CN114494399A - Vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter verification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium - Google Patents
Vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter verification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114494399A CN114494399A CN202111536796.9A CN202111536796A CN114494399A CN 114494399 A CN114494399 A CN 114494399A CN 202111536796 A CN202111536796 A CN 202111536796A CN 114494399 A CN114494399 A CN 114494399A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- parameter
- camera
- parameters
- around
- world coordinate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 63
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 42
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 claims description 97
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000010200 validation analysis Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 abstract description 6
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000013473 artificial intelligence Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010801 machine learning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 101100234408 Danio rerio kif7 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100221620 Drosophila melanogaster cos gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100398237 Xenopus tropicalis kif11 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000003491 array Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013135 deep learning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003058 natural language processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013307 optical fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001953 sensory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/60—Analysis of geometric attributes
- G06T7/62—Analysis of geometric attributes of area, perimeter, diameter or volume
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/22—Matching criteria, e.g. proximity measures
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/80—Analysis of captured images to determine intrinsic or extrinsic camera parameters, i.e. camera calibration
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2200/00—Indexing scheme for image data processing or generation, in general
- G06T2200/32—Indexing scheme for image data processing or generation, in general involving image mosaicing
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
The utility model discloses a verification method and a device of vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter, an electronic device and a storage medium, based on the image collected by the looking-around camera, the camera coordinate parameter of the looking-around camera is obtained, the camera coordinate parameter is converted into a world coordinate system, a first world coordinate parameter is obtained, a second world coordinate parameter of the target looking-around parameter is obtained, wherein the target looking-around parameter is a preset parameter, the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter are compared, and if the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter of the looking-around camera is determined to meet the requirement. And on the basis of converting the to-be-verified image acquired by the looking-around camera when the vehicle leaves the factory into a world coordinate parameter, simultaneously, taking the target looking-around parameter as the coordinate parameter in the world coordinate system, and judging whether the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter meets the factory standard or the standard after maintenance by using the same world coordinate system to realize the rapid evaluation of the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter.
Description
Technical Field
The present disclosure relates to the field of vehicle technologies, and in particular, to a method and an apparatus for verifying a vehicle-mounted look-around parameter, an electronic device, and a storage medium.
Background
The vehicle-mounted looking-around system is used as a key for collecting images, and is generally a panoramic looking-around system formed by splicing images collected by fisheye cameras arranged in four directions of the front, the back, the left and the right of a vehicle body.
Generally, the vehicle leaves a factory, the looking-around parameters of the vehicle-mounted looking-around system are set, but at present, a method for verifying the looking-around parameters is not available, and in order to ensure the accuracy of the vehicle-mounted looking-around system for collecting images, a verification method for the vehicle-mounted looking-around system is designed, which is a problem to be solved urgently at present.
Disclosure of Invention
The disclosure provides a verification method and device of vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameters, electronic equipment and a storage medium.
According to an aspect of the present disclosure, a verification method for vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters is provided, including:
the method comprises the steps of acquiring camera coordinate parameters of a looking-around camera based on an image acquired by the looking-around camera, converting the camera coordinate parameters into a world coordinate system, and acquiring first world coordinate parameters;
acquiring a second world coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter, wherein the target look-around parameter is a preset parameter and comprises the second world coordinate parameter in a world coordinate system;
comparing the first world coordinate parameter to the second world coordinate parameter;
and if the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameter of the all-round looking camera meets the requirement.
Optionally, the method further includes:
and if the error of the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter exceeds the preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter does not meet the requirement, and referring to the target all-around viewing parameter to adjust all the all-around viewing cameras.
Optionally, the comparing the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter includes:
acquiring a first column vector in the first world coordinate parameter;
acquiring a second column vector in the second world coordinate parameter;
comparing the first column vector with the second column vector using similarity.
According to a second aspect of the present disclosure, a verification method for vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters is provided, which includes:
acquiring a first camera coordinate parameter under a camera coordinate system of a look-around camera based on an image acquired by the look-around camera;
converting the world coordinate parameters of the target all-round looking parameters into second camera coordinate parameters under the camera coordinate system, wherein the target all-round looking parameters are preset parameters and comprise the world coordinate parameters;
comparing the first camera coordinate parameter to the second camera coordinate parameter;
and if the error between the first camera coordinate parameter and the second camera coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter of the all-round-looking camera meets the requirement.
Optionally, the comparing the first camera coordinate parameter with the second camera coordinate parameter includes:
acquiring a first line vector in the first world coordinate parameter;
acquiring a second row vector in the second world coordinate parameter;
comparing the first column vector with the second row vector with a similarity.
According to a third aspect of the present disclosure, a verification method for vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters is provided, which includes:
the method comprises the steps that camera coordinate parameters of a looking-around camera are obtained based on images collected by the looking-around camera, and the camera coordinate parameters are converted into first reference coordinate parameters under a reference coordinate system;
converting the coordinate parameters of the target look-around parameters into a second reference coordinate parameter under the reference coordinate system, wherein the target look-around parameters are preset parameters and comprise reference coordinate parameters;
comparing the first reference coordinate parameter with the second reference coordinate parameter;
and if the error between the first reference coordinate parameter and the second reference coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameter of the all-round looking camera meets the requirement.
Optionally, the comparing the first reference coordinate parameter with the second reference coordinate parameter includes:
acquiring a first row vector in the first reference coordinate parameter;
acquiring a second row vector in the second reference coordinate parameter;
comparing the first column vector with the second row vector with similarity;
or,
acquiring a third column vector in the first reference coordinate parameter;
acquiring a fourth column vector in the second reference coordinate parameter;
comparing the third column vector with the fourth row vector using similarity.
According to a fourth aspect of the present disclosure, there is provided a verification apparatus for vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters, comprising:
the system comprises a first acquisition unit, a second acquisition unit and a third acquisition unit, wherein the first acquisition unit is used for acquiring camera coordinate parameters of a panoramic camera based on an image acquired by the panoramic camera;
the first conversion unit is used for converting the camera coordinate parameters into a world coordinate system to obtain first world coordinate parameters;
the second acquisition unit is used for acquiring a second world coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter, wherein the target look-around parameter is a preset parameter and comprises the second world coordinate parameter in a world coordinate system;
the first comparison unit is used for comparing the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter;
the first determining unit is used for determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter of the all-around viewing camera meets the requirement when the comparing unit determines that the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
Optionally, the apparatus further comprises:
the second determining unit is used for determining that the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter does not meet the requirement when the comparing unit determines that the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter exceeds the preset allowable range;
and the adjusting unit is used for adjusting all the all-around cameras by referring to the target all-around parameters.
Optionally, the first comparing unit includes:
the first acquisition module is used for acquiring a third column vector in the first world coordinate parameter;
the second acquisition module is used for acquiring a fourth column vector in the second world coordinate parameter;
a comparison module for comparing the first column vector with the second column vector using similarity.
According to a fifth aspect of the present disclosure, there is provided a verification apparatus for vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters, comprising:
the third acquisition unit is used for acquiring a first camera coordinate parameter under a camera coordinate system of the all-round camera based on an image acquired by the all-round camera;
the second conversion unit is used for converting the coordinate parameters of the target all-round looking parameters into second camera coordinate parameters under the camera coordinate system, wherein the target all-round looking parameters are preset parameters and comprise world coordinate parameters;
a second comparing unit for comparing the first camera coordinate parameter with the second camera coordinate parameter;
and the third determining unit is used for determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter of the all-around viewing camera meets the requirement when the comparing unit determines that the error between the first camera coordinate parameter and the second camera coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
Optionally, the second comparing unit includes:
a first obtaining module, configured to obtain a first row vector in the first world coordinate parameter;
the second acquisition module is used for acquiring a second row vector in the second world coordinate parameter;
a comparison module for comparing the first column vector with the second row vector using similarity.
According to a sixth aspect of the present disclosure, there is provided a verification apparatus for vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters, comprising:
the fourth acquisition unit is used for acquiring the camera coordinate parameter of the panoramic camera based on the image acquired by the panoramic camera and converting the camera coordinate parameter into a reference coordinate system to acquire a first reference coordinate parameter;
the third conversion unit is used for converting the coordinate parameters of the target all-round looking parameters into a second reference coordinate parameter under the reference coordinate system, wherein the target all-round looking parameters are preset parameters and comprise reference coordinate parameters;
a third comparing unit, configured to compare the first reference coordinate parameter with the second reference coordinate parameter;
and the fourth determining unit is used for determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameters of the all-round looking camera meet requirements when the error between the first reference coordinate parameter and the second reference coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
Optionally, the third comparing unit includes:
the first acquisition module is used for acquiring a first row vector in the first reference coordinate parameter;
the second obtaining module is used for obtaining a second row vector in the second reference coordinate parameter;
a first comparing module, configured to compare the first column vector with the second row vector by using similarity;
or,
a third obtaining module, configured to obtain a third column vector in the first reference coordinate parameter;
a fourth obtaining module, configured to obtain a fourth column vector in the second reference coordinate parameter;
and the second comparison module is used for comparing the third column vector with the fourth row vector by utilizing similarity.
According to a seventh aspect of the present disclosure, there is provided a vehicle comprising the on-board visibility around parameter verification apparatus of the fourth, fifth or sixth aspect.
The method and the device for verifying the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter, the electronic device and the storage medium provided by the disclosure are used for acquiring a camera coordinate parameter of an all-around viewing camera based on an image acquired by the all-around viewing camera, converting the camera coordinate parameter into a world coordinate system, acquiring a first world coordinate parameter, and acquiring a second world coordinate parameter of a target all-around viewing parameter, wherein the target all-around viewing parameter is a preset parameter and comprises a second world coordinate parameter under the world coordinate system, comparing the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter, and if the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter of the all-around viewing camera meets requirements. And on the basis of converting the to-be-verified image acquired by the looking-around camera when the vehicle leaves the factory into the world coordinate parameter, simultaneously, judging whether the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter meets the factory standard or the standard after maintenance by using the same world coordinate system, wherein the target looking-around parameter is also the coordinate parameter under the world coordinate system, and realizing the rapid evaluation of the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter.
It should be understood that the statements in this section do not necessarily identify key or critical features of the embodiments of the present application, nor do they limit the scope of the present application. Other features of the present application will become apparent from the following description.
Drawings
The drawings are included to provide a better understanding of the present solution and are not to be construed as limiting the present disclosure. Wherein:
fig. 1 is a schematic flowchart of a first method for verifying vehicle-mounted panoramic parameters according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
fig. 2 is a schematic flowchart of a second method for verifying vehicle-mounted panoramic parameters according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
fig. 3 is a schematic flowchart of a third method for verifying vehicle-mounted look-around parameters according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
fig. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a first vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter verification device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
fig. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a second vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter verification device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
fig. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a third vehicle-mounted viewing parameter verification apparatus according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
fig. 7 is a schematic structural diagram of a fourth apparatus for verifying vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
fig. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of a fifth vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter verification apparatus according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
fig. 9 is a schematic structural diagram of a sixth vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter verification apparatus according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
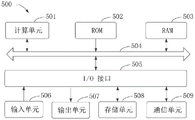
fig. 10 is a schematic block diagram of an example electronic device 500 provided by embodiments of the present disclosure.
Detailed Description
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure are described below with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which various details of the embodiments of the disclosure are included to assist understanding, and which are to be considered as merely exemplary. Accordingly, those of ordinary skill in the art will recognize that various changes and modifications of the embodiments described herein can be made without departing from the scope and spirit of the present disclosure. Also, descriptions of well-known functions and constructions are omitted in the following description for clarity and conciseness.
The following describes a verification method, an apparatus, an electronic device, and a storage medium for vehicle-mounted look-around parameters according to embodiments of the present disclosure with reference to the drawings.
In the related art, a method for verifying and evaluating the vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter is not available, and the vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter verification method provided in the embodiment of the application can be used for rapidly verifying the vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter.
As shown in fig. 1, fig. 1 is a method for verifying a vehicle-mounted look-around parameter provided in an embodiment of the present application, where the method includes:
101. the method comprises the steps of obtaining camera coordinate parameters of a look-around camera based on images collected by the look-around camera, and converting the camera coordinate parameters into a world coordinate system to obtain first world coordinate parameters.
The embodiment of the application is applied to an application scene that a vehicle-mounted all-around system is verified and evaluated after the vehicle leaves a factory, wherein the vehicle-mounted all-around system comprises: the panoramic all-around vision system is formed by splicing images collected by all-around vision cameras arranged in multiple directions of a vehicle body.
In the embodiment of the application, a mode of converting the acquired image to be verified into a world coordinate system is adopted, and the purpose of converting the coordinate system is that the acquired image to be verified coordinate parameters and the set target panoramic parameters have the same reference object, so that rapid verification and evaluation can be realized.
In the specific implementation process, the plurality of panoramic cameras based on the vehicle panoramic all-around system respectively collect images and are spliced into the images to be verified, the camera coordinate parameters of the images to be verified are determined according to the camera coordinate system of the vehicle panoramic all-around system, and the camera coordinate parameters are converted into first world coordinate parameters in a world coordinate system. For a specific implementation manner of converting the camera coordinate parameter into the first world coordinate parameter in the world coordinate system, reference may be made to any implementation manner in the related art, which is not described in detail in this embodiment of the present application.
102. And acquiring a second world coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter, wherein the target look-around parameter is a preset parameter and comprises the second world coordinate parameter in a world coordinate system.
The target look-around parameters are set before leaving the factory and are used as reference bases for producing vehicles.
In the embodiment of the present application, the coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter is a known quantity, and the parameter is a parameter in a world coordinate system, and a second world coordinate parameter corresponding to the parameter is directly obtained.
The first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter are described in the first and second ways, which are only used to distinguish different world coordinate parameters, and do not represent other meanings.
103. Comparing the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter.
Different coordinate parameters are converted into the same coordinate system, namely the world coordinate system, so that the equivalent comparison of data can be realized, and the verification correctness basis is improved.
104. And if the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameter of the all-round looking camera meets the requirement.
And if the error of the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter exceeds the preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter does not meet the requirement, and referring to the target all-around viewing parameter to adjust all the all-around viewing cameras.
The preset allowable range is an experimental value, flexible configuration can be carried out according to different vehicle types, and in an ideal state, the first world coordinate parameter is completely consistent with the second world coordinate parameter, but slight variation of the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter can be caused due to the difference of the production process.
The vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter verification method provided by the embodiment of the application obtains a camera coordinate parameter of an all-round-looking camera based on an image acquired by the all-round-looking camera, converts the camera coordinate parameter into a world coordinate system, obtains a first world coordinate parameter, obtains a second world coordinate parameter of a target all-round-looking parameter, wherein the target all-round-looking parameter is a preset parameter, comprises the second world coordinate parameter under the world coordinate system, compares the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter, and determines that the vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter of the all-round-looking camera meets requirements if the error of the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range. And on the basis of converting the to-be-verified image acquired by the looking-around camera when the vehicle leaves the factory into the world coordinate parameter, simultaneously, judging whether the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter meets the factory standard or the standard after maintenance by using the same world coordinate system, wherein the target looking-around parameter is also the coordinate parameter under the world coordinate system, and realizing the rapid evaluation of the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter.
As an implementation manner of the embodiment of the present application, comparing the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter in the same world coordinate parameter includes: and acquiring a first column vector in the first world coordinate parameter, acquiring a second column vector in the second world coordinate parameter, and comparing the first column vector with the second column vector by utilizing similarity. As an implementation manner of the embodiment of the present application, the first column vector and the second column vector use cosine similarity to determine whether they are consistent, when the cosine value is closer to 1, the included angle between the first column vector and the second column vector is closer to 0 degree, that is, the more similar the first row vector and the second row vector, the more 0 degree of the included angle between the first row vector and the second row vector in the ideal state, i.e. the first column vector and the second column vector are completely coincident, but the first column vector and the second column vector are not completely coincident due to installation errors in the production process, so that the preset allowable range is introduced in the embodiment of the application, the preset allowable range is an experimental value and can be flexibly set according to different vehicle styles or production processes, and as another implementation manner of the embodiment of the application, the preset allowable range can be compared based on the included angle between two columns of vectors of the first column of vectors and the second column of vectors. For example, the included angle between two vectors is ± 2 °, or the cosine value of two vectors is between + cos2 ° and-cos 2 °, and the preset allowable range is not illustrated in the embodiment of the present application.
As a third implementation manner of the embodiment of the present application, after the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter are obtained through conversion, areas corresponding to the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter may be respectively calculated, and the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter are compared by an area formed by the coordinate parameters.
As another implementation manner of the embodiment of the present application, when the camera coordinate parameter of the image to be verified is converted into the first world coordinate parameter, the conversion is performed in the following manner, including: and acquiring a geographic area coordinate parameter corresponding to the image to be verified, and converting the geographic area coordinate parameter into a world coordinate system to obtain a first world coordinate parameter.
In the above embodiment, the on-board looking-around parameter and the target looking-around parameter are converted into the world coordinate system for comparison and verification.
The following two embodiments are described, one is to convert the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters and the target looking-around parameters into a camera coordinate system for comparison, and the other is to convert the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameters and the target looking-around parameters into a reference coordinate system for comparison, where the reference coordinate system may be any one coordinate system without limitation to dimensionality.
As shown in fig. 2, fig. 2 is a flowchart of a second method for verifying a vehicle-mounted look-around parameter according to an embodiment of the present disclosure, where the method includes:
201. and acquiring a first camera coordinate parameter under a camera coordinate system of the all-round camera based on an image acquired by the all-round camera.
202. And converting the world coordinate parameters of the target all-round looking parameters into second camera coordinate parameters under the camera coordinate system, wherein the target all-round looking parameters are preset parameters and comprise the world coordinate parameters.
203. Comparing the first camera coordinate parameter to the second camera coordinate parameter.
204. And if the error between the first camera coordinate parameter and the second camera coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter of the all-round-looking camera meets the requirement.
The difference between the method shown in fig. 2 and the method shown in fig. 1 is that the target all-around viewing parameters in the world coordinate system are converted into the camera coordinate system, and the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameters and the target all-around viewing parameters are converted into the camera coordinate system for comparison and verification.
For the detailed description of the other steps, please refer to fig. 1, which is not repeated herein.
As a refinement to the above embodiment, when step 203 is executed to compare the first camera coordinate parameter with the second camera coordinate parameter, the method specifically includes: and acquiring a first row vector in the first world coordinate parameter, acquiring a second row vector in the second world coordinate parameter, and comparing the first column vector with the second row vector by utilizing similarity. For the comparison process, reference may be made to the corresponding description of the above embodiments, and the comparison principle is the same.
As shown in fig. 3, fig. 3 is a flowchart of a third method for verifying a vehicle-mounted look-around parameter according to an embodiment of the present disclosure, where the method includes:
301. the method comprises the steps of acquiring camera coordinate parameters of a looking-around camera based on images acquired by the looking-around camera, and converting the camera coordinate parameters into a reference coordinate system to acquire first reference coordinate parameters.
302. And converting the coordinate parameters of the target look-around parameters into a second reference coordinate parameter under the reference coordinate system, wherein the target look-around parameters are preset parameters and comprise reference coordinate parameters.
303. Comparing the first reference coordinate parameter with the second reference coordinate parameter.
304. And if the error between the first reference coordinate parameter and the second reference coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameter of the all-round looking camera meets the requirement.
The method shown in fig. 3 is different from the methods shown in fig. 1 and fig. 2 in that the vehicle-mounted panoramic parameter and the target panoramic parameter are both converted into coordinate systems and converted into reference coordinate systems.
For the detailed description of the other steps, please refer to fig. 1, which is not repeated herein.
As a refinement to the above embodiment, when the step 303 is executed to compare the first reference coordinate parameter with the second reference coordinate parameter, the method specifically includes: acquiring a first row vector in the first reference coordinate parameter; acquiring a second row vector in the second reference coordinate parameter; comparing the first column vector with the second row vector with a similarity. Or acquiring a third column vector in the first reference coordinate parameter, acquiring a fourth column vector in the second reference coordinate parameter, and comparing the third column vector with the fourth column vector by using similarity. For the comparison process, reference may be made to the corresponding descriptions of the above embodiments, and the comparison principles are the same, which are not described herein again.
The method for verifying the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter comprises the steps of obtaining a camera coordinate parameter of an all-around viewing camera based on an image collected by the all-around viewing camera, converting the camera coordinate parameter into a world coordinate system, obtaining a first world coordinate parameter, and obtaining a second world coordinate parameter of a target all-around viewing parameter, wherein the target all-around viewing parameter is a preset parameter and comprises the second world coordinate parameter under the world coordinate system, comparing the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter, and if the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter of the all-around viewing camera meets requirements. And on the basis of converting the to-be-verified image acquired by the looking-around camera when the vehicle leaves the factory into a world coordinate parameter, simultaneously, taking the target looking-around parameter as the coordinate parameter in the world coordinate system, and judging whether the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter meets the factory standard or the standard after maintenance by using the same world coordinate system to realize the rapid evaluation of the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter.
Fig. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a first vehicle-mounted viewing parameter verification apparatus provided in an embodiment of the present disclosure, and as shown in fig. 4, an embodiment of the present disclosure provides a vehicle-mounted viewing parameter verification apparatus, including:
a first obtaining unit 21, configured to obtain a camera coordinate parameter of a panoramic camera based on an image collected by the panoramic camera;
the first conversion unit 22 is configured to convert the camera coordinate parameter into a world coordinate system, so as to obtain a first world coordinate parameter;
the second obtaining unit 23 is configured to obtain a second world coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter, where the target look-around parameter is a preset parameter and includes the second world coordinate parameter in a world coordinate system;
a first comparing unit 24, configured to compare the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter;
a first determining unit 25, configured to determine that the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter of the looking-around camera meets a requirement when the comparing unit determines that the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
Further, in a possible implementation manner of this embodiment, as shown in fig. 5, the apparatus further includes:
a second determining unit 26, configured to determine that the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter does not meet the requirement when the comparing unit determines that the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter exceeds the preset allowable range;
an adjusting unit 27, configured to adjust all the panoramic cameras with reference to the target panoramic parameters.
Further, in a possible implementation manner of this embodiment, as shown in fig. 5, the first comparing unit 24 includes:
a first obtaining module 241, configured to obtain a first column vector in the first world coordinate parameter;
a second obtaining module 242, configured to obtain a second column vector in the second world coordinate parameter;
a comparing module 243, configured to compare the first column vector with the second column vector by using similarity.
Fig. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a first vehicle-mounted viewing parameter verification apparatus provided in an embodiment of the present disclosure, and as shown in fig. 6, an embodiment of the present disclosure provides a third vehicle-mounted viewing parameter verification apparatus, including:
a third obtaining unit 31, configured to obtain a first camera coordinate parameter in a camera coordinate system of the panoramic camera based on an image collected by the panoramic camera;
the second conversion unit 32 is configured to convert the coordinate parameters of the target panoramic parameters into the camera coordinate system, so as to obtain second camera coordinate parameters, where the target panoramic parameters are preset parameters and include world coordinate parameters;
a second comparing unit 33 for comparing the first camera coordinate parameter with the second camera coordinate parameter;
a third determining unit 34, configured to determine that the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter of the looking-around camera meets a requirement when the comparing unit determines that the error between the first camera coordinate parameter and the second camera coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
Further, in a possible implementation manner of this embodiment, as shown in fig. 5, the second comparing unit 33 includes:
a first obtaining module 331, configured to obtain a first row vector in the first world coordinate parameter;
a second obtaining module 332, configured to obtain a second row vector in the second world coordinate parameter;
a comparing module 333, configured to compare the first column vector with the second row vector by using similarity.
Fig. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of a fifth vehicle-mounted viewing parameter verification apparatus according to an embodiment of the present disclosure, and as shown in fig. 8, a sixth vehicle-mounted viewing parameter verification apparatus according to an embodiment of the present disclosure includes:
a fourth obtaining unit 41, configured to obtain a camera coordinate parameter of the panoramic camera based on an image acquired by the panoramic camera, and convert the camera coordinate parameter into a reference coordinate system to obtain a first reference coordinate parameter;
a third converting unit 42, configured to convert the coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter into the reference coordinate system, and obtain a second reference coordinate parameter, where the target look-around parameter is a preset parameter and includes a reference coordinate parameter;
a third comparing unit 43, configured to compare the first reference coordinate parameter with the second reference coordinate parameter;
a fourth determining unit 44, configured to determine that the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter of the looking-around camera meets a requirement when an error between the first reference coordinate parameter and the second reference coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
Further, in a possible implementation manner of this embodiment, as shown in fig. 9, the third comparing unit 43 includes:
a first obtaining module 431, configured to obtain a first row vector in the first reference coordinate parameter;
a second obtaining module 432, configured to obtain a second row vector in the second reference coordinate parameter;
a first comparing module 433, configured to compare the first column vector with the second row vector by using similarity;
or,
a third obtaining module 434, configured to obtain a third column vector in the first reference coordinate parameter;
a fourth obtaining module 435, configured to obtain a fourth column vector in the second reference coordinate parameter;
a second comparing module 436, configured to compare the third column vector with the fourth row vector by using similarity.
The verification device for the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameters obtains camera coordinate parameters of the all-around viewing camera based on images collected by the all-around viewing camera, converts the camera coordinate parameters into a world coordinate system, obtains first world coordinate parameters, and obtains second world coordinate parameters of the target all-around viewing parameters, wherein the target all-around viewing parameters are preset parameters and comprise second world coordinate parameters in the world coordinate system, the first world coordinate parameters and the second world coordinate parameters are compared, and if errors of the first world coordinate parameters and the second world coordinate parameters are within a preset allowable range, the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameters of the all-around viewing camera are determined to meet requirements. And on the basis of converting the to-be-verified image acquired by the looking-around camera when the vehicle leaves the factory into the world coordinate parameter, simultaneously, judging whether the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter meets the factory standard or the standard after maintenance by using the same world coordinate system, wherein the target looking-around parameter is also the coordinate parameter under the world coordinate system, and realizing the rapid evaluation of the vehicle-mounted looking-around parameter.
The embodiment of the application also provides a vehicle, and the vehicle comprises the vehicle-mounted around-the-eye parameter verification device shown in any one of figures 4 to 9.
It should be noted that the foregoing explanation of the method embodiment is also applicable to the apparatus of the present embodiment, and the principle is the same, and the present embodiment is not limited thereto.
The present disclosure also provides an electronic device, a readable storage medium, and a computer program product according to embodiments of the present disclosure.
FIG. 10 shows a schematic block diagram of an example electronic device 500 that may be used to implement embodiments of the present disclosure. Electronic devices are intended to represent various forms of digital computers, such as laptops, desktops, workstations, personal digital assistants, servers, blade servers, mainframes, and other appropriate computers. The electronic device may also represent various forms of mobile devices, such as personal digital processing, cellular phones, smart phones, wearable devices, and other similar computing devices. The components shown herein, their connections and relationships, and their functions, are meant to be examples only, and are not meant to limit implementations of the disclosure described and/or claimed herein.
As shown in fig. 10, the device 500 includes a computing unit 501 that can perform various appropriate actions and processes in accordance with a computer program stored in a ROM (Read-Only Memory) 502 or a computer program loaded from a storage unit 508 into a RAM (Random Access Memory) 503. In the RAM 503, various programs and data required for the operation of the device 500 can also be stored. The calculation unit 501, the ROM 502, and the RAM 503 are connected to each other by a bus 504. An I/O (Input/Output) interface 505 is also connected to the bus 504.
A number of components in the device 500 are connected to the I/O interface 505, including: an input unit 506 such as a keyboard, a mouse, or the like; an output unit 507 such as various types of displays, speakers, and the like; a storage unit 508, such as a magnetic disk, optical disk, or the like; and a communication unit 509 such as a network card, modem, wireless communication transceiver, etc. The communication unit 509 allows the device 500 to exchange information/data with other devices through a computer network such as the internet and/or various telecommunication networks.
The computing unit 501 may be a variety of general-purpose and/or special-purpose processing components having processing and computing capabilities. Some examples of the computing Unit 501 include, but are not limited to, a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a GPU (graphics Processing Unit), various dedicated AI (Artificial Intelligence) computing chips, various computing Units running machine learning model algorithms, a DSP (Digital Signal Processor), and any suitable Processor, controller, microcontroller, and the like. The calculation unit 501 executes the respective methods and processes described above, such as the verification method of the in-vehicle around-the-view parameter. For example, in some embodiments, the method of verifying the in-vehicle look-around parameters may be implemented as a computer software program tangibly embodied on a machine-readable medium, such as storage unit 508. In some embodiments, part or all of the computer program may be loaded and/or installed onto the device 500 via the ROM 502 and/or the communication unit 509. When loaded into RAM 505 and executed by the computing unit 501, may perform one or more steps of the method described above. Alternatively, in other embodiments, the computing unit 501 may be configured to perform the aforementioned verification method of the vehicle-mounted look-around parameters by any other suitable means (e.g., by means of firmware).
Various implementations of the systems and techniques described here above may be realized in digital electronic circuitry, Integrated circuitry, FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate arrays), ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated circuits), ASSPs (Application Specific Standard products), SOCs (System On Chip, System On a Chip), CPLDs (Complex Programmable Logic devices), computer hardware, firmware, software, and/or combinations thereof. These various embodiments may include: implemented in one or more computer programs that are executable and/or interpretable on a programmable system including at least one programmable processor, which may be special or general purpose, receiving data and instructions from, and transmitting data and instructions to, a storage system, at least one input device, and at least one output device.
Program code for implementing the methods of the present disclosure may be written in any combination of one or more programming languages. These program codes may be provided to a processor or controller of a general purpose computer, special purpose computer, or other programmable data processing apparatus, such that the program codes, when executed by the processor or controller, cause the functions/operations specified in the flowchart and/or block diagram to be performed. The program code may execute entirely on the machine, partly on the machine, as a stand-alone software package partly on the machine and partly on a remote machine or entirely on the remote machine or server.
In the context of this disclosure, a machine-readable medium may be a tangible medium that can contain, or store a program for use by or in connection with an instruction execution system, apparatus, or device. The machine-readable medium may be a machine-readable signal medium or a machine-readable storage medium. A machine-readable medium may include, but is not limited to, an electronic, magnetic, optical, electromagnetic, infrared, or semiconductor system, apparatus, or device, or any suitable combination of the foregoing. More specific examples of a machine-readable storage medium would include an electrical connection based on one or more wires, a portable computer diskette, a hard disk, a RAM, a ROM, an EPROM (Electrically Programmable Read-Only-Memory) or flash Memory, an optical fiber, a CD-ROM (Compact Disc Read-Only-Memory), an optical storage device, a magnetic storage device, or any suitable combination of the foregoing.
To provide for interaction with a user, the systems and techniques described here can be implemented on a computer having: a Display device (e.g., a CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) or LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) monitor) for displaying information to a user; and a keyboard and a pointing device (e.g., a mouse or a trackball) by which a user can provide input to the computer. Other kinds of devices may also be used to provide for interaction with a user; for example, feedback provided to the user can be any form of sensory feedback (e.g., visual feedback, auditory feedback, or tactile feedback); and input from the user may be received in any form, including acoustic, speech, or tactile input.
The systems and techniques described here can be implemented in a computing system that includes a back-end component (e.g., as a data server), or that includes a middleware component (e.g., an application server), or that includes a front-end component (e.g., a user computer having a graphical user interface or a web browser through which a user can interact with an implementation of the systems and techniques described here), or any combination of such back-end, middleware, or front-end components. The components of the system can be interconnected by any form or medium of digital data communication (e.g., a communication network). Examples of communication networks include: LAN (Local Area Network), WAN (Wide Area Network), internet, and blockchain Network.
The computer system may include clients and servers. A client and server are generally remote from each other and typically interact through a communication network. The relationship of client and server arises by virtue of computer programs running on the respective computers and having a client-server relationship to each other. The Server can be a cloud Server, also called a cloud computing Server or a cloud host, and is a host product in a cloud computing service system, so as to solve the defects of high management difficulty and weak service expansibility in the traditional physical host and VPS service ("Virtual Private Server", or simply "VPS"). The server may also be a server of a distributed system, or a server incorporating a blockchain.
It should be noted that artificial intelligence is a subject for studying a computer to simulate some human thinking processes and intelligent behaviors (such as learning, reasoning, thinking, planning, etc.), and includes both hardware and software technologies. Artificial intelligence hardware technologies generally include technologies such as sensors, dedicated artificial intelligence chips, cloud computing, distributed storage, big data processing, and the like; the artificial intelligence software technology mainly comprises a computer vision technology, a voice recognition technology, a natural language processing technology, machine learning/deep learning, a big data processing technology, a knowledge map technology and the like.
It should be understood that various forms of the flows shown above may be used, with steps reordered, added, or deleted. For example, the steps described in the present disclosure may be executed in parallel, sequentially, or in different orders, as long as the desired results of the technical solutions disclosed in the present disclosure can be achieved, and the present disclosure is not limited herein.
The above detailed description should not be construed as limiting the scope of the disclosure. It should be understood by those skilled in the art that various modifications, combinations, sub-combinations and substitutions may be made in accordance with design requirements and other factors. Any modification, equivalent replacement, and improvement made within the spirit and principle of the present disclosure should be included in the scope of protection of the present disclosure.
Claims (14)
1. A verification method for vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameters is characterized by comprising the following steps:
the method comprises the steps that camera coordinate parameters of a look-around camera are obtained based on images collected by the look-around camera, and the camera coordinate parameters are converted into first world coordinate parameters under a world coordinate system;
acquiring a second world coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter, wherein the target look-around parameter is a preset parameter and comprises the second world coordinate parameter in a world coordinate system;
comparing the first world coordinate parameter to the second world coordinate parameter;
and if the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameter of the all-round looking camera meets the requirement.
2. The authentication method of claim 1, further comprising:
and if the error of the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter exceeds the preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter does not meet the requirement, and referring to the target all-around viewing parameter to adjust all the all-around viewing cameras.
3. The validation method of claim 1, wherein the comparing the first world coordinate parameter to the second world coordinate parameter comprises:
acquiring a first column vector in the first world coordinate parameter;
acquiring a second column vector in the second world coordinate parameter;
comparing the first column vector with the second column vector using similarity.
4. A verification method for vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameters is characterized by comprising the following steps:
acquiring a first camera coordinate parameter under a camera coordinate system of a look-around camera based on an image acquired by the look-around camera;
converting the world coordinate parameters of the target all-round looking parameters into second camera coordinate parameters under the camera coordinate system, wherein the target all-round looking parameters are preset parameters and comprise the world coordinate parameters;
comparing the first camera coordinate parameter to the second camera coordinate parameter;
and if the error between the first camera coordinate parameter and the second camera coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter of the all-round-looking camera meets the requirement.
5. The authentication method of claim 4, wherein said comparing the first camera coordinate parameter to the second camera coordinate parameter comprises:
acquiring a first line vector in the first world coordinate parameter;
acquiring a second row vector in the second world coordinate parameter;
comparing the first column vector with the second row vector with a similarity.
6. A verification method for vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameters is characterized by comprising the following steps:
the method comprises the steps that camera coordinate parameters of a looking-around camera are obtained based on images collected by the looking-around camera, the camera coordinate parameters are converted into a reference coordinate system, and first reference coordinate parameters are obtained;
converting the coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter into the reference coordinate system to obtain a second reference coordinate parameter, wherein the target look-around parameter is a preset parameter and comprises a reference coordinate parameter;
comparing the first reference coordinate parameter with the second reference coordinate parameter;
and if the error between the first reference coordinate parameter and the second reference coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range, determining that the vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameter of the all-round looking camera meets the requirement.
7. The verification method of claim 6, wherein the comparing the first reference coordinate parameter to the second reference coordinate parameter comprises:
acquiring a third row vector in the first reference coordinate parameter;
acquiring a fourth row vector in the second reference coordinate parameter;
comparing the first column vector with the second row vector using similarity;
or,
acquiring a third column vector in the first reference coordinate parameter;
acquiring a fourth column vector in the second reference coordinate parameter;
comparing the third column vector with the fourth row vector using similarity.
8. A verification device for vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameters is characterized by comprising:
the system comprises a first acquisition unit, a second acquisition unit and a third acquisition unit, wherein the first acquisition unit is used for acquiring camera coordinate parameters of a panoramic camera based on an image acquired by the panoramic camera;
the conversion unit is used for converting the camera coordinate parameters into a world coordinate system to obtain first world coordinate parameters;
the second acquisition unit is used for acquiring a second world coordinate parameter of the target look-around parameter, wherein the target look-around parameter is a preset parameter and comprises the second world coordinate parameter in a world coordinate system;
a comparison unit for comparing the first world coordinate parameter with the second world coordinate parameter;
the first determining unit is used for determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter of the all-around viewing camera meets the requirement when the comparing unit determines that the error between the first world coordinate parameter and the second world coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
9. A verification device for vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameters is characterized by comprising:
the system comprises an acquisition unit, a processing unit and a display unit, wherein the acquisition unit is used for acquiring a first camera coordinate parameter under a camera coordinate system of a panoramic camera based on an image acquired by the panoramic camera;
the conversion unit is used for converting the world coordinate parameters of the target all-round looking parameters into second camera coordinate parameters under the camera coordinate system, wherein the target all-round looking parameters are preset parameters and comprise the world coordinate parameters;
a comparison unit for comparing the first camera coordinate parameter with the second camera coordinate parameter;
the determining unit is used for determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter of the all-around viewing camera meets the requirement when the comparing unit determines that the error between the first camera coordinate parameter and the second camera coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
10. A verification device for vehicle-mounted all-round looking parameters is characterized by comprising:
the system comprises an acquisition unit, a processing unit and a processing unit, wherein the acquisition unit is used for acquiring a camera coordinate parameter of a panoramic camera based on an image acquired by the panoramic camera and converting the camera coordinate parameter into a reference coordinate system to acquire a first reference coordinate parameter;
the conversion unit is used for converting the coordinate parameters of the target all-round looking parameters into second reference coordinate parameters under the reference coordinate system, wherein the target all-round looking parameters are preset parameters and comprise reference coordinate parameters;
a comparison unit for comparing the first reference coordinate parameter with the second reference coordinate parameter;
the determining unit is used for determining that the vehicle-mounted all-around viewing parameter of the all-around viewing camera meets requirements when the error between the first reference coordinate parameter and the second reference coordinate parameter is within a preset allowable range.
11. A vehicle comprising the on-board visibility around parameter verification apparatus of claim 8, claim 9 or claim 10.
12. An electronic device, comprising:
at least one processor; and
a memory communicatively coupled to the at least one processor; wherein,
the memory stores instructions executable by the at least one processor to enable the at least one processor to perform the method of any one of claims 1-3, 4-5, or 6-7.
13. A non-transitory computer readable storage medium having stored thereon computer instructions for causing the computer to perform the method of any of claims 1-3, 4-5, or 6-7.
14. A computer program product comprising a computer program which, when executed by a processor, implements the method according to any one of claims 1-3, 4-5 or 6-7.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111536796.9A CN114494399A (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2021-12-15 | Vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter verification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111536796.9A CN114494399A (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2021-12-15 | Vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter verification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114494399A true CN114494399A (en) | 2022-05-13 |
Family
ID=81494715
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111536796.9A Pending CN114494399A (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2021-12-15 | Vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter verification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114494399A (en) |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20150092058A1 (en) * | 2013-10-01 | 2015-04-02 | Application Solutions (Electronics and Vision) Ltd. | System, Vehicle and Method for Online Calibration of a Camera on a Vehicle |
| US20150139556A1 (en) * | 2013-11-21 | 2015-05-21 | Hyundai Mobis Co., Ltd. | Apparatus for compensating camera image and operating method thereof |
| US20150329048A1 (en) * | 2014-05-16 | 2015-11-19 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Surround-view camera system (vpm) online calibration |
| CN110378966A (en) * | 2019-06-11 | 2019-10-25 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Camera extrinsic scaling method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN111612852A (en) * | 2020-05-20 | 2020-09-01 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method and apparatus for verifying camera parameters |
| EP3809363A1 (en) * | 2019-10-15 | 2021-04-21 | Continental Automotive GmbH | Method and device for providing a surround view image, and vehicle |
| CN112991453A (en) * | 2019-12-17 | 2021-06-18 | 杭州海康机器人技术有限公司 | Calibration parameter calibration method and device for binocular camera and electronic equipment |
| CN113379852A (en) * | 2021-08-10 | 2021-09-10 | 禾多科技(北京)有限公司 | Method, device, electronic equipment and medium for verifying camera calibration result |
| CN113436271A (en) * | 2021-06-23 | 2021-09-24 | 三一专用汽车有限责任公司 | Calibration method, calibration device, vehicle and readable storage medium |
| CN113781575A (en) * | 2021-08-09 | 2021-12-10 | 上海奥视达智能科技有限公司 | Camera parameter calibration method, device, terminal and storage medium |
-
2021
- 2021-12-15 CN CN202111536796.9A patent/CN114494399A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20150092058A1 (en) * | 2013-10-01 | 2015-04-02 | Application Solutions (Electronics and Vision) Ltd. | System, Vehicle and Method for Online Calibration of a Camera on a Vehicle |
| US20150139556A1 (en) * | 2013-11-21 | 2015-05-21 | Hyundai Mobis Co., Ltd. | Apparatus for compensating camera image and operating method thereof |
| US20150329048A1 (en) * | 2014-05-16 | 2015-11-19 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Surround-view camera system (vpm) online calibration |
| CN110378966A (en) * | 2019-06-11 | 2019-10-25 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Camera extrinsic scaling method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| EP3809363A1 (en) * | 2019-10-15 | 2021-04-21 | Continental Automotive GmbH | Method and device for providing a surround view image, and vehicle |
| CN112991453A (en) * | 2019-12-17 | 2021-06-18 | 杭州海康机器人技术有限公司 | Calibration parameter calibration method and device for binocular camera and electronic equipment |
| CN111612852A (en) * | 2020-05-20 | 2020-09-01 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method and apparatus for verifying camera parameters |
| CN113436271A (en) * | 2021-06-23 | 2021-09-24 | 三一专用汽车有限责任公司 | Calibration method, calibration device, vehicle and readable storage medium |
| CN113781575A (en) * | 2021-08-09 | 2021-12-10 | 上海奥视达智能科技有限公司 | Camera parameter calibration method, device, terminal and storage medium |
| CN113379852A (en) * | 2021-08-10 | 2021-09-10 | 禾多科技(北京)有限公司 | Method, device, electronic equipment and medium for verifying camera calibration result |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3637317B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for generating vehicle damage information | |
| CN115880555B (en) | Target detection method, model training method, device, equipment and medium | |
| CN113379813A (en) | Training method and device of depth estimation model, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| WO2021052010A1 (en) | Method and apparatuses for face orientation estimation and network training, and electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN113627361B (en) | Training method and device for face recognition model and computer program product | |
| CN114332977A (en) | Key point detection method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113361710A (en) | Student model training method, picture processing device and electronic equipment | |
| CN112580666A (en) | Image feature extraction method, training method, device, electronic equipment and medium | |
| CN113781653B (en) | Object model generation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN115575931A (en) | Calibration method, calibration device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114332993A (en) | Face recognition method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN114120454A (en) | Training method and device of living body detection model, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114119990A (en) | Method, apparatus and computer program product for image feature point matching | |
| JP7425169B2 (en) | Image processing method, device, electronic device, storage medium and computer program | |
| CN112966670A (en) | Face recognition method, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN114494399A (en) | Vehicle-mounted all-round-looking parameter verification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN116129069A (en) | Method and device for calculating area of planar area, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN112990328A (en) | Feature fusion method, device, apparatus, storage medium, and program product | |
| CN115049895B (en) | Image attribute identification method, attribute identification model training method and device | |
| CN114429631A (en) | Three-dimensional object detection method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113591847B (en) | Vehicle positioning method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114494818B (en) | Image processing method, model training method, related device and electronic equipment | |
| CN115223374B (en) | Vehicle tracking method and device and electronic equipment | |
| CN114049615B (en) | Traffic object fusion association method and device in driving environment and edge computing equipment | |
| CN110647519B (en) | Method and device for predicting missing attribute value in test sample |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |