CN113824754A - Communication method of network device, network device and storage medium - Google Patents
Communication method of network device, network device and storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113824754A CN113824754A CN202010567922.6A CN202010567922A CN113824754A CN 113824754 A CN113824754 A CN 113824754A CN 202010567922 A CN202010567922 A CN 202010567922A CN 113824754 A CN113824754 A CN 113824754A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- upstream network
- network device
- communication
- upstream
- information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000006854 communication Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 210
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 209
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 106
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 406
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims description 26
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002457 bidirectional effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010076 replication Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007723 transport mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/10—Protocols in which an application is distributed across nodes in the network
- H04L67/104—Peer-to-peer [P2P] networks
- H04L67/1061—Peer-to-peer [P2P] networks using node-based peer discovery mechanisms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/02—Details
- H04L12/16—Arrangements for providing special services to substations
- H04L12/18—Arrangements for providing special services to substations for broadcast or conference, e.g. multicast
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/60—Network streaming of media packets
- H04L65/61—Network streaming of media packets for supporting one-way streaming services, e.g. Internet radio
- H04L65/611—Network streaming of media packets for supporting one-way streaming services, e.g. Internet radio for multicast or broadcast
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
The application discloses a communication method of network equipment, the network equipment and a storage medium, wherein the method comprises the following steps: receiving query messages sent by more than two upstream network devices, wherein the query messages comprise multicast interception discovery protocol (MLD) query messages or Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) query messages, the MLD query messages or the IGMP query messages comprise extension fields, and the extension fields comprise information of the upstream network devices; determining the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network devices of the query message; and executing corresponding communication strategies on the more than two upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the more than two upstream network devices. By the method, the upstream network equipment can be distinguished, and technical support is provided for avoiding network bandwidth waste and avoiding the situation that a user side receives multiple copies of streams.
Description
Technical Field
The present application relates to the field of communications technologies, and in particular, to a communication method for a network device, and a storage medium.
Background
The Multicast Listener discovery Protocol (MLD) and the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) are designed primarily for discovery and Management of Multicast users, and with the development of technologies, new extensions are applied to the Multicast users, for example, in the field of Bit Index Replication (BIER) technology, the MLD and the IGMP are used for overlay layer Protocol, and find bits to be forwarded to a Router (BFIR) node in a Forwarding Ingress Router (BFIR), and forward the bits to a Router (BFER).
When the network environment is simple, the MLD or IGMP querier sender may be directly used as the incoming upstream network device of the downstream network device BFER, but when there are multiple upstream network devices in the network, if the downstream network device BFER does not perform distinguishing identification, the multiple upstream network devices may forward multiple copies of the same multicast traffic to the downstream network device BFER, resulting in network bandwidth waste, and if the user's terminal does not support repeat processing, even resulting in failure to view multicast video.
Disclosure of Invention
Based on this, embodiments of the present application provide a communication method for a network device, and a storage medium, which can distinguish an upstream network device and provide technical support for avoiding network bandwidth waste and avoiding a user side receiving multiple streams.
In a first aspect, the present application provides a communication method of a network device, where the method includes:
when a multicast source is detected, sending a query message, wherein the query message comprises a multicast interception discovery protocol (MLD) query message or an Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) query message, the MLD query message or the IGMP query message comprises an extension field, and the extension field comprises information of upstream network equipment so that downstream network equipment can determine the communication priority and the corresponding communication strategy of the upstream network equipment.
In a second aspect, the present application provides a communication method of a network device, the method including:
receiving query messages sent by more than two upstream network devices, wherein the query messages comprise multicast interception discovery protocol (MLD) query messages or Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) query messages, the MLD query messages or the IGMP query messages comprise extension fields, and the extension fields comprise information of the upstream network devices;
determining the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network devices of the query message;
and executing corresponding communication strategies on the more than two upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the more than two upstream network devices.
In a third aspect, the present application provides a network device comprising communication circuitry, a memory, and a processor, the communication circuitry to communicate; the memory is used for storing a computer program; the processor is configured to execute the computer program and to implement the communication method of the network device as described above in the first aspect when executing the computer program.
In a fourth aspect, the present application provides a network device comprising communication circuitry, a memory, and a processor, the communication circuitry to communicate; the memory is used for storing a computer program; the processor is configured to execute the computer program and to implement the communication method of the network device according to the second aspect when executing the computer program.
In a fifth aspect, the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium storing a computer program, which, when executed by a processor, causes the processor to implement the communication method of the network device according to the first aspect.
In a sixth aspect, the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium storing a computer program, which, when executed by a processor, causes the processor to implement the communication method of the network device according to the second aspect.
The embodiment of the application provides a communication method of a network device, the network device and a storage medium, wherein the method of the network device comprises the following steps: and when a multicast source is detected, sending a query message, wherein the query message comprises an MLD query message or an IGMP query message, the MLD query message or the IGMP query message comprises an expanded field, and the expanded field comprises information of upstream network equipment so that downstream network equipment can determine the communication priority and the corresponding communication strategy of the upstream network equipment. Because the extension field of the query message has the information of the upstream network equipment, the upstream network equipment can be distinguished by the method; the information of the upstream network equipment is used for the downstream network equipment to determine the communication priority of the upstream network equipment and the corresponding communication strategy, and half technical support is provided for the downstream network equipment to determine the communication priority of the upstream network equipment and the corresponding communication strategy. The method of another network device includes: receiving query messages sent by more than two upstream network devices; determining the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network devices of the query message; and executing corresponding communication strategies on the more than two upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the more than two upstream network devices. Because the query message of the upstream network device carries the information of the upstream network device, the downstream network device can determine the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device, and further execute corresponding communication strategies for the more than two upstream network devices respectively. For example: for the multicast traffic of the same multicast group or the same multicast source group, the downstream network device can choose to send the join message to the upstream network device with high communication priority and send the leave message to the other upstream network devices with low communication priority, so that the downstream network device can only receive one multicast traffic, the waste of network bandwidth can be avoided, only one multicast traffic is forwarded to the terminal, the situation that the user side receives multiple streams and the terminal cannot watch the multicast video because the terminal does not support repeated processing can be avoided.
Drawings
Fig. 1 is a schematic flowchart of an embodiment of a communication method of a network device according to the present application;
FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating another embodiment of a communication method of a network device according to the present application
Fig. 3 is a schematic flow chart diagram illustrating a communication method of a network device according to another embodiment of the present application;
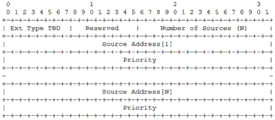
fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of a message expansion format of an embodiment of an MLD query message or an IGMP query message in the method according to the embodiment of the present application;
fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of a message expansion format of another embodiment of an MLD query message or an IGMP query message in the method according to the embodiment of the present application;
fig. 6 is a multicast topology diagram of an application scenario of a method according to an embodiment of the present application;
FIG. 7 is a schematic block diagram of an embodiment of a network device of the present application;
fig. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of another embodiment of a network device according to the present application.
Detailed Description
The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present application, and it is obvious that the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present application, and not all the embodiments. All other embodiments, which can be derived by a person skilled in the art from the embodiments given herein without making any creative effort, shall fall within the protection scope of the present application.
The flow diagrams depicted in the figures are merely illustrative and do not necessarily include all of the elements and operations/steps, nor do they necessarily have to be performed in the order depicted. For example, some operations/steps may be decomposed, combined or partially combined, so that the actual execution sequence may be changed according to the actual situation.
In the following description, suffixes such as "module", "component", or "unit" used to denote elements are used only for the convenience of description of the present application, and have no peculiar meaning by themselves. Thus, "module", "component" or "unit" may be used mixedly.
The communication method of the embodiment of the present application includes a communication method of an upstream network device (referred to as an upstream network device side method for short) and a communication method of a downstream network device (referred to as a downstream network device side method for short). For convenience of description and to facilitate better understanding of the communication method of the embodiments of the present application, the upstream network device side method and the downstream network device side method are described in detail below in combination.
It should be noted that, although the upstream network device method and the downstream network device method are described in combination, the upstream network device method and the downstream network device method are independent from each other, and the upstream network device method provides half technical support for the downstream network device to distinguish and identify the communication priority of the upstream network device and determine the corresponding communication policy; the downstream network equipment end method distinguishes and identifies the communication priority of different upstream network equipment for the downstream network equipment, and provides the other half of technical support for executing corresponding communication strategies respectively according to the communication priority; when the upstream network equipment end method and the downstream network equipment end method are combined together, the downstream network equipment can distinguish and identify the communication priorities of different upstream network equipment, and respectively execute corresponding communication strategies according to the communication priorities, so that technical support can be provided for avoiding network bandwidth waste, and technical support can be provided for avoiding that a user side receives multiple streams and a terminal cannot watch multicast videos because the terminal does not support repeated processing.
Referring to fig. 1 to fig. 3, fig. 1 is a schematic flowchart of an embodiment of a communication method of a network device of the present application, fig. 2 is a schematic flowchart of another embodiment of a communication method of a network device of the present application, and fig. 3 is a schematic flowchart of another embodiment of a communication method of a network device of the present application. It should be noted that the method in fig. 1 is an upstream network device side method, the method in fig. 2 is a downstream network device side method, and the method in fig. 3 is a method in which the upstream network device side method and the downstream network device side method are combined together.
The upstream network equipment side method comprises the following steps: step S101; the downstream network equipment side method comprises the following steps: step S201, step S202, and step S203.
The upstream network equipment side method comprises the following steps:
step S101: when a multicast source is detected, sending a query message, wherein the query message comprises a multicast interception discovery protocol (MLD) query message or an Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) query message, the MLD query message or the IGMP query message comprises an extension field, and the extension field comprises information of upstream network equipment so that downstream network equipment can determine the communication priority and the corresponding communication strategy of the upstream network equipment.
Upstream network devices and downstream network devices include, but are not limited to: routers, switches, bridges, gateways, and the like. The upstream network device may discover or detect the Multicast source through Multicast traffic or Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) registration, or other mechanisms. PIM directly uses the routing information of the unicast routing table to perform Reverse Path Forwarding (RDF) check on the multicast message, create a multicast routing table entry, and forward the multicast message.
In this embodiment, the query packet is a packet obtained by improving the existing packet, so that the communication process or the communication flow can be simplified, and the function can be extended on the basis of the existing query packet. The query message includes an MLD query message or an IGMP query message, and the MLD query message or the IGMP query message includes an extension field, and the extension field includes information of the upstream network device. When the upstream network device discovers or detects a multicast source, it needs to send an inquiry packet to determine whether there is a multicast user in the network where the upstream network device is located, and then determines whether forwarding is needed.
The information of the upstream network device may be information related to the upstream network device that can facilitate determination of a communication priority of the upstream network device. For example: routing information associated with the upstream network device, communication priority information for the upstream network device, and the like.
The communication policy may be a policy for the downstream network device to communicate with the upstream network device, which corresponds to the communication priority of the upstream network device or the relative communication priority of the upstream network device (i.e., may be the relative communication priority of the upstream network device compared with each other by a plurality of upstream network devices). For example: the communication priority of the upstream network device includes communication priority 1, communication priority 2 and communication priority 3, the communication policy corresponding to communication priority 1 is that the downstream network device receives and forwards the multicast traffic of the upstream network device, the communication policy corresponding to communication priority 2 is that the downstream network device receives but does not forward (discards) the multicast traffic of the upstream network device, and the communication policy corresponding to communication priority 3 is that the downstream network device refuses to receive the multicast traffic of the upstream network device.
In more application scenarios, when a downstream network device discovers that an upstream network device can communicate, the downstream network device may communicate with the upstream network device according to a normal communication procedure or flow, and when the downstream network device discovers that a plurality of upstream network devices can communicate, the downstream network device may compare information of the plurality of upstream network devices with each other to obtain a relative communication priority of the upstream network device, and then determine a corresponding communication policy according to the relative communication priority of the upstream network device.
In the embodiment of the application, the downstream network device may communicate with a plurality of upstream network devices, and the downstream network device may select different communication strategies to communicate with the plurality of upstream network devices according to actual requirements. It should be noted that the downstream network device can flexibly determine the communication policy according to the actual requirement.
The method of the downstream network equipment side comprises the following steps:
step S201: receiving query messages sent by more than two upstream network devices, where the query messages include multicast interception discovery protocol (MLD) query messages or Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) query messages, where the MLD query messages or the IGMP query messages include extension fields, and the extension fields include information of the upstream network devices.
Step S202: and determining the communication priority of the more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network devices of the query message.
Step S203: and executing corresponding communication strategies on the more than two upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the more than two upstream network devices.
In this embodiment, after receiving the query packet sent by more than two upstream network devices, the downstream network device needs to determine the communication priority of the more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network devices carried in the query packet, and then respectively execute corresponding communication policies on the more than two upstream network devices according to the communication priority.
The method for the upstream network equipment in the embodiment of the application comprises the following steps: and when a multicast source is detected, sending a query message, wherein the query message comprises an MLD query message or an IGMP query message, the MLD query message or the IGMP query message comprises an expanded field, and the expanded field comprises information of upstream network equipment so that downstream network equipment can determine the communication priority and the corresponding communication strategy of the upstream network equipment. Because the query message carries the information of the upstream network equipment, the plurality of upstream network equipment can be distinguished by the mode; the information of the upstream network equipment is used for the downstream network equipment to determine the communication priority of the upstream network equipment and the corresponding communication strategy, and half technical support is provided for the downstream network equipment to determine the communication priority of the upstream network equipment and the corresponding communication strategy. The method of the downstream network device comprises the following steps: receiving query messages of more than two upstream network devices; determining the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network devices of the query message; and executing corresponding communication strategies on the more than two upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the more than two upstream network devices. Because the query message of the upstream network device carries the information of the upstream network device, the downstream network device can determine the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device, and further execute corresponding communication strategies for the more than two upstream network devices respectively.
Wherein the information of the upstream network device comprises information of a unicast route of the upstream network device to the multicast source. The information of the unicast routing of the upstream network device to the multicast source includes but is not limited to: unicast routing table, priority information Preference, overhead information Metric, source address, multicast address, etc.
Further, the information of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source includes a priority information Preference of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source. Or the information of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source comprises priority information Preference and overhead information Metric of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source.
As shown in fig. 4, fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of a message expansion format of an embodiment of an MLD query message or an IGMP query message in the method according to the embodiment of the present application. The extension field of the message comprises: priority information Preference and overhead information Metric of unicast routing of the upstream network device to the multicast source.
The determining, by the downstream network device side and in step S202, the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device of the query packet may include: and determining the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the unicast routing information from the upstream network devices to the multicast source, which is carried by the query message.
In step S202, the determining, according to the information of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source carried in the query packet, the communication priority of two or more upstream network devices may further include: determining the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the priority information Preference of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source carried by the query message; or determining the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the priority information Preference and the overhead information Metric of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source carried by the query message.
For example: in an embodiment, the communication priorities of two upstream network devices are compared, and the priority information Preference and the overhead information Metric in the extension fields of two query messages may be compared in the following order: comparing the Preference first, and setting the communication priority of the upstream network equipment with the smaller Preference to be more optimal; if the preferences are the same, comparing the Metric, and setting the communication priority of the upstream network equipment with small Metric to be more optimal; if the metrics are the same, the source IP of the query message is compared, and the communication priority of the upstream network equipment with the large source IP can be set to be better.
Wherein the information of the upstream network device includes communication priority information of the upstream network device. The upstream network device may also set a communication priority for itself, and the downstream network device may determine the communication priority of the upstream network device and a corresponding communication policy according to the communication priority information of the upstream network device.
As shown in fig. 5, fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of a message expansion format of another embodiment of an MLD query message or an IGMP query message in the method according to the embodiment of the present application. The extension field of the message comprises: communication Priority information Priority of the upstream network device.
The determining, by the downstream network device side and in step S202, the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device of the query packet may include: and determining the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the communication priority information of the upstream network devices carried by the query message.
For example: the communication priority information set by one upstream network device is communication priority A, and the communication priority information set by the other upstream network device is communication priority B, wherein the communication priority A is set to be superior to the communication priority B; in an application scenario, one upstream network device is a primary upstream network device, and the other upstream network device is a standby upstream network device (i.e., a standby upstream network device), at this time, the primary upstream network device may be set to a communication priority a, and the standby upstream network device may be set to a communication priority B.
At the downstream network device side, in step S201, when the downstream network device receives more than two query messages, the receiving process is usually sequential.
If more than two query messages are received within a short time period (e.g., a preset time period), it can be considered that the upstream network device receives more than two query messages at the same time. The upstream network device may determine the communication priority of more than two upstream network devices according to the above information, and execute corresponding communication policies on the more than two upstream network devices respectively.
For example: if two query messages are received, the communication priority of the upstream network device 1 is superior to the communication priority of the upstream network device 2 through comparison, the downstream network device selects to communicate with the upstream network device 1, and at this time, the downstream network device can respond to the query message of the upstream network device 1 and send a response message to the upstream network device 1. The downstream network device may not respond to the query message of the upstream network device 2 and may not send a response message to the upstream network device 2. The downstream network device may also send a leave message to the upstream network device 2 in response to the query message of the upstream network device 2.
At this time, corresponding to the upstream network device side, for the upstream network device 1, after the step S101, after the multicast source is detected and the query packet is sent, the method may further include: and receiving an adding message of the downstream network equipment responding to the query message. For the upstream network device 2, after the step S101, after the sending the query packet after detecting the multicast source, the method may further include: and receiving a leaving message of the downstream network equipment responding to the query message, wherein the leaving message is sent when the downstream network equipment determines that the communication priority of the upstream network equipment is low.
If the time interval between receiving more than two query messages is relatively long (for example, exceeds a preset time period), it may be considered that the downstream network device receives more than two query messages in sequence. In many scenarios, the downstream network device receives more than two query messages in sequence, for example, the downstream network device receives more than two query messages in sequence.
It is exemplified that the downstream network device receives more than two query messages in sequence. If the downstream network device receives more than two query messages sequentially, before step S202, the method may further include: if a first multicast group user or a first multicast source group user is determined to be local according to a first query message of first upstream network equipment received first, sending a join message to the first upstream network equipment, and storing information of the first upstream network equipment.
In this embodiment, when the downstream network device receives a first query message of the first upstream network device first and determines that there is a first multicast group user or a first multicast source group user locally, the downstream network device sends a join message to the first upstream network device according to a normal communication flow, and stores information of the first upstream network device.
Step S202 is executed if a second query message of the second upstream network device is subsequently received.
In an embodiment, if it is stated that the same multicast traffic is forwarded by the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device according to the multicast group user or the multicast source group user corresponding to the second query message of the second upstream network device being the same as the multicast group user or the multicast source group user corresponding to the first query message of the first upstream network device, it is obvious that network bandwidth is wasted, at this time, the downstream network device may select one of the upstream network devices with a high communication priority to communicate, and refuse to communicate with the other upstream network device with a low communication priority.
That is, in step S202, the determining the communication priority of two or more upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device of the query packet may include: if the first multicast group user or the first multicast source group user is determined to be local according to the received second query message of the second upstream network device, determining the communication priority between the second upstream network device and the first upstream network device according to the information of the second upstream network device and the information of the first upstream network device.
In this embodiment, when the downstream network device receives a second query packet of a second upstream network device and determines that a first multicast group user or a first multicast source group user is present locally, it indicates that the same multicast traffic is forwarded by the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device, and accordingly, the communication priority between the second upstream network device and the first upstream network device may be determined according to the information of the second upstream network device and the stored information of the first upstream network device.
In this case, in step S203, the executing the corresponding communication policy on each of the two or more upstream network devices according to the communication priority of the two or more upstream network devices may include: and if the communication priority of the second upstream network equipment is higher than that of the first upstream network equipment, sending a joining message to the second upstream network equipment and sending a leaving message to the first upstream network equipment.
At this time, corresponding to the upstream network device side, for the first upstream network device, step S101, after detecting the multicast source, after sending the query packet, further includes: receiving an adding message of the downstream network equipment responding to the query message, and then receiving a leaving message of the downstream network equipment, wherein the leaving message is sent when the downstream network equipment determines that the communication priority of the upstream network equipment is low.
After the downstream network device sends the leave packet to the first upstream network device, the first upstream network device may stop forwarding the multicast traffic to the downstream network device. After the downstream network device sends the join packet to the second upstream network device, the second upstream network device may forward the multicast traffic to the downstream network device, and the downstream network device may receive and forward the multicast traffic of the second upstream network device.
In another embodiment, a plurality of upstream network devices perform load sharing, and a downstream network device configures a load sharing policy locally. When configuring the load sharing policy, it may be set that there is no difference between the communication priorities of the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device. If the multicast group user or the multicast source group user corresponding to the second query message of the second upstream network device is different from the multicast group user or the multicast source group user corresponding to the first query message of the first upstream network device, it indicates that the receiving objects of the multicast traffic forwarded by the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device are different, and the downstream network device needs to determine whether the communication priorities of the plurality of upstream network devices are different, so as to determine whether the plurality of upstream network devices perform load sharing.
That is, in step S202, the determining the communication priority of two or more upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device of the query packet may include: if a second multicast group user or a second multicast source group user is determined to be local according to a second query message of a second upstream network device received later, determining the communication priority between the second upstream network device and the first upstream network device according to the information of the second upstream network device and the information of the first upstream network device.
In this embodiment, the second multicast group and the first multicast group may be different multicast groups of the same multicast source, that is, the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device forward multicast traffic of different multicast groups of the same multicast source, that is, the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device are both connected to one multicast source, the multicast source has multiple multicast groups, and the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device forward multicast traffic of different multicast groups. The second multicast source group and the first multicast source group may be different multicast sources, that is, the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device forward multicast traffic of different multicast sources, that is, the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device are respectively connected to two different multicast sources.
The downstream network device receives a second query message of a second upstream network device, and when it is determined that a second multicast group user or a second multicast source group user exists locally, it indicates that the multicast traffic receiving objects forwarded by the first upstream network device and the second upstream network device are different, so that the communication priority between the second upstream network device and the first upstream network device can be determined according to the information of the second upstream network device and the stored information of the first upstream network device.
In this case, in step S203, the executing the corresponding communication policy on each of the two or more upstream network devices according to the communication priority of the two or more upstream network devices may include:
(1) and if the communication priority of the second upstream network device is the same as that of the first upstream network device and a load sharing policy is locally configured, calculating through the flow characteristic keywords in the first query message and the second query message.
(2) And selecting one upstream network device as the upstream network device of the second multicast group user or the second multicast source group user according to the calculation result.
(3) And sending a joining message to one selected upstream network device according to the selection result, and sending a leaving message to the other upstream network device.
If the communication priority of the second upstream network device is the same as the communication priority of the first upstream network device and a load sharing policy is locally configured, it may be determined that the second upstream network device and the first upstream network device perform load sharing, and at this time, the downstream network device needs to select one upstream network device for the first multicast group user or the first multicast source group user as an upstream network device for forwarding the multicast traffic of the group for itself, and select another upstream network device for the second multicast group user or the second multicast source group user as an upstream network device for forwarding the multicast traffic of the group for itself. And calculating through the flow characteristic keywords in the first query message and the second query message, selecting according to the calculation result, and sending a join message or a leave message to two upstream network devices according to the selection result.
The calculating by using the traffic feature keywords in the first query packet and the second query packet may include: and performing hash calculation according to the multicast source address or the multicast source address and the group address in the first query message and the second query message. It is possible to provide: and selecting the upstream network equipment as the downstream network equipment when the calculated hash value is large.
For example: first upstream network equipment sends a first query message, and downstream network equipment determines that a first multicast group user exists locally and sends a join message to the first upstream network equipment; after sending the join packet to the first upstream network device, the downstream network device receives and forwards the multicast traffic of the first upstream network device (the multicast traffic may include a first multicast traffic whose receiving object is a first multicast group user or a first multicast source group user, or may include a second multicast traffic whose receiving object is a second multicast group user or a second multicast source group user).
And after the second upstream network equipment sends a second query message, the downstream network equipment determines that a second multicast group user exists locally, after comparison, the communication priorities of the first upstream network equipment and the second upstream network equipment are the same, a load sharing strategy is locally configured, hash calculation is carried out according to the multicast source address and the group address in the first query message and the second query message, if the hash value obtained by calculating the multicast source address and the group address in the second query message is large, a join message is sent to the second upstream network equipment, and a leave message is sent to the first upstream network equipment. Sending a join message to a second upstream network device, sending a leave message to a first upstream network device (the first upstream network device stops forwarding a second multicast flow of which a receiving object is a second multicast group user or a second multicast source group user to a downstream network device), receiving and forwarding the second multicast flow of the second upstream network device by the downstream network device (corresponding to the second multicast group user or the second multicast source group user), and continuously receiving and forwarding a first multicast flow of which the receiving object is the first multicast group user or the first multicast source group user by the first upstream network device.
In another embodiment, the upstream network devices have different communication priorities, and the downstream network device is locally configured with a dual hot standby policy, so that the dual hot standby function can be implemented. The dual-root hot standby strategy may be that the plurality of upstream network devices include a main upstream network device and a standby upstream network device, a communication priority of the main upstream network device is superior to a communication priority of the standby upstream network device, the main upstream network device selects to receive and forward a traffic of the main upstream network device, the standby upstream network device serves as a standby, and the main upstream network device selects to receive and forward a traffic of the standby upstream network device when the main upstream network device is abnormal. By the method, if the main upstream network equipment is abnormal, the main upstream network equipment can be switched to the standby upstream network equipment to forward the flow, so that the aim of quick switching is fulfilled.
That is, in step S202, the executing the corresponding communication policy on the two or more upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the two or more upstream network devices may include: and if the communication priority of the second upstream network equipment is superior to that of the first upstream network equipment and the dual hot standby strategies are locally configured, sending a join message to the second upstream network equipment.
In this embodiment, in order to implement seamless fast handover when the primary upstream network device is abnormal, a leave packet is not sent to the first upstream network device, that is, the traffic of the first upstream network device is still received.
At this time, the method further includes: receiving multicast traffic of the first upstream network device and multicast traffic of the second upstream network device, respectively; and forwarding the multicast traffic of the second upstream network device, and discarding the multicast traffic of the first upstream network device. That is, the downstream network device receives and forwards the multicast traffic of the second upstream network device, and receives and discards the multicast traffic of the first upstream network device.
The method further comprises the following steps: if the second upstream network device is detected to be abnormal, forwarding the multicast traffic of the first upstream network device, and discarding the multicast traffic of the second upstream network device.
Because the downstream network device receives and forwards the multicast traffic of the second upstream network device and receives and discards the multicast traffic of the first upstream network device under the normal condition of the main upstream network device; and under the condition that the main upstream network equipment is abnormal, the downstream network equipment receives and forwards the multicast traffic of the first upstream network equipment, and receives and discards the multicast traffic of the second upstream network equipment.
The following describes a multicast topology diagram of an application scenario of the method according to the embodiment of the present application, and introduces an actual application of the method according to the application scenario in combination with the multicast topology diagram of the application scenario.
Referring to fig. 6, the multicast topology includes a BIER network for forwarding, two upstream network devices BFIR-1 and BFIR-2 at the edge of the BIER network, a downstream network device BFER at the edge of the BIER network, a network before forwarding (abbreviated as multicast source and network device R1) including a multicast source and network device R1 connected to the BFIR-1 and BFIR-2, respectively, and a receiving network (abbreviated as multicast receiver in the figure) including a multicast receiver connected to the BFER. It should be noted that the topology structure of fig. 6 is only a topology structure of an application scenario of the method in the embodiment of the present application, and the application scenario of the method in the embodiment of the present application is not limited thereto.
The first embodiment is as follows:
this embodiment selects an implementation method of upstream network devices BFIR-1, BFIR-2 for the downstream network device BFER.
(1) As shown in fig. 6, the BIER network of the multicast source side has two upstream network devices BFIR-1 and BFIR-2, and these two upstream network devices send a specific source group query message after discovering the multicast source through multicast traffic or PIM registration mechanism, etc.;
(2) as shown in fig. 4, the extension field carried in the query packet indicates the unicast route Preference and Metric from the BFIR to the multicast source;
(3) if BFER receives the above two inquiry messages in short time, then inquires the local multicast group user or multicast source group user, then it needs to send join message;
(4) before sending, it is necessary to compare the route to the specific multicast source S in the current query message with the route learned and queried to the specific multicast source S, and the comparison sequence is: comparing Preference, smaller and more preferable; the Preference is the same and is better than the Metric; the Metric compares the source IP of the query message again, and the Metric is larger and better. If the extension field of the BFIR-1 specific source group query message is better than that of BFIR-2 for the specific multicast source S, sending a join message to BFIR-1;
(5) if the BFER receives the specific source group query of the BFIR-2, the multicast group user or the multicast source group user is queried locally, the Preference and the Metric of the multicast source S of the BFIR-2 are recorded, and meanwhile, a join message is sent to the BFIR-2;
(6) after BFER, receiving specific source group inquiry sent by BFIR-1, inquiring local multicast group user or multicast source group user, finding that specific source group inquiry of BFIR-2 has been received, comparing extension fields of both, finding that BFIR-1 is more excellent, then sending joining message to BFIR-1, and simultaneously sending leaving message to BFIR-2;
(7) after step 5, the BFER only receives the flow sent by BFER-1 for the specific multicast source S, and discards the flow if the flow comes from other direction.
Example two:
the present embodiment is a method for load sharing among multiple upstream network devices.
(1) As shown in fig. 6, for the multicast source S, there are a plurality of multicast groups G1-GN; the unicast routes Preference and Metric from BFIR-1 and BFIR-2 to the multicast source S are the same, and the BFER locally configures the multicast load sharing function;
(2) after discovering a multicast source through multicast flow or a mechanism such as PIM registration, the BFIR-2 sends a specific source group query message, which carries a Preference and a Metric extension field as shown in fig. 4;
(3) after receiving the query message, the BFER stores the Preference and the Metric of the message and sends a message adding response BFIR-2;
(4) after the BFIR-1 detects the multicast flow, it will also send the query message, carrying the Preference and Metric extension field;
(5) after receiving the BFER, comparing the information Preference and the Metric of the BFIR-2 stored originally, finding that the information Preference and the Metric of the BFIR-1 and the BFIR-2 are the same and a load sharing strategy is configured locally, giving flow characteristic keywords such as a multicast source address and a group address to perform hash calculation, selecting one of the BFIR-1 and the BFIR-2 as own upstream network equipment, sending a join message, and sending a leave message to the other;
in this embodiment, for the multicast source S, there are multiple multicast groups G1-GN, and through the hash calculation in step 5, part of the traffic is forwarded through BFIR-1, and the other part of the traffic is forwarded through BFIR-2, so as to achieve the purpose of load sharing and reduce the forwarding burden of BFIR.
Example three:
this example is a method of performing a double hot standby.
(1) The BFER enables double hot standby functions, and the steps (1) to (5) in the same embodiment I are carried out;
(2) after BFER, receiving specific source group query sent by BFIR-1, finding that specific source group query of BFIR-2 has been received, comparing extension fields of both, finding that BFIR-1 is more excellent, sending specific source group joining message to BFIR-1, at the same time continuously sending specific source group joining message, and responding BFIR-2;
(3) on the BFER, the BFIR-1 is used as a main root (main upstream network equipment), the BFER normally receives and forwards the flow of the BFIR-1, the BFIR-2 is used as a standby root (standby upstream network equipment), and the BFER receives and discards the flow forwarded by the BFIR-2;
(4) when detecting that the BFIR-1 is abnormal by methods such as Point-to-multipoint master station (P2MP, Point 2Multiple Point) Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD), flow Detection and the like, switching to receiving and Forwarding the Forwarding flow of the BFIR-2 to achieve the purpose of fast switching.
Example four:
this embodiment is an implementation method in which a downstream network device (BFER) selects an upstream network device (BFIR-1, BFIR-2) through communication priority information of the upstream network device.
(1) As shown in fig. 6, the BIER network of the multicast source side has two upstream network devices BFIR-1 and BFIR-2, and these two upstream network devices send a specific source group query message after discovering the multicast source through multicast traffic or PIM registration mechanism, etc.;
(2) as shown in fig. 5, Priority of the extension field carried in the query packet indicates the communication Priority of the upstream network device itself;
(3) if BFER receives the above two inquiry messages in short time, then inquires the local multicast group user or multicast source group user, then it needs to send join message;
(4) before sending, the communication priorities of the upstream network devices in the two query messages need to be compared, the Priority is smaller and better, if the priorities are the same, the source addresses of the query messages are compared, and the address is larger and better; if the communication priority of BFIR-1 is better than that of BFIR-2, sending an adding message to BFIR-1;
(5) if the BFER receives the specific source group query of BFIR-2, the multicast group user or the multicast source group user is queried locally, the Priority of BFIR-2 is recorded, and meanwhile, a join message is sent to BFIR-2;
(6) after BFER, receiving specific source group query sent by BFIR-1, querying local multicast group user or multicast source group user, finding that specific source group query of BFIR-2 has been received, comparing the extended field Priority of the two, finding that BFIR-1 is more optimal, sending an adding message to BFIR-1, and sending a leaving message to BFIR-2;
(7) after step 5, the BFER only receives the flow sent by BFER-1 for the specific multicast source S, and discards the flow if the flow comes from other direction.
Referring to fig. 7, fig. 7 is a schematic structural diagram of an embodiment of a network device of the present application, it should be noted that the network device of the present embodiment can implement the communication method of the upstream network device, and for a detailed description of related contents, please refer to the communication method portion of the upstream network device, which is not described herein again.
The network device 100 comprises a communication circuit 3, a memory 1 and a processor 2, wherein the communication circuit 3 is used for communication; the memory 1 is used for storing a computer program; the processor 2 is configured to execute the computer program and implement the communication method of the upstream network device side as described in any one of the above when executing the computer program.
The processor 2 may be a micro-control unit, a central processing unit, a digital signal processor, or the like. The memory 1 may be a Flash chip, a read-only memory, a magnetic disk, an optical disk, a usb-disk or a removable hard disk, etc.
Referring to fig. 8, fig. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of another embodiment of the network device of the present application, it should be noted that the network device of the present embodiment can implement the communication method of the downstream network device, and for a detailed description of related contents, please refer to the communication method portion of the downstream network device, which is not described herein again.
The network device 200 comprises a communication circuit 33, a memory 11 and a processor 22, wherein the communication circuit 33 is used for communication; the memory 11 is used for storing a computer program; the processor 22 is configured to execute the computer program and implement the communication method of the downstream network device side as described in any one of the above items when executing the computer program.
The processor 22 may be a micro-control unit, a central processing unit, a digital signal processor, or the like. The memory 11 may be a Flash chip, a read-only memory, a magnetic disk, an optical disk, a usb-disk or a removable hard disk, etc.
The present application also provides a computer-readable storage medium, which stores a computer program, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the processor is caused to implement the communication method on the upstream network device side according to any one of the above.
The computer-readable storage medium may be an internal storage unit of the upstream network device, such as a hard disk or a memory. The computer readable storage medium may also be an external storage device of the upstream network device, such as a plug-in hard drive, smart memory card, secure digital card, flash memory card, etc. as described above.
The present application also provides another computer-readable storage medium, which stores a computer program, and the computer program, when executed by a processor, causes the processor to implement the communication method at the downstream network device side according to any one of the above.
The computer-readable storage medium may be an internal storage unit of the downstream network device, such as a hard disk or a memory. The computer readable storage medium may also be an external storage device of the downstream network device, such as a plug-in hard disk, a smart memory card, a secure digital card, a flash memory card, etc., provided.
One of ordinary skill in the art will appreciate that all or some of the steps of the methods, systems, functional modules/units in the devices disclosed above may be implemented as software, firmware, hardware, and suitable combinations thereof.
In a hardware implementation, the division between functional modules/units mentioned in the above description does not necessarily correspond to the division of physical components; for example, one physical component may have multiple functions, or one function or step may be performed by several physical components in cooperation. Some or all of the physical components may be implemented as software executed by a processor, such as a central processing unit, digital signal processor, or microprocessor, or as hardware, or as an integrated circuit, such as an application specific integrated circuit. Such software may be distributed on computer readable media, which may include computer storage media (or non-transitory media) and communication media (or transitory media). The term computer storage media includes volatile and nonvolatile, removable and non-removable media implemented in any method or technology for storage of information such as computer readable instructions, data structures, program modules or other data, as is well known to those of ordinary skill in the art. Computer storage media includes, but is not limited to, RAM, ROM, EEPROM, flash memory or other memory technology, CD-ROM, Digital Versatile Disks (DVD) or other optical disk storage, magnetic cassettes, magnetic tape, magnetic disk storage or other magnetic storage devices, or any other medium which can be used to store the desired information and which can accessed by a computer. In addition, communication media typically embodies computer readable instructions, data structures, program modules or other data in a modulated data signal such as a carrier wave or other transport mechanism and includes any information delivery media as known to those skilled in the art.
The preferred embodiments of the present application have been described above with reference to the accompanying drawings, and are not intended to limit the scope of the claims of the application accordingly. Any modifications, equivalents and improvements which may occur to those skilled in the art without departing from the scope and spirit of the present application are intended to be within the scope of the claims of the present application.
Claims (13)
1. A method of communication of a network device, the method comprising:
when a multicast source is detected, sending a query message, wherein the query message comprises a multicast interception discovery protocol (MLD) query message or an Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) query message, the MLD query message or the IGMP query message comprises an extension field, and the extension field comprises information of upstream network equipment so that downstream network equipment can determine the communication priority and the corresponding communication strategy of the upstream network equipment.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein the information of the upstream network device comprises information of a unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source, or comprises communication priority information of the upstream network device; the information of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source comprises a priority information Preference of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source, or comprises a priority information Preference and an overhead information Metric of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source.
3. The method according to claim 1, wherein after the sending the query message after detecting the multicast source, further comprising:
receiving an adding message of the downstream network equipment responding to the query message;
or,
and receiving a leaving message of the downstream network equipment responding to the query message.
4. A method of communication of a network device, the method comprising:
receiving query messages sent by more than two upstream network devices, wherein the query messages comprise multicast interception discovery protocol (MLD) query messages or Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) query messages, the MLD query messages or the IGMP query messages comprise extension fields, and the extension fields comprise information of the upstream network devices;
determining the communication priority of the more than two upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network devices of the query message;
and executing corresponding communication strategies on the more than two upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the more than two upstream network devices.
5. The method according to claim 4, wherein before determining the communication priority of the two or more upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device of the query packet, the method further comprises:
if a first multicast group user or a first multicast source group user is determined to be local according to a first query message of first upstream network equipment received first, sending a join message to the first upstream network equipment, and storing information of the first upstream network equipment.
6. The method according to claim 5, wherein the determining the communication priority of the two or more upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device of the query packet comprises:
if the first multicast group user or the first multicast source group user is determined to be local according to a second query message of second upstream network equipment received later, determining the communication priority of the second upstream network equipment and the first upstream network equipment according to the information of the second upstream network equipment and the information of the first upstream network equipment;
the executing the corresponding communication strategies to the two or more upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the two or more upstream network devices respectively includes:
if the communication priority of the second upstream network equipment is higher than that of the first upstream network equipment, sending a joining message to the second upstream network equipment and sending a leaving message to the first upstream network equipment;
the method further comprises the following steps: and receiving and forwarding the multicast traffic of the second upstream network device.
7. The method according to claim 5, wherein the determining the communication priority of the two or more upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device of the query packet comprises:
if a second multicast group user or a second multicast source group user is determined to be local according to a second query message of second upstream network equipment received later, determining the communication priority between the second upstream network equipment and the first upstream network equipment according to the information of the second upstream network equipment and the information of the first upstream network equipment;
the executing the corresponding communication strategies to the two or more upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the two or more upstream network devices respectively includes:
if the communication priority of the second upstream network device is the same as that of the first upstream network device and a load sharing policy is locally configured, calculating through the flow characteristic keywords in the first query message and the second query message;
selecting one upstream network device as the upstream network device of the second multicast group user or the second multicast source group user according to the calculation result;
sending a joining message to one selected upstream network device according to the selection result, and sending a leaving message to the other upstream network device;
the method further comprises the following steps:
and receiving and forwarding the first multicast traffic of the first upstream network device and the second multicast traffic of the second upstream network device respectively.
8. The method according to claim 5, wherein the determining the communication priority of the two or more upstream network devices according to the information of the upstream network device of the query packet comprises:
if the first multicast group user or the first multicast source group user is determined to be local according to a second query message of second upstream network equipment received later, determining the communication priority of the second upstream network equipment and the first upstream network equipment according to the information of the second upstream network equipment and the information of the first upstream network equipment;
the executing the corresponding communication strategies to the two or more upstream network devices according to the communication priorities of the two or more upstream network devices respectively includes:
if the communication priority of the second upstream network device is superior to that of the first upstream network device and the dual hot standby strategies are locally configured, sending a join message to the second upstream network device;
the method further comprises the following steps:
receiving multicast traffic of the first upstream network device and multicast traffic of the second upstream network device, respectively;
forwarding the multicast traffic of the second upstream network device, and discarding the multicast traffic of the first upstream network device;
if the second upstream network device is detected to be abnormal, forwarding the multicast traffic of the first upstream network device, and discarding the multicast traffic of the second upstream network device.
9. The method of claim 4, wherein the information of the upstream network device comprises information of a unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source, or comprises communication priority information of the upstream network device; the information of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source comprises a priority information Preference of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source, or comprises a priority information Preference and an overhead information Metric of the unicast route from the upstream network device to the multicast source.
10. A network device comprising communication circuitry, memory, and a processor, the communication circuitry to communicate; the memory is used for storing a computer program; the processor is adapted to execute the computer program and to implement the communication method of the network device according to any of claims 1-3 when executing the computer program.
11. A network device comprising communication circuitry, memory, and a processor, the communication circuitry to communicate; the memory is used for storing a computer program; the processor is adapted to execute the computer program and to implement the communication method of the network device according to any of claims 4-9 when executing the computer program.
12. A computer-readable storage medium, characterized in that the computer-readable storage medium stores a computer program which, when executed by a processor, causes the processor to implement the communication method of the network device according to any one of claims 1 to 3.
13. A computer-readable storage medium, characterized in that the computer-readable storage medium stores a computer program which, when executed by a processor, causes the processor to implement the communication method of the network device according to any one of claims 4 to 9.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010567922.6A CN113824754A (en) | 2020-06-19 | 2020-06-19 | Communication method of network device, network device and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010567922.6A CN113824754A (en) | 2020-06-19 | 2020-06-19 | Communication method of network device, network device and storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113824754A true CN113824754A (en) | 2021-12-21 |
Family
ID=78912114
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010567922.6A Pending CN113824754A (en) | 2020-06-19 | 2020-06-19 | Communication method of network device, network device and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113824754A (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101296103A (en) * | 2007-04-27 | 2008-10-29 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and system for requesting multicast information, method and system for controlling multicast service |
| CN101877678A (en) * | 2010-07-01 | 2010-11-03 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and device for multicast users of specific source group to leave quickly |
| CN102217260A (en) * | 2011-05-17 | 2011-10-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Processing method for multicast data streams, user facing provider edge (UPE) and network facing provider edge (NPE) |
| US20130279518A1 (en) * | 2012-04-19 | 2013-10-24 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | System and Apparatus for Router Advertisement Options for Configuring Networks to Support IPv6 to IPv4 Multicast Translation |
| CN104144125A (en) * | 2013-05-10 | 2014-11-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for filtering multicast data, network device and router |
-
2020
- 2020-06-19 CN CN202010567922.6A patent/CN113824754A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101296103A (en) * | 2007-04-27 | 2008-10-29 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and system for requesting multicast information, method and system for controlling multicast service |
| CN101877678A (en) * | 2010-07-01 | 2010-11-03 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and device for multicast users of specific source group to leave quickly |
| CN102217260A (en) * | 2011-05-17 | 2011-10-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Processing method for multicast data streams, user facing provider edge (UPE) and network facing provider edge (NPE) |
| US20130279518A1 (en) * | 2012-04-19 | 2013-10-24 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | System and Apparatus for Router Advertisement Options for Configuring Networks to Support IPv6 to IPv4 Multicast Translation |
| CN104144125A (en) * | 2013-05-10 | 2014-11-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for filtering multicast data, network device and router |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| LUIS M. CONTRERAS; HITOSHI ASAEDA; CARLOS J. BCRNARDOS; NIC LEYMANN: "Enabling New Multicast Distribution Architectures Through the Introduction of IGMP/MLD Proxy with Multiple Upstream Interfaces", IEEE, 16 August 2018 (2018-08-16) * |
| 胡升亮: "组播IGMP在EPON系统中的设计与实现", 中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库, 31 October 2012 (2012-10-31) * |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110798403B (en) | Communication method, communication device and communication system | |
| US9160616B2 (en) | Multicast packet transmission method, related device and system | |
| US7778266B2 (en) | Switch and network fault recovery method | |
| US20240323115A1 (en) | Loop Avoidance Communications Method, Device, and System | |
| EP2541847A1 (en) | Method for establishing associated bidirectional label switching path and system thereof | |
| CN101651609A (en) | Method and device for realizing multicast load sharing | |
| WO2022253084A1 (en) | Path protection method, node device, controller, and storage medium | |
| CN113615132A (en) | Fast flooding topology protection | |
| US11909546B2 (en) | Method and network node for sending and obtaining assert packet | |
| US10742431B2 (en) | Centralized database based multicast converging | |
| CN108234358B (en) | Multicast message transmission method, device and machine readable storage medium | |
| CN113973020B (en) | Method, device and system for sending multicast message | |
| US9313037B2 (en) | Method, apparatus and system for forwarding data under protocol independent multicast dual join | |
| CN111385195B (en) | Information processing method, device and storage medium | |
| CN113824754A (en) | Communication method of network device, network device and storage medium | |
| CN102404218B (en) | Method and device for switching tunnels | |
| CN106059925B (en) | Multicast processing method and equipment | |
| CN112511443A (en) | Message processing method, device, equipment, storage medium and system | |
| CN103516548B (en) | RP equipment management method and equipment | |
| CN117811995A (en) | Method and device for determining node | |
| CN115226038A (en) | Multicast implementation method, routing device and storage medium | |
| CN117118802A (en) | Path fault detection method, path fault detection device, network equipment and storage medium | |
| KR20090132659A (en) | Apparatus for internet group management protocol proxy |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |