarding method comprises the following steps: receiving a first FAR (forwarding behavior rule) for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet; executing a first FAR if a first condition is satisfied, the first condition including at least one of: receiving a first instruction, wherein the first instruction is used for instructing execution of a first FAR; receiving a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data; receiving a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding; the first FAR is different from the currently used FAR. According to the application, the time for transmitting the forwarding behavior rules and the time for transmitting the data in the process of replacing the EAS IP address are determined, and the problems of discontinuous service, data packet loss and the like caused by EAS switching can be effectively solved.
Description
Technical Field
The application belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and particularly relates to a data forwarding method, a data forwarding device and communication equipment.
Background
In an Edge computing scenario, in order to implement an unaware switching of an Edge Application Server (EAS) of a terminal (User Equipment, UE), a scheme for replacing an EAS IP (Internet Protocol, Internet interconnection Protocol) is proposed at present, that is: when the UE moves to cause the switching of the edge Application server or the switching of the edge Application server is caused by load balancing, an Application Function (AF) provides an IP address and a port number of a target EAS, a 5G core network (5G core network, 5GC) configures a new Forwarding Action Rule (FAR) in a User Plane Function (UPF) according to the situation of the IP address of the target EAS, and only adds header information to an outward forwarded data packet at the UPF (while replacing the old FAR) on the premise of not changing the IP accessed by the UE for Forwarding processing and Forwarding to the new target IP, which is as follows:
ascending:
UE → UPF: the source (source) IP is the UE IP, and the target (target) IP is the source EAS IP;
UPF to target EAS: due to the switching, the source EAS is already switched to the target EAS and UPF, packet header information is added to the data packet forwarded outwards, the source IP is still the UE IP, and the target IP is changed to the target EAS IP.
Descending:
EAS → UPF: the source IP is a target EAS IP, and the target IP is a UE IP;
UPF → UE: the source IP is changed back to the source EAS IP, and the destination IP is the UE IP.
In the whole process, the target IP always accessed by the UE is the source EAS IP, the UPF is responsible for modifying the target IP according to the switching condition, the UE does not sense the switching, and the UE does not need to search a new EAS IP address again, so that the UE is thoroughly unaware.
However, in the above scheme, there are the following problems: in the whole process of replacing the EAS IP address, the UPF executes a new FAR to send the data packet to a new target EAS, but in the process of EAS handover and before handover is completed, some data packets sent to the old EAS may still be in the process of transmission, and the old ESA is directly switched to the new EAS without being processed, which not only affects the service continuity of the EAS side, but also causes the data packet still transmitted to the old EAS to be lost.
Disclosure of Invention
An object of the embodiments of the present application is to provide a data forwarding method, an apparatus, and a communication device, which can solve the problems of service discontinuity and data packet loss in an EAS IP address replacement process.
In order to solve the technical problem, the present application is implemented as follows:
in a first aspect, a data forwarding method is provided, which is performed by a first communication device, and includes:
receiving a first FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
executing the first FAR if a first condition is met, the first condition including at least one of:
receiving a first indication for indicating execution of the first FAR;
receiving a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
receiving a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
the first FAR is different from the FAR currently used.
In a second aspect, a data forwarding method is provided, which is performed by a second communication device, and includes:
receiving first information indicating that a handover of the EAS has been completed;
according to the first information, performing at least one of the following operations:
generating a first FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
transmitting the first FAR;
sending a first indication, wherein the first indication is used for indicating to execute a first FAR;
sending a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
sending a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
sending a fourth indication, the fourth indication indicating removal of the old FAR.
In a third aspect, a data forwarding apparatus is provided, including:
a first receiving module, configured to receive a first FAR, where the first FAR is used to instruct how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
a first execution module, configured to execute the first FAR if a first condition is satisfied, where the first condition includes at least one of:
receiving a first indication for indicating execution of the first FAR;
receiving a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
receiving a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
the first FAR is different from the FAR currently used.
In a fourth aspect, a data forwarding apparatus is provided, including:
a first receiving module, configured to receive first information, where the first information is used to indicate that an EAS handover has been completed;
a first executing module, configured to execute at least one of the following operations according to the first information:
generating a first FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
transmitting the first FAR;
sending a first indication, wherein the first indication is used for indicating to execute a first FAR;
sending a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
sending a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
sending a fourth indication, the fourth indication indicating removal of the old FAR.
In a fifth aspect, there is provided a communication device, the terminal comprising a processor, a memory, and a program or instructions stored on the memory and executable on the processor, the program or instructions, when executed by the processor, implementing the steps of the method according to the first aspect; alternatively, the program or instructions, when executed by the processor, implement the steps of the method according to the second aspect.
In a sixth aspect, there is provided a readable storage medium on which a program or instructions are stored, which program or instructions, when executed by a processor, performs the steps of the method according to the first aspect, or performs the steps of the method according to the second aspect.
In a seventh aspect, a chip is provided, where the chip includes a processor and a communication interface, where the communication interface is coupled to the processor, and the processor is configured to execute a network-side device program or instruction, implement the method according to the first aspect, or implement the method according to the second aspect.
In an eighth aspect, there is provided a program product stored in a non-volatile storage medium for execution by at least one processor to implement the method of the first aspect, or to implement the method of the second aspect.
In the embodiment of the application, the time for transmitting the forwarding behavior rule and the time for transmitting data in the process of replacing the EAS IP address are determined, so that the problems of service discontinuity and data packet loss caused by EAS switching can be effectively solved.
Drawings
Fig. 1 is a flowchart illustrating a data forwarding method performed by a first communication device according to an embodiment of the present application;
fig. 2 is a schematic flowchart of a data forwarding method performed by a first communication device according to another embodiment of the present application;
fig. 3 is a schematic flowchart of a data forwarding method executed by a second communication device according to an embodiment of the present application;
fig. 4 is a schematic flowchart of a data forwarding method executed by a second communication device according to another embodiment of the present application;
fig. 5 is a schematic flowchart of a data forwarding method according to a first embodiment of the present application;
fig. 6 is a schematic flowchart of a data forwarding method according to a second embodiment of the present application;
fig. 7 is a schematic flowchart of a data forwarding method according to a third embodiment of the present application;
fig. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of a data forwarding apparatus according to an embodiment of the present application;
fig. 9 is a schematic structural diagram of a data forwarding apparatus according to another embodiment of the present application;
fig. 10 is a schematic structural diagram of a communication device according to an embodiment of the present application.
Detailed Description
The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present application, and it is obvious that the described embodiments are some, but not all, embodiments of the present application. All other embodiments, which can be derived by a person skilled in the art from the embodiments given herein without making any creative effort, shall fall within the protection scope of the present application.
The terms first, second and the like in the description and in the claims of the present application are used for distinguishing between similar elements and not necessarily for describing a particular sequential or chronological order. It should be understood that the data so used are interchangeable under appropriate circumstances such that embodiments of the application can be practiced in sequences other than those illustrated or described herein, and the terms "first" and "second" used herein generally do not denote any order, nor do they denote any order, for example, the first object may be one or more. In addition, "and/or" in the specification and the claims means at least one of connected objects, and a character "/" generally means that a preceding and succeeding related objects are in an "or" relationship.
It is worth pointing out that the embodiments of the present application describeThe techniques are not limited to Long Term Evolution (LTE)/LTE Evolution (LTE-Advanced) systems, but may also be used in other wireless communication systems, such as Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA), Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA), Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), Single-carrier Frequency-Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA), and other systems. The terms "system" and "network" in the embodiments of the present application are often used interchangeably, and the described techniques can be used for both the above-mentioned systems and radio technologies, as well as for other systems and radio technologies. However, the following description describes a New Radio (NR) system for purposes of example, and NR terminology is used in much of the description below, although the techniques may also be applied to applications other than NR system applications, such as 6 th generation (6 th generation) th Generation, 6G) communication system.
The following describes in detail a data forwarding method, an apparatus, and a communication device provided in the embodiments of the present application through specific embodiments and application scenarios thereof with reference to the accompanying drawings.
It should be noted that, the data forwarding method in the embodiment of the present application is applied to an EAS IP address replacement process, where the EAS IP address replacement process refers to: when the UE moves or the EAS is switched due to reasons such as load balance and the like, an Application Function (AF) provides an IP address and a port number of a switched target EAS to core network equipment, the core network equipment configures a new FAR for user plane equipment according to the IP address and the port number of the target EAS, and only adds packet header information to an outward forwarded data packet at the user plane equipment on the premise of not changing the target IP accessed by the UE, and then forwards the packet header information to the new target IP, so that the non-perception switching of the EAS of the UE is realized.
The FAR is used to define an execution method for data on a user plane device, the execution of the data comprising at least one of:
a buffer (Buffered);
discard (Dropped);
forwarding (Forwarded).
The buffer is used for indicating the user plane equipment to buffer the data needing uplink transmission and suspend data transmission.
Wherein the forwarding is used to instruct the user plane device how to perform forwarding of data packets arriving, and forwarding the FAR includes: an Outer header creation (Outer header creation), where the Outer header creation is to instruct a user plane device to add header information to the outside of a current data packet, where the header information includes at least one of the following: IP + UDP (user datagram protocol) + GTP (GPRS tunneling protocol); VLAN tag (virtual local area network tag); IP + challenge UDP (possibly UDP).
Referring to fig. 1, an embodiment of the present application provides a data forwarding method, which is executed by a first communication device, and the method includes:
step 11: receiving a first FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
the first FAR, namely the forwarding FAR introduced in the above, is used to instruct the user plane device how to perform forwarding of upstream data on the arriving data packet.
In this embodiment, optionally, the first communication device is a User Plane Function (UPF), a protocol data unit session anchor (PDU session anchor, PSA), an Uplink Classifier (UL CL), or a branch Point (Branching Point, BP). Among them, BP is consistent with the function of UL CL, and is generally used in the scenario of IPV 6. The PSA may be a local PSA. The first communication device may also be referred to collectively as a user plane device.
In the embodiment of the application, if the user plane device does not need to be switched in the EAS switching process, the first communication device is a source user plane device, and if the user plane device needs to be switched in the EAS switching process, the first communication device is a target user plane device after switching.
The first FAR may be transmitted by the second communication device. Herein, the second communication device may be a core network device, for example, a Session Management Function (SMF).
Step 12: executing the first FAR if a first condition is met, the first condition including at least one of:
receiving a first indication for indicating execution of the first FAR;
receiving a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
receiving a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
the first FAR is different from the FAR currently used.
The first indication, the second indication and/or the third indication may be sent by the core network device.
In this embodiment of the present application, the first FAR is executed, that is, the first FAR is used to replace or update an old FAR, where the old FAR may be a forwarding FAR or a cache FAR.
In the embodiment of the application, the opportunity of forwarding the behavior rule and the opportunity of data forwarding in the process of replacing the EAS IP address are determined, that is, the opportunity of executing the first FAR is determined through the indication of the core network device, and the core network device can issue the indication after the EAS switching is completed or issue the indication after the EAS switching is completed and no data sent to the old EAS exists, so that the problems of service discontinuity and data packet loss caused by the EAS switching can be effectively solved.
In this embodiment of the application, optionally, please refer to fig. 2, before executing the first FAR, the method further includes:
step 101: receiving a second FAR, wherein the second FAR is used for indicating to cache uplink data;
the second FAR, namely the buffer (Buffered) FAR introduced in the foregoing, is used to instruct the user plane device to buffer the uplink data.
In this embodiment, optionally, the second FAR is sent by the core network device.
Step 102: performing, in accordance with the second FAR, at least one of:
stopping sending the uplink data;
caching uplink data;
an end-marker and/or a flow-end-marker is sent.
Wherein, optionally, the end-of-stream flag is sent to the old EAS to indicate that the forwarding of the old EAS upstream data has ended.
And if the user plane equipment is also switched in the EAS switching process, sending an end mark to the switched target user plane equipment to indicate that the data forwarded by the target user plane equipment from the source user plane equipment before switching to the target user plane equipment is ended.
In the embodiment of the application, before the EAS handover is completed, the core network device may first send the second FAR to the user plane device to instruct the user plane device to cache the uplink data, and not forward the uplink data to the new EAS until the EAS handover is completed, or the EAS handover is completed and there is no more data to be sent to the old EAS, so as to avoid data loss and effectively solve the problems of service discontinuity and data packet loss caused by the EAS handover.
Referring to fig. 3, an embodiment of the present application further provides a data forwarding method, which is executed by a second communication device, and the method includes:
step 31: receiving first information indicating that a handover of the EAS has been completed;
in this embodiment of the application, optionally, the first information may be: the Nsmf _ EventExposure _ applocationinfo is information, which is transmitted by an AF (application function) to the second communication device after the EAS completes the handover during the EAS handover, and may also be referred to as a late notification, to indicate that the handover of the EAS has been completed.
In this embodiment of the present application, the second communication device may be a core network device, and optionally, the second communication device is a Session Management Function (SMF).
In this application, the first information is optionally sent by an AF (application function) and/or a NEF (network open function).
Step 32: according to the first information, performing at least one of the following operations:
1) generating a first FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
in the embodiment of the present application, the operation of generating the first FAR may not be performed in step 32, and may be performed before step 32, for example, before the first information is received.
2) Transmitting the first FAR;
in the embodiment of the present application, the operation of sending the first FAR may not be performed in step 32, and may be performed before step 32, for example, before the first information is received.
3) Sending a first indication, wherein the first indication is used for indicating to execute a first FAR;
4) sending a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
5) sending a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
6) sending a fourth indication, the fourth indication indicating removal of the old FAR. The old FAR may be a cached FAR or a forwarded FAR.
In the embodiment of the application, the core network device indicates the opportunity to execute the first FAR, and the core network device may issue the indication after the EAS handover is completed, or issue the indication after the EAS handover is completed and there is no more data to be sent to the old EAS, so that the problems of service discontinuity and data packet loss caused by the EAS handover can be effectively solved.
In this embodiment of the application, optionally, please refer to fig. 4, before receiving the first information, the method further includes:
step 301: receiving second information, the second information comprising EAS IP address replacement information;
in this embodiment of the application, optionally, the second information is:
npcf _ SMPolicyControl _ UpdateNotify; or
Nsmf_EventExposure_AppRelocationInfo。
Wherein, the Nsmf _ EventExposure _ apprelocation info is sent by the AF to the second communication device after the EAS pre-handover is completed and/or the EAS handover information is prepared, and is used to provide the information of the target EAS, which may also be referred to as early notification.
In this embodiment of the present application, optionally, the EAS IP address replacement information includes at least one of:
a source EAS IP address;
a source EAS port number;
a destination EAS IP address;
the destination EAS port number.
Step 302: performing at least one of the following operations according to the EAS IP address replacement information:
generating a first FAR;
sending the first FAR;
sending the second FAR;
and sending a fifth instruction, wherein the fifth instruction is used for instructing to stop sending the uplink data.
In this embodiment, optionally, performing at least one of the following operations according to the EAS IP address replacement information includes:
performing one of the following operations based on the EAS IP address replacement information:
1) generating and sending the first FAR;
and the user plane equipment does not execute the first FAR when the first condition is not met, and executes the first FAR only when the first condition is met.
2) Generating the first FAR and transmitting after receiving the first information;
that is, the first FAR is generated but is not transmitted in step 302, and is transmitted in step 32 described above.
3) Generating the first FAR after receiving the first information.
That is, in step 302, the first FAR is not generated, but is generated in step 32 described above.
In this embodiment of the application, after receiving the first information, the method further includes:
if the source first communication device needs to be switched to the target first communication device in the EAS switching process, sending a third FAR to the source first communication device, wherein the third FAR is used for instructing to forward data from the source first communication device to the target first communication device through an N9 tunnel; the third FAR includes routing information for an N9 tunnel forwarding data from the source first communication device to the target first communication device, the target first communication device selected based on the EAS IP address replacement information in the received second information;
an N9 tunnel is established between the source first communication device and the target first communication device.
That is, before the EAS handover, data is routed from the source first communication device to the source EAS via the third FAR to modify the data routing to: data is forwarded from the source first communication device to the target first communication device via the N9 tunnel.
In this embodiment of the application, optionally, after receiving the first information, the method further includes:
if the source first communication device needs to be switched to the target first communication device in the EAS switching process, a sixth indication is sent to the source first communication device, the sixth indication is used for indicating the source first communication device to be released, and the target first communication device is selected according to the EAS IP address replacement information in the received second information.
The following describes the above data forwarding method according to the present application with reference to a specific scenario.
The first embodiment of the application: different EAS switching scenes under the same Data Network Access Identifier (DNAI)
Referring to fig. 5, a data forwarding method according to an embodiment of the present application includes:
step 1: the L-PSA (local PSA) performs an EAS IP address replacement, establishing an IP connection of the UE to the old target EAS;
the step 1 comprises the following steps:
Step 2: the AF detects EAS and requires load balance (load balance) and switches to the new EAS.
And step 3: the AF decides on potential target EAS and provides the SMF with information of EAS IP address replacement through a traffic initialization procedure (a procedure in which parameters provided by the AF affect core network routing). The EAS is not switched at this time.
And 4, step 4: the SMF, based on the EAS IP address replacement information provided by the AF, discovers that the L-PSA does not need to switch, and performs at least one of the following operations:
generating a first FAR;
sending the first FAR;
sending a second FAR, and instructing the L-PSA to cache all data sent to the upstream;
and sending a fifth instruction, wherein the fifth instruction is used for instructing the L-PSA to stop sending the upstream data.
The L-PSA is instructed to send an end-of-flow flag (flow end marker) to the old target EAS.
After the old target EAS receives the flow end marker, it knows that there is no more uplink data to it, and it is ready for switching.
And 5: the SMF sends Nsmf _ EventExposure _ Notify to the AF, or the SMF sends a notice to the AF via the NEF: and sending Nsmf _ EventExposure _ Notify to the NEF, and after receiving the NEF, sending Nnef _ TrafficiInfluency _ Notify to the AF. Notifying the EAS switch;
step 6: EAS handover and context migration, etc.
And 7: the AF sends to the SMF, or the AF sends this instruction to the SMF via the NEF, Nsmf _ EventExosure _ AppRescrocationInfo, which indicates that the EAS handoff has been completed.
And 8: after receiving the Nsmf _ EventExposure _ apprelocation info sent by the AF, the SMF performs at least one of the following operations after knowing that the EAS is switched over:
generating a first FAR; if step 4 is not generated, it is generated in step 8, if step 4 is already generated, it is not necessary to generate in step 8;
sending the first FAR to the L-PSA; if the step 4 is not transmitted, the step 8 is transmitted, and if the step 4 is transmitted, the step 8 is not required to be transmitted;
sending a first indication to the L-PSA, the first indication instructing the L-PSA to perform a first FAR;
sending a second indication to the L-PSA, wherein the second indication is used for indicating the L-PSA to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for indicating the buffer uplink data;
sending a third indication to the L-PSA, the third indication instructing the L-PSA to begin forwarding upstream data to the new target EAS;
sending a fourth indication to the L-PSA instructing the L-PSA to remove old FAR.
And step 9: the EAS IP address replacement process begins execution.
and step 9 b: UL traffic (Src IP: UE IP, Dst IP: New Target EAS IP), DL traffic (Src IP: New Target EAS IP, Dst IP: UE IP).
The second embodiment of the application: scenarios for different DNAI switching, L-PSA switching
Referring to fig. 6, a data forwarding method according to an embodiment of the present application includes:
step 1: L-PSA1 performs an EAS IP address replacement to establish the UE's IP connection to the old target EAS.
The step 1 comprises the following steps:
Step 2: the UE moves, and a 5GC (5G core network) senses the movement of the UE and determines that handover may be caused.
And step 3: the SMF sends Nsmf _ EventExposure _ Notify to the AF, or the SMF sends a notice to the AF via the NEF: and sending Nsmf _ EventExposure _ Notify to the NEF, and after receiving the NEF, sending Nnef _ TrafficiInfluency _ Notify to the AF. Informing the UE that the movement results in handover;
and 4, step 4: the AF determines the target DNAI and the new target EAS IP address based on the list of target DNAIs sent by the SMF.
And 5: the AF sends to SMF or the AF sends to SMF via NEF: and the Nsmf _ EventExporure _ AppRescrocationInfo contains EAS IP address replacement information.
Step 6: the SMF selects L-PSA2 based on EAS IP address replacement information sent by the AF, while the SMF performs at least one of the following:
generating a first FAR;
sending the first FAR to the L-PSA 2;
send a second FAR to L-PSA2, instructing L-PSA2 to cache all data sent upstream;
sending a fifth indication to the L-PSA2, the fifth indication to instruct the L-PSA2 to stop upstream data transmission.
In this step, the SMF may send the first FAR to the L-PSA2, but the execution condition is not satisfied at this time, and thus the first FAR cannot be executed.
And 7: SMF sends a third FAR to L-PSA1, then establishes an N9 tunnel between L-PSA1 and L-PSA 2; the third FAR is used for instructing the L-PSA1 to remove the old FAR (EAS IP address replacement corresponding FAR), and forwarding the received data, which the UE intends to the source EAS, from the L-PSA1 to the L-PSA2 through the N9 tunnel; the third FAR includes routing information for an N9 tunnel forwarding data from L-PSA1 to L-PSA 2;
and 8: SMF instructs UL CL to start sending data to L-PSA 2.
When the UL CL diverts data to the L-PSA2, the UL CL may generate an end marker and/or a flow end marker for transmission to the L-PSA2 and/or the old target EAS, respectively. The L-PSA2 knows that there is no more data to send from the L-PSA1 and the old target EAS knows that there is no more upstream data to send to it. This is the EAS switchable opportunity.
And step 9: the SMF sends Nsmf _ EventExposure _ Notify to the AF or through the NEF, and the switching can be performed after the preparation of the network plane is finished.
Step 10: EAS handover and context migration.
Step 11: the AF sends an Nsmf _ EventExposure _ AppReLocation Info to the SMF to indicate that the EAS migration is complete.
Step 12: after receiving the Nsmf _ EventExposure _ apprelocation info, the SMF performs at least one of the following operations;
generating a first FAR; if step 6 is not generated, it is generated in step 12, if step 6 is already generated, it is not necessary to generate in step 12;
sending the first FAR to the L-PSA 2; if step 6 is not sent, then it is sent in step 12, if step 6 is already sent, then it is not needed in step 12;
sending a first indication to the L-PSA2, the first indication to instruct the L-PSA2 to perform a first FAR;
sending a second indication to the L-PSA2, the second indication instructing the L-PSA2 to stop executing a second FAR, the second FAR instructing to cache upstream data;
sending a third indication to L-PSA2, the third indication instructing L-PSA2 to begin forwarding upstream data to the new target EAS;
sending a fourth indication to L-PSA2, the fourth indication to instruct L-PSA2 to remove old FAR.
Sending a sixth indication to the L-PSA1, the sixth indication indicating that the L-PSA1 was released.
Step 13: EAS IP address replacement is performed.
Step 13 comprises:
The third embodiment of the application: under different DNAI, scenarios of UL CL switching and L-PSA switching
Please refer to fig. 7
Step 1: L-PSA1 performs an EAS IP address replacement to establish the UE's IP connection to the old target EAS.
The step 1 comprises the following steps:
Step 2: the UE moves, and the 5GC (5G core network) senses the movement of the UE and determines that handover may be caused.
And step 3: the SMF sends Nsmf _ EventExposure _ Notify to the AF, or the SMF sends a notice to the AF via the NEF: and sending Nsmf _ EventExposure _ Notify to the NEF, and after receiving the NEF, sending Nnef _ TrafficiInfluency _ Notify to the AF. Informing the UE that the movement results in handover;
and 4, step 4: the AF determines the target DNAI and the new target EAS IP address based on the list of target DNAIs sent by the SMF.
And 5: the AF sends to the SMF or via the NEF Nsmf _ EventExosure _ AppRetationInfo, which contains EAS IP address replacement information.
Step 6: the SMF selects L-PSA2 and the target UL CL based on EAS IP address replacement information sent by the AF, while the SMF performs at least one of the following:
generating a first FAR;
sending the first FAR to the L-PSA 2;
send a second FAR to the L-PSA2 instructing the L-PSA2 to cache all data going upstream;
sending a fifth indication to the L-PSA2, the fifth indication to instruct the L-PSA2 to stop upstream data transmission.
In this step, the SMF may send the first FAR to the L-PSA2, but the execution condition is not satisfied at this time, and thus the first FAR cannot be executed.
And 7: SMF sends the third FAR to L-PSA1, sends the third FAR to source UL CL1, and then establishes an N9 tunnel between L-PSA1 and L-PSA2 and an N9 tunnel between the target UL CL to the source UL CL; the third FAR is used for instructing the L-PSA1 to remove the old FAR, and forwarding the received data, which the UE intends to the source EAS, from the L-PSA1 to the L-PSA2 through the N9 tunnel, and forwarding the data from the target UL CL to the source UL CL through the N9 tunnel; the third FAR includes routing information for the N9 tunnel forwarding data from L-PSA1 to L-PSA2, and routing information for the N9 tunnel forwarding data from the target UL CL to the source UL CL;
and 8: SMF indicates target UL CL and starts sending data to L-PSA 2.
When the target UL CL diverts data to L-PSA2, the target UL CL may generate an end marker and/or a flow end marker for L-PSA2 and/or old target EAS, respectively. The L-PSA2 knows that there is no more data to send from the L-PSA1 and the old target EAS knows that there is no more upstream data to send to it.
And step 9: the SMF sends an Nsmf _ EventExposure _ Notify to the AF or via the NEF, which indicates that the network plane is ready and can be switched.
Step 10: EAS handover and context migration.
Step 11: the AF sends Nsmf _ EventExposure _ AppReRecoverationInfo to the SMF or via the NEF to indicate that the EAS migration is complete.
Step 12: after receiving the Nsmf _ EventExposure _ apprelocation info, the SMF performs at least one of the following operations;
generating a first FAR; if step 6 is not generated, it is generated in step 12, if step 6 is already generated, it is not necessary to generate in step 12;
sending the first FAR to the L-PSA 2; if step 6 is not sent, then it is sent in step 12, if step 6 is already sent, then it is not needed in step 12;
sending a first indication to the L-PSA2, the first indication to instruct the L-PSA2 to perform a first FAR;
sending a second indication to L-PSA2, the second indication to instruct L-PSA2 to stop executing a second FAR, the second FAR to instruct buffering of upstream data;
sending a third indication to L-PSA2, the third indication instructing L-PSA2 to begin forwarding upstream data to the new target EAS;
sending a fourth indication to the L-PSA2, the fourth indication instructing the L-PSA2 to remove the old FAR.
Sending a sixth indication to the L-PSA1, the sixth indication indicating that the L-PSA1 was released.
Step 13: EAS IP address replacement is performed.
Step 13 comprises:
It should be noted that, in the data forwarding method provided in the embodiment of the present application, the execution main body may be a data forwarding apparatus, or a control module in the data forwarding apparatus for executing the data forwarding method. In the embodiment of the present application, data forwarding is performed by a data forwarding apparatus as an example, and the data forwarding apparatus provided in the embodiment of the present application is described.
Referring to fig. 8, an embodiment of the present application provides a data forwarding apparatus 81, including:
a first receiving module 81, configured to receive a first FAR, where the first FAR is used to instruct how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
a first executing module 82, configured to execute the first FAR if a first condition is met, where the first condition includes at least one of:
receiving a first indication for indicating execution of the first FAR;
receiving a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
receiving a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
the first FAR is different from the FAR currently used.
Optionally, the data forwarding apparatus further includes:
a second receiving module, configured to receive the second FAR;
a second execution module, configured to perform at least one of the following operations according to the second FAR:
stopping sending the uplink data;
caching uplink data;
send end marker and/or flow end marker.
The data forwarding device provided in the embodiment of the present application can implement each process implemented by the method embodiments in fig. 1 to fig. 2, and achieve the same technical effect, and is not described here again to avoid repetition.
Referring to fig. 9, an embodiment of the present application further provides a data forwarding apparatus 90, including:
a first receiving module, configured to receive first information, where the first information is used to indicate that an EAS handover has been completed;
a first executing module, configured to execute at least one of the following operations according to the first information:
generating a first FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
transmitting the first FAR;
sending a first indication, wherein the first indication is used for indicating to execute a first FAR;
sending a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
sending a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
sending a fourth indication, the fourth indication instructing removal of an old FAR.
Optionally, the first information is Nsmf _ EventExposure _ apprelocation info.
Optionally, the data forwarding apparatus further includes:
a second receiving module, configured to receive second information, where the second information includes EAS IP address replacement information;
a second execution module for executing at least one of the following operations according to the EAS IP address replacement information:
generating a first FAR;
sending the first FAR;
sending the second FAR;
and sending a fifth instruction, wherein the fifth instruction is used for instructing to stop sending the uplink data.
Optionally, the second execution module is configured to execute the following operations according to the EAS IP address replacement information:
generating and sending the first FAR;
or,
generating the first FAR and transmitting the first FAR after receiving the first information;
or
Generating the first FAR after receiving the first information.
Optionally, the second information is:
Npcf_SMPolicyControl_UpdateNotify
or
Nsmf_EventExposure_AppRelocationInfo。
Optionally, the EAS IP address replacement information includes at least one of:
a source EAS IP address;
a source EAS port number;
a destination EAS IP address;
the destination EAS port number.
Optionally, the data forwarding apparatus further includes:
a sending module, configured to send a third FAR to the source first communication device if it is required to switch from the source first communication device to the target first communication device in an EAS handover process, where the third FAR is used to instruct to forward data from the source first communication device to the target first communication device through an N9 tunnel; the third FAR includes routing information for an N9 tunnel forwarding data from the source first communication device to the target first communication device, the target first communication device selected based on the EAS IP address replacement information in the received second information;
an establishing module for establishing an N9 tunnel between the source first communication device and the target first communication device.
Optionally, the first executing module is further configured to send a sixth indication to the source first communication device if it is required to switch from the source first communication device to the target first communication device in the EAS switching process, where the sixth indication is used to indicate that the source first communication device is released, and the target first communication device is selected according to the EAS IP address replacement information in the received second information.
The data forwarding device provided in the embodiment of the present application can implement each process implemented by the method embodiments of fig. 3 to fig. 4, and achieve the same technical effect, and is not described here again to avoid repetition.
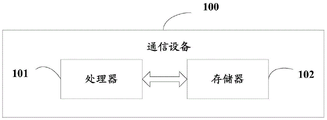
As shown in fig. 10, an embodiment of the present application further provides a communication device 100, which includes a processor 101, a memory 102, and a program or an instruction stored on the memory 102 and executable on the processor 101, for example, when the communication device 100 is a first communication device, the program or the instruction is executed by the processor 101 to implement the processes of the data forwarding method embodiment executed by the first communication device, and the same technical effect can be achieved. When the communication device 100 is a second communication device, the program or the instruction is executed by the processor 101 to implement the processes of the data forwarding method embodiment executed by the second communication device, and the same technical effect can be achieved, and for avoiding repetition, details are not described here again.
The embodiments of the present application further provide a readable storage medium, where a program or an instruction is stored, and when the program or the instruction is executed by a processor, the program or the instruction implements the processes of the foregoing data forwarding method embodiment, and can achieve the same technical effects, and in order to avoid repetition, details are not repeated here.
Wherein, the processor is the processor in the terminal described in the above embodiment. The readable storage medium includes a computer readable storage medium, such as a Read-Only Memory (ROM), a Random Access Memory (RAM), a magnetic disk or an optical disk, and so on.
The embodiment of the present application further provides a chip, where the chip includes a processor and a communication interface, the communication interface is coupled to the processor, and the processor is configured to run a network-side device program or an instruction, to implement each process of the foregoing data forwarding method embodiment, and can achieve the same technical effect, and in order to avoid repetition, details are not repeated here.
It should be understood that the chips mentioned in the embodiments of the present application may also be referred to as a system-on-chip, a system-on-chip or a system-on-chip, etc.
The embodiment of the present application further provides a program product, where the program product is stored in a non-volatile storage medium, and the program product is executed by at least one processor to implement each process of the foregoing data forwarding method embodiment, and can achieve the same technical effect, and in order to avoid repetition, details are not repeated here.
The embodiment of the present application further provides a program product, where the program product is stored in a non-volatile storage medium, and the program product is executed by at least one processor to implement each process of the foregoing data forwarding method embodiment, and can achieve the same technical effect, and in order to avoid repetition, details are not repeated here.
It should be noted that, in this document, the terms "comprises," "comprising," or any other variation thereof, are intended to cover a non-exclusive inclusion, such that a process, method, article, or apparatus that comprises a list of elements does not include only those elements but may include other elements not expressly listed or inherent to such process, method, article, or apparatus. Without further limitation, an element defined by the phrase "comprising an … …" does not exclude the presence of other like elements in a process, method, article, or apparatus that comprises the element. Further, it should be noted that the scope of the methods and apparatus of the embodiments of the present application is not limited to performing the functions in the order illustrated or discussed, but may include performing the functions in a substantially simultaneous manner or in a reverse order based on the functions involved, e.g., the methods described may be performed in an order different than that described, and various steps may be added, omitted, or combined. In addition, features described with reference to certain examples may be combined in other examples.
Through the above description of the embodiments, those skilled in the art will clearly understand that the method of the above embodiments can be implemented by software plus a necessary general hardware platform, and certainly can also be implemented by hardware, but in many cases, the former is a better implementation manner. Based on such understanding, the technical solutions of the present application may be embodied in the form of a software product, which is stored in a storage medium (such as ROM/RAM, magnetic disk, optical disk) and includes instructions for enabling a terminal (such as a mobile phone, a computer, a server, an air conditioner, or a network device) to execute the method according to the embodiments of the present application.
While the present embodiments have been described with reference to the accompanying drawings, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the precise embodiments described above, which are meant to be illustrative and not restrictive, and that various changes may be made therein by those skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims.
Claims (19)
1. A method of data forwarding, performed by a first communications device, the method comprising:
receiving a first forwarding table (FAR) as a rule FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
executing the first FAR if a first condition is met, the first condition including at least one of:
receiving a first indication for indicating execution of the first FAR;
receiving a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
receiving a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
the first FAR is different from the FAR currently used.
2. The method as recited in claim 1, wherein prior to executing the first FAR, further comprising:
receiving the second FAR;
performing, in accordance with the second FAR, at least one of:
stopping sending the uplink data;
caching uplink data;
an end-marker and/or an end-of-flow-marker is sent.
3. Method according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the first communication device is a user plane function, UPF, a protocol data unit, session anchor, PSA, an uplink classifier, UL CL, or a branch point, BP.
4. A method of data forwarding, performed by a second communications device, the method comprising:
receiving first information indicating that a handover of an edge application server EAS has been completed;
according to the first information, performing at least one of the following operations:
generating a first FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
transmitting the first FAR;
sending a first indication, wherein the first indication is used for indicating to execute a first FAR;
sending a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
sending a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
sending a fourth indication, the fourth indication indicating removal of the old FAR.
5. The method as claimed in claim 4, wherein the first information is Nsmf _ EventExposure _ apprelocation info.
6. The method of claim 4, wherein receiving the first information further comprises:
receiving second information, the second information comprising EAS IP address replacement information;
performing at least one of the following operations according to the EAS IP address replacement information:
generating a first FAR;
sending the first FAR;
sending the second FAR;
and sending a fifth instruction, wherein the fifth instruction is used for instructing to stop sending the uplink data.
7. The method of claim 6, wherein performing at least one of the following operations based on the EAS IP address replacement information comprises:
performing the following operations according to the EAS IP address replacement information:
generating and sending the first FAR;
or,
generating the first FAR and transmitting the first FAR after receiving the first information;
or alternatively
Generating the first FAR after receiving the first information.
8. The method of claim 6, wherein the second information is:
Npcf_SMPolicyControl_UpdateNotify
or
Nsmf_EventExposure_AppRelocationInfo。
9. The method of claim 6, wherein the EAS IP address replacement information comprises at least one of:
a source EAS IP address;
a source EAS port number;
a destination EAS IP address;
the destination EAS port number.
10. The method of claim 4, wherein receiving the first information further comprises:
if the source first communication device needs to be switched to the target first communication device in the EAS switching process, sending a third FAR to the source first communication device, wherein the third FAR is used for instructing to forward data from the source first communication device to the target first communication device through an N9 tunnel; the third FAR includes routing information for an N9 tunnel forwarding data from the source first communication device to the target first communication device, the target first communication device selected based on the EAS IP address replacement information in the received second information;
an N9 tunnel is established between the source first communication device and the target first communication device.
11. The method of claim 4, wherein receiving the first information further comprises:
if the source first communication device needs to be switched to the target first communication device in the EAS switching process, a sixth indication is sent to the source first communication device, the sixth indication is used for indicating the source first communication device to be released, and the target first communication device is selected according to the EAS IP address replacement information in the received second information.
12. The method according to any of claims 4 to 11, characterized in that the second communication device is a session management function, SMF.
13. A data forwarding apparatus, comprising:
a first receiving module, configured to receive a first FAR, where the first FAR is used to instruct how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
a first execution module, configured to execute the first FAR if a first condition is met, where the first condition includes at least one of:
receiving a first indication for indicating execution of the first FAR;
receiving a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
receiving a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
the first FAR is different from the FAR currently used.
14. The apparatus of claim 13, further comprising:
a second receiving module, configured to receive the second FAR;
a second execution module, configured to perform at least one of the following operations according to the second FAR:
stopping sending the uplink data;
caching uplink data;
send end marker and/or flow end marker.
15. A data forwarding apparatus, comprising:
a first receiving module, configured to receive first information, where the first information is used to indicate that a handover of EAS has been completed;
a first executing module, configured to execute at least one of the following operations according to the first information:
generating a first FAR, wherein the first FAR is used for indicating how to forward uplink data to an arriving data packet;
transmitting the first FAR;
sending a first indication, wherein the first indication is used for indicating to execute a first FAR;
sending a second instruction, wherein the second instruction is used for instructing to stop executing a second FAR, and the second FAR is used for instructing to cache uplink data;
sending a third instruction, wherein the third instruction is used for instructing to execute uplink data forwarding;
sending a fourth indication, the fourth indication indicating removal of the old FAR.
16. The apparatus of claim 15, further comprising:
a second receiving module, configured to receive second information, where the second information includes EAS IP address replacement information;
a second execution module for executing at least one of the following operations according to the EAS IP address replacement information:
generating a first FAR;
sending the first FAR;
sending the second FAR;
and sending a fifth instruction, wherein the fifth instruction is used for instructing to stop sending the uplink data.
17. The apparatus of claim 16,
the second execution module is configured to execute the following operations according to the EAS IP address replacement information:
generating and sending the first FAR;
or,
generating the first FAR and transmitting the first FAR after receiving the first information;
or
Generating the first FAR after receiving the first information.
18. A communication device comprising a processor, a memory and a program or instructions stored on the memory and executable on the processor, the program or instructions when executed by the processor implementing the steps of the data forwarding method of any one of claims 1 to 3; alternatively, the program or instructions, when executed by the processor, implement the steps of the data forwarding method of any one of claims 4 to 12.
19. A readable storage medium, characterized in that a program or instructions are stored thereon, which program or instructions, when executed by a processor, implement the data forwarding method of any one of claims 1 to 3, or the steps of the data forwarding method of any one of claims 4 to 12.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110164796.4A CN114885384A (en) | 2021-02-05 | 2021-02-05 | Data forwarding method and device and communication equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110164796.4A CN114885384A (en) | 2021-02-05 | 2021-02-05 | Data forwarding method and device and communication equipment |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114885384A true CN114885384A (en) | 2022-08-09 |
Family
ID=82667359
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110164796.4A Pending CN114885384A (en) | 2021-02-05 | 2021-02-05 | Data forwarding method and device and communication equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114885384A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116133159B (en) * | 2022-12-12 | 2023-11-21 | 湖南星网云信息科技有限公司 | GTP data packet processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060229896A1 (en) * | 2005-04-11 | 2006-10-12 | Howard Rosen | Match-based employment system and method |
| CN110139122A (en) * | 2013-04-06 | 2019-08-16 | 草谷加拿大公司 | System and method for media distribution and management |
| CN110679192A (en) * | 2017-06-23 | 2020-01-10 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method, equipment and system for realizing service continuity |
| CN111586670A (en) * | 2020-04-30 | 2020-08-25 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Method for realizing service continuity and related equipment |
| WO2020224556A1 (en) * | 2019-05-06 | 2020-11-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for managing routing rule and communication device |
| CN112135320A (en) * | 2019-06-24 | 2020-12-25 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for transmitting service message |
| WO2021016631A2 (en) * | 2019-11-08 | 2021-01-28 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for mobility management |
-
2021
- 2021-02-05 CN CN202110164796.4A patent/CN114885384A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060229896A1 (en) * | 2005-04-11 | 2006-10-12 | Howard Rosen | Match-based employment system and method |
| CN110139122A (en) * | 2013-04-06 | 2019-08-16 | 草谷加拿大公司 | System and method for media distribution and management |
| CN110679192A (en) * | 2017-06-23 | 2020-01-10 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method, equipment and system for realizing service continuity |
| WO2020224556A1 (en) * | 2019-05-06 | 2020-11-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for managing routing rule and communication device |
| CN112135320A (en) * | 2019-06-24 | 2020-12-25 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for transmitting service message |
| WO2021016631A2 (en) * | 2019-11-08 | 2021-01-28 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for mobility management |
| CN111586670A (en) * | 2020-04-30 | 2020-08-25 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Method for realizing service continuity and related equipment |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| APPLE: "S6-200498 "Correction and enhancements to the common information elements sent by the Application Client"", 3GPP TSG_SA\\WG6_MISSIONCRITICAL, no. 6, 3 April 2020 (2020-04-03) * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116133159B (en) * | 2022-12-12 | 2023-11-21 | 湖南星网云信息科技有限公司 | GTP data packet processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108738086B (en) | User plane reselection method and device | |
| CN109673024B (en) | Processing method, device and system of data transmission channel | |
| EP3949270B1 (en) | Local user plane function control | |
| EP4191951A1 (en) | Session processing method, apparatus, and system | |
| JP6910549B2 (en) | Transmission control methods, equipment, and systems | |
| US11589291B2 (en) | Big packet protocol mobility instructions for 5G handovers | |
| CN110650513B (en) | Method and device for updating user plane path and computer storage medium | |
| US10531274B2 (en) | Data processing method and device | |
| US10536457B2 (en) | User data processing apparatus and method, and system | |
| US9961045B2 (en) | Service path changing method and apparatus | |
| US8355382B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing WiMAX (worldwide interoperability for microwave access) anchor mode service on a system with distributed forwarding planes | |
| EP2850912B1 (en) | Efficient distribution of signaling messages in a mobility access gateway or local mobility anchor | |
| EP3909285A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for user plane resource selection for 5g core | |
| CN114650569A (en) | Method and device for data distribution in self-return IAB network and network side equipment | |
| CN114885384A (en) | Data forwarding method and device and communication equipment | |
| CN113543152A (en) | 5G communication system, data communication method, and non-volatile storage medium | |
| CN109644384B (en) | Network management method and controller | |
| CN110313195A (en) | Communication means and device | |
| CN104604294B (en) | A kind of data transmission method and equipment | |
| CN113259498A (en) | Local service distribution method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114006934B (en) | Data filtering method, medium and electronic equipment | |
| CN109327871B (en) | Communication method, network equipment and communication system | |
| WO2022028051A1 (en) | Session control method, apparatus, system, network element, and medium | |
| CN112449367B (en) | Data transmission method and core network equipment | |
| CN118509950A (en) | Method, device, medium and program product for switching transmission paths of PDU session |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |