CN113101295A - Use of stilbene analogues in the treatment of diabetic renal disease - Google Patents
Use of stilbene analogues in the treatment of diabetic renal disease Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113101295A CN113101295A CN202010202539.0A CN202010202539A CN113101295A CN 113101295 A CN113101295 A CN 113101295A CN 202010202539 A CN202010202539 A CN 202010202539A CN 113101295 A CN113101295 A CN 113101295A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- pharmaceutically acceptable
- formula
- present disclosure
- ages
- acceptable salt
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 208000007342 Diabetic Nephropathies Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 39
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 title claims description 10
- PJANXHGTPQOBST-UHFFFAOYSA-N stilbene Chemical class C=1C=CC=CC=1C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PJANXHGTPQOBST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title description 3
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 80
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 60
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 59
- 208000033679 diabetic kidney disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 34
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 108010005094 Advanced Glycation End Products Proteins 0.000 claims description 90
- 239000003642 reactive oxygen metabolite Substances 0.000 claims description 38
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 claims description 25
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 claims description 25
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 102100031455 NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 15
- 108010041191 Sirtuin 1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 102000011990 Sirtuin Human genes 0.000 claims description 7
- 108050002485 Sirtuin Proteins 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000002671 adjuvant Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 102100036009 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 Human genes 0.000 claims 4
- 101000783681 Homo sapiens 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 Proteins 0.000 claims 4
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 41
- HPSWAEGGWLOOKT-VUNDNAJOSA-N cis-Mulberroside A Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1OC(C=C1O)=CC=C1\C=C\C1=CC(O)=CC(O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)=C1 HPSWAEGGWLOOKT-VUNDNAJOSA-N 0.000 description 38
- HPSWAEGGWLOOKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N cis-mulberroside A Natural products OC1C(O)C(O)C(CO)OC1OC(C=C1O)=CC=C1C=CC1=CC(O)=CC(OC2C(C(O)C(O)C(CO)O2)O)=C1 HPSWAEGGWLOOKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 37
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 26
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 26
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 25
- DDRJAANPRJIHGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N creatinine Chemical compound CN1CC(=O)NC1=N DDRJAANPRJIHGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 24
- PDHAOJSHSJQANO-OWOJBTEDSA-N Oxyresveratrol Chemical compound OC1=CC(O)=CC=C1\C=C\C1=CC(O)=CC(O)=C1 PDHAOJSHSJQANO-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 22
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 description 19
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 14
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 description 13
- QNVSXXGDAPORNA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Resveratrol Natural products OC1=CC=CC(C=CC=2C=C(O)C(O)=CC=2)=C1 QNVSXXGDAPORNA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- LUKBXSAWLPMMSZ-OWOJBTEDSA-N Trans-resveratrol Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1\C=C\C1=CC(O)=CC(O)=C1 LUKBXSAWLPMMSZ-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 229940109239 creatinine Drugs 0.000 description 12
- 235000021283 resveratrol Nutrition 0.000 description 12
- 229940016667 resveratrol Drugs 0.000 description 12
- 206010012601 diabetes mellitus Diseases 0.000 description 11
- 210000003734 kidney Anatomy 0.000 description 10
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 10
- 241000699666 Mus <mouse, genus> Species 0.000 description 9
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 9
- 210000002700 urine Anatomy 0.000 description 8
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 7
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 6
- 208000020832 chronic kidney disease Diseases 0.000 description 6
- 206010061989 glomerulosclerosis Diseases 0.000 description 6
- -1 oxygen ions Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 235000006708 antioxidants Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 5
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000003834 intracellular effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000003907 kidney function Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229920005615 natural polymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920001059 synthetic polymer Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 150000003626 triacylglycerols Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Aminoethan-1-ol Chemical compound NCCO HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 4
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 4
- RYYVLZVUVIJVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N caffeine Chemical compound CN1C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C2=C1N=CN2C RYYVLZVUVIJVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000006059 cover glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000011534 incubation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 210000002966 serum Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 description 4
- GETQZCLCWQTVFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethylamine Chemical compound CN(C)C GETQZCLCWQTVFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000002485 urinary effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WWZKQHOCKIZLMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Caprylic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(O)=O WWZKQHOCKIZLMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propanedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)CC(O)=O OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102000000477 Sirtuin 2 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108010041216 Sirtuin 2 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- PNNCWTXUWKENPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N [N].NC(N)=O Chemical compound [N].NC(N)=O PNNCWTXUWKENPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000004113 cell culture Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000013355 food flavoring agent Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 210000003292 kidney cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 230000000069 prophylactic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- ZSJLQEPLLKMAKR-GKHCUFPYSA-N streptozocin Chemical compound O=NN(C)C(=O)N[C@H]1[C@@H](O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O ZSJLQEPLLKMAKR-GKHCUFPYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 3
- WXTMDXOMEHJXQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC(O)=CC=C1O WXTMDXOMEHJXQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 2
- CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N Ascorbic acid Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(O)=C1O CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-N D-gluconic acid Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicyclohexylamine Chemical compound C1CCCCC1NC1CCCCC1 XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 206010016654 Fibrosis Diseases 0.000 description 2
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formaldehyde Chemical compound O=C WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DSLZVSRJTYRBFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Galactaric acid Natural products OC(=O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)=O DSLZVSRJTYRBFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AEMRFAOFKBGASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycolic acid Chemical compound OCC(O)=O AEMRFAOFKBGASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 2
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LPHGQDQBBGAPDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isocaffeine Natural products CN1C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C2=C1N(C)C=N2 LPHGQDQBBGAPDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QIAFMBKCNZACKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-benzoylglycine Chemical compound OC(=O)CNC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 QIAFMBKCNZACKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Niacin Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229930040373 Paraformaldehyde Natural products 0.000 description 2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperazine Chemical compound C1CNCCN1 GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperidine Chemical compound C1CCNCC1 NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000001253 Protein Kinase Human genes 0.000 description 2
- LCTONWCANYUPML-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyruvic acid Chemical compound CC(=O)C(O)=O LCTONWCANYUPML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZSJLQEPLLKMAKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Streptozotocin Natural products O=NN(C)C(=O)NC1C(O)OC(CO)C(O)C1O ZSJLQEPLLKMAKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000010913 Type 1 Angiotensin Receptor Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010062481 Type 1 Angiotensin Receptor Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 2
- UDMBCSSLTHHNCD-KQYNXXCUSA-N adenosine 5'-monophosphate Chemical compound C1=NC=2C(N)=NC=NC=2N1[C@@H]1O[C@H](COP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O UDMBCSSLTHHNCD-KQYNXXCUSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N adipic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCC(O)=O WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000010171 animal model Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WGQKYBSKWIADBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzylamine Chemical compound NCC1=CC=CC=C1 WGQKYBSKWIADBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229960001948 caffeine Drugs 0.000 description 2
- VJEONQKOZGKCAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N caffeine Natural products CN1C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C2=C1C=CN2C VJEONQKOZGKCAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N choline Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CCO OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229960001231 choline Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 2
- GHVNFZFCNZKVNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N decanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCC(O)=O GHVNFZFCNZKVNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylamine Chemical compound CCNCC HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylselenoniopropionate Natural products CCC(O)=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004043 dyeing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 201000000523 end stage renal failure Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000004761 fibrosis Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000019634 flavors Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000009760 functional impairment Effects 0.000 description 2
- DSLZVSRJTYRBFB-DUHBMQHGSA-N galactaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)C(O)=O DSLZVSRJTYRBFB-DUHBMQHGSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N glycine betaine Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CC([O-])=O KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IPCSVZSSVZVIGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O IPCSVZSSVZVIGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000009200 high fat diet Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000007489 histopathology method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003345 hyperglycaemic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000007529 inorganic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- SUMDYPCJJOFFON-UHFFFAOYSA-N isethionic acid Chemical compound OCCS(O)(=O)=O SUMDYPCJJOFFON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KQNPFQTWMSNSAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N isobutyric acid Chemical compound CC(C)C(O)=O KQNPFQTWMSNSAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JJWLVOIRVHMVIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N isopropylamine Chemical compound CC(C)N JJWLVOIRVHMVIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N lactic acid Chemical compound CC(O)C(O)=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanoic acid Natural products OC=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- XTEGVFVZDVNBPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene-1,5-disulfonic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(S(=O)(=O)O)=CC=CC2=C1S(O)(=O)=O XTEGVFVZDVNBPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PXQPEWDEAKTCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N orotic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC(=O)NC(=O)N1 PXQPEWDEAKTCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000036542 oxidative stress Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229920002866 paraformaldehyde Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000002085 persistent effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 108060006633 protein kinase Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 235000018102 proteins Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 210000005084 renal tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N salicylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 2
- CXMXRPHRNRROMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N sebacic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O CXMXRPHRNRROMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000007480 spreading Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003892 spreading Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229960001052 streptozocin Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 208000032598 susceptibility microvascular complications of diabetes Diseases 0.000 description 2
- YAPQBXQYLJRXSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N theobromine Chemical compound CN1C(=O)NC(=O)C2=C1N=CN2C YAPQBXQYLJRXSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000008719 thickening Effects 0.000 description 2
- ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiocyanic acid Chemical compound SC#N ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N triformin Chemical compound O=COCC(OC=O)COC=O UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000005239 tubule Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- QBYIENPQHBMVBV-HFEGYEGKSA-N (2R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid Chemical compound O[C@@H](C(O)=O)c1ccccc1.O[C@@H](C(O)=O)c1ccccc1 QBYIENPQHBMVBV-HFEGYEGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WRIDQFICGBMAFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (E)-8-Octadecenoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCC(O)=O WRIDQFICGBMAFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MIOPJNTWMNEORI-GMSGAONNSA-N (S)-camphorsulfonic acid Chemical compound C1C[C@@]2(CS(O)(=O)=O)C(=O)C[C@@H]1C2(C)C MIOPJNTWMNEORI-GMSGAONNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-REOHCLBHSA-N (S)-malic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-M .beta-Phenylacrylic acid Natural products [O-]C(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CC=C1 WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-M 0.000 description 1
- GEYOCULIXLDCMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-phenylenediamine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC=C1N GEYOCULIXLDCMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SJJCQDRGABAVBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=C(O)C(C(=O)O)=CC=C21 SJJCQDRGABAVBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RTBFRGCFXZNCOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methylsulfonylpiperidin-4-one Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)N1CCC(=O)CC1 RTBFRGCFXZNCOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FRPZMMHWLSIFAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 10-undecenoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCCCCCC=C FRPZMMHWLSIFAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MSWZFWKMSRAUBD-IVMDWMLBSA-N 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucopyranose Chemical compound N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O MSWZFWKMSRAUBD-IVMDWMLBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BFSVOASYOCHEOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-diethylaminoethanol Chemical compound CCN(CC)CCO BFSVOASYOCHEOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940013085 2-diethylaminoethanol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- KPGXRSRHYNQIFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-oxoglutaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCC(=O)C(O)=O KPGXRSRHYNQIFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LQJBNNIYVWPHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 20:1omega9c fatty acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O LQJBNNIYVWPHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-azaniumyl-2-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound NCC(O)C(O)=O BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UOQHWNPVNXSDDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-bromoimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-6-carbonitrile Chemical compound C1=CC(C#N)=CN2C(Br)=CN=C21 UOQHWNPVNXSDDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FWBHETKCLVMNFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4',6-Diamino-2-phenylindol Chemical compound C1=CC(C(=N)N)=CC=C1C1=CC2=CC=C(C(N)=N)C=C2N1 FWBHETKCLVMNFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)aniline Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC(N)=CC=2)=C1 OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QCXJEYYXVJIFCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-acetamidobenzoic acid Chemical compound CC(=O)NC1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C1 QCXJEYYXVJIFCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WUBBRNOQWQTFEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-aminosalicylic acid Chemical compound NC1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C(O)=C1 WUBBRNOQWQTFEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WRFYIYOXJWKONR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromo-2-methoxyaniline Chemical compound COC1=CC(Br)=CC=C1N WRFYIYOXJWKONR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UPJKSWLLCONYMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5'-Adenosine monophosphate Natural products COc1cc(O)c(C(=O)C)c(OC2OC(COC3OC(C)C(O)C(O)C3O)C(O)C(O)C2O)c1 UPJKSWLLCONYMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODHCTXKNWHHXJC-VKHMYHEASA-N 5-oxo-L-proline Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H]1CCC(=O)N1 ODHCTXKNWHHXJC-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- QSBYPNXLFMSGKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-Heptadecensaeure Natural products CCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O QSBYPNXLFMSGKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000014156 AMP-Activated Protein Kinases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010011376 AMP-Activated Protein Kinases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000009027 Albumins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010088751 Albumins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010001580 Albuminuria Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004475 Arginine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 206010003694 Atrophy Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000283690 Bos taurus Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000002083 C09CA01 - Losartan Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002947 C09CA04 - Irbesartan Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011740 C57BL/6 mouse Methods 0.000 description 1
- LSPHULWDVZXLIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Camphoric acid Natural products CC1(C)C(C(O)=O)CCC1(C)C(O)=O LSPHULWDVZXLIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000282472 Canis lupus familiaris Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000005632 Capric acid (CAS 334-48-5) Substances 0.000 description 1
- WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-SREVYHEPSA-N Cinnamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C1=CC=CC=C1 WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-SREVYHEPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UDMBCSSLTHHNCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Coenzym Q(11) Natural products C1=NC=2C(N)=NC=NC=2N1C1OC(COP(O)(O)=O)C(O)C1O UDMBCSSLTHHNCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N D-gluconic acid Natural products OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102100030013 Endoribonuclease Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101710199605 Endoribonuclease Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000283086 Equidae Species 0.000 description 1
- PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylenediamine Chemical compound NCCN PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000282326 Felis catus Species 0.000 description 1
- IAJILQKETJEXLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Galacturonsaeure Natural products O=CC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)=O IAJILQKETJEXLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glutamic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000003964 Histone deacetylase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000353 Histone deacetylase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P L-argininium(2+) Chemical compound NC(=[NH2+])NCCC[C@H]([NH3+])C(O)=O ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P 0.000 description 1
- CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N L-aspartic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-histidine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CN=CN1 HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-lysine Chemical compound NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005639 Lauric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lysine Natural products NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 240000000249 Morus alba Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000008708 Morus alba Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- UEEJHVSXFDXPFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-dimethylaminoethanol Chemical compound CN(C)CCO UEEJHVSXFDXPFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HTLZVHNRZJPSMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-ethylpiperidine Chemical compound CCN1CCCCC1 HTLZVHNRZJPSMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MBBZMMPHUWSWHV-BDVNFPICSA-N N-methylglucamine Chemical compound CNC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO MBBZMMPHUWSWHV-BDVNFPICSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000013901 Nephropathies and tubular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005642 Oleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oleic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000021314 Palmitic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 241001494479 Pecora Species 0.000 description 1
- ODHCTXKNWHHXJC-GSVOUGTGSA-N Pyroglutamic acid Natural products OC(=O)[C@H]1CCC(=O)N1 ODHCTXKNWHHXJC-GSVOUGTGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IWYDHOAUDWTVEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N R-2-phenyl-2-hydroxyacetic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(O)C1=CC=CC=C1 IWYDHOAUDWTVEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010038536 Renal tubular atrophy Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 240000004808 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000014680 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 101710113029 Serine/threonine-protein kinase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229940123518 Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000000692 Student's t-test Methods 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Succinic acid Natural products OC(=O)CCC(O)=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tartaric acid Natural products [H+].[H+].[O-]C(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethanolamine Chemical compound OCCN(CCO)CCO GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000013504 Triton X-100 Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920004890 Triton X-100 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODHCTXKNWHHXJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N acide pyroglutamique Natural products OC(=O)C1CCC(=O)N1 ODHCTXKNWHHXJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000001361 adipic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011037 adipic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960000250 adipic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000007605 air drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000003172 aldehyde group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- IAJILQKETJEXLJ-QTBDOELSSA-N aldehydo-D-glucuronic acid Chemical compound O=C[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)C(O)=O IAJILQKETJEXLJ-QTBDOELSSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000783 alginic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960001126 alginic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000004781 alginic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- OBETXYAYXDNJHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-ethylcaproic acid Natural products CCCCC(CC)C(O)=O OBETXYAYXDNJHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AWUCVROLDVIAJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-glycerophosphate Natural products OCC(O)COP(O)(O)=O AWUCVROLDVIAJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-hydroxysuccinic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(O)CC(O)=O BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229960004909 aminosalicylic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000000540 analysis of variance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- JFCQEDHGNNZCLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N anhydrous glutaric acid Natural products OC(=O)CCCC(O)=O JFCQEDHGNNZCLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005557 antagonist Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006907 apoptotic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N arginine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCCNC(N)=N ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003121 arginine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000002565 arteriole Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 235000010323 ascorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011668 ascorbic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960005070 ascorbic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000003704 aspartic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960005261 aspartic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000037444 atrophy Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002469 basement membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000000227 basophil cell of anterior lobe of hypophysis Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940092714 benzenesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000010233 benzoic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960004365 benzoic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- GONOPSZTUGRENK-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl(trichloro)silane Chemical compound Cl[Si](Cl)(Cl)CC1=CC=CC=C1 GONOPSZTUGRENK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MSWZFWKMSRAUBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-D-galactosamine Natural products NC1C(O)OC(CO)C(O)C1O MSWZFWKMSRAUBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002351 beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N beta-D-glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-carboxyaspartic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(N)C(C(O)=O)C(O)=O OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003237 betaine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036772 blood pressure Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004204 blood vessel Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-NUQCWPJISA-N butanedioic acid Chemical compound O[14C](=O)CC[14C](O)=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-NUQCWPJISA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006227 byproduct Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- LSPHULWDVZXLIL-QUBYGPBYSA-N camphoric acid Chemical compound CC1(C)[C@H](C(O)=O)CC[C@]1(C)C(O)=O LSPHULWDVZXLIL-QUBYGPBYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001713 canagliflozin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- VHOFTEAWFCUTOS-TUGBYPPCSA-N canagliflozin hydrate Chemical compound O.CC1=CC=C([C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)C=C1CC(S1)=CC=C1C1=CC=C(F)C=C1.CC1=CC=C([C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)C=C1CC(S1)=CC=C1C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 VHOFTEAWFCUTOS-TUGBYPPCSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KHAVLLBUVKBTBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N caproleic acid Natural products OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=C KHAVLLBUVKBTBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbonic acid Chemical compound OC(O)=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006143 cell culture medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005754 cellular signaling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001684 chronic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000013985 cinnamic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229930016911 cinnamic acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006735 deficit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000502 dialysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960005215 dichloroacetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethanolamine Chemical compound OCCNCCO ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000003292 diminished effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000676 disease causative agent Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 description 1
- MOTZDAYCYVMXPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecyl hydrogen sulfate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCOS(O)(=O)=O MOTZDAYCYVMXPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 231100000673 dose–response relationship Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 208000028208 end stage renal disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000002889 endothelial cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002255 enzymatic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- AFAXGSQYZLGZPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethanedisulfonic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)CCS(O)(=O)=O AFAXGSQYZLGZPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CCIVGXIOQKPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-M ethanesulfonate Chemical compound CCS([O-])(=O)=O CCIVGXIOQKPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 230000029142 excretion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000021050 feed intake Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000019253 formic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012458 free base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001530 fumaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940083124 ganglion-blocking antiadrenergic secondary and tertiary amines Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000002068 genetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960005219 gentisic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000000585 glomerular basement membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000024924 glomerular filtration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000174 gluconic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012208 gluconic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960002442 glucosamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229930182478 glucoside Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000008131 glucosides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940097043 glucuronic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000013922 glutamic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004220 glutamic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002414 glycolytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006206 glycosylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000001963 growth medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940093915 gynecological organic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N histidine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CN=CN1 HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960002885 histidine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000002868 homogeneous time resolved fluorescence Methods 0.000 description 1
- XGIHQYAWBCFNPY-AZOCGYLKSA-N hydrabamine Chemical compound C([C@@H]12)CC3=CC(C(C)C)=CC=C3[C@@]2(C)CCC[C@@]1(C)CNCCNC[C@@]1(C)[C@@H]2CCC3=CC(C(C)C)=CC=C3[C@@]2(C)CCC1 XGIHQYAWBCFNPY-AZOCGYLKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 201000001421 hyperglycemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008595 infiltration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001764 infiltration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002757 inflammatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003914 insulin secretion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000037041 intracellular level Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003456 ion exchange resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003303 ion-exchange polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960002198 irbesartan Drugs 0.000 description 1
- YCPOHTHPUREGFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N irbesartan Chemical compound O=C1N(CC=2C=CC(=CC=2)C=2C(=CC=CC=2)C=2[N]N=NN=2)C(CCCC)=NC21CCCC2 YCPOHTHPUREGFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- QXJSBBXBKPUZAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N isooleic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QXJSBBXBKPUZAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004310 lactic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000014655 lactic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940099563 lactobionic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000037356 lipid metabolism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 210000004185 liver Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229960004773 losartan Drugs 0.000 description 1
- KJJZZJSZUJXYEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N losartan Chemical compound CCCCC1=NC(Cl)=C(CO)N1CC1=CC=C(C=2C(=CC=CC=2)C=2[N]N=NN=2)C=C1 KJJZZJSZUJXYEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003646 lysine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000012139 lysis buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 159000000003 magnesium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011976 maleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001630 malic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011090 malic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 210000001161 mammalian embryo Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229960002510 mandelic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002609 medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000037353 metabolic pathway Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004060 metabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940098779 methanesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl p-hydroxycinnamate Natural products OC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000004784 molecular pathogenesis Effects 0.000 description 1
- WQEPLUUGTLDZJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Pentadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O WQEPLUUGTLDZJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-hexanoic acid Natural products CCCCCC(O)=O FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229950006238 nadide Drugs 0.000 description 1
- KVBGVZZKJNLNJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC(S(=O)(=O)O)=CC=C21 KVBGVZZKJNLNJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930027945 nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide Natural products 0.000 description 1
- BOPGDPNILDQYTO-NNYOXOHSSA-N nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide Chemical compound C1=CCC(C(=O)N)=CN1[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@@H]2[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H](O2)N2C3=NC=NC(N)=C3N=C2)O)O1 BOPGDPNILDQYTO-NNYOXOHSSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000001968 nicotinic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011664 nicotinic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960003512 nicotinic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910017604 nitric acid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000007523 nucleic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 102000039446 nucleic acids Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108020004707 nucleic acids Proteins 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960002969 oleic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960005010 orotic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000006408 oxalic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940116315 oxalic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940098695 palmitic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- WLJNZVDCPSBLRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pamoic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(CC=3C4=CC=CC=C4C=C(C=3O)C(=O)O)=C(O)C(C(O)=O)=CC2=C1 WLJNZVDCPSBLRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N papa-hydroxy-benzoic acid Natural products OC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010827 pathological analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 231100000915 pathological change Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000036285 pathological change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002978 peroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000825 pharmaceutical preparation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940127557 pharmaceutical product Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000026731 phosphorylation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006366 phosphorylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000557 podocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229920000768 polyamine Polymers 0.000 description 1
- WSHYKIAQCMIPTB-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium;2-oxo-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)chromen-4-olate Chemical compound [K+].[O-]C=1C2=CC=CC=C2OC(=O)C=1C(CC(=O)C)C1=CC=CC=C1 WSHYKIAQCMIPTB-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 150000003141 primary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- MFDFERRIHVXMIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N procaine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CCOC(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=C1 MFDFERRIHVXMIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004919 procaine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007425 progressive decline Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011321 prophylaxis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000019260 propionic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000003212 purines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940107700 pyruvic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000171 quenching effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- IUVKMZGDUIUOCP-BTNSXGMBSA-N quinbolone Chemical compound O([C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@]4(C=CC(=O)C=C4CC3)C)CC[C@@]21C)C1=CCCC1 IUVKMZGDUIUOCP-BTNSXGMBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000005962 receptors Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108020003175 receptors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960004889 salicylic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940116353 sebacic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- AWUCVROLDVIAJX-GSVOUGTGSA-N sn-glycerol 3-phosphate Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)COP(O)(O)=O AWUCVROLDVIAJX-GSVOUGTGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000010186 staining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960004274 stearic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000006228 supernatant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012353 t test Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000002906 tartaric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011975 tartaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960001367 tartaric acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960004559 theobromine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000000451 tissue damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000827 tissue damage Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 208000037816 tissue injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000002054 transplantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- YFTHZRPMJXBUME-UHFFFAOYSA-N tripropylamine Chemical compound CCCN(CCC)CCC YFTHZRPMJXBUME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tris Chemical compound OCC(N)(CO)CO LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004418 trolamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960000281 trometamol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 208000001072 type 2 diabetes mellitus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000003606 umbilical vein Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229960002703 undecylenic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000000391 vinyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K31/7028—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages
- A61K31/7034—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/045—Hydroxy compounds, e.g. alcohols; Salts thereof, e.g. alcoholates
- A61K31/05—Phenols
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P13/00—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system
- A61P13/12—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system of the kidneys
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
- A61P3/10—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis for hyperglycaemia, e.g. antidiabetics
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Endocrinology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
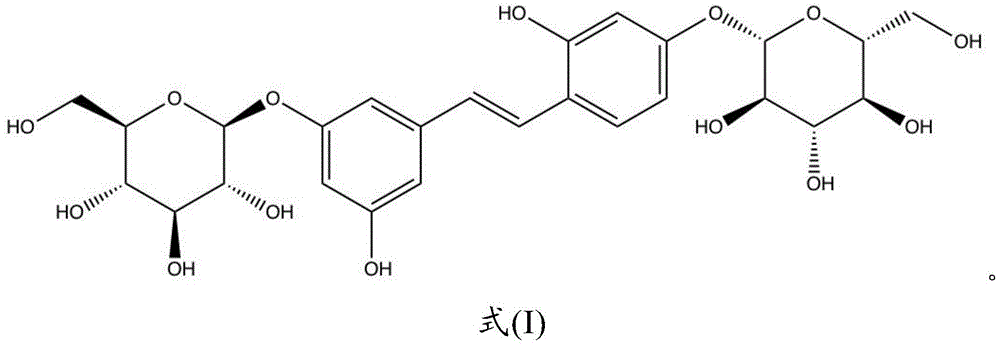
Disclosed is the use of a compound of formula (I), formula (II) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in the manufacture of a medicament for treating or inhibiting diabetic kidney disease:
Description
FIELD
The present disclosure relates generally to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry. More specifically, the present disclosure relates to stilbene analogs.
Background
Approximately 4.25 million diabetics worldwide by 2017, and approximately 6.29 million people are predicted to have diabetes by 2045 (international diabetes union, IDF). About 1.14 hundred million diabetics exist in 2017, namely about every 10 adults in China have one diabetic, and the total number of the diabetics is the first in the world.
Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD), which is known as Diabetic Nephropathy (DN), is a Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) caused by diabetes. One of the major microvascular complications of diabetes is the common cause of End-stage renal disease (ESRD). About 20-40% of diabetic patients will suffer from diabetic kidney disease, eventually worsening to end-stage renal disease, requiring dialysis treatment, even kidney transplantation. Up to 10% of diabetic patients die from diabetic kidney disease.
Diabetic renal disease patients suffer from renal tissue damage and functional impairment due to chronic hyperglycemia. The pathological changes can affect the whole kidney (including glomerulus, renal tubule, renal interstitium, renal blood vessel, etc.), and can be manifested by thickening of glomerular basement membrane, widening of mesangial matrix, glomerular sclerosis and loss of podocyte; thickening of renal tubule basement membrane, renal tubular atrophy and increase of apoptosis, interstitial inflammatory infiltration of kidney, interstitial fibrosis of kidney, and sparse peritubular capillary; the appearance of the wall of the arteriole changes. Clinical manifestations are mainly characterized by persistent albuminuria and/or progressive decline in Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR).
Currently, only angiotensin II-type 1 receptor (AT1R) antagonists (blood pressure lowering: losartan and irbesartan) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors (urine glucose excretion: canagliflozin) are clinically approved drugs for treating diabetic renal diseases, and specific drugs for treating diabetic renal diseases are lacked. Thus, there is a great unmet clinical need in this field.
Diabetes is primarily characterized by persistent, chronically abnormally elevated blood glucose levels. Under hyperglycemic conditions, a series of highly active stable end products, collectively referred to as advanced glycation end products (AGEs), are formed between glucose and free amino groups of proteins, fatty acids or nucleic acids through non-enzymatic glycosylation reactions (Maillard reactions) via the aldehyde groups of the glucose, which are in a range higher than normal. High glucose also causes the body cells to block glycolytic metabolic pathways, which in turn generates active dihydroxy groups, which in turn are converted to AGEs.
In the process of conversion of diabetes to diabetic kidney disease, high AGEs lead to progressive changes in the kidney, such as glomerulosclerosis, interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, and diminished kidney function. Renal function impairment, whose ability to eliminate AGEs is correspondingly reduced, leads in the opposite direction to an increase in the concentration of circulating AGEs in the body, further leading to structural and functional impairment of the kidney.
There are many studies in developing drugs that can inhibit the formation of AGEs and slow down their induced damage to the terminal organs. At present, no relevant medicine is on the market.
Researches on molecular pathogenesis and treatment mechanism of type 2 diabetes (more than 95% of diabetes subtypes) show that adenylate activated protein kinase (AMPK) and sirtuin 2-related enzyme 1(SIRT1, sirtuin 1, silent information regulator 2homolog 1) play important roles.
SUMMARY
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on AMPK:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound represented by formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for reducing the inhibitory effect of high concentrations of glucose on AMPK:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on SIRT 1:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for inhibiting the increase of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) induced by advanced glycation end products (AGEs):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound represented by formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound represented by formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds represented by formula (II) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for reducing AMPK inhibition by high concentrations of glucose:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on SIRT 1:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for inhibiting increased Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) induced by advanced glycation end products (AGEs):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds represented by formula (II) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of reducing the inhibition of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on AMPK, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I), formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of reducing the inhibition of SIRT1 by advanced glycation end products (AGEs) comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of high concentrations of glucose, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (II):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of inhibiting advanced glycation end products (AGEs) induced increases in Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of a compound of formula (I), formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a combination thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on SIRT1, comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a combination thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to a pharmaceutical composition for reducing AMPK inhibition by high concentrations of glucose, comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (II):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to a pharmaceutical composition for inhibiting advanced glycation end products (AGEs) induced increase in Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (I):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to pharmaceutical compositions for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease comprising a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of a compound represented by formula (I), formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a combination thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvant:
brief description of the drawings
FIG. 1 shows that MBA inhibits AGEs-induced reduction of AMPK in HUVEC cells.
FIG. 2 shows that MBA inhibits AGEs-induced reduction of SIRT1 in HUVEC cells.
FIG. 3 shows that MBA inhibits AGEs-induced ROS production in HUVEC cells.
Figure 4 shows the activation of cellular AMPK activity by RES and OXY.
Figure 5 shows MBA reduces mouse Triglycerides (TG).
Figure 6 shows that MBA reduces mouse serum Creatinine (CREA) levels.
Figure 7 shows that MBA reduces mouse blood urea nitrogen levels.
Figure 8 shows MBA reduces total urine volume in mice for 24 hours.
Figure 9 shows MBA reduced mouse urine microalbumin (marlb).
Figure 10 shows MBA reduces total urinary Creatinine (CREA) in mice.
Figure 11 shows MBA inhibits glomerular sclerosis lesions in mice.
Figure 12 shows MBA inhibits mouse glomerulosclerosis lesions.
Detailed description of the invention
In the following description, certain specific details are included to provide a thorough understanding of various disclosed embodiments. One skilled in the relevant art will recognize, however, that the embodiments can be practiced without one or more of the specific details, or with other methods, components, materials, and so forth.
Throughout this specification and the claims which follow, unless the context requires otherwise, the words "comprise", "comprising", and "have" are to be construed in an open, inclusive sense, i.e., "including but not limited to".
Reference throughout the specification to "one embodiment," "an embodiment," "in another embodiment," or "in certain embodiments" means that a particular reference element, structure, or characteristic described in connection with the embodiment is included in at least one embodiment. Thus, the appearances of the phrases "in one embodiment" or "in an embodiment" or "in another embodiment" or "in certain embodiments" in various places throughout this specification are not necessarily all referring to the same embodiment. Furthermore, the particular elements, structures, or characteristics may be combined in any suitable manner in one or more embodiments.
Definition of
In the present disclosure, the term "mulberroside A" refers to 3- { (E) -2- [4- (β -D-glucopyranosyloxy) -2-hydroxyphenyl ] vinyl } -5-hydroxyphenyl- β -D-glucopyranoside.
In the present disclosure, the term "oxyresveratrol" refers to 4- [2- (3, 5-dihydroxyphenyl) ethenyl ] benzene-1, 3-diol, which includes both cis and trans configurations.
In the present disclosure, the term "Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD)" refers to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) caused by diabetes, which is one of the major microvascular complications of diabetes.
In the present disclosure, the term "AMPK (5' -adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase)" refers to AMP-activated protein kinase, which is a kind of serine/threonine protein kinase and is an important energy receptor in cells.
In the present disclosure, the term "SIRT 1 (silence information regulator 2homolog 1)" refers to Sirtuin 2-related enzyme 1, a highly conserved nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent class III histone deacetylase, the first discovered Sirtuin family member in mammals, which is the homolog with the highest homology to saccharomyces cerevisiae Sirtuin 2 (Sir 2).
In the present disclosure, the term "ROS (reactive oxygen species)" refers to a byproduct of aerobic metabolism of organisms, including oxygen ions, peroxides, and oxygen-containing radicals. Excessive levels of reactive oxygen species can cause damage to cells and genetic structures.
In the present disclosure, the term "pharmaceutically acceptable salts" includes "acceptable acid addition salts" and "acceptable base addition salts".
In the present disclosure, the term "acceptable acid addition salts" refers to those salts that retain the biological effectiveness and properties of the free base, which are biologically or otherwise suitable and are formed using inorganic acids such as, but not limited to, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, and the like, or organic acids such as, but not limited to, acetic acid, 2-dichloroacetic acid, adipic acid, alginic acid, ascorbic acid, aspartic acid, benzenesulfonic acid, benzenecarboxylic acid, 4-acetamidobenzenecarboxylic acid, camphoric acid, camphor-10-sulfonic acid, capric acid, hexanoic acid, octanoic acid, carbonic acid, cinnamic acid, citric acid, cyclohexanesulfamic acid, dodecylsulfuric acid, ethane-1, 2-disulfonic acid, ethanesulfonic acid, 2-hydroxyethanesulfonic acid, formic acid, fumaric acid, and the like, Mucic acid, gentisic acid, glucoheptonic acid, gluconic acid, glucuronic acid, glutamic acid, glutaric acid, 2-oxo-glutaric acid, glycerophosphoric acid, glycolic acid, hippuric acid, isobutyric acid, lactic acid, lactobionic acid, lauric acid, maleic acid, malic acid, malonic acid, mandelic acid, methanesulfonic acid, mucic acid, naphthalene-1, 5-disulfonic acid, naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid, 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, nicotinic acid, oleic acid, orotic acid, oxalic acid, palmitic acid, pamoic acid, propionic acid, pyroglutamic acid, pyruvic acid, salicylic acid, 4-aminosalicylic acid, sebacic acid, stearic acid, succinic acid, tartaric acid, thiocyanic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, undecylenic acid, and the like.
In the present disclosure, the term "acceptable base addition salts" refers to those salts that retain the biological effectiveness and properties of the free acid, which are biologically or otherwise suitable. These salts are prepared by adding an inorganic or organic base to the free acid. Salts derived from inorganic bases include, but are not limited to, sodium, potassium, lithium, ammonium, calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, copper, manganese, aluminum salts, and the like. In certain embodiments, the inorganic salts are ammonium, sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium salts. Salts derived from organic bases include, but are not limited to, salts of primary, secondary and tertiary amines, substituted amines including naturally occurring substituted amines, salts of cyclic amines and basic ion exchange resins, such as ammonia, isopropylamine, trimethylamine, diethylamine, triethylamine, tripropylamine, diethanolamine, ethanolamine, 2-dimethylaminoethanol, 2-diethylaminoethanol, dicyclohexylamine, lysine, arginine, histidine, caffeine, procaine, hydrabamine, choline, betaine, benzylamine, phenylenediamine, ethylenediamine, glucosamine, methylglucamine, theobromine, triethanolamine, tromethamine, purines, piperazine, piperidine, N-ethylpiperidine, polyamine resins and the like. In certain embodiments, the organic base is isopropylamine, diethylamine, ethanolamine, trimethylamine, dicyclohexylamine, choline, and caffeine.
In the present disclosure, the term "adjuvant" refers to a general term for other ingredients in the composition besides the drug having the active ingredient.
In the present disclosure, the term "pharmaceutically acceptable excipient" refers to an excipient and additive used in the production of a pharmaceutical product and the formulation of a prescription, which are substances that have been reasonably evaluated in terms of safety in addition to active ingredients and are included in a pharmaceutical composition.
In the present disclosure, the term "therapeutically effective amount" refers to an amount of a compound represented by formula (I), formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof that ameliorates, attenuates, or eliminates a particular disease or condition and symptoms of a particular disease or condition, or delays the onset of a particular disease or condition or symptoms of a particular disease or condition. The amount of the compound represented by formula (I), formula (II) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof described in the present disclosure constituting the "therapeutically effective amount" will vary depending on the compound represented by formula (I), formula (II) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, the disease state and its severity, and the age, body weight, etc. of the subject to be treated, but the amount of the compound represented by formula (I), formula (II) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof described in the present disclosure can be conventionally determined by one skilled in the art based on its own knowledge and the present disclosure.
As used in this disclosure, "treating" or "treatment" encompasses treating a related disease or disease state in a subject, e.g., a mammal, e.g., a human, suffering from the related disease or disorder and includes:
(i) preventing the occurrence of a disease or condition in an individual, particularly when the individual is susceptible to said disease condition but has not yet been diagnosed as having such a disease condition;
(ii) inhibiting a disease or disease state, i.e., preventing its occurrence; or
(iii) Alleviating the disease or condition, even if the disease or condition regresses or does not progress.
As used in this disclosure, the terms "disease" and "disease state" may be used interchangeably, or may be different, in that a particular disease or disease state may not have a known causative agent (and therefore cannot be explained by etiology), and thus is not recognized as a disease, but rather is considered an undesirable disease state or condition, in which a clinician has identified a more or less specific series of symptoms.
In the present disclosure, the term "prevention" refers to an action taken to inhibit or reduce the severity or symptoms of a particular disease or condition prior to the onset of the development of the disease or condition in an individual.
In the present disclosure, the term "prophylactically effective amount" refers to an amount sufficient to prevent a disease or condition or to prevent recurrence thereof. A prophylactically effective amount of a compound of formula (I), formula (II) refers to an amount that alone or in combination with other drugs provides a prophylactic benefit in preventing disease. The term "prophylactically effective amount" can include an amount that improves overall prophylaxis or enhances the prophylactic efficacy of another prophylactic agent.
In the present disclosure, the term "mammal" refers to animals including, for example, dogs, cats, cattle, sheep, horses, and humans.
Detailed Description
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on AMPK:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound represented by formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for reducing the inhibitory effect of high concentrations of glucose on AMPK:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on SIRT 1:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for inhibiting the increase of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) induced by advanced glycation end products (AGEs):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound represented by formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to the use of a compound represented by formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (II) or pharmaceutically acceptable thereof for use in reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of high concentrations of glucose:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on SIRT 1:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for inhibiting increased Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) induced by advanced glycation end products (AGEs):
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to compounds represented by formula (II) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease:
certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of reducing the inhibition of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on AMPK, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I):
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of individuals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, mammals.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of mammals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, humans.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of reducing the inhibition of SIRT1 by advanced glycation end products (AGEs) comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I):
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of individuals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, mammals.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of mammals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, humans.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of high concentrations of glucose, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (II):
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of individuals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, mammals.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of mammals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, humans.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of inhibiting advanced glycation end products (AGEs) induced increases in Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I):
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of individuals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, mammals.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of mammals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, humans.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods of treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of a compound of formula (I), formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of individuals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, mammals.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of mammals that can be used in the methods of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, humans.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a combination thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient:
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of pharmaceutically acceptable excipients that can be used in the pharmaceutical compositions of the present disclosure for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on AMPK include, but are not limited to, preservatives, antioxidants, flavoring agents, coloring agents, surfactants, and polymeric compounds.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of the polymer compound that can be used in the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, natural polymer compounds and synthetic polymer compounds.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on SIRT1, comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a combination thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient:
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of pharmaceutically acceptable excipients that can be used in the pharmaceutical compositions of the present disclosure for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on SIRT1 include, but are not limited to, preservatives, antioxidants, flavorants, colorants, surfactants, and polymeric compounds.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of the polymer compound that can be used in the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, natural polymer compounds and synthetic polymer compounds.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to a pharmaceutical composition for reducing AMPK inhibition by high concentrations of glucose, comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (II):
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of pharmaceutically acceptable excipients that can be used in the pharmaceutical compositions of the present disclosure for reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of high concentrations of glucose include, but are not limited to, preservatives, antioxidants, flavoring agents, coloring agents, surfactants, and polymeric compounds.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of the polymer compound that can be used in the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, natural polymer compounds and synthetic polymer compounds.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to a pharmaceutical composition for inhibiting advanced glycation end products (AGEs) induced increase in Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (I):
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of pharmaceutically acceptable excipients that can be used in the disclosed pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting advanced glycation end products (AGEs) induced increase in Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) include, but are not limited to, preservatives, antioxidants, flavoring agents, coloring agents, surfactants, and polymeric compounds.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of the polymer compound that can be used in the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, natural polymer compounds and synthetic polymer compounds.
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to pharmaceutical compositions for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease comprising a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of a compound represented by formula (I), formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a combination thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvant:
in certain embodiments, illustrative examples of pharmaceutically acceptable excipients that can be used in the pharmaceutical compositions of the present disclosure for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease include, but are not limited to, preservatives, antioxidants, flavors, colorants, surfactants, and polymeric compounds.
In certain embodiments, illustrative examples of the polymer compound that can be used in the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, natural polymer compounds and synthetic polymer compounds.
Hereinafter, the present disclosure will be explained in detail by the following examples in order to better understand various aspects of the present application and advantages thereof. It should be understood, however, that the following examples are not limiting and are merely illustrative of certain embodiments of the present disclosure.
Examples
Example 1
Mulberroside A (MBA) reduces the inhibition of Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on AMPK and SIRT1 in HUVEC cells and the induced generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
Experimental materials:
cell: human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) (ATCC)
Mulberroside a (Mulberroside a, MBA): from Shanghai Dingrui chemical industry (Shanghai) Co., Ltd
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs): prepared according to the literature method (Xu et al, Journal of Ethnopharmacology137(2011)359-
Antibody: AMPK antibody ((Cell Signaling Technology) CST, cat No. 5832 s); SIRT1 antibody (Santa Cruz, cat # SC74504)
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) detection kit (chemiluminescence method): purchased from Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Co., Ltd, cat #: s0033
The experimental method comprises the following steps:
(1) spreading HUVEC cells in a porous cell culture plate with a glass slide spread at the bottom, and treating the cells according to experimental groups after the cells are attached stably;
(2) grouping experiments: each test was divided into three groups, namely a normal group, a model group (AGEs: 300. mu.g/mL), and an MBA treatment group (AGEs 300. mu.g/mL + MBA 40. mu.M), and the test was administered and incubated for 24 hours;
(3) detecting the total amount of AMPK and SIRT1 protein in cells: after 24 hours of incubation, the following procedure was performed for the indicated cells:
1) cell fixation and perforation: removing cell well culture solution, washing cells with PBS, fixing with 4% paraformaldehyde, washing with PBS, perforating with 0.25% triton X-100, and washing with PBS;
2) blocking incubation primary antibody: blocking with 2% BSA for 30 min, washing twice with PBS, adding primary antibody (AMPK or SIRT-1 antibody) diluted at a ratio of 1:200, and incubating overnight at 4 deg.C;
3) and (3) secondary antibody incubation: removing the primary antibody on the third day of the experiment, washing with PBS, adding a fluorescent secondary antibody with the same species as the primary antibody, incubating at 37 ℃ in a dark place, and washing with PBS;
4) dyeing and sealing the core: adding 0.5 mu g/mL DAPI (PBS) for dyeing (keeping out of the light), washing with PBS, taking out the cover glass attached with cells from the PBS, placing the cover glass in the place where the cover glass is kept out of the light for air drying, and dropwise adding an anti-fluorescence quenching sealing tablet;
5) and (5) observing under a laser confocal microscope, and taking a picture.
(4) Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) detection: according to the instructions of a Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) detection kit. After the administration and incubation for 24 hours, removing the cell well culture solution, adding a DCFH-DA solution, incubating, then washing with PBS, fixing the cells with 4% paraformaldehyde, washing with PBS, fixing the glass slide attached with the cells on a cover glass, and observing and taking a picture under a laser confocal microscope;
(5) and (4) analyzing results: the collected cell images are converted into corresponding signal data by software analysis. Analysis of differences between experimental groups was performed using ANOVA or t-test.
The experimental results are as follows:
(1) inhibitory effect of mulberroside A on reduction of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on HUVEC cells AMPK and SIRT1
AGEs (300. mu.g/mL) treated HUVEC cells for 24 hours inhibited the intracellular levels of AMPK and SIRT1 proteins, and the addition of MBA (40. mu.M) significantly inhibited AGEs-induced reduction of intracellular AMPK (FIG. 1) and SIRT1 (FIG. 2) proteins.
(2) Mulberroside A (MBA) inhibits the induced generation of advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs) on ROS in HUVEC cells
AGEs (300. mu.g/mL) treated HUVEC cells for 24 hours significantly increased the oxidative stress of the cells, as evidenced by an increase in the oxidative stress product Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), while the addition of MBA (40. mu.M) significantly inhibited AGEs-induced increases in intracellular ROS (FIG. 3).
Example 2
Activation effect of mulberroside A, oxyresveratrol and resveratrol on HEK cell AMPK under normal and high-sugar conditions
Experimental materials:
cell: human embryonic kidney cell 293(Human embryo kidney cells, HEK293) (ATCC)
Total AMPK cell kit (Total AMPK cellular kit-500T) (Cisbio)
Phospho-AMPK (Thr172) cell kit (Phospho-AMPK (Thr172) cellular kit-500T) (Cisbio)
Glucose: purchased from Sigma, cat # G7021
Mulberroside A: from Shanghai Dingrui chemical industry (Shanghai) Co., Ltd
Oxidizing resveratrol: from Shanghai Dingrui chemical industry (Shanghai) Co., Ltd
Resveratrol: from Shanghai Dingrui chemical industry (Shanghai) Co., Ltd
The experimental method comprises the following steps:
(1) spreading HEK293 cells in a porous cell culture plate, and processing the cells according to experimental groups after the cells are attached stably;
(2) grouping experiments: the experiments were divided into 3 groups, experimental group 1: resveratrol (RES); experimental group 2: oxyresveratrol (OXY) group, experimental group 3: mulberroside A (MBA) group. In each large group, two subsets of treatment conditions were divided, with the cell culture medium containing 5.5mM glucose subset and 30mM glucose subset. Each compound was tested for its effect at different final concentrations.
(3) And (3) cell administration treatment: cells were incubated for 24 hours at different concentrations of each compound and glucose, grouped according to the above experiments.
(4) Intracellular total AMPK (T-AMPK) and activated state phosphorylated AMPK (P-AMPK) assays: according to the kit operation instructions. Cell well supernatants were removed, cells were washed with PBS, lysed with lysis buffer, the appropriate amount was removed, incubated overnight with the corresponding HTRF premixed P-AMPK or T-AMPK antibodies, respectively, and the fluorescence emission values in the 650 and 620nM wavelength bands were read using a plate reader.
(5) And (4) analyzing results: the 650/620nM fluorescence ratio was calculated, and the ratio of phosphorylated AMPK (P-AMPK) to total AMPK was calculated.
The experimental results are as follows:
as shown in fig. 4, human embryonic kidney cells 293(HEK293) were cultured in a medium containing normal glucose (5.5mM) for 24 hours, and added with Resveratrol (RES) and Oxyresveratrol (OXY) at different concentrations to increase intracellular AMPK activity in a dose-dependent manner, as indicated by an increase in phosphorylated AMPK (P-AMPK) concentration. When HEK293 is cultured in a culture medium with high glucose concentration (30mM) for 24 hours, compared with the result of normal cell culture, the P-AMPK of phosphorylation AMPK (P-AMPK) of cells cultured by high sugar is obviously reduced, and the reduction amplitude is inhibited by adding Resveratrol (RES) and Oxyresveratrol (OXY). Mulberroside A (MBA) has no effect on AMPK activity in HEK293 cells under normal and high-concentration glucose culture conditions. The results show that Resveratrol (RES) and Oxyresveratrol (OXY) have the effects of activating the AMPK activity of HEK293 cells and reducing the inhibition of high-concentration glucose on the AMPK activity of the cells.
Example 3
Therapeutic effect of mulberroside A on diabetic kidney disease of mice
Experimental materials:
test compounds: mulberroside a (Mulberroside a, MBA): from Shanghai Dingrui chemical industry (Shanghai) Co., Ltd
Experimental animals: male C57BL/6 Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) mice
The experimental method comprises the following steps:
model establishment and administration mode: streptozotocin (STZ) was injected subcutaneously 48 hours after neonatal mice and female mice were nursed for four weeks. A total of 12 hyperglycemic male mice were picked four weeks later, randomly divided into 2 groups, and High Fat Diet (HFD) feeding was started. After 1 week, experiment group 2 orally drenches 5 mg/kg/day detection compound for 49 days, and experiment group 1 drenches blank solvent group
The experimental detection indexes are as follows: during animal model establishment and administration, and after animal sacrifice, kidney and liver are collected to determine the following indexes:
animal weight and feed intake
Animal serology biochemistry and kidney function detection: serum blood glucose, total Triglycerides (TG), Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) and Creatinine (CREA) concentrations were measured.
Total volume of urine, urinary Creatinine (CREA), urine albumin content (mALB) was determined by the Elisa method for 24-hour urine.
Histopathological analysis:
kidney: PAS staining, pathological analysis of glomerular injury, calculation of glomerular sclerosis index.
Results of the experiment
The mice injected with STZ in the experiment have the insulin secretion reduced because part of islet beta-cells are damaged, so that the blood sugar of the newborn mice is increased and exceeds the normal value, and the mice become diabetic mice in 1 month after the mice are injected with STZ. Under the condition of continuous high-fat feeding, the weight, the blood sugar and the serum triglyceride of the mouse are gradually increased, the kidney function and the tissues are damaged, and the mouse becomes a Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) mouse.
(1) Mulberroside A remarkably improves lipid metabolism balance of high-fat-fed mice
Mice in the administered group had significantly reduced Triglyceride (TG) compared to the blank control group (fig. 5).
(2) Mulberry bark glucoside A can significantly improve renal function of Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) mice and inhibit renal tissue injury
In the experiment, blood and urine of the diabetic kidney disease mouse are collected and subjected to biochemical detection on the 49 th day of the last administration of the mulberroside A. The results show that the mulberroside A significantly reduces the serum Creatinine (CREA) level of the mice (figure 6) and has the trend of reducing the blood urea nitrogen level (figure 7) compared with the blank control group; mice were significantly reduced in total urine volume at 24 hours (figure 8), urinary microalbumin (mALB) (figure 9) and total urinary Creatinine (CREA) (figure 10).
After the experiment was completed, the mice were sacrificed, kidneys were harvested, formalin fixed, and kidney histopathological analysis was performed. Mulberroside a significantly inhibited glomerulosclerosis lesions compared to the blank control results (fig. 11 and 12).
In the present disclosure, relational terms such as first and second, and the like may be used solely to distinguish one entity or action from another entity or action without necessarily requiring or implying any actual such relationship or order between such entities or actions.
From the foregoing it will be appreciated that, although specific embodiments of the disclosure have been described herein for purposes of illustration, various modifications or improvements may be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the disclosure. Such variations and modifications are intended to fall within the scope of the appended claims of this disclosure.
Claims (11)
7. a pharmaceutical composition for reducing the AMPK inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a combination thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient:
8. a pharmaceutical composition for reducing the inhibitory effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on SIRT1, comprising an inhibitory effective amount of a compound represented by formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a combination thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient:
11. a pharmaceutical composition for treating or preventing diabetic kidney disease, comprising a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of a compound represented by formula (I), formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a combination thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvant:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010202539.0A CN113101295A (en) | 2020-03-20 | 2020-03-20 | Use of stilbene analogues in the treatment of diabetic renal disease |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010202539.0A CN113101295A (en) | 2020-03-20 | 2020-03-20 | Use of stilbene analogues in the treatment of diabetic renal disease |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113101295A true CN113101295A (en) | 2021-07-13 |
Family
ID=76708896
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010202539.0A Pending CN113101295A (en) | 2020-03-20 | 2020-03-20 | Use of stilbene analogues in the treatment of diabetic renal disease |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113101295A (en) |
Citations (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1398838A (en) * | 2001-07-26 | 2003-02-26 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院放射医学研究所 | Diphenylethylene compound and its prepn and application in preventing and treating diabetes |
| CN101257897A (en) * | 2005-07-07 | 2008-09-03 | 西特里斯药业公司 | Methods and related compositions for treating or preventing obesity, insulin resistance disorders, and mitochondrial-associated disorders |
| CN101416957A (en) * | 2008-12-10 | 2009-04-29 | 山西亚宝药业集团股份有限公司 | Use of resveratrol or naringenin in preventing and treating diabetic nephropathy |
| CN101502527A (en) * | 2009-02-12 | 2009-08-12 | 浙江康恩贝制药股份有限公司 | Application of mulberroside in preparing medicament for inhibiting uric acid reabsorption transporter |
| CN101530417A (en) * | 2009-02-12 | 2009-09-16 | 浙江康恩贝制药股份有限公司 | Application of mulberry skin glucoside in preventing and treating hyperuricemia and gout |
| CN101716165A (en) * | 2009-12-23 | 2010-06-02 | 华东理工大学 | Use of oxyresveratrol |
| CN102083438A (en) * | 2008-05-01 | 2011-06-01 | 西特里斯药业公司 | Quenolines and related analogs as sirtuin modulators |
| CN102631358A (en) * | 2012-04-25 | 2012-08-15 | 中山大学 | Application of polydatin in preparing medicament for treating diabetic nephropathy |
| CN102836145A (en) * | 2012-09-24 | 2012-12-26 | 南京大学 | Applications of pterostilbene in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating chronic glomerular disease |
| CN102961375A (en) * | 2012-12-05 | 2013-03-13 | 苏州大学 | AMPK (Adenosine Monophosphate Activated Protein Kinase) activating agent and application thereof in preparation of medicaments for treating diabetes mellitus and/or diabetic complication |
| CN103476408A (en) * | 2011-03-28 | 2013-12-25 | 同和药品株式会社 | Use of compounds isolated from morus bark |
| CN105377831A (en) * | 2013-05-01 | 2016-03-02 | 细胞基因公司 | Synthesis of 3-(5-amino-2-methyl-4-oxoquinazolin-3(4h)-yl) piperidine-2,6-dione |
| WO2018043852A1 (en) * | 2016-08-31 | 2018-03-08 | 영남대학교 산학협력단 | Pharmaceutical composition containing burdock root extract as active ingredient for preventing or treating diabetic complications |
| CN110840905A (en) * | 2019-11-11 | 2020-02-28 | 中国药科大学 | Application of icariin or derivatives and compositions thereof in preventing and treating nephropathy |
-
2020
- 2020-03-20 CN CN202010202539.0A patent/CN113101295A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1398838A (en) * | 2001-07-26 | 2003-02-26 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院放射医学研究所 | Diphenylethylene compound and its prepn and application in preventing and treating diabetes |
| CN101257897A (en) * | 2005-07-07 | 2008-09-03 | 西特里斯药业公司 | Methods and related compositions for treating or preventing obesity, insulin resistance disorders, and mitochondrial-associated disorders |
| CN102083438A (en) * | 2008-05-01 | 2011-06-01 | 西特里斯药业公司 | Quenolines and related analogs as sirtuin modulators |
| CN101416957A (en) * | 2008-12-10 | 2009-04-29 | 山西亚宝药业集团股份有限公司 | Use of resveratrol or naringenin in preventing and treating diabetic nephropathy |
| CN101502527A (en) * | 2009-02-12 | 2009-08-12 | 浙江康恩贝制药股份有限公司 | Application of mulberroside in preparing medicament for inhibiting uric acid reabsorption transporter |
| CN101530417A (en) * | 2009-02-12 | 2009-09-16 | 浙江康恩贝制药股份有限公司 | Application of mulberry skin glucoside in preventing and treating hyperuricemia and gout |
| CN101716165A (en) * | 2009-12-23 | 2010-06-02 | 华东理工大学 | Use of oxyresveratrol |
| CN103476408A (en) * | 2011-03-28 | 2013-12-25 | 同和药品株式会社 | Use of compounds isolated from morus bark |
| CN102631358A (en) * | 2012-04-25 | 2012-08-15 | 中山大学 | Application of polydatin in preparing medicament for treating diabetic nephropathy |
| CN102836145A (en) * | 2012-09-24 | 2012-12-26 | 南京大学 | Applications of pterostilbene in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating chronic glomerular disease |
| CN102961375A (en) * | 2012-12-05 | 2013-03-13 | 苏州大学 | AMPK (Adenosine Monophosphate Activated Protein Kinase) activating agent and application thereof in preparation of medicaments for treating diabetes mellitus and/or diabetic complication |
| CN105377831A (en) * | 2013-05-01 | 2016-03-02 | 细胞基因公司 | Synthesis of 3-(5-amino-2-methyl-4-oxoquinazolin-3(4h)-yl) piperidine-2,6-dione |
| WO2018043852A1 (en) * | 2016-08-31 | 2018-03-08 | 영남대학교 산학협력단 | Pharmaceutical composition containing burdock root extract as active ingredient for preventing or treating diabetic complications |
| CN110840905A (en) * | 2019-11-11 | 2020-02-28 | 中国药科大学 | Application of icariin or derivatives and compositions thereof in preventing and treating nephropathy |
Non-Patent Citations (7)
| Title |
|---|
| CHENG W,等: "Intrathecal Injection of Resveratrol Attenuates Burn Injury Pain by Activating Spinal Sirtuin 1", PHARMACOGN MAG, vol. 12, no. 2, pages 201 - 205 * |
| LU, HAI PENG,等: "DNA protection activity of a hydroethanol extract and six polyphenol monomers from Morus alba L. (mulberry) twig", INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF FOOD PROPERTIES, vol. 20, no. 2, pages 276 - 277 * |
| SHI YW,等: "Antihyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of resveratrol and its analogues in hyperuricemic mice", MOL NUTR FOOD RES, vol. 56, no. 9, pages 1 - 13 * |
| 梁威: "脑出血破入脑室患者死亡危险因素探讨", 白求恩军医学院学报, vol. 10, no. 03, pages 208 - 209 * |
| 王晶洁: "桑枝多糖对2型糖尿病大鼠心肌及肾功能的保护作用", 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, vol. 17, no. 19, pages 2936 - 2938 * |
| 金英善,等: "桑根活性成分反式二苯乙烯抗糖尿病作用研究", 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), vol. 30, no. 01 * |
| 金英善,等: "桑根活性成分反式二苯乙烯抗糖尿病作用研究", 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版, vol. 30, no. 01 * |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20220048865A1 (en) | Novel Phenyl Derivatives | |
| JP4556009B2 (en) | Anti-inflammatory agents, preventive or ameliorating agents for allergic diseases and functional foods | |
| WO2011037223A1 (en) | Agent for reducing visceral fat weight | |
| KR20130020623A (en) | Compositon for preventing or treating complication of diabetes containing extract of quamoclit | |
| KR100879253B1 (en) | treatment for hypertension and diabetic nephropathy using ADP-ribosyl cyclase inhibitors | |
| CN112316150B (en) | Pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating metabolic or injury related diseases | |
| CN113101295A (en) | Use of stilbene analogues in the treatment of diabetic renal disease | |
| WO2009155753A1 (en) | The use of inositol derivative or salts thereof in the manufacture of medicaments as glycosidase inhibitors or medicaments for treating diabetes | |
| WO2022245171A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating diabetes mellitus in animal of family canidae, comprising enavogliflozin | |
| JP6657101B2 (en) | Compounds for the treatment of diabetes and disease complications resulting therefrom | |
| CN104582730B (en) | A kind of method improving Metabolism of Mitochondria function and application | |
| AU2018100291A4 (en) | Hepatoprotective composition | |
| US11179408B2 (en) | Use of cyanoglucosides and pharmaceutical formulations thereof in the treatment of diabetes | |
| JP6388786B2 (en) | Evaluation method, screening method, and production method of prophylactic / therapeutic agent for type 2 diabetes using hyperglycemic silkworm | |
| Rani et al. | BIOCHEMICAL MODULATIONS IN HYPOGLYCEMIC ALBINO RAT ALONG WITH MICRONUTRIENTS. | |
| TWI723171B (en) | Use of a polysaccharide mixture for the manufacture of a medicament for treating hyperglycemia | |
| WO2022215950A1 (en) | Compound for prevention or treatment of kidney disease | |
| US8247407B2 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition with anti-diabetic action | |
| CN109223735A (en) | The purposes for the reactive compound isolated from aspergillus versicolor secondary metabolites | |
| KR20220018738A (en) | Composition for prevention or treatment of multiple sclerosis | |
| Kolisnyk et al. | Pharmacological evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets containing Vaccinium myrtillus leaf dry extract as an alpha-glucosidase inhibitory drug | |
| CN116509870A (en) | New use of rape pollen alkaloid A in neuroprotection and brain disease prevention and treatment | |
| CN115634230A (en) | Application of sodium mannolite in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating severe acute pancreatitis | |
| Umar et al. | Oral hypoglycaemic agent metformin reduces oxidative stress and improves kidney histologyin streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats | |
| US20150265644A1 (en) | Therapeutic methods and compositions for treating diabetes utilizing diterpenoid compounds |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |
Application publication date: 20210713 |
|
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |