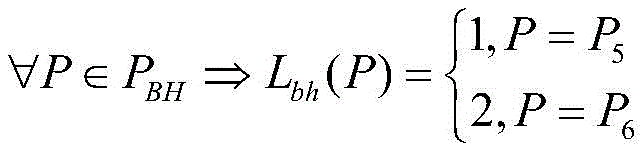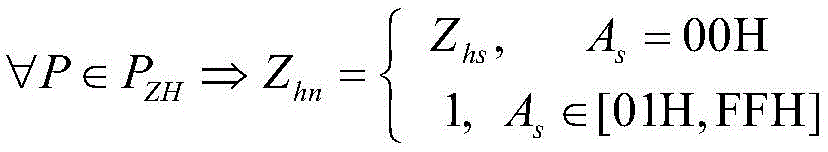CN114825607A - Attack behavior monitoring method and device for relay protection information processing system - Google Patents
Attack behavior monitoring method and device for relay protection information processing system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114825607A CN114825607A CN202111675512.4A CN202111675512A CN114825607A CN 114825607 A CN114825607 A CN 114825607A CN 202111675512 A CN202111675512 A CN 202111675512A CN 114825607 A CN114825607 A CN 114825607A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- message
- attack
- relay protection
- indicating
- judging
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000010365 information processing Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 81
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 53
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 148
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 114
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 38
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 34
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 claims description 33
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000008186 active pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000007405 data analysis Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013475 authorization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006854 communication Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007123 defense Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 2
- NAWXUBYGYWOOIX-SFHVURJKSA-N (2s)-2-[[4-[2-(2,4-diaminoquinazolin-6-yl)ethyl]benzoyl]amino]-4-methylidenepentanedioic acid Chemical compound C1=CC2=NC(N)=NC(N)=C2C=C1CCC1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(=C)C(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1 NAWXUBYGYWOOIX-SFHVURJKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010063385 Intellectualisation Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000010485 coping Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007619 statistical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J13/00—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network
- H02J13/00002—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network characterised by monitoring
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J13/00—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network
- H02J13/00006—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network characterised by information or instructions transport means between the monitoring, controlling or managing units and monitored, controlled or operated power network element or electrical equipment
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J13/00—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network
- H02J13/00006—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network characterised by information or instructions transport means between the monitoring, controlling or managing units and monitored, controlled or operated power network element or electrical equipment
- H02J13/00028—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network characterised by information or instructions transport means between the monitoring, controlling or managing units and monitored, controlled or operated power network element or electrical equipment involving the use of Internet protocols
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J13/00—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network
- H02J13/00032—Systems characterised by the controlled or operated power network elements or equipment, the power network elements or equipment not otherwise provided for
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J13/00—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network
- H02J13/00032—Systems characterised by the controlled or operated power network elements or equipment, the power network elements or equipment not otherwise provided for
- H02J13/00036—Systems characterised by the controlled or operated power network elements or equipment, the power network elements or equipment not otherwise provided for the elements or equipment being or involving switches, relays or circuit breakers
- H02J13/0004—Systems characterised by the controlled or operated power network elements or equipment, the power network elements or equipment not otherwise provided for the elements or equipment being or involving switches, relays or circuit breakers involved in a protection system
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/14—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for detecting or protecting against malicious traffic
- H04L63/1408—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for detecting or protecting against malicious traffic by monitoring network traffic
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a method and a device for monitoring attack behaviors of a relay protection information processing system, which are used for extracting application layer messages of flow data of the relay protection information processing system captured in real time and analyzing the flow data according to an IEC60870-5-103 protocol. And secondly, carrying out clock tampering attack detection on the message. And then carrying out abnormal message attack detection on the message format according to the protocol requirement. And finally, establishing normal behavior models of various system services, and carrying out attack behavior detection of an application layer on system flow data according to the normal behavior models. The method overcomes the defects that the existing method for detecting the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system focuses on data analysis of the measuring point of the relay protection device and lacks of detecting the attack behavior aiming at the message of the flow data application layer, and improves the accuracy of detecting the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of information security of power systems, in particular to a method and a device for monitoring attack behaviors of a relay protection information processing system.
Background
With the continuous improvement of the automation and dispatching automation level of the transformer substation, the informatization and intellectualization degrees of the power system are gradually enhanced. A relay protection information processing system composed of a relay protection device, a safety automatic device, and a fault recorder has become an important component of an electric power system. The relay protection information processing system can acquire the action information and the running state information of the relay protection device in real time, automatically and deeply analyze the action information of the protection device, and assist power dispatching personnel to quickly judge protection action behaviors, position faults, make decisions and process accidents. Therefore, reliable transmission and correct processing of relay protection information have important significance for safe and stable operation of the power system.
The relay protection information processing system adopts an IEC60870-5-103 protocol to transmit information, and due to the fact that the protocol is designed to have the fragility of lacking an authentication mechanism, lacking an authorization mechanism and lacking an encryption mechanism, the relay protection information processing system faces network attacks such as message stealing, interception, tampering and the like. However, the existing network attack detection method for the relay protection system focuses on data analysis of measurement points of the relay protection device, so that problems of false alarm, missing report and the like easily occur, and meanwhile, detection of attack behaviors on a message layer aiming at specific relay protection services is lacked. Therefore, it is urgently needed to invent a new method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system, so as to improve the accuracy of detecting the attack behavior and enhance the network security defense capability of the power system.
Disclosure of Invention
The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide a method and a device for monitoring the attack behavior of a relay protection information processing system aiming at the defects of the prior art, effectively solve the limitation that the prior detection method cannot detect the attack behavior of the relay protection system service in an application layer, and improve the safety and reliability of the relay protection information processing system.
In order to solve the technical problems, the technical scheme adopted by the invention is as follows: a method for monitoring attack behaviors of a relay protection information processing system comprises the following steps:
s1, capturing a relay protection information processing system flow data packet in real time, and extracting an application layer message of current frame flow data;
s2, performing field level analysis on the application layer message;
s3, performing clock tampering attack detection on the analyzed message, if the clock range, clock logic, clock synchronization and clock delay of the message do not accord with normal clock characteristics, judging that clock tampering attack exists, otherwise, entering S4;
s4, carrying out abnormal message attack detection on the analyzed message, if the length field, the type identification, the transmission reason, the information sequence number value and the protocol requirement of the message are not in accordance, judging that abnormal message attack exists, otherwise, entering the step S5;
and S5, according to the service system to which the analyzed message belongs, carrying out attack detection on the analyzed message, if the analyzed message is not in accordance with the normal service model, judging that service logic attack exists, otherwise, judging that the current frame flow data is normal flow.
The method analyzes the message of the application layer of the flow data of the relay protection information processing system (analyzes the message according to IEC60870-5-103 protocol), and performs clock tampering attack detection, malformed message attack detection and service logic attack detection on the analyzed message, thereby effectively solving the limitation that the existing detection method cannot perform attack behavior detection on the application layer aiming at the service of the relay protection system, and improving the safety and reliability of the relay protection information processing system.
In step S3, the specific implementation process of performing clock tampering attack detection on the analyzed packet includes:
1) judgment formula Y t ∈[1970,2069]Whether the attack is established or not is judged, if not, the attack is judged to be clock tampering attack, and if not, the step 2) is carried out; wherein,Y t year, y, of the time scale t A year identification byte value representing a time stamp;
2) judgment formulaWhether the clock is true or not is judged, if not, the clock is judged to be attacked by tampering, otherwise, the step 3) is carried out; wherein,indicating a full-scale word "optional", P being the application layer message parsed in step S2, P DS Representing IEC60870-5-103 time tick messages, A g (P) represents the high 8-bit value of the ASDU address of the message, F represents 15 of 16-system, and H represents the value of 16-system;
3) judgment formulaWhether the clock is true or not is judged, if not, the clock is judged to be attacked by tampering, otherwise, the step 4) is carried out; wherein, P DZ Represents one of IEC60870-5-103 alarm, remote signaling deflection and action event data uploading message, T js (P) represents the event substation reception time, T sj (P) represents an actual occurrence time of the event;
4) detecting whether the time period for sending the historical fault information by the substation is consistent with the time period for calling the fault historical information by the main station, if the time periods are not consistent, determining that the clock is tampered and attacked, and if not, entering the step 5);
5) judgment formulaWhether the clock is true or not is judged, if not, the clock is judged to be clock tampering attack, and if not, the step S4 is carried out; wherein,P XC indicating IEC60870-5-103 main-substation information transfer message, T cs (P) denotes an information transfer time, T max Denotes the maximum delay time, P 1 Indicating relay protectionProtect device action information transfer message, P 2 Message, P, representing the transmission of analog measurement values of a relay protection device 3 Transmitting messages, P, indicating the operating state of the protective relaying device 4 And indicating the relay protection device to transmit a message according to the fixed value.
The invention can identify the attack behavior aiming at the clock characteristics such as clock range, clock logic, clock synchronization, clock delay and the like by carrying out clock tampering attack detection on the flow data of the relay protection information processing system, and overcomes the defect that the conventional detection method focuses on the numerical analysis of time scales and cannot carry out abnormal detection aiming at the characteristics such as the time scale logic and the like. The clock tampering attack detection effectively avoids the occurrence of abnormal working conditions of various relay protection devices caused by clock abnormity, and simultaneously can prevent attackers from maliciously expanding the time range of information uploading and illegally acquiring system information, thereby improving the capability of the relay protection information processing system for coping with non-numerical time scale tampering attack.
The specific implementation process of carrying out the malformed message attack detection on the analyzed message comprises the following steps:
I) judgment formulaWhether the abnormal message attack is established or not is judged, if not, the abnormal message attack is judged, and if not, the step II) is carried out; wherein, P IEC103 Representing IEC60870-5-103 message, F l (P) represents the theoretical length of the message, L s (P) representing the actual length of the message;
II) judgment formulaWhether the abnormal message attack is established or not is judged, if not, the abnormal message attack is judged, and if not, the step III) is carried out;
III) judgment formulaWhether the abnormal message attack is established or not is judged, if not, the abnormal message attack is judged, and if not, the step IV is carried out); wherein, F t (P) indicating a message type identification field value;
IV) judgmentFormula (II)Whether the abnormal message attack is established or not is judged, if not, the abnormal message attack is judged, and if not, the step V) is carried out; wherein, F c (P) a value representing a message transmission reason field;
v) judgment formulaIf not, determining that the malformed message is attacked, otherwise, entering step S5; f i (P) represents a message information sequence number field value.
The abnormal message attack detection process can identify the abnormal message under the condition of correct message format, including message length abnormality, message field threshold abnormality and the like, and overcomes the limitation that the existing method can only carry out validity check on the message format. Meanwhile, the abnormal message attack detection finds the abnormal part of the specific service before the specific service to which the message belongs is not executed, so that the abnormal message attack detection quickly reacts to a dispatching center, reestablishes the communication process of the service in the relay protection information processing system, and sends a normal service message, thereby avoiding the abnormal message after being executed from influencing the execution process of the normal service.
In step S5, when the message configures a service for the reader substation, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed message includes:
judgment formulaWhether the configuration data are established or not is judged, if not, the configuration data malicious interception attack exists, otherwise, a formula is judgedIf not, judging that data tampering attack exists, otherwise, judging that the current frame traffic data is normal traffic; wherein, P BT Indicating a reading substation configuration service message in a relay protection information processing system, B n (P) number of titles sent on substation, B s Representing station configurationWith number of titles, B zh (P) group number, C, of each entry representing the same group of header information zh A group number indicating the current group header information.
The reading substation configuration service logic attack behavior detection can realize the detection of whether the configuration information is completely uploaded and whether the items and the group numbers of the configuration information are consistent. The complete uploading of the configuration information and the consistency of the items and the group numbers are the premise of guaranteeing the normal operation of the relay protection device, the detection method overcomes the defects that the existing detection method for the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system focuses on data analysis of a measurement point of the relay protection device and lacks of detection for the attack behavior aiming at the service logic of a flow data application layer message, and effectively avoids the risk of interception and falsification of the configuration information.
In step S5, when the packet is a protection event upload service, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed packet includes:
A) judgment formulaWhether the two-point information is established or not is judged, if not, the two-point information malicious tampering attack is judged, and if not, the step B) is carried out; wherein, P BH Presentation of protection events in a relay protection information processing system, message D pi (P) represents a two-point information value;
B) detecting whether the switching value displacement, the action signal and the message logic of the front frame and the rear frame of the pressing plate state are correct or not, and if the front frame of the switching value displacement is opened/closed, the rear frame is still opened/closed; the former frame of the action signal is reset/action, and the latter frame is still reset/action; if the former frame of the pressing plate state is not input/input and the latter frame is still not input/input, judging that malicious opening and closing attack exists, otherwise, entering the step C);
C) judgment formulaIf not, judging that the illegal uploading attack of the action event exists, otherwise, judging the current frame flow data as normal flow; wherein L is bh (P) represents protectionEvent message type identification, P 5 Message indicating an alarm or a switching value change event, P 6 Representing an action event message.
The protection event uploading service logic attack behavior detection can realize malicious tampering attack detection and illegal uploading attack detection of various protection events in the relay protection information processing system. The service logic attack behavior of the protection event can be highly hidden in normal flow data, and the high-energy stealth attack behavior is difficult to detect only by analyzing the data of the measurement point of the relay protection device in the conventional method. The invention further fuses the uploading service logic of the protection event in the message of the flow data application layer, thereby improving the accuracy of the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system.
In step S5, when the message is a wave recording presentation delivery service, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed message includes:
i) judgment formulaIf not, judging that the tripping phase malicious tampering attack exists, otherwise, entering a step ii); wherein, P LB Presentation of a message of a wave recording presentation service in a relay protection information processing system, G xb (P) represents the phase of failure, Z xb (P) indicates the phase of trip;
ii) judgment formulaWhether the ground fault flag bit data are true or not is judged, if not, the ground fault flag bit data tampering attack is judged, and if not, the step iii) is carried out; wherein D is 3 Indicating the value of the flag bit of the message short-circuit earth fault, D 0 Indicating the value of the flag bit of the short-circuit fault of the A phase of the message, D 1 Indicating the value of the short-circuit fault flag bit of the B-phase of the message, D 2 Representing the value of the flag bit of the short circuit fault of the C phase of the message;
and iii) detecting whether the reclosure in the recording brief report is abnormal, if the reclosure exists after the fault occurs and the reclosure time is 0 or the reclosure does not exist and is not 0, judging that tampering attack of the reclosure time exists, and otherwise, judging the current frame flow data to be normal flow.
The detection of the attack behavior of the wave recording brief report uploading service logic can judge the malicious tampering attack of a trip phase, the tampering attack of ground fault flag bit data and the tampering attack of reclosing time. Information of the recorded brief report uploading service such as trip phase, fault mark, reclosing time and the like needs to be extracted through field level deep analysis of a message of a flow data application layer of a relay protection information system, and the attack behavior cannot be identified only through format verification of the message. The attack behavior detection method provided by the invention overcomes the limitation that the existing detection method cannot detect the time sequence and the context logic of the wave recording brief report, and improves the capability of protecting the integrity and the accuracy of the wave recording brief report data.
In step S5, when the packet is a fixed-value operation service, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed packet includes:
judgment logic X g1 →X g2 →X g3 →X g4 →X g5 →X g6 →X g7 →X g8 Whether the current frame flow data are normal flow is judged, if not, whether malicious tampering attack of the relay protection device setting value exists is judged, and otherwise, the current frame flow data are judged to be normal flow; wherein, X g1 Message, X, indicating the current running fixed-value area code of the calling device g2 Message, X, indicating the current running fixed-value area code of the substation uploading device g3 Message, X, indicating the fixed value of the calling device of the Master station g4 Message, X, indicating the fixed value of the uploading means of the substation g5 Presentation substation downloading of definite value message, X g6 Message, X, indicating the value of the response substation g7 Indicating execution of a constant value modification message, X g8 The substation responds to the fixed value modification message.
The attack behavior detection of the fixed value operation service logic can judge the malicious tampering attack of the setting value of the relay protection device in the fixed value modification process according to the normal fixed value modification logic and actively block the attack behavior of the malicious tampering of the fixed value. The existing method for analyzing the data of the measurement point of the relay protection device can only detect the tampered fixed value and cannot monitor and block the modification of the fixed value in time. The method for detecting the logic attack behavior of the fixed value operation service provided by the invention is deep into an application layer of flow data, can effectively prevent the set value of the relay protection device from being maliciously tampered, and has important significance for the correct action of the relay protection device.
In step S5, when the packet is a total call service, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed packet includes:
judgment logic Z h1 →Z h2 →Z h3 If not, judging that the illegal general calling attack exists, otherwise, judging a formulaIf not, judging that the illegal general calling attack exists, otherwise, judging that the current frame traffic data is normal traffic; wherein Z is h1 Indicating the master station initiating a total call message, Z h2 Indicating information messages sent from substations Z h3 Indicating the end of the total call, P ZH Indicating a total call service of the relay protection information processing system, Z hn Indicating the number of messages sent on the substation, Z hs Indicating the number of devices in the substation, A s Indicating the address of the message ASDU and H indicating the value is 16.
The total calling service logic attack behavior detection can judge illegal total calling attacks according to the normal service logic of the total calling. The illegal total calling attack can combine the constructed total calling service message with the normal total calling service message in a tampering or injection mode, so as to illegally obtain data. The attack behavior cannot be identified only by the validity check of the message field and the consistency analysis of the telemetering data, and the attack behavior must be identified deeply to the service logic level of the message. The total calling service logic attack behavior detection provided by the invention can effectively identify the attack behavior aiming at the total calling service by detecting the logic and the range of the total calling service, and prevent redundant uploading and incomplete uploading of information.
In step S5, when the message is "ONThe specific implementation process of using the file transmission service to carry out attack detection on the analyzed message comprises the following steps: detecting whether the file name only contains a directory name and a wildcard character, if so, judging that the illegal file uploading attack exists, otherwise, judging a formulaIf not, judging that the file clock tampering attack exists, otherwise, judging that the current frame traffic data is normal traffic; wherein, P WJ Representing relay protection information processing system file list upload message, T lb (P) represents a file list upload time, C q Query start time, C, when representing a list of files z The query termination time when representing the list of files.
The universal file transmission service logic attack behavior detection can judge illegal file uploading attack and file clock tampering attack. Once the illegal file containing the attack code is uploaded to the master station, the master station loses the control authority; the file clock tampering attack is to tamper the time of the file uploading list, so that information is illegally stolen. The detection of the logic attack behavior of the universal file transmission service overcomes the limitation that the prior method focuses on the statistical analysis of network layer flow, and can effectively prevent the occurrence of the situations that an attacker crashes a main station and steals files due to uploading malicious file data or tampering with the files.
A computer apparatus comprising a memory, a processor and a computer program stored on the memory; the processor executes the computer program to implement the steps of the method of the present invention.
Compared with the prior art, the invention has the beneficial effects that:
(1) the invention provides a method for detecting the attack behavior of the message of the flow data application layer aiming at the network attack risks of message stealing, interception, tampering and the like faced by a relay protection information processing system, and overcomes the limitation that the existing attack detection method focuses on the analysis of the data of the measurement point of a relay protection device.
(2) The invention provides clock tampering attack and malformed message attack detection aiming at the flow data application layer message of the relay protection information processing system, and overcomes the defects that the IEC60870-5-103 protocol lacks an authentication mechanism, lacks an authorization mechanism and lacks an encryption mechanism.
(3) According to the method and the device, the power service normal behavior model is established according to the service characteristics of the relay protection information processing system, the attack behavior detection is carried out on the application layer message of the flow data, the active defense of the attack behavior of the flow data of the relay protection information processing system on the application layer is realized, and the safety of information transmission of the service system is improved.
Drawings
Fig. 1 is a flowchart of a method for monitoring an attack behavior of a relay protection information processing system in an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of an attack behavior monitoring system of a relay protection information processing system in the embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 3 is a system unit diagram of a clock tampering attack detection module in the embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 4 is a system unit diagram of a malformed message attack detection module in an embodiment of the invention.
Fig. 5 is a system unit diagram of a service logic attack detection module in the embodiment of the present invention.
Detailed Description
Fig. 1 is a flowchart of a method for monitoring an attack behavior of a relay protection information processing system according to an embodiment of the present invention, and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
step S1: capturing a flow data packet of a relay protection information processing system in real time, and extracting an application layer message of current frame flow data;
step S2: performing field level analysis on the message according to an IEC60870-5-103 protocol, acquiring specific numerical values and clock characteristics of a message length field, a type identifier, a transmission reason and an information sequence number, and determining a system service to which the message belongs;
step S3: performing clock tampering attack detection on the message analyzed in the step S2, if the clock range, clock logic, clock synchronization and clock delay of the message do not accord with normal clock characteristics, judging that clock tampering attack exists, otherwise, entering the step S4;
step S4: carrying out abnormal message attack detection on the message analyzed in the step S2, if the length field, the type identifier, the transmission reason, the information sequence number value and the protocol requirement of the message are not in accordance, judging that abnormal message attack exists, otherwise, entering the step S5;
step S5: and establishing a normal behavior model according to the system service to which the message belongs, carrying out attack detection on the message according to the normal behavior model, judging that service logic attack exists if the message does not conform to the normal service model, and otherwise, judging the current frame flow data as normal flow.
Further, step S3 includes:
s3-1: and detecting whether the time mark year of the message is in a normal range, if the time mark year exceeds the limit, namely, the clock is violated (1), judging that the clock is tampered and attacked, and if not, entering the step S3-2.
Y t ∈[1970,2069] (1)
Wherein, Y t Year, y, of the time scale t The year identification byte value representing the time stamp.
S3-2: and detecting whether the time tick message is broadcast time tick. The master station issues a broadcast time tick command, and when time tick is performed on all devices, the upper 8 bits of the public address (ASDU address for short) of the application service data unit of the message at this time are FFH, which indicates that broadcast is performed on all devices in the substation, if the broadcast violates the form (3), the attack is determined to be clock tampering attack, otherwise, the step S3-3 is performed.
Wherein,meaning the full term "arbitrary", P is the application layer message analyzed in step S2, P DS Representing IEC60870-5-103 time tick messages, A g (P) represents the upper 8-bit value of the ASDU address of the message, F represents 15 in 16-system, and H represents the value in 16-system.
S3-3: and detecting whether the logic of the actual occurrence time of the alarm, the remote signaling deflection and the action event and the receiving time of the substation is correct or not. The relay protection device records the actual occurrence time of the event after the alarm, the remote signaling deflection and the action event occur, and the substation receives the fault information with a certain delay, so that the receiving time of the substation is always greater than the actual occurrence time, if the fault is contrary to the form (4), the clock tampering attack is determined, and otherwise, the step S3-4 is carried out.
Wherein, P DZ Represents one of IEC60870-5-103 alarm, remote signaling deflection and action event data uploading message, T js (P) represents the event substation reception time, T sj (P) represents the actual time of occurrence of the event.
S3-4: and detecting whether the time period for sending the historical fault information by the substation is consistent with the time period for calling the fault historical information by the main station, if the time periods are not consistent, determining that the clock is tampered and attacked, and otherwise, entering the step S3-5.
S3-5: it is detected whether the master-slave station information transfer is timed out. If the information transmission time exceeds the maximum delay time required by the specifications, i.e., the equation (5) is violated, it is determined as a clock tampering attack, otherwise, the process proceeds to step S4.
Wherein, P XC Indicating IEC60870-5-103 main-substation information transfer message, T cs (P)Indicating the time of information transfer, T max Denotes the maximum delay time, P 1 Message, P, indicating relay protection device action information transfer 2 Message, P, representing the transmission of analog measurement values of a relay protection device 3 Transmitting messages, P, indicating the operating state of the protective relaying device 4 And indicating the relay protection device to transmit a message according to the fixed value.
Further, step S4 includes:
s4-1: and (4) aiming at the message analyzed in the step (S2), detecting whether the theoretical length and the actual length of the message calculated by the length field are equal, if not, violating the formula (7), judging that the message is a malformed message attack, otherwise, entering the step (S4-2).
Wherein, P IEC103 Representing IEC60870-5-103 message, F l (P) represents the theoretical length of the message, L s (P) represents the actual length of the message.
S4-2: and detecting whether the actual length of the message is greater than 2048 bytes or not, if so, violating the formula (8), judging that the message is in a malformed message attack, and otherwise, entering the step S4-3.
S4-3: and detecting whether the type identification field value of the message is valid, if the type identification field value of the message is invalid, namely violating the formula (9), judging that the message is attacked by the malformed message, and otherwise, entering the step S4-4.
Wherein, F t (P) represents a message type identification field value.
S4-4: and detecting whether the value of the transmission reason field of the message is valid, if the value is invalid, namely violating the formula (10), judging that the message is attacked by the malformed message, and otherwise, entering the step S4-5.
Wherein, F c (P) represents a message transfer reason field value.
S4-5: and detecting whether the information sequence number field value of the message is valid, if the information sequence number field value of the message is invalid, namely violating the formula (11), judging that the message is attacked in a malformed state, and if not, entering the step S5.
Wherein, F i (P) represents a message information sequence number field value.
Further, step S5 includes:
s5-1: classifying and detecting the attack behavior aiming at the service to which the message obtained in the step S2 belongs, and entering the step S5-2 if the message is a reading substation configuration service; if the message is a protection event uploading service, the step S5-3 is carried out; if the message is a recording brief report uploading service, the step S5-4 is carried out; if the message is a fixed value operation service, the step S5-5 is carried out; if the message is the total calling service, the step S5-6 is carried out; if the message is a general file transmission service, the step S5-7 is carried out;
s5-2: analyzing the normal logic of the configuration service of the reading substation according to the technical specification of the relay protection information processing system, establishing a normal behavior model of the configuration service of the reading substation based on the normal service logic, detecting the attack behavior of the flow data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, judging that the logic attack of the configuration service of the reading substation exists if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, and otherwise, judging the flow data of the current frame as the normal flow.
S5-3: analyzing the normal logic of the protection event uploading service according to the technical specification of the relay protection information processing system, establishing a normal behavior model of the protection event uploading service based on the normal service logic, carrying out attack behavior detection on the traffic data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, judging that the protection event uploading service logic attack exists if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, and otherwise, judging the current frame traffic data as normal traffic.
S5-4: analyzing the normal logic of the wave recording brief report uploading service according to the technical specification of the relay protection information processing system, establishing a normal behavior model of the wave recording brief report uploading service based on the normal service logic, carrying out attack behavior detection on the flow data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, judging that the wave recording brief report uploading service logic attack exists if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, and otherwise, judging the current frame flow data as the normal flow.
S5-5: analyzing the normal logic of the constant value operation service according to the technical specification of the relay protection information processing system, establishing a normal behavior model of the constant value operation service based on the normal service logic, detecting the attack behavior of the traffic data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, judging that the constant value operation service logic attack exists if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, and otherwise, judging the current frame traffic data as the normal traffic.
S5-6: analyzing the normal logic of the total calling service according to the technical specification of the relay protection information processing system, establishing a normal behavior model of the total calling service based on the normal service logic, detecting the attack behavior of the flow data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, judging that the total calling service logic attack exists if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, and otherwise, judging the current frame flow data as normal flow.
S5-7: analyzing the normal logic of the general file transmission service according to the technical specification of the relay protection information processing system, establishing a normal behavior model of the general file transmission service based on the normal service logic, detecting the attack behavior of the traffic data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, judging that the general file transmission service logic attack exists if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, and otherwise, judging the current frame traffic data as normal traffic.
Further, step S5-2 includes:
s5-2-1: and detecting whether the number of the titles sent by the substation is complete when the relay protection information processing system reads each set of titles configured by the substation, if the number of the titles is incomplete, namely violating the formula (12), judging that malicious interception attack of the configuration data exists, and otherwise, entering the step S5-2-2.
Wherein, P BT Indicating a reading substation configuration service message in a relay protection information processing system, B n (P) number of titles sent on substation, B s Indicating the number of all titles of the substation configuration.
S5-2-2: and detecting whether the group numbers of all the items of the same group of header information are consistent, if not, violating the formula (13), judging that data tampering attack exists, otherwise, judging the current frame traffic data as normal traffic.
Wherein, B zh (P) group number, C, of each entry representing the same group of header information zh A group number indicating the current group header information.
Further, step S5-3 includes:
s5-3-1: and detecting whether the two-point information uploading of the protection event is abnormal, if the two-point information state is not in a specified range, namely violating the formula (14), judging that the two-point information malicious tampering attack exists, and otherwise, entering the step S5-3-2.
Wherein, P BH Indicating protection events in a relay protection information processing systemSending messages on the part, D pi (P) represents a two-point information value.
S5-3-2: detecting whether the switching value displacement, the action signal and the message logic of the front frame and the rear frame of the pressing plate state are correct or not, and if the front frame of the switching value displacement is opened/closed, the rear frame is still opened/closed; the former frame of the action signal is reset/action, and the latter frame is still reset/action; and if the former frame of the pressing plate state is not input/input and the latter frame is not input/input, judging that malicious opening and closing attacks exist, and otherwise, entering the step S5-3-3.
S5-3-3: and detecting whether the type identifier adopted by the protection event uploading is correct, wherein the alarm and the switching value displacement event can only be uploaded by adopting the type identifier 1, the action event can only be uploaded by adopting the type identifier 2, if the formula (15) is violated, judging that the action event is illegally uploaded, and otherwise, judging the current frame flow data as normal flow.
Wherein L is bh (P) indicates protection event message type identification, P 5 Message indicating an alarm or a switching value change event, P 6 Representing an action event message.
Further, step S5-4 includes:
s5-4-1: and detecting whether the fault phase in the wave recording brief report is consistent with the trip phase, if not, violating the formula (16), judging that the trip phase is maliciously tampered with, and otherwise, entering the step S5-4-2.
Wherein, P LB Presentation of a message of a wave recording presentation service in a relay protection information processing system, G xb (P) represents the phase of failure, Z xb (P) represents the phase of tripping.
S5-4-2: and detecting whether the short circuit ground fault flag bit in the wave recording brief report is correct, if not, violating the formula (17), judging that the ground fault flag bit data is tampered and attacked, and otherwise, entering the step S5-4-3.
Wherein D is 3 Indicating the value of the flag bit of the message short-circuit earth fault, D 0 Indicating the value of the flag bit of the short-circuit fault of the A phase of the message, D 1 Indicating the value of the short-circuit fault flag bit of the B-phase of the message, D 2 And the value of the flag bit of the short circuit fault of the C phase of the message is represented.
S5-4-3: and detecting whether the reclosing in the recording brief report is abnormal or not. If reclosing exists after the fault occurs, but the reclosing time is 0 or not, but the reclosing time is not 0, judging that tampering attack of the reclosing time exists, and otherwise, judging the current frame flow data to be normal flow.
Further, step S5-5 includes:
s5-5-1: and detecting whether the relay protection device setting value modification logic is correct or not, if the logic is wrong, namely violating a formula (18), judging that the relay protection device setting value malicious tampering attack exists, and otherwise, judging the current frame flow data as normal flow.
X g1 →X g2 →X g3 →X g4 →X g5 →X g6 →X g7 →X g8 (18)
Wherein, X g1 Message, X, indicating the current running fixed-value area code of the calling device g2 Message, X, indicating the current running fixed-value area code of the substation uploading device g3 Message, X, indicating the fixed value of the calling device of the Master station g4 Message, X, indicating the fixed value of the uploading means of the substation g5 Presentation substation downloading of definite value message, X g6 Message, X, indicating the value of the response substation g7 Indicating execution of a constant value modification message, X g8 The substation responds to the fixed value modification message.
Further, step S5-6 includes:
s5-6-1: and (4) detecting whether the total summoned service flow is abnormal, if the actual total summoned service flow is not consistent with the normal flow, namely violating a formula (19), judging that an illegal total summoning attack exists, and otherwise, entering a step S5-6-2.
Z h1 →Z h2 →Z h3 (19)
Wherein Z is h1 Indicating the master station initiating a total call message, Z h2 Indicating information messages sent from substations Z h3 Indicating a total call completion message.
S5-6-2: and detecting whether the number of the information sent by the substation is correct. After receiving the total calling command of the master station, the substation replies specified information according to the ASDU address in the message, and replies switching value information of a specific device when the ASDU address is not equal to zero; the communication status of each device of the slave station and the operation status of each device are answered when the ASDU address equals zero. And if the formula (20) is violated, judging that the illegal total calling attack exists, and otherwise, judging the current frame traffic data as normal traffic.
Wherein, P ZH Z representing the total call service of the relay protection information processing system hn Indicating the number of messages sent on the substation, Z hs Indicating the number of devices in the substation, A s Indicating the address of the message ASDU and H indicating the value is 16.
Further, step S5-7 includes:
s5-7-1: and detecting whether the file name only contains a directory name and a wildcard character (.
S5-7-2: and detecting whether the file list uploading is within the query time range. When the master station calls the file list, query starting time and query ending time are given, the file list uploaded by the substation needs to be within the time range, if the query starting time and the query ending time exceed the time range, namely the query ending time violates a formula (21), file clock tampering attack is judged to exist, and otherwise, the current frame flow data is judged to be normal flow.
Wherein, P WJ Representing relay protection information processing system file list upload message, T lb (P) represents a file list upload time, C q Query start time, C, when representing a list of files z The query termination time when representing the list of files.
The method depends on the flow data of a mass relay protection information processing system, extracts the application layer message of the flow data and analyzes the message according to the IEC60870-5-103 protocol to obtain the specific numerical value of the message characteristic field and the system service to which the message belongs. And secondly, performing clock tampering attack detection and malformed message attack detection according to the specific numerical value of the message characteristic field. And finally, establishing a normal service model according to the specific system service to which the message belongs, and carrying out service logic attack detection according to the normal service model, thereby realizing comprehensive monitoring of the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system and ensuring safe and reliable operation of the power system.
Fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for monitoring an attack behavior of a relay protection information processing system according to an embodiment of the present invention, where the system is adapted to execute a method according to any embodiment of the present invention, and the method includes: the system comprises a flow data acquisition module 100, an application layer message analysis module 200, a clock tampering attack detection module 300, a malformed message attack detection module 400 and a service logic attack detection module 500.
The flow data acquisition module 100 is configured to acquire flow data of the relay protection information processing system and extract an application layer message.
The application layer message analysis module 200 is configured to perform field level analysis on an application layer message according to an IEC60870-5-103 protocol, and acquire a specific relay protection service represented by the message.
The clock tampering attack detection module 300 is configured to detect a clock range, clock logic, clock synchronization, and clock delay of a packet, and determine whether a clock tampering attack exists.
The malformed message attack detection module 400 is configured to verify a message format according to a protocol requirement, and determine whether a malformed message attack exists.
The service logic attack detection module 500 is configured to establish a normal behavior model for a system service to which a packet belongs, perform detection according to the normal behavior model, and determine whether a service logic attack exists.
The output end of the flow data obtaining module 100 is connected to the input end of the application layer message parsing module 200, and is configured to input the extracted application layer message.
The output end of the application layer message analysis module 200 is connected to the input end of the clock tampering attack detection module 300, and is used for inputting application layer messages and analysis results thereof.
The output end of the clock tampering attack detection module 300 is connected to the input end of the malformed message attack detection module 400, and is used for inputting application layer messages and analysis results thereof.
The output end of the malformed message attack detection module 400 is connected to the input end of the service logic attack detection module 500, and is used for inputting application layer messages and analysis results thereof.
As shown in fig. 3, further, the clock tampering attack detecting module 300 includes: a data acquisition unit 301, a first detection unit 302, a second detection unit 303, a third detection unit 304, a fourth detection unit 305, and a fifth detection unit 306.
The output end of the data obtaining unit 301 is connected to the input end of the first detecting unit 302, and is used for inputting an application layer message and an analysis result thereof.
The output end of the first detection unit 302 is connected to the input end of the second detection unit 303, the output end of the second detection unit 303 is connected to the input end of the third detection unit 304, the output end of the third detection unit 304 is connected to the input end of the fourth detection unit 305, and the output end of the fourth detection unit 305 is connected to the input end of the fifth detection unit 306.
In one embodiment, the data obtaining unit 301 reads an application layer packet of the traffic data and an analysis result thereof, and transfers the read information to the first detecting unit 302, the second detecting unit 303, the third detecting unit 304, the fourth detecting unit 305, and the fifth detecting unit 306.
The first detecting unit 302 is configured to detect whether a time scale year of the packet is within a normal range, and determine that the clock tampering attack occurs if the time scale year is out of limit.
The second detecting unit 303 is configured to detect whether the time tick message is broadcast time tick, and if not, determine that the time tick message is a clock tampering attack.
The third detecting unit 304 is configured to detect whether the actual occurrence time and the substation receiving time in the alarm, the remote signaling displacement, and the action event data are logically correct, and if not, determine that the clock tampering attack is performed.
The fourth detecting unit 305 is configured to detect whether a time period for sending the historical failure information by the substation is consistent with a time period for calling the failure by the master station, and if not, determine that the clock tampering attack is performed.
The fifth detecting unit 306 is configured to determine whether the master-slave station information transmission is overtime, and if yes, determine that the clock tampering attack is performed.
As shown in fig. 4, further, the malformed message attack detection module 400 includes: a data acquisition unit 401, a message length field detection unit 402, a message length threshold detection unit 403, a type identification field detection unit 404, a transmission reason field detection unit 405, and an information sequence number field detection unit 406.
The output end of the data obtaining unit 401 is connected to the input end of the message length field detecting unit 402, and is used for inputting an application layer message and an analysis result thereof.
The output end of the message length field detection unit 402 is connected to the input end of the message length threshold detection unit 403, the output end of the message length threshold detection unit 403 is connected to the input end of the type identifier field detection unit 404, the output end of the type identifier field detection unit 404 is connected to the input end of the transmission reason field detection unit 405, and the output end of the transmission reason field detection unit 405 is connected to the input end of the information sequence number field detection unit 406.
In an embodiment, the data obtaining unit 401 reads the traffic data application layer packet and the parsing result thereof, and the unit transfers the read information to the packet length field detecting unit 402, the packet length threshold detecting unit 403, the type identifier field detecting unit 404, the transfer reason field detecting unit 405, and the information sequence number field detecting unit 406.
The message length field detection unit 402 is configured to detect whether the theoretical length of the message calculated by the length field is equal to the actual length, and if not, determine that the message is an abnormal message attack.
The message length threshold detection unit 403 is configured to detect whether the actual length of the message is greater than 2048 bytes, and if so, determine that the message is an abnormal message attack.
The type identifier field detecting unit 404 is configured to detect whether the type identifier field value of the packet is valid, and if the type identifier field value of the packet is invalid, determine that the malformed packet attacks.
The transmission reason field detection unit 405 is configured to detect whether a transmission reason field value of the packet is valid, and if the transmission reason field value of the packet is invalid, determine that the malformed packet attacks.
The information sequence number field detecting unit 406 is configured to detect whether the information sequence number field value of the packet is valid, and if the information sequence number field value of the packet is invalid, determine that the malformed packet attacks.
As shown in fig. 5, further, the service logic attack detection module 500 includes: a data obtaining unit 501, a reading substation configuration service detecting unit 502, a protection event uploading service detecting unit 503, a recording presentation uploading service detecting unit 504, a customized operation service detecting unit 505, a total calling service detecting unit 506, and a general file transmission service detecting unit 507.
The output end of the data acquisition unit 501 is connected to the input end of the reading substation configuration service detection unit 502, and is used for inputting the relay protection service to which the message belongs.
The output end of the reading substation configuration service detection unit 502 is connected with the input end of a protection event uploading service detection unit 503, the output end of the protection event uploading service detection unit 503 is connected with the input end of a wave-recording brief report uploading service detection unit 504, the output end of the wave-recording brief report uploading service detection unit 504 is connected with the input end of a customized operation service detection unit 505, the output end of the customized operation service detection unit 505 is connected with the input end of a total calling service detection unit 506, and the output end of the total calling service detection unit 506 is connected with the input end of a general file transmission service detection unit 507.
In one embodiment, the data obtaining unit 501 obtains a specific relay protection service to which a message belongs, and the unit transmits read information to the reading substation configuration service detecting unit 502, the protection event uploading service detecting unit 503, the recording brief report uploading service detecting unit 504, the customized operation service detecting unit 505, the total call service detecting unit 506, and the general file transmission service detecting unit 507.
The reading substation configuration service detection unit 502 is configured to detect whether there is an attack behavior in the reading substation configuration service in the relay protection information processing system.
In one embodiment, a normal behavior model of the configuration service of the reading substation is established, attack behavior detection is performed on the flow data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, it is determined that there is a logic attack of the configuration service of the reading substation, and the unit uses the detection result as the output end of the service logic attack detection module 500.
The protection event upload service detection unit 503 is configured to detect whether an attack action exists in the protection event upload service.
In one embodiment, a normal behavior model of a service uploaded by a protection event is established, attack behavior detection is performed on flow data of the service in a relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, if a message does not conform to the normal behavior model, it is determined that a service logic attack uploaded by the protection event exists, and the unit takes a detection result as an output end of the service logic attack detection module 500.
The recording brief report delivery service detection unit 504 is configured to detect whether there is an attack behavior in the recording brief report delivery service.
In one embodiment, a normal behavior model of the recorded wave briefing uploading service is established, attack behavior detection is performed on the traffic data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, it is determined that there is a recorded wave briefing uploading service logic attack, and the unit takes the detection result as the output end of the service logic attack detection module 500.
The customized operation service detection unit 505 is configured to detect whether an attack behavior exists in the fixed-value operation service.
In one embodiment, a normal behavior model of a fixed-value operation service is established, attack behavior detection is performed on flow data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, if a message does not conform to the normal behavior model, it is determined that a customized operation service logic attack exists, and the unit takes a detection result as an output end of the service logic attack detection module 500.
The total call service detection unit 506 is configured to detect whether there is an attack behavior in the total call service.
In one embodiment, a normal behavior model of the total call service is established, attack behavior detection is performed on flow data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, it is determined that there is a total call service logic attack, and the unit takes the detection result as the output end of the service logic attack detection module 500.
The universal file transmission service detection unit 507 is configured to detect whether there is an attack behavior in the universal file transmission service.
In one embodiment, a normal behavior model of the general file transmission service is established, attack behavior detection is performed on the traffic data of the service in the relay protection information processing system according to the normal behavior model, if the message does not conform to the normal behavior model, it is determined that a general file transmission service logic attack exists, and the unit takes the detection result as the output end of the service logic attack detection module 500.
Claims (10)
1. A method for monitoring attack behaviors of a relay protection information processing system is characterized by comprising the following steps:
s1, capturing a relay protection information processing system flow data packet in real time, and extracting an application layer message of current frame flow data;
s2, performing field level analysis on the application layer message;
s3, performing clock tampering attack detection on the analyzed message, if the clock range, clock logic, clock synchronization and clock delay of the message do not accord with normal clock characteristics, judging that clock tampering attack exists, otherwise, entering S4;
s4, carrying out abnormal message attack detection on the analyzed message, if the length field, the type identification, the transmission reason, the information sequence number value and the protocol requirement of the message are not in accordance, judging that abnormal message attack exists, otherwise, entering the step S5;
and S5, according to the service system to which the analyzed message belongs, carrying out attack detection on the analyzed message, if the analyzed message does not conform to the normal service model, judging that service logic attack exists, otherwise, judging that the current frame flow data is normal flow.
2. The method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system according to claim 1, wherein in step S3, the specific implementation process of performing the clock tamper attack detection on the analyzed message includes:
1) judgment formula Y t ∈[1970,2069]Whether the clock is true or not is judged, if not, the clock is judged to be attacked by tampering, otherwise, the step 2) is carried out; wherein,Y t year, y, of the time scale t A year identification byte value representing a time stamp;
2) judgment formulaIf true, it is determined as clock tamperingChanging attack, otherwise, entering step 3); wherein,indicating a full-scale word "optional", P being the application layer message parsed in step S2, P DS Representing IEC60870-5-103 time tick messages, A g (P) represents the high 8-bit value of the ASDU address of the message, F represents the 15 of the 16-system, and H represents the value of the 16-system;
3) judgment formulaWhether the clock is true or not is judged, if not, the clock is judged to be attacked by tampering, otherwise, the step 4) is carried out; wherein, P DZ Represents one of IEC60870-5-103 alarm, remote signaling deflection and action event data uploading message, T js (P) represents the event substation reception time, T sj (P) represents an actual occurrence time of the event;
4) detecting whether the time period for sending the historical fault information by the substation is consistent with the time period for calling the fault historical information by the main station, if the time periods are not consistent, determining that the clock is tampered and attacked, and if not, entering the step 5);
5) judgment formulaWhether the clock is true or not is judged, if not, the clock is judged to be clock tampering attack, and if not, the step S4 is carried out; wherein,P XC indicating IEC60870-5-103 main-substation information transfer message, T cs (P) denotes an information transfer time, T max Denotes the maximum delay time, P 1 Message, P, indicating relay protection device action information transfer 2 Message, P, representing the transmission of analog measurement values of a relay protection device 3 Transmitting messages, P, indicating the operating state of the protective relaying device 4 And indicating the relay protection device to transmit a message according to the fixed value.
3. The method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system according to claim 1, wherein the specific implementation process for performing the malformed message attack detection on the analyzed message comprises:
I) judgment formulaWhether the abnormal message attack is established or not is judged, if not, the abnormal message attack is judged, and if not, the step II) is carried out; wherein, P IEC103 Representing IEC60870-5-103 message, F l (P) represents the theoretical length of the message, L s (P) representing the actual length of the message;
II) judgment formulaWhether the abnormal message attack is established or not is judged, if not, the abnormal message attack is judged, and if not, the step III) is carried out;
III) judgment formulaWhether the abnormal message attack is established or not is judged, if not, the abnormal message attack is judged, and if not, the step IV is carried out); wherein, F t (P) indicating a message type identification field value;
IV) judgment formulaWhether the abnormal message attack is established or not is judged, if not, the abnormal message attack is judged, and if not, the step V) is carried out; wherein, F c (P) a value representing a message transmission reason field;
4. The method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system according to claim 1, wherein in step S5, when the message configures a service for the reading substation, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed message includes:
judgment formulaWhether the configuration data are established or not is judged, if not, the configuration data malicious interception attack exists, otherwise, a formula is judgedIf not, judging that data tampering attack exists, otherwise, judging that the current frame traffic data is normal traffic; wherein, P BT Indicating a reading substation configuration service message in a relay protection information processing system, B n (P) number of titles sent on substation, B s Number of all titles, B, representing the configuration of the substation zh (P) group number, C, of each entry representing the same group of header information zh A group number indicating the current group header information.
5. The method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system according to claim 1, wherein in step S5, when the packet is a protection event upload service, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed packet includes:
A) judgment formulaIf the two-point information is true, if not, judging that the two-point information malicious tampering attack exists, otherwise, entering the step B); wherein, P BH Presentation of protection events in a relay protection information processing system, D pi (P) represents a two-point information value;
B) detecting whether the switching value displacement, the action signal and the message logic of the front frame and the rear frame of the pressing plate state are correct or not, and if the front frame of the switching value displacement is opened/closed, the rear frame is still opened/closed; the former frame of the action signal is reset/action, and the latter frame is still reset/action; if the former frame of the pressing plate state is not input/input and the latter frame is still not input/input, judging that malicious opening and closing attack exists, otherwise, entering the step C);
C) judgment formulaIf not, judging that the illegal uploading attack of the action event exists, otherwise, judging the current frame flow data as normal flow; wherein L is bh (P) indicates protection event message type identification, P 5 Message indicating an alarm or a switching value change event, P 6 Representing an action event message.
6. The method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system according to claim 1, wherein in step S5, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed message when the message is a wave recording presentation reporting service includes:
i) judgment formulaIf not, judging that the tripping phase malicious tampering attack exists, otherwise, entering a step ii); wherein, P LB Presentation of a message of a wave recording presentation service in a relay protection information processing system, G xb (P) represents the phase of failure, Z xb (P) indicates the phase of trip;
ii) judgment formulaWhether the ground fault flag bit data are true or not is judged, if not, the ground fault flag bit data tampering attack is judged, and if not, the step iii) is carried out; wherein D is 3 Indicating the value of the flag bit of the message short-circuit earth fault, D 0 Indicating the value of the flag bit of the short-circuit fault of the A phase of the message, D 1 Indicating the value of the short-circuit fault flag bit of the B-phase of the message, D 2 Representing the value of the flag bit of the short circuit fault of the C phase of the message;
and iii) detecting whether the reclosure in the recording brief report is abnormal, if the reclosure exists after the fault occurs and the reclosure time is 0 or the reclosure does not exist and is not 0, judging that tampering attack of the reclosure time exists, and otherwise, judging the current frame flow data to be normal flow.
7. The method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system according to claim 1, wherein in step S5, when the packet is a fixed value operation service, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed packet includes:
judgment logic X g1 →X g2 →X g3 →X g4 →X g5 →X g6 →X g7 →X g8 Whether the current frame flow data are normal flow is judged, if not, whether malicious tampering attack of the relay protection device setting value exists is judged, and otherwise, the current frame flow data are judged to be normal flow; wherein, X g1 Message, X, indicating the current running fixed-value area code of the calling device g2 Message, X, indicating the current running fixed-value area code of the substation uploading device g3 Message, X, indicating the fixed value of the calling device of the Master station g4 Message, X, indicating the fixed value of the uploading device of the substation g5 Presentation substation downloading of definite value message, X g6 Message, X, indicating the value of the response substation g7 Indicating execution of a constant value modification message, X g8 The substation responds to the fixed value modification message.
8. The method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system according to claim 1, wherein in step S5, when the packet is a total call service, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed packet includes:
logic of judgement Z h1 →Z h2 →Z h3 If not, judging that the illegal general calling attack exists, otherwise, judging a formulaIf not, judging that the illegal general calling attack exists, otherwise, judging that the current frame traffic data is normal traffic; wherein Z is h1 Indicating the master station initiating a total call message, Z h2 Presentation substation uploadingInformation message, Z h3 Indicating a total call completion message, P ZH Z representing the total call service of the relay protection information processing system hn Indicating the number of messages sent on the substation, Z hs Indicating the number of devices in the substation, A s Indicating the address of the message ASDU and H indicating the value is 16.
9. The method for monitoring the attack behavior of the relay protection information processing system according to claim 1, wherein in step S5, when the packet is a general file transfer service, the specific implementation process of performing attack detection on the analyzed packet includes:
detecting whether the file name only contains a directory name and a wildcard character, if so, judging that the illegal file uploading attack exists, otherwise, judging a formulaIf not, judging that the file clock tampering attack exists, otherwise, judging that the current frame traffic data is normal traffic;
wherein, P WJ Representing relay protection information processing system file list upload message, T lb (P) represents a file list upload time, C q Query start time, C, when representing a list of files z The query termination time when representing the list of files.
10. A computer apparatus comprising a memory, a processor and a computer program stored on the memory; characterized in that the processor executes the computer program to carry out the steps of the method according to one of claims 1 to 9.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111675512.4A CN114825607A (en) | 2021-12-31 | 2021-12-31 | Attack behavior monitoring method and device for relay protection information processing system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111675512.4A CN114825607A (en) | 2021-12-31 | 2021-12-31 | Attack behavior monitoring method and device for relay protection information processing system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114825607A true CN114825607A (en) | 2022-07-29 |
Family
ID=82527096
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111675512.4A Pending CN114825607A (en) | 2021-12-31 | 2021-12-31 | Attack behavior monitoring method and device for relay protection information processing system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114825607A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115913784A (en) * | 2023-01-05 | 2023-04-04 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Network attack defense system, method and device and electronic equipment |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080208680A1 (en) * | 2006-06-06 | 2008-08-28 | Ergonotech Inc | DriveOn Pay(TM) as WiMAX-compatible Menu-Driven Dashtop Mobile Payment Platform |
| CN101316051A (en) * | 2008-07-03 | 2008-12-03 | 绍兴电力局 | Internetwork communication log analysis system and method based on IEC61850 transforming plant automatization system |
| CN210578609U (en) * | 2019-10-25 | 2020-05-19 | 国网湖北省电力有限公司电力科学研究院 | Ethernet photoelectric digital signal detection device based on real-time clock |
-
2021
- 2021-12-31 CN CN202111675512.4A patent/CN114825607A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080208680A1 (en) * | 2006-06-06 | 2008-08-28 | Ergonotech Inc | DriveOn Pay(TM) as WiMAX-compatible Menu-Driven Dashtop Mobile Payment Platform |
| CN101316051A (en) * | 2008-07-03 | 2008-12-03 | 绍兴电力局 | Internetwork communication log analysis system and method based on IEC61850 transforming plant automatization system |
| CN210578609U (en) * | 2019-10-25 | 2020-05-19 | 国网湖北省电力有限公司电力科学研究院 | Ethernet photoelectric digital signal detection device based on real-time clock |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 王晓芳;周有庆;袁旭龙;黄肇;: "基于时钟状态估计的电力系统广域冗余对时模型", 电力系统保护与控制, no. 01, 1 January 2009 (2009-01-01) * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115913784A (en) * | 2023-01-05 | 2023-04-04 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Network attack defense system, method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN115913784B (en) * | 2023-01-05 | 2023-08-08 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Network attack defense system, method and device and electronic equipment |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114124478B (en) | Method and system for detecting abnormal industrial control flow of power system | |
| CN114362368B (en) | Intelligent substation network flow abnormal behavior monitoring method and system | |
| CN107241224A (en) | The network risks monitoring method and system of a kind of transformer station | |
| CN106982235A (en) | A kind of power industry control network inbreak detection method and system based on IEC 61850 | |
| CN103905451A (en) | System and method for trapping network attack of embedded device of smart power grid | |
| CN114825607A (en) | Attack behavior monitoring method and device for relay protection information processing system | |
| CN104464114A (en) | System and method for managing and monitoring safety of application of financial terminals | |
| CN116317171B (en) | Electric quantity and non-electric quantity internet of things monitoring device | |
| CN111711627A (en) | Industrial Internet data security monitoring method and system based on block chain | |
| CN114938287B (en) | Power network abnormal behavior detection method and device integrating service characteristics | |
| CN115147956A (en) | Data processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114697081A (en) | Intrusion detection method and system based on IEC61850 SV message operation situation model | |
| CN112671801B (en) | Network security detection method and system | |
| CN107277070A (en) | A kind of computer network instrument system of defense and intrusion prevention method | |
| CN206003100U (en) | Metering safety device | |
| CN108206826B (en) | Lightweight intrusion detection method for integrated electronic system | |
| CN104794774B (en) | Driver training anti-cheating timing system and method | |
| CN114745152A (en) | Intrusion detection method and system based on IEC61850GOOSE message operation situation model | |
| CN109450934A (en) | Terminal accesses data exception detection method and system | |
| CN113542221B (en) | Method and system for judging falsification of sensor data of intelligent substation, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN115310833B (en) | Electrochemical energy storage container accident analysis method and device | |
| CN118170662A (en) | Fuzzy test method and device for power protocol and power protocol test system | |
| CN117811839B (en) | Network security monitoring device and method for monitoring Internet of things equipment | |
| CN214226063U (en) | Intelligent voice prompt device for high-low voltage electrical cabinet | |
| CN219392651U (en) | Webpage safety remote monitoring alarm system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |