CN113223944A - Manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of fast recovery chip and fast recovery chip - Google Patents
Manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of fast recovery chip and fast recovery chip Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113223944A CN113223944A CN202110351049.1A CN202110351049A CN113223944A CN 113223944 A CN113223944 A CN 113223944A CN 202110351049 A CN202110351049 A CN 202110351049A CN 113223944 A CN113223944 A CN 113223944A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- diffusion
- platinum
- silicon wafer
- phosphorus
- boron
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 81
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 42
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 248
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 213
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 138
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 127
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 127
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 127
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 97
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 96
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 96
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 85
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 85
- -1 platinum ions Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 26
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 claims description 30
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910001873 dinitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 235000012431 wafers Nutrition 0.000 description 88
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 9
- GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium Chemical compound [Ga] GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000005488 sandblasting Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 5
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012864 cross contamination Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005202 decontamination Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003588 decontaminative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013467 fragmentation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000006062 fragmentation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003698 laser cutting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004518 low pressure chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- GVVPGTZRZFNKDS-JXMROGBWSA-N geranyl diphosphate Chemical compound CC(C)=CCC\C(C)=C\CO[P@](O)(=O)OP(O)(O)=O GVVPGTZRZFNKDS-JXMROGBWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910001385 heavy metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007943 implant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000004437 phosphorous atom Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000005554 pickling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007517 polishing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005215 recombination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006798 recombination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66083—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched, e.g. two-terminal devices
- H01L29/6609—Diodes
- H01L29/66136—PN junction diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01J—ELECTRIC DISCHARGE TUBES OR DISCHARGE LAMPS
- H01J37/00—Discharge tubes with provision for introducing objects or material to be exposed to the discharge, e.g. for the purpose of examination or processing thereof
- H01J37/30—Electron-beam or ion-beam tubes for localised treatment of objects
- H01J37/317—Electron-beam or ion-beam tubes for localised treatment of objects for changing properties of the objects or for applying thin layers thereon, e.g. for ion implantation
- H01J37/3171—Electron-beam or ion-beam tubes for localised treatment of objects for changing properties of the objects or for applying thin layers thereon, e.g. for ion implantation for ion implantation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/26—Bombardment with radiation
- H01L21/263—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation
- H01L21/265—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation
- H01L21/26506—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation in group IV semiconductors
- H01L21/26513—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation in group IV semiconductors of electrically active species
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
- H01L29/8613—Mesa PN junction diodes
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Abstract
The application discloses a manufacturing method, manufacturing equipment and a fast recovery chip of a fast recovery chip, wherein the manufacturing method comprises the following steps: carrying out phosphorus diffusion on the silicon wafer by using a phosphorus source to form a phosphorus diffusion structural layer on at least one surface of the silicon wafer; removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one surface of the silicon wafer; carrying out boron diffusion on the silicon wafer by using a boron source so as to form a boron diffusion structural layer on one surface of the silicon wafer, which is removed from the phosphorus diffusion structural layer; platinum ion implantation is carried out through the surface of the boron diffusion structure layer to realize platinum diffusion; performing platinum deep diffusion in a preset temperature range; preparing a fast recovery chip by adopting the silicon chip subjected to the platinum deep diffusion; platinum diffusion is carried out in an ion implantation mode, namely platinum ions are implanted into the boron diffusion structure layer to carry out platinum diffusion, so that the platinum diffusion is more uniform, the original structure of the silicon wafer is prevented from being damaged due to the uneven platinum distribution, and meanwhile, the recovery characteristic of the fast recovery chip is improved.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductor electronic component manufacturing, in particular to a manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of a fast recovery chip and the fast recovery chip.
Background
The main circuit in modern power electronic circuit, whether it adopts a thyristor switched off by current conversion or a novel power electronic device with self-turn-off capability, needs a power fast recovery diode connected in parallel with it to reduce the charging time of the main switch device capacitor by the reactive current in the load, and at the same time, it restrains the high voltage induced by the parasitic inductance when the load current is instantaneously reversed. In recent years, with the continuous progress of the manufacturing technology of power semiconductor devices, the design and manufacture of novel power semiconductor devices such as vertical double-diffused metal-oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (DMOSFETs) and Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) of main switch devices in power electronic circuits have made great progress, and the frequency performance is continuously improved, which puts higher requirements on fast power recovery diodes used in cooperation with the fast power recovery diodes. Therefore, the diode must have a short reverse recovery time and excellent overall performance. Fast recovery diodes with P-i-N structures are the first choice devices for high voltage applications with high withstand voltage and high switching speed.
The production process of the semiconductor chip needs to carry out platinum expanding treatment after boron expanding and before GPP production, stir and evenly coat the prepared platinum source, and then load the chip into a boat, feed the chip into a furnace, discharge the chip from the furnace and cool the chip. However, in the prior art, when the platinum is diffused, the phenomenon of uneven diffusion occurs on the chip, and the recovery characteristic of the product is affected.
Disclosure of Invention
The application aims to provide a manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of a fast recovery chip and the fast recovery chip, which can improve the dispersion uniformity of platinum in a silicon wafer, thereby simultaneously improving the recovery characteristic of the chip.
The application discloses a manufacturing method of a fast recovery chip, which comprises the following steps:
carrying out phosphorus diffusion on the silicon wafer by using a phosphorus source to form a phosphorus diffusion structural layer on at least one surface of the silicon wafer;
removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one surface of the silicon wafer;
carrying out boron diffusion on the silicon wafer by using a boron source so as to form a boron diffusion structural layer on one surface of the silicon wafer, which is removed from the phosphorus diffusion structural layer;
platinum ion implantation is carried out through the surface of the boron diffusion structure layer, so that platinum diffusion is realized;
performing platinum deep diffusion in a preset temperature range;
and preparing the fast recovery chip by adopting the silicon chip subjected to the platinum deep diffusion.
Optionally, platinum ion implantation is performed on the surface of the silicon wafer on which the boron diffusion structure layer is formed, and in the step of performing platinum diffusion, the depth of the implanted platinum ion is 2-4 micrometers.
Optionally, the implantation dose of the platinum ions is 2e15cm2To 4e15cm2The implantation energy of the platinum ions is 50KeV to 70 KeV.
Optionally, in the step of performing platinum deep diffusion within a preset temperature range, the preset temperature range is 800-950 ℃.
Optionally, in the step of removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one side of the silicon wafer, the thickness of the silicon wafer is controlled to be 235-245 μm when the phosphorus diffusion structure layer is removed.
Optionally, the step of removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one side of the silicon wafer includes:
and polishing the silicon wafer with the phosphorus diffusion structure layer removed.
Optionally, in the step of polishing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer to be removed, the polished silicon wafer is cleaned by using hydrofluoric acid.
Optionally, in the step of performing platinum diffusion and the step of performing platinum deep diffusion within a preset temperature range, nitrogen is introduced at a rate of 5-7 liters per minute on the surface of the silicon wafer on which the boron diffusion structure layer is formed.
The application also discloses a fast recovery chip, which comprises a phosphorus region, a base region and a boron region, wherein the phosphorus region is the cathode of the fast recovery chip; the base region is arranged on the phosphorus region; the boron region is arranged on the base region and is an anode of the fast recovery chip; and a platinum ion injection region is formed on one surface of the boron region, which is far away from the base region, and platinum ions are diffused from the platinum ion injection region to be uniformly distributed in the phosphorus region, the base region and the boron region.
The application also discloses a manufacturing device of the fast recovery chip, which comprises a plurality of different diffusion devices and an ion implanter; the different diffusion devices respectively realize phosphorus diffusion, boron diffusion and platinum diffusion of the silicon wafer; the ion implanter is used for implanting platinum ions into the silicon wafer subjected to boron diffusion; the manufacturing equipment of the fast recovery chip uses any one of the manufacturing methods of the fast recovery chip to manufacture the fast recovery chip.
This application carries out platinum ion implantation at the silicon chip that the surface is the boron junction, and when carrying out platinum diffusion, platinum can be even diffusion to the platinum ion implantation zone of silicon chip in, carries out platinum deep diffusion in a predetermined temperature range, and platinum can each region of uniform diffusion to the silicon chip, prevents that platinum diffusion is inhomogeneous and destroys other structures in the silicon chip, and platinum has splendid turn-on speed simultaneously, thereby has improved the recovery characteristic of fast recovery chip.
Drawings
The accompanying drawings, which are included to provide a further understanding of the embodiments of the application, are incorporated in and constitute a part of this specification, illustrate embodiments of the application and together with the description serve to explain the principles of the application. It is obvious that the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the application, and that for a person skilled in the art, other drawings can be derived from them without inventive effort. In the drawings:
fig. 1 is a schematic flowchart illustrating a method for manufacturing a fast recovery chip according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of a fast recovery chip according to an embodiment of the present application;
FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view of a fast recovery chip according to an embodiment of the present application;
fig. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a manufacturing apparatus for a fast recovery chip according to an embodiment of the present application.
Wherein, 100, fast recovery chip; 110. polishing the surface; 120. a boron region; 130. a base region; 140. A phosphorus region; 150. a platinum ion implantation region; 200. a manufacturing device; 210. a diffusion device; 211. A phosphorus diffusion device; 212. a boron diffusion device; 213. a platinum diffusion device; 220. provided is a polishing device.
Detailed Description
It is to be understood that the terminology, the specific structural and functional details disclosed herein are for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only, and are representative, but that the present application may be embodied in many alternate forms and should not be construed as limited to only the embodiments set forth herein.
In the description of the present application, the terms "first", "second" are used for descriptive purposes only and are not to be construed as indicating relative importance or as implicitly indicating the number of technical features indicated. Thus, unless otherwise specified, a feature defined as "first" or "second" may explicitly or implicitly include one or more of that feature; "plurality" means two or more. The terms "comprises" and "comprising," and any variations thereof, are intended to cover a non-exclusive inclusion, such that one or more other features, integers, steps, operations, elements, components, and/or combinations thereof may be present or added.
Further, terms of orientation or positional relationship indicated by "center", "lateral", "upper", "lower", "left", "right", "vertical", "horizontal", "top", "bottom", "inner", "outer", and the like, are described based on the orientation or relative positional relationship shown in the drawings, are simply for convenience of description of the present application, and do not indicate that the referred device or element must have a specific orientation, be constructed and operated in a specific orientation, and thus, should not be construed as limiting the present application.
Furthermore, unless expressly stated or limited otherwise, the terms "mounted," "connected," and "connected" are to be construed broadly and may include, for example, fixed connections, removable connections, and integral connections; can be mechanically or electrically connected; either directly or indirectly through intervening media, or through both elements. The specific meaning of the above terms in the present application can be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art as appropriate.
The present application will now be described in detail with reference to the drawings and alternative embodiments, it being understood that any combination of the various embodiments or technical features described below may form new embodiments without conflict.
As shown in fig. 1, as another embodiment of the present application, a method for manufacturing a fast recovery chip is disclosed, which includes the steps of:
s1: carrying out phosphorus diffusion on the silicon wafer by using a phosphorus source to form a phosphorus diffusion structural layer on at least one surface of the silicon wafer;
s2: removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one surface of the silicon wafer;
s3: carrying out boron diffusion on the silicon wafer by using a boron source so as to form a boron diffusion structural layer on one surface of the silicon wafer, which is removed from the phosphorus diffusion structural layer;
s4: performing platinum ion implantation through the surface of the boron diffusion structure layer to perform platinum diffusion;
s5: performing platinum deep diffusion in a preset temperature range;
s6: and preparing the fast recovery chip by adopting the silicon chip subjected to the platinum deep diffusion.
Platinum is as a heavy metal, if the internal structure of the silicon chip can seriously be destroyed to the inhomogeneous diffusion in the silicon chip, carry out platinum ion implantation at the silicon chip that the surface is the boron junction, when carrying out platinum diffusion, the mode of ion implantation can make platinum evenly diffuse in the silicon chip, carry out platinum deep diffusion in a predetermined temperature range, further make platinum uniform diffusion to other each region of silicon chip in platinum ion implantation district, prevent that platinum diffusion is inhomogeneous to destroy other structures in the silicon chip, platinum has fabulous conduction velocity simultaneously, prevent that platinum distributes inhomogeneous original structure who destroys the silicon chip, can also improve the recovery characteristic of chip simultaneously.
Specifically, in step S1, the phosphorus source refers to a phosphorus material used as a diffusion source, and phosphorus diffusion is performed on the silicon wafer by using the phosphorus source, which may specifically be: and (3) putting the phosphorus source and the silicon wafer into a diffusion furnace for diffusion reaction. Usually, a phosphorus paper source is selected as a phosphorus material, a piece of phosphorus paper source is added between two silicon wafers, phosphorus in the phosphorus paper source is diffused to the upper and lower silicon wafers, and after the phosphorus diffusion is carried out on the silicon wafers, a phosphorus diffusion structure layer is formed on one surface, which is in contact with the phosphorus paper source, in each silicon wafer. The phosphorus diffusion structure layer is a layer structure with a phosphorus diffusion junction, wherein the thickness range of the silicon wafer before phosphorus diffusion is 245-255, and the thickness of the silicon wafer after phosphorus diffusion is unchanged from the thickness of the silicon wafer before phosphorus diffusion.
In some embodiments, prior to step S1, the method may further include: and (4) performing decontamination treatment on the surface of the silicon wafer. The decontamination treatment may be, for example: and (3) pickling and cleaning the silicon wafer to remove dirt, an oxide layer and the like on the surface of the silicon wafer.
In step S2, the step of removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one side of the silicon wafer may specifically be: and removing the phosphorus diffusion junction in the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one surface of the silicon wafer after phosphorus diffusion through sand blasting, and controlling the thickness of the silicon wafer to be 235-245 microns. And removing the phosphorus diffusion junction and the phosphorus diffusion source by sand blasting to carry out the next step, so that the phosphorus diffusion junction is prevented from influencing polishing, and the junction depth and the thickness of the boron junction are prevented from being changed due to the residual phosphorus diffusion source.
In step S3, the boron source refers to a boron material used as a diffusion source, and the boron source may be a liquid boron source. The method for carrying out boron diffusion on the silicon wafer by using the boron source specifically comprises the following steps: and coating a liquid boron source on one surface of the silicon wafer with the phosphorus removal diffusion structure layer, and putting the silicon wafer into a diffusion furnace for diffusion reaction. And after boron diffusion is carried out on the silicon wafer, a boron diffusion structural layer is formed on one surface of the silicon wafer, which is removed from the phosphorus diffusion structural layer. The boron diffusion structure layer is a layer of structure formed by diffusing boron diffusion junctions on the silicon wafer and is adjacent to the phosphorus diffusion layer structure.
In some embodiments, before step S3, the method may further include: and polishing the silicon wafer with the phosphorus diffusion structure layer removed. Namely, polishing is carried out before boron diffusion, so that the boron diffusion is more uniform, and the yield of products is improved. Of course, in some other embodiments, the silicon wafer may also be polished before step S1, and the polishing is performed on the premise that the silicon wafer is not damaged, so that the surface of the silicon wafer contacting with the phosphorus is smoother, and the phosphorus diffusion is more uniform.
In step S4, platinum ion implantation is performed on the side of the silicon wafer on which the boron diffusion structure layer is formed, specifically, an ion implanter is used to inject the silicon wafer to the polished side, related parameters in the ion implanter can be adjusted during the implantation process, and generally, the implantation dose of the platinum ion is controlled to be 2e15cm2To 4e15cm2The implantation energy of the platinum ions is 50KeV to 70KeV, the implantation depth of the platinum ions is 2-4 micrometers, the depth is strictly controlled, and the platinum ions are prevented from being implanted too deeply to penetrate through the silicon wafer. The recovery characteristics of the specific ion implantation depth versus the fast recovery chip refer to the following table one, where H is the platinum ion implantation depth:
watch 1
In step S4, the method further includes: introducing nitrogen at the rate of 5-7 liters per minute to perform platinum diffusion and platinum deep diffusion, and introducing the nitrogen to form a PN junction with phosphorus atoms in the silicon wafer; platinum diffusion is carried out within a preset temperature range, after platinum ion implantation is carried out, due to the fact that parameters of an existing ion implanter have certain specifications, the implantation depth of platinum ions is limited, and if platinum needs to be diffused into the whole silicon wafer, further platinum deep diffusion needs to be carried out; the platinum deep diffusion means that platinum ions can be diffused to deeper positions of the silicon wafer after ion implantation, so that platinum atoms can be uniformly distributed in each region of the silicon wafer.
The preset temperature range can be any temperature of 800-950 ℃, but cannot exceed or be lower than the preset temperature range, if the preset temperature range exceeds 950 ℃, the boron junction is deeper, the whole structure of the silicon wafer is influenced, if the preset temperature range is lower than 800 ℃, the surface concentration is changed, the change of the TRR value is influenced, the recovery characteristic is influenced, and naturally diffused, but the effect is worse than the platinum deep diffusion in the preset temperature range.
In step S5, a fast recovery chip is prepared by using a silicon wafer after platinum diffusion, which may specifically be: and etching, sintering, coating and the like are carried out on the silicon wafer subjected to platinum diffusion to prepare the fast recovery chip. The fast recovery chip prepared by the silicon wafer after platinum diffusion can be a fast recovery diode and the like.
In this embodiment, an ion implanter is used to implant platinum ions into a silicon wafer, and the platinum ions can be uniformly distributed into the silicon wafer in an ion implantation manner.
In some other embodiments, after step S3 and before step S4, the method may further comprise: and step S6, polishing the surface of the boron diffusion structure layer. So when platinum diffusion, can make platinum more even diffusion to the silicon chip in, prevent that platinum distributes inhomogeneous original structure that destroys the silicon chip, platinum has fabulous conduction speed simultaneously, can improve the recovery characteristic of chip, can refer to following two:
| take 200V SF50mil product as an example | TRR |
| Normal abrasive sheet (unpolished) | 29-35 |
| Experimental polishing pad (polishing) | 30-32 |
Watch two
The TRR is the reverse recovery time of the diode, the current can reversely flow in the process of forward conduction to reverse blocking of the diode, the time required by internal carrier recombination is the TRR, the TRR value is generally within a reference standard of 30-35, the more concentrated the TRR value within the standard range, the better the recovery characteristic is, namely the small discreteness recovery characteristic is high, and after polishing, the TRR value is obviously superior to the non-polished TRR value.
In addition, the thickness of the polished silicon wafer is 3-5 microns smaller than that of the silicon wafer before polishing, the polishing thickness is represented by X, and the recovery characteristic can be further improved by controlling the polishing thickness, specifically referring to the following table III:
watch III
With the above-described embodiment, by performing the polishing process on the surface for platinum diffusion and then performing the platinum ion implantation, the platinum ions can be more uniformly implanted into the surface for platinum diffusion, and thus can be more uniform when diffused.
In step S6, a fast recovery chip is prepared by using a silicon wafer after platinum diffusion, which may specifically be: and etching, sintering, coating and the like are carried out on the silicon wafer subjected to platinum diffusion to prepare the fast recovery chip. The fast recovery chip prepared by the silicon wafer after platinum diffusion can be a fast recovery diode and the like.
As another embodiment of the present application, a method of manufacturing a fast recovery chip is disclosed, including the steps of:
(1) treating the surface of a primary silicon wafer, and immersing the primary silicon wafer into hydrofluoric acid for acid cleaning;
(2) stacking the processed silicon wafer and the phosphorus paper source together, and placing the silicon wafer and the phosphorus paper source together in a diffusion furnace for phosphorus diffusion after arrangement;
(3) putting the silicon wafer from which phosphorus is diffused into hydrofluoric acid for slicing treatment and cleaning treatment;
(4) carrying out sand blasting treatment on the silicon wafer after the phosphorus fragmentation to remove phosphorus diffusion junctions and controlling the thickness of the silicon wafer to be 235-245 um;
(5) cleaning the material subjected to sand blasting, then performing boron diffusion, coating a liquid boron source on a sand blasting removal surface, and performing diffusion to form a boron junction;
(6) and (3) polishing the surface of the boron zone surface of the boron-expanded material to be about 3-5um, and cleaning after polishing.
(7) Coating a liquid platinum source on the polished silicon wafer, uniformly coating the platinum source on the polished surface, and performing platinum diffusion after coating, wherein the temperature is controlled at 800-950 ℃.
(8) After platinum diffusion, the silicon wafer is cleaned, coated with photoresist, exposed and developed, and then etched by mixed acid at the temperature of-5-1 ℃ to form a groove.
(9) After the trench was opened, the chip was subjected to RCA cleaning, and then LPCVD was performed to form a SIPOS film (semi-insulating polysilicon film) on the surface.
(10) And (4) coating photoresist glass after SIPOS, and carrying out glass sintering after exposure and development.
(11) LTO (low temperature oxidation) is performed after glass sintering, and a silicon dioxide film is grown.
(12) And (4) removing the oxidation layer on the table top of the chip after the step (11) through gluing, exposing and developing.
(13) And (4) carrying out primary nickel plating on the chip in the step (12), sintering, carrying out secondary nickel plating and then carrying out gold plating treatment.
(14) And cutting the gold-plated chip into single crystal grains by using a laser cutting machine.
(15) The grains are cleaned and then packaged.
Wherein, in the step (1), the surface smut, oxide layer and the like of the original silicon wafer are mainly removed, in the step (2), when phosphorus is diffused, the temperature range is 1150-; during boron diffusion, namely in the step (5), introducing oxygen 12LPM and nitrogen 3LPM at the temperature of 1200-1300 ℃ according to the ratio of 4: 1; the surface polishing treatment is added after the boron is expanded, so that the surface is smoother, a platinum source can be more uniformly tiled to polish the surface in the platinum coating process, the TRR value of the whole silicon wafer is more uniform finally, and the discreteness is small.
In the step (7), the platinum material is a liquid platinum source, the liquid platinum source is uniformly coated on the polishing surface to diffuse platinum, the liquid platinum source is required to diffuse, the platinum can be more uniformly coated on the polishing surface, and the platinum can be more uniformly diffused after the platinum material is uniformly coated; and the diffusion temperature in the step (7) is controlled at 800-950 ℃, the requirement on the temperature during platinum diffusion is higher, if the temperature is too high, a boron junction is deeper, the whole structure of the silicon wafer is influenced, and if the temperature is too low, the surface concentration is changed, the change of a TRR value is influenced, and the recovery characteristic is influenced.
As another embodiment of the present application, a method of manufacturing a fast recovery chip is disclosed, including the steps of:
(1) treating the surface of a primary silicon wafer, and immersing the primary silicon wafer into hydrofluoric acid for acid cleaning;
(2) stacking the processed silicon wafer and the phosphorus paper source together, and placing the silicon wafer and the phosphorus paper source together in a diffusion furnace for phosphorus diffusion after arrangement;
(3) putting the silicon wafer from which phosphorus is diffused into hydrofluoric acid for slicing treatment and cleaning treatment;
(4) carrying out sand blasting treatment on the silicon wafer after the phosphorus fragmentation to remove phosphorus diffusion junctions and controlling the thickness of the silicon wafer to be 235-245 um;
(5) adding boron material, then carrying out boron diffusion, coating a liquid boron source on the sand blasting removal surface, and diffusing to form boron junctions;
(6) and (3) polishing the surface of the boron zone surface of the boron-expanded material to be about 3-5um, and cleaning after polishing.
(7) And (3) performing platinum ion implantation on the polished silicon wafer, wherein the depth of the implanted platinum ions is 2-4 microns, performing platinum deep diffusion after the platinum ions are implanted, and controlling the temperature at 800-950 ℃.
(8) After platinum diffusion, the silicon wafer is cleaned, coated with photoresist, exposed and developed, and then etched by mixed acid at the temperature of-5-1 ℃ to form a groove.
(9) After the trench was opened, the chip was subjected to RCA cleaning, and then LPCVD was performed to form a SIPOS film (semi-insulating polysilicon film) on the surface.
(10) And (4) coating photoresist glass after SIPOS, and carrying out glass sintering after exposure and development.
(11) LTO (low temperature oxidation) is performed after glass sintering, and a silicon dioxide film is grown.
(12) And (3) removing the oxidation layer on the table top of the chip obtained in the step (10) through gluing, exposing and developing.
(13) And (4) carrying out primary nickel plating on the chip in the step (11), sintering, carrying out secondary nickel plating and then carrying out gold plating treatment.
(14) And cutting the gold-plated chip into single crystal grains by using a laser cutting machine.
(15) The grains are cleaned and then packaged.
Wherein, polishing treatment can be carried out before gallium diffusion or boron diffusion so as to lead the diffusion to be more uniform.
As shown in fig. 2, as another embodiment of the present application, a fast recovery chip 100 is disclosed, which includes a phosphorus region 140, a base region 130, and a boron region 120, where the phosphorus region 140 is a cathode of the fast recovery chip; the base region 130 is disposed on the phosphor region; the boron region 120 is arranged on the base region and is an anode of the fast recovery chip; and a platinum ion injection region is formed on one surface of the boron region, which is far away from the base region, and platinum ions are diffused from the platinum ion injection region to be uniformly distributed in the phosphorus region, the base region and the boron region.
As another embodiment of the present application, a polished surface is formed on a side of the boron region away from the base region, and platinum is uniformly distributed in each region after being diffused from the polished surface; the polishing surface is formed before platinum diffusion, so that the platinum can be more uniformly diffused into the silicon wafer during the platinum diffusion, the TRR value is more uniform, and a fast recovery chip with good recovery characteristics is obtained; and after polishing, platinum ion implantation is carried out to form a platinum ion implantation area, and then platinum deep diffusion is carried out, so that the effect of ion implantation on a polished surface is more obvious.
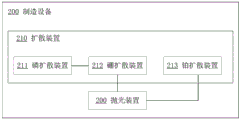
As shown in fig. 3, as another embodiment of the present application, there is disclosed a manufacturing apparatus 200 of a fast recovery chip, including a plurality of different diffusion devices 210, an ion implanter and a polishing device 220; the plurality of different diffusion devices 210 respectively realize phosphorus diffusion, boron diffusion and platinum diffusion of the silicon wafer; the polishing device is used for polishing the silicon wafer subjected to boron diffusion; the manufacturing equipment of the fast recovery chip adopts the manufacturing method in any embodiment to manufacture the fast recovery chip, and the ion implanter performs platinum ion implantation on a silicon wafer with a boron junction on the surface after boron diffusion, and performs platinum diffusion.
The phosphorus diffusion, the boron diffusion and the platinum diffusion are carried out in different diffusion furnaces, each diffusion is carried out in an independent diffusion furnace to prevent mutual pollution, particularly, products with a boron source coming out of the diffusion furnace are wasted during phosphorus diffusion, so that diffusion cannot be carried out in the same diffusion furnace, the diffusion devices 210 are a phosphorus diffusion device 211 for phosphorus diffusion, a boron diffusion device 212 for boron diffusion and a platinum diffusion device 213 for platinum diffusion, and the diffusion devices are independent to prevent cross pollution caused by the fact that one diffusion device is shared, and the production yield of products is influenced.
Furthermore, the manufacturing equipment of the fast recovery chip also comprises a diffusion device for realizing gallium diffusion, the phosphorus diffusion, the gallium diffusion, the boron diffusion and the platinum diffusion are carried out in different diffusion furnaces, each diffusion is carried out in a separate diffusion furnace to prevent mutual pollution, and particularly, products with boron sources coming out from the inside are wasted during the phosphorus diffusion, so the diffusion cannot be carried out in the same diffusion furnace.
The gallium diffusion device 214 for gallium diffusion is independent from the diffusion devices, so that cross contamination caused by one diffusion device is prevented from being shared, the production yield of products is prevented from being affected, generally, gallium diffusion is carried out before boron diffusion, the junction depth formed by the gallium diffusion is far more gentle than that formed by direct boron diffusion, the voltage discreteness and surge capacity of the existing fast recovery diode products are improved, and meanwhile, the voltage drop characteristic of the fast recovery diode is improved.
Of course, the gallium diffusion and the boron diffusion can be carried out in a single diffusion furnace without cross-contamination with each other.
It should be noted that, the limitations of each step in the present disclosure are not considered to limit the order of the steps without affecting the implementation of the specific embodiments, and the steps written in the foregoing may be executed first, or executed later, or even executed simultaneously, and as long as the present disclosure can be implemented, all the steps should be considered as belonging to the protection scope of the present application.
The foregoing is a more detailed description of the present application in connection with specific alternative embodiments, and the specific implementations of the present application are not to be considered limited to these descriptions. For those skilled in the art to which the present application pertains, several simple deductions or substitutions may be made without departing from the concept of the present application, and all should be considered as belonging to the protection scope of the present application.
Claims (10)
1. A method for manufacturing a fast recovery chip, comprising the steps of:
carrying out phosphorus diffusion on the silicon wafer by using a phosphorus source to form a phosphorus diffusion structural layer on at least one surface of the silicon wafer;
removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one surface of the silicon wafer;
carrying out boron diffusion on the silicon wafer by using a boron source so as to form a boron diffusion structural layer on one surface of the silicon wafer, which is removed from the phosphorus diffusion structural layer;
performing platinum ion implantation on one surface of the silicon wafer on which the boron diffusion structure layer is formed to realize platinum diffusion;
performing platinum deep diffusion in a preset temperature range;
and preparing the fast recovery chip by adopting the silicon chip subjected to the platinum deep diffusion.
2. The method for manufacturing a fast recovery chip as claimed in claim 1, wherein in the step of performing platinum ion implantation on the side of the silicon wafer on which the boron diffusion structure layer is formed, the depth of the implanted platinum ions is 2-4 μm.
3. The method of claim 2, wherein the platinum ions are implanted at a dose of 2e15cm2To 4e15cm2The implantation energy of the platinum ions is 50KeV to 70 KeV.
4. The method as claimed in claim 1, wherein the predetermined temperature range is 800-950 ℃.
5. The method as claimed in claim 1, wherein in the step of removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one side of the silicon wafer, the silicon wafer is controlled to have a thickness of 235-245 μm when the phosphorus diffusion structure layer is removed.
6. The method of claim 1, wherein the step of removing the phosphorus diffusion structure layer on one side of the silicon wafer comprises:
and polishing the silicon wafer with the phosphorus diffusion structure layer removed.
7. The method for manufacturing a fast recovery chip as claimed in claim 6, wherein in the step of polishing the silicon wafer from which the phosphorus diffusion structure layer is removed, the polished silicon wafer is cleaned with hydrofluoric acid.
8. The method for manufacturing a fast recovery chip as claimed in any one of claims 1 to 7, wherein in the step of performing platinum ion implantation on the side of the silicon wafer on which the boron diffusion structure layer is formed and performing platinum deep diffusion within a predetermined temperature range, nitrogen gas is introduced at a rate of 5 to 7 liters per minute.
9. A fast recovery chip, comprising:
the phosphorus region is the cathode of the fast recovery chip;
a base region disposed on the phosphorus region;
the boron region is arranged on the base region and is an anode of the fast recovery chip;
and a platinum ion injection region is formed on one surface of the boron region, which is far away from the base region, and platinum ions are diffused from the platinum ion injection region to be uniformly distributed in the phosphorus region, the base region and the boron region.
10. An apparatus for manufacturing a fast recovery chip, comprising:
the different diffusion devices are used for respectively realizing phosphorus diffusion, boron diffusion and platinum diffusion of the silicon wafer;
the ion implanter is used for implanting platinum ions into the silicon wafer subjected to boron diffusion;
wherein the manufacturing equipment of the fast recovery chip uses the manufacturing method of the fast recovery chip of any one of claims 1 to 8 to manufacture the fast recovery chip.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110351049.1A CN113223944B (en) | 2021-03-31 | 2021-03-31 | Manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of fast recovery chip and fast recovery chip |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110351049.1A CN113223944B (en) | 2021-03-31 | 2021-03-31 | Manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of fast recovery chip and fast recovery chip |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113223944A true CN113223944A (en) | 2021-08-06 |
| CN113223944B CN113223944B (en) | 2022-09-27 |
Family
ID=77086268
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110351049.1A Active CN113223944B (en) | 2021-03-31 | 2021-03-31 | Manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of fast recovery chip and fast recovery chip |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113223944B (en) |
Citations (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB991174A (en) * | 1960-12-09 | 1965-05-05 | Western Electric Co | Semiconductor devices and methods of making them |
| US5227315A (en) * | 1990-11-29 | 1993-07-13 | Consorzio Per La Ricerca Sulla Microelettronica Nel Mezzogiorno | Process of introduction and diffusion of platinum ions in a slice of silicon |
| CN101866854A (en) * | 2010-05-11 | 2010-10-20 | 襄樊三瑞达电力半导体有限公司 | Production method of ultrafast soft recovery diode chip |
| CN102087976A (en) * | 2010-12-10 | 2011-06-08 | 天津中环半导体股份有限公司 | Fast recovery diode (FRD) chip and production process thereof |
| US20120326317A1 (en) * | 2011-06-27 | 2012-12-27 | Semiconductor Manufacturing International (Beijing) Corporation | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method therefor |
| CN104157569A (en) * | 2014-08-26 | 2014-11-19 | 清华大学 | Technology for manufacturing fast recovery diode |
| CN104201102A (en) * | 2014-08-28 | 2014-12-10 | 苏州启澜功率电子有限公司 | Fast recovery diode FRD chip and production process for same |
| CN104616986A (en) * | 2015-01-08 | 2015-05-13 | 北京时代民芯科技有限公司 | Preparation method of fast recovery diode |
| CN105244274A (en) * | 2015-11-19 | 2016-01-13 | 株洲南车时代电气股份有限公司 | Reverse conducting-type IGBT device and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN105428234A (en) * | 2015-11-14 | 2016-03-23 | 中国振华集团永光电子有限公司(国营第八七三厂) | Preparation method of planar triode chip |
| CN105914255A (en) * | 2016-04-19 | 2016-08-31 | 中利腾晖光伏科技有限公司 | Solar cell and manufacturing method therefor |
| CN105977154A (en) * | 2016-06-06 | 2016-09-28 | 北京时代民芯科技有限公司 | Diffusion-technology-based manufacture method for fast recovery diode chip having double buffering layers |
| CN109638083A (en) * | 2018-12-29 | 2019-04-16 | 捷捷半导体有限公司 | A kind of fast recovery diode and preparation method thereof |
| CN109686666A (en) * | 2018-12-26 | 2019-04-26 | 常州星海电子股份有限公司 | A kind of fast recovery chip manufacture method |
-
2021
- 2021-03-31 CN CN202110351049.1A patent/CN113223944B/en active Active
Patent Citations (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB991174A (en) * | 1960-12-09 | 1965-05-05 | Western Electric Co | Semiconductor devices and methods of making them |
| US5227315A (en) * | 1990-11-29 | 1993-07-13 | Consorzio Per La Ricerca Sulla Microelettronica Nel Mezzogiorno | Process of introduction and diffusion of platinum ions in a slice of silicon |
| CN101866854A (en) * | 2010-05-11 | 2010-10-20 | 襄樊三瑞达电力半导体有限公司 | Production method of ultrafast soft recovery diode chip |
| CN102087976A (en) * | 2010-12-10 | 2011-06-08 | 天津中环半导体股份有限公司 | Fast recovery diode (FRD) chip and production process thereof |
| US20120326317A1 (en) * | 2011-06-27 | 2012-12-27 | Semiconductor Manufacturing International (Beijing) Corporation | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method therefor |
| CN102856177A (en) * | 2011-06-27 | 2013-01-02 | 中芯国际集成电路制造(北京)有限公司 | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same |
| CN104157569A (en) * | 2014-08-26 | 2014-11-19 | 清华大学 | Technology for manufacturing fast recovery diode |
| CN104201102A (en) * | 2014-08-28 | 2014-12-10 | 苏州启澜功率电子有限公司 | Fast recovery diode FRD chip and production process for same |
| CN104616986A (en) * | 2015-01-08 | 2015-05-13 | 北京时代民芯科技有限公司 | Preparation method of fast recovery diode |
| CN105428234A (en) * | 2015-11-14 | 2016-03-23 | 中国振华集团永光电子有限公司(国营第八七三厂) | Preparation method of planar triode chip |
| CN105244274A (en) * | 2015-11-19 | 2016-01-13 | 株洲南车时代电气股份有限公司 | Reverse conducting-type IGBT device and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN105914255A (en) * | 2016-04-19 | 2016-08-31 | 中利腾晖光伏科技有限公司 | Solar cell and manufacturing method therefor |
| CN105977154A (en) * | 2016-06-06 | 2016-09-28 | 北京时代民芯科技有限公司 | Diffusion-technology-based manufacture method for fast recovery diode chip having double buffering layers |
| CN109686666A (en) * | 2018-12-26 | 2019-04-26 | 常州星海电子股份有限公司 | A kind of fast recovery chip manufacture method |
| CN109638083A (en) * | 2018-12-29 | 2019-04-16 | 捷捷半导体有限公司 | A kind of fast recovery diode and preparation method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113223944B (en) | 2022-09-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7285475B2 (en) | Integrated circuit having a device wafer with a diffused doped backside layer | |
| JP3929557B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| CN109244125B (en) | Reverse conduction IGBT (insulated Gate Bipolar translator) introducing epitaxial layer field stop area and preparation method thereof | |
| CN102986011A (en) | Manufacturing method for semi-conductor device | |
| CN109411344B (en) | Semiconductor device comprising a CZ semiconductor body and method for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprising a CZ semiconductor body | |
| US20180005831A1 (en) | Method of Reducing an Impurity Concentration in a Semiconductor Body | |
| CN102104074B (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| WO2024037276A1 (en) | Igbt device having deep buffer layer and high-density trenches, and preparation method for igbt device | |
| US10847658B2 (en) | Fast recovery inverse diode | |
| US10249499B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprising a thin semiconductor wafer | |
| CN113223944B (en) | Manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of fast recovery chip and fast recovery chip | |
| US7534666B2 (en) | High voltage non punch through IGBT for switch mode power supplies | |
| CN113223953B (en) | Manufacturing method and manufacturing equipment of fast recovery chip and fast recovery chip | |
| CN113178385B (en) | Chip manufacturing method and device and chip | |
| US20170294527A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| CN113178388B (en) | Method for manufacturing high-voltage-resistant chip and high-voltage-resistant chip | |
| EP0774167B1 (en) | A power semiconductor device | |
| US11038028B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method | |
| US6168978B1 (en) | Method for producing a power semiconductor component on a two-sided substrate that blocks on both sides of the substrate | |
| EP3772749A1 (en) | Methods and devices related to radio frequency devices | |
| CN118738124A (en) | MOSFET chip structure for improving reverse voltage resistance and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR100886809B1 (en) | High voltage semiconductor device having deep trench terminations and method for fabricating the same | |
| KR20050078139A (en) | Diode having ultra fast recovery time and its manufacturing method | |
| CN118538606A (en) | High-reliability terminal structure and preparation method | |
| JP2006147739A (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |