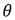CN114027783A - First-eye strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology - Google Patents
First-eye strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114027783A CN114027783A CN202111439549.7A CN202111439549A CN114027783A CN 114027783 A CN114027783 A CN 114027783A CN 202111439549 A CN202111439549 A CN 202111439549A CN 114027783 A CN114027783 A CN 114027783A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- strabismus
- eye
- target object
- patient
- point
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 208000004350 Strabismus Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 70
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 28
- 230000004424 eye movement Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 22
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 20
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 14
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 210000001747 pupil Anatomy 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 abstract description 4
- 230000000873 masking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005094 computer simulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000004087 cornea Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 201000005743 paralytic squint Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000028254 paralytic strabismus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000005180 public health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001028 reflection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012827 research and development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B3/00—Apparatus for testing the eyes; Instruments for examining the eyes
- A61B3/02—Subjective types, i.e. testing apparatus requiring the active assistance of the patient
- A61B3/08—Subjective types, i.e. testing apparatus requiring the active assistance of the patient for testing binocular or stereoscopic vision, e.g. strabismus
- A61B3/085—Subjective types, i.e. testing apparatus requiring the active assistance of the patient for testing binocular or stereoscopic vision, e.g. strabismus for testing strabismus
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B3/00—Apparatus for testing the eyes; Instruments for examining the eyes
- A61B3/0016—Operational features thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B3/00—Apparatus for testing the eyes; Instruments for examining the eyes
- A61B3/0091—Fixation targets for viewing direction
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Eye Examination Apparatus (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a first eye strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and an eye movement tracking technology, which comprises the following steps: s1, measuring the strabismus degree, wherein the strabismus degree is obtained by calculating the position point of the strabismus eye in the virtual three-dimensional space, the fixation point of the dominant eye in the virtual three-dimensional space and the real fixation direction vector of the strabismus eye; s2, a breaking point and a recovery point are measured, the breaking point and the recovery point need the target object to move from far to near and from near to far in the virtual reality scene, and the breaking point and the recovery point are obtained through calculation of the pupil position data of the human eye. The first eye position strabismus diagnosis method can avoid the problem of subjective misdiagnosis of doctors, so that the patient can concentrate on the target fixation point more, the accuracy of the determination result is improved, the determination process is simple, convenient and quick, the patient can obtain strabismus degree, the breaking point and the recovery point by watching a target object, the movement of eyes can be observed when the simulated sight line is shielded, and the purpose of automatic accurate diagnosis of strabismus is realized.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of strabismus diagnosis, virtual reality and eye movement tracking, in particular to a first eye position strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology.
Background
Strabismus refers to the condition that the eyes of a patient cannot watch the target at the same time, and can be divided into common strabismus and paralytic strabismus. The child strabismus has become a major public health problem in China due to large population base, high morbidity and great harm. The strabismus of children can be cured if the children intervene in time, but the life of the children can be affected if the treatment is delayed. The cultivation difficulty of the squint specialist is high, the number of the specialist is seriously insufficient, and the non-squint specialist cannot master the squint diagnosis and treatment clearly, so that missed diagnosis can be caused, or limited specialist resources are wasted due to excessive referral. The existing methods for examining the eye position and measuring the squint angle comprise a cornea reflection method, an alternative masking method, a prism masking method and the like, the results are highly subjective mainly by manual examination of doctors, the difference between inspectors is large, and the experience of the inspectors is also excessively depended, so that the research and development of the automatic and accurate squint examination becomes a clinical problem which needs to be solved urgently.
The virtual reality technology can provide a three-dimensional virtual environment generated by computer simulation, has the characteristic of enabling people to be personally on the scene, and can perform visual and auditory interaction with a user. The eye movement tracking technology can capture eye movement through an infrared camera and acquire information such as sight line direction and the like. The strabismus diagnosis environment is designed through a virtual reality technology, strabismus symptoms of a patient are induced, eye kinematics information is obtained through an eye movement tracking technology, then the eye position is checked, the strabismus degree is measured, and therefore strabismus diagnosis is achieved.
The strabismus diagnosis method based on the virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology has many advantages, can avoid subjective errors of doctors, can provide various scenes to enable a patient to concentrate on a target fixation point, can improve the accuracy of strabismus degree determination, can still observe the movement of eyes when the vision is simulated to be blocked, and can be realized through a computer and VR equipment to realize automatic accurate diagnosis of strabismus.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above technical problems in the related art, the present invention provides a first method for diagnosing strabismus based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology, which can overcome the above disadvantages in the prior art.
In order to achieve the technical purpose, the technical scheme of the invention is realized as follows:
a first eye position strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology comprises the following steps:
s1 determination of the degree of strabismus:
s11, building a virtual three-dimensional space, wherein a target object is arranged in the space, and the doctor regulates and controls the target object to be positioned right in front of the visual field of the squint patient;
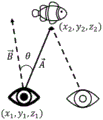
s12, enabling the strabismus patient to watch the target object, and acquiring the position point coordinates of the strabismus eye in the virtual three-dimensional space by the eye movement tracking deviceAnd obtaining the fixation point coordinate of the dominant eye in the virtual three-dimensional space;
S3 obtaining the assumed gaze direction vector of the strabismus from the position point coordinates and the gaze point coordinatesThen, the real gazing direction vector of the strabismus eye is obtained through the eye movement tracking deviceCalculating a direction vectorAnd direction vectorAngle therebetweenAngle of rotationThe degree of strabismus of the patient is obtained;
s2 determination of the point of rupture and recovery:
s21, keeping the target object right in front of the visual field of the patient, adjusting the distance between the target object and the eyes by the doctor, enabling the target object to move from far to near and then from near to far away from the eyes, enabling the squint patient to watch the target object, and enabling the eye movement tracking equipment to acquire the pupil position data of the eyes;
s22, in the process of moving the target object from far to near, the distance between the corresponding target object and the human eye when the distance between the pupils of the human eye is minimum is a breaking point, and in the process of moving the target object from near to far, the distance between the corresponding target object and the human eye when the distance between the pupils of the human eye is minimum is a recovery point.
Further, in S11, the doctor adjusts and controls the target object to be located at 6m right in front of the visual field of the patient.
Further, in S12, the squint patient is made to look at the target object for 30S.
Further, in S21, the doctor adjusts the distance between the target object and the human eye to 2m, and then moves the target object from far to near and then from near to far, and repeats the operation 5 times.
The invention has the beneficial effects that: the first eye strabismus diagnosis method can avoid the problem of subjective misdiagnosis of doctors, so that the patient can concentrate more on the target fixation point, the accuracy of the determination result is improved, the determination process is simple, convenient and quick, the strabismus degree, the breaking point and the recovery point can be obtained when the patient watches the target object, the movement of the eyes can be observed when the vision shielding is simulated, and the purpose of automatic and accurate diagnosis of strabismus is realized.
Drawings
In order to more clearly illustrate the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art, the drawings needed in the embodiments will be briefly described below, and it is obvious that the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present invention, and it is obvious for those skilled in the art to obtain other drawings without creative efforts.
Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of a first method for diagnosing an eye strabismus based on virtual reality and eye-tracking technology according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Detailed Description
The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention, and it is obvious that the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present invention, and not all of the embodiments. All other embodiments that can be derived by one of ordinary skill in the art from the embodiments given herein are intended to be within the scope of the present invention.
As shown in fig. 1, a first method for diagnosing an eye strabismus based on virtual reality and eye-movement tracking technology according to an embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
s1 determination of the degree of strabismus:
s11, building a virtual three-dimensional space, wherein a target object is arranged in the space, and the doctor regulates and controls the target object to be positioned right in front of the visual field of the squint patient;
s12, enabling the strabismus patient to watch the target object, and acquiring the position point coordinates of the strabismus eye in the virtual three-dimensional space by the eye movement tracking deviceAnd obtaining the fixation point coordinate of the dominant eye in the virtual three-dimensional space;
S3 obtaining the assumed gaze direction of the strabismus from the position point coordinates and the gaze point coordinates(Vector)Then, the real gazing direction vector of the strabismus eye is obtained through the eye movement tracking deviceCalculating a direction vectorAnd direction vectorAngle therebetweenAngle of rotationThe degree of strabismus of the patient is obtained;
s2 determination of the point of rupture and recovery:
s21, keeping the target object right in front of the visual field of the patient, adjusting the distance between the target object and the eyes by the doctor, enabling the target object to move from far to near and then from near to far away from the eyes, enabling the squint patient to watch the target object, and enabling the eye movement tracking equipment to acquire the pupil position data of the eyes;
s22, in the process of moving the target object from far to near, the distance between the corresponding target object and the human eye when the distance between the pupils of the human eye is minimum is a breaking point, and in the process of moving the target object from near to far, the distance between the corresponding target object and the human eye when the distance between the pupils of the human eye is minimum is a recovery point.
The doctor adjusts and controls the target object to be located at the position 6m right in front of the visual field of the patient in the above S11.
In S12, the target object is held by the squint patient for 30 seconds.
In S21, the doctor controls the distance between the target object and the human eye to be 2m, and then moves the target object from far to near and then from near to far, and repeats the operation 5 times.
In order to facilitate understanding of the above-described technical aspects of the present invention, the above-described technical aspects of the present invention will be described in detail below in terms of specific usage.
When the system is used specifically, a squint patient wears a VR helmet to carry out sight line calibration, then starts squint diagnosis, in the diagnosis process, the patient needs to watch a target object in a virtual reality scene all the time, a doctor can regulate and control the distance of the target object in the virtual reality scene, firstly, the doctor regulates and controls the distance between the target object and human eyes to be 6m, the patient watches the target object to be 30s, therefore, the determination of the squint degree is completed, then, the doctor regulates and controls the distance between the target object and the human eyes to be 2m, the target object moves from far to near and from near to far, and repeats for 5 times, and therefore, the determination of a breaking point and a recovery point is completed.
In conclusion, by means of the technical scheme, the problem of subjective misdiagnosis of doctors can be avoided, so that the patient can concentrate more on the target fixation point, the accuracy of the measurement result is improved, the measurement process is simple, convenient and quick, the patient can obtain the degree of strabismus, the breaking point and the recovery point by watching the target object, the movement of eyes can be observed when the vision is simulated to be blocked, and the purpose of automatic and accurate diagnosis of strabismus is achieved.
The above description is only for the purpose of illustrating the preferred embodiments of the present invention and is not to be construed as limiting the invention, and any modifications, equivalents, improvements and the like that fall within the spirit and principle of the present invention are intended to be included therein.
Claims (4)
1. A first eye position strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology is characterized by comprising the following steps:
s1 determination of the degree of strabismus:
s11, building a virtual three-dimensional space, wherein a target object is arranged in the space, and the doctor regulates and controls the target object to be positioned right in front of the visual field of the squint patient;
s12, enabling the strabismus patient to watch the target object, and acquiring the position point coordinates of the strabismus eye in the virtual three-dimensional space by the eye movement tracking deviceAnd obtaining the fixation point coordinate of the dominant eye in the virtual three-dimensional space;
S3 obtaining the assumed gaze direction vector of the strabismus from the position point coordinates and the gaze point coordinatesThen, the real gazing direction vector of the strabismus eye is obtained through the eye movement tracking deviceCalculating a direction vectorAnd direction vectorAngle therebetweenAngle of rotationThe degree of strabismus of the patient is obtained;
s2 determination of the point of rupture and recovery:
s21, keeping the target object right in front of the visual field of the patient, adjusting the distance between the target object and the eyes by the doctor, enabling the target object to move from far to near and then from near to far away from the eyes, enabling the squint patient to watch the target object, and enabling the eye movement tracking equipment to acquire the pupil position data of the eyes;
s22, in the process of moving the target object from far to near, the distance between the corresponding target object and the human eye when the distance between the pupils of the human eye is minimum is a breaking point, and in the process of moving the target object from near to far, the distance between the corresponding target object and the human eye when the distance between the pupils of the human eye is minimum is a recovery point.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein said S11 is where said biometric target object is located 6m directly in front of the visual field of the patient.
3. The method for diagnosing first eye strabismus according to claim 1, wherein the strabismus patient is allowed to fixate on the target object for 30S in S12.
4. The method of claim 1, wherein the doctor in S21 regulates and controls the distance between the target object and the human eye to be 2m, and repeats the operation 5 times after moving the target object from far to near and then from near to far.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111439549.7A CN114027783A (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2021-11-30 | First-eye strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111439549.7A CN114027783A (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2021-11-30 | First-eye strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114027783A true CN114027783A (en) | 2022-02-11 |
Family
ID=80145949
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111439549.7A Pending CN114027783A (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2021-11-30 | First-eye strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114027783A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116027910A (en) * | 2023-03-29 | 2023-04-28 | 广州视景医疗软件有限公司 | Eye bitmap generation method and system based on VR eye movement tracking technology |
-
2021
- 2021-11-30 CN CN202111439549.7A patent/CN114027783A/en active Pending
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116027910A (en) * | 2023-03-29 | 2023-04-28 | 广州视景医疗软件有限公司 | Eye bitmap generation method and system based on VR eye movement tracking technology |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9439592B2 (en) | Eye tracking headset and system for neuropsychological testing including the detection of brain damage | |
| US6659611B2 (en) | System and method for eye gaze tracking using corneal image mapping | |
| US9872615B2 (en) | Systems and methods for improved ease and accuracy of gaze tracking | |
| Chandra et al. | Eye tracking based human computer interaction: Applications and their uses | |
| CN111587086A (en) | Systems and methods for visual field analysis | |
| CA3049379A1 (en) | Improved accuracy of displayed virtual data with optical head mount displays for mixed reality | |
| JP2018508254A (en) | Method and system for automatic vision diagnosis | |
| CN114983775A (en) | Head-mounted visual detection and visual training equipment | |
| CN109634431B (en) | Medium-free floating projection visual tracking interaction system | |
| CN108064366B (en) | Binocular brightness sensitivity measurement method and device based on wearable display device and mobile terminal | |
| EP3402387B1 (en) | Method, system and computer readable medium to determine a strabismus angle between the eyes of an individual | |
| Yang et al. | Wearable eye-tracking system for synchronized multimodal data acquisition | |
| CN114027783A (en) | First-eye strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology | |
| KR102304369B1 (en) | SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR EXAMINATING ophthalmic using VR | |
| CN114931353A (en) | Convenient and fast contrast sensitivity detection system | |
| CN113138664A (en) | Eyeball tracking system and method based on light field perception | |
| Dilbeck et al. | Quotidian profile of vergence angle in ambulatory subjects monitored with wearable eye tracking glasses | |
| WO2024035896A1 (en) | Cover-uncover test in a vr/ar headset | |
| US11614623B2 (en) | Holographic real space refractive system | |
| CN114027782A (en) | Non-commonality strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology | |
| CN117204850A (en) | Device and method for detecting micro consciousness state based on virtual reality | |
| CN114052649A (en) | Alternate covering strabismus diagnosis method based on virtual reality and eye movement tracking technology | |
| CN113662822A (en) | Visual target adjusting method based on eye movement, visual training method and device | |
| US20230404388A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for measuring relative afferent pupillary defects | |
| JP2023032224A (en) | Eye position abnormality detection system, eye position abnormality detection method, and eye position abnormality detection program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |