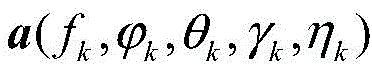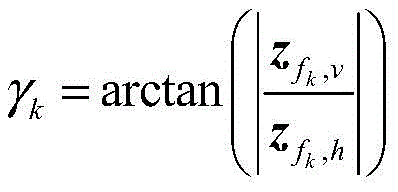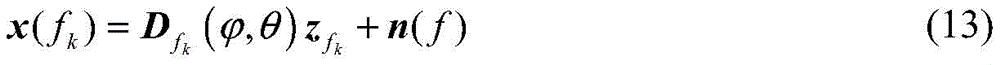CN114047473B - Arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on polarization sensitive annular array - Google Patents
Arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on polarization sensitive annular array Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114047473B CN114047473B CN202111210703.3A CN202111210703A CN114047473B CN 114047473 B CN114047473 B CN 114047473B CN 202111210703 A CN202111210703 A CN 202111210703A CN 114047473 B CN114047473 B CN 114047473B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- polarization
- angle
- signal
- annular array
- signals
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000010287 polarization Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 163
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 52
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 37
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 claims description 43
- 238000000691 measurement method Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 abstract description 9
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000004422 calculation algorithm Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005404 monopole Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005672 electromagnetic field Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005290 field theory Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010363 phase shift Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001131 transforming effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S3/00—Direction-finders for determining the direction from which infrasonic, sonic, ultrasonic, or electromagnetic waves, or particle emission, not having a directional significance, are being received
- G01S3/02—Direction-finders for determining the direction from which infrasonic, sonic, ultrasonic, or electromagnetic waves, or particle emission, not having a directional significance, are being received using radio waves
- G01S3/14—Systems for determining direction or deviation from predetermined direction
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A90/00—Technologies having an indirect contribution to adaptation to climate change
- Y02A90/10—Information and communication technologies [ICT] supporting adaptation to climate change, e.g. for weather forecasting or climate simulation
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Variable-Direction Aerials And Aerial Arrays (AREA)
Abstract
The invention provides an arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on a polarization sensitive annular array, which is used for receiving data of a plurality of signals through the polarization sensitive annular array; constructing an orthogonal polarization redundant dictionary for each signal according to the spatial sparsity of the signal; sparse reconstruction is carried out on the signals through the obtained orthogonal polarization redundant dictionary to determine the two-dimensional arrival angle of the signals and the rough measurement value of the signal polarization angle; reconstructing an orthogonal polarization redundant dictionary according to the known two-dimensional arrival angle, and performing sparse reconstruction on the signals to obtain an accurate measurement value of the signal polarization angle; the method utilizes the polarization sensitive annular array, reduces the influence of antenna mismatch on the direction-finding performance, decomposes the signal multidimensional parameter joint measurement into independent processing of a frequency domain, a space domain and a polarization domain, and avoids the multidimensional joint search process, thereby greatly improving the parameter calculation efficiency and realizing the joint rapid measurement of angles and polarizations.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the field of array signal processing, in particular to an arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on a polarization sensitive annular array.
Background
The conventional direction-finding antenna array generally adopts a monopole array mode, as shown in fig. 1, and a plurality of single-polarized antenna units are annularly and uniformly arranged to form an array. The space electromagnetic signals possibly arrive at the antenna array in any polarization mode, the traditional monopole antenna uniform array mode has the problem of partial antenna unit polarization mismatch, the antenna unit mismatch gain loss is 20-25 dB, the effective antenna units of the antenna array are directly reduced, the direction finding error is increased, and the problems of high-frequency range direction finding is fuzzy, even direction finding cannot be achieved and the like are directly caused.
The existing array direction finding algorithm is mainly represented by a multiple signal classification (Multiple Signal Classification, MUSIC) method and a sparse reconstruction method.
For K far-field signals in space to be incident on the array, the array receiving data x (t) at the time t is:
in the formula Represents the center frequency, pitch, azimuth angle of arrival, polarization amplitude angle and polarization phase angle, etc., of the kth signal, +.>A steering vector representing the kth signal, s (t) being the signal vector, n (t) being the noise vector, A representing the array pattern, < >>
The prior MUSIC direction finding algorithm carries out eigenvalue decomposition on an array received data covariance matrix, utilizes orthogonality of a signal subspace and a noise subspace, obtains a space spectrum through multidimensional parameter joint search, and corresponds to a two-dimensional arrival angle and a polarization angle of a signal at the position of a maximum value of a spectrum peak, wherein a spectrum peak search calculation formula is as follows
The existing direction-finding method based on sparse reconstruction utilizes sparsity of signal incoming wave directions in a space domain to construct a multidimensional joint redundant dictionary, a sparse reconstruction model of signals is obtained, and a two-dimensional arrival angle of space signals is obtained by solving positions of non-zero coefficients in a sparse vector z (t), wherein the redundant dictionary and the sparse reconstruction model are shown in the formulas (3) - (4):
x(t)=Dz(t)+n(t) (4)
the existing MUSIC algorithm and sparse reconstruction algorithm both need to measure the two-dimensional arrival angle and polarization of the signal through a multi-dimensional search process (frequency domain, angle domain, polarization domain and the like), and the higher the required direction finding precision is, the wider the frequency band is, the denser the search grid division is, the larger the calculation amount of spectral peak search or sparse reconstruction solution is, the more obvious the parameter calculation efficiency is reduced, and the real-time processing requirement is difficult to meet.
Disclosure of Invention
Aiming at the problems that in the prior art, in the combined measurement of the two-dimensional arrival angle and polarization, the array unit antenna is mismatched, the operand is large, the direction finding real-time requirement is difficult to meet, and the like, the method for measuring the arrival angle and the polarization angle based on the polarization sensitive annular array is provided, and the combined measurement of the center frequency, the two-dimensional arrival angle and the polarization parameter can be obtained at the same time.
The technical scheme adopted by the invention is as follows: an arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on a polarization sensitive annular array comprises the following steps:
and 6, repeating the steps 3-5 to obtain rough measurement values of the two-dimensional arrival angles and the polarization angles of all signals.
Further, in the step 2, the method for constructing the orthogonal polarization redundant dictionary includes:
based on the spatial sparsity of the signal, the frequency is f k The two-dimensional arrival angle of the signals is discretely divided, and the number of grids is N s Constructing orthogonal polarization redundant dictionary
Further, in the step 3, a space-polarization sparse representation model of the signal:
wherein ,x(fk ) Is of frequency f k A space-polarization sparse representation model of the signal of (c),for the sparse vector, n (f) represents the noise vector.
Further, the specific process of the step 4 is as follows: solving a space-polarization sparse representation model to obtain a sparse vector, solving non-zero elements, and converting the sparse vector into a convex optimization problem to solve in the solving process; the convex optimization problem is expressed as follows:
wherein z is a sparse vector, D is a redundant dictionary, x is a signal vector, and ε represents a reconstruction error.
Further, the method for calculating the coarse measurement value of the signal polarization angle in step 5 comprises the following steps:
wherein ,(γk ,η k ) As the polarization angle of the signal,the polarization components of the polarization angles of the signals in the h and v directions are respectively.
Furthermore, the method also comprises a high-precision signal polarization angle measurement method, wherein the polarization angle is uniformly and discretely divided on the known signal arrival angle, a new polarization redundancy dictionary is constructed, and the accurate measurement value of the signal polarization angle can be obtained by executing the steps 3-5 by adopting the new polarization redundancy dictionary.
Further, the new polarization redundancy dictionary is:
where γ represents the argument in polarization angle.
Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects of adopting the technical scheme are as follows: the method provided by the invention can be used for simultaneously obtaining the measurement of the signal center frequency, the two-dimensional arrival angle and the polarization parameter. The method utilizes the polarization sensitive annular array, reduces the influence of antenna mismatch on the direction-finding performance, decomposes the signal multidimensional parameter joint measurement into independent processing of a frequency domain, a space domain and a polarization domain, and avoids the multidimensional joint search process, thereby greatly improving the parameter calculation efficiency and realizing the joint rapid measurement of angles and polarizations.
Drawings
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a prior art single polarized annular array.
Fig. 2 is a flow chart of the angle and polarization angle measurement method according to the present invention.
Fig. 3 is a schematic view of a polarization-sensitive annular array according to the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the construction of a measuring apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of two-dimensional angle of arrival measurement according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating the measurement results of the polarization angle according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 7 is a schematic diagram showing the comparison of the measurement accuracy of the measurement scheme proposed by the present invention and the measurement accuracy of the angle of the single polarized annular array.
FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram showing the comparison of the calculation time of the measurement method and the multidimensional joint search method according to the present invention.
Detailed Description
The invention is further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
The invention solves the problems of mismatching of array unit antennas, large operand and the like in the joint measurement of the angle and the polarization of the array signals. Compared with the traditional angle and polarization combined measurement method, the scheme reduces the influence of antenna mismatch on the direction-finding performance, avoids the multidimensional combined search process, greatly reduces the operation amount, has higher calculation efficiency, and can improve the real-time direction-finding performance of the array signals. The specific scheme is as follows:
as shown in fig. 2, a method for measuring an arrival angle and a polarization angle based on a polarization sensitive annular array is provided, which comprises the following steps:
and 6, repeating the steps 3-5 to obtain rough measurement values of the two-dimensional arrival angles and the polarization angles of all signals.
Considering K fully polarized far-field narrowband signals in space of interest to be incident on an antenna array, wherein the center frequency, angle of arrival, polarization angle of the kth (k=1, 2,..k) signal are f, respectively k 、 wherein θk 、γ k E [0, pi/2) represents the polarization auxiliary angle, eta k E [ -pi, pi) represents the polarization phase difference, then the polarization sensitive annular array received data x (t) can be expressed as
Wherein A= [ a ] 1 ,a k ,...,a K ]For array flow pattern, s (t) = [ s ] 1 (t),s 2 (t),...,s K (t)]Is a signal vector s k (t) represents the kth signal, n (t) represents the mean value 0, and the variance is σ 2 Is a complex gaussian white noise of (c). a, a k Kronecker product of polarization-oriented vectors and spatial-oriented vectors, i.e.
in the formula ,is a airspace guide vector,>and steering vectors for the polarization domain. The center of the polarization sensitive annular array is used as a reference point (namely the origin of a coordinate system), and the number of the polarization sensitive annular array is +.>Is the direction unit vector on the space rectangular coordinate system, l m For each element antenna position vector, the space phase shift factor of the incident signal to the array isThen airspace guide vector +.>Can be expressed as
For an orthogonal dual polarized element antenna, its polarization steering vector can be expressed as
Transforming the received data of the polarization sensitive annular array into a frequency domain to obtain a frequency domain model representation model as
After the signals are transformed into the frequency domain, the signals of all frequencies can be independently processed, so that the frequency domain joint search is avoided, and the processing dimension is reduced. The space electromagnetic signal can be incident on the antenna array in any polarization mode, the polarization sensitive annular array adopts orthogonal dual polarization sensitive array elements, so that the problem of polarization mismatch is effectively avoided, and the number of effective antennas of the array under any polarization incidence is ensured. The polarization sensitive annular array acquires polarization information of the space electromagnetic signals by utilizing each polarization sensitive array element, and acquires DOA information of the space electromagnetic signals by utilizing an array geometry structure to perform airspace sampling, so that joint measurement of signal angles and polarization angles is obtained.
According to the sparse reconstruction theory, an incident signal is sparse in a space domain, so that a sparse reconstruction model can be established in the space domain, the most direct method is to take a guide vector of any potential DOA and polarization angle of the signal as a column vector thereof to construct an angle-polarization multi-dimensional joint redundant dictionary, but the length of the multi-dimensional joint redundant dictionary is the product of the grid number of parameters of each dimension, the computation amount of sparse reconstruction is huge, and real-time calculation is difficult. Therefore, on the premise that signals can be sparsely represented, how to reduce the length of the redundant dictionary is particularly critical.
According to electromagnetic field theory, any polarized electromagnetic wave can be represented by a group of bases, i.e. any polarized electromagnetic wave can be decomposed into the following forms
e=he h +ve v (10)
in the formula eh and ev The unit polarization vectors of the directions are respectively, h and v are complex coefficients after polarization decomposition, and the polarization auxiliary angle and the phase angle of the signal can be expressed as
The polarization information characterizing the incident signal is responsive to different polarization components of the polarization sensitive annular array.
Based on the spatial sparsity of the signal, the frequency is f k The two-dimensional arrival angle of the signals is discretely divided, and the number of grids is N s Constructing orthogonal polarization redundant dictionaryAs shown in (12)
in the formula Is made up of the different polarization component responses of the array (any polarization can be synthesized). The constructed redundant dictionary is irrelevant to DOA, polarization mode and the like of an actual information source, and the polarization domain and the angle domain are independently processed. Multiple signals (i.e., co-frequency multiple signals) may exist at the same frequency, where all possible angle values are discretely divided, and a redundant dictionary is created to simultaneously estimate the angles of arrival of all signals at that frequency.
Sparse representation can be performed on signals by using redundant dictionaries to obtain the frequency f k An angle-polarization domain sparse representation model of the signal of (2) as shown in formula (13)
in the formula ,for sparse vectors, ++>In which there are only K non-zero coefficients and N s -K zeros (or approximately zero), the positions of the non-zero elements in the redundant dictionary corresponding to the actual directions of arrival of the K spatial signals, x (f) k ) Is of frequency f k A spatio-polar sparse representation model of the signal of +.>For the sparse vector, n (f) represents the noise vector.
. Solving for sparse vectorsThe two-dimensional arrival angle estimation of the corresponding signal can be obtained. According to the sparse reconstruction theory, the non-zero element solution can be converted into a convex optimization problem shown in equation (14).
Wherein z is a sparse vector, D is a redundant dictionary, x is a signal vector, and ε represents a reconstruction error.
Solving by a sparse reconstruction algorithmAfter that, pass->Middle NOTThe position of the zero element in the redundant dictionary is calculated to obtain the two-dimensional arrival angle of the signal; the redundant dictionary is a grid divided according to angles, so that positions and angle values of non-zero elements are in one-to-one correspondence, and corresponding angles are obtained by obtaining the positions of the non-zero elements. The polarization angle of the signal can be determined by the polarization component of the non-zero element +.> andThe amplitude is calculated as shown in formula (15).
The result of the calculation using the formula (15) is a rough measurement of the polarization angle.
If it is necessary to obtain high-precision polarization angle measurement (mainly polarization auxiliary angle), the polarization angle can be uniformly and discretely divided on the known signal arrival angle, and the number of divided grids is N s And constructing a polarization redundancy dictionary as shown in a formula (16).
Gamma denotes the argument in polarization angle.
And (3) performing sparse reconstruction on the signals in a polarization domain by using the formula (16), so as to obtain accurate measurement of the polarization auxiliary angle.
In this embodiment, the arrival angle and polarization measurement of a plurality of radiation source signals are performed by performing a radiation source test in a microwave darkroom as shown in fig. 4, and it has been verified that the method proposed by the present invention has the following test conditions:
1) 4 radiation source antennas are erected in a microwave darkroom, a direction finding system is arranged on a turntable, and the angles of the radiation sources areAre set to (-17 °,5 °), (-5 °, -10 °), (2 °,15 °), (15 °, -3 °) respectively. The polarization angle of the antenna of the radiation source 1 can be changed from 0-90 degrees by controlling the polarization synthesis source, the radiation source 2 is horizontally polarized, the radiation source 3 is vertically polarized, and the radiation source 4 is obliquely polarized by 45 degrees.
2) The radiation sources 1,2, 3, 4 are arranged to radiate analog pulse signals, and the signals overlap in the time domain
Specifically, the antenna array adopts a polarization sensitive annular array as shown in fig. 3, the unit antennas are orthogonal dual-polarized antennas, the phase centers are coincident, and M (m=8) unit antennas are arranged in an annular shape. The radio frequency signals received by the antenna array are subjected to down-conversion to intermediate frequency signals through a switch assembly, a frequency conversion assembly and the like, then the intermediate frequency signals are subjected to parallel sampling processing through a multichannel digital acquisition processor, and sampling data are transmitted to a signal processor for storage and processing.
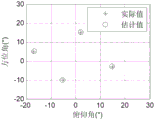
And executing the measuring method on the sampling data to obtain a two-dimensional arrival angle, a polarization angle rough measuring value and a polarization angle accurate measuring value. As shown in fig. 5, the present invention enables accurate measurement of the two-dimensional angle of arrival of all 4 radiation sources. The results of fig. 6 show that the present invention can correctly measure the polarization angles of 4 radiation sources.
The method of the invention is compared with the traditional single-pole annular array method. Switching on the No. 2 and No. 3 radiation sources, controlling the output power of the signal source, so that the received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is changed from 0dB to 15dB, and respectively counting root mean square errors (counted according to the processing results of 1000 pulse data under each SNR) of two-dimensional angle measurement; as shown in FIG. 7, the method of the invention can accurately measure the two-dimensional arrival angles and polarization of a plurality of frequency signals in a wide frequency band, the maximum value of the root mean square error is not more than 0.5 DEG under the condition of high signal-to-noise ratio, and the maximum value of the root mean square error is not more than 0.2 DEG under the condition of low signal-to-noise ratio. In contrast, if the single-polarized annular array is adopted, the number of effective array elements is reduced and the angle measurement accuracy is obviously reduced due to antenna mismatch, so that the polarization-sensitive annular array mode of the method is proved to be obviously superior to the single-polarized annular array mode.
The method of the present invention is compared with a conventional multidimensional joint search method. The angle of the single-open No. 4 radiation source is-45 degrees, the polarization angle is 0-90 degrees, the stepping interval is adjusted, 2 degrees, 1.5 degrees, 1 degrees, 0.5 degrees, 0.3 degrees, 0.2 degrees and 0.1 degrees are respectively taken, and the angle and the polarization measurement time (according to the total time result statistics of continuous 100 times of angle and polarization measurement) of the multi-dimensional combined search method and the method are counted. As shown in FIG. 8, the invention adopts the independent processing mode of frequency domain, angle domain and polarization domain, improves the measurement efficiency, and basically keeps the operand unchanged under the condition of reducing the search interval of angle and polarization. In contrast, if the multidimensional joint search mode (for example, angle and polarization joint search) is directly adopted, the operand is obviously increased, and the requirement of real-time direction finding cannot be met. Therefore, the direction finding processing real-time performance of the method is proved to be obviously superior to that of a multidimensional joint search method.
The verification shows that the polarization sensitive annular array is adopted to reduce the influence of antenna mismatch on the direction finding performance, signals are decomposed into a frequency domain, an angle domain and a polarization domain for independent processing, a multidimensional joint search process is avoided, the operand is greatly reduced, and the high-precision real-time measurement of the two-dimensional arrival angle and the polarization angle can be realized.
The invention is not limited to the specific embodiments described above. The invention extends to any novel one, or any novel combination, of the features disclosed in this specification, as well as to any novel one, or any novel combination, of the steps of the method or process disclosed. It is intended that insubstantial changes or modifications from the invention as described herein be covered by the claims below, as viewed by a person skilled in the art, without departing from the true spirit of the invention.
All of the features disclosed in this specification, or all of the steps in a method or process disclosed, may be combined in any combination, except for mutually exclusive features and/or steps.
Any feature disclosed in this specification may be replaced by alternative features serving the same or equivalent purpose, unless expressly stated otherwise. That is, each feature is one example only of a generic series of equivalent or similar features, unless expressly stated otherwise.
Claims (7)
1. The arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on the polarization sensitive annular array is characterized by comprising the following steps of:
step 1, receiving data of a plurality of signals through a polarization sensitive annular array, carrying out Fourier transform on the received data to obtain a frequency domain model, and measuring the frequency of each signal according to the frequency model; the unit antennas of the polarization sensitive annular array are orthogonal dual-polarized antennas, the phase centers are coincident, and the unit antennas are arranged according to an annular shape;
step 2, constructing an orthogonal polarization redundant dictionary for each signal according to the spatial sparsity of the signal;
step 3, performing sparse reconstruction on the corresponding signals on the orthogonal polarization redundant dictionary to obtain a space-polarization sparse representation model of the signals;
step 4, solving the space-polarization sparse representation model to obtain a sparse vector, and extracting non-zero elements in the sparse vector;
step 5, determining the two-dimensional arrival angle of the signal through the position of the non-zero element in the orthogonal polarization redundant dictionary; meanwhile, calculating a coarse measurement value of the signal polarization angle according to the polarization components of non-zero elements in the sparse vector;
and 6, repeating the steps 3-5 to obtain rough measurement values of the two-dimensional arrival angles and the polarization angles of all signals.
2. The method for measuring the arrival angle and the polarization angle based on the polarization sensitive annular array according to claim 1, wherein in the step 2, the method for constructing the orthogonal polarization redundancy dictionary is as follows:
based on the spatial sparsity of the signal, the frequency isThe two-dimensional arrival angle of the signals of (2) is discretely divided, and the number of grids is +.>Constructing an orthogonal polarization redundancy dictionary>:
3. The method for measuring arrival angle and polarization angle based on polarization sensitive annular array according to claim 2, wherein in the step 3, the space-polarization sparse representation model of the signal:
4. The method for measuring the arrival angle and the polarization angle based on the polarization-sensitive annular array according to claim 1 or 3, wherein the specific process of the step 4 is as follows: solving a space-polarization sparse representation model to obtain a sparse vector, solving non-zero elements, and converting the sparse vector into a convex optimization problem to solve in the solving process; the convex optimization problem is expressed as follows:
5. The method for measuring the arrival angle and the polarization angle based on the polarization-sensitive annular array according to claim 4, wherein the method for calculating the rough measurement value of the signal polarization angle in the step 5 is as follows:
6. The method for measuring the arrival angle and the polarization angle based on the polarization sensitive annular array according to claim 1 or 5, further comprising a high-precision signal polarization angle measuring method, wherein the accurate measurement value of the signal polarization angle can be obtained by constructing a new polarization redundancy dictionary by uniformly and discretely dividing the polarization angle on the known signal arrival angle and performing the steps 3-5 by adopting the new polarization redundancy dictionary.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111210703.3A CN114047473B (en) | 2021-10-18 | 2021-10-18 | Arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on polarization sensitive annular array |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111210703.3A CN114047473B (en) | 2021-10-18 | 2021-10-18 | Arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on polarization sensitive annular array |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114047473A CN114047473A (en) | 2022-02-15 |
| CN114047473B true CN114047473B (en) | 2023-06-06 |
Family
ID=80205480
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111210703.3A Active CN114047473B (en) | 2021-10-18 | 2021-10-18 | Arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on polarization sensitive annular array |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114047473B (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114019445B (en) * | 2021-09-22 | 2023-06-06 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十九研究所 | Two-dimensional arrival angle measurement method based on position clustering dynamic sparse reconstruction |
| CN114428225B (en) * | 2022-04-06 | 2022-06-14 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十九研究所 | Multi-radiation source arrival angle measuring method and device based on quasi-matched filtering |
| CN114442032B (en) * | 2022-04-07 | 2022-06-14 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十九研究所 | Direction finding method based on multi-polarization vector antenna array compression sampling |
| CN116995451B (en) * | 2023-09-27 | 2023-12-15 | 成都金支点科技有限公司 | Polarization sensitive array arranging method |
| CN117630810B (en) * | 2024-01-23 | 2024-04-05 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十九研究所 | Direction finding method steady to target polarization change |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3033841A1 (en) * | 1979-09-12 | 1981-04-02 | Bayly Engineering Ltd., Ajax, Ontario | BEARING SYSTEM |
| DE3519528A1 (en) * | 1985-05-31 | 1986-12-04 | ANT Nachrichtentechnik GmbH, 7150 Backnang | METHOD FOR GENERATING A CONTROL SIGNAL FOR THE POLARIZATION ORIENTATION OF AN ANTENNA |
| CN106324558A (en) * | 2016-08-30 | 2017-01-11 | 东北大学秦皇岛分校 | Broadband signal DOA estimation method based on co-prime array |
| CN112731278A (en) * | 2020-12-28 | 2021-04-30 | 杭州电子科技大学 | Angle and polarization parameter underdetermined joint estimation method for partially polarized signal |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2393498C2 (en) * | 2008-09-18 | 2010-06-27 | Закрытое акционерное общество "Научно-производственное предприятие "Бриг" (ЗАО "НПП "Бриг") | Method of polarisation sensitive radio signal direction finding (versions) |
| FR3034874B1 (en) * | 2015-04-09 | 2017-04-28 | Thales Sa | SOURCE SEPARATION METHOD FOR PARCIMONIOUS SIGNALS |
| CN104849694B (en) * | 2015-04-29 | 2017-06-09 | 陕西理工学院 | Quaternary number ESPRIT method for parameter estimation of the electromagnetic dipole to array |
| CN106249196B (en) * | 2016-06-20 | 2019-04-16 | 陕西理工大学 | Three-component acoustic vector sensors thinned array quaternary number ambiguity solution method |
| CN107015191B (en) * | 2017-05-18 | 2019-09-27 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | One kind single dipole polarization sensitization array dimensionality reduction DOA estimation method under multi-path jamming environment |
| CN107870314B (en) * | 2017-10-31 | 2021-06-29 | 西安电子科技大学 | Complete electromagnetic component weighting fusion direction-finding optimization method based on polarization sensitive array |
| CN108519575A (en) * | 2018-04-11 | 2018-09-11 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十九研究所 | Interferometer system antenna structure, radiation source polarization parameter measures and polarizing field signal enhancing method |
| CN110444886B (en) * | 2019-07-16 | 2021-02-19 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十九研究所 | Method for reducing phase difference error between antennas caused by polarization change |
| CN110716171A (en) * | 2019-08-28 | 2020-01-21 | 上海无线电设备研究所 | Polarization DOA joint estimation method based on genetic algorithm |
| CN112505685A (en) * | 2020-10-15 | 2021-03-16 | 中国人民解放军空军预警学院 | BSBL-EM algorithm-based separated polarization sensitive array coherent signal DOA and polarization parameter estimation |
| CN112748407B (en) * | 2020-12-15 | 2024-09-17 | 杭州电子科技大学 | Space domain-polarization domain joint spectrum estimation method based on polarization sensitive area array |
| CN113253194B (en) * | 2021-04-21 | 2022-07-08 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十九研究所 | Broadband arrival angle and polarization combined measurement method based on sparse representation |
-
2021
- 2021-10-18 CN CN202111210703.3A patent/CN114047473B/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3033841A1 (en) * | 1979-09-12 | 1981-04-02 | Bayly Engineering Ltd., Ajax, Ontario | BEARING SYSTEM |
| DE3519528A1 (en) * | 1985-05-31 | 1986-12-04 | ANT Nachrichtentechnik GmbH, 7150 Backnang | METHOD FOR GENERATING A CONTROL SIGNAL FOR THE POLARIZATION ORIENTATION OF AN ANTENNA |
| CN106324558A (en) * | 2016-08-30 | 2017-01-11 | 东北大学秦皇岛分校 | Broadband signal DOA estimation method based on co-prime array |
| CN112731278A (en) * | 2020-12-28 | 2021-04-30 | 杭州电子科技大学 | Angle and polarization parameter underdetermined joint estimation method for partially polarized signal |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114047473A (en) | 2022-02-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114047473B (en) | Arrival angle and polarization angle measuring method based on polarization sensitive annular array | |
| CN113253194B (en) | Broadband arrival angle and polarization combined measurement method based on sparse representation | |
| CN103983944B (en) | Based on arrowband, the far field DOA estimation method of covariance matrix rarefaction representation | |
| CN103353596A (en) | Wave beam space domain meter wave radar height measurement method based on compressed sensing | |
| CN113835063B (en) | Unmanned aerial vehicle array amplitude and phase error and signal DOA joint estimation method | |
| CN102662158B (en) | Quick processing method for sensor antenna array received signals | |
| CN111352063B (en) | Two-dimensional direction finding estimation method based on polynomial root finding in uniform area array | |
| CN110398732B (en) | Target direction detection method for low-calculation-quantity self-adaptive step size iterative search | |
| CN104793177A (en) | Microphone array direction finding method based on least square methods | |
| CN109521393A (en) | A kind of DOA estimation algorithm based on signal subspace revolving property | |
| CN103399308A (en) | Rapid estimation method of radar target angle under main lobe and side lobe jamming backgrounds | |
| CN105093200B (en) | Target Wave arrival direction estimating method outside a kind of grid based on amendment dictionary | |
| CN112763972B (en) | Sparse representation-based double parallel line array two-dimensional DOA estimation method and computing equipment | |
| CN111580042B (en) | Deep learning direction finding method based on phase optimization | |
| CN113267746A (en) | Weighted broadband direction of arrival estimation method based on group sparsity | |
| CN116774136B (en) | Lorentz high-precision direction finding method based on combination constraint | |
| CN109870670B (en) | Mixed signal parameter estimation method based on array reconstruction | |
| CN116500543B (en) | Incoming wave angle rapid estimation method based on reference direction transformation | |
| CN114563760B (en) | Second-order super-beam forming method, equipment and medium based on SCA array | |
| CN105572631A (en) | Maximum likelihood target DOA estimation method based on multi-wave potential combined treatment | |
| CN115575941A (en) | Sparse array-oriented frequency control array MIMO radar target parameter estimation method | |
| CN114236462A (en) | High-precision spatial spectrum direction finding method based on specific non-equidistant array structure | |
| CN109061564B (en) | Simplified near-field positioning method based on high-order cumulant | |
| CN114019445A (en) | Two-dimensional arrival angle measuring method based on position clustering dynamic sparse reconstruction | |
| CN113376568A (en) | Circular array DOA estimation method based on subspace orthogonal compensation |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |