CN112513021A - ROR gamma antagonist and application thereof in medicine - Google Patents
ROR gamma antagonist and application thereof in medicine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112513021A CN112513021A CN201980045075.2A CN201980045075A CN112513021A CN 112513021 A CN112513021 A CN 112513021A CN 201980045075 A CN201980045075 A CN 201980045075A CN 112513021 A CN112513021 A CN 112513021A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- phenyl
- trifluoromethyl
- ring
- compound
- membered
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/02—Drugs for skeletal disorders for joint disorders, e.g. arthritis, arthrosis
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D207/08—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon radicals, substituted by hetero atoms, attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D207/08—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon radicals, substituted by hetero atoms, attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D207/09—Radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms, not forming part of a nitro radical
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D207/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D207/12—Oxygen or sulfur atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D207/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D207/16—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D211/08—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/18—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D211/08—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/18—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/20—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms with hydrocarbon radicals, substituted by singly bound oxygen or sulphur atoms
- C07D211/22—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms with hydrocarbon radicals, substituted by singly bound oxygen or sulphur atoms by oxygen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D211/08—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/18—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/26—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms with hydrocarbon radicals, substituted by nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D211/08—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/18—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/34—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms with hydrocarbon radicals, substituted by carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D211/36—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/60—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/68—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having one double bond between ring members or between a ring member and a non-ring member
- C07D211/72—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having one double bond between ring members or between a ring member and a non-ring member with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms, with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/74—Oxygen atoms
- C07D211/76—Oxygen atoms attached in position 2 or 6
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D241/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings
- C07D241/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D241/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D265/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings having one nitrogen atom and one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D265/28—1,4-Oxazines; Hydrogenated 1,4-oxazines
- C07D265/30—1,4-Oxazines; Hydrogenated 1,4-oxazines not condensed with other rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D267/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing rings of more than six members having one nitrogen atom and one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D267/02—Seven-membered rings
- C07D267/08—Seven-membered rings having the hetero atoms in positions 1 and 4
- C07D267/10—Seven-membered rings having the hetero atoms in positions 1 and 4 not condensed with other rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D413/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D413/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D413/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing only aliphatic carbon atoms
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
The invention relates to a ROR gamma antagonist compound, which is a compound shown as a formula (I). The compounds or pharmaceutical compositions can be used to modulate retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (ROR γ t). The invention also relates to methods for preparing such compounds and pharmaceutical compositions, and their use in the treatment or prevention of inflammatory or autoimmune diseases mediated by roryt in mammals, particularly humans.
Description
Technical Field
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a small molecular compound, a composition, a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the compound or the composition can be used as an antagonist of retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (ROR gamma t) and is used for preventing or treating diseases related to immunity.
Background
Retinoic acid-related nocosomal receptors are a subfamily of transcription factors in the steroid hormone nuclear receptor superfamily. The family of retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptors includes ROR α, ROR β, and ROR γ, each encoded by a distinct gene (RORA, RORB, and RORC). Retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptors contain four major domains: an N-terminal A/B domain, a DNA binding domain, a hinge domain, and a ligand binding domain.
Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (ROR γ t) is one of two isoforms of retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma (ROR γ), and may also be referred to as ROR γ 2. It has been shown that ROR γ t is expressed only in lymphoid lineage and embryonic lymphoid tissue inducer cells (Sun et al, Science 288:2369-2372, 2000; Eberl et al, Nat Immunol.5:64-73,2004). ROR gamma T, a characteristic transcription factor of helper T cells (Th17), plays an important role in Th17 cell differentiation, and is a key regulator of Th17 cell differentiation (Ivanov, II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, et al. cell 2006; 126(6): 1121-33).
Th17 can secrete interleukin 17 (IL-17) and other proinflammatory cytokines, and has important significance in autoimmune diseases and body defense response. IL-17 is a proinflammatory cytokine for inflammatory progression and various autoimmune diseases, and is closely associated with a variety of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthritis, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis, among others (Jetten et al, Nucl. Recept. Signal,2009,7: e 003; Manel et al, Nat. Immunol.,2008,9, 641-649).
The role ROR γ t plays in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases or inflammation has been extensively studied and fully elucidated (Jetten et al, adv. Dev. biol., 2006,16: 313-supplement 355; Meier et al Immunity,2007,26: 643-654; Aloisi et al, Nat. Rev. Immunol.,2006,6: 205-supplement 217; Jager et al., J. Immunol.,2009,183: 7169-supplement 7177; Barnes et al, Nat. Rev. Immunol.,2008,8: 183-supplement 192). Therefore, inhibition of ROR γ t will effectively inhibit cell differentiation of Th17, regulate the production and secretion levels of IL-17 and other proinflammatory cytokines, thereby modulating the body's immune system, treating immune and inflammatory diseases associated with ROR γ t regulation.
Summary of The Invention
The following is a summary of some aspects of the invention only and is not intended to be limiting. These aspects and others are described more fully below. All references in this specification are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety. When the disclosure of the present specification differs from the cited documents, the disclosure of the present specification controls.
The invention provides a compound as a retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (ROR gamma t) antagonist, which is used for preparing a medicament for preventing or treating ROR gamma t-mediated inflammation or autoimmune diseases, such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ophthalmopathy, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, Crohn's disease or Kawasaki disease and the like; the compound can well inhibit ROR gamma t, and has excellent physicochemical property and pharmacokinetic property.
The invention also provides processes for the preparation of these compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds and methods of using these compounds or compositions in the treatment of the above-mentioned diseases in mammals, especially humans.
Specifically, the method comprises the following steps:
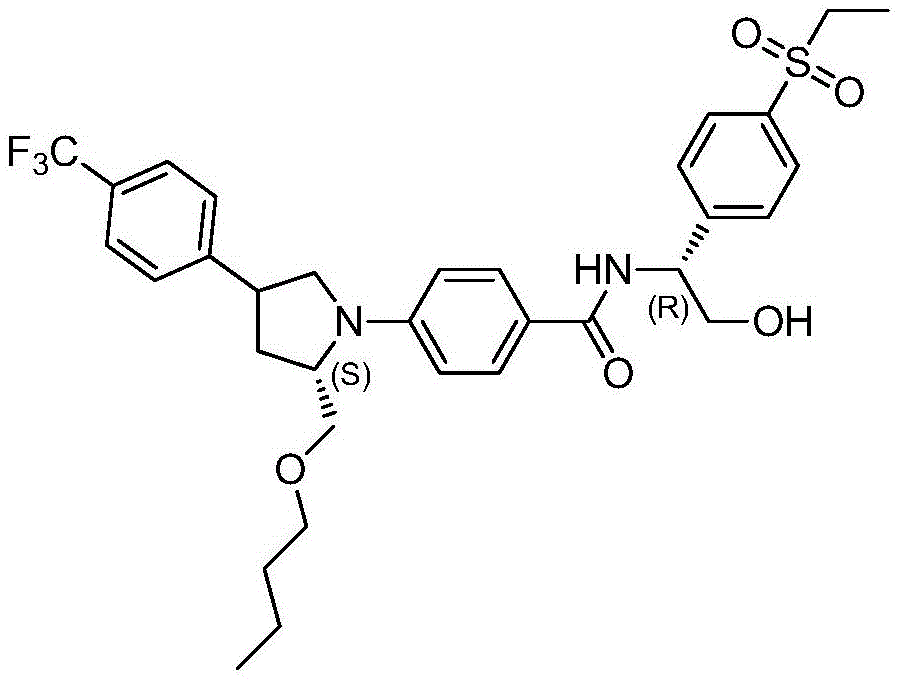
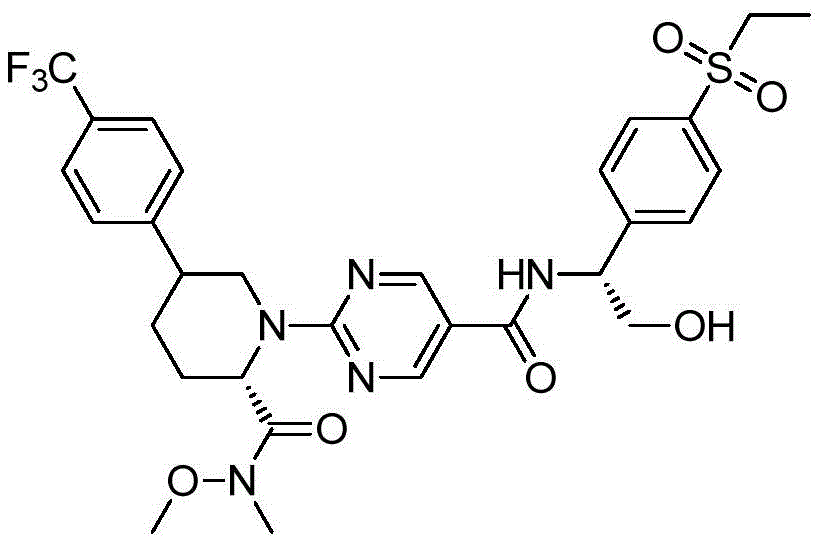
in one aspect, the invention relates to a compound of formula (I) or a stereoisomer, geometric isomer, tautomer, nitrogen oxide, hydrate, solvate, metabolite, ester, pharmaceutically acceptable salt of a compound of formula (I) or a prodrug thereof,
wherein:
r is C1-4Alkyl radical, C1-4Alkoxy radical, C1-4Alkylamino radical, C1-4Haloalkyl or C1-4A haloalkoxy group;
Z1、Z2、Z3、Z4、Z5、Z6、Z7and Z8Each independently is CR1Or N;
each R1Independently isHydrogen, deuterium, C1-6Alkyl, cyano, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Hydroxyalkyl, -C1-6alkylene-C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl or 3-8 membered heterocyclyl;
ring A is a 3-12 membered heterocyclic ring, said 3-12 membered heterocyclic ring optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2Substitution;
each R2Independently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydroxy, oxo (═ O), amino, nitro, cyano, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, -C0-6alkylene-OR a、-C0-4Alkylene- (C ═ O)m-Rb、-C0-4Alkylene- (O)n-(C=O)p-NRcRd5-10 membered heteroaryl, -C0-4Alkylene- (3-12 membered heterocyclyl), -C0-4Alkylene- (5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl) or-C0-4Alkylene- (4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl); the R is2Optionally substituted by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RfSubstitution;
each RaIndependently of one another is hydrogen, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 5-10 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl or 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl; each Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 4-12 membered fused ring group, 5-12 membered spiro ring group, 5-10 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiro heterocyclyl or 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl; or Rc、RdAnd the N atom to which they are attached together form a 4-8 membered heterocyclic ring; each of said Ra、Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RgSubstitution;
each RfAnd RgIndependently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, oxo (═ O), hydroxy, amino, nitro, cyano, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Hydroxyalkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C6-10Aryl radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 4-12 membered fused ring group, 5-12 membered spiro ring group, 3-12 membered heterocyclic group, 5-12 membered spiro heterocyclic group, 4-12 membered fused heterocyclic group, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylamino or C 1-6A haloalkoxy group;
ring B is C6-10Aryl, 5-12 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl, 4-12 membered fused cyclic, 5-12 membered spirocyclic or C3-8Cycloalkyl, wherein said B ring is optionally substituted with 1,2, 3 or 4ReSubstitution;
each ReIndependently hydrogen, deuterium, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, nitro, hydroxyl, amino, C1-4Alkyl radical, C1-4Alkoxy radical, C3-6Cycloalkyl radical, C1-4Haloalkyl or C1-4A haloalkoxy group; or, any two adjacent ReAnd the atoms to which they are attached together form C3-8A carbocyclic ring or a 3-8 membered heterocyclic ring; or, optionally, two R's attached to the same carbon atomeAnd together with the atom to which they are attached form C3-8A carbocyclic ring or a 3-8 membered heterocyclic ring;
L1is-S (O)2-NH-、-NH-S(O)2-, -s (O) -NH-, -NH-s (O) -, -C (═ O) NH-, or-NHC (═ O) -;
L2is a bond or-CR3R4-;
Each R3And R4Independently is hydrogen or C1-6A hydroxyalkyl group;
m is independently 0, 1 or 2;
n is independently 0 or 1;
p is independently 0, 1 or 2. In some embodiments, R is methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, or isopropoxy.
In some embodiments, each R is 1Independently hydrogen, cyano, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethylA group, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, methoxymethylene, ethoxymethylene, n-propoxymethylene, isopropoxymethylene, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl.
In some embodiments, each R is3And R4Independently hydrogen, hydroxymethyl, hydroxyethyl or hydroxy-n-propyl.
In some embodiments, ring B is phenyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, azetidinyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, oxazolyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, azetidinyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, said B ring being optionally substituted with 1,2, 3 or 4ReAnd (4) substitution.
In some embodiments, each R iseIndependently hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, cyano, nitro, hydroxy, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, monofluoromethoxy, difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy, or 1, 2-difluoroethoxy.
In some embodiments, ring a is a 5-12 membered heterocyclic ring, optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5R2And (4) substitution.
Wherein each Y is1And Y2independently-O-, -S-, -N-, -NH-or-CH2-;
Said A ring being optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2And (4) substitution.
In some embodiments, ring a is Wherein each Y is1And Y2Independently is-O-, -S-, N, -NH-or-CH2-; said A ring being optionally substituted by 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2And (4) substitution.
In still other embodiments, ring A is Wherein said A ring is optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2And (4) substitution.
Wherein said A ring is optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2And (4) substitution.
In some embodiments, each R is2Independently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydroxy, oxo (═ O), amino, nitro, cyano, C1-4Alkyl radical, C1-4Haloalkyl, C1-4Alkoxy radical, C3-6Cycloalkyl, -C0-4alkylene-ORa、-C0-4Alkylene oxideRadical- (C ═ O)m-Rb、-C0-4Alkylene- (O)n-(C=O)p-NRcRd5-6 membered heteroaryl, -C0-4Alkylene- (3-to 8-membered heterocyclic group), -C0-4Alkylene- (5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl) or-C0-4Alkylene- (4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl);
wherein, R is2Optionally substituted by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6R fAnd (4) substitution.
In some embodiments, each R is2Independently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydroxyl, oxo (═ O), amino, nitro, cyano, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclohexyl, -C0-4alkylene-ORa、-C0-4Alkylene- (C ═ O)m-Rb、-C0-4Alkylene- (O)n-(C=O)p-NRcRdOxazolyl, thiazolyl, thienyl, imidazolyl, pyridazinyl, pyridyl,
Wherein, R is2Optionally substituted by 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RfAnd (4) substitution.
In some embodiments, each R isaIndependently hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1,1, 1-trifluoroethyl, oxirane, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, oxepanyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl; each Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl N-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1,1, 1-trifluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, oxirane, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, oxepanyl, oxacycloheptanyl, and mixtures thereof, Cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl; or RcAnd RdForm a 4-8 membered heterocyclic ring with the N atom to which it is attached;
wherein each R isa、Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently optionally substituted with 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RgAnd (4) substitution.
In some embodiments, each R isfAnd RgIndependently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, oxo (═ O), hydroxy, amino, nitro, cyano, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, -CH2OH, fluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, phenyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, oxiranyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, oxa-ethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, phenyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, oxiranyl, oxa-cyclobutyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, trifluoromethyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclohexyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, monofluoromethoxy, difluoromethoxy or trifluoromethoxy.
In another aspect, the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of formula (I) of the present invention, or a stereoisomer, geometric isomer, tautomer, nitrogen oxide, hydrate, solvate, metabolite, pharmaceutically acceptable salt, or prodrug thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, carrier, adjuvant, or combination thereof;
the pharmaceutical composition further comprises other drugs or any combination thereof for preventing or treating inflammatory syndromes or autoimmune diseases.
In another aspect, the invention relates to the use of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutical composition thereof in the manufacture of a medicament for the prevention or treatment of an inflammatory or autoimmune disease mediated by roryt in a mammal, including a human.
In some embodiments, the present invention relates to the use of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutical composition thereof in the manufacture of a medicament for the prevention or treatment of psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ocular disease, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, crohn's disease, or kawasaki disease.
In another aspect, the invention relates to methods for the preparation, isolation and purification of compounds of formula (I).
Biological test results show that the compound provided by the invention has good inhibitory activity on ROR gamma t and good pharmacokinetic characteristics.
Any embodiment of any aspect of the invention may be combined with other embodiments, as long as they do not contradict. Furthermore, in any embodiment of any aspect of the invention, any feature may be applicable to that feature in other embodiments, so long as they do not contradict.
The foregoing merely summarizes certain aspects of the invention and is not intended to be limiting. These and other aspects will be more fully described below.
Detailed description of the invention
Definitions and general terms
Reference will now be made in detail to certain embodiments of the invention, examples of which are illustrated by the accompanying structural and chemical formulas. The invention is intended to cover alternatives, modifications and equivalents, which may be included within the scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims. Those skilled in the art will recognize that many methods and materials similar or equivalent to those described herein can be used in the practice of the present invention. The present invention is in no way limited to the methods and materials described herein. In the event that one or more of the incorporated documents, patents, and similar materials differ or contradict this application (including but not limited to defined terminology, application of terminology, described techniques, and the like), this application controls.
It will be further appreciated that certain features of the invention, which are, for clarity, described in the context of separate embodiments, may also be provided in combination in a single embodiment. Conversely, various features of the invention which are, for brevity, described in the context of a single embodiment, may also be provided separately or in any suitable subcombination.
Unless defined otherwise, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. All patents and publications referred to herein are incorporated by reference in their entirety.
The following definitions as used herein should be applied unless otherwise indicated. For the purposes of the present invention, the chemical elements are in accordance with the CAS version of the periodic Table of the elements, and the handbook of chemistry and Physics, 75 th edition, 1994. In addition, general principles of Organic Chemistry can be referred to as described in "Organic Chemistry", Thomas Sorrell, University Science Books, Sausaltito: 1999, and "March's Advanced Organic Chemistry" by Michael B.Smith and Jerry March, John Wiley & Sons, New York:2007, the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference.
The articles "a," "an," and "the" as used herein are intended to include "at least one" or "one or more" unless otherwise indicated or clearly contradicted by context. Thus, as used herein, the articles refer to articles of one or more than one (i.e., at least one) object. For example, "a component" refers to one or more components, i.e., there may be more than one component contemplated for use or use in embodiments of the described embodiments.
The term "subject" as used herein refers to an animal. Typically the animal is a mammal. Subjects, e.g., also primates (e.g., humans, males or females), cows, sheep, goats, horses, dogs, cats, rabbits, rats, mice, fish, birds, etc. In certain embodiments, the subject is a primate. In other embodiments, the subject is a human.
The term "patient" as used herein refers to humans (including adults and children) or other animals. In some embodiments, "patient" refers to a human.
The term "comprising" is open-ended, i.e. includes the elements indicated in the present invention, but does not exclude other elements.
"stereoisomers" refers to compounds having the same chemical structure but differing in the arrangement of atoms or groups in space. Stereoisomers include enantiomers, diastereomers, conformers (rotamers), geometric isomers (cis/trans), atropisomers, and the like.
"chiral" is a molecule having the property of not overlapping its mirror image; and "achiral" refers to a molecule that can overlap with its mirror image.
"enantiomer" refers to two isomers of a compound that are not overlapping but are in mirror image relationship to each other.
"diastereomer" refers to a stereoisomer having two or more chiral centers and whose molecules are not mirror images of each other. Diastereomers have different physical properties, such as melting points, boiling points, spectral properties, and reactivities. Mixtures of diastereomers may be separated by high resolution analytical procedures such as electrophoresis and chromatography, e.g., HPLC.
The stereochemical definitions and rules used in the present invention generally follow the general definitions of S.P. Parker, Ed., McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Chemical Terms (1984) McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York; and Eliel, E.and Wilen, S., "Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds", John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1994.
Many organic compounds exist in an optically active form, i.e., they have the ability to rotate the plane of plane polarized light. In describing optically active compounds, the prefixes D and L or R and S are used to denote the absolute configuration of a molecule with respect to one or more of its chiral centers. The prefixes d and l or (+) and (-) are the symbols used to specify the rotation of plane polarized light by the compound, where (-) or l indicates that the compound is left-handed. Compounds prefixed with (+) or d are dextrorotatory. A particular stereoisomer is an enantiomer and a mixture of such isomers is referred to as an enantiomeric mixture. A50: 50 mixture of enantiomers is referred to as a racemic mixture or racemate, which may occur when there is no stereoselectivity or stereospecificity in the chemical reaction or process.
Any asymmetric atom (e.g., carbon, etc.) of a compound disclosed herein can exist in racemic or enantiomerically enriched forms, such as the (R) -, (S) -or (R, S) -configuration. In certain embodiments, each asymmetric atom has at least 50% enantiomeric excess, at least 60% enantiomeric excess, at least 70% enantiomeric excess, at least 80% enantiomeric excess, at least 90% enantiomeric excess, at least 95% enantiomeric excess, or at least 99% enantiomeric excess in the (R) -or (S) -configuration.
Depending on the choice of starting materials and methods, the compounds of the invention may exist as one of the possible isomers or as mixtures thereof, for example as racemates and diastereomeric mixtures (depending on the number of asymmetric carbon atoms). Optically active (R) -or (S) -isomers can be prepared using chiral synthons or chiral reagents, or resolved using conventional techniques. If the compound contains a double bond, the substituents may be in the E or Z configuration; if the compound contains a disubstituted cycloalkyl group, the substituents of the cycloalkyl group may have cis or trans configuration.
Any resulting mixture of stereoisomers may be separated into pure or substantially pure geometric isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, depending on differences in the physicochemical properties of the components, for example, by chromatography and/or fractional crystallization.
The racemates of any of the resulting end products or intermediates can be resolved into the optical enantiomers by known methods using methods familiar to those skilled in the art, e.g., by separation of the diastereomeric salts obtained. The racemic product can also be isolated by chiral chromatography, e.g., high performance liquid chromatography using a chiral adsorbent (HPLC: column: Chiralpak AD-H (4.6 mm. times.250 mm,5 μm); mobile phase: n-hexane: ethanol 40:60, isocratic elution; flow rate: 1 mL/min). In particular, Enantiomers can be prepared by asymmetric synthesis, for example, see Jacques, et al, Enantiomers, racemes and solutions (Wiley Interscience, New York, 1981); principles of Asymmetric Synthesis (2) nd Ed.Robert E.Gawley,Jeffrey Aubé,Elsevier,Oxford,UK,2012);Eliel,E.L.Stereochemistry of Carbon Compounds(McGraw-Hill,NY,1962);Wilen,S.H.Tables of Resolving Agents and Optical Resolutions p.268(E.L.Eliel,Ed.,Univ.of Notre Dame Press,Notre Dame,IN 1972);Chiral Separation Techniques:A Practical Approach(Subramanian,G.Ed.,Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH&Co.KGaA,Weinheim,Germany,2007)。
The compounds of the invention may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents, as described herein, in compounds of the general formula above, or as specifically exemplified, sub-classes, and classes of compounds encompassed by the invention.
In general, the term "substituted" means that one or more hydrogen atoms in a given structure are replaced with a particular substituent. Unless otherwise indicated, a substituted group may have one substituent substituted at each substitutable position of the group. When more than one position in a given formula can be substituted with one or more substituents selected from a particular group, the substituents may be substituted at each position, identically or differently.
The term "unsubstituted" means that the specified group bears no substituent.
The term "optionally substituted with … …" is used interchangeably with the term "unsubstituted or substituted with … …", i.e., the structure is unsubstituted or substituted with one or more substituents described herein. Substituents described herein include, but are not limited to, D, oxo (═ O), F, Cl, Br, I, N3、CN、NO2、OH、SH、NH2、S(O)2Carboxyl, aldehyde, alkyl, haloalkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, alkoxy, haloalkoxy, alkylamino, hydroxyalkyl, alkylenealkoxy, carbocyclyl, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, spiroheterocyclyl, fused heterocyclyl, fused cyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, and the like.
In addition, unless otherwise explicitly indicated, the descriptions of the terms "… independently" and "… independently" and "… independently" used in the present invention are interchangeable and should be understood in a broad sense to mean that the specific items expressed between the same symbols do not affect each other in different groups or that the specific items expressed between the same symbols in the same groups do not affect each other.
In the various parts of this specification, substituents of the disclosed compounds are disclosed in terms of group type or range. It is specifically intended that the invention includes each and every independent subcombination of the various members of these groups and ranges. For example, the term "C1-6Alkyl "means in particular independently disclosed methyl, ethyl, C3Alkyl radical, C4Alkyl radical, C5Alkyl and C6An alkyl group.
In each of the parts of the invention, linking substituents are described. Where the structure clearly requires a linking group, the markush variables listed for that group are understood to be linking groups. For example, if the structure requires a linking group and the markush group definition for the variable recites "alkyl" or "aryl," it is understood that the "alkyl" or "aryl" represents an attached alkylene group or arylene group, respectively.
The term "alkyl" or "alkyl group" as used herein, denotes a saturated straight or branched chain monovalent hydrocarbon radical, wherein the alkyl group may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents as described herein. Unless otherwise specified, alkyl groups contain 1-20 carbon atoms. In one embodiment, the alkyl group contains 1 to 12 carbon atoms; in another embodiment, the alkyl group contains 3 to 12 carbon atoms; in another embodiment, the alkyl group contains 1 to 6 carbon atoms; in yet another embodiment, the alkyl group contains 1 to 4 carbon atoms; in yet another embodiment, the alkyl group contains 1 to 3 carbon atoms.
Examples of alkyl groups include, but are not limited to, methyl (Me, -CH)3) Ethyl group (Et, -CH)2CH3) N-propyl (n-Pr, -CH)2CH2CH3) Isopropyl group (i-Pr, -CH (CH)3)2) N-butyl (n-Bu, -CH)2CH2CH2CH3) Isobutyl (i-Bu, -CH)2CH(CH3)2) Sec-butyl (s-Bu, -CH (CH)3)CH2CH3) Tert-butyl (t-Bu, -C (CH)3)3) N-pentyl (-CH)2CH2CH2CH2CH3) 2-pentyl (-CH (CH)3)CH2CH2CH3) 3-pentyl (-CH (CH)2CH3)2) 2-methyl-2-butyl (-C (CH)3)2CH2CH3) 3-methyl-2-butyl (-CH (CH)3)CH(CH3)2) 3-methyl-1-butyl (-CH)2CH2CH(CH3)2) 2-methyl-1-butyl (-CH)2CH(CH3)CH2CH3) N-hexyl (-CH)2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3) 2-hexyl (-CH (CH) 3)CH2CH2CH2CH3) 3-hexyl (-CH (CH)2CH3)(CH2CH2CH3) 2-methyl-2-pentyl (-C (CH))3)2CH2CH2CH3) 3-methyl-2-pentyl (-CH (CH)3)CH(CH3)CH2CH3) 4-methyl-2-pentyl (-CH (CH)3)CH2CH(CH3)2) 3-methyl-3-pentyl (-C (CH)3)(CH2CH3)2) 2-methyl-3-pentyl (-CH (CH)2CH3)CH(CH3)2) 2, 3-dimethyl-2-butyl (-C (CH)3)2CH(CH3)2) 3, 3-dimethyl-2-butyl (-CH (CH)3)C(CH3)3) N-heptyl, n-octyl, and the like.
The term "alkylene" refers to a saturated divalent hydrocarbon radical resulting from the removal of two hydrogen atoms from a saturated straight or branched chain hydrocarbon radical. Unless otherwise specified, the alkylene group contains from 0 to 12 carbon atoms. In one embodiment, the alkylene group contains 1 to 6 carbon atoms; in another embodiment, the alkylene group contains 1 to 4 carbon atoms; in one embodiment, the alkylene group contains 1 to 3 carbon atoms; in another embodiment, the alkylene group contains 1 to 2 carbon atoms; in yet another embodiment, the alkylene group contains from 0 to 6 carbon atoms; in yet another embodiment, the alkylene group contains from 0 to 4 carbon atoms. When the alkylene group contains 0 carbon atoms, it means that no alkylene group is present. Examples of this include methylene (-CH)2-, ethylene (-CH)2CH2-, isopropylidene (-CH (CH)3)CH2-) and the like. The term "alkoxy" means an alkyl group attached to the rest of the molecule through an oxygen atom, wherein the alkyl group has the meaning as described herein. Unless otherwise specified, the alkoxy group contains 1 to 12 carbon atoms. In one embodiment, the alkoxy group contains 1 to 6 carbon atoms; in another embodiment, the alkoxy group contains 1 to 4 carbon atoms; in yet another embodiment, the alkoxy group contains 1 to 3 carbon atoms. The alkoxy group may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents described herein.
Examples of alkoxy groups include, but are not limited to, methoxy (MeO, -OCH)3) Ethoxy (EtO, -OCH)2CH3) N-propoxy (n-PrO, n-propoxy, -OCH2CH2CH3) I-propoxy (i-PrO, i-propoxy, -OCH (CH)3)2) N-butoxy (n-BuO, n-butoxy, -OCH)2CH2CH2CH3) 2-methyl-l-propoxy (i-BuO, i-butoxy, -OCH)2CH(CH3)2) 2-butoxy (s-BuO, s-butoxy, -OCH (CH)3)CH2CH3) T-butoxy (t-BuO, t-butoxy, -OC (CH)3)3) 1-pentyloxy (n-pentyloxy, -OCH)2CH2CH2CH2CH3) 2-pentyloxy (-OCH (CH)3)CH2CH2CH3) 3-pentyloxy (-OCH (CH))2CH3)2) 2-methyl-2-butoxy (-OC (CH))3)2CH2CH3) 3-methyl-2-butoxy (-OCH (CH)3)CH(CH3)2) 3-methyl-l-butoxy (-OCH)2CH2CH(CH3)2) 2-methyl-l-butoxy (-OCH)2CH(CH3)CH2CH3) And so on.
The term "alkylamino" includes "N-alkylamino" and "N, N-dialkylamino" in which the amino groups are each independently substituted with one or two alkyl groups; the alkyl group has the meaning described in the present invention. In some of these embodiments, the alkylamino group is one or two C1-6The alkyl group is attached to a lower alkylamino group formed on the nitrogen atom. In other embodiments, the alkylamino group is one or two C1-3To the nitrogen atom to form an alkylamino group. Suitable alkylamino groups can be monoalkylamino or dialkylamino, and such examples include, but are not limited to, N-methylamino, N-ethylamino, N-dimethylamino, N-diethylamino, and the like.
The terms "haloalkyl", "haloalkoxy" or "haloalkylamino" denote alkyl, alkoxy or alkylamino groups substituted with one or more halogen atoms, wherein alkyl, alkoxy or alkylamino groups have the meaning as described herein, examples of which include, but are not limited to, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, 2,2, 2-trifluoroethyl, 2,2,3, 3-tetrafluoropropyl, monofluoromethoxy, difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy, 1, 2-difluoroethoxy, trifluoromethylamino and the like.
The term "hydroxyalkyl" means an alkyl group substituted with one or more hydroxyl groups, wherein the alkyl group has the meaning as described herein, examples of which include, but are not limited to, hydroxymethyl, 1-hydroxyethyl, 2-hydroxyethyl, and the like. Such as "C1-4Hydroxyalkyl "means an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms substituted with a hydroxyl group.
The term "alkoxyalkylene" is used interchangeably with "alkylenealkoxy" and means that the alkoxy group is attached to the rest of the molecule through an alkylene group, where alkoxy and alkylene groups have the meaning as described herein. Examples include, but are not limited to, methoxymethylene, ethoxymethylene, isopropoxymethylene, and the like.
The term "cycloalkyl" denotes a monovalent or polyvalent saturated monocyclic hydrocarbon radical containing 3 to 12 carbon atoms. In one embodiment, cycloalkyl groups contain 7 to 12 carbon atoms; in yet another embodiment, the cycloalkyl group contains 3 to 8 carbon atoms; in yet another embodiment, the cycloalkyl group contains 3 to 6 carbon atoms; in still other embodiments, the cycloalkyl group contains 5 to 12 carbon atoms. The cycloalkyl groups may be independently unsubstituted or substituted with one or more substituents described herein.
The term "carbocycle" or "carbocyclyl" refers to a monovalent or multivalent, non-aromatic, saturated or partially unsaturated monocyclic hydrocarbon group containing 3 to 12 carbon atoms. Suitable carbocyclyl groups include, but are not limited to, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, and cycloalkynyl. In one embodiment, carbocyclyl contains 3 to 10 carbon atoms; in one embodiment, carbocyclyl contains 3 to 8 carbon atoms; in yet another embodiment, carbocyclyl contains 3 to 6 carbon atoms. Examples of carbocyclyl groups further include cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, 1-cyclopentyl-1-alkenyl, 1-cyclopentyl-2-alkenyl, 1-cyclopentyl-3-alkenyl, cyclohexyl, 1-cyclohexyl-1-alkenyl, 1-cyclohexyl-2-alkenyl, 1-cyclohexyl-3-alkenyl, cyclohexadienyl, cycloheptyl, cyclooctyl, cyclononyl, cyclodecyl, cycloundecyl, cyclododecyl, and the like. The carbocyclyl groups may independently be unsubstituted or substituted with one or more substituents described herein.
The terms "heterocyclyl" and "heterocycle" are used interchangeably herein and refer to a saturated or partially unsaturated, non-aromatic, monovalent or polyvalent, monocyclic ring containing 3 to 12 ring atoms, wherein at least one ring atom is selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen atoms. Wherein, in some embodiments, the 3-12 ring atoms of the heterocyclyl group contain 2-9 carbon atoms; in still other embodiments, the 3-12 ring atoms of the heterocyclyl group contain 2-8 carbon atoms; in still other embodiments, the 3-12 ring atoms of the heterocyclyl group contain 2-6 carbon atoms; in still other embodiments, the 3-12 ring atoms of the heterocyclyl group contain 2-5 carbon atoms. In some embodiments, heterocyclyl groups comprise a ring system of 3-8 ring atoms; in still other embodiments, heterocyclyl groups contain a ring system of 5-12 ring atoms. Unless otherwise indicated, a heterocyclyl group may be attached to other groups in the molecule through a carbon atom, may be attached to other groups in the molecule through a nitrogen atom, and-CH2-the group may optionally be replaced by-C (═ O) -. The sulfur atom of the ring may optionally be oxidized to the S-oxide. The nitrogen atom of the ring may optionally be oxidized to an N-oxygen compound. Examples of heterocyclyl groups include, but are not limited to: oxiranyl, azetidinyl, oxetanyl, thietanyl, pyrrolidinyl, 2-pyrrolidinyl, 3-pyrrolidinyl, pyrazolidinyl, imidazolidinyl, tetrahydrofuryl, dihydrofuranyl, tetrahydrothienyl, dihydrothienyl, 1, 3-dioxolanyl, dithiocyclopentyl, tetrahydropyranyl, dihydropyranyl, 2H-pyranyl, 4H-pyranyl, tetrahydrothiopyranyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, piperazinyl, dioxanyl, dithianyl, thiaxanyl, homopiperazinyl, homopiperidinyl, diazepanyl, oxepanyl, thietanyl, oxazepanyl, and the like Radical diazaRadical, sulfur nitrogen heteroAnd (4) a base. In heterocyclic radicals of-CH2Examples of-groups substituted by-C (═ O) -include, but are not limited to, 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, oxo-1, 3-thiazolidinyl, 2-piperidinonyl, 3, 5-dioxopiperidinyl and pyrimidinedione. Examples of the sulfur atom in the heterocyclic group being oxidized include, but are not limited to, sulfolane group, 1-dioxothiomorpholinyl group. The heterocyclyl group may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents as described herein.
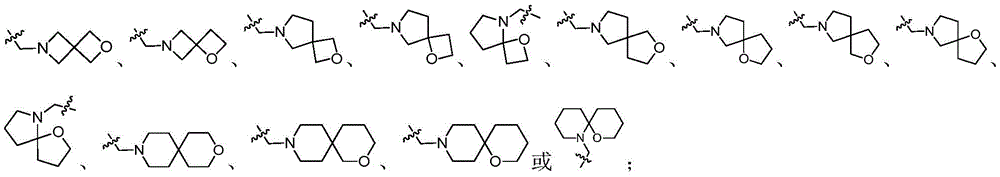
The term "spirocyclyl" refers to a saturated or partially unsaturated, non-aromatic, monovalent or polyvalent, bicyclic or tricyclic ring containing 5 to 12 ring atoms, wherein the ring shares a carbon atom with the ring. Unless otherwise indicated, the spiro group may be attached to other groups in the molecule through a carbon atom, and-CH2-the group may optionally be replaced by-C (═ O) -. Examples of spiro rings include, but are not limited to:
the terms "spiroheterocyclyl" and "spiroheterocycle" are used interchangeably herein and refer to a saturated or partially unsaturated, non-aromatic, monovalent or polyvalent, bicyclic or tricyclic ring containing 5 to 12 ring atoms, wherein at least one ring atom is selected from nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen atoms, and the ring shares a carbon atom with the ring. Wherein, in some embodiments, the 5-12 ring atoms of the spiroheterocyclyl group contain 4-9 carbon atoms; in yet other embodiments, the 5-12 ring atoms of the spiroheterocyclyl group contain 4-8 carbon atoms; in still other embodiments, the 5-12 ring atoms of the spiroheterocyclyl group contain 4-6 carbon atoms. Unless otherwise indicated, spiroheterocyclic groups may be attached to other groups in the molecule through a carbon atom, or may be attached to the molecule through a nitrogen atom Other groups in the molecule being linked, and-CH2-the group may optionally be replaced by-C (═ O) -. The sulfur atom of the ring may optionally be oxidized to the S-oxide. The nitrogen atom of the ring may optionally be oxidized to an N-oxygen compound. Examples of spiroheterocycles include, but are not limited to:
the term "fused cyclic group" refers to a saturated or partially unsaturated, non-aromatic, mono-or polyvalent, bicyclic or tricyclic ring containing from 4 to 12 ring atoms, and the ring shares a ring edge with the ring. Unless otherwise indicated, fused ring groups may be attached to other groups in the molecule through a carbon atom, and-CH2-the group may optionally be replaced by-C (═ O) -. Examples of fused rings include, but are not limited to:
the terms "fused heterocyclyl" and "fused heterocycle" are used interchangeably herein and refer to a saturated or partially unsaturated, non-aromatic, monovalent or polyvalent, bicyclic or tricyclic ring containing from 4 to 12 ring atoms, wherein at least one ring atom is selected from nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen atoms, and the ring shares a ring edge with the ring. Wherein, in some embodiments, the fused heterocyclic group contains 3 to 9 carbon atoms in 4 to 12 ring atoms; in still other embodiments, the fused heterocyclic group contains 3 to 8 carbon atoms in 4 to 12 ring atoms; in still other embodiments, the fused heterocyclic group contains 3-6 carbon atoms in 4-12 ring atoms. Unless otherwise indicated, fused heterocyclic groups may be attached to other groups in the molecule through a carbon atom, may also be attached to other groups in the molecule through a nitrogen atom, and-CH 2-the group may optionally be replaced by-C (═ O) -. The sulfur atom of the ring may optionally be oxidized to the S-oxide. The nitrogen atom of the ring may optionally be oxidized to an N-oxygen compound. Examples of fused heterocycles include, but are not limited to:
the term "unsaturated" as used herein means that the group contains one or more unsaturations.
The term "heteroatom" refers to O, S, N, P and Si, including N, S and any oxidation state form of P; primary, secondary, tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium salt forms; or a form in which a hydrogen on a nitrogen atom in the heterocycle is substituted, for example, N (like N in 3, 4-dihydro-2H-pyrrolyl), NH (like NH in pyrrolidinyl) or NR (like NR in N-substituted pyrrolidinyl).
The term "halogen" or "halogen atom" means a fluorine atom (F), chlorine atom (Cl), bromine atom (Br) or iodine atom (I).
The term "cyano" or "CN" denotes a cyano structure, which group may be attached to another group.
The term "nitro" or "NO2"denotes a nitro structure, which may be linked to other groups.
The term "amino" or "NH2"denotes an amino structure, which may be linked to other groups.
The term "aryl" denotes a monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic all carbocyclic ring system containing 6 to 14 ring atoms, or 6 to 12 ring atoms, or 6 to 10 ring atoms, wherein at least one ring is aromatic and has one or more attachment points to the rest of the molecule. The term "aryl" may be used interchangeably with the term "aromatic ring". In one embodiment, aryl is a carbocyclic ring system consisting of 6 to 10 ring atoms and containing at least one aromatic ring therein. Examples of the aryl group may include phenyl, naphthyl and anthracenyl. The aryl group may independently be optionally substituted with one or more substituents described herein.
The term "heteroaryl" denotes a monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic ring containing 5 to 12 ring atoms, wherein at least one ring is aromatic and at least one ring contains one or more heteroatoms and has one or more attachment points to the rest of the molecule. The term "heteroaryl" may be used interchangeably with the terms "heteroaromatic ring" or "heteroaromatic compound". Wherein, in some embodiments, the 5-12 ring atoms of the heteroaryl group contain 1-9 carbon atoms; in still other embodiments, the heteroaryl group contains 1 to 7 carbon atoms in 5 to 12 ring atoms; in still other embodiments, the heteroaryl group contains 1 to 5 carbon atoms in 5 to 12 ring atoms; the heteroaryl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents described herein. In one embodiment, heteroaryl is a heteroaryl consisting of 5 to 12 ring atoms containing 1,2,3, or 4 heteroatoms independently selected from O, S and N; in another embodiment, heteroaryl is a heteroaryl consisting of 5 to 6 ring atoms containing 1,2,3, or 4 heteroatoms independently selected from O, S and N.
Examples of heteroaryl groups include, but are not limited to, 2-furyl, 3-furyl, N-imidazolyl, 2-imidazolyl, 4-imidazolyl, 5-imidazolyl, 3-isoxazolyl, 4-isoxazolyl, 5-isoxazolyl, 2-oxazolyl, 4-oxazolyl, 5-oxazolyl, oxadiazolyl (e.g., 1,2, 3-oxadiazolyl, 1,2, 5-oxadiazolyl, 1,2, 4-oxadiazolyl), oxadiazolyl (e.g., 1,2,3, 4-oxadiazolyl), 2-thiazolyl, 4-thiazolyl, 5-thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, 2-thiadiazolyl (e.g., 1,3, 4-thiadiazolyl, 1,2, 3-thiadiazolyl, 1,2, 5-thiadiazolyl) Thiatriazolyl (e.g., 1,2,3, 4-thiatriazolyl), tetrazolyl (e.g., 2H-1,2,3, 4-tetrazolyl, 1H-1,2,3, 4-tetrazolyl), triazolyl (e.g., 2H-1,2, 3-triazolyl, 1H-1,2, 4-triazolyl, 4H-1,2, 4-triazolyl), 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 1H-pyrazolyl (e.g., 1H-pyrazol-3-yl, 1H-pyrazol-4-yl, 1H-pyrazol-5-yl), 1,2, 3-thiadiazolyl, 1,3, 4-thiadiazolyl, 1,2, 5-thiadiazolyl, N-pyrrolyl, 2-pyrrolyl, 3-pyrrolyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl, 2-pyrimidinyl, 4-pyrimidinyl, 5-pyrimidinyl, pyridazinyl (e.g., 3-pyridazinyl, 4-pyridazinyl), 2-pyrazinyl, triazinyl (e.g., 1,3, 5-triazine), tetrazinyl (e.g., 1,2,4, 5-tetrazine, 1,2,3, 5-tetrazine); the following bicyclic rings are also included, but are in no way limited to these: benzimidazolyl, benzofuranyl, benzothienyl, indolyl (e.g., 2-indolyl), purinyl, quinolyl (e.g., 2-quinolyl, 3-quinolyl, 4-quinolyl), isoquinolyl (e.g., 1-isoquinolyl, 3-isoquinolyl, or 4-isoquinolyl), imidazo [1,2-a ] pyridyl, pyrazolo [1,5-a ] pyrimidinyl, imidazo [1,2-b ] pyridazinyl, [1,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b ] pyridazinyl, [1,2,4] triazolo [1,5-a ] pyrimidinyl, [1,2,4] triazolo [1,5-a ] pyridyl, and the like.
The term "carboxy", whether used alone or in combination with other terms, such as "carboxy", denotes-CO2H; the term "carbonyl", whether used alone or in combination with other terms, such as "aminocarbonyl" or "acyloxy", denotes- (C ═ O) -.
As described herein, a ring system formed on a ring wherein a substituent is bonded to the center (as shown in formula b) represents that the substituent may be substituted at any substitutable position on the ring. For example, formula b represents a substituent R which may be mono-or polysubstituted at any possible position on the ring, including, but not limited to, those shown in formulas b1 through b 9.
As described herein, the attachment of a linker to the ring system (as shown in formula c) means that the ring may be attached to the rest of the molecule at any attachable position on the ring system via said linker. Formula c represents that the ring may be attached to the rest of the molecule via any possible attachment position on the ring, including, but not limited to, as shown in formulas c 1-c 6.
As described herein, the attachment of a linker to the ring system (as shown in formula d) means that the ring may be attached to the rest of the molecule at any attachable position on the ring system via said linker. Formula d represents that the ring may be attached to the rest of the molecule via any possible attachment position on the ring, including, but not limited to, as shown in formulas d 1-d 8.
The term "protecting group" or "PG" refers to a substituent that, when reacted with other functional groups, is generally used to block or protect a particular functionality. For example, "amino protecting group" means a substituent attached to an amino group to block or protect the functionality of the amino group in a compound, and suitable amino protecting groups include acetyl, trifluoroacetyl, t-butoxycarbonyl (BOC ), benzyloxycarbonyl (CBZ ) and 9-fluorenylmethyleneoxycarbonyl (Fmoc). Similarly, "hydroxyl protecting group" refers to the functionality of a substituent of a hydroxyl group to block or protect the hydroxyl group, and suitable protecting groups include acetyl and silyl groups. "carboxy protecting group" refers to the functionality of a substituent of a carboxy group to block or protect the carboxy group, and typical carboxy protecting groups include-CH2CH2SO2Ph, cyanoethyl, 2- (trimethylsilyl) ethyl, 2- (trimethylsilyl) ethoxymethyl, 2- (p-toluenesulfonyl) ethyl, 2- (p-nitrobenzenesulfonyl) ethyl, 2- (diphenylphosphino) ethyl, nitroethyl, and the like. General descriptions of protecting groups can be found in the literature: greene, Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, John Wiley&Sons,New York,1991;and P.J.Kocienski,Protecting Groups,Thieme,Stuttgart,2005.
The term "prodrug", as used herein, represents a compound that is converted in vivo to a compound of formula (I). Such conversion is effected by hydrolysis of the prodrug in the blood or by enzymatic conversion to the parent structure in the blood or tissue. The prodrug compound of the invention can be ester, and in the prior invention, the ester can be used as the prodrug and comprises phenyl ester and aliphatic (C) 1-C24) Esters, acyloxymethyl esters, carbonates, carbamates and amino acid esters. For example, a compound of the present invention contains a hydroxy group, i.e., it can be acylated to provide the compound in prodrug form. Other prodrug forms include phosphate esters, such as those obtained by phosphorylation of a hydroxyl group on the parent. Complete discussion of prodrugsReference may be made to the following documents: T.Higuchi and V.Stella, Pro-drugs as Novel Delivery Systems, Vol.14 of the A.C.S.Symphosis Series, Edward B.Roche, ed., Bioreversible Carriers in Drug designs, American Pharmaceutical Association and Pergamon Press,1987, J.Rautio et al, Prodrugs in Design and Clinical Applications, Nature Review Drug Discovery,2008,7, 255-.
"metabolite" refers to the product of a particular compound or salt thereof obtained by metabolism in vivo. Metabolites of a compound can be identified by techniques well known in the art, and its activity can be characterized by assay methods as described herein. Such products may be obtained by administering the compound by oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, amidation, deamidation, esterification, defatting, enzymatic cleavage, and the like. Accordingly, the present invention includes metabolites of compounds, including metabolites produced by contacting a compound of the present invention with a mammal for a sufficient period of time.
As used herein, "pharmaceutically acceptable salts" refer to organic and inorganic salts of the compounds of the present invention. Pharmaceutically acceptable salts are well known in the art, as are: berge et al, description of the scientific acceptable salts in detail in J. pharmaceutical Sciences,1977,66:1-19. Pharmaceutically acceptable non-toxic acid salts include, but are not limited to, salts of inorganic acids formed by reaction with amino groups such as hydrochlorides, hydrobromides, phosphates, sulfates, perchlorates, and salts of organic acids such as acetates, oxalates, maleates, tartrates, citrates, succinates, malonates, or those obtained by other methods described in the literature above, such as ion exchange. Other pharmaceutically acceptable salts include adipates, alginates, ascorbates, aspartates, benzenesulfonates, benzoates, bisulfates, borates, butyrates, camphorates, camphorsulfonates, cyclopentylpropionates, digluconatesDodecyl sulfate, ethanesulfonate, formate, fumarate, glucoheptonate, glycerophosphate, gluconate, hemisulfate, heptanoate, hexanoate, hydroiodide, 2-hydroxy-ethanesulfonate, lactobionate, lactate, laurate, lauryl sulfate, malate, methanesulfonate, 2-naphthalenesulfonate, nicotinate, nitrate, oleate, palmitate, pamoate, pectinate, persulfate, 3-phenylpropionate, picrate, pivalate, propionate, stearate, thiocyanate, p-toluenesulfonate, undecanoate, valerate, and the like. Salts obtained with appropriate bases include alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, ammonium and N +(C1-4Alkyl radical)4A salt. The present invention also contemplates quaternary ammonium salts formed from compounds containing groups of N. Water-soluble or oil-soluble or dispersion products can be obtained by quaternization. Alkali or alkaline earth metal salts include sodium, lithium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and the like. Pharmaceutically acceptable salts further include suitable, non-toxic ammonium, quaternary ammonium salts and amine cations resistant to formation of counterions, such as halides, hydroxides, carboxylates, sulfates, phosphates, nitrates, C1-8Sulfonates and aromatic sulfonates.
"solvate" of the present invention refers to an association of one or more solvent molecules with a compound of the present invention. Solvents that form solvates include, but are not limited to, water, isopropanol, ethanol, methanol, dimethyl sulfoxide, ethyl acetate, acetic acid, and aminoethanol. The term "hydrate" refers to an association of solvent molecules that is water.
When the solvent is water, the term "hydrate" may be used. In some embodiments, a molecule of a compound of the present invention may be associated with a molecule of water, such as a monohydrate; in other embodiments, one molecule of the compound of the present invention may be associated with more than one molecule of water, such as a dihydrate, and in still other embodiments, one molecule of the compound of the present invention may be associated with less than one molecule of water, such as a hemihydrate. It should be noted that the hydrates of the present invention retain the biological effectiveness of the compound in its non-hydrated form.
The term "treating" any disease or condition, as used herein, means all that can slow, halt, arrest, control or halt the progression of the disease or condition, but does not necessarily mean that all the symptoms of the disease or condition have disappeared, and also includes prophylactic treatment of the symptoms, particularly in patients susceptible to such disease or disorder. In some of these embodiments, refers to ameliorating the disease or disorder (i.e., slowing or arresting or reducing the development of the disease or at least one clinical symptom thereof). In other embodiments, "treating" or "treatment" refers to moderating or improving at least one physical parameter, including physical parameters that may not be perceived by the patient. In other embodiments, "treating" or "treatment" refers to modulating the disease or disorder, either physically (e.g., stabilizing a perceptible symptom) or physiologically (e.g., stabilizing a parameter of the body), or both. In other embodiments, "treating" or "treatment" refers to preventing or delaying the onset, occurrence, or worsening of a disease or disorder.
The term "therapeutically effective amount" or "therapeutically effective dose" as used herein refers to an amount of a compound of the invention that is capable of eliciting a biological or medical response (e.g., reducing or inhibiting enzyme or protein activity, or ameliorating symptoms, alleviating a disorder, slowing or delaying the progression of a disease, or preventing a disease, etc.) in a subject. In one non-limiting embodiment, the term "therapeutically effective amount" refers to an amount that, when administered to a subject, is effective for: (1) at least partially alleviating, inhibiting, preventing and/or ameliorating a disorder or disease (i) mediated by roryt, or (ii) associated with roryt activity, or (iii) characterized by abnormal activity of roryt; or (2) reduces or inhibits the activity of ROR γ t; or (3) reduces or inhibits expression of ROR γ t. In another embodiment, the term "therapeutically effective amount" refers to an amount that, when administered to a cell, or organ, or non-cellular biological substance, or vehicle, at least partially reduces or inhibits ROR γ t activity; or an amount of a compound of the invention effective to at least partially reduce or inhibit ROR γ t expression.
The terms "administration" and "administering" of a compound as used herein shall be understood as providing a compound of the invention or a prodrug of a compound of the invention to a subject in need thereof. It will be appreciated that one skilled in the art can treat a patient currently suffering from such a disorder or prophylactically treat a patient suffering from such a disorder by using an effective amount of a compound of the present invention.
The term "composition" as used herein refers to a product comprising the specified ingredients in the specified amounts, as well as any product which results, directly or indirectly, from combination of the specified ingredients in the specified amounts. The meaning of such terms in relation to pharmaceutical compositions includes products comprising the active ingredient(s) and the inert ingredient(s) that make up the carrier, as well as any product which results, directly or indirectly, from mixing, complexation or aggregation of any two or more of the ingredients, or from decomposition of one or more of the ingredients, or from other types of reactions or interactions of one or more of the ingredients. Accordingly, the pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention include any composition prepared by admixing a compound of the present invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Description of the Compounds of the invention
The invention discloses sulfonyl substituted (hetero) aromatic ring derivatives, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, pharmaceutical preparations and compositions thereof, which can be used as ROR gamma t inhibitors and have potential application in treating inflammatory or autoimmune diseases mediated by ROR gamma t, such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ophthalmopathy, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, Crohn's disease or Kawasaki disease.
In one aspect, the invention relates to a compound of formula (I) or a stereoisomer, a nitrogen oxide, a solvate, a metabolite, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of a compound of formula (I) or a prodrug thereof,
wherein, ring A, ring B, and ring L1、L2、R、Z1、Z2、Z3、Z4、Z5、Z6、Z7And Z8Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, R is C1-4Alkyl radical, C1-4Alkoxy radical, C3-6Cycloalkyl radical, C1-4Haloalkyl or C1-4A haloalkoxy group.
In other embodiments, R is methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, or isopropoxy.
In some embodiments, Z1Is CR1Or N, wherein R1Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, Z2Is CR1Or N, wherein R1Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, Z3Is CR1Or N, wherein R1Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, Z4Is CR1Or N, wherein R1Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, Z5Is CR1Or N, wherein R1Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, Z6Is CR1Or N, wherein R1Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, Z7Is CR1Or N, wherein R1Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, Z8Is CR1Or N, wherein R1Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each R is1Independently of one another is hydrogen, C1-6Alkyl, cyano, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Hydroxyalkyl, -C1-6alkylene-C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl or 3-8 membered heterocyclyl.
In other embodiments, each R is1Independently hydrogen, cyano, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, methoxymethylene, ethoxymethylene, n-propoxymethylene, isopropoxymethylene, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl.
In some embodiments, ring B is C6-10Aryl, 5-12 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl, 4-12 membered fused cyclic, 5-12 membered spirocyclic or C3-8Cycloalkyl, wherein said B ring is optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3 or 4ReSubstitution; reHave the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, ring B is C6-10Aryl, 5-8 membered heteroaryl, 5-8 membered heterocyclyl, 4-8 membered fused heterocyclyl, 5-8 membered spiroheterocyclyl, 4-8 membered fused cyclic, 5-8 membered spirocyclic or C3-6Cycloalkyl, wherein said B ring is optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3 or 4ReSubstitution; reHave the meaning as described in the present invention.
In other embodiments, ring B is phenyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, azetidinyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, thiazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, azetidinyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, thiazolyl, Wherein the B ring is optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3 or 4ReSubstitution; reHave the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each R iseIndependently hydrogen, deuterium, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, nitro, hydroxyl, amino, C 1-4Alkyl radical, C1-4Alkoxy radical, C3-6Cycloalkyl radical, C1-4Haloalkyl or C1-4A haloalkoxy group.
In other embodiments, each R iseIndependently hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, cyano, nitro, hydroxy, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, monofluoromethoxy, difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy, or 1, 2-difluoroethoxy; or, any two adjacent ReAnd together with the atom to which they are attached form C3-8A carbocyclic ring or a 3-8 membered heterocyclic ring; or, optionally, two R's attached to the same carbon atomeAnd together with the atom to which they are attached form C3-8Carbocyclic or 3-8 membered heterocyclic.
In some embodiments, L is1is-S (O)2-NH-、-NH-S(O)2-, -s (O) -NH-, -NH-s (O) -, -C (═ O) NH-, or-NHC (═ O) -.
In some embodiments, L is2Is a bond or CR3R4(ii) a Wherein R is3And R4Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each R is3And R4Independently is hydrogen or C1-6A hydroxyalkyl group.
In other embodiments, each R is3And R4Independently hydrogen, hydroxymethyl, hydroxyethyl or hydroxy-n-propyl.
In some embodiments, ring A is a 3-12 membered heterocyclic ring, further said 3-12 membered heterocyclic ring optionally substituted with 1,2, 3, 4 or 5R 2Substitution; wherein R is2Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, ring A is a 5-12 membered heterocyclic ring, further said 5-12 membered heterocyclic ring optionally being optionally substituted1. 2, 3, 4 or 5R2Substitution; wherein R is2Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In other embodiments, ring A is Further said A ring may optionally be substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2Substitution; wherein R is2、Y1And Y2Having the definitions set out in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each Y is1And Y2independently-O-, -S-, -N-, -NH-or-CH2-。
In some embodiments, ring a is Further said A ring may optionally be substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2Substitution; wherein R is2、Y1And Y2Having the definitions set out in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each Y is1And Y2independently-O-, -S-, -N-, -NH-or-CH2-。
In other embodiments, ring A is Further said A ring may optionally be substituted by 1, 2,3. 4 or 5R2Substitution; wherein R is2Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In still other embodiments, ring A is Further said A ring may optionally be substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2Substitution; wherein R is2Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each R is 2Independently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydroxy, oxo (═ O), amino, nitro, cyano, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, -C0-6alkylene-ORa、-C0-4Alkylene- (C ═ O)m-Rb、-C0-4Alkylene- (O)n-(C=O)p-NRcRd5-10 membered heteroaryl, -C0-4Alkylene- (3-12 membered heterocyclyl), -C0-4Alkylene- (5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl) or-C0-4Alkylene- (4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl); the R is2Optionally substituted by 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RfSubstitution; wherein, the m, n, p and Ra、Rb、Rc、RdAnd RfHave the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each R is2Independently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydroxyl, oxo, amino, nitro, cyano, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, cyclopropylalkyl, cyclobutylalkyl, cyclohexylalkyl, -C1-4alkylene-ORa、-C0-4Alkylene- (C ═ O)m-Rb、-C0-4Alkylene- (O)n-(C=O)p-NRcRdOxazolyl, thiazolyl, thienyl, imidazolyl, pyridazinyl, pyridyl, Wherein, R is2Unsubstituted or substituted by 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6R fSubstitution; wherein, the m, n, p and Ra、Rb、Rc、RdAnd RfHave the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each R isaIndependently of one another is hydrogen, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 5-10 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl or 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl; each Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 4-12 membered fused ring group, 5-12 membered spiro ring group, 5-10 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiro heterocyclyl or 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl; or Rc、RdAnd the N atom to which they are attached together form a 4-8 membered heterocyclic ring; each of said Ra、Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently optionally substituted with 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RgSubstitution; the R isgHave the meaning as described in the present invention.
In other embodiments, each R isaIndependently hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1,1, 1-trifluoroethyl, oxirane, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranAlkyl, oxacycloheptyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl; r b、RcAnd RdEach independently of the others hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1,1, 1-trifluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, oxiranyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, oxepanyl, Cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl; or Rc、RdTogether with the N atom to which they are attached form a 4-8 membered heterocyclic ring;
wherein each R isa、Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently optionally substituted with 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RgSubstitution; the R isgHave the meaning as described in the present invention.
In some embodiments, each R isfAnd RgIndependently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, oxo (═ O), hydroxy, amino, nitro, cyano, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Hydroxyalkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C6-10Aryl radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 4-12 membered fused ring group, 5-12 membered spiro ring group, 3-12 membered heterocyclic group, 5-12 membered spiro heterocyclic group, 4-12 membered fused heterocyclic group, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylamino or C1-6A haloalkoxy group.
In other embodiments, each R isfAnd RgIndependently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, oxo (═ O), hydroxy, amino, nitro, cyano, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, -CH 2OH, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethylTrifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, phenyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, pyrazolyl, oxiranyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, oxacyclofuranyl, oxa, oxacyclo, Cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclohexyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, monofluoromethoxy, difluoromethoxy or trifluoromethoxy.
In some embodiments, m is independently 0, 1, or 2.
In some embodiments, n is independently 0 or 1.
In some embodiments, p is independently 0, 1, or 2.
In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compounds, or stereoisomers, nitroxides, solvates, metabolites, pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs thereof, of one of the following, but in no way limited to these compounds:
unless otherwise specified, stereoisomers, solvates, metabolites, pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds of formula (I) and prodrugs thereof are included within the scope of the present invention.
In another aspect, the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of formula (I) of the present invention or a stereoisomer, geometric isomer, tautomer, nitrogen oxide, hydrate, solvate, metabolite, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, carrier, adjuvant or combination thereof.
In some embodiments, the pharmaceutical composition further comprises other agents or any combination thereof for preventing or treating inflammatory syndromes or autoimmune diseases.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition may be in a liquid, solid, semi-solid, gel or spray dosage form.
In another aspect, the invention relates to the use of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutical composition thereof in the manufacture of a medicament for the prevention or treatment of an inflammatory or autoimmune disease mediated by roryt in a mammal, including a human.
In some embodiments, the present invention relates to the use of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutical composition thereof in the manufacture of a medicament for the prevention or treatment of psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ocular disease, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, crohn's disease, or kawasaki disease.
In another aspect, the invention relates to methods for the preparation, isolation and purification of compounds of formula (I).
In another aspect, the invention relates to intermediates for the preparation of compounds of formula (I).
The compounds of the present disclosure may contain asymmetric or chiral centers and thus may exist in different stereoisomeric forms. The present invention contemplates that all stereoisomeric forms of the compounds of formula (I), including but not limited to diastereomers, enantiomers, atropisomers and geometric (or conformational) isomers, and mixtures thereof, such as racemic mixtures, are integral to the invention.
In the structures disclosed herein, when the stereochemistry of any particular chiral atom is not specified, then all stereoisomers of that structure are contemplated as within this invention and are included as disclosed compounds in this invention. When stereochemistry is indicated by a solid wedge (solid wedge) or dashed line representing a particular configuration, then the stereoisomers of the structure are so well-defined and defined.
The compounds of formula (I) may exist in different tautomeric forms and all such tautomers are included within the scope of the invention.
The compounds of formula (I) may be present in the form of salts. In one embodiment, the salt refers to a pharmaceutically acceptable salt. The term "pharmaceutically acceptable" means that the substance or composition must be compatible chemically and/or toxicologically with the other ingredients comprising the formulation and/or the mammal being treated therewith. In another embodiment, the salts need not be pharmaceutically acceptable salts and may be intermediates useful in the preparation and/or purification of compounds of formula (I) and/or in the isolation of enantiomers of compounds of formula (I).
Pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts may be formed from the disclosed compounds of the invention by the action of an inorganic or organic acid, for example, acetate, aspartate, benzoate, benzenesulfonate, bromide/hydrobromide, bicarbonate/carbonate, bisulfate/sulfate, camphorsulfonate, chloride/hydrochloride, chlorotheyl salt, citrate, edisylate, fumarate, glucoheptonate, gluconate, glucuronate, hippurate, hydroiodide, isethionate, lactate, lactobionate, lauryl sulfate, malate, maleate, malonate, mandelate, methanesulfonate, methylsulfate, naphthoate, naphthalenesulfonate, nicotinate, nitrate, octadecanoate, oleate, oxalate, palmitate, pamoate, phosphate/biphosphate/dihydrogen phosphate, phosphate, Polysilonolactates, propionates, stearates, succinates, sulfosalicylates, tartrates, tosylates and trifluoroacetates.
Pharmaceutically acceptable base addition salts may be formed from the disclosed compounds by reaction with an inorganic or organic base.
Inorganic bases from which salts can be derived include, for example, ammonium salts and metals of groups I to XII of the periodic table. In certain embodiments, the salts are derived from sodium, potassium, ammonium, calcium, magnesium, iron, silver, zinc, and copper; particularly suitable salts include ammonium, potassium, sodium, calcium and magnesium salts.
Organic bases from which salts can be derived include primary, secondary and tertiary amines, and substituted amines include naturally occurring substituted amines, cyclic amines, basic ion exchange resins, and the like. Some organic amines include, for example, isopropylamine, benzathine (benzathine), choline salts (cholinate), diethanolamine, diethylamine, lysine, meglumine (meglumine), piperazine, and tromethamine.
The pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the present invention can be synthesized from the parent compound, basic or acidic moiety, by conventional chemical methods. In general, such salts can be prepared by reacting the free acid forms of these compounds with a stoichiometric amount of the appropriate base (e.g., Na, Ca, Mg, or K hydroxide, carbonate, bicarbonate, etc.), or by reacting the free base forms of these compounds with a stoichiometric amount of the appropriate acid. Such reactions are usually carried out in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of both. Generally, where appropriate, it is desirable to use a non-aqueous medium such as diethyl ether, ethyl acetate, ethanol, isopropanol or acetonitrile. In, for example, "Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences", 20 th edition, Mack Publishing Company, Easton, Pa., (1985); and "handbook of pharmaceutically acceptable salts: properties, Selection and application (Handbook of Pharmaceutical Salts: Properties, Selection, and Use) ", Stahl and Wermuth (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2002) may find some additional lists of suitable Salts.
In addition, the compounds disclosed herein, including their salts, may also be obtained in the form of their hydrates or in the form of solvents containing them (e.g., ethanol, DMSO, etc.), for their crystallization. The compounds disclosed herein may form solvates with pharmaceutically acceptable solvents (including water), either inherently or by design; thus, the present invention is intended to include both solvated and unsolvated forms of the disclosed compounds.
Any formulae given herein are also intended to represent the non-isotopically enriched forms as well as the isotopically enriched forms of these compounds. Isotopically enriched compounds have the structure depicted by the formulae given herein, except that one or more atoms are replaced by an atom having a selected atomic mass or mass number. Exemplary isotopes that can be incorporated into compounds of the invention include isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, fluorine and chlorine, such as2H、3H、11C、13C、14C、15N、17O、18O、18F、31P、32P、35S、36Cl and125I。
in another aspect, the compounds of the invention include isotopically enriched compounds as defined herein, e.g. wherein a radioisotope, e.g. is present3H、14C and18those compounds of F, or in which a non-radioactive isotope is present, e.g.2H and 13Those of C. The isotopically enriched compounds can be used for metabolic studies (use)14C) Reaction kinetics study (using, for example2H or3H) Detection or imaging techniques such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) including drug or substrate tissue distribution determination, or may be used in radiotherapy of a patient.18F-enriched compounds are particularly desirable for PET or SPECT studies. Isotopically enriched compounds of formula (I) can be prepared by conventional techniques known to those skilled in the art or by the procedures and examples described in the present invention using a suitable isotopically labelled reagent in place of the original used unlabelled reagent.
In addition, heavier isotopes are, in particular, deuterium (i.e.,2substitution of H or D) may provide certain therapeutic advantages resulting from greater metabolic stability. For example, increased in vivo half-life or decreased dosage requirements or improved therapeutic index. It is to be understood that deuterium in the present invention is to be considered as a substituent of the compound of formula (I). The concentration of such heavier isotopes, particularly deuterium, can be defined by isotopic enrichment factors. The term "isotopic enrichment factor" as used herein refers to the ratio between the isotopic and natural abundance of a given isotope. If a substituent of a compound of the invention is designated as deuterium, the compound has an isotopic enrichment factor for each designated deuterium atom of at least 3500 (52.5% deuterium incorporation at each designated deuterium atom), at least 4000 (60% deuterium incorporation), at least 4500 (67.5% deuterium incorporation), at least 5000 (75% deuterium incorporation), at least 5500 (82.5% deuterium incorporation), at least 6000 (90% deuterium incorporation), at least 6333.3 (95% deuterium incorporation), at least 6466.7 (97% deuterium incorporation), at least 6600 (99% deuterium incorporation), or at least 6633.3 (99.5% deuterium incorporation). Pharmaceutically acceptable solvates of the invention include those in which the crystallization solvent may be isotopically substituted, e.g. D 2O, acetone-d6、DMSO-d6Those solvates of (a).
Pharmaceutical compositions, formulations and administration of the compounds of the invention
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound disclosed herein, for example, as set forth in the examples; and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, carrier, adjuvant, or combination thereof.
The present invention provides methods of treating, preventing or ameliorating a disease or condition comprising administering a safe and effective amount of a combination comprising a compound of the present disclosure and one or more therapeutically active agents. Wherein the combination comprises one or more additional agents for the prophylaxis or treatment of an inflammatory syndrome, disorder or disease.
The amount of compound in the pharmaceutical composition disclosed herein is effective to detect inhibition of retinoic acid-related nocosomal receptor gamma t in a biological sample or patient. The dosage of the active ingredient in the composition of the present invention may vary, however, the amount of the active ingredient must be such that a suitable dosage form is obtained. The active ingredient may be administered to patients (animals and humans) in need of such treatment at dosages that provide optimal pharmaceutical efficacy. The selected dosage depends on the desired therapeutic effect, on the route of administration and on the duration of the treatment. The dosage will vary from patient to patient depending on the nature and severity of the disease, the weight of the patient, the particular diet of the patient, the concurrent use of drugs, and other factors that will be recognized by those skilled in the art. The dosage range is generally about 0.5mg to 1.0g per patient per day and may be administered in a single dose or in multiple doses. In one embodiment, the dosage range is from about 0.5mg to 500mg per patient per day; from about 0.5mg to 200mg per patient per day in another embodiment; and in yet another embodiment from about 5mg to 50mg per patient per day.
It will also be appreciated that certain compounds of the invention may be present in free form and used in therapy, or if appropriate in the form of a pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof. Pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives include pharmaceutically acceptable prodrugs, salts, esters, salts of such esters, or any additional adduct or derivative that upon administration to a patient in need thereof provides, directly or indirectly, a compound of the present invention or a metabolite or residue thereof.
The medicaments or pharmaceutical compositions disclosed herein may be prepared and packaged in bulk (bulk) form, wherein a safe and effective amount of the compound of formula (I) may be extracted and then administered to a patient in the form of a powder or syrup. Typically, the administration is to the patient at a dosage level of between 0.0001 and 10mg/kg body weight per day to achieve effective inhibition of retinoic acid-related nociceptor γ t. Alternatively, the pharmaceutical compositions disclosed herein can be prepared and packaged in unit dosage forms, wherein each physically discrete unit contains a safe and effective amount of a compound of formula (I). When prepared in unit dosage form, the disclosed pharmaceutical compositions can generally contain, for example, from 0.5mg to 1g, or from 1mg to 700mg, or from 5mg to 100mg of the disclosed compounds.
When the pharmaceutical composition of the invention contains one or more other active ingredients in addition to the compound of the invention, the compound weight ratio of the compound of the invention to the second active ingredient may vary and depends on the effective dose of each ingredient. Generally, an effective dose of each is used. Thus, for example, when a compound of the present invention is mixed with another pharmaceutical agent, the weight ratio of the compound of the present invention to the other pharmaceutical agent typically ranges from about 1000: 1 to about 1: 1000, e.g., from about 200: 1 to about 1: 200. Mixtures of the compounds of the invention with other active ingredients are generally also within the above-mentioned ranges, but in each case an effective dose of each active ingredient should be used.
As used herein, "pharmaceutically acceptable excipient" means a pharmaceutically acceptable material, mixture or vehicle, which is compatible with the dosage form or pharmaceutical composition to be administered. Each excipient, when mixed, must be compatible with the other ingredients of the pharmaceutical composition to avoid interactions that would substantially reduce the efficacy of the disclosed compounds and which would result in a pharmaceutical composition that is not pharmaceutically acceptable when administered to a patient. Furthermore, each excipient must be pharmaceutically acceptable, e.g., of sufficiently high purity.
Suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients will vary depending on the particular dosage form selected. In addition, pharmaceutically acceptable excipients may be selected for their specific function in the composition. For example, certain pharmaceutically acceptable excipients may be selected to aid in the production of a uniform dosage form. Certain pharmaceutically acceptable excipients may be selected to aid in the production of stable dosage forms. Certain pharmaceutically acceptable excipients may be selected to facilitate carrying or transporting the disclosed compounds from one organ or portion of the body to another organ or portion of the body when administered to a patient. Certain pharmaceutically acceptable excipients may be selected that enhance patient compliance.
Suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients include the following types of excipients: diluents, fillers, binders, disintegrants, lubricants, glidants, granulating agents, coating agents, wetting agents, solvents, co-solvents, suspending agents, emulsifiers, sweeteners, flavoring agents, taste masking agents, colorants, anti-caking agents, humectants, chelating agents, plasticizers, viscosity increasing agents, antioxidants, preservatives, stabilizers, surfactants and buffers. The skilled artisan will recognize that certain pharmaceutically acceptable excipients may provide more than one function, and provide alternative functions, depending on how many such excipients are present in the formulation and which other excipients are present in the formulation.
The skilled person is knowledgeable and skilled in the art to enable them to select suitable amounts of suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients for use in the present invention. Furthermore, there is a large amount of resources available to the skilled person, who describes pharmaceutically acceptable excipients and is used to select suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. Examples include Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences (Mack Publishing Company), The Handbook of Pharmaceutical Additives (Gower Publishing Limited), and The Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients (The American Pharmaceutical Association and The Pharmaceutical Press).
Various carriers for formulating pharmaceutically acceptable compositions, and well known techniques for their preparation, are disclosed in Remington, The Science and Practice of Pharmacy,21st edition,2005, ed.D.B.Troy, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, and Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology, eds.J.Swarbrick and J.C.Boylan, 1988. Annu 1999, Marcel Dekker, New York, The contents of each of which are incorporated herein by reference. Except insofar as any conventional carrier is incompatible with the disclosed compounds, such as by producing any undesirable biological effect or interacting in a deleterious manner with any other ingredient in a pharmaceutically acceptable composition, its use is contemplated as falling within the scope of the present invention.
The pharmaceutical compositions disclosed herein are prepared using techniques and methods known to those skilled in the art. Some commonly used methods in the art are described in Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences (Mack Publishing Company).
Thus, in another aspect, the invention relates to a process for preparing a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound disclosed herein and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, carrier, adjuvant or combination thereof, which process comprises admixing the ingredients. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the disclosed compounds may be prepared by mixing, for example, at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure.
The compounds disclosed herein are generally formulated in a dosage form suitable for administration to a patient by a desired route. For example, dosage forms include those suitable for the following routes of administration: (1) oral administration, such as tablets, capsules, caplets, pills, troches, powders, syrups, elixirs, suspensions, solutions, emulsions, sachets and cachets; (2) parenteral administration, such as sterile solutions, suspensions, and reconstituted powders; (3) transdermal administration, such as transdermal patches; (4) rectal administration, e.g., suppositories; (5) inhalation, such as aerosols, solutions, and dry powders; and (6) topical administration, such as creams, ointments, lotions, solutions, pastes, sprays, foams and gels.
In one embodiment, the compounds disclosed herein may be formulated in oral dosage forms. In another embodiment, the compounds disclosed herein may be formulated in an inhalation dosage form. In another embodiment, the compounds disclosed herein can be formulated for nasal administration. In yet another embodiment, the compounds disclosed herein can be formulated for transdermal administration. In yet another embodiment, the compounds disclosed herein may be formulated for topical administration.
The pharmaceutical compositions provided by the present invention may be provided as compressed tablets, milled tablets, chewable lozenges, fast-dissolving tablets, double-compressed tablets, or enteric-coated, sugar-coated or film-coated tablets. Enteric coated tablets are compressed tablets coated with a substance that is resistant to the action of gastric acid but dissolves or disintegrates in the intestine, thereby preventing the active ingredient from contacting the acidic environment of the stomach. Enteric coatings include, but are not limited to, fatty acids, fats, phenyl salicylate, waxes, shellac, ammoniated shellac, and cellulose acetate phthalate. Sugar-coated tablets are compressed tablets surrounded by a sugar coating, which can help to mask unpleasant tastes or odors and prevent oxidation of the tablet. Film-coated tablets are compressed tablets covered with a thin layer or film of a water-soluble substance. Film coatings include, but are not limited to, hydroxyethyl cellulose, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol 4000, and cellulose acetate phthalate. Film coatings are endowed with the same general characteristics as sugar coatings. A tabletted tablet is a compressed tablet prepared over more than one compression cycle, including a multi-layer tablet, and a press-coated or dry-coated tablet.
Tablet dosage forms may be prepared from the active ingredient in powder, crystalline or granular form, alone or in combination with one or more carriers or excipients described herein, including binders, disintegrants, controlled release polymers, lubricants, diluents and/or colorants. Flavoring and sweetening agents are particularly useful in forming chewable tablets and lozenges.
The pharmaceutical composition provided by the present invention may be provided in soft or hard capsules, which may be prepared from gelatin, methylcellulose, starch or calcium alginate. The hard gelatin capsules, also known as Dry Fill Capsules (DFC), consist of two segments, one inserted into the other, thus completely encapsulating the active ingredient. Soft Elastic Capsules (SEC) are soft, spherical shells, such as gelatin shells, which are plasticized by the addition of glycerol, sorbitol or similar polyols. The soft gelatin shell may contain a preservative to prevent microbial growth. Suitable preservatives are those as described herein, including methyl and propyl parabens, and sorbic acid. The liquid, semi-solid and solid dosage forms provided by the present invention may be encapsulated in a capsule. Suitable liquid and semi-solid dosage forms include solutions and suspensions in propylene carbonate, vegetable oils or triglycerides. Capsules containing such solutions may be as described in U.S. patent nos.4,328,245; 4,409,239 and 4,410,545. The capsules may also be coated as known to those skilled in the art to improve or maintain dissolution of the active ingredient.
The pharmaceutical compositions provided herein may be provided in liquid and semi-solid dosage forms, including emulsions, solutions, suspensions, elixirs and syrups. Emulsions are two-phase systems in which one liquid is dispersed throughout another in the form of globules, which can be either oil-in-water or water-in-oil. Emulsions may include pharmaceutically acceptable non-aqueous liquids and solvents, emulsifiers and preservatives. Suspensions may include a pharmaceutically acceptable suspending agent and a preservative. The aqueous alcoholic solution may comprise pharmaceutically acceptable acetals, such as di (lower alkyl) acetals of lower alkyl aldehydes, e.g. acetaldehyde diethyl acetal; and water-soluble solvents having one or more hydroxyl groups, such as propylene glycol and ethanol. Elixirs are clear, sweetened, hydroalcoholic solutions. Syrups are concentrated aqueous solutions of sugars, such as sucrose, and may also contain preservatives. For liquid dosage forms, for example, a solution in polyethylene glycol may be diluted with a sufficient amount of a pharmaceutically acceptable liquid carrier, such as water, for precise and convenient administration.
Other useful liquid and semi-solid dosage forms include, but are not limited to, those comprising the active ingredients provided herein and a secondary mono-or poly-alkylene glycol, including: 1, 2-dimethoxymethane, diglyme, triglyme, tetraglyme, polyethylene glycol-350-dimethyl ether, polyethylene glycol-550-dimethyl ether, polyethylene glycol-750-dimethyl ether, where 350, 550, 750 refer to the approximate average molecular weight of the polyethylene glycol. These formulations may further include one or more antioxidants, such as Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT), Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA), propyl gallate, vitamin E, hydroquinone, hydroxycoumarins, ethanolamine, lecithin, cephalin, ascorbic acid, malic acid, sorbitol, phosphoric acid, bisulfite, sodium metabisulfite, thiodipropionic acid and its esters, and dithiocarbamates.
Dosage unit formulations for oral administration may be microencapsulated, where appropriate. They may also be prepared as extended or sustained release compositions, for example by coating or embedding the particulate material in a polymer, wax or the like.
The oral pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention can also be provided in the form of liposome, micelle, microsphere or nano system. Micellar dosage forms can be prepared using the methods described in U.S. Pat. No.6,350,458.
The pharmaceutical compositions provided herein can be provided as non-effervescent or effervescent granules and powders for reconstitution into liquid dosage forms. Pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and excipients used in non-effervescent granules or powders may include diluents, sweeteners and wetting agents. Pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and excipients used in effervescent granules or powders may include organic acids and sources of carbon dioxide.
Coloring and flavoring agents may be used in all of the above dosage forms.
The disclosed compounds may also be conjugated to soluble polymers as targeted drug carriers. Such polymers include polyvinylpyrrolidone, pyran copolymer, polyhydroxypropylmethacrylamide-phenol, polyhydroxyethylaspartamidephenol or polyoxyethylene polylysine substituted with palmitoyl residues. In addition, the disclosed compounds may be combined with a class of biodegradable polymers used in achieving controlled release of a drug, such as polylactic acid, polyepsilon caprolactone, polyhydroxy butyric acid, polyorthoesters, polyacetals, polydihydropyrans, polycyanoacrylates, and crosslinked or amphiphilic block copolymers of hydrogels.
The pharmaceutical compositions provided by the present invention may be formulated into immediate or modified release dosage forms, including delayed-, sustained-, pulsed-, controlled-, targeted-, and programmed release forms.
The pharmaceutical compositions provided by the present invention may be co-formulated with other active ingredients that do not impair the intended therapeutic effect, or with substances that supplement the intended effect.
The pharmaceutical compositions provided by the present invention may be administered parenterally by injection, infusion or implantation for local or systemic administration. Parenteral administration as used herein includes intravenous, intraarterial, intraperitoneal, intrathecal, intraventricular, intraurethral, intrasternal, intracranial, intramuscular, intrasynovial and subcutaneous administration.
The pharmaceutical compositions provided herein can be formulated in any dosage form suitable for parenteral administration, including solutions, suspensions, emulsions, micelles, liposomes, microspheres, nanosystems and solid forms suitable for solution or suspension in a liquid prior to injection. Such dosage forms may be prepared according to conventional methods known to those skilled in The art of pharmaceutical Science (see Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, supra).
Pharmaceutical compositions intended for parenteral administration may include one or more pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and excipients, including, but not limited to, aqueous vehicles, water-miscible vehicles, non-aqueous vehicles, antimicrobial agents or preservatives to inhibit microbial growth, stabilizers, solubility enhancers, isotonic agents, buffers, antioxidants, local anesthetics, suspending and dispersing agents, wetting or emulsifying agents, complexing agents, sequestering or chelating agents, cryoprotectants, thickening agents, pH adjusting agents, and inert gases.
Suitable aqueous carriers include, but are not limited to: water, saline, normal saline or Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS), sodium chloride injection, Ringers injection, isotonic glucose injection, sterile water injection, dextrose and lactated Ringers injection. Non-aqueous vehicles include, but are not limited to, fixed oils of vegetable origin, castor oil, corn oil, cottonseed oil, olive oil, peanut oil, peppermint oil, safflower oil, sesame oil, soybean oil, hydrogenated vegetable oils, hydrogenated soybean oil, and the medium chain triglycerides of coconut oil, and palm seed oil. Water-miscible vehicles include, but are not limited to, ethanol, 1, 3-butanediol, liquid polyethylene glycols (e.g., polyethylene glycol 300 and polyethylene glycol 400), propylene glycol, glycerol, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, N-dimethylacetamide, and dimethylsulfoxide.
Suitable antimicrobial agents or preservatives include, but are not limited to, phenol, cresol, mercurial, benzyl alcohol, chlorobutanol, methyl and propyl parabens, thimerosal, benzalkonium chloride (e.g., benzethonium chloride), methyl and propyl parabens, and sorbic acid. Suitable isotonic agents include, but are not limited to, sodium chloride, glycerol and glucose. Suitable buffers include, but are not limited to, phosphate and citrate. Suitable antioxidants are those as described herein, including bisulfite and sodium metabisulfite. Suitable local anesthetics include, but are not limited to, procaine hydrochloride. Suitable suspending and dispersing agents are those as described herein, including sodium carboxymethylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and polyvinylpyrrolidone. Suitable emulsifiers include those described herein, including polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate. Polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate 80 and triethanolamine oleate. Suitable sequestering or chelating agents include, but are not limited to, EDTA. Suitable pH adjusters include, but are not limited to, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, citric acid, and lactic acid. Suitable complexing agents include, but are not limited to, cyclodextrins, including alpha-cyclodextrin, beta-cyclodextrin, hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin, sulfobutyl ether-beta-cyclodextrin, and sulfobutyl ether 7-beta-cyclodextrin (f: (f)) CyDex,Lenexa,KS)。
The pharmaceutical compositions provided herein may be formulated for single or multiple dose administration. The single dose formulations are packaged in ampoules, vials or syringes. The multi-dose parenteral formulation must contain a bacteriostatic or fungistatic concentration of the antimicrobial agent. All parenteral formulations must be sterile, as is known and practiced in the art.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition is provided as a ready-to-use sterile solution. In another embodiment, the pharmaceutical compositions are provided as sterile dried soluble products, including lyophilized powders and subcutaneous injection tablets, which are reconstituted with a carrier prior to use. In yet another embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition is formulated as a ready-to-use sterile suspension. In yet another embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition is formulated as a sterile, dry, insoluble product that is reconstituted with a carrier prior to use. In yet another embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition is formulated as a sterile emulsion ready for use.
The pharmaceutical composition may be formulated as a suspension, solid, semi-solid, or thixotropic liquid for depot administration for implantation. In one embodiment, the disclosed pharmaceutical compositions are dispersed in a solid internal matrix surrounded by an outer polymeric membrane that is insoluble in body fluids but allows diffusion therethrough of the active ingredient in the pharmaceutical composition.
Suitable internal matrices include polymethylmethacrylate, polybutylmethacrylate, plasticized or unplasticized polyvinyl chloride, plasticized nylon, plasticized polyethylene terephthalate, natural rubber, polyisoprene, polyisobutylene, polybutadiene, polyethylene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, silicone rubber, polydimethylsiloxane, silicone carbonate copolymers, hydrogels of hydrophilic polymers such as esters of acrylic and methacrylic acids, collagen, crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol, and crosslinked partially hydrolyzed polyvinyl acetate.
Suitable outer polymeric films include polyethylene, polypropylene, ethylene/propylene copolymers, ethylene/ethyl acrylate copolymers, ethylene/vinyl acetate copolymers, silicone rubber, polydimethylsiloxane, neoprene, chlorinated polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, copolymers of chlorinated ethylene and vinyl acetate, vinylidene chloride, ethylene and propylene, ionomers polyethylene terephthalate, butyl rubber chlorohydrin rubber, ethylene/vinyl alcohol copolymers, ethylene/vinyl acetate/vinyl alcohol terpolymers, and ethylene/ethyleneoxyethanol copolymers.
In another aspect, the disclosed pharmaceutical compositions may be formulated in any dosage form suitable for administration to a patient by inhalation, such as a dry powder, aerosol, suspension, or solution composition. In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical compositions disclosed herein may be formulated in a dosage form suitable for inhaled administration to a patient as a dry powder . In yet another embodiment, the disclosed pharmaceutical compositions may be formulated in a dosage form suitable for inhalation administration to a patient via a nebulizer. Dry powder compositions for delivery to the lung by inhalation typically comprise a finely powdered compound disclosed herein and one or more finely powdered pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. Pharmaceutically acceptable excipients that are particularly suitable for use as dry powders are known to those skilled in the art and include lactose, starch, mannitol, and mono-, di-and polysaccharides. Fine powders may be prepared, for example, by micronization and milling. Generally, the size-reduced (e.g., micronized) compound may pass through a D of about 1 to 10 microns50Values (e.g., measured by laser diffraction).
Aerosols can be formulated by suspending or dissolving the disclosed compounds in a liquefied propellant. Suitable propellants include chlorinated hydrocarbons, hydrocarbons and other liquefied gases. Representative propellants include: trichlorofluoromethane (propellant 11), dichlorofluoromethane (propellant 12), dichlorotetrafluoroethane (propellant 114), tetrafluoroethane (HFA-134a), 1-difluoroethane (HFA-152a), difluoromethane (HFA-32), pentafluoroethane (HFA-12), heptafluoropropane (HFA-227a), perfluoropropane, perfluorobutane, perfluoropentane, butane, isobutane and pentane. Aerosols comprising the compounds disclosed herein are typically administered to a patient via a Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI). Such devices are known to those skilled in the art.
The aerosol may contain additional pharmaceutically acceptable excipients that may be used by MDIs, such as surfactants, lubricants, co-solvents, and other excipients, to improve the physical stability of the formulation, to improve valve characteristics, to improve solubility, or to improve taste.
Pharmaceutical compositions suitable for transdermal administration may be prepared as discrete patches intended to remain in intimate contact with the epidermis of the patient for an extended period of time. For example, the active ingredient may be delivered from a patch agent by iontophoresis, as generally described in Pharmaceutical Research,3(6),318 (1986).
Pharmaceutical compositions suitable for topical administration may be formulated as ointments, creams, suspensions, lotions, powders, solutions, pastes, gels, sprays, aerosols or oils. For example, ointments, creams and gels may be formulated with a water or oil base, and suitable thickeners and/or gelling agents and/or solvents. Such bases may include, water, and/or oils such as liquid paraffin and vegetable oils (e.g., peanut oil or castor oil), or solvents such as polyethylene glycol. Thickeners and gelling agents used according to the nature of the base include soft paraffin, aluminium stearate, cetostearyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, lanolin, beeswax, carbopol and cellulose derivatives, and/or glyceryl monostearate and/or non-ionic emulsifiers.
Lotions may be formulated with an aqueous or oily base and will in general also contain one or more emulsifying agents, stabilizing agents, dispersing agents, suspending agents or thickening agents.
Powders for external use may be formed in the presence of any suitable powder base, for example talc, lactose or starch. Drops may be formulated with an aqueous or non-aqueous base containing one or more dispersing agents, solubilising agents, suspending agents or preservatives.
Topical formulations may be administered by application to the affected area one or more times per day; an occlusive dressing covering the skin is preferably used. Adhesive depot systems allow for continuous or extended administration.
Use of the Compounds and compositions of the invention
The compounds or pharmaceutical compositions disclosed herein can be used in the preparation of medicaments for the treatment, prevention, amelioration, control or alleviation of inflammatory or autoimmune diseases mediated by ROR γ t in mammals, including humans, as well as in the preparation of other medicaments for the inhibition of ROR γ t.
Specifically, the amount of the compound in the composition of the present invention is effective to detectably inhibit ROR γ t, and the compound of the present invention is useful as a medicament for preventing or treating human psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ocular disease, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, crohn's disease, or kawasaki disease.
The compounds or compositions of the present invention may be used, but are in no way limited to, for administration to a patient for preventing, treating or alleviating psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ocular disease, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, crohn's disease or kawasaki disease in a mammal, including a human, using an effective amount of a compound or composition of the present invention.
In addition to being beneficial for human therapy, the compounds and pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention may also find application in veterinary therapy for pets, animals of the introduced species and mammals in farm animals. Examples of other animals include horses, dogs, and cats. Herein, the compound of the present invention includes pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives thereof.
General synthetic procedure
To illustrate the invention, the following examples are set forth. It is to be understood that the invention is not limited to these embodiments, but is provided as a means of practicing the invention.
In general, the compounds of the present invention may be prepared by the methods described herein, wherein the substituents are as defined in formula (I), unless otherwise indicated. The following reaction schemes and examples serve to further illustrate the context of the invention.
Those skilled in the art will recognize that: the chemical reactions described herein may be used to suitably prepare a number of other compounds of the invention, and other methods for preparing the compounds of the invention are considered to be within the scope of the invention. For example, the synthesis of those non-exemplified compounds according to the present invention can be successfully accomplished by those skilled in the art by modification, such as appropriate protection of interfering groups, by the use of other known reagents in addition to those described herein, or by some routine modification of reaction conditions. In addition, the reactions disclosed herein or known reaction conditions are also recognized as being applicable to the preparation of other compounds of the present invention.
The examples described below, unless otherwise indicated, are all temperatures set forth in degrees Celsius. Reagents were purchased from commercial suppliers such as Aldrich Chemical Company, Arco Chemical Company and Alfa Chemical Company and were used without further purification unless otherwise indicated. General reagents were purchased from Shantou Wen Long chemical reagent factory, Guangdong Guanghua chemical reagent factory, Guangzhou chemical reagent factory, Tianjin Haojian Yunyu chemical Co., Ltd, Tianjin Shucheng chemical reagent factory, Wuhan Xin Huayuan scientific and technological development Co., Ltd, Qingdao Tenglong chemical reagent Co., Ltd, and Qingdao Kaolingyi factory.
The anhydrous tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, toluene and ether are obtained through reflux drying of metal sodium. The anhydrous dichloromethane and chloroform are obtained by calcium hydride reflux drying. Ethyl acetate, petroleum ether, N-hexane, N, N-dimethylacetamide and N, N-dimethylformamide were used as they were previously dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
The following reactions are generally carried out under positive pressure of nitrogen or argon or by sleeving a dry tube over an anhydrous solvent (unless otherwise indicated), the reaction vial being stoppered with a suitable rubber stopper and the substrate being injected by syringe. The glassware was dried.
The column chromatography is performed using a silica gel column. Silica gel (300 and 400 meshes) was purchased from Qingdao oceanic chemical plants.
NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker 400MHz or 600MHz NMR spectrometer, CDC13、DMSO-d6、CD3OD or acetone-d6TMS (0ppm) or chloroform (7.26ppm) was used as a reference standard for the solvent (in ppm). When multiple peaks occur, the following abbreviations will be used: s (singleton), d (doublet), t (triplet), m (multiplet), br (broad), dd (doublet of doublets), dt (doublet of triplets). Coupling constants are expressed in hertz (Hz).
The conditions for determining low resolution Mass Spectrometry (MS) data were: agilent 6120 four-stage rod HPLC-M (column model: Zorbax SB-C18,2.1X30 mm)3.5 microns, 6min, flow rate 0.6 mL/min. Mobile phase: 5% -95% (CH containing 0.1% formic acid)3CN) in (H containing 0.1% formic acid)2O) by electrospray ionization (ESI) at 210nm/254nm, with UV detection.
The purity of the compound was determined by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), using Agilent 1260HPLC (column model: Agilent zorbax Eclipse PlusC18) and detected by DAD detector, and finally calculated by area normalization to obtain the purity of the compound.
The following acronyms are used throughout the invention:
1,4-dioxane Et3N TEA Triethylamine
AcOH acetic acid EDCI 1-ethyl- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbonyl diimine
Ag2CO3Silver carbonate hydrochloride
BH3Borane HATU 2- (7-azobenzotriazol) -N, N, N ', N' -tetramethyl
CuI cuprous iodide; urea hexafluorophosphate esters
CO HOBt 1-hydroxybenzotriazole
CuBr cuprous H bromide2O water
CDC13Deuterated chloroform HCHO formaldehyde
CH2Cl2DCM dichloromethane i-PrOH isopropanol
Cs2CO3Cesium carbonate KOH potassium hydroxide
DAST diethylaminosulfur trifluoride K2CO3Potassium carbonate
DMFN, N-dimethylformamide LIBH4Lithium borohydride
DIPEA N, N-diisopropylethylamine MeCN acetonitrile
DMSO dimethyl sulfoxide MeOH methanol
DMSO-d6Deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide MeONa methoxide
dccp·HBF41, 3-bis (dicyclohexylphosphine) propanebis (MeCHO acetaldehyde tetrafluoroborate)
Salt) NaNO2Sodium nitrite
EtOAc EA ethyl acetate Na2CO3Sodium carbonate
EtOH ethanol NaHCO3Sodium bicarbonate
NaOH sodium hydroxide TFA trifluoroacetic acid
Na2SO4Sodium sulfate Tf2O-Trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride
Na2S2O4Sodium dithionite xanthphos 4, 5-bis (diphenylphosphino) -9, 9-dimethyl xanthene
G of NaCl sodium chloride
NH4Cl ammonium chloride for h
NaH sodium hydride min
NaBH3CN cyano sodium borohydride mmol
NH2OH HCl hydroxylamine hydrochloride M mol per liter
NH4F ammonium fluoride ℃/° c
Pd2(dba)3Tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium mL, ml ml of
Pd(dppf)Cl2[1,1' -bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene]Palladium dichloride RT, r.t. room temperature
Pd(OAc)2Palladium acetate rpm revolutions per minute
Pd(P(o-Tol)3)2(OAc)2Bis (tri-o-tolylphosphorus) palladium acetate Dess-Martin reagent (1,1, 1-triacetoxy) -1, 1-dihydro-
PE petroleum ether; 1, 2-Benzoiodoxy-3 (1H) -ones
Pd(PPh3)2Cl2Bis triphenylphosphine palladium dichloride Rt Retention time
Pd/C palladium/carbon TMSCF3(trifluoromethyl) trimethylsilane;
P(OPh)3triphenyl phosphite TBSOTf-butyldimethylsilyl triflate;
Toluene Toluene TMSCF2Br difluorobromomethyltrimethylsilane;
TLC thin layer chromatography Selectfluor selective fluorinating agent;
THF tetrahydrofuran
Typical synthetic procedures for preparing the disclosed compounds of the invention are shown in the following synthetic schemes. Unless otherwise indicated, ring A, ring B, ring L1、L2、R、R2、R3、R4、Z1、Z2、Z3、Z4And Z5Have the meaning as described in the present invention.
Synthesizing an intermediate:
in the formula, X1Represents a leaving group including, but not limited to, methanesulfonyloxy, p-methylbenzenesulfonyloxy, and the like, and PG represents an amino protecting group.
The intermediate (a) can be prepared by the following process:
reacting the compound (aa) under appropriate conditions to produce a compound (ab), subjecting the compound (ab) and the compound (ac) to a cross-coupling reaction to obtain a compound (ad), and deprotecting the compound (ad) to obtain an intermediate compound (a).
Synthesis scheme 1
In the formula, X represents a halogen atom, and PG represents an amino protecting group.
Compound (9a) can be prepared by the following procedure:
reacting the compound (1a) with the compound (2a) to generate a compound (3a), deaminating the compound (3a) to generate a compound (4a), performing a coupling reaction on the compound (4a) and the compound (5a) to obtain a compound (6a), performing a reduction reaction on the compound (6a) to obtain a compound (7a), and finally performing a condensation reaction on the compound (7a) and the compound (8a) to obtain a compound (9 a).
Synthesis scheme 2
In the formula, X represents a halogen atom, PG represents an amino-protecting group, T1And T2Selected from carboxyl or amino, and T1And T2Cannot be the same group.
The compound (6b) or (6 b') can be prepared by the following process:
the compound (1b) and the compound (2b) are subjected to condensation reaction to generate a compound (3b) or (3b '), the compound (3b) or (3b ') and the compound (2a) are reacted to generate a compound (4b) or (4b '), the compound (4b) or (4b ') is subjected to deamination protection to generate a compound (5b) or (5b '), and the compound (5b) or (5b ') and the compound (1a) are subjected to substitution reaction to obtain a compound (6b) or (6b ').
Synthesis scheme 3
In the formula, X0Represents a leaving group including, but not limited to, a halogen atom, a methanesulfonyloxy group, a p-methylbenzenesulfonyloxy group and the like, X represents a halogen atom, PG represents an amino-protecting group, T represents a leaving group1And T2Selected from carboxyl or amino, and T1And T2Cannot be the same group.
The compound (6c) or (6 c') can be prepared by the following process:
the compound (1b) and the compound (1c) are subjected to condensation reaction to generate a compound (2c) or (2c '), the compound (2c) or (2c ') is further subjected to coupling reaction with the compound (3c) to generate a compound (4c) or (4c '), the compound (4c) or (4c ') is deprotected to obtain a compound (5c) or (5c '), and the compound (5c) or (5c ') and the compound (1a) are subjected to substitution reaction to obtain a compound (6c) or (6c ').
Synthesis scheme 4
In the formula, X represents a halogen atom, PG represents an amino-protecting group, T1And T2Selected from carboxyl or amino, and T1And T2Cannot be the same group.
The compound (6d) or (6 d') can be prepared by the following process:
the compound (3a) and the compound (2b) are subjected to substitution reaction to generate a compound (1d), the compound (1d) is subjected to reduction reaction to generate a compound (2d), the compound (2d) and the compound (3d) are subjected to condensation reaction to generate a compound (4d) or (4d '), the compound (4d) or (4d ') is deprotected to generate a compound (5d) or (5d '), and the compound (5d) or (5d ') is subjected to substitution reaction to generate a compound (6d) or (6d ').
Synthesis scheme 5
In the formula, PG represents an amino protecting group, T1And T2Selected from carboxyl or amino, and T1And T2Cannot be the same group at the same time.
The compounds (2e) and (2 e') can be prepared by the following procedures:
and (3) carrying out substitution reaction on the intermediate compound (a) and the compound (2b) to obtain a compound (1e), and carrying out condensation reaction on the compound (1e) and the compound (1b) to generate a compound (2e) or (2 e').
The compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof provided by the present invention are further illustrated below in connection with the examples.
Examples
Synthesis of intermediate 1: synthesis of (2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-4- (((trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl) oxo) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1, 2-dicarboxylate
(S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4-oxopyrrolidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (19.91g,81.90mmol) and DIPEA (23.1mL,139.77mmol) were dissolved in DCM (100mL) at-10 deg.C and Tf was added dropwise2O (18.0mL,106.99mmol), 1h after dropping, warm to room temperature and stir for 8 h. Then, H was slowly added to the reaction solution2The reaction was quenched with O (65mL), the organic phase was extracted, the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, washed with saturated NaCl solution (60mL), anhydrous Na2SO4After drying, concentration is carried out under reduced pressure, the crude product is isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM (v/v) ═ 10/1),a pale yellow transparent oil (29.00g, 95%) was obtained.
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=398.1[M+23]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):5.74(dd,J=18.9,1.7Hz,1H),5.13–4.94(m,1H),4.46–4.22(m,2H),3.78(s,3H),1.47(d,J=22.2Hz,9H).
Step two: synthesis of (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1H-pyrrole-1, 2(2H,5H) -dicarboxylate
(4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) boronic acid (16.00g,84.20mmol), (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4- (((trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl) oxy) -1H-pyrrole-1, 2(2H,5H) -dicarboxylate (29.00g,77.30mmol) and Pd (dppf) Cl were added under nitrogen2(2.00g,2.65mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (80.0mL) and Cs was added2CO3(25.10g,77.00mmol), heated to 100 ℃ and stirred for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue diluted with DCM (80mL) followed by saturated NaHCO 3The solution (40mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a pale yellow solid (25.40g, 88%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:394.2[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of (S) -tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate
(S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1H-pyrrole-1, 2(2H,5H) -dicarboxylate (7.10g,19.10mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous THF (45mL), the reaction was cooled to-10 deg.C, and LiBH was added4(830mg,37.40mmol) and then warmed to room temperature and stirred for 8 h. Saturated NH is added dropwise to the reaction solution4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (35mL), the mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a colorless clear oil (4.80g, 73%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:244.1[M-100+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
(S) -tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (3.05g,8.88mmol) was dissolved in EtOAc (30mL) under hydrogen and Pd/C (280mg, 10%) was added and stirred at room temperature for 6H. Celite was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a colorless transparent liquid (3.00g, 98%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:246.1[M-100+1]+.
Synthesis of intermediate 2: synthesis of ((2S) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-yl) methanol
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylic acid ester
The reaction product of (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (2.94g,11.4mmol), P (OPh)3(6.0mL,23mmol) and TEA (4.8mL,34mmol) were dissolved in DCM (20mL) and Br was stirred at-20 deg.C2A solution of (1.0mL,20mmol) in DCM (5mL) was slowly added dropwise to the reaction over 30min, and the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and then with saturated NaHCO in sequence3The solution (30mL) was washed with NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1) to give a yellow oily liquid (1.84g, 50%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 342.0[ M +23 ]]+.
Step two: synthesis of (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylate
Under nitrogen protection, (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylate (1.84g,5.75mmol), (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) boronic acid (2.20 g),11.6mmol),Pd(dppf)Cl2(420mg,0.574mmol) and Cs2CO3(3.80g,11.7mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 24 h. Cooled to room temperature, the reaction was spin dried under reduced pressure, and the residue was diluted with DCM (80mL) and, in turn, saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1) to give a yellow oily liquid (1.60g, 72%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=408.2[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid ester
(S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylate (1.60g,4.15mmol) and Pd/C (200mg, 10%) were suspended in a mixed solvent of MeOH/THF (10mL/10mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 12H. The reaction was then filtered and the filtrate was concentrated to give a yellow oily liquid (1.53g, 95%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=410.2[M+23]+。
Step four: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
At room temperature, LiBH is added4(220mg,10.10mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (1.53g,3.95mmol) in THF (16mL) and stirred for 3.0 h. Then saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL) and then extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.3), and the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 2/1/1) to give a light yellow oily liquid (1.31g, 92%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=382.2[M+23]+.
Step five: synthesis of ((2S) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-yl) methanol
Mixing (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl)Yl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid ester (557mg,1.55mmol) was dissolved in a solution of HCl in i-PrOH (10mL,45.8mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Then, saturated Na was added to the reaction mixture2CO3Solution (20mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oily liquid (364mg, 91%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=260.2[M+1]+.
Example 12- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of benzyl 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate
Under nitrogen protection, 1-bromo-4- (trifluoromethyl) benzene (2.0mL,14.0mmol), benzyl 2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (24mL,134.0mmol), Pd (P (o-Tol)3)2(OAc)2(632mg,0.67mmol) and Ag2CO3(3.72g,13.5mmol) was dissolved in DMF (30mL) and DIPEA (9.2mL,53.0mmol) was added to the reaction and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 24 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (100mL), and then sequentially saturated NaHCO3The solution (10 mL. times.6) and a saturated NaCl solution (10 mL. times.2) were washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 20/1/1) to give a yellow oily liquid (4.52g, 91%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=348.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
Pd/C (2.01g, 10%) was added to a solution of 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylic acid benzyl ester (2.04g,5.87mmol) in MeOH (20mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 4H. Filtering the reaction solution to obtain anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure,a yellow oily liquid (354mg, 28%) was obtained.
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=216.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 1- (4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
Under the protection of nitrogen, adding Cs2CO3(2.68g,8.23.0mmol) was added to a solution of 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (350mg,1.63.0mmol) and 1-fluoro-4-nitrobenzene (2.32g,16.4.0mmol) in DMF (10mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with EtOAc (60mL) and washed successively with water (10mL) and saturated NaCl solution (10 mL. times.5), and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (197mg, 36%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=337.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline
Pd/C (21mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 1- (4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (195mg,0.58mmol) in MeOH (5mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was filtered and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a dark yellow solid (176mg, 99%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=307.4[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
Under nitrogen, TEA (0.16mL,1.1mmol) was added to a solution of 4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline (174mg,0.57mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (162mg,0.71mmol), EDCI (170mg,0.89mmol) and HOBt (119mg,0.88mmol) in DCM (6mL) and the reaction stirred at RT for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L), saturated NaHCO3The solution (10mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give an off-white solid (170mg, 58%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) m/z=517.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO)δ(ppm):9.92(s,1H),7.84(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.69(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.40(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),6.54(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),3.73(s,2H),3.71–3.66(m,1H),3.64(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),3.48–3.33(m,3H),3.26(dd,J=13.3,7.4Hz,2H),2.42(d,J=8.0Hz,1H),2.15–2.04(m,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
13C NMR(151MHz,DMSO)δ(ppm):197.22,167.12,147.72,144.14,142.57,136.68,130.10,128.10,128.04,127.79,125.28,125.26,120.93,111.45,54.05,49.21,47.49,43.05,42.84,40.06,32.36,7.15.
Example 2N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
Under nitrogen protection, 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (80mg,0.37mmol), N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodobenzamide (150mg,0.35mmol), Pd 2(dba)3(90mg,0.095mmol), XantPhos (43mg,0.07mmol) and Cs2CO3(500mg,1.50mmol) was added to 1,4-dioxane (50mL), and the mixture was stirred at 100 ℃ for 10 h. Cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, filtering, and collecting filtrate with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a pale yellow solid (15mg, 8%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=517.6[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.84(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),7.53(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),6.59(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),4.74(d,J=5.1Hz,2H),3.87–3.76(m,1H),3.62(d,J=6.9Hz,2H),3.49(dd,J=27.6,8.1Hz,2H),3.11(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.50(s,1H),2.21(d,J=8.5Hz,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 32- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of benzyl 3- (4- (2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamido) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate
2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4-iodophenyl) acetamide (500mg,1.17mmol), benzyl 2, 5-dihydropyrrole-1-carboxylate (0.41g,2.0mmol), Pd (P (o-Tol) under nitrogen protection3)2(OAc)2(150mg,0.16mmol),Ag2CO3(320mg,1.16mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.00mmol) were dissolved in DMF (40mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 8 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a pale yellow solid (130mg, 22%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=505.6[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (pyrrolidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide
Pd/C (155mg, 5%) was added to a solution of benzyl 3- (4- (2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamido) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (120mg,0.24mmol) in MeOH (50mL) under hydrogen atmosphere and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 6H. The reaction solution was filtered through celite, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a brown solid (80mg, 90%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=373.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide
Under nitrogen, 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (pyrrolidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide (70mg,0.19mmol), 1-bromo-4- (trifluoromethyl) benzene (0.51g,2.30mmol), Pd2(dba)3(20mg,0.021mmol), XantPhos (13mg,0.022mmol) and Cs2CO3(165mg,0.51mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 120 ℃ for 8 h. Cooled to room temperature and filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a pale yellow solid (30mg, 31%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=517.6[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.90(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,4H),7.22(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),6.56(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),3.81(s,2H),3.75–3.66(m,1H),3.52(dd,J=16.6,8.4Hz,2H),3.47–3.39(m,1H),3.34(t,J=8.7Hz,1H),3.12(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.45-2.35(m,1H),2.13(dd,J=19.3,10.6Hz,1H),1.29(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 42- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) cyclohexyl) pyrrolidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide
At room temperature, NaBH is added 3CN (100mg,1.21mmol) was added to a solution of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (pyrrolidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide (200mg,0.54mmol) and 4- (trifluoromethyl) cyclohexanone (0.1mL,0.7mmol) in MeOH (20mL) and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was separated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) and preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) in this order to give a pale yellow solid (160mg, 57%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=523.6[M+1]+;
1H NMR(600MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.82(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.80(s,1H),7.51(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.40(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.22(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),3.76(s,2H),3.32–3.22(m,1H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.83(dt,J=12.4,6.2Hz,2H),2.60(ddd,J=15.1,10.1,7.2Hz,2H),2.32(m,1H),2.30–2.22(m,1H),2.07(dd,J=14.5,10.2Hz,1H),1.95(d,J=13.8Hz,1H),1.89(d,J=16.0Hz,1H),1.87–1.73(m,3H),1.67–1.54(m,2H),1.44(dt,J=12.3,6.4Hz,2H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 5N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-3-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4-bromo-N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
4-Bromobenzoic acid (1.03g,5.12mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (1.02g,5.12mmol), EDCI (1.43g,7.46mmol) and HOBt (1.0g,7.40mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen, and TEA (1.4mL,10mmol) was added to the reaction and stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (1.42g, 72%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=382.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of benzyl 4- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate
Under nitrogen protection, 4-bromo-N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide (368mg,0.96mmol), benzyl 2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (1.72mL,9.58mmol), Pd (P (Tol))3)2(OAc)2(50mg,0.05mmol) and Ag2CO3(265mg,0.96mmol) was dissolved in DMF (5mL) and DIPEA (0.5mL,3.0mmol) was added and the mixture was stirred at 100 ℃ for 24 h. Cooled to room temperature, the reaction was diluted with EtOAc (100mL) and then sequentially with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oily liquid (372mg, 77%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=505.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (pyrrolidin-3-yl) benzamide
Pd/C (155mg, 5%) was added to a solution of benzyl 4- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (372mg,0.73mmol) in MeOH (10mL) under hydrogen atmosphere and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 6H. The reaction solution was filtered through celite, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a brown solid (220mg, 80%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=373.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-3-yl) benzamide N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (pyrrolidin-3-yl) benzamide (92mg,0.25mmol), 1-bromo-4- (trifluoromethyl) benzene (0.06mL,0.40mmol), Pd, was reacted at room temperature2(dba)3(13mg,0.01mmol),XantPhos(10mg,0.017mmol),Cs2CO3(267mg,0.82mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous Toluene (3mL) and stirred at 80 ℃ for 24 h. Cooled to room temperature, the reaction was diluted with EtOAc (80mL) and washed successively with water (15mL) and saturated NaCl solution (15mL) over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EA (v/v) ═ 10/1) and preparative plate chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 20/1) in that order to give a yellow solid (18mg, 11%). .
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=517.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.84(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.81(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.52(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.47(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.36(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.70(t,J=6.0Hz,1H),6.59(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),4.75(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),3.82–3.73(m,1H),3.65–3.52(m,2H),3.52–3.44(m,1H),3.43–3.37(m,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.52–2.43(m,1H),2.16(dd,J=12.4,8.8Hz,1H),1.25(d,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 62- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 3- (((trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl) oxy) -5, 6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
3-Oxopiperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (2.00g,10.0mmol) and DMAP (3.80g,30.8mmol) were dissolved in DCM (30mL) under nitrogen, and Tf was cooled with stirring at-10 deg.C2O (2.60mL,13.0mmol) was slowly added dropwise to the reaction system, and after the addition, the temperature was raised to room temperature and stirred for 5 h. The reaction was then quenched with water (35mL) in an ice bath, extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), and the organic phases combined and washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EA (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a colorless transparent liquid (1.15g, 35%).
Step two: synthesis of (4- (2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamido) phenyl) boronic acid
(4-aminophenyl) boronic acid (600mg,3.49mmol),2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (800mg,3.50mmol), EDCI (1.10g,5.62mmol) and HOBt (600mg,4.30mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) and stirred at room temperature for 7 h. The reaction was quenched by the addition of HCl solution (30mL,1mol/L) to precipitate a large amount of white solid, which was filtered to give a white solid (820mg, 67%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=348.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of tert-butyl 5- (4- (2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamido) phenyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate
(4- (2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamido) phenyl) boronic acid (210mg,0.60mmol),3- (((trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl) oxo) -5, 6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (220mg,0.66mmol), Pd (dppf) Cl under nitrogen protection2(101mg,0.13mmol) and Cs2CO3(500mg,1.53mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (40mL) and stirred at 105 ℃ for 7 h. Subsequently, it was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (103mg, 35%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 485.6[ M +1 ═ M ]+.
Step four: synthesis of tert-butyl 3- (4- (2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetylamino) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
Pd/C (860mg, 5%) was added to a solution of tert-butyl 5- (4- (2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetylamino) phenyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (200mg,0.41mmol) in MeOH (50mL) under hydrogen atmosphere, stirred at room temperature for 4H, then filtered through celite, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the resulting crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a yellow solid (90mg, 45%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=509.3[M+23]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (piperidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide
Tert-butyl 3- (4- (2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamido) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (200mg,0.41mmol) was dissolved in DCM (50mL) and TFA (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 0.5 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a pale yellow liquid (151mg, 95%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=387.5[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide
Under nitrogen protection, 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (piperidin-3-yl) phenyl) acetamide (100mg,0.26mmol), 1-bromo-4- (trifluoromethyl) benzene (100mg,0.44mmol), Pd2(dba)3(39mg,0.041mmol), XantPhos (43mg,0.072mmol) and Cs 2CO3(295mg,0.90mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 120 ℃ for 8 h. It was filtered off at room temperature, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was subjected to silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a pale yellow solid (10mg, 7%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=531.6[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.91(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.44(t,J=8.3Hz,4H),7.22(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.18(s,1H),6.92(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),3.83(m,2H),3.81(s,2H),3.12(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.90–2.79(m,3H),2.06-1.97(m,2H),1.87-1.75(m,2H),1.30(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 7N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (1-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- (1- (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-2-yl) benzoic acid
Under nitrogen protection, 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (1.0g,3.20mmol), 4-iodobenzoic acid (245mg,0.99mmol), Pd (P (o-Tol)3)2(OAc)2(13mg,0.014mmol) and Ag2CO3(270mg,0.98mmol) was dissolved in DMF (10mL) and DIPEA (0.70mL,4.19mmol) was added and the mixture was stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. The temperature was reduced to room temperature and the reaction was diluted with EtOAc (100mL) and then sequentially with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EA (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (198mg, 46%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 456.1[ M +23 ]]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- (1- (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) -benzoic acid
Pd/C (50mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 4- (1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-2-yl) benzoic acid (198mg,0.46mmol) in MeOH (8mL) and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2H under an atmosphere of hydrogen. The filtrate was then concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (198mg, 100%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=458.1[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of tert-butyl 2- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate 4- (1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoic acid (198mg,0.46mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenylmethanamine (122mg,0.61mmol), EDCI (1)75mg,0.91mmol) and HOBt (124mg,0.92mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL), TEA (0.20mL,1.40mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and then with saturated NaHCO in sequence3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (122mg, 44%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.2[M-56+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzamide
Tert-butyl 2- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate (122mg,0.20mmol) was dissolved in a solution of HCl in i-PrOH (5mL,30mmol,6mol/L) and stirred at room temperature for 2.0 h. Concentrated under reduced pressure, then the residue was diluted with DCM (60mL), followed by saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (102mg, 100%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=517.1[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (1-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzamide
N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzamide (102mg,0.20mmol), AcOH (0.02mL,0.30mmol) and HCHO (30mg,1.0mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (5mL), stirred at room temperature for 2.0h, then NaBH was added3CN (120mg,1.91mmol), and stirring was continued for 5.0 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a white solid (67mg, 64%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=531.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.87(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.82(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.55(m,8H),6.66(br,1H),4.77(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),3.47–3.39(m,1H),3.34(m,1H),3.12(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.86(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),2.78–2.68(m,1H),2.23(s,3H),2.04(m,1H),1.79(dd,J=19.5,9.8Hz,1H),1.29(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
13C NMR(151MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):167.58,145.08,137.50,132.97,130.06,128.74,128.35,127.90,127.64,127.50,125.63,125.61,71.89,64.03,50.52,46.01,43.54,41.76,40.48,29.28,7.35.
Example 8N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (1-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- (4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoate
4- (1- (tert-Butoxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoic acid (557mg,1.28mmol) was dissolved in HCl in MeOH (15mL, 20%) and stirred at room temperature for 2 h. Adding SOCl 2(0.24mL,3.30mmol) was added to the system and after the addition, the reaction was heated in a 70 ℃ oil bath with stirring for 3 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, and saturated Na was added to the reaction mixture2CO3The reaction was quenched with solution (30mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a dark brown oily liquid (440mg, 99%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=350.0[M+1]+..
Step two: synthesis of methyl 4- (1-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoate
Methyl 4- (4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoate (142mg,0.41mmol), AcOH (0.05mL,0.90mmol) and HCHO (60mg,2.00mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (5mL), stirred at room temperature for 1.5h, then NaBH was added3CN (252mg,4.01mmol), stirred at room temperature, added to the reaction mixtureSaturated Na2CO3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Drying and concentration under reduced pressure gave a tan solid (145mg, 98%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 364.3[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- (1-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoic acid
NaOH (51mg,1.28mmol) was added to a solution of methyl 4- (1-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoate (145mg,0.40mmol) in THF/MeOH (3mL/3mL) and stirred at room temperature for 5 h. Water (20mL) was added to the reaction mixture, HCl solution (1mol/L) was added dropwise to the reaction mixture, the pH of the solution was adjusted to about 3, and the aqueous phase was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (135mg, 97%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=350.3[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (1-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzamide
4- (1-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoic acid (135mg,0.39mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (104mg,0.45mmol), EDCI (150mg,0.78mmol) and HOBt (107mg,0.79mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and TEA (0.32mL,2.30mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. DCM (60mL) was added to the reaction solution, followed by saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and saturated NaHCO in that order3Solution (20mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a green solid (38mg, 18%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.76(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.89(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.66(q,J=8.1Hz,6H),7.49(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),5.14(dd,J=13.8,6.9Hz,1H),5.03(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),3.78–3.66(m,2H),3.55–3.46(m,1H),3.26(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.20(m,1H),2.82–2.76(m,1H),2.76–2.68(m,1H),2.14(s,3H),2.05–1.94(m,1H),1.60(dd,J=18.2,11.1Hz,1H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 94- (1-Ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- (1-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoate
Methyl 4- (4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoate hydrochloride (142mg,0.41mmol), AcOH (0.05mL,0.90mmol) and MeCHO (0.20mL,3.60mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (5mL), stirred at room temperature for 1.5h, then NaBH was added 3CN (252mg,4.01mmol), and stirring was continued at room temperature for 12 h. Then, saturated Na was added to the reaction mixture2CO3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Drying and concentration under reduced pressure gave the crude product as a tan solid (150mg, 98%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=378.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- (1-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoic acid
NaOH (51mg,1.28mmol) was added to a solution of methyl 4- (1-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoate (150mg,0.40mmol) in THF/MeOH (3mL/3mL) and stirred at room temperature for 5 h. Water (20mL) was added to the reaction mixture, HCl solution (1mol/L) was added dropwise to the reaction mixture, the pH of the solution was adjusted to about 3, and the aqueous phase was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (140mg, 97%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 364.3[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- (1-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- (1-Ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoic acid (135mg,0.37mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (104mg,0.45 mmol)mmol), EDCI (150mg,0.78mmol) and HOBt (107mg,0.79mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and TEA (0.32mL,2.30mmol) was added and stirred at RT for 20 h. DCM (60mL) was added to the reaction, followed by saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a green solid (20mg, 9%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=575.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.75(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),7.88(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.84(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.66(q,J=9.0Hz,6H),7.50(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),5.14(dd,J=13.8,6.9Hz,1H),5.05(t,J=5.7Hz,1H),3.79–3.66(m,2H),3.59–3.49(m,2H),3.43(m,2H),3.26(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.75(dd,J=16.6,7.3Hz,1H),2.71–2.64(m,1H),2.02(dd,J=14.1,6.9Hz,1H),1.60(dd,J=19.9,9.5Hz,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),1.00(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).
Example 102- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylic acid methyl ester
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 2- (4- (methoxycarbonyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
TEA (0.30mL,2.20mmol) and methyl chloroformate (0.10mL,1.30mmol) were added sequentially to a solution of methyl 4- (4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoate hydrochloride (142mg,0.41mmol) in THF (5mL) under ice-cooling, and after addition, the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a tan solid (160mg, 97%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 408.1[ M +1 ═ M +1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- (1- (methoxyformyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoic acid
LiOH (211mg,5.03mmol) was added to methyl 2- (4- (methoxycarbonyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate (160mg,0.39mmol) in THF/H 2O (10mL/3mL) solution, heated to 50 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature and H was added2O (20mL), then HCl solution (1mol/L) was added dropwise to adjust the pH of the system to about 3, and the aqueous phase was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (150mg, 97%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=394.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of methyl 2- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
4- (1- (Methoxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) benzoic acid (150mg,0.38mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (104mg,0.45mmol), EDCI (155mg,0.81mmol) and HOBt (107mg,0.79mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and TEA (0.16mL,1.1mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. DCM (60mL) was added to the reaction, followed by saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a pale yellow solid (40mg, 17%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=605.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.77(d,J=7.3Hz,1H),7.92–7.80(m,4H),7.68(t,J=7.3Hz,4H),7.58(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),5.15(dd,J=13.7,6.9Hz,1H),5.04(td,J=5.8,2.1Hz,1H),4.93(m,1H),4.21(m,1H),3.80–3.67(m,2H),3.61–3.51(m,3H),3.40(dd,J=11.9,6.9Hz,2H),3.27(q,J=7.5Hz,2H),2.81(m,1H),1.87(dd,J=21.6,11.3Hz,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 112- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (3-methyl-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 1- (2-methyl-4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (100mg,0.46mmol), 1-fluoro-2-methyl-4-nitrobenzene (87mg,0.56mmol), K2CO3(203mg,1.47mmol) were added to DMSO (4mL) in sequence, warmed to 70 ℃ and stirred for 22 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (60mL), washed successively with water (15mL) and saturated NaCl solution (15 mL. times.3), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 8/1) to give a pale yellow solid (100mg, 61%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 351.0[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step two: synthesis of 3-methyl-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline
Pd/C (20mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 1- (2-methyl-4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (118mg,0.34mmol) in MeOH (6mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 23 h. The reaction mixture was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a pale yellow liquid (90mg, 83%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=321.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (3-methyl-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide EDCI (80mg,0.42mmol), HOBt (58mg,0.43mmol), 3-methyl-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline (90mg,0.28mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (77mg,0.34mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 21 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a white powder solid (101mg, 68%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=531.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=6.8Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.53(d,J=6.8Hz,2H),7.42(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.28(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),7.22(s,2H),6.84(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),3.75(s,2H),3.53–3.34(m,3H),3.30(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.45-2.36(m,1H),2.28(s,3H),2.08–1.98(m,1H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 122- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (2-methyl-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 1- (3-methyl-4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (200mg,0.93mmol), 4-fluoro-2-methyl-1-nitrobenzene (174mg,1.12mmol) and K2CO3(386mg,2.79mmol) was dissolved in DMSO (6mL), warmed to 70 ℃ and stirred for 23 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (60mL), and then sequentially with H2O (15mL) and saturated NaCl solution (15 mL. times.3) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 8/1) to give a pale yellow solid (240mg, 74%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 351.3[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2-methyl-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline
Pd/C (40mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 1- (3-methyl-4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (203mg,0.58mmol) in MeOH (6mL) under hydrogen atmosphere and reacted at room temperature for 21 h. The reaction solution was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow liquid (93mg, 50%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=321.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (2-methyl-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
HATU (164mg,0.43mmol), TEA (0.10mL,0.70mmol), 2-methyl-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline (93mg,0.29mmol) and 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (79mg,0.35mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a white powder solid (120mg, 78%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=531.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.89(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.0Hz,4H),7.36(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.31(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),6.90(s,1H),6.42(d,J=9.6Hz,1H),6.38(s,1H),3.80(s,2H),3.69(t,J=8.3Hz,1H),3.60–3.51(m,2H),3.50–3.44(m,1H),3.44–3.38(m,1H),3.36–3.31(m,1H),3.11(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.45-2.41(m,1H),2.08(s,3H),1.27(d,J=7.3Hz,3H).
13C NMR(101MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):168.01,146.84,146.08,141.52,137.55,132.81,130.22,128.73,128.17,127.42,126.22,125.52,123.95,113.24,109.70,54.28,50.63,47.53,43.83,33.04,18.42,18.12,7.37.
Example 132- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (3-methoxy-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 1- (2-methoxy-4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (100mg,0.46mmol), 1-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene (193mg,1.13mmol) and K2CO3(380mg,2.75mmol) was dissolved in DMSO (6mL), warmed to 70 ℃ and stirred for 13 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (80mL), and washed with water (15mL) followed by saturated water And NaCl solution (15 mL. times.5), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 8/1) to give a pale yellow solid (180mg, 51%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=367.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 3-methoxy-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline
Pd/C (40mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 1- (2-methoxy-4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (130mg,0.35mmol) in MeOH (6mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 13 h. The reaction mixture was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EA (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a pale yellow solid (90mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=337.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (3-methoxy-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
EDCI (79mg,0.41mmol), HOBT (53mg,0.39mmol), 3-methoxy-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline (92mg,0.27mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (76mg,0.33mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at RT for 23 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a white powder solid (108mg, 72%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=547.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.53(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=7.9Hz,3H),7.29(s,1H),6.80(s,1H),6.68(s,1H),3.80(s,2H),3.76(s,3H),3.68–3.58(m,1H),3.58–3.42(m,3H),3.42–3.25(m,1H),3.11(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.44–2.34(m,1H),2.10–1.98(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
13C NMR(151MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):167.20,150.37,147.60,141.12,137.38,136.40,130.25,128.67,127.63,125.39,125.12,123.31,114.88,112.43,105.11,57.72,55.65,50.61,50.50,44.13,43.60,32.93,7.37.
Example 14N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -3-methoxy-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodo-3-methoxybenzamide
(4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (1.44g,7.23mmol), 4-iodo-3-methoxybenzoic acid (1.00g,3.60mmol), EDCI (1.04g,5.43mmol) and HOBt (729mg,5.40mmol) were dissolved in a solution of DCM (32mL) and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was then concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a white solid (1.55g, 94%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 359.9[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step two: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -3-methoxy-4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
N23- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (81mg,0.38mmol), N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodo-3-methoxybenzamide (266mg,0.58mmol), Pd, with protection2(dba)3(50mg,0.05mmol), XantPhos (61mg,0.11mmol) and Cs2CO3(241mg,0.74mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (8mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 2 h. The reaction was then cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and DCM (40mL) was added to the residue, which was then washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a white powder (50mg, 24%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=547.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.80(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.49(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=1.7Hz,1H),7.41(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.30(dd,J=8.3,1.8Hz,1H),6.74(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.63(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),4.71(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),3.85(s,3H),3.83(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),3.71-3.64(m,1H),3.62-3.56(m,2H),3.54-3.48(m,1H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.43–2.35(m,1H),2.15–2.01(m,1H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 15N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -3- (methoxymethyl) -4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4-bromo-N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -3- (methoxymethyl) benzamide
4-bromo-3- (methoxymethyl) benzoic acid (300mg,1.22mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (360mg,1.81mmol) and HATU (688mg,1.81mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 22 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and then with saturated NaHCO in sequence3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give the product as a white solid (305mg, 58%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=428.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -3- (methoxymethyl) -4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (81mg,0.38mmol), 4-bromo-N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -3- (methoxymethyl) benzamide (241mg,0.57mmol), Pd were added under nitrogen 2(dba)3(36mg,0.04.0mmol), XantPhos (44mg,0.08mmol) and Cs2CO3(643mg,0.97mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (8mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was diluted with DCM (40mL) and then with saturated NaHCO in sequence3The solution (15mL) and saturated NaCl solution (15mL) were washed,anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a white solid (40mg, 19%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.79(d,J=2.1Hz,1H)7.77(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.71(dd,J=8.6,2.1Hz,1H),7.59(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.47(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.40(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.86(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.76(d,J=8.7Hz,1H),4.69(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.49(q,J=11.6Hz,2H),3.86-3.80(m,1H),3.84-3.61(m,2H),3.58-3.53(m,2H),3.36(s,3H),3.07(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.44-2.39(m,1H),2.16-2.09(m,1H),1.24(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 162- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (5- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-2-yl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 2-nitro-5- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridine
Under the protection of nitrogen, 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (800mg,3.72mmol), 5-bromo-2-nitropyridine (900mg,4.43mmol), Pd were added2(dba)3(339mg,0.36mmol), XantPhos (243mg,0.41mmol) and Cs2CO3(2.50g,7.67mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 120 ℃ for 8 h. The reaction was cooled to rt, filtered, the filtrate concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give the product as a yellow solid (560mg, 45%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=338.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 5- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-2-amine
Pd/C (86mg, 5%) was added to a solution of 2-nitro-5- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridine (560mg,1.66mmol) in MeOH (50mL) and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5h under hydrogen. The reaction solution was filtered through celite, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a brown solid (400mg, 78%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=308.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (5- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-2-yl) acetamide
5- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-2-amine (400mg,1.30mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (350mg,1.53mmol), EDCI (400mg,2.04mmol) and HOBt (300mg,2.15mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) and stirred at RT for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and then with saturated NaHCO in sequence3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (160mg, 24% Yield).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=518.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.32(s,1H),8.08(d,J=9.0Hz,1H),7.91(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.66–7.52(m,5H),7.40(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.96(dd,J=9.0,2.7Hz,1H),3.82(s,2H),3.74(t,J=8.3Hz,1H),3.68–3.57(m,1H),3.54(td,J=8.7,3.4Hz,1H),3.46(dd,J=16.1,8.3Hz,1H),3.38(t,J=8.3Hz,1H),3.13(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.50(dt,J=10.4,6.8Hz,1H),2.18(dq,J=12.3,8.3Hz,1H),1.31(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 172- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 5-nitro-2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridine
Under the protection of nitrogen, 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (800mg,3.72mmol), 2-bromo-5-nitropyridine (900mg,4.43mmol), Pd were added2(dba)3(339mg,0.36mmol), XantPhos (243mg,0.41mmol) and Cs2CO3(2.50g,7.67mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and heated to 120 ℃ with stirring for 8 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a pale yellow solid (600mg, 48%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=338.6[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine
Pd/C (680mg, 5%) was added to a solution of 5-nitro-2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridine (600mg,1.78mmol) in MeOH (50mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 5 h. The reaction was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a brown solid (500mg, 91%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=308.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide
6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (450mg,1.46mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (400mg,1.75mmol), EDCI (1.10g,5.62mmol) and HOBT (600mg,4.31mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) under nitrogen and stirred at RT for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (220mg, 29%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=518.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.14(d,J=2.0Hz,1H),8.00(s,1H),7.85(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.37(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.39(d,J=9.1Hz,1H),3.99–3.91(m,1H),3.81(s,2H),3.74–3.66(m,1H),3.54(dt,J=18.2,7.9Hz,3H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.51–2.42(m,1H),2.14(ddd,J=17.6,11.9,8.6Hz,1H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 182- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidin-5-yl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of benzyl 3- (((trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl) oxy) -2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate
Under the protection of nitrogen, Tf is put into a cold bath at-5 ℃ under stirring2O (6.0mL,36mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of 3-oxopyrrolidine-1-carboxylic acid benzyl ester (5.03g,22.90mmol) and DIPEA (8.00mL,48.41mmol) in DCM (50mL) and after 30min the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 3.5 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (40mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1) to give a yellow oily liquid (1.33g, 17%).
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.37(s,5H),5.75(d,J=21.9Hz,1H),5.17(s,2H),4.30(m,3H),3.93(t,J=9.6Hz,1H).
Step two: synthesis of benzyl 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate
Benzyl 3- (((trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl) oxy) -2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (1.33g,3.79mmol), (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) boronic acid (890mg,4.69mmol), Pd (dppf) Cl under nitrogen 2(278mg,0.38mmol) and Cs2CO3(3.70g,11.4mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (14mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue diluted with DCM (80mL) followed by saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, and separating the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/DCM/Et)OAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1), yielding a yellow solid (705mg, 54%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 348.1[ M +1 ═ M]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.61(m,2H),7.48(m,2H),7.39(m,5H),6.28(d,J=19.9Hz,1H),5.21(s,2H),4.59(dd,J=15.6Hz,2H),4.43(m,2H).
Step three: synthesis of 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
Pd/C (700mg, 10%) was added to a solution of benzyl 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (705mg,2.03mmol) in MeOH (10mL) under hydrogen, stirred at rt for 8H, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=216.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 5-nitro-2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine
3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (423mg,1.97mmol) and 2-chloro-5-nitropyrimidine (313mg,1.96mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (10mL), DIPEA (1.0mL,5.80mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with DCM (60mL), and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1) to give a yellow solid (379mg, 57%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=339.1[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidin-5-amine
Pd/C (96mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 5-nitro-2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine (379mg,1.12mmol) in MeOH (10mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere, and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a dark yellow oil (300mg, 87%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=309.1[M+1]+.
Step six: 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl)Synthesis of pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidin-5-yl) acetamide 2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidin-5-amine (300mg,0.97mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (336mg,1.47mmol), EDCI (375mg,1.96mmol) and HOBt (264mg,1.95mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL), TEA (0.54mL,3.90mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) and saturated Na2CO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 3/1/1) to give a yellow solid (395mg, 78%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=519.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):10.12(s,1H),8.52(s,2H),7.84(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.69(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),4.02(dd,J=10.6,7.6Hz,1H),3.78(s,2H),3.77–3.69(m,1H),3.62(dd,J=15.9,8.3Hz,1H),3.58–3.51(m,1H),3.46(dd,J=20.0,9.5Hz,1H),3.30–3.23(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.39(m,1H),2.15–2.01(m,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 192- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 3-methoxy-5-nitro-2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridine
Under the protection of nitrogen, adding K2CO3(386mg,2.79mmol) was added to a solution of 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (200mg,0.93mmol) and 2-fluoro-3-methoxy-5-nitropyridine (238mg,1.38mmol) in DMSO (6mL), and the mixture was stirred at 70 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with EtOAc (60mL) and washed successively with water (15mL) and saturated NaCl solution (15 mL. times.5), and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, filtering, concentrating under reduced pressure, and separating the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent): PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a pale yellow solid (212mg, 62%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=368.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine
Pd/C (40mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 3-methoxy-5-nitro-2- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridine (200mg,0.54mmol) in MeOH (8mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 11 h. The reaction was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give the product as a purple solid (140mg, 76%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=338.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide
TEA (0.10mL,0.70mmol) was added to a solution of 5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (80mg,0.24mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (85mg,0.37mmol) and HATU (136mg,0.36mmol) in DCM (6mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 5 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and then with saturated NaHCO in sequence3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give the product as a white powder solid (70mg, 53%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=548.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.63(s,1H),7.61(s,1H),7.56(d,J=8.0Hz,3H),7.53(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.40(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),4.00(dd,J=10.7,7.7Hz,1H),3.78-3.76(m,2H),3.78(s,3H),3.76(s,3H),3.66(dd,J=10.7,7.7Hz,1H),3.49-3.41(m,1H),3.11(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.36-2.30(m,1H),2.07-1.96(m,2H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 20N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
Under nitrogen, 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (210mg,0.98mmol), methyl 6-chloro-5-methoxynicotinate (192mg,0.95mmol) and K2CO3(386mg,2.79mmol) was dissolved in DMSO (6mL), warmed to 100 ℃ and stirred for 5 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (60mL) and successively with H 2O (15mL) and saturated NaCl solution (15 mL. times.5) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a pale yellow solid (280mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=381.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (140mg,3.34mmol) in H2O (2mL) solution was added to a solution of methyl 5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (250mg,0.66mmol) in MeOH (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 7 h. Adding HCl solution (1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 5, concentrating under reduced pressure, and adding H into the residue2O (15mL) dilution, followed by extraction with EtOAc (30 mL. times.3), combined organic phases and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, filtration and concentration under reduced pressure gave a yellow solid (180mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=367.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
TEA (0.20ml,1.45mmol) was added to 5-methoxy-6- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (150mg,0.41mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) under nitrogen) Phenyl) methylamine (160mg,0.80mmol) and HATU (236mg,0.62mmol) in DCM (6mL) were stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a white powder solid (100mg, 45%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=548.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.22(d,J=1.8Hz,1H),7.75(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=7.8Hz,3H),7.40(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.92(t,J=5.7Hz,1H),4.69(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.19(dd,J=11.3,7.5Hz,1H),4.40-3.94(m,1H),3.90–3.82(m,1H),3.80(s,3H),3.78–3.73(m,1H),3.51–3.41(m,1H),3.07(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.3–2.32(m,1H),2.09–2.02(m,1H),1.24(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 212- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl (2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylate
(2S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1, 2-dicarboxylate (2.00g,5.36mmol) was dissolved in DCM (40mL) and TFA (25mL) and stirred at room temperature for 7 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a pale yellow liquid (910mg, 62%).
Step two: synthesis of methyl (2S) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylate
Under the protection of nitrogen, (2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (910mg,3.33mmol), 1-iodo-4-nitrobenzene (900mg,3.61mmol), Pd2(dba)3(340mg,0.36mmol), XantPhos (243mg,0.41mmol) and Cs2CO3(2.50g,7.67mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and the temperature was raisedStirring for 8h to 100 ℃. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (370mg, 32%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=395.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of ((2S) -1- (4-aminophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol
(2S) -methyl 1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylate (370mg,0.94mmol) was dissolved in THF (30mL) under nitrogen, and LiBH was added slowly with stirring at room temperature4The THF solution of (1.0mL,2.00mmol,2mol/L) was stirred at room temperature for 6h after the addition was completed. The reaction was transferred to ice bath and saturated NH was added dropwise to the reaction system4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, and the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (20 mL). The organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a colorless transparent liquid (160mg, 47%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=337.2[M+1]+;
Step four: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
((2S) -1- (4-aminophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (80mg,0.23mmol),2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (100mg,0.44mmol), EDCI (100mg,0.51mmol) and HOBt (100mg,0.51mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction system 3The reaction was quenched with solution (30mL), separated, and the organic phase was successively treated with H2O (50mL) and saturated NaCl solution (50mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (62mg, 49%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=547.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.36(dd,J=14.3,9.6Hz,1H),7.32–7.26(m,2H),6.74–6.49(m,2H),4.04(dt,J=12.8,9.9Hz,1H),3.88(dd,J=10.7,3.0Hz,1H),3.76(s,2H),3.71(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),3.68–3.60(m,1H),3.61–3.48(m,1H),3.41(dt,J=26.7,9.1Hz,1H),3.11(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.66–2.47(m,1H),2.34(dd,J=19.6,11.8Hz,1H),1.28(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 222- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2R) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl (2R) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylate
(2R) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1, 2-dicarboxylate (2.01g,5.40mmol) was dissolved in DCM (50mL) and TFA (25mL) and stirred at room temperature for 5 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and then with saturated NaHCO in sequence3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a pale yellow liquid (800mg, 54%).
Step two: synthesis of methyl (2R) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylate
Under the protection of nitrogen, (2R) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (800mg,2.93mmol), 1-iodo-4-nitrobenzene (900mg,3.61mmol), Pd2(dba)3(339mg,0.36mmol), XantPhos (243mg,0.41mmol) and Cs 2CO3(2.50g,7.67mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 8 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (560mg, 49%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=395.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of ((2R) -1- (4-aminophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol
(2R) -1- (4-Nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (370mg,0.94mmol) was dissolved in THF (32mL) under nitrogen and slowly added LiBH while stirring at room temperature4The THF solution of (1.0mL,2.00mmol,2mol/L) was stirred at room temperature for 6h after the addition was completed. The reaction was transferred to ice bath and saturated NH was added dropwise to the reaction system4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, and the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (20 mL). The organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a colorless transparent liquid (110mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=337.2[M+1]+;
Step four: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2R) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
((2R) -1- (4-aminophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (110mg,0.33mmol),2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (100mg,0.44mmol), EDCI (100mg,0.51mmol) and HOBt (80mg,0.57mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction system 3The reaction was quenched with solution (30mL), separated, and the organic phase was successively treated with H2O (50mL) and saturated NaCl solution (50mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a light yellow solid (20mg, 11%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=547.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.81(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.75(s,1H),7.57(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.49(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.46–7.38(m,2H),7.28(s,1H),6.59(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),4.08–3.95(m,1H),3.81(dt,J=16.9,8.5Hz,1H),3.70(s,3H),3.64(d,J=11.3Hz,1H),3.58–3.46(m,1H),3.39(dt,J=17.2,8.6Hz,1H),3.09(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.61–2.48(m,1H),2.32(dd,J=19.8,11.6Hz,1H),2.04(d,J=4.0Hz,1H),1.26(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 232- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
NaH (10mg,0.25mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of ((2S) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (80mg,0.22mmol) in THF (10mL) with stirring in a cold bath at-20 ℃ under nitrogen, after 2h MeI (0.10mL,2.00mmol) was added slowly and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Adding NaHCO into the reaction system3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove organic solvent, the residue was extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4The crude product was dried and isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (70mg, 84%).
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline
Pd/C (860mg, 5%) was added to a solution of (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (80mg,0.21mmol) in MeOH (50mL) under hydrogen atmosphere, and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM (v/v) ═ 1/10) to give a yellow solid (70mg, 95%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=351.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline (80mg,0.23mmol),2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (100mg,0.44mmol), EDCI (100mg,0.44mmol) under nitrogen34mmol) and HOBt (80mg,0.51mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) and stirred at room temperature for 8 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (30mL), separated, and the organic phase was successively treated with H2O (50mL) and saturated NaCl solution (50mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (50mg, 39%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.55(dd,J=18.4,8.1Hz,4H),7.42(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.38(s,1H),7.31(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),6.62(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),4.04(s,1H),3.75(s,2H),3.70(t,J=8.3Hz,1H),3.62(dd,J=9.4,2.8Hz,1H),3.54(dd,J=17.1,8.3Hz,1H),3.47–3.36(m,1H),3.33(dd,J=10.8,3.8Hz,1H),3.30(s,3H),3.11(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.72–2.60(m,1H),2.18(ddd,J=12.5,10.2,7.2Hz,1H),1.27(d,J=7.6Hz,3H).
Example 24N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
NaH (40mg,1.00mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of tert-butyl (2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (250mg,0.72mmol) in anhydrous THF (12mL) under cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen, after 2h MeI (0.20mL,3.0mmol) was slowly added and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction was then diluted with DCM (50mL) and then saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give the product as a white solid (150mg, 58%).
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
A solution of HCl in EtOAc (6.5mL,6.5mmol,1.0M) was added to a solution of tert-butyl (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (150mg,0.417mmol) in DCM (50mL) and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 2 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to give the product as a pale yellow liquid (105mg, 97%).
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
Under nitrogen protection, (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (105mg,0.40mmol), N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodobenzamide (150mg,0.35mmol), Pd2(dba)3(50mg,0.053mmol), XantPhos (30mg,0.050mmol) and Cs2CO3(500mg,1.50mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 8 h. The reaction was then cooled to rt, filtered, the filtrate concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give the product as a pale yellow solid (28mg, 12%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.77(t,J=7.7Hz,4H),7.60(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.49(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.66(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),4.69(d,J=5.7Hz,2H),4.15(dd,J=7.7,5.6Hz,1H),3.86–3.79(m,1H),3.63(dd,J=9.4,2.6Hz,1H),3.54(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.42(ddd,J=19.1,16.4,9.5Hz,2H),3.31(s,3H),3.07(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.74–2.61(m,1H),2.23(ddd,J=23.4,14.4,9.2Hz,1H),1.28(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 25N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
NaH (60mg,1.50mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of tert-butyl (2R) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (275mg,0.79mmol) in anhydrous THF (12mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen, after 2h MeI (0.30mL,5.0mmol) was slowly added and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction was then diluted with DCM (50mL) and then saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give the product as a white solid (320mg, 81%).
Step two: synthesis of (2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
A solution of HCl in EtOAc (6.5mL,6.5mmol,1.0mol/L) was added to a solution of tert-butyl (2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (320mg,0.89mmol) in DCM (60mL) and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to give the product as a pale yellow liquid (195mg, 85%).
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
Under the protection of nitrogen, (2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (80mg,0.40mmol), N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodobenzamide (150mg,0.35mmol), Pd2(dba)3(50mg,0.053mmol), XantPhos (23mg,0.038mmol) and Cs2CO3(500mg,1.50mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to rt, filtered, the filtrate concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give the product as a pale yellow solid (31mg, 18%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.80(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.67(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),4.71(d,J=5.8Hz,2H),4.27–4.03(m,1H),3.83(t,J=8.3Hz,1H),3.64(dd,J=9.3,2.3Hz,1H),3.53(dd,J=19.7,10.3Hz,1H),3.50–3.35(m,2H),3.31(s,3H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.77–2.58(m,1H),2.23(dt,J=17.9,10.2Hz,1H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 264- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
NaH (3mg,0.075mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide (21mg,0.038mmol) in THF (5mL) with stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen, after 10min EtI (0.30mL,4.0mmol) was slowly added, the temperature was raised to room temperature and stirred for 10h the reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), and saturated NaHCO was used3The solution (35mL) was washed and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4The crude product was dried and isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a white foamy solid (15mg, 68%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=575.6[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.73(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.69(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),6.46(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),4.74(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.23–4.14(m,1H),3.88–3.80(m,1H),3.70(dd,J=9.6,3.0Hz,1H),3.55(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.50–3.38(m,4H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.78–2.67(m,1H),2.24(ddd,J=11.2,10.2,5.6Hz,1H),1.29(d,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.16(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).
Example 27N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
Under nitrogen protection ((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (2.20g,8.97mmol), 4-iodobenzonitrile (1.89g,8.25mmol), Pd2(dba)3(400mg,0.42mmol), XantPhos (270mg,0.45mmol) and Cs2CO3(6.02g,18.50mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (55mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to rt, filtered, the filtrate concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1/1) to give a yellow solid (1.18g, 38%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=347.5[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (110mg,2.75mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (505mg,1.46mmol) in DMF (16mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen and after 5min 1-fluoro-2-iodoethane (1.50mL) was added slowly and stirring continued at this temperature for 3 h. The reaction solution was warmed to room temperature, ice water (30mL) was added to the system to quench the reaction, the mixture was extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (332mg, 58%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 393.2[ M +1 ═ 393.2]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- ((2S) -2- ((2-Fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (225mg,0.57mmol) and NaOMe (550mg,9.88mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (8mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 25 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, the residue was added to HCl solution (10mL,0.5mol/L), the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), and combined The organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a yellow solid (200mg, 85%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=412.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.30mL,2.00mmol) was added to a solution of (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (70mg,0.35mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (105mg,0.26mmol) and HATU (140mg,0.36mmol) in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (25mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (29mg, 19%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 593.1[ M +1 ═ M]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.80(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.45&7.42(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.67(d,J=8.4Hz,3H),4.71(d,J=5.8Hz,2H),4.57(dt,J=47.6,4.0Hz,2H),4.20(dd,J=15.4,7.6Hz,1H),3.98–3.70(m,3H),3.66(dd,J=13.6,8.2Hz,1H),3.62–3.53(m,2H),3.48(dd,J=16.9,8.2Hz,1H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.80–2.67(m,1H),2.38–2.21(m,1H),1.26(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 284- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (100mg,2.50mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (505mg,1.46mmol) in DMF (16mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen and after 1h bromomethylcyclopropane (0.5mL) was slowly added and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction was quenched by adding ice water (120mL) to the reaction system, followed by extraction with DCM (50 mL. times.2), and the combined organic phases were washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (422mg, 72%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=401.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (422mg,1.05mmol) and NaOMe (550mg,9.86mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (8mL) and warmed to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) was added to the residue with ice-bath cooling, then the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give the product as a yellow solid (210mg, 48%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=420.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.50mL,3.0mmol) was added to a solution of (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (95mg,0.48mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (151mg,0.36mmol) and HATU (169mg,0.43mmol) in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 13 h. The reaction was then quenched with DCM (20 m)L) and then successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L), saturated NaHCO3The solution (25mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) and preparative chromatography (developer: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (65mg, 30%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=601.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.79(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.48(t,J=9.1Hz,4H),6.68(d,J=8.8Hz,3H),4.71(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),4.25–4.11(m,1H),3.83(t,J=8.3Hz,1H),3.71(dt,J=12.0,6.0Hz,1H),3.56(t,J=9.3Hz,1H),3.47(dt,J=9.5,7.8Hz,2H),3.29–3.15(m,2H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.74(dt,J=14.9,7.6Hz,1H),2.26(ddd,J=12.6,10.1,7.0Hz,1H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.03–0.92(m,1H),0.49(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),0.15(d,J=4.3Hz,2H).
Example 29N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (propoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (propoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
NaH (110mg,2.75mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (505mg,1.33mmol) in DMF (6mL) under nitrogen in ice bath and after 5min 1-bromopropane (1.5mL) was slowly added and the reaction stirred at this temperature for a further 3 h. Then, the reaction mixture was warmed to room temperature, poured into ice water (30mL), the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, washed with a saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), and dried over Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (332mg, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=422.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (propoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (propoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (210mg,0.50mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2O (10mL/4mL) solution, warmed to 55 ℃ and stirred for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, slowly added dropwise with HCl solution (6mol/L) in ice bath, adjusted to pH 6 or so, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (110mg, 54%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=408.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (propoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.50mL,3.00mmol) was added to a solution of (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (110mg,0.55mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (propoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (105mg,0.26mmol) and HATU (100mg,0.26mmol) in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL) and successively with HCl solution (10mL,0.1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was separated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) and preparative chromatography (developing solvent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a white solid (40mg, 26%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=589.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.80(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.68(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),6.64(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),4.71(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.19(qd,J=7.1,3.1Hz,1H),3.87–3.79(m,1H),3.68(dd,J=9.6,2.9Hz,1H),3.55(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.50–3.41(m,2H),3.40–3.26(m,2H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.72(dt,J=13.1,7.6Hz,1H),2.26(ddd,J=12.7,10.3,7.0Hz,1H),1.59–1.49(m,2H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.88(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 304- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
NaH (110mg,2.75mmol, 60%) was added under nitrogen protection to a solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (455mg,1.20mmol) in DMF (5mL) in ice bath and after 5min 1-bromobutane (1.5mL) was added slowly and stirring continued at this temperature for 10 h. The reaction was then quenched by adding water (30mL), the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a light yellow oil (162mg, 31%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=436.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (210mg,0.48mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2In O (5mL/3mL), the mixture was stirred at 65 ℃ for 12 hours. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, water (10mL) was added to the residue, HCl solution (6mol/L) was slowly added dropwise with cooling in an ice bath to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, and then extracted with EtOAc (50mL), and the organic phase was extracted with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) ) Washing with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (110mg, 54%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 422.2[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.50mL,3.0mmol) was added to a solution of (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (70mg,0.35mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (75mg,0.18mmol) and HATU (100mg,0.26mmol) in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with HCl solution (10mL,0.1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (15mL) and saturated NaCl solution (10mL) were washed and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (40mg, 37%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 603.1[ M +1 ═ M]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.79(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.49(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.67(d,J=8.7Hz,3H),4.72(t,J=6.6Hz,2H),4.18(q,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.88–3.77(m,1H),3.67(dd,J=9.6,2.8Hz,1H),3.54(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.50–3.29(m,4H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.71(dt,J=14.9,7.6Hz,1H),2.25(ddd,J=12.6,10.2,7.0Hz,1H),1.55–1.45(m,2H),1.33(dt,J=15.6,4.2Hz,2H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.88(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 31N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((2-methoxyethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-methoxyethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (55mg,1.38mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (255mg,0.74mmol) in DMF (6mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen and after 1h 1-bromo-2-methoxyethane (0.30mL,3.00mmol) was added slowly and stirred at room temperature for 5 h. Ice water (120mL) was added to the reaction mixture, extraction was performed with DCM (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined, washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow oil (122mg, 41%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=405.5[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-methoxyethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- ((2S) -2- ((2-methoxyethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (120mg,0.30mmol) and NaOMe (350mg,6.28mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (7mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 10 h. The reaction was then cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, HCl solution (30mL,1mol/L) was added to the residue, then the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a tan solid (120mg, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=424.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((2-methoxyethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.50mL,3.0mmol) was added to a solution of (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (80mg,0.40mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-methoxyethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (120mg,0.28mmol) and HATU (500mg,1.30mmol) in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30 mL. times.2) and a saturated NaCl solution (30mL) were washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (45mg, 26%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=605.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.76(d,J=8.4Hz,4H),7.59(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.47(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.80(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.65(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.69(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),4.25–4.11(m,1H),3.88(t,J=8.5Hz,1H),3.81–3.69(m,2H),3.69–3.59(m,2H),3.58–3.53(m,2H),3.49(t,J=9.0Hz,1H),3.39(s,3H),3.24(t,J=9.6Hz,1H),3.07(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.50(dd,J=12.4,6.4Hz,1H),2.22(td,J=12.2,8.2Hz,1H),1.24(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 324- ((2S) -2-Ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2R) -tert-butyl 2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate
Dess-Martin reagent (1.54g,3.59mmol) was added to a solution of tert-butyl (2R) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (255mg,0.74mmol) in DCM (42mL) and stirred at RT for 6 h. The reaction was filtered and saturated NaHCO was added slowly under ice-bath 3The solution (100mL) was then extracted with DCM (150 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined, washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a colorless liquid (150mg, 59%).
Step two: synthesis of (2R) -tert-butyl 4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2-vinylpyrrolidine 1-carboxylate
NaH (220mg,5.50mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of methyl (triphenyl) phosphonium bromide (1.55g,4.34mmol) in anhydrous THF (82mL) under nitrogen with cooling and stirring at-20 ℃ after 2h(2R) -tert-butyl 2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate (800mg,2.33mmol) was added slowly and after addition the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 5 h. Adding saturated NH to the reaction liquid4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (20mL), concentrated under reduced pressure, the residue was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a colorless liquid (620mg, 42%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=286.1[M+1-56]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl-2-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate
Pd/C (760mg, 5%) was added to a solution of (2R) -tert-butyl 4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2-vinylpyrrolidine 1-carboxylate (220mg,0.64mmol) in MeOH (50mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 2 h. The reaction mixture was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a colorless oily liquid (100mg, 45%).
Step four: synthesis of (2S) -2-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
A solution of HCl in EtOAc (3.5mL,3.50mmol,1mol/L) was added to a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate (100mg,0.29mmol) in DCM (50mL) and stirred at room temperature for 1 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a pale yellow liquid (55mg, 77%).
Step five: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
Under nitrogen protection, (2S) -2-ethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (80mg,0.33mmol), N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodobenzamide (150mg,0.35mmol), Pd2(dba)3(33mg,0.04mmol), XantPhos (20mg,0.03mmol) and Cs2CO3(500mg,1.50mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 8 h. Cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, filtering, concentrating the filtrate under reduced pressure, separating the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1), to obtainTo a brown solid (8mg, 4%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=545.6[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.73(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.42(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),6.61(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),6.44–6.37(m,1H),4.74(d,J=5.7Hz,2H),3.96–3.88(m,1H),3.88–3.81(m,1H),3.57–3.50(m,1H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.75–2.65(m,1H),2.35(t,J=7.6Hz,2H),2.25–2.19(m,1H),1.30(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.88(t,J=6.6Hz,3H).
Example 33N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DAST (0.14mL,1.0mmol) was added to a solution of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide (45mg,0.082mmol) in DCM (42mL) with stirring at room temperature under nitrogen and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 3.5 h. Saturated NaHCO was slowly added to the system 3The solution (100mL) was then extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) and preparative plate chromatography on silica gel (developer: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give the product as a colourless liquid (15mg, 33% Yield).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=549.5[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.79(dd,J=25.4,7.6Hz,4H),7.63(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=7.2Hz,2H),7.40(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),6.93(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.61(s,1H),4.87(t,J=12.7Hz,1H),4.72(d,J=5.2Hz,2H),4.19(d,J=7.4Hz,1H),3.85(d,J=11.3Hz,1H),3.09(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.05–2.99(m,1H),2.89(dd,J=27.8,15.5Hz,2H),2.52(d,J=10.3Hz,1H),2.04–1.83(m,1H),1.27(d,J=7.4Hz,3H).
19F NMR(376MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):-62.54(s),-180.90(s).
Example 344- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
Dess-Martin reagent (200mg,0.47mmol) was added to a solution of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide (100mg,0.18mmol) in DCM (42mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction solution was filtered, and saturated NaHCO was slowly added to the filtrate under ice-cooling3The solution (100mL) was then extracted with DCM (150 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (55mg, 55%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=545.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
DAST (0.20mL,1.00mmol) was added slowly under nitrogen to a solution of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide (125mg,0.23mmol) in DCM (42mL) and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The solution (100mL) was extracted with DCM (150 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4The crude product was dried and chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give the product as a white solid (20mg, 15%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=567.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.78(dd,J=8.5,5.5Hz,4H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.46(dd,J=13.5,8.2Hz,4H),6.74(d,J=8.6Hz,3H),6.00(ddd,J=57.5,55.2,2.4Hz,1H),4.71(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.44(dt,J=15.2,7.3Hz,1H),3.92(t,J=8.0Hz,1H),3.56(dd,J=18.3,8.9Hz,1H),3.49(dd,J=17.8,9.5Hz,1H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.68(dt,J=15.4,7.9Hz,1H),2.41(ddd,J=13.1,10.2,6.8Hz,1H),1.24(d,J=7.4Hz,3H).19F NMR(376MHz,CDCl3)δ-62.52(s),-126.74(dd,J=2020.5,286.2Hz).
Example 35N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (3-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of tert-butyl 4-methyl-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate
Under nitrogen protection, tert-butyl 3-methyl-2, 5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (2.80g,15mmol), 1-bromo-4- (trifluoromethyl) benzene (707mg,3.14mmol), Pd (P (o-Tol)3)2(OAc)2(590mg,0.63mmol),Ag2CO3(897mg,3.25mmol) and DIPEA (2mL,12.10mmol) were dissolved in DMF (15mL) and stirred at 130 ℃ for 18 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure to remove DMF, the residue was taken up in saturated NaCl solution (80mL) and extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.3), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a grey oil (860mg, 84%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=272.1[M+1-56]+.
Step two: synthesis of tert-butyl 3-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
Pd/C (3.25g, 10%) was added to a solution of tert-butyl 4-methyl-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (991mg,3.03mmol) in MeOH (15mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 24H. Celite was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a grey oil (981mg, 98%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=274.0[M+1-56]+.
Step three: synthesis of 3-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
Tert-butyl 3-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (981mg,2.98mmol) was dissolved in DCM (15mL) and TFA (8mL) under ice-bath and stirred at RT for 12 h. Concentrating under reduced pressure, adding saturated NaHCO into the residue3The pH of the solution is adjusted to about 8, and then the solution is extracted by EtOAc (30mL multiplied by 3) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 8/1) to give a yellow oil (231mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=230.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (3-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
Under nitrogen protection, 3-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (141mg,0.62mmol), N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodobenzamide (543mg,1.26mmol), Pd 2(dba)3(133mg,0.15mmol), XantPhos (172mg,0.30mmol) and NaOt-Bu (127mg,1.32mmol) were dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (8mL) and the reaction was heated to 110 ℃ by microwave for 4 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, the solvent was removed, water (50mL) was added to the residue to dissolve the solid, which was then extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a grey solid (111mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=531.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.80(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),7.83(t,J=9.1Hz,4H),7.69(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.37(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.65(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.55(d,J=5.8Hz,2H),3.77(tt,J=8.8,4.5Hz,1H),3.67(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),3.59(dd,J=9.7,7.0Hz,1H),3.26(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.06(dd,J=9.7,6.8Hz,1H),2.80(dt,J=13.5,6.7Hz,1H),1.99(dt,J=13.5,6.9Hz,1H),1.09(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.68(d,J=6.9Hz,3H).
Example 364- ((2S) -2- ((dimethylamino) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide (60mg,0.11mmol) and dimethylamine hydrochloride (40mg,0.49mmol) were dissolved in anhydrous EtOH (17mL), stirred at room temperature for 1h, NaBH added3CN (40mg,0.60mmol), the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 5 h. The reaction solution is concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue is saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) and EtOAc (30mL) were dissolved, separated, and the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (25mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) and preparative plate chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc/MeOH (v/v) ═ 5/4/1) to give a white solid (16mg, 25% Yield).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=574.7[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.82(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.51(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.69(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),6.63(t,J=5.5Hz,1H),4.72(d,J=5.7Hz,2H),4.16(dd,J=13.3,6.7Hz,1H),3.89–3.77(m,1H),3.57(t,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.52–3.40(m,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.82(dd,J=12.1,8.1Hz,2H),2.37(s,6H),2.33–2.17(m,2H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 37N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide (44mg,0.081mmol) and tetrahydropyrrole (0.05mL,0.60mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (22mL), stirred at room temperature for 1h, then NaBH was added3CN (100mg,1.51mmol), the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) and preparative chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc/MeOH (v/v) ═ 2/2/1) to give the product as a pale yellow solid (30mg, 62%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=600.8[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.45(t,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.68(dd,J=16.5,8.7Hz,2H),6.56(d,J=5.7Hz,1H),4.75(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.16(d,J=7.2Hz,1H),3.95–3.83(m,1H),3.55(dd,J=21.6,12.0Hz,1H),3.52–3.41(m,1H),3.11(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.86–2.74(m,1H),2.73–2.63(m,2H),2.56–2.45(m,1H),2.26(ddd,J=19.7,13.9,7.3Hz,2H),1.83(d,J=10.9Hz,4H),1.29(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 38N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -1- (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (2.00g,46.70mmol) was added to (2S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1, 2-dicarboxylate (4.00g,10.70mmol) in MeOH/H2O (10mL/27mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction solution is decompressed and concentrated, HCl solution (6mol/L) is slowly dropped to adjust the pH of the system to about 6 under ice bath, then EtOAc (50mL) is used for extraction, and an organic phase is washed by saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) to give a yellow solid (2.32g, 60%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=304.2[M-56+1]+;
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
DIPEA (0.70mL,3.94mmol) was added to a solution of morpholine (0.80mL,9.00mmol), (2S) -1- (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (1.54g,4.29mmol) and HATU (2.25g,5.74mmol) in DCM (55mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (1.45g, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=329.2[M-1+100]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate
Under ice bath, BH is added3·SMe2To a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (1.45g,3.38mmol) in THF (40mL) was added dropwise a solution of THF (2.0mL,20mmol,2.0mol/L) and stirred at room temperature for 6h after the addition. Slowly dropwise adding saturated NH into the system under ice bath 4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, Na anhydrous2SO4The crude product was dried and chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (1.31g, 93%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=415.0[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- (((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methyl) morpholine
A solution of HCl in EtOAc (12mL,1mol/L) was added to a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate (1.33g,3.21mmol) in DCM (15mL) and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Concentration under reduced pressure gave the hydrochloride salt of the product as a pale yellow solid (884mg, 100%).
Step five: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, 4- (((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methyl) morpholine (385mg,1.22mmol), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (450mg,2.09mmol), Pd2(dba)3(120mg,0.13mmol), RuPhos (60mg,0.12mmol) and Cs2CO3(850mg,2.60mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (45mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (430mg, 78%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=449.3[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (430mg,0.96mmol) and LiOH. H2O (1.25g,29.20mmol) in THF/H2In O (16mL/16mL), the temperature was raised to 55 ℃ and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, the pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to about 4 by slowly adding dropwise HCl solution (6.0mol/L) to the residue, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (25 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (300mg, 72%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=435.2[M+1]+.
Step seven: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.60mL,3.00mmol) was added under nitrogen to 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (195mg,0.45mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (120mg,0.60mmol) and HATU (240mg, 0.00 mmol)61mmol) in DCM (25mL) and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3Aqueous solution (25mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (69mg, 25%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=616.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.84(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.74(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.53(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.68(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),6.50(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),4.73(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.13(dd,J=11.3,5.6Hz,1H),3.88–3.80(m,1H),3.70(s,4H),3.57(t,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.51–3.39(m,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.73(dd,J=11.9,8.3Hz,2H),2.58–2.40(m,4H),2.35(dd,J=12.6,7.8Hz,1H),2.30–2.20(m,1H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 39 methyl (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate
Under the protection of nitrogen, (2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (510mg,1.87mmol), N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodobenzamide (789mg,1.84mmol), Pd2(dba)3(120mg,0.13mmol), RuPhos (120mg,0.24mmol) and Cs2CO3(1.20g,3.68mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (55mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to rt, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) and silica gel preparative plate chromatography (developing solvent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/5) to give the product as a white solid (168mg, 16%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=575.7[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.73(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.51(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),6.56(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.71(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.54(t,J=7.9Hz,1H),4.00–3.91(m,1H),3.71(s,3H),3.70–3.64(m,1H),3.59(ddd,J=17.5,9.8,7.7Hz,1H),3.09(q,J=7.5Hz,2H),2.91(dt,J=12.9,7.5Hz,1H),2.30(ddd,J=12.5,10.8,8.1Hz,1H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 40(2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
Methyl (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (100mg,0.17mmol) and LiOH. H 2O (151mg,3.60mmol) in MeOH/H2O (10mL/4mL), the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction mixture was added dropwise to HCl solution (1mol/L) to adjust the pH of the solution to about 4, followed by extraction with EtOAc (25mL × 2), and the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, filtration and concentration under reduced pressure gave the crude product which was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 5/1) and silica gel preparative plate chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 7/1) to give the product as a white solid (54mg, 55%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.60(d,J=6.2Hz,4H),7.53(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),7.36(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.29(d,J=7.1Hz,2H),6.40(d,J=6.4Hz,2H),4.46(s,2H),4.35(s,1H),3.94–3.70(m,1H),3.49(dd,J=21.4,9.3Hz,2H),2.98(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.88–2.68(m,1H),2.27-2.14(m,1H),1.14(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 41(2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
DIPEA (0.40mL,2.0mmol) was added to (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxylic acid (100mg,0.18mmol), NH under nitrogen4A solution of Cl (109mg,1.79mmol) and HATU (0.15g,0.38mmol) in DCM (17mL) was stirred at RT for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) were washed and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, filtration, concentration under reduced pressure and column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) and preparative plate chromatography on silica gel (developing agent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) afforded a white solid (88mg, 80%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=560.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.80(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.60(s,1H),7.55(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.13(s,1H),6.58(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.55(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),4.24(t,J=8.1Hz,1H),3.97(t,J=7.1Hz,1H),3.60(dd,J=16.2,7.4Hz,2H),3.25(q,J=7.6Hz,2H),2.88–2.77(m,1H),2.09(dd,J=20.3,11.4Hz,1H),1.08(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 42(2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
DIPEA (0.40mL,2.0mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (96mg,0.17mmol), methylamine hydrochloride (79mg,1.17mmol) and HATU (0.15g,0.38mmol) in DCM (17mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was then diluted with DCM (40mL) followed by dilute HCl solution (20mL,0.5mol/L),Saturated NaHCO3The aqueous solution (30mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) were washed, and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) and preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a white solid (40mg, 41%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=574.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.80(t,J=5.7Hz,1H),8.06(dd,J=8.7,4.1Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),6.57(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),4.54(d,J=5.5Hz,2H),4.27(t,J=7.9Hz,1H),3.98(t,J=6.7Hz,1H),3.67–3.55(m,2H),3.27(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.84–2.75(m,1H),2.56(d,J=4.5Hz,3H),2.07(dd,J=19.8,9.8Hz,1H),1.08(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 43(2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxamide
DIPEA (0.40mL,2.0mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (96mg,0.17mmol), dimethylamine hydrochloride (59mg,0.72mmol) and HATU (150mg,0.38mmol) in DCM (17mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was then diluted with DCM (100mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (30mL), water (30mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) were washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, filtration, concentration under reduced pressure and chromatography of the crude product on two silica gel columns (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) and preparative chromatography (developer: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) afforded a white solid (75mg, 74%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=588.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δδ(ppm):7.77(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.45(s,4H),6.84(t,1H),6.42(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),4.84(t,J=7.8Hz,1H),4.64(d,J=5.0Hz,2H),3.97(t,J=8.2Hz,1H),3.67(t,J=9.7Hz,1H),3.54(dt,J=25.1,8.6Hz,1H),3.19(s,3H),3.07(q,J=7.2Hz,2H),2.97(s,3H),2.93–2.81(m,1H),2.16(dd,J=20.5,11.5Hz,1H),1.24(t,J=7.1Hz,3H).
Example 44(2S) -N, N-diethyl-1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
DIPEA (0.40mL,2.0mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (100mg,0.18mmol), diethylamine (79mg,1.08mmol) and HATU (0.15g,0.38mmol) in DCM (17mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The aqueous solution (30mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) were washed, and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) and preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (88mg, 80%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=616.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.76(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.1Hz,4H),6.93(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.43(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.77(t,J=7.9Hz,1H),4.62(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),3.96(t,J=8.4Hz,1H),3.67(t,J=9.8Hz,1H),3.6--3.55(m,1H),3.53-3.45(m,2H),3.44–3.30(m,2H),3.06(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.86(dt,J=12.6,7.6Hz,1H),2.16(td,J=11.8,8.4Hz,1H),1.30(t,J=7.1Hz,3H),1.23(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.09(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).
Example 45(2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
DIPEA (0.40mL,2.0mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (96mg,0.17mmol), N-methoxymethanamine hydrochloride (79mg,0.81mmol) and HATU (150mg,0.38mmol) in DCM (17mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3Washed with aqueous solution (30mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) and preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (75mg, 73%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=604.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.73(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),6.99(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.49(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.95(t,J=8.0Hz,1H),4.61(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),3.96(t,J=8.0Hz,1H),3.79(s,3H),3.67–3.48(m,2H),3.19(s,3H),3.05(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.90(dt,J=12.9,7.5Hz,1H),2.21(td,J=11.7,8.6Hz,1H),1.22(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 464- ((2S) -2-acetyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
Cooling and stirring the MeMgBr in the nitrogen at the temperature of-20 ℃ to obtain Et of the MeMgBr2O solution (0.30mL,0.9mmol,3.0mol/L) was added slowly dropwise to (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acidAfter the addition of amine (143mg,0.24mmol) in THF (32mL) for 1h, the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 5 h. The reaction was then quenched by pouring the reaction into HCl solution (15mL,0.5mol/L), diluted with water (30mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove THF, the residue extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases combined and washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4The crude product was dried and isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (40mg, 30%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=559.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.78(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.48(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.90(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.51(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),4.70(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.46(dd,J=9.3,7.6Hz,1H),4.04(t,J=8.5Hz,1H),3.73(t,J=9.8Hz,1H),3.62(dt,J=17.7,8.6Hz,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.88–2.76(m,1H),2.18–2.05(s&m,4H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 47N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((S) -1-hydroxyethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide/N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((R) -1-hydroxyethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
Cooling and stirring the MeMgBr in the nitrogen at the temperature of-20 ℃ to obtain Et of the MeMgBr2O solution (0.2mL,0.6mmol,3.0mol/L) was slowly added dropwise to N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2-formylAfter 3h of addition of the phenyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide (91mg,0.17mmol) in THF (32mL), the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 3 h. The reaction solution was poured into saturated NaHCO3The reaction was quenched in solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove THF, the remaining aqueous solution was extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) and silica gel preparative plate chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give 47-1(10mg, 11%, Rt ═ 11.54min) as a white solid and 47-2(8.3mg, 9%, Rt ═ 11.10min) as a yellow solid.
47-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.81(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.73(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.46(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.65(d,J=8.9Hz,3H),4.72(t,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.46(q,J=6.4Hz,1H),4.05(t,J=7.4Hz,1H),3.89(t,J=8.6Hz,1H),3.55(t,J=10.2Hz,1H),3.38(ddd,J=18.7,11.1,7.7Hz,1H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.55–2.36(m,2H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.22(d,J=6.5Hz,3H).
47-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.80(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.49(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.77(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),6.73(d,J=5.9Hz,1H),4.70(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),4.30–4.08(m,2H),3.97–3.83(m,1H),3.51(t,J=10.1Hz,1H),3.38(dt,J=17.6,8.7Hz,1H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.58(dt,J=14.3,7.2Hz,1H),2.10–2.00(m,1H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.15(d,J=5.8Hz,3H).
Example 484- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
Under nitrogen protection ((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (1.14g,4.65mmol), N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4-iodobenzamide (1.55g,3.61mmol), Pd2(dba)3(200mg,0.21mmol), XantPhos (100mg,0.17mmol) and Cs2CO3(2.95g,9.04mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (60mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 13 h. The reaction was then cooled to room temperature, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (760mg, 30%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=547.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
2, 2-difluoro-2- (fluorosulfonyl) acetic acid (0.30mL,3.00mmol) was added to a suspension of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide (100mg,0.18mmol) and CuI (50mg,0.26mmol) in MeCN (22mL,420mmol) under nitrogen, and the temperature was raised to 55 ℃ and stirred for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was dissolved in DCM (30mL) and then saturated NaHCO 3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a white solid (28mg, 26%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=597.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.82(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.51(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.67(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),6.61(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.18(t,J=74.3Hz,1H),4.72(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.27(qd,J=7.1,2.9Hz,1H),4.12(dd,J=10.3,2.8Hz,1H),3.93–3.79(m,2H),3.59(t,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.54–3.44(m,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.81–2.69(m,1H),2.25(ddd,J=12.8,10.5,7.3Hz,1H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 49N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under the protection of nitrogen, (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (1.50g,5.78mmol), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (2.50g,11.60mmol), Pd2(dba)3(280mg,0.30mmol),XantPhos(153mg,0.26mmol),Cs2CO3(5.20g,16.00mmol) was added to Toluene (33mL) and the mixture was stirred for 8h at 100 ℃. The reaction was then cooled to rt, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (2.0g, 88%).
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (2.44g,6.20mmol) and LiOH. H 2O (2.20g,51.40mmol) in THF/H2O (50mL/50mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added dropwise to the reaction solution to adjust the system pH to about 4, followed by extraction with EtOAc (25 mL. times.2), washing of the organic phase with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a pale yellow solid (1.90g, 79%).
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (200mg,0.53mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (170mg,0.74mmol), EDCI (100mg,0.51mmol) and HOBt (60mg,0.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (120mg, 39%)
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=591.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.85(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.74(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.98(d,J=5.6Hz,1H),6.67(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.26(dd,J=10.9,4.4Hz,1H),4.17(qd,J=7.2,3.2Hz,1H),3.99(ddd,J=15.8,11.2,4.0Hz,2H),3.87–3.79(m,1H),3.63(dd,J=9.5,1.4Hz,1H),3.55(t,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.48–3.39(m,2H),3.31(d,J=1.5Hz,3H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.76–2.64(m,2H),2.25(ddd,J=12.8,10.5,7.2Hz,1H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 504- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (110mg,2.75mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (228mg,0.66mmol) in DMF (10mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen, after 1h EtI (0.50mL,6.0mmol) was added dropwise and the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature and stir for 5 h. Adding ice water to the reaction solutionThe reaction was quenched (120mL), then extracted with EtOAc (15 mL. times.3), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (180mg, 73%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=375.6[M+1]+;
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (53mg,0.14.0mmol) and NaOMe (550mg,9.88mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (8mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 22 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and to the residue was added HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) under ice-bath, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 3, and then extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a brown solid (50mg, 90%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 394.1[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.50mL,3.03mmol) was added to a solution of (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (69mg,0.30mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (120mg,0.31mmol) and HATU (0.20g,0.51mmol) in DCM (17mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (100mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (45mg, 24%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 605.1[ M +1 ═ M]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,2H for major isomer),7.42(d,J=8.5Hz,2H for minor isomer),6.96(d,J=5.1Hz,1H),6.68(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),5.28(d,J=3.9Hz,1H),4.17(dd,J=6.8,4.9Hz,1H),4.07–3.93(m,2H),3.93–3.73(m,2H),3.67(t,J=11.8Hz,1H),3.54(dd,J=17.8,8.5Hz,1H),3.44(dt,J=14.8,7.6Hz,3H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.79–2.67(m,1H),2.29–2.18(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.16(t,J=6.9Hz,3H).
Example 51N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (isopropoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (isopropoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (100mg,2.50mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (302mg,0.87mmol) in DMF (10mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen, after 1h 2-iodopropane (0.30mL,3.01mmol) was slowly added and the reaction warmed to room temperature and stirred for 3h after completion. The reaction was quenched by adding ice water (120mL) to the reaction solution, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.3), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (52mg, 15%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=389.5[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (isopropoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- ((2S) -2- (Isopropoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (53mg,0.14mmol) and NaOMe (550mg,9.88mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (8mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and to the residue was added HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) in an ice bathThe aqueous phase was then extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (50mg, 90%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=408.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (isopropoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (Isopropoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (83mg,0.20mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (70mg,0.31mmol), HOBt (50mg,0.36mmol) and EDCI (100mg,0.51mmol) were dissolved in DCM (30mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (15mg, 12%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=619.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.87(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.42(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.91(d,J=5.8Hz,1H),6.65(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),5.33–5.26(m,1H),4.13(t,J=8.7Hz,1H),4.09–3.95(m,2H),3.93–3.85(m,1H),3.84–3.71(m,1H),3.71–3.51(m,2H),3.41(t,J=8.8Hz,1H),3.26(t,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.09(q,J=7.2Hz,2H),2.48(dd,J=12.3,6.4Hz,1H),2.04-1.99(m,1H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.18(s,6H).
Example 52N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.30mL, 2) was added under nitrogen0mmol) to a solution of (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (70mg,0.31mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (105mg,0.26mmol) and HATU (0.20g,0.51mmol) in DCM (20mL) was stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.2mol/L) and saturated NaHCO 3Washed with aqueous solution (20mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/2) and preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (35mg, 22%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=623.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.85(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.46(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.01(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),6.67(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),5.27(d,J=5.4Hz,1H),4.68–4.40(m,2H),4.20(dd,J=17.3,8.0Hz,1H),4.06–3.93(m,2H),3.88–3.64(m,4H),3.63–3.56(m,2H),3.47(dt,J=17.0,8.4Hz,1H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.73(dt,J=14.9,7.7Hz,1H),2.32(dd,J=15.1,7.5Hz,1H),1.29(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 53N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (propoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.30mL,2.0mmol) was added to a solution of (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (140mg,0.61mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (propoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (150mg,0.37mmol) and HATU (189mg,0.48mmol) in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3Washed with aqueous solution (20mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressureThe crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/2) and preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/2) to give a white solid (85mg, 37%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=619.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.85(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.74(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.58(dd,J=14.9,8.2Hz,4H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.97(d,J=6.4Hz,1H),6.67(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.27(dd,J=10.6,4.3Hz,1H),4.19(td,J=9.5,2.9Hz,1H),3.99(ddd,J=16.1,11.3,4.3Hz,2H),3.89–3.76(m,1H),3.67(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),3.55(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.51–3.41(m,2H),3.40–3.25(m,2H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.77–2.66(m,1H),2.26(ddd,J=12.6,10.3,7.0Hz,1H),1.54(dq,J=14.0,7.0Hz,2H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.88(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 544- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.30mL,2.0mmol) was added to a solution of (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (80mg,0.35mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (75mg,0.18mmol) and HATU (89mg,0.23mmol) in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3Washed with aqueous solution (20mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a white solid (35mg, 31%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 633.1[ M +1 ═ M]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.73(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.01(d,J=6.8Hz,1H),6.66(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.24(dd,J=10.8,4.4Hz,1H),4.23–4.11(m,1H),3.97(ddd,J=16.2,11.2,4.1Hz,2H),3.85–3.78(m,1H),3.66(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),3.54(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.49–3.28(m,4H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.76–2.67(m,1H),2.26(ddd,J=12.7,10.3,7.1Hz,1H),1.50(dt,J=13.3,6.5Hz,2H),1.33(dt,J=15.5,7.7Hz,2H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.88(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 554- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.30mL,2.0mmol) was added to a solution of (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (100mg,0.44mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (150mg,0.36mmol) and HATU (0.30g,0.77mmol) in DCM (23mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (15mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.2mol/L) and saturated NaHCO 3Washed with aqueous solution (20mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, the filtrate was concentrated and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) and preparative chromatography (developer: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (95mg, 42%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=630.9[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.83(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.74(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.58(dd,J=19.7,8.0Hz,4H),7.44(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.00(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),6.66(t,J=9.2Hz,2H),5.23(d,J=4.0Hz,1H),4.24–4.11(m,1H),3.97(ddd,J=16.1,11.3,4.2Hz,2H),3.83(dt,J=17.7,9.0Hz,1H),3.75–3.64(m,1H),3.55(dd,J=19.3,9.9Hz,1H),3.48–3.31(m,2H),3.31–3.15(m,2H),3.07(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.75(dt,J=15.0,6.7Hz,1H),2.32–2.20(m,1H),1.26(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),1.12–0.92(m,1H),0.60–0.44(m,2H),0.19(d,J=4.5Hz,2H).
Example 564- ((2S,4S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide/4- ((2S,4R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under the protection of nitrogen, adding TMSCF2Br (1.0mL,6.40mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (362mg,0.95mmol) and KOAc (910mg,9.18mmol) in DCM/H2O (1.0mL/1.0mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 13 h. The reaction was poured slowly into water (45mL), then DCM (30 mL. times.2) was added and the extracts were extracted, the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a brown oil (210mg, 51%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=430.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in H2O (3mL), and the solution was added to 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethane)To a solution of methyl oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (189mg,0.44mmol) in THF (7mL) was heated to 55 deg.C and stirred for 6 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, the residue was slowly added dropwise with HCl solution (1mol/L) at 0 ℃ to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), washing the organic phase with saturated NaCl (30mL), and extracting with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (160mg, 88%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=416.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S,4S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide/4- ((2S,4R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
Under nitrogen, (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (100mg,0.44mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (110mg,0.26mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.70mL,4.92mmol) were dissolved in DCM (21mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentration under reduced pressure and chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) gave white solid (100mg, 60%) which was separated by manual prep chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give white solid 56-1(35mg, 21%, Rt ═ 10.95min) and white solid 56-2(12mg, 7%, Rt ═ 14.46 min).
56-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=627.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.88(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.92(d,J=6.8Hz,1H),6.68(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),6.18(t,J=74.3Hz,1H),5.30(dd,J=10.6,4.0Hz,1H),4.34–4.20(m,1H),4.13(dd,J=10.3,2.6Hz,1H),4.08–3.96(m,2H),3.94–3.82(m,2H),3.59(t,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.51(dd,J=15.8,6.0Hz,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.83–2.71(m,1H),2.33–2.24(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
56-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=627.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.87(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.95(d,J=6.8Hz,1H),6.67(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),6.18(t,J=74.3Hz,1H),5.28(dd,J=10.8,4.4Hz,1H),4.31–4.23(m,1H),4.12(dd,J=10.3,2.6Hz,1H),4.01(ddd,J=15.7,11.0,4.0Hz,2H),3.92–3.82(m,2H),3.59(t,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.55–3.44(m,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.81–2.69(m,1H),2.33–2.17(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 574- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under the protection of nitrogen, adding TMSCF2Br (2.0mL,12.80mmol) was added dropwise methyl 4- ((2R) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (600mg,1.58mmol) and KOAc (1.60g,16.10mmol) in DCM/H 2O (2.0mL/2.0mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was poured slowly into water (45mL), then DCM (30 mL. times.2) was added and the extracts were extracted, the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a brown oil (420mg, 62%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=430.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (350mg,8.17mmol) in H2To O (3mL) was added a solution of methyl 4- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (420mg,0.98mmol) in THF (10mL) and the temperature was raised to 55 ℃ and stirred for 6 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, the residue was slowly added dropwise with HCl solution (1mol/L) at 0 ℃ to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), washing the organic phase with saturated NaCl (30mL), and extracting with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (400mg, 98%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=416.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
Under nitrogen, (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (130mg,0.57mmol), 4- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (220mg,0.53mmol), HATU (250mg,0.64mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) were dissolved in DCM (31mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) to give a white solid (180mg, 54%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 627.1[ M +1 ═ M]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.85(t,J=12.2Hz,2H),7.79(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.61(dd,J=22.3,8.0Hz,4H),7.46(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.05(d,J=6.8Hz,1H),6.69(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),6.23(dd,J=91.9,56.5Hz,1H),5.29(s,1H),4.29(d,J=4.8Hz,1H),4.14(d,J=10.2Hz,1H),4.00(dt,J=11.0,6.3Hz,2H),3.95–3.83(m,2H),3.60(t,J=9.5Hz,1H),3.53(dd,J=17.1,8.0Hz,1H),3.11(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.84–2.72(m,1H),2.33–2.21(m,1H),1.29(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 584- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
NaH (110mg,2.75mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (210mg,0.53mmol) in DMF (6mL) under nitrogen and after 5min 3-bromo-3, 3-difluoropropyl-1-ene (0.5mL, 4.91mmol) was added slowly and stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The reaction was poured slowly into water (45mL) and extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (110mg, 44%).
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (190mg,0.41mmol) and LiOH. H2O (100mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2In O (10mL/2mL), the mixture was heated to 55 ℃ and stirred for 12 hours. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and slowly added dropwise with HCl (6mol/L) in ice bath to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, followed by extraction of the aqueous phase with EtOAc (25 mL. times.2), washing of the organic phase with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, and separating the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to obtainBrown oil (120mg, 63%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=442.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Pd/C (30mg, 5%) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (120mg,0.26mmol) in EtOAc (10mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction mixture was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless transparent liquid (110mg, 91%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=444.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) was added to a solution of (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (50mg,0.22mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (90mg,0.20mmol) and HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) in DCM (13mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (15mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (25mg, 19%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=655.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.88(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.92(d,J=6.9Hz,1H),6.68(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.30(d,J=6.4Hz,1H),4.25(ddd,J=10.7,6.8,2.9Hz,1H),4.15(dd,J=10.3,2.9Hz,1H),4.03(ddd,J=16.0,11.2,4.2Hz,2H),3.84(ddd,J=17.0,9.4,7.3Hz,2H),3.55(dd,J=16.2,6.9Hz,1H),3.52–3.43(m,1H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.74(q,J=7.4Hz,1H),2.26–2.18(m,1H),2.00–1.91(m,2H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.02(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 594- ((2S) -2- ((3, 3-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((3, 3-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
NaH (110mg,2.75mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (210mg,0.53mmol) in DMF (6mL) under nitrogen and after 5min 3-bromo-3, 3-difluoropropyl-1-ene (0.5mL, 4.91mmol) was added slowly and stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The reaction was poured slowly into water (45mL) and extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (120mg, 48%).
Step two: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((3, 3-difluoropropyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Pd/C (30mg, 5%) was added to a solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (120mg,0.26mmol) in EtOAc (10mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction mixture was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless transparent liquid (110mg, 91%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=458.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((3, 3-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((3, 3-difluoropropyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (110mg,0.23mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2In O (10mL/2mL), the mixture was stirred at 50 ℃ for 10 hours. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and slowly added dropwise with HCl (6mol/L) in ice bath to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, followed by extraction of the aqueous phase with EtOAc (25 mL. times.2), washing of the organic phase with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a brown oil (96mg, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=444.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((3, 3-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) was added to a solution of (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (55mg,0.25mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((3, 3-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (96mg,0.23mmol) and HATU (220mg,0.56mmol) in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (22mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (33mg, 22%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=655.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.88(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.60(t,J=9.5Hz,4H),7.43(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.92(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),6.68(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.86(tt,J=56.6,4.5Hz,2H),5.30(dd,J=10.2,4.1Hz,1H),4.19(s,1H),4.12–3.93(m,2H),3.88–3.76(m,1H),3.68(dd,J=15.8,6.5Hz,2H),3.59–3.42(m,4H),3.10(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.74–2.62(m,1H),2.27–2.17(m,1H),2.10–2.00(m,2H),1.28(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 60N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxo) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (1.00g,4.08mmol), ethyl 4-iodobenzoate (1.46g,5.29mmol), Pd under nitrogen2(dba)3(373mg,0.41mmol), XantPhos (354mg,0.61mmol) and Cs2CO3(2.66g,8.16mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (30mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 16 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was diluted with DCM (80mL) and, in turn, with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a brown solid (1.12g, 70%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 394.1[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxo) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
NaH (100mg,2.50mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of (R) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl methanesulfonate (633mg,3.81mmol) and ethyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (300mg,0.76mmol) in THF (6mL) with stirring while cooling in an ice bath under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction was quenched by adding HCl solution (1mol/L) to the reaction mixture and adjusting the pH of the solution to about 5, the mixture was diluted with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and then extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a yellow solid (70mg, 21%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=436.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxo) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- ((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxo) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (530mg,0.07mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (18mg,0.08mmol), EDCI (26mg,0.14mmol), HOBt (18mg,0.13mmol) and TEA (13mg,0.13mmol) were dissolved in DCM (4mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give the product as a white solid (25mg, 56%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=647.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.85(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.04–6.97(m,1H),6.66(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),5.27(dd,J=10.4,4.3Hz,1H),4.23–4.16(m,1H),4.04–3.93(m,3H),3.89–3.76(m,3H),3.73(dd,J=8.1,4.0Hz,1H),3.71–3.63(m,2H),3.63–3.56(m,1H),3.55–3.42(m,3H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.75–2.67(m,1H),2.28–2.18(m,1H),1.94(dt,J=11.2,3.8Hz,1H),1.28(d,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 61N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
DAST (0.54mL,4.00mmol) was added slowly under nitrogen to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (248mg,0.72mmol) in DCM (12mL) and stirred at room temperature for 5 h. Under ice-bath, the reaction solution was poured intoSlowly adding saturated NaHCO3The solution (100mL) was then extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a brown solid (245mg, 98%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=349.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (250mg,0.72mmol) and MeONa (550mg,9.88mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (8mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 8 h. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and to the residue was added HCl solution (30mL,1mol/L), the pH of the system was adjusted to about 3, a tan solid precipitated, and the insoluble solid was filtered and washed with water (50mL) to give a brown solid (250mg, 95%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=368.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (70mg,0.31mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (90mg,0.25mmol), EDCI (100mg,0.51mmol) and HOBt (50mg,0.36mmol) were dissolved in DCM (30mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (64mg, 45%)
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=579.7[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.80(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.74(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.52(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.40(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.14(d,J=7.0Hz,1H),6.90(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),5.22(dd,J=10.7,4.4Hz,1H),4.91–4.65(m,1H),4.21–4.12(m,1H),3.94(ddd,J=15.9,11.1,3.8Hz,2H),3.84(d,J=12.3Hz,1H),3.06(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.94(ddd,J=14.9,14.5,8.5Hz,2H),2.86(t,J=12.0Hz,1H),2.50(dd,J=10.7,4.6Hz,1H),1.99–1.84(m,1H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
19F NMR(376MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):-62.50(s),-180.77(s).
Example 624- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
Dess-Martin reagent (1.66g,3.87mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (870mg,2.51mmol) in DCM (45mL) and stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The reaction was filtered and the filtrate was slowly added with saturated NaHCO in ice bath3Solution (100mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow liquid (860mg, 99%).
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
DAST (0.20mL,1.00mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (125mg,0.36mmol) in DCM (42mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Aqueous solution (100mL) and then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a white solid (120mg, 90%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=367.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (53mg,0.14mmol) and MeONa (550mg,9.88mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (8mL) under nitrogen and stirred at 100 deg.C for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and to the residue was added HCl solution (1mol/L) under ice-bath to adjust the pH of the system to about 3, then the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (25 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (25mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (50mg, 90%).
MS(ESI,neg.ion)m/z=383.0[M-1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (55mg,0.14mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (50mg,0.22mmol), EDCI (80mg,0.41mmol) and HOBt (40mg,0.29mmol) were dissolved in DCM (30mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (14mg, 16%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=597.7[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.84(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.42(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.04(d,J=6.1Hz,1H),6.71(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),5.98(t,J=56.2Hz,1H),5.26(dd,J=10.3,4.4Hz,1H),4.35–4.21(m,1H),4.11–3.90(m,3H),3.84(dt,J=18.4,9.3Hz,1H),3.31(t,J=9.6Hz,1H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.63(dd,J=13.2,6.7Hz,1H),2.34–2.22(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 63N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (1-fluoroethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((R) -1-hydroxyethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
Cooling and stirring at-20 deg.C under nitrogen protection, adding Et of MeMgBr2The O solution (2.2mL,6.6mmol,3.0mol/L) was added dropwise to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2-formyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (660mg,1.92mmol) in THF (32mL), stirred at low temperature for 3h, then warmed to room temperature and stirred for 3 h. Saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution 3The reaction was quenched with solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove THF, the aqueous phase extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.2), the organic phases combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a pale yellow solid (550mg, 80%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=361.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (1-fluoroethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
DAST (0.84mL,6.20mmol) was added slowly under nitrogen to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- ((R) -1-hydroxyethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (680mg,1.89mmol) in DCM (12mL) and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (100mL), then extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.3), the organic phases combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a brown solid (245mg, 36%).
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (1-fluoroethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Reacting 4- ((2S) -2- (1-fluoroethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) Benzonitrile (203mg,0.56mmol) and MeONa (550mg,9.88mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (8mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 28 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and to the residue was added HCl solution (1mol/L) under ice bath, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 3, and then extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a brown solid (130mg, 61%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=382.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (1-fluoroethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.5mL,3.0mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (1-fluoroethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (120mg,0.31mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (69mg,0.30mmol) and HATU (0.20g,0.51mmol) in DCM (17mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (100mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (45mg, 24%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=593.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ7.81(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.73(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.53(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.41(t,J=9.4Hz,2H),7.08(t,J=15.0Hz,1H),6.88(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.22(dd,J=10.8,4.4Hz,1H),5.05–4.81(m,1H),4.60–4.37(m,1H),3.95(ddd,J=16.3,11.3,4.4Hz,2H),3.64–3.45(m,1H),3.06(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.04–2.98(m,2H),2.96-2.82(m,1H),2.32–2.19(m,1H),2.13(td,J=20.5,11.7Hz,1H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.19(d,J=6.4Hz,3H).
Example 64N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinylmethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.30mL,2.0mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (195mg,0.45mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (110mg,0.48mmol) and HATU (250mg,0.64mmol) in DCM (20mL) under nitrogen and the reaction stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) and preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) to give the title compound as a pale yellow solid (45mg, 16%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=646.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.80(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.53(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.14(d,J=5.2Hz,1H),6.64(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),5.22(d,J=4.5Hz,1H),4.12(d,J=5.8Hz,1H),3.92(dt,J=11.4,6.7Hz,2H),3.82(t,J=8.4Hz,1H),3.68(s,4H),3.55(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.44(dt,J=16.7,8.5Hz,1H),3.06(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.73(d,J=12.6Hz,2H),2.46(d,J=21.6Hz,4H),2.28(ddd,J=30.1,15.9,9.7Hz,2H),1.24(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 65N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S,4S) -2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide/N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S,4R) -2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (S) -1- (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid
Under nitrogen protection, (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1H-pyrrole-1, 2(2H,5H) -dicarboxylate (6.50g,17.50mmol) and LiOH. H2O (4.50g,105mmol) in MeOH/H2O (35mL/12mL) was stirred at room temperature for 5 hours. HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added dropwise to the reaction solution to adjust the system pH to about 4, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), washing of the organic phase with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Drying and concentration under reduced pressure gave a yellow solid (6.00g, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=302.0[M-56+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (S) -tert-butyl 2- ((S) -3-methylmorpholine-4-formyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate
DIPEA (0.10mL,0.61mmol) was added to a solution of (S) -1- (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid (800mg,2.24mmol) and (3S) -3-methylmorpholine (460mg,4.55mmol) and HATU (1.00g,2.55mmol) in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 20H. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was separated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a colorless transparent liquid (680mg, 69%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=341.3[M-100+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrole-1-carboxylate
Pd/C (80 mg) was added under a hydrogen atmosphere5%) to a solution of (S) -tert-butyl 2- ((S) -3-methylmorpholine-4-formyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxylate (800mg,1.82mmol) in MeOH (15mL) was added and stirred at room temperature for 3H. The reaction solution was filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless oily liquid (700mg, 87%). The colorless oily liquid compound was dissolved in THF (40mL) under nitrogen protection, and BH was added under cooling and stirring in an ice bath 3·SMe2The THF solution (1.0mL,10mmol,2mol/L) was added dropwise to the reaction system, and after the addition was completed, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 hours. Slowly adding saturated NH into the reaction liquid under ice bath4The reaction was quenched in Cl solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove THF, the aqueous phase extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.3), the organic phases combined and Na anhydrous2SO4The crude product was dried and chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (240mg, 29%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=429.4[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of (3S) -3-methyl-4- (((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methyl) morpholine
A solution of HCl in EtOAc (5mL,18mmol,1mol/L) was added to a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrole-1-carboxylate (240mg,0.59mmol) in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless transparent oil (160mg, 84%).
Step five: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, (3S) -3-methyl-4- (((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methyl) morpholine (385mg,1.17mmol), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (450mg,2.09mmol), Pd2(dba)3(120mg,0.13mmol), RuPhos (60mg,0.12mmol) and Cs 2CO3(85mg,2.60mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (45mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (430mg, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=463.4[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (115mg,0.25mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2In O (10mL/2mL), the temperature was raised to 55 ℃ and the mixture was stirred for 10 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, then concentrated under reduced pressure to remove THF, slowly added dropwise with HCl solution (6mol/L) in ice bath to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, extracted with EtOAc (25 mL. times.2), and the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (100mg, 90%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=449.3[M+1]+.
Step seven: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S,4S) -2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide/N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S,4R) -2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.20mL,1.0mmol) was added to a solution of (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (60mg,0.26mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (((S) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (100mg,0.22mmol) and HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) in DCM (11mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) and silica gel preparative plate chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give 65-1(25mg, 17%, Rt ═ 7.85min) as a pale yellow solid and 65-2(2.5mg, 2%, Rt ═ 11.67min) as a white solid.
65-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=660.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.89(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.90(d,J=6.4Hz,1H),6.69(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),5.36–5.29(m,1H),4.12(dd,J=14.4,7.2Hz,2H),4.07–3.98(m,2H),3.81(dd,J=17.0,9.1Hz,2H),3.74–3.67(m,1H),3.67–3.61(m,2H),3.27–3.18(m,1H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.92(d,J=10.1Hz,1H),2.78–2.69(m,1H),2.55(d,J=5.6Hz,2H),2.33(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),2.24–2.19(m,1H),2.03–1.97(m,1H),1.30(d,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.84(d,J=6.0Hz,3H).
65-2:
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.89(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.91(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),6.70(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),5.37–5.29(m,1H),4.04(ddd,J=16.1,11.1,4.3Hz,3H),3.85–3.79(m,1H),3.73–3.66(m,2H),3.57(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.46(dd,J=17.8,7.8Hz,1H),3.34–3.26(m,1H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.74(dt,J=11.7,6.0Hz,2H),2.48–2.35(m,2H),2.30–2.21(m,2H),2.05–1.97(m,1H),1.29(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.98(d,J=6.1Hz,3H).
Example 66N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (((R) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (3S) -3-methyl-4- (((2R) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methyl) morpholine
A solution of HCl in EtOAc (7.5mL,7.50mmol,1mol/L) was added to a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (((R) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrole-1-carboxylate (250mg,0.60mmol) in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless transparent oil (130mg, 68%).
Step two: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((R) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, (3S) -3-methyl-4- (((2R) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methyl) morpholine (130mg,0.40mmol), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (150mg,0.70mmol), Pd2(dba)3(120mg,0.12mmol), RuPhos (60mg,0.12mmol) and Cs2CO3(350mg,1.10mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (45mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (130mg, 71%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=463.4[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (((R) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((R) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (130mg,0.28mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2In O (10mL/2mL), the temperature was raised to 55 ℃ and the mixture was stirred for 10 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, then concentrated under reduced pressure to remove THF, slowly added dropwise with HCl solution (6mol/L) in ice bath to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, extracted with EtOAc (25 mL. times.2), and the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (80mg, 64%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=449.3[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((S) -2- (((R) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
DIPEA (0.10mL,0.56mmol) was added to (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (50mg,0.23mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (((R) -3-methylmorpholine) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (70mg,0.16mmol) and HATU (100mg,0.26mmol) in DCM (10 m) under nitrogenL) solution, stirring at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) and silica gel preparative plate chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (35mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=660.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.05(d,J=6.9Hz,1H),6.66(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),5.26(dd,J=10.3,4.5Hz,1H),4.11(dd,J=14.2,7.1Hz,1H),3.97(ddd,J=16.2,11.3,4.5Hz,2H),3.80(dd,J=14.9,7.5Hz,2H),3.72–3.54(m,3H),3.47(dd,J=18.8,10.9Hz,1H),3.24(dd,J=11.0,8.8Hz,1H),3.08(q,J=7.5Hz,2H),2.91(d,J=11.5Hz,1H),2.72(dt,J=14.6,7.4Hz,1H),2.40–2.30(m,2H),2.20(ddd,J=13.2,9.2,6.4Hz,1H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),0.72(d,J=6.2Hz,3H).
Example 67(2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
N-Methoxymethylamine hydrochloride (600mg,6.15mmol), (2S) -1- (tert-butoxy) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (800mg,2.23mmol), HATU (1.25g,3.19mmol) and DIPEA (0.4mL,2.42mmol) were dissolved in DCM (55mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 13 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressureThe crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (800mg, 89%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=303.2[M-100+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxamide
A solution of HCl in EtOAc (5mL,18mmol,1mol/L) was added to a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (800mg,1.99mmol) in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless transparent oil (584mg, 97%).
Step three: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, (2S) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxamide (585mg,1.94mmol), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (650mg,3.02mmol), Pd2(dba)3(110mg,0.12mmol), RuPhos (80mg,0.16mmol) and Cs2CO3(1.35g,4.14mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (45mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (700mg, 83%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=436.9[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (700mg,1.60mmol) and LiOH. H2O (1.10g,25.7mmol) in THF/H2O (16mL/16mL), and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove THF, then HCl solution (1mol/L) was added dropwise to the system to adjust the pH of the system to about 4, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, and concentrating under reduced pressure to obtain yellow solidBody (290mg, 43%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=423.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (249mg,1.08mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (390mg,0.92mmol), HATU (0.60g,1.50mmol) and DIPEA (0.60mL,3.63mmol) were dissolved in DCM (28mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (180mg, 31%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=634.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.83(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=6.4Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.55–7.48(m,2H),7.45(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.06(d,J=6.0Hz,1H),6.61–6.45(m,2H),5.14(d,J=4.2Hz,1H),4.98(dd,J=15.0,7.4Hz,1H),4.03-3.95(m,1H),3.87(s,2H),3.82&3.81(s,3H),3.67(dd,J=19.9,9.9Hz,1H),3.62–3.51(m,1H),3.21(d,J=9.2Hz,3H),3.08(q,J=7.2Hz,2H),2.93(d,J=9.1Hz,1H),2.22(dd,J=20.7,11.4Hz,1H),1.26(t,J=7.2Hz,3H).
Example 68(2S) -N-Ethyl-1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (ethyl (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
N-methylethylamine (140mg,2.37mmol), (2S) -1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (300mg,0.84mmol), HATU (390mg,0.99mmol) and DIPEA (0.80mL,5.0mmol) were dissolved in DCM (55mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (200mg, 60%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=301.2[M-100+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -N-ethyl-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
A solution of HCl in EtOAc (5mL,18mmol,1mol/L) was added to a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (ethyl (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (200mg,0.50mmol) in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless transparent oil (145mg, 97%).
Step three: synthesis of ethyl 4- ((2S) -2- (ethyl (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, (2S) -N-ethyl-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (162mg,0.54mmol), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (160mg,0.74mmol), Pd2(dba)3(70mg,0.074mmol), RuPhos (40mg,0.081mmol) and Cs2CO3(350mg,1.07mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (25mL) and stirred at 105 ℃ for 11 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (90mg, 38%).
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (ethyl (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Ethyl 4- ((2S) -2- (ethyl (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (150mg,0.35mmol) and LiOH. H2O(350mg,8.17mmol) in THF/H2In O (10mL/10mL), the mixture was heated to 55 ℃ and stirred for 5 hours. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, slowly added dropwise with HCl solution (1mol/L) in ice bath to adjust the system pH to about 6, then extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (100mg, 69%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=421.3[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of (2S) -N-ethyl-1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 2-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (86mg,0.38mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (ethyl (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (110mg,0.26mmol), HATU (300mg,0.77mmol) and DIPEA (0.30mL,1.58mmol) were dissolved in DCM (20mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (80mg, 48%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=632.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.78(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.68(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.46-7.41(m,4H),7.20(t,J=6.8Hz,1H),6.42(dd,J=15.1,8.6Hz,2H),5.07–4.96(m,1H),4.82(td,J=16.7,8.5Hz,1H),4.11(q,J=7.1Hz,1H),3.96(dd,J=16.8,8.3Hz,1H),3.76(s,2H),3.70–3.60(m,1H),3.59–3.47(m,2H),3.40(dt,J=17.3,7.1Hz,1H),3.18(s,3H),3.15(s,3H),3.05(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.93(s,3H),2.89(s,3H),2.84(dd,J=13.3,6.2Hz,1H),2.15(dt,J=19.7,10.1Hz,1H),1.33&1.30(t,J=7.2Hz,3H),1.24(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.10&1.07(t,J=7.1Hz,3H).
Example 692- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
MeI (0.20mL,3.2.0mmol) was added dropwise to a suspension of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine 1-carboxylate (744mg,2.15mmol) and NaOH (105mg,2.63mmol) in MeCN (5mL) at room temperature and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL), the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1) to give a yellow solid (472mg, 61%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=382.1[M+23]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
(2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (472mg,1.31mmol) was dissolved in a solution of HCl in i-PrOH (9mL,54.0mmol,6mol/L) and stirred at room temperature. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a pale yellow oil (337mg, 100%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=260.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -5-nitropyridine
Under nitrogen protection, (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (337mg,1.30mmol), 2-bromo-5-nitropyridine (402mg,1.98mmol), Cs2CO3(860mg,2.64mmol),Pd2(dba)3(128mg,0.14mmol) and XantPhos (91mg,0.15mmol) were dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (6mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 21 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with DCM (60mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1) to give the product as a yellow solid (439mg, 89%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 382.3[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step four: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine
Pd/C (84mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -5-nitropyridine (437mg,1.15mmol) in MeOH (5mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction solution was filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a purple oily solid (403mg, 100%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=352.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide
6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (189mg,0.54mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (172mg,0.75mmol), EDCI (225mg,1.17mmol) and HOBT (154mg,1.14mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) under nitrogen and TEA (0.24mL,1.70mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale purple solid (67mg, 22%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 562.2[ M +1 []+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.14(s,1H),7.90(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.81(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),7.59(d,J=4.2Hz,4H),7.43(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.40–7.31(m,1H),6.52(d,J=9.1Hz,1H),4.32(s,1H),4.11–4.02(m,1H),3.82(s,2H),3.74–3.66(m,1H),3.59–3.53(m,1H),3.50(d,J=9.8Hz,1H),3.42(s,1H),3.35(s,3H),3.21(s,3H),3.12(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.70–2.61(m,1H),2.23–2.14(m,1H),1.31–1.27(m,J=7.3Hz,3H).13C NMR(151MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):168.33,153.97,145.21,141.20,137.38,132.76,130.42,129.36,129.15,128.74,127.82,125.66,125.18,124.65,123.35,108.17,74.01,59.45,58.36,55.10,50.76,43.79,42.79,37.04,27.11,7.53.
Example 702- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (5- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-2-yl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 5- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -2-nitropyridine
Under nitrogen protection, (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (301mg,1.16mmol), 5-bromo-2-nitropyridine (281mg,1.38mmol), Pd 2(dba)3(56mg,0.061mmol), XantPhos (68mg,0.12mmol) and Cs2CO3(976mg,2.30mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (5mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 24 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, saturated NaCl solution (50mL) was added to the reaction, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (236mg, 53%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=382.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 5- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-2-amine
Pd/C (407mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 5- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -2-nitropyridine (236mg,0.62mmol) in MeOH (10mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Celite filtration gave a grey oily solid (181mg, 83%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=352.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (5- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-2-yl) acetamide
5- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-2-amine (181mg,0.52mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (192mg,0.84mmol), EDCI (174mg,0.91mmol) and HOBt (108mg,0.80mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) under nitrogen and TEA (0.22mL,1.60mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (20mL), followed by extraction with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a white solid (127mg, 44%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=562.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):10.48(s,1H),7.89–7.79(m,4H),7.70(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.60(t,J=8.1Hz,4H),7.14(dd,J=9.0,2.6Hz,1H),4.11(t,J=7.7Hz,1H),3.81(s,2H),3.75(t,J=6.9Hz,1H),3.53–3.42(m,3H),3.41–3.36(m,1H),3.26(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.21(s,3H),2.61(dt,J=14.2,7.1Hz,1H),2.06(dd,J=18.2,11.0Hz,1H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 71N- (6- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
NaOH (131mg,3.28mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (498mg,1.44mmol) in DMF (3mL) under nitrogen, followed by additionEtI (0.24mL,3.0mmol) was added and the mixture was warmed to 70 ℃ and stirred for 8 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure to remove DMF, water (50mL) was added to the system, followed by extraction with EtOAc (60 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a white solid (280mg, 52%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=396.1[M+23]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
(2S) -tert-butyl 2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (390mg,1.04mmol) was dissolved in DCM (5mL) and TFA (0.65mL) and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure, and saturated NaHCO was added to the residue 3The solution (30mL) was then extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (250mg, 88%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=274.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -5-nitropyridine
Under nitrogen protection, (2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (250mg,0.91mmol), 2-bromo-5-nitropyridine (387mg,1.91mmol), Pd2(dba)3(185mg,0.20mmol), XantPhos (65mg,0.11mmol) and Cs2CO3(628mg,1.93mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (5mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 22 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, saturated NaCl solution (80mL) was added, followed by extraction with EtOAc (80 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (350mg, 97%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=396.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine
Pd/C (559mg, 10%) was added to a solution of 2- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -5-nitropyridine (350mg,0.89mmol) in MeOH (10mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Celite was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a brown oil (188mg, 58%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=366.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of N- (6- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide
6- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (188mg,0.51mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (190mg,0.83mmol), EDCI (173mg,0.90mmol) and HOBt (153mg,1.13mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) under nitrogen and TEA (0.25mL,1.80mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), followed by extraction with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a brown solid (124mg, 42%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=576.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):10.05(s,1H),8.26(s,1H),7.85(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),7.77–7.66(m,3H),7.60(m,4H),6.58(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),4.29–4.16(m,1H),4.11–3.97(m,1H),3.76(s,2H),3.72(d,J=9.3Hz,1H),3.52–3.39(m,2H),3.35(s,3H),3.27(q,J=7.2Hz,,2H),2.66–2.54(m,1H),2.15–2,05(m,1H),1.10(t,J=7.2Hz,3H).
Example 72N- (6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ((2S) -1- (5-nitropyridin-2-yl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol
Under nitrogen protection ((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (350mg,1.43mmol), 2-bromo-5-nitropyridine (614mg,3.02mmol), Pd 2(dba)3(131mg,0.14mmol), XantPhos (180mg,0.31mmol) and Cs2CO3(1.48g,4.54mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (10mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 24 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, a saturated NaCl solution (40mL) was added to the reaction solution, followed by extraction with DCM (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (196mg, 37%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 368.2[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -5-nitropyridine
((2S) -1- (5-nitropyridin-2-yl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (196mg,0.53 mmol) and CuI (52mg,0.27mmol) were dissolved in MeCN (10mL) under nitrogen, warmed to 50 ℃ with stirring, and 2, 2-difluoro-2- (fluorosulfonyl) acetic acid (0.11mL,1.10mmol) was added dropwise to the system and thermal stirring was continued for 5 h. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, and saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction solution3The solution (30mL) was then extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a yellow oil (85mg, 38%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=418.4[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine
Pd/C (132mg, 10%) was dissolved in MeOH (8mL) added 2- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -5-nitropyridine (85mg,0.20mmol) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Celite was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a red-brown solid (77mg, 98%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=388.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- (6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide
6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (104mg,0.27mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (114mg,0.50mmol), EDCI (83mg,0.43mmol), HOBt (62mg,0.46mmol) and TEA (0.06mL,0.40mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (50 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a brown solid (77mg, 48%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=598.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):10.08(s,1H),8.28(s,1H),7.85(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.71(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.61(m,4H),6.64(t,J=76.1Hz,1H),6.60(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),4.35(dd,J=4.7Hz,1H),4.21(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),4.01(dd,J=15.7,8.1Hz,2H),3.77(s,2H),3.52–3.39(m,2H),3.27(q,J=7.0Hz,2H),2.68–2.57(m,1H),2.10(dd,J=19.8,11.1Hz,1H),1.10(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).
Example 73N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
Under the protection of nitrogen, (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine(1.00g,3.86mmol), 6-bromo-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester (1.61g,7.45mmol), Pd2(dba)3(185mg,0.20mmol), XantPhos (244mg,0.42mmol) and Cs2CO3(2.64g,8.10mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (15mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure, a saturated NaCl solution (80mL) was added to the residue, followed by extraction with EtOAc (80 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (652mg, 43%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=395.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (550mg,1.40mmol) and LiOH. H2O (137mg,3.27mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (5mL/2.5mL/2mL), and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. Adding HCl solution (1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, extracting the aqueous phase with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), combining the organic phases and adding anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (471mg, 89%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=381.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (153mg,0.40mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (135mg,0.68 mmol), EDCI (116mg,0.60mmol) and HOBt (90mg,0.67mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) under nitrogen and TEA (0.18mL,1.30mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), followed by extraction with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, and passing the crude product through silica gelColumn chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) gave a white solid (170mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=562.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.91(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),8.68(d,J=1.9Hz,1H),7.99(dd,J=9.0,2.1Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),6.67(d,J=9.0Hz,1H),4.56(d,J=5.8Hz,2H),4.37(q,J=10.2Hz,1H),4.25–4.14(m,1H),3.70(dd,J=9.1,2.9Hz,1H),3.55(dd,J=9.1,6.0Hz,1H),3.52–3.43(m,1H),3.40(d,J=10.0Hz,1H),3.29–3.23(m,5H),2.68–2.58(m,1H),2.13(dd,J=19.6,11.5Hz,1H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 746- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
Under nitrogen protection, 6-bromopyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester (660mg,3.06mmol), ((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl l) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (1.05g,4.28mmol), Pd 2(dba)3(300mg,0.32mmol),XantPhos(200mg,0.34mmol),Cs2CO3(2.50g,7.67mmol) was dissolved in Toluene (23mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 13 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a yellow solid (350mg, 22%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=381.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
NaH (110mg,2.75mmol, 60%) was added to 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pir-inyl under nitrogen protection at-20 ℃ with cooling and stirringPyrrolidine-1-yl) nicotinic acid methyl ester (185mg,0.49mmol) in DMF (6mL) was stirred for 1 hour, ethyl iodide (0.50mL,6.00mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction system, and after the addition was completed, the reaction system was stirred at room temperature for 5 hours. Pouring the reaction solution into saturated NH4Cl solution (45mL), followed by extraction with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the combined organic phases were washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2) and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a light yellow oil (110mg, 57%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=395.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) nicotinamide
(4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (69mg,0.35mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (85mg,0.22mmol), HATU (0.20g,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.50mL,3.03mmol) were dissolved in DCM (20mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (25mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (45mg, 36%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=576.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.65(d,J=2.2Hz,1H),7.93(dd,J=8.9,2.4Hz,1H),7.80(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.64(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.51(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),4.72(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.40(td,J=10.4,7.6Hz,1H),4.24–4.12(m,1H),3.77(dd,J=9.5,3.1Hz,1H),3.63(dd,J=9.5,5.7Hz,1H),3.54–3.37(m,4H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.69(dt,J=14.8,7.5Hz,1H),2.33–2.20(m,1H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.15(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).
Example 756- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (500mg,1.31mmol) and CuI (150mg,0.79mmol) were dissolved in MeCN (42mL) under nitrogen, 2-difluoro-2- (fluorosulfonyl) acetic acid (0.5mL,5.0mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction system with stirring at 55 deg.C, and after addition, stirring was continued for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was dissolved in DCM (30mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a yellow solid (128mg, 23%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=431.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (145mg,0.34mmol) and LiOH. H2O (100mg,2.34mmol) in MeOH/H2O (14mL/7mL), and stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The reaction solution was cooled in an ice bath, then HCl solution (1mol/L) was added dropwise to adjust the pH of the system to about 4, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), the combined organic phases were washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a brown solid (123mg, 88%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=417.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) nicotinamide
Under nitrogen protection, (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (45mg,0.23mmol), 6- ((2)S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (61mg,0.15mmol), HATU (69mg,0.18mmol) and DIPEA (0.40mL,2.42mmol) were dissolved in DCM (15mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (25mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (25mg, 29%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=598.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.65(d,J=2.0Hz,1H),7.96(dd,J=8.9,2.3Hz,1H),7.81(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.63(t,J=5.7Hz,1H),6.47(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),6.18(t,J=74.8Hz,1H),4.72(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),4.53(d,J=4.5Hz,1H),4.32–4.15(m,2H),4.05(t,J=7.5Hz,1H),3.58–3.39(m,2H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.73–2.58(m,1H),2.30(dd,J=20.7,11.4Hz,1H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 76N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (300mg,0.79mmol) and LiOH. H2O (280mg,6.54mmol) in THF/H2O (10mL/2mL), the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 hours. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, water (10mL) was added to the residue, HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added to adjust the pH of the system to about 6 with stirring in an ice bath, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, vacuum concentrating, passing the crude product through silica gel columnChromatography (eluent: EtOAc/DCM (v/v) ═ 1/1) gave a yellow solid (130mg, 45%).
Step two: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
(4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (120mg,0.60mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (195mg,0.53mmol), HATU (240mg,0.61mmol) and DIPEA (0.60mL,3.64mmol) were dissolved in DCM (25mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and then successively with HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L), saturated NaHCO3The solution (25mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow solid (69mg, 24%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=548.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.60(s,1H),8.07(d,J=8.7Hz,1H),7.77(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.60(t,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=7.9Hz,3H),6.52(d,J=9.0Hz,1H),4.69(d,J=5.1Hz,2H),4.37(dd,J=15.4,7.8Hz,1H),3.97(t,J=7.9Hz,1H),3.79(d,J=11.4Hz,1H),3.69–3.61(m,1H),3.52(dt,J=11.3,8.4Hz,2H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.59(dt,J=11.9,6.0Hz,1H),1.89(dd,J=22.1,11.0Hz,1H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 77N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
NaH (102mg,2.55mmol, 60%) was added to 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pir-inyl under nitrogen protection at-20 ℃ with cooling and stirringPyrrolidine-1-yl) nicotinic acid methyl ester (205mg,0.54mmol) in DMF (11mL) was added slowly to the reaction system after 5min, and after addition, the reaction was stirred at that temperature for 8 h. The reaction was poured into water (50mL), then extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (162mg, 71%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 427.2[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (400mg,0.94mmol) and LiOH. H2O (350mg,8.17mmol) in THF/H2O (10mL/12mL), the reaction was stirred in a 55 ℃ oil bath with heating for 3 h. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, slowly added dropwise with HCl solution (1mol/L) while stirring under ice-bath cooling to adjust the system pH to about 6, then extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: EtOAc/DCM (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (170mg, 44%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=413.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
Under nitrogen, (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (120mg,0.60mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (195mg,0.47mmol), HATU (240mg,0.61mmol) and DIPEA (0.60mL,3.64mmol) were dissolved in DCM (25mL) and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO 3The solution (25mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure,the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (109mg, 39%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=594.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.68(s,1H),7.93(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),7.67(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.57(dd,J=8.0,2.6Hz,2H),7.47–7.35(m,4H),7.29(s,1H),6.45&6.41(d,J=9.0Hz,1H),4.63(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),4.61–4.51(m,1H),4.50–4.34(m,2H),4.18–3.92(m,1H),3.82(td,J=9.6,3.0Hz,1H),3.79–3.45(m,4H),3.44–3.32(m,1H),3.04(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.69–2.45(m,1H),2.33–2.15(m,1H),1.20(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 78N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
6- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (151mg,0.40mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (114mg,0.50mmol), EDCI (144mg,0.75mmol) and HOBt (106mg,0.78mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) under nitrogen and TEA (0.18mL,1.30mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), followed by extraction with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/7) to give a yellow solid (135mg, 57%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=592.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.69(d,J=2.2Hz,1H),8.56(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),8.00(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.66(d,J=9.0Hz,1H),5.14(q,J=6.1Hz,1H),5.02(dd,J=5.8,4.0Hz,1H),4.45–4.31(m,1H),4.25–4.13(m,1H),3.80–3.63(m,3H),3.61–3.53(m,1H),3.47(dd,J=12.5,6.1Hz,1H),3.43–3.36(m,1H),3.26(q,J=7.3Hz2H),3.25&3.24(s,3H),2.61(dd,J=12.7,7.1Hz,1H),2.13(dd,J=19.8,11.6Hz,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 796- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (69mg,0.30mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (110mg,0.28mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.50mL,3.03mmol) were dissolved in DCM (17mL) under nitrogen and stirred at RT for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3Aqueous solution (25mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (45mg, 27%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=606.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.67(s,1H),7.93–7.86(m,1H),7.83(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=6.6Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.20–7.09(m,1H),6.49(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),5.27(dd,J=10.5,4.8Hz,1H),4.38(s,1H),4.23–4.10(m,1H),3.98(ddd,J=16.5,11.5,4.4Hz,2H),3.75(dd,J=9.4,2.7Hz,1H),3.63(dd,J=9.1,5.8Hz,1H),3.53–3.37(m,4H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.72–2.63(m,1H),2.32–2.22(m,1H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.15(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).
Example 806- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
NaH (80mg,2.00mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (100mg,0.26mmol) in DMF (10mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen and after 1h bromomethylcyclopropane (0.20mL,2.06mmol) was added to the reaction and the reaction was allowed to stir at room temperature for 13 h. The reaction was quenched by adding ice water (40mL) to the reaction solution, then extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (90mg, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=435.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (150mg,0.35mmol) and LiOH. H2O (130mg,3.04mmol) in THF/H2O (10mL/10mL), and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, HCl solution (6mol/L) was slowly added dropwise to adjust the pH of the system to about 6 under ice bath, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a yellow solid (105mg, 72%).
Step three: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
Under nitrogen protection, (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (90mg,0.39mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid(120mg,0.29mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) were dissolved in DCM (15mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO 3Washed with aqueous solution (20mL) and saturated NaCl solution (20mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) and afforded a light yellow solid (20mg, 11%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=632.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.70(s,1H),7.95(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),7.85(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.47(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.18(d,J=6.5Hz,1H),6.53(d,J=9.0Hz,1H),5.29(dd,J=9.6,4.9Hz,1H),4.43(d,J=5.7Hz,1H),4.22–4.12(m,1H),4.01(ddd,J=16.5,11.4,4.5Hz,2H),3.78(dd,J=9.5,2.6Hz,1H),3.67(dd,J=9.5,5.4Hz,1H),3.54(t,J=9.9Hz,1H),3.49–3.39(m,1H),3.26(d,J=6.8Hz,2H),3.09(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.76–2.65(m,1H),2.34–2.24(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.04–0.93(m,1H),0.49(d,J=7.1Hz,2H),0.16(d,J=7.1Hz,2H).
Example 81N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (110mg,0.48mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (195mg,0.47mmol), HATU (0.25g,0.64mmol) and DIPEA (0.30mL,1.82mmol) were dissolved in DCM (20mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 13 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.2mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/2) to givePale yellow solid (85mg, 29%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=624.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.67(s,1H),7.89(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),7.82(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.64–7.57(m,2H),7.54(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.45(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.16(t,J=7.9Hz,1H),6.51–6.40(m,1H),5.25(dd,J=10.0,4.5Hz,1H),4.58(dt,J=23.3,3.9Hz,1H),4.48(dd,J=15.6,11.8Hz,2H),4.14–3.89(m,3H),3.88–3.75(m,2H),3.68(d,J=3.9Hz,1H),3.66–3.57(m,1H),3.50(dd,J=18.6,8.6Hz,1H),3.45–3.34(m,1H),3.07(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.71–2.62(m,1H),2.51(dd,J=12.4,6.5Hz,1H),2.38–2.15(m,1H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 826- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
Under nitrogen, (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (20mg,0.09mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (30mg,0.07mmol), EDCI (20mg,0.10mmol), HOBt (15mg,0.11mmol) and TEA (10mg,0.10mmol) were added to DCM (4mL) and stirred at rt for 23 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a white solid (35mg, 77%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=628.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.68(d,J=1.9Hz,1H),7.93(dd,J=8.9,2.3Hz,1H),7.86(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.61(t,J=6.2Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.02(d,J=6.8Hz,1H),6.46(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),6.18(t,J=74.7Hz,1H),5.29(dd,J=10.9,4.4Hz,1H),4.57(d,J=31.5Hz,1H),4.25(dt,J=18.8,6.5Hz,2H),4.01(ddd,J=15.9,11.0,4.2Hz,3H),3.57–3.36(m,2H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.72–2.63(m,1H),2.30(dd,J=20.2,11.8Hz,1H),1.28(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 836- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
Under nitrogen, (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (20mg,0.09mmol), 6- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (30mg,0.07mmol), EDCI (20mg,0.10mmol), HOBt (15mg,0.11mmol) and TEA (10mg,0.10mmol) were added to DCM (4mL) and stirred at rt for 23 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a white solid (35mg, 77%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=628.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.76–8.54(m,1H),7.90(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),7.78(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.52(t,J=12.1Hz,2H),7.43(dd,J=14.8,7.4Hz,3H),6.41(t,J=10.6Hz,1H),6.21(dd,J=90.5,59.1Hz,1H),5.25(d,J=5.3Hz,1H),4.51(s,1H),4.22(dt,J=9.7,8.8Hz,2H),4.03(d,J=7.1Hz,1H),3.93(ddd,J=16.7,11.3,4.6Hz,2H),3.58–3.42(m,2H),3.07(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.73–2.60(m,1H),2.29(dd,J=20.6,11.3Hz,1H),1.24(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 846- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxo) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
NaH (150mg,3.75mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (210mg,0.55mmol) in DMF (10mL) under nitrogen and after 5min, 3-bromo-3, 3-difluoropropyl-1-ene (0.50mL, 4.91mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. Pouring the reaction solution into H2The reaction was quenched in O (45mL), then extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a colorless clear oil (160mg, 64%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=457.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
Pd/C (30mg, 5%) was added to a solution of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxo) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (130mg,0.28mmol) in EtOAc (10mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction mixture was filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless transparent liquid (110mg, 84%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=459.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (110mg,0.24mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2In O (10mL/2mL), the mixture was stirred at 60 ℃ for 12 hours. The reaction solution is decompressed and concentrated to remove the organic solvent, HCl solution (1mol/L) is slowly dropped to adjust the pH of the system to about 6 under the cooling and stirring of ice bath, then the EtOAc (50mL multiplied by 2) is used for extraction, and the organic solvent and the EtOAc are combinedThe organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (90mg, 84%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=445.3[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (50mg,0.22mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (50mg,0.11mmol), HATU (100mg,0.26mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (15mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a brown solid (25mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=656.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.68(s,1H),7.94(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),7.86(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.07(d,J=6.5Hz,1H),6.46(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),5.30(dd,J=8.8,5.0Hz,1H),4.57–4.43(m,1H),4.22(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),4.19–4.08(m,2H),4.01(ddd,J=29.7,11.4,4.5Hz,2H),3.53–3.43(m,2H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.73–2.63(m,1H),2.30–2.23(m,1H),1.99–1.89(m,2H),1.28(d,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.00(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 85N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S,4S) -2- ((trifluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide/N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S,4R) -2- ((trifluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((trifluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (500mg,1.31mmol), AgOTf (700mg,2.72mmol), selectfluor (740mg,1.98mmol) and KF (230mg,3.96mmol) were dissolved in EtOAc (5mL) under nitrogen, 2-fluoropyridine (0.25mL,2.80mmol) was added, and CF was slowly added dropwise 3TMS (0.40mL,3.00mmol) was added dropwise over 30min, and stirred at room temperature for 30 h. Saturated NaHCO was slowly added to the reaction solution3The solution (40mL) was then extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product isolated by column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give the product as a yellow solid (140mg, 24%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=449.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((trifluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((trifluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (40mg,0.089mmol) and LiOH. H2O (70mg,1.64mmol) in MeOH/H2O (5mL/1mL), and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. Concentrating the reaction solution under reduced pressure to remove organic solvent, adding H into the residue2O (15mL), HCl solution (1mol/L) is slowly added dropwise to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, the aqueous phase is extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2),the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a brown solid (30mg, 77%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=435.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S,4S) -2- ((trifluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide/N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S,4R) -2- ((trifluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (30mg,0.13mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- ((trifluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (31mg,0.071mmol), HATU (0.10g,0.26mmol) and DIPEA (0.10mL,0.61mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) under nitrogen and stirred at RT for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) to give a yellow solid (30mg, 65%). The product was further separated by chiral chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give product 85-1(15mg, 32%, Rt ═ 9.13min) as a white solid and 85-2(15mg, 32%, Rt ═ 18.09min) as a white solid.
85-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=646.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.70(d,J=1.9Hz,1H),7.97(d,J=6.9Hz,1H),7.88(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.42(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.99(d,J=6.3Hz,1H),6.45(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),5.31(dd,J=9.5,5.1Hz,1H),4.68(t,J=10.6Hz,1H),4.33–4.18(m,2H),4.02(ddd,J=19.1,9.7,5.5Hz,3H),3.89–3.76(m,1H),3.39(t,J=9.7Hz,1H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.51(dd,J=12.7,6.7Hz,1H),2.37–2.28(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
85-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=646.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.68(d,J=1.6Hz,1H),7.96(dd,J=8.8,2.0Hz,1H),7.89(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.94(d,J=6.6Hz,1H),6.47(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),5.31(t,J=7.3Hz,1H),4.60(dd,J=14.6,7.8Hz,1H),4.46–4.40(m,1H),4.35(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),4.12–3.95(m,3H),3.52(dt,J=18.1,9.1Hz,2H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.75–2.65(m,1H),2.36–2.19(m,1H),1.29(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 86N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 6- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate
(2S) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (450mg,1.49mmol), methyl 6-fluoropyridine-3-carboxylate (400mg,2.58mmol) and K under nitrogen 2CO3(1.58g,8.82mmol) was added to MeCN (50mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure, ice water (10mL) was added to the residue, followed by extraction with EtOAc (30 mL. times.3), and the organic phase was extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a pale yellow solid (380mg, 58%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=438.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Ethyl 6- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (210mg,0.48mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2In O (10mL/2mL),stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added dropwise to the residue under cooling in ice bath with stirring to adjust the system pH to about 6, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (140mg, 69%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=424.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (96mg,0.42mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (150mg,0.35mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) were dissolved in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 13 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (20mg, 9%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=635.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.60&8.55(s,1H),7.92(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),7.83(t,J=7.5Hz,2H),7.79(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.50(t,J=8.1Hz,1H),7.47–7.42(m,2H),7.40(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.20–7.07(m,1H),6.45&6.41(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),5.23(dd,J=16.7,8.0Hz,1H),5.16(dd,J=10.4,4.7Hz,1H),4.09–3.99(m,1H),3.94&3.92(s,3H),3.90-3.83(m,2H),3.77–3.66(m,1H),3.64–3.52(m,1H),3.26&3.24(s,3H),3.11–3.01(m,2H),2.83(dt,J=13.7,6.9Hz,1H),2.18(dd,J=21.7,11.7Hz,1H),1.26&124(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 87N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S) -2- ((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- (((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
NaH (100mg,2.50mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of (R) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl housesulfonate (505mg,3.04mmol) and ethyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinate (120mg,0.30mmol) in THF (6mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was quenched by adding HCl solution (1mol/L) to the reaction mixture and adjusting the pH of the system to about 5, then the mixture was diluted with saturated NaCl solution (15mL), extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a yellow solid (30mg, 23%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 437.1[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step two: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S) -2- (((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) EtOH (30mg,0.13mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- ((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (50mg,0.11mmol), EDCI (32mg,0.17mmol), HOBt (23mg,0.17mmol) and TEA (0.1mL,0.72mmol) were dissolved in DCM (4mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give the product as a white solid (25mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=648.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.68(s,1H),7.92(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),7.86(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.07(t,J=6.0Hz,1H),6.48(d,J=7.9Hz,1H),5.30(dd,J=5.7,3.9Hz,1H),4.44(dd,J=17.7,10.5Hz,1H),4.12(d,J=9.3Hz,1H),4.04(d,J=6.5Hz,2H),3.97(dd,J=11.1,5.0Hz,1H),3.76(ddd,J=14.5,11.0,5.2Hz,4H),3.67(dd,J=13.2,8.7Hz,2H),3.46(ddd,J=25.6,13.7,8.7Hz,2H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.71–2.62(m,1H),2.24(dd,J=17.5,9.2Hz,1H),2.02–1.92(m,2H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 882- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (2- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidin-5-yl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of N- (2-chloropyrimidin-5-yl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide
2-Chloropyrimidin-5-amine (202mg,1.56mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (451mg,1.98mmol), EDCI (441mg,2.30mmol), HOBt (334mg,2.47mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) under nitrogen and TEA (0.65mL,4.70mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. To the reaction mixture was added a saturated NaCl solution (50mL), followed by extraction with DCM (50 mL. times.2) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a yellow solid (177mg, 33%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=340.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (2- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidin-5-yl) acetamide
DIPEA (0.47mL,2.60mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (238mg,0.92mmol), N- (2-chloropyrimidin-5-yl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide (177mg,0.52mmol) in DMF (2mL) under nitrogen, and the mixture was warmed to 90 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (40)mL), then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a yellow solid (51mg, 17%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=563.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):10.15(s,1H),8.53(s,2H),7.85(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.69(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.59(t,J=8.8Hz,4H),4.37(dd,J=9.6,7.5Hz,1H),4.25(dd,1H),3.79(s,2H),3.74(d,J=6.5Hz,1H),3.60–3.50(m,1H),3.46-3.38(m,2H),3.28(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.24(s,3H),2.64–2.54(m,1H),2.13(dd,J=20.3,11.6Hz,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 892- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Under nitrogen protection ((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (111mg,0.45mmol) and K2CO3(250mg,1.40mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (50mL), and 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (85mg,0.54mmol) was added under stirring at room temperature, and after the addition was completed, stirring at room temperature for 2 hours, and stirring at 55 ℃ for 12 hours. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, ice water (10mL) was added to the residue, an HCl solution (1mol/L) was added dropwise to the system, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 3, a solid precipitated, and the solid was collected by filtration to give a pale yellow solid (109mg, 66%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=368.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Under the protection of nitrogen, the mixture is subjected to2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (100mg,0.27mmol) and CuI (50mg,0.26mmol) were dissolved in MeCN (22mL), then 2, 2-difluoro-2- (fluorosulfonyl) acetic acid (0.30mL,3.0mmol) was added and the mixture was warmed to 55 ℃ and stirred for 10 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was dissolved in DCM (60mL), washed with HCl solution (30mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) to give a yellow solid (28mg, 25%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=418.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
Under nitrogen, (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (55mg,0.28mmol), 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (101mg,0.24mmol), HATU (169mg,0.43mmol) and DIPEA (0.40mL,2.42mmol) were dissolved in DCM (15mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (25mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (15mg, 10%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=599.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.82(s,2H),7.74(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.44(t,J=7.7Hz,4H),6.85(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),6.20(t,J=74.6Hz,1H),4.71(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.59(dd,J=10.3,6.6Hz,1H),4.51(ddd,J=10.1,8.0,2.4Hz,1H),4.37(dd,J=9.9,5.2Hz,1H),4.22(dd,J=9.9,2.3Hz,1H),3.54–3.37(m,2H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.74–2.63(m,1H),2.33(dt,J=21.2,10.5Hz,1H),1.25(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 90N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -2- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Under nitrogen ((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (900mg,3.67mmol) and K2CO3(2.00g,11.20mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (50mL), and ethyl 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (630mg,3.38mmol) was slowly added to the reaction with stirring at room temperature, and stirring was continued at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction solution was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, ice water (10mL) was added to the residue, the aqueous solution was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.3), and the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a pale yellow solid (1.11g, 77%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=396.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
NaH (210mg,5.25mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (340mg,0.86mmol) in DMF (16mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen and after 5min 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane (0.5mL,70mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction and after addition the reaction was stirred at this temperature for a further 3 h. Pouring the reaction solution into H2The reaction was quenched in O (50mL), then extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (332mg, 87%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=442.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (400mg,0.91mmol) and LiOH. H2O (280mg,6.54mmol) in THF/H2In O (10mL/2mL), the temperature was raised to 55 ℃ and the mixture was stirred for 6 hours. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added to adjust the pH of the system to about 6 while stirring and cooling in an ice bath, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (320mg, 85%).
Step four: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -2- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (140mg,0.61mmol), 2- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (150mg,0.36mmol), HATU (189mg,0.48mmol) and DIPEA (0.30mL,1.82mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/2) to give a light yellow solid (25mg, 11%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=625.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.79(d,J=3.4Hz,2H),7.80(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.59(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.31(t,J=6.0Hz,1H),5.26(d,J=3.0Hz,1H),4.62–4.40(m,4H),4.04–3.90(m,2H),3.87(s,2H),3.75–3.60(m,2H),3.49(t,J=10.8Hz,1H),3.45–3.33(m,1H),3.07(q,J=7.2Hz,2H),2.71–2.62(m,1H),2.36(dd,J=20.4,11.5Hz,1H),1.25(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 912- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
NaH (140mg,3.50mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (295mg,0.75mmol) in DMF (20mL) with cooling stirring at-20 ℃ under nitrogen and after 1h bromomethylcyclopropane (0.45mL,4.60mmol) was added slowly and after addition was displaced at room temperature and stirred for 6 h. The reaction was poured into ice water (80mL), then extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow oil (152mg, 45%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=450.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (150mg,0.33mmol) and LiOH. H2O (130mg,3.04mmol) in THF/H2O (10mL/2mL), and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added while cooling in ice bath and stirring to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a yellow solid (130mg, 92%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=422.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (60mg,0.26mmol), 2- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (85mg,0.20mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) were dissolved in DCM (11mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (65mg, 51%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=633.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.81(s,2H),7.90(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.50(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.94(d,J=6.4Hz,1H),5.32(dd,J=9.8,4.3Hz,1H),4.58(dd,J=10.8,7.4Hz,1H),4.51(dd,J=15.0,7.7Hz,1H),4.05(ddd,J=32.7,11.4,4.2Hz,2H),3.88(d,J=9.2Hz,1H),3.79(dd,J=9.4,5.6Hz,1H),3.54(t,J=10.9Hz,1H),3.49–3.38(m,1H),3.31(d,J=6.7Hz,2H),3.12(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.75–2.65(m,1H),2.44–2.33(m,1H),1.31(t,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.03(tt,J=11.7,5.8Hz,1H),0.52(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),0.20(d,J=4.5Hz,2H).
Example 922- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (50mg,0.22mmol), 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (81mg,0.19mmol) under nitrogen,HATU (120mg,0.31mmol) and DIPEA (0.30mL,1.82mmol) were dissolved in DCM (22mL) and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (100mL) and then successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L), saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (14mg, 11%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=629.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.83(s,2H),7.92(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.46(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.93(d,J=6.3Hz,1H),6.23(t,J=74.6Hz,1H),5.33(dd,J=6.6,3.8Hz,1H),4.66–4.58(m,1H),4.53(dd,J=10.4,6.9Hz,1H),4.40(dd,J=9.9,5.1Hz,1H),4.24(d,J=9.9Hz,1H),4.13–3.99(m,2H),3.56–3.44(m,2H),3.12(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.75–2.66(m,1H),2.03(dd,J=14.1,6.7Hz,1H),1.32(d,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 932- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (50mg,0.22mmol), 2- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (81mg,0.19mmol), HATU (120mg,0.31mmol) and DIPEA (0.30mL,1.82mmol) were dissolved in DCM (22mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (100mL) and then successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L), saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (14mg, 11%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=629.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.80(d,J=4.8Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.61(t,J=7.5Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.49–7.38(m,3H),6.24(td,J=74.6,21.4Hz,1H),5.25(d,J=5.6Hz,1H),4.63–4.42(m,2H),4.36(dd,J=9.7,5.0Hz,1H),4.25–4.08(m,1H),3.88(dd,J=42.0,11.7Hz,2H),3.61(s,1H),3.55–3.37(m,2H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.75–2.60(m,1H),2.38–2.24(m,1H),1.24(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 942- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Under nitrogen protection ((2S) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (3.20g,13.0mmol) and K2CO3(6.70g,37.40mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (50mL), and then methyl 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (2.50g,13.40mmol) was added to the reaction system, which was stirred at room temperature for 8 h. Filtering the reaction solution, concentrating the filtrate under reduced pressure, and adding H into the residue 2O (10mL) was then extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.3), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a light yellow solid (3.05g, 59%).
Step two: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxo) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
NaH (160mg,4.00mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (280mg,0.71mmol) in DMF (16mL) under nitrogen, stirred at room temperature for 5min, 3-bromo-3, 3-difluoropropyl-1-ene (0.5mL, 4.91mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction system and the reaction system was cooledStirring was continued for 3h at room temperature. Pouring the reaction solution into H2O (45mL), extracted with DCM (50 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a pale yellow solid (160mg, 48%).
Step three: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Pd/C (30mg, 5%) was added to a solution of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (120mg,0.25mmol) in EtOAc (10mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 5 h. The reaction mixture was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a colorless transparent liquid (100mg, 83%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=474.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (120mg,0.25mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2O (10mL/2mL) was stirred at room temperature for 22 hours. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added dropwise to the residue with stirring and cooling in ice bath to adjust the system pH to about 6, followed by extraction with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a colorless liquid (90mg, 80%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=446.3[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (50mg,0.22mmol), 2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (80mg,0.18mmol), HATU (100mg,0.26mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (15mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (25mg, 21%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=657.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.81(s,2H),7.85(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.42(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.14(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),5.27(dd,J=6.0,4.0Hz,1H),4.58(dd,J=8.5,5.4Hz,1H),4.51(dd,J=13.5,7.5Hz,1H),4.32(dd,J=9.9,5.3Hz,1H),4.21(d,J=9.9Hz,1H),4.00(ddd,J=16.2,11.4,4.3Hz,2H),3.51–3.33(m,2H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.70–2.62(m,1H),2.36–2.25(m,1H),2.00–1.89(m,2H),1.27(d,J=7.4Hz,3H),1.00(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 95N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -2- ((2S) -2- (((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
NaH (126mg,3.15mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of (R) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl methanesulfonate (630mg,3.79mmol) and ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (250mg,0.63mmol) in THF (6mL) with stirring under nitrogen cooling in an ice bath, and after addition, the mixture was removed at room temperatureStirring for 24 h. The reaction was quenched by adding HCl solution (1mol/L) to the reaction mixture and adjusting the pH of the solution to about 5, saturated NaCl solution (20mL) was added to the mixture, followed by extraction with EtOAc (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a yellow solid (50mg, 18%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=438.0[M+1]+.
Step two: n- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -2- ((2S) -2- ((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (31mg,0.14mmol), 2- ((2S) -2- ((((S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (50mg,0.11mmol), EDCI (32mg,0.17mmol), HOBt (23mg,0.17mmol) and TEA (23mg,0.23mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 20/1) to give a white solid (35mg, 47%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=649.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.79(s,2H),7.85(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.13(t,J=7.5Hz,1H),5.28(dd,J=10.5,4.3Hz,1H),4.53(dd,J=10.5,6.9Hz,1H),4.48–4.39(m,1H),4.10–4.04(m,1H),4.02(d,J=2.7Hz,1H),3.96(dd,J=11.0,4.9Hz,1H),3.87–3.80(m,1H),3.78(d,J=4.2Hz,2H),3.75(d,J=4.5Hz,1H),3.67(ddd,J=13.6,9.6,6.3Hz,2H),3.52–3.43(m,1H),3.39(dd,J=18.0,10.7Hz,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.70–2.60(m,1H),2.31(dd,J=19.8,11.6Hz,1H),2.02–1.95(m,1H),1.95–1.85(m,1H),1.27(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 96N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Under the protection of nitrogen, adding K 2CO3(1.80g,10.1mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (450mg,1.49mmol) and ethyl 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (440mg,2.36mmol) in MeCN (45mL) and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. Filtering the reaction solution, concentrating the filtrate under reduced pressure, and adding H to the residue2O (30mL) and then extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a pale yellow solid (510mg, 76%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=453.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (210mg,0.46mmol) and LiOH. H2O (150mg,3.50mmol) in THF/H2O (10mL/2mL), and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. Concentrating the reaction solution under reduced pressure to remove organic solvent, adding the residue into H2O (15mL), slowly adding HCl solution (1mol/L) under ice bath, adjusting system pH to about 6, then extracting with EtOAc (50mL × 2), combining organic phases and washing with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/5) to give a yellow solid (140mg, 71%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 425.3[ M +1 ═ M ]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (96mg,0.42mmol), 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (140mg,0.33mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) were dissolved in DCM (13mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow solid (50mg, 24%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=636.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.80–8.66(m,2H),7.84(d,J=6.3Hz,2H),7.60(d,J=5.0Hz,2H),7.55–7.32(m,4H),7.17–7.04(m,1H),5.24–5.15(m,2H),4.63–4.47(m,1H),4.02-3.96(m,2H),3.91(s,3H),3.72(dd,J=19.8,10.2Hz,1H),3.63–3.48(m,1H),3.27&3.26(s,3H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.93–2.82(m,1H),2.18(dd,J=22.4,11.2Hz,1H),1.26(t,J=7.4Hz,,3H).
Example 97N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -N- (2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -2-hydroxyacetamide
2-Hydroxyacetic acid (1.01g,13.3mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (2.00g,10.0mmol), HATU (6.05g,15.4mmol) and DIPEA (2.0mL,12.12mmol) were dissolved in DCM (40mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. Pouring the reaction solution into H 2O (100mL) and extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phase was successively saturated withAnd NaHCO3Washed with aqueous solution (30mL) and saturated NaCl solution (30mL) over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a light yellow solid (2.10g, 62%).
Step two: synthesis of 2- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) amino) ethanol
N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -2-hydroxyacetamide (2.30g,8.94mmol) was dissolved in THF (32mL) under nitrogen, and BH was stirred under cooling in an ice bath3·SMe2The THF solution (3.5mL,35mmol,10mol/L) was added dropwise to the reaction system, and after the addition was completed, the reaction system was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. Slowly adding saturated NH into the reaction liquid under ice bath4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, the remaining aqueous solution was extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (400mg, 18%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=244.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -N- (2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzamide
2- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) amino) ethanol (105mg,0.43mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (200mg,0.53mmol), EDCI (500mg,2.56mmol) and HOBt (100mg,0.72mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give (50mg, 19%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=605.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.94(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.55–7.48(m,2H),7.42(dd,J=19.3,11.6Hz,4H),6.65(t,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.88(s,2H),4.14(d,J=4.0Hz,1H),3.85–3.78(m,2H),3.64(d,J=9.9Hz,3H),3.54(t,J=9.3Hz,1H),3.48–3.36(m,2H),3.34(d,J=7.7Hz,3H),3.16(dd,J=14.8,7.4Hz,2H),2.76–2.66(m,1H),2.29–2.20(m,1H),2.03(d,J=5.6Hz,1H),1.65(d,J=7.5Hz,1H),1.29(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 984- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) ethanol (60mg,0.26mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (60mg,0.14mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.70mL,4.24mmol) were dissolved in DCM (21mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: EtOAc/DCM (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a white solid (50mg, 55%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=628.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.79(s,1H),8.04(d,J=7.4Hz,1H),7.99(d,J=7.4Hz,1H),7.79(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.46(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.08(d,J=3.4Hz,1H),6.70(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),6.21(t,J=74.4Hz,1H),5.38-5.30(m,1H),4.37–4.21(m,1H),4.14(d,J=10.0Hz,2H),4.03(d,J=11.2Hz,1H),3.92(dt,J=22.2,8.7Hz,2H),3.66–3.47(m,2H),3.41(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.86–2.71(m,1H),2.34–2.21(m,1H),1.33(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 994- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) ethanol (100mg,0.43mmol), 4- ((2R) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (190mg,0.46mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.40mL,2.42mmol) were dissolved in DCM (20mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: EtOAc/DCM (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a white solid (100mg, 35%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 628.1[ M +1 ═ M]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.73(s,1H),7.96(s,2H),7.76(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.46(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.28(s,1H),6.66(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),6.20(t,J=74.3Hz,1H),5.29(s,1H),4.29(d,J=4.7Hz,1H),4.12(d,J=10.2Hz,1H),4.05(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),3.92(ddd,J=28.8,14.3,6.1Hz,3H),3.59(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.50(dd,J=17.2,9.1Hz,1H),3.37(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.83–2.71(m,1H),2.27(dd,J=19.2,11.1Hz,1H),1.30(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 1004- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) ethanol (50mg,0.22mmol), 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (50mg,0.11mmol), HATU (100mg,0.26mmol) and DIPEA (0.20mL,1.21mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction solution was washed with DCM (15mL) Diluting with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a light yellow solid (25mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=656.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.76(s,1H),8.01(d,J=8.1Hz,1H),7.96(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.75(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.05(d,J=7.0Hz,1H),6.68(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.31(dd,J=6.0,4.0Hz,1H),4.30–4.20(m,1H),4.18–4.05(m,2H),4.00(dd,J=11.2,4.3Hz,1H),3.91–3.78(m,2H),3.60–3.51(m,1H),3.51–3.43(m,1H),3.38(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.80–2.70(m,1H),2.26–2.16(m,1H),2.02–1.89(m,2H),1.30(t,J=7.5Hz,3H),1.02(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 1016- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) ethanol (60mg,0.26mmol), 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (90mg,0.22mmol), HATU (0.17g,0.43mmol) and DIPEA (0.50mL,3.03mmol) were dissolved in DCM (15mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: EtOAc/DCM (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a white solid (30mg, 22%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 629.1[ M +1 ═ M]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.74(s,1H),8.67(s,1H),7.99(dd,J=17.2,8.2Hz,2H),7.93(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),7.62(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.14(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),6.46(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),6.18(t,J=74.8Hz,1H),5.34-5.27(m,1H),4.57-4.51(m,1H),4.26(dt,J=23.3,8.0Hz,2H),4.04(dtd,J=15.2,11.1,3.8Hz,3H),3.56–3.42(m,2H),3.38(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.72–2.62(m,1H),2.31(dd,J=20.9,10.9Hz,1H),1.30(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 1022- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (5- (ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) ethanol (70mg,0.30mmol), 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) pyrrolidine-5-carboxylic acid (120mg,0.29mmol), HATU (200mg,0.51mmol) and DIPEA (0.70mL,4.24mmol) were dissolved in DCM (21mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (10mL) and successively with HCl solution (25mL,0.5mol/L), saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: EtOAc/DCM (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a white solid (75mg, 41%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=630.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.80(d,J=1.4Hz,2H),8.69(s,1H),7.97(s,2H),7.61(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.31(d,J=6.9Hz,1H),6.20(t,J=74.6Hz,1H),5.29(d,J=4.4Hz,1H),4.57(dd,J=9.5,5.9Hz,1H),4.53–4.45(m,1H),4.36(dd,J=9.7,5.1Hz,1H),4.20(d,J=9.6Hz,1H),4.12(dd,J=14.3,7.2Hz,1H),4.07–3.93(m,2H),3.47(dd,J=19.0,8.7Hz,1H),3.36(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.72–2.61(m,1H),2.32(dd,J=21.2,11.5Hz,1H),1.29(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 1034- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid ester
Under nitrogen protection, a solution of (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) magnesium bromide (25mL,25mmol,1.0mol/L) was slowly added dropwise with cooling stirring at-78 ℃ to a solution of (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4-oxopyrrolidine-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid ester (2.64g,10.3mmol) in THF (32mL), after which stirring was continued for 2h at this temperature and then in a-10 ℃ cold bath for 25 h. Adding saturated NH into the reaction system under cooling and stirring at the temperature of minus 10 DEG C 4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, the residue was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and taken up with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (800mg, 20%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=412.1[M+23]+.
Step two: synthesis of tert-butyl 4-hydroxy-2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
Under the protection of nitrogen, cooling and stirring at-10 ℃, and reacting LiBH4(30mg,1.35mmol) was added to a solution of 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid ester (300mg,0.77mmol) in THF (10mL), and after addition, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 h. Under the condition of ice bath cooling and stirring, dropwise adding H into the system2The reaction was quenched with O (20mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, the residue was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a clear liquid (210mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=384.1[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of tert-butyl 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
Tert-butyl 4-hydroxy-2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (210mg,0.58mmol) and KOAc (500mg,5.04mmol) were dissolved in DCM/H under nitrogen 2O (2mL/1mL), then CF is added dropwise2BrTMS (0.70mL,5.00mmol) was stirred at room temperature for 10 h. Slowly pouring the reaction solution into H2O (30mL), extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (140mg, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=434.1[M+23]+.
Step four: synthesis of 5- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-3-ol
Tert-butyl 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (140mg,0.34mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (10mL) and HCl in MeOH (10mL,3mol/L) was added to the reaction and stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a pale yellow solid (100mg, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=312.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of methyl 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, 4-iodobenzoic acid methyl ester (85mg,0.32mmol),5- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-3-ol (90mg,0.29mmol), Pd2(dba)3(90mg,0.095mmol), XantPhos (50mg,0.084mmol) and Cs2CO3(400mg,1.23mmol) was dissolved in Toluene (5mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 16 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (68mg, 53%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=446.2[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (68mg,0.15mmol) and LiOH. H2O (90mg,2.10mmol) in MeOH/H2O (10mL/1mL), and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, HCl solution (1mol/L) was added dropwise to the remaining solution under ice bath to adjust the pH of the system to about 6, followed by extraction with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (60mg, 91%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=432.1[M+1]+.
Step seven: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (40mg,0.17mmol), 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (60mg,0.14mmol), HATU (100mg,0.26mmol) and DIPEA (0.10mL,0.61mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) and saturated NaHCO 3The solution (15mL) and saturated NaCl solution (15mL) were washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (19mg, 21%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=643.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,MeOD)δ(ppm):7.90(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.86(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.79(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=7.9Hz,4H),6.78(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),6.49(t,J=75.5Hz,1H),5.28(t,J=6.1Hz,1H),4.37–4.22(m,3H),3.92(t,J=9.3Hz,3H),3.67(d,J=10.5Hz,1H),3.21(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.70(dd,J=13.1,7.2Hz,1H),2.49(d,J=13.5Hz,1H),1.23(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 1044- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid ester
DAST (0.44mL,3.2mmol) was added slowly dropwise to a solution of 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl-4-hydroxy-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid ester (120mg,0.31mmol) in DCM (10mL) under nitrogen, and after addition was stirred at room temperature for an additional 6 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The solution (30mL) was then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a clear oil (65mg, 54%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=336.1[M-56+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of tert-butyl 4-fluoro-2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
Under the protection of nitrogen, cooling and stirring at-10 ℃, and reacting LiBH 4(20mg,0.90mmol) was added to a solution of 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid ester (150mg,0.38mmol) in THF (10mL), and after addition, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Under ice bath, H is dropwise added into the system2The reaction was quenched with O (30mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, the residue was extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a clear oil (110mg, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=308.1[M-56+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of tert-butyl 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
Tert-butyl 4-fluoro-2- (hydroxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (122mg,0.34mmol) and KOAc (400mg,4.03mmol) were dissolved in DCM/H under nitrogen2O (1mL/1mL), then adding CF2BrTMS (0.50mL,3.00mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. Adding H to the reaction solution2O (30mL) was then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a clear oil (120mg, 86%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=358.0[M-56+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
Tert-butyl 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (120mg,0.29mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (10mL) at room temperature, and HCl in MeOH (10mL,3mol/L) was added to the reaction and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was diluted with DCM (40mL) and saturated NaHCO3Solution (35mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (90mg, 99%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=314.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of methyl 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (90mg,0.29mmol), methyl 4-iodobenzoate (85mg,0.32mmol), Pd2(dba)3(90mg,0.095mmol), XantPhos (50mg,0.084mmol) and Cs2CO3(400mg,1.23mmol) was dissolved in Toluene (5mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 15 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (40mg, 31%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 448.1[ M +1 ═ M ]+.
Step six: synthesis of 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoate (50mg,0.11mmol) and LiOH. H2O (50mg,1.17mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (5mL/5mL/1mL), and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added dropwise to the residue under ice bath to adjust the system pH to about 6, then the aqueous solution was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a brown solid (30mg, 62%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=434.1[M+1]+.
Step seven: synthesis of 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
(R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (30mg,0.13mmol), 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -4-fluoro-4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (35mg,0.081mmol), HATU (100mg,0.26mmol) and DIPEA (0.10mL,0.61mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 13 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and successively with HCl solution (15mL,0.5mol/L), saturated NaHCO 3The solution (15mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (15mg, 29%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=645.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.85(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.05(d,J=7.0Hz,1H),6.65(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),6.20(t,J=74.1Hz,1H),5.26(dd,J=10.7,4.2Hz,1H),4.57–4.48(m,1H),4.14(td,J=10.5,3.5Hz,2H),4.06–3.81(m,4H),3.08(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.92–2.81(m,1H),2.71-2.55(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 1052- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 3- (((trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl) oxy) -5, 6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
Stirring at-10 deg.C under nitrogen protection, adding Tf2O (2.65mL,13.00mmol) was added slowly dropwise to a solution of tert-butyl 3-oxopiperidine-1-carboxylate (2.00g,10.0mmol) and DMAP (3.80g,30.8mmol) in DCM (30mL) for 1.0h, after which it was stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Adding H into the reaction system under ice bath2The reaction was quenched with O (35mL), separated, the aqueous phase extracted with DCM (30mL), the organic phases combined and Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a colorless oily liquid (1.15g, 35%).
Step two: synthesis of 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -5, 6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
Under nitrogen protection, (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) boronic acid (600mg,3.32mmol), 3- (((trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl) oxy) -5, 6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (970mg,3.02mmol), Pd (dppf) 2Cl2(220mg,0.30mmol) and Cs2CO3(3.30g,9.06mmol) was dissolved in 1, 4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 105 ℃ for 8 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1:1) to give a pale yellow solid (690mg, 72%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=272.2[M+1-56]+.
Step three: synthesis of tert-butyl 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
Pd/C (760mg, 5%) was added to a solution of tert-butyl 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -5, 6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (800mg,2.44mmol) in MeOH (50mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 3H. Filtration over celite and concentration of the filtrate under reduced pressure gave a colorless oil (700mg, 87%).
Step four: synthesis of 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine
Tert-butyl 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (700mg,2.13mmol) was dissolved in DCM/TFA (50mL/5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 2 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to give the hydrochloride of the product as a pale yellow liquid (391mg, 80%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=230.1[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 1- (4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine
Under the protection of nitrogen, 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine hydrochloride (800mg,3.49mmol), 1-iodo-4-nitrobenzene (900mg,3.61mmol), Pd 2(dba)3(339mg,0.35mmol), XantPhos (243mg,0.35mmol) and Cs2CO3(2.50g,6.98mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (560mg, 46%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=351.3[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of 4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) aniline
Pd/C (860mg, 5%) was added to a solution of 1- (4-nitrophenyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine (580mg,1.66mmol) in MeOH (50mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 3.5 h. Celite was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/DCM (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a colorless transparent liquid (470mg, 87%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=321.2[M+23]+.
Step seven: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) aniline (480mg,1.50mmol),2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (300mg,1.31mmol), EDCI (400mg,2.04mmol) and HOBt (300mg,2.15mmol) were dissolvedIn DCM (50mL), stir at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (50mL) and dried over anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (440mg, 55%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=531.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.90(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.58(dd,J=13.7,8.0Hz,4H),7.37(dd,J=17.1,8.3Hz,4H),6.90(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),3.79(s,2H),3.68(d,J=11.8Hz,2H),3.13(dd,J=14.8,7.3Hz,2H),3.00(t,J=11.1Hz,1H),2.78(t,J=11.5Hz,2H),2.05(d,J=11.9Hz,1H),1.96–1.76(m,2H),1.72–1.62(m,1H),1.30(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 1062- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 2-bromo-1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethanol
Under ice bath, NaBH is added4(210mg,5.55mmol) was added to a solution of 2-bromo-1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethanone (502mg,1.88mmol) in MeOH (8mL) and stirring was continued for 1 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL) and then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless oily liquid (502mg, 99%).
Step two: synthesis of 2-amino-1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethanol
2-bromo-1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethanol (502mg,1.87mmol) was dissolved in NH3MeOH (10ml,7mol/L,70mmol), stirred at room temperature for 48 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure, the residue was filtered and washed with DCM, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow liquid (300mg, 78%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=206.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2-hydroxy-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) amino) phenyl) acetamide 2-amino-1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethanol (300mg,1.46mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4-iodophenyl) acetamide (941mg,2.19mmol), CuI (66mg,0.07mmol), ethylene glycol (0.08mL,2.00mmol), K 3PO4(627mg,2.95mmol) was dissolved in i-PrOH (8mL), warmed to 90 ℃ and stirred for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with H2O (25mL) and saturated NaCl solution (25mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (251mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=507.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- (4- ((2-chloroethyl) (2-hydroxy-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) -amino) phenyl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide
Chloroacetaldehyde (0.32mL,2.00mmol, 40%) was added to a solution of AcOH (0.02mL,0.30mmol) and 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2-hydroxy-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -ethyl) -amino) phenyl) acetamide (103mg,0.20mmol) in EtOH (5mL), stirred at room temperature for 2h, then AcOH (2mL) and NaBH were added3CN (195mg,3.10mmol), and stirring was continued for 5 h. Adding saturated Na to the reaction solution2CO3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), the aqueous phase extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (15mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (112mg, 97%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=569.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) phenyl) acetamide
NaH (15mg,0.37mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of N- (4- ((2-chloroethyl) (2-hydroxy-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) amino) phenyl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide (112mg,0.20mmol) in DMF (6mL) on an ice bath and, after addition, warmed to room temperature and stirred for 16 h.Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with a solution (20mL), and the mixture was diluted with EtOAc (80mL), followed by saturated NaHCO3The solution (10 mL. times.4) and a saturated NaCl solution (10 mL. times.3) were washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a yellow solid (18mg, 17%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=533.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.88(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.56–7.51(m,4H),7.37(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),7.21(s,1H),6.87(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.73(dd,J1=10.1Hz,1H),4.18(dd,J1=11.3Hz,1H),4.00–3.90(td,J=11.6Hz,6.8Hz,1H),3.77(s,2H),3.56(dd,J=11.7Hz,1H),3.46(dd,J=11.7Hz,1H),3.11(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.94(dd,J=11.7,3.3Hz,1H),2.70–2.62(m,1H),1.29(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 107N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 2-chloro-N- (2-hydroxy-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) acetamide
2-amino-1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethanol (2.0g,9.7mmol) and TEA (1.50mL,11.00mmol) were dissolved in DCM (20mL), cooled in an ice bath and stirred, 2-chloroacetyl chloride (0.80mL,10.00mmol) was added slowly and stirred at room temperature for 17 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was dissolved in DCM (80mL) and then saturated NaHCO was used successively3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (1.11g, 43%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=282.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholin-3-one
Will K2CO3(1.53g,11.1mmol) was added to a solution of 2-chloro-N- (2-hydroxy-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) acetamide (1.0g,3.6mmol) in DMF (25mL), stirred at room temperature for 12h, warmed to 60 ℃ and stirred for 24 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (80mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.6) and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (378mg, 43%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=246.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine
Mixing LiAlH4(400mg,10.54mmol) was added to a solution of 6- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholin-3-one (378mg,1.54mmol) in THF (10mL), the temperature was raised to 80 ℃ and stirred for 5 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, poured into NaOH solution (20mL,2.0mol/L), the aqueous phase extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oily liquid (233mg, 65%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=232.3[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) benzonitrile
Under the protection of nitrogen, 2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine (233mg,1.01mmol), 4-bromoxynil (367mg,2.02mmol) and Pd2(dba)3(92mg,0.10mmol), XantPhos (64mg,0.11mmol) and Cs2CO3(669mg,2.05mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (5mL) and stirred at 110 ℃ for 24 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with DCM (80mL), and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 5/1/1) to give a yellow solid (138mg, 41%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=333.1[M+1]+。
Step five: synthesis of 4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) benzoic acid
MeONa (488mg,8.71mmol) was added to a solution of 4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) benzonitrile (138mg,0.415mmol) in EtOH (4mL), and the mixture was warmed to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure, HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) was added to the residue, then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (138mg, 95%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=352.1[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) benzamide
4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) benzoic acid (59mg,0.17mmol), (4-ethanesulfonylphenyl) methylamine (50mg,0.25mmol), EDCI (64mg,0.33mmol) and HOBt (50mg,0.37mmol) were dissolved in DCM (3mL) and TEA (0.10mL,0.72mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) and saturated Na 2CO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (52mg, 58%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=533.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.75(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.55(t,J=8.1Hz,4H),6.93(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),6.47(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),4.73(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),4.71(dd,1H),4.22(dd,J=11.4,2.6Hz,1H),3.95(td,J=11.6,2.8Hz,1H),3.76(d,J=12.5Hz,1H),3.66(d,J=12.4Hz,1H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.06–3.01(m,1H),2.79(dd,J=12.1,10.7Hz,1H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
EXAMPLE 108 Synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) benzamide
4- (2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholine) benzoic acid (64mg,0.182mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethanesulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (62mg,0.27mmol), EDCI (70mg,0.36mmol) and HOBt (50mg,0.370mmol) were dissolved in DCM (3mL), TEA (0.10mL,0.72mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,1.0mol/L) and saturated Na2CO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a yellow solid (67mg, 65%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=563.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.92(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.80(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.68(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.58(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),6.95(m,3H),5.39–5.31(m,2H),4.75(dd,J=10.5,2.3Hz,1H),4.25(dd,J=11.6,2.3Hz,1H),4.14–4.02(m,2H),4.02–3.94(m,1H),3.79(d,J=11.9Hz,1H),3.69(d,J=12.6Hz,1H),3.12(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.12-3.06(m,1H),2.82(dd,J=12.2,10.7Hz,1H),1.31(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 109N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (4-methyl-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperazin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of tert-butyl (2- ((2-ethoxy-2-methoxyethyl) amino) -2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) carboxylate tert-butyl (2-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) carboxylate (1.78g,5.87mmol) and 2, 2-dimethoxyethylamine (1.30mL,11.90mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (10mL) and AcOH (0.70mL,12.00mmol) was added and after stirring at room temperature for 1h, NaBH was added 3CN (3.70g,58.9mmol), stirring was continued at room temperature for 5 h. The reaction solution was poured into saturated Na2CO3The reaction was quenched in solution (40mL), the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and saturated Na was usedCl solution (30mL) washing, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow oily solid (520mg, 22%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=407.4[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of tert-butyl (2- ((2-ethoxy-2-methoxyethyl) (methyl) amino) -2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) carboxylate
Tert-butyl (2- ((2-ethoxy-2-methoxyethyl) amino) -2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) carboxylate (316mg,0.78mmol), HCHO (70mg,2.33mmol) and AcOH (0.10mL,1.70mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (4mL), stirred at room temperature for 1h, then NaBH was added3CN (501mg,7.97mmol), stirring was continued at room temperature for 12 h. Adding saturated Na to the reaction solution2CO3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), the aqueous phase extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a white solid (317mg, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=421.5[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 1-methyl-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperazine
Tert-butyl (2- ((2-ethoxy-2-methoxyethyl) (methyl) amino) -2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) carboxylate (316mg,0.75mmol) was dissolved in a solution of HCl in i-PrOH (10mL,45.80mmol,4.58mol/L) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Adding NaBH into the reaction solution 3CN (800mg,12.73mmol), stirring was continued at room temperature for 5 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid. The solid was dissolved in THF (10mL) and LiAlH was added4(460mg,12.12mmol) was heated under reflux in an 80 ℃ oil bath for 20 h. The reaction was poured into NaOH solution (30mL,5mol/L), then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure to obtain yellow oilLiquid (211mg, 71%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=245.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- (4-methyl-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile
Under nitrogen protection, 1-methyl-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperazine (103mg,0.42mmol), 4-iodobenzonitrile (203mg,0.89mmol), Pd2(dba)3(80mg,0.09mmol), XantPhos (54mg,0.09mmol) and Cs2CO3(280mg,0.86mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (4mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 21 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (10mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a dark yellow solid (44mg, 30%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=346.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 4- (4-methyl-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperazin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (100mg,1.79mmol) was added to a solution of 4- (4-methyl-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile (44mg,0.13mmol) in EtOH (2mL), and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl in 1, 4-dioxane (4.8mol/L) was added to the reaction, the solution pH was adjusted to about 3, concentrated under reduced pressure, DCM (10mL) was added to the residue, filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated to give a yellow solid (46mg, 99%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=365.2[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (4-methyl-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperazin-1-yl) benzamide
4- (4-methyl-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperazin-1-yl) benzoic acid (46mg,0.13mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (35mg,0.15mmol), EDCI (54mg,0.28mmol) and HOBt (35mg,0.26mmol) were dissolved in DCM (3mL) and TEA (0.10mL,0.72mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3Solution (20mL) and saturationNaCl solution (20mL) wash, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc/MeOH (v/v/v) ═ 20/10/1) to give a yellow solid (6mg, 8%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=576.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.89(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),7.74(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),7.64(d,J=8.1Hz,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.54(d,J=8.1Hz,1H),6.89(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),5.34(d,J=4.7Hz,1H),5.32(s,1H),4.09–3.98(m,2H),3.81(d,J=11.5Hz,1H),3.65(d,J=12.1Hz,1H),3.19(dd,J=26.5,11.4Hz,1H),3.09(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.88–2.80(m,1H),2.60(dd,J=15.2,6.9Hz,1H),2.50(dd,J=23.1,2.4Hz,1H),2.38–2.31(m,1H),2.25–2.18(m,1H),2.09(s,3H),1.29(d,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 110N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholin-2-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4-acetyl-N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
4-Acetylbenzoic acid (2.0g,12.00mmol), (4-ethylsulfonylphenyl) methylamine (2.02g,10.10mmol), EDCI (3.82g,19.90mmol) and HOBt (2.70g,20.00mmol) were dissolved in DCM (20mL) and TEA (4.20mL,30.13mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was diluted with DCM (200mL) and successively with HCl solution (50mL,1mol/L), saturated NaCl solution (35mL) and NaHCO3Solution (35mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a white solid (2.6g, 74%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=346.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):8.03(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.91(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.86(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.75(t,J=6.0Hz,1H),4.77(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.64(s,3H),1.27(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Step two: synthesis of 4- (2-bromoacetyl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide NBS (2.47g,13.88mmol) was dissolved in THF (10mL) and this solution was added slowly dropwise to TsOH H2O (1.45g,7.62mmol) and 4-acetyl-N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide (2.58g,7.47mmol) in THF (20mL) were stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (120mL) and, in turn, saturated Na2CO3The solution (40mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (40mL) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (3.18g, 100%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=424.0[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (2-oxoacetyl) benzamide
4- (2-Bromoacetyl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide (502mg,1.18mmol) was dissolved in DMSO/H2O (4mL/0.1mL) in the mixed solvent, the temperature was raised to 50 ℃ and the mixture was stirred for 3.5 hours. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (80mL), and then with saturated NaHCO3The solution (15 mL. times.3) and a saturated NaCl solution (15mL) were washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (390mg, 92%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=360.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (1-hydroxy-2- ((4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -amino) ethyl) benzamide N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (2-oxoacetyl) benzamide (295mg,0.82mmol) and 4- (trifluoromethyl) aniline (160mg,0.99mmol) were dissolved in EtOH (8mL) and AcOH (0.10mL,1.7mmol) was added, stirred at room temperature for 4h, then NaBH was added3CN (530mg,8.43mmol), stirring was continued at room temperature for 12 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction liquid 3The solution (30mL) was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), and the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure,the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (233.4mg, 56%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=507.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 4- (2- (chloromethyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) oxazolin-5-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (1-hydroxy-2- ((4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -amino) ethyl) benzamide (100mg,0.23mmol), TsOH. H.under nitrogen protection2O (184mg,0.97mmol) and 2-chloroacetaldehyde (5.20g,26.00mmol, 40%) were dissolved in Toluene (6mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was diluted with DCM (60mL) and, in turn, with saturated NaHCO3The solution (30mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oily liquid (128mg, 99%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 567.2[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step six: synthesis of 4- (2- ((2-chloroethyl) (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) amino) -1-hydroxy-ethyl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
Reacting NaBH3CN (150mg,2.39mmol) was added to a solution of 4- (2- (chloromethyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) oxazolin-5-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide (128mg,0.23mmol) in AcOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 50 ℃ and stirred for 5 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature and saturated Na was slowly added 2CO3Solution (30mL) until no bubbles were formed, extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.3), and the organic phase was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a yellow solid (120mg, 93%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=569.1[M+1]+.
Step seven: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) morpholin-2-yl) benzamide
Will K2CO3(256mg,1.11mmol) 4- (2- ((2-chloroethyl) (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) amino) -1-hydroxy-ethyl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) was addedPhenyl) benzamide (120mg,0.21mmol) was dissolved in DMF (4mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with EtOAc (60mL), followed by saturated NaHCO3The solution (10mL) was washed with NaCl solution (10mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (25mg, 22%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=533.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(m,4H),7.53(m,6H),6.94(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),6.62(t,J=6.1Hz,1H),4.76(d,J=6.1Hz,2H),4.73(d,J=10.9Hz,1H),4.22(d,J=11.4Hz,1H),3.95(t,J=10.5Hz,1H),3.72(d,J=12.7Hz,1H),3.62(d,J=12.0Hz,1H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.07–3.00(m,1H),2.82–2.72(m,1H),2.02(m,1H),1.28(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 111N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (5-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-4-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 3-chloro-N- (2-hydroxy-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) propionamide
2-amino-1- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethanol (2.0g,9.70mmol), 3-chloropropionic acid (872mg,8.04mmol), HATU (4.52g,11.9mmol) and DIPEA (2.70mL,16.1mmol) were dissolved in DCM (30mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (100mL) and Na was added successively 2CO3The solution (40mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a white solid (1.02g, 43%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=296.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-5-one
Under the protection of nitrogen, 3-chloro-N-, (2-hydroxy-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) ethyl) propanamide (1.02g,3.45mmol) and K2CO3(2.50g,18.1mmol) was dissolved in DMF (30mL) and stirred at room temperature for 38 h. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was added EtOAc (80mL) and H2O (10mL), separation, washing of the organic phase with saturated NaCl solution (10 mL. times.5), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a white solid (890mg, 99%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=260.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of methyl 4- (5-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-4-yl) benzoate under Nitrogen protection 2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-5-one (503mg,0.87mmol, 45%), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (543mg,2.53mmol), Pd2(dba)3(90mg,0.10mmol), XantPhos (86mg,0.15mmol) and Cs2CO3(946mg,2.90mmol) was dissolved in Toluene (10mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. Cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, concentrating under reduced pressure, and adding H to the residue 2O (30mL) dissolved the solid, then the aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 2/1/1) to give a yellow solid (180mg, 52%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 394.1[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- (5-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-4-yl) benzoic acid LiOH. H2O (50mg,1.19mmol) was added to methyl 4- (5-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-4-yl) benzoate (180mg,0.46mmol) in THF/H2To the O (3mL/1mL) solution, the mixture was heated to 50 ℃ and stirred for 3 hours. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (60mL), washed successively with HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) and saturated NaCl solution (10mL), the organic phases combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (171mg, 99%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=380.2[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (5-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-4-yl) benzamide
4- (5-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-4-yl) benzoic acid (85mg,0.22mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (62mg,0.27mmol), EDCI (89mg,0.46mmol) and HOBt (64mg,0.47mmol) were dissolved in DCM (4mL), TEA (0.10mL,0.72mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO 3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) followed by preparative plate chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc/EtOH (v/v) ═ 5/5/1) to give a yellow solid (25mg, 19%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=591.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(600MHz,d6-DMSO&CDCl3)δ(ppm):(ppm):7.92(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.80(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.60–7.54(m,4H),7.45(d,J=15.8Hz,1H),6.76(d,J=15.8Hz,1H),5.69(d,J=4.3Hz,1H),4.81–4.77(m,1H),3.74(m,4H),3.53–3.47(m,2H),3.16(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),1.13(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
EXAMPLE 112N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- (5-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepin-4-yl) benzamide
4- (5-oxo-2- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -1, 4-oxazepan-4-yl) benzoic acid (85mg,0.22mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (55mg,0.28mmol), EDCI (89mg,0.46mmol) and HOBt (64mg,0.47mmol) were dissolved in DCM (4mL), TEA (0.10mL,0.72mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4DryingConcentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (14mg, 11%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.2[M+1]+.
Example 113N- (4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) phenyl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ((2S) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-yl) methanol
Mixing Cs2CO3(1.0g,3.10mmol) to a solution of ((2S) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-yl) methanol (400mg,1.54mmol) and 1-fluoro-4-nitrobenzene (0.17mL,1.60mmol) in DMF (6mL) was added and stirred at room temperature for 46 h. The reaction was diluted with EtOAc (60mL), washed successively with water (10mL) and saturated NaCl solution (10 mL. times.5), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow solid (294mg, 50%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=381.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine
EtI (1.0mL,13.00mmol) was added to a suspension of ((2S) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-yl) methanol (120mg,0.32mmol) and NaOH (22mg,0.55mmol) in DMF (4mL) and the temperature was raised to 60 ℃ and stirred for 7 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc (80mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (10 mL. times.6) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a dark yellow solid (107mg, 90%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=409.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) aniline
Pd/C (50mg, 10%) was added to a solution of (2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine (107mg,0.262mmol) in MeOH (6mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. The reaction mixture was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (100mg, 100%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=379.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- (4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) phenyl) -2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetamide
4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) aniline (100mg,0.26mmol), 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (100mg,0.44mmol), EDCI (100mg,0.52mmol) and HOBt (73mg,0.54mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and TEA (0.12mL,0.86mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with HCl solution (20mL,0.5mol/L) and saturated Na2CO3The solution (20mL) was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a yellow solid (32mg, 21%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=589.3[M+1]+.
Example 114N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, 3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine (30mg,0.13mmol), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (110mg,0.51mmol), Pd2(dba)3(20mg,0.02mmol), XantPhos (13mg,0.02mmol) and NaOt-Bu (100mg,1.01mmol) were dissolved in Toluene (40mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 8 h. Cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, filtering, concentrating the filtrate under reduced pressure, and separating the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/E) Ioac (v/v) ═ 10/1), yielding a yellow solid (28mg, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=364.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Adding H of NaOH2O solution (13.0mL,13.00mmol,1mol/L) was added to methyl 4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (515mg,1.42mmol) in H2O solution (8mL) was stirred at room temperature for 13 h. To the reaction solution, HCl solution (1mol/L) was slowly added dropwise to adjust the system pH to about 5, followed by extraction with EtOAc (30 mL. times.3), and the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30mL), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a pale yellow solid (460mg, 93%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=350.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- (3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (150mg,0.43mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (110mg,0.48mmol), EDCI (150mg,0.77mmol) and HOBt (90mg,0.65mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (80mL) and successively with saturated NaHCO3Solution (30mL), H2O (30mL) and saturated NaCl solution (50mL) washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/ETOAC (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (120mg, 50%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.86(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.07(d,J=6.9Hz,1H),6.92(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),5.27(dd,J=10.9,4.4Hz,1H),4.00(ddd,J=15.6,11.0,4.0Hz,2H),3.95–3.88(m,2H),3.10(q,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.95(dd,J=14.0,7.9Hz,3H),2.13–2.05(m,1H),1.97–1.89(m,1H),1.74(dd,J=15.1,11.7Hz,2H),1.27(d,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 115N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -methyl 5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylate
(2S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (4.05g,10.50mmol) was dissolved in DCM/TFA (20mL/6mL) under ice-bath and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The solution (80mL) was adjusted to pH 8 and then extracted with DCM (80mL × 2), the organic phases were combined and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a colorless oil (1.7g, 56%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=288.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -methyl 1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylate
Under nitrogen protection, (2S) -methyl 5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylate (1.69g,5.88mmol), 4-bromoxynil (1.48g,8.13mmol), Pd2(dba)3(549mg,0.60mmol), RuPhos (1.08g,2.31mmol) and Cs2CO3(5.79g,17.80mmol) was dissolved in Toluene (20mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 16 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, filtered through celite, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow oil (1.8g, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=389.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
Under ice bath, LiBH is added4(22mg,1.01mmol) was dissolved in THF (3mL) and the solution was slowly added to (2S) -methyl 1- (4-cyanoTo a solution of phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylate (107mg,0.28mmol) in THF (6mL) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with a solution (20mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, and the remaining aqueous phase was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2) and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a colorless oil (47mg, 47%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=361.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
DAST (0.05mL,0.40mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (47mg,0.13mmol) in DCM (3mL) under ice-bath and stirred at RT for 12 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The solution (15mL) was extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a colorless oil (36mg, 76%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=363.1[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.21g,22.40mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (75mg,0.21mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 15 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction mixture to adjust the pH of the system to about 2, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (72mg, 91%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=382.2[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
Mixing 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (tri-methyl)Fluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (32mg,0.08mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (35mg,0.18mmol), EDCI (35mg,0.18mmol), HOBt (28mg,0.21mmol) and TEA (0.03mL,0.20mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. DCM (40mL) was added to the reaction solution for dilution, and then the reaction solution was washed with a saturated NaCl solution (50 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) to give a yellow solid (24mg, 51%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=563.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(600MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.85(t,J=10.7Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.78(t,J=9.6Hz,2H),7.71(t,J=6.4Hz,2H),7.66–7.59(m,2H),7.56(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.02(d,J=8.7Hz,1H),6.87(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),4.82–4.66(m,1H),4.64–4.57(m,1H),4.54(t,J=12.9Hz,2H),4.41–4.28(m,1H),4.01(d,J=13.0Hz,1H),3.56(dd,J=25.2,9.7Hz,1H),3.26(d,J=7.2Hz,2H),3.17–3.08(m,1H),2.16–2.09(m,1H),1.99–1.88(m,1H),1.82–1.66(m,1H),1.63–1.50(m,1H),1.09(t,J=7.2Hz,3H).
Example 1164- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (2.31g,42.80mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (161mg,0.45mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 15 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction mixture to adjust the pH of the system to about 2, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2) and anhydrous Na2SO4Drying gave a yellow oil (142mg, 84%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=380.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (142mg,0.37mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (168mg,0.84mmol), EDCI (154mg,0.80mmol), HOBt (101mg,0.75mmol) and TEA (0.20mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a yellow solid (151mg, 72%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
2-Iodoylbenzoic acid (98mg,0.35mmol) was added to a solution of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide (82mg,0.15mmol) in DMSO (3mL) and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The solution (15mL) was then extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.2) and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a yellow oil (53mg, 65%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=559.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
DAST (0.05mL,0.40mmol) was added to a solution of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide (53mg,0.10mmol) in DCM (3mL) under ice-bath and after addition was stirred at room temperature for 13 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The solution (10mL) was then extracted with DCM (25 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, and collecting the crude product from silica gel Column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) gave a white solid (21mg, 38%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 581.1[ M + 1[ ]]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.89(s,1H),7.84(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.05(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),6.59(td,J=55.4,5.2Hz,1H),4.55(d,J=5.3Hz,2H),4.48(s,1H),3.75(d,J=11.6Hz,1H),3.29(d,J=6.9Hz,1H),3.25(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.95(s,1H),2.05(d,J=10.9Hz,1H),2.00–1.89(m,2H),1.87(s,1H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1174- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
Iodothane (0.06mL,0.80mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (152mg,0.42mmol) and NaOH (64mg,1.60mmol) in DMF (1mL) under nitrogen, and after addition, the reaction was heated in a 70 ℃ oil bath with stirring for 20 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature and H was added2O (20mL) and then extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a white solid (71mg, 43%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=389.5[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.21g,22.48mmol) was added to a solution of (S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (71mg,0.18mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 110 ℃ and stirred for 15 h. Cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, adding the reaction solution HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L), adjust system pH to about 3, then extract with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), combine organic phases and use anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (70mg, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=408.0[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (ethoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (70mg,0.17mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (53mg,0.27mmol), EDCI (56mg,0.29mmol), HOBt (41mg,0.30mmol) and TEA (0.05mL,0.40mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50 mL. times.2) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (42mg, 42%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=589.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.85(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.98(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.54(d,J=5.6Hz,2H),4.28(s,1H),3.72(dd,J=21.7,12.7Hz,2H),3.47(dd,J=7.3,4.8Hz,2H),3.44(s,1H),3.28–3.22(m,2H),3.08(t,J=12.2Hz,1H),2.93(d,J=11.4Hz,1H),1.99(dd,J=24.8,13.6Hz,2H),1.82(d,J=15.8Hz,2H),1.09(t,J=7.1Hz,6H).
Example 1184- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
2, 2-difluoro-2- (fluorosulfonyl) -acetic acid (0.05mL,0.50mmol) was added dropwise to N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) acid with stirring and heating in a 50 ℃ oil bath under nitrogen ) To a solution of benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide (72mg,0.13mmol) and CuI (29mg,0.15mmol) in MeCN (4mL) was added, and the temperature was raised to 50 ℃ and stirred for 24 h. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, and saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure, extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a white solid (18mg, 23%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=611.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(s,1H),7.83(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.66(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.00(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),6.69(t,J=76.2Hz,1H),4.54(d,J=5.1Hz,2H),4.40(s,1H),4.23–4.14(m,1H),4.02(d,J=5.9Hz,1H),3.70(d,J=10.7Hz,1H),3.28–3.22(m,2H),3.13(t,J=12.3Hz,1H),2.92(s,1H),2.03–1.92(m,2H),1.83(d,J=17.3Hz,2H),1.08(t,J=7.1Hz,3H).
Example 119(2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid
Mixing KMnO4(200mg,1.27mmol) of H2A solution of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide (66mg,0.12mmol) and NaOH (403mg,10.08mmol) in 1,4-dioxane (5mL) was added to a solution of O (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. Celite filtration was performed, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the residue to adjust the pH of the system to about 3, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and anhydrous Na was used2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (15mg, 22%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 575.3[ M +1 ═ M ]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),7.82(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.58–7.52(m,4H),6.98(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.86(d,J=4.1Hz,1H),4.54(d,J=5.8Hz,2H),3.82(d,J=7.9Hz,1H),3.51(s,1H),3.24(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.98(s,1H),2.33(d,J=13.4Hz,1H),1.98(s,2H),1.90(d,J=10.6Hz,1H),1.65–1.57(m,1H),1.08(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 120(2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (140mg,3.34mmol) was added methyl (2S) -methyl 1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (571mg,1.47mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (5mL/2.5mL/2mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 15 h. To the reaction solution was added HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L), the pH of the system was adjusted to about 4, the organic solvent was removed by concentration under reduced pressure, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and anhydrous Na was used2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10:1) to give a yellow oil (455mg, 83%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=375.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
(2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (455mg,1.22mmol), dimethylamine (309mg,3.79mmol), EDCI (468mg,2.44mmol) and HOBt (343mg,2.54mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) and TEA (0.85mL,6.10mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. To the reaction mixture was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), followed by extraction with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the mixtures were combined Organic phase combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a yellow solid (328mg, 67%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=402.5[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (dimethylcarbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.11g,20.50mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide (91mg,0.23mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the reaction was heated to reflux in a 90 ℃ oil bath for 15 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 2, the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (80mg, 84%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=421.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (dimethylcarbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (80mg,0.19mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (97mg,0.49mmol), EDCI (105mg,0.55mmol), HOBt (71mg,0.53mmol) and TEA (0.11mL,0.79mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (80 mL. times.2), the organic phases combined and washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a yellow solid (61mg, 53%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=602.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.86(s,1H),7.83(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),7.74(dd,J=18.4,8.0Hz,4H),7.55(d,J=7.4Hz,4H),6.94(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),5.18(s,1H),4.55(s,2H),3.83–3.72(m,1H),3.59(t,J=11.7Hz,1H),3.25(d,J=7.0Hz,2H),3.12(s,3H),2.96(s,1H),2.81(s,3H),2.03(d,J=36.0Hz,2H),1.81(s,2H),1.08(s,3H).
Example 121(2S) -N-Ethyl-1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N-ethyl-N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
(2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (316mg,0.84mmol), methylethylamine (0.15mL,1.70mmol), EDCI (412mg,2.15mmol) and HOBt (239mg,1.77mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) and TEA (0.60mL,4.30mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 13 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (50mL), followed by extraction with DCM (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a yellow oil (185mg, 53%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=416.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (ethyl (methyl) carbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid MeONa (2.41g,44.60mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N-ethyl-N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide (185mg,0.45mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 4, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10:1) to give a yellow oil (182mg, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=435.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -N-ethyl-1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (Ethyl (methyl) aminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (80mg,0.18mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (76mg,0.38mmol), EDCI (124mg,0.65mmol), HOBt (81mg,0.60mmol) and TEA (0.14mL,1.00mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (52mg, 46%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=616.1[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.86(s,1H),7.83(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=7.9Hz,4H),6.96(dd,J=20.5,8.6Hz,2H),5.23–5.09(m,1H),4.54(d,J=5.7Hz,2H),3.84–3.71(m,1H),3.58(t,J=12.0Hz,1H),3.33–3.21(m,4H),3.10(s,2H),2.97(s,1H),2.77(s,1H),2.05(dd,J=30.2,15.2Hz,2H),1.84(d,J=15.4Hz,2H),1.15(t,J=6.9Hz,1H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.99(t,J=7.0Hz,2H).
Example 122(2S) -N-Ethyl-1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (Ethyl (methyl) carbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (102mg,0.23mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (83mg,0.36mmol), EDCI (143mg,0.75mmol), HOBT (102mg,0.75mmol) and TEA (0.18mL,1.29mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction solution was washed with DCM (50mL), saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/6) to give a white solid (63mg, 42)%);
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=646.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.48(d,J=7.2Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),6.95(dd,J=19.8,8.6Hz,2H),5.23–5.09(m,2H),5.01(s,1H),3.83–3.67(m,3H),3.58(t,J=11.9Hz,1H),3.33–3.20(m,4H),3.10(s,2H),2.97(d,J=4.6Hz,1H),2.77(s,1H),2.11–1.96(m,2H),1.84(dd,J=24.8,7.4Hz,2H),1.16(t,J=7.0Hz,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.99(t,J=6.8Hz,2H).
Example 123(2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methoxy-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (260mg,0.69mmol), methanol (0.15mL,3.70mmol), EDCI (398mg,2.08mmol), HOBt (278mg,2.06mmol) and TEA (0.50mL,3.59mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a yellow oil (198mg, 73%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=394.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4- (methoxycarbonyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid
2-Iodoylbenzoic acid (443mg,1.58mmol) was added to a DMSO (2mL) solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (119mg,0.30mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (40 mL) ) Extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.2), the organic phases are combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (108mg, 88%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=407.9[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxyaminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
((2S) -1- (4- (methoxycarbonyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (210mg,0.52mmol), O-methylhydroxylamine hydrochloride (149mg,1.78mmol), EDCI (316mg,1.65mmol), HOBt (231mg,1.71mmol) and TEA (0.75mL,5.40mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL), stirred at room temperature for 24h the reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a yellow oil (221mg, 98%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=437.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxyaminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (78mg,1.86mmol) methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxyaminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (221mg,0.51mmol) in THF/MeOH/H 2O (5mL/2.5mL/2mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 16 h. Adding HCl solution (6mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure, removing the organic solvent, extracting the aqueous phase with EtOAc (30mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (63mg, 30%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=423.0[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methoxy-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (methoxyaminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (63mg,0.15mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (42mg,0.18mmol), EDCI (135mg,0.70mmol), HOBt (110mg,0.81mmol) and TEA (0.12mL,0.86mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (39mg, 41%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=634.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):11.32(s,1H),8.51(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),7.81(dd,J=13.8,8.3Hz,4H),7.72(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.97(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.12(dd,J=13.6,6.7Hz,1H),4.56(s,1H),3.85–3.78(m,1H),3.78–3.65(m,3H),3.58(s,3H),3.51(s,1H),3.25(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.99–2.93(m,1H),2.16(d,J=12.6Hz,1H),2.02–1.96(m,1H),1.86(d,J=13.8Hz,2H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1244- ((2S) -2- ((dimethylamino) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethanesulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
2-Iodoylbenzoic acid (472mg,1.69mmol) was added to a DMSO (3mL) solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (301mg,0.84mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The solution (20mL) was then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, and separating the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to obtainYellow oil (129mg, 43%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=359.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((dimethylamino) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
4- ((2S) -2-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (129mg,0.36mmol) and dimethylamine (66mg,0.81mmol) were dissolved in a mixed solvent of EtOH/THF (3mL/3mL), stirred at room temperature for 1h, and NaBH was added3CN (252mg,4.01mmol), stirred at room temperature for 18 h. Adding saturated Na to the reaction solution2CO3The reaction was quenched with a solution (30mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, the remaining aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (87mg, 62%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=388.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((dimethylamino) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.23g,22.80mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- ((dimethylamino) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (87mg,0.22mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 20 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 3, the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (86mg, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=407.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((dimethylamino) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- ((dimethylamino) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (86mg,0.21mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (141mg,0.71mmol), EDCI (82mg,0.43mmol), HOBt (73mg,0.54mmol) and TEA (0.12mL,0.86mmol) were dissolved inDCM (8mL) was stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 15/1) to give a yellow solid (46mg, 37%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=588.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.99(s,1H),7.84(d,J=6.0Hz,4H),7.71(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),7.66(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.13(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),4.61(s,1H),4.55(d,J=4.1Hz,2H),3.71(d,J=12.8Hz,1H),3.51(s,2H),3.26(d,J=7.1Hz,2H),3.05(d,J=7.1Hz,1H),2.85(s,1H),2.70(s,6H),2.02–1.90(m,2H),1.88–1.75(m,2H),1.08(t,J=6.9Hz,3H).
Example 125N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
4- ((2S) -2-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (153mg,0.43mmol) and tetrahydropyrrole (0.07mL,0.90mmol) were dissolved in a mixed solvent of EtOH/THF (3mL/3mL), stirred at room temperature for 1h, and NaBH was added3CN (283mg,4.50mmol), stirred at RT for 15 h. Adding saturated Na to the reaction solution2CO3The reaction was quenched with a solution (20mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, then extracted with EtOAc (80mL), and the organic phases combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (136mg, 77%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=414.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.75g,32.40mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (136mg,0.33mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the reaction warmed to 100 ℃ and stirred for 15 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (40mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 2, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (132mg, 93%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=433.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (132mg,0.31mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (132mg,0.66mmol), EDCI (118mg,0.62mmol), HOBt (91mg,0.67mmol) and TEA (0.20mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (18mg, 10%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=614.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.88(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.79(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.02(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),4.55(d,J=5.8Hz,2H),4.38(s,1H),3.68(d,J=11.8Hz,1H),3.51(s,1H),3.26(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.13(s,1H),2.89(t,J=11.7Hz,2H),2.78–2.69(m,1H),2.68(s,1H),2.02(s,1H),1.92(t,J=12.9Hz,1H),1.78(s,2H),1.74(s,4H),1.24(s,2H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 126N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
4- ((2S) -2-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (139mg,0.39mmol) and piperidine (0.08mL,0.90mmol) were dissolved in a mixed solvent of EtOH/THF (3mL/3mL), stirred at room temperature for 1h, and NaBH was added 3CN (289mg,4.60mmol), stirring was continued at RT for 20 h. Adding saturated Na to the reaction solution2CO3The reaction was quenched with solution (30mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, then extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (152mg, 92%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=428.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.95g,36.10mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (152mg,0.36mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 3, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Drying gave a yellow oil (152mg, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=447.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (piperidin-1-ylmethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (152mg,0.34mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (220mg,1.10mmol), EDCI (185mg,0.97mmol), HOBt (148mg,1.10mmol) and TEA (0.20 mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. Inverse direction The reaction solution was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a yellow solid (45mg, 21%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=628.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.85(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),6.98(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.54(d,J=5.8Hz,2H),4.32(s,1H),3.63(d,J=9.4Hz,1H),3.51(s,1H),3.25(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.04(t,J=12.0Hz,1H),2.89(t,J=11.7Hz,1H),2.77(s,1H),2.35(s,2H),2.07(d,J=10.4Hz,1H),1.95–1.84(m,1H),1.77(t,J=11.2Hz,2H),1.47(s,4H),1.35(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),1.23(s,2H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 127N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S,5R) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide/N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S,5S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
4- ((2S) -2 formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (149mg,0.42mmol) and morpholine (0.08mL,0.90mmol) were dissolved in a mixed solvent of EtOH/THF (3mL/3mL) and stirred at room temperatureAfter 1h, add NaBH3CN (271mg,4.31mmol), and stirring was continued at room temperature for 24 h. Adding saturated Na to the reaction solution2CO3The reaction was quenched with a solution (20mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, then extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a white solid (168mg, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=430.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (2.20g,41.00mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (168mg,0.39mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (30mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 2, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (168mg, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=449.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S,5R) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide/N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S,5S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (168mg,0.37mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (224mg,1.12mmol), EDCI (288mg,1.50mmol), HOBt (224mg,1.66mmol) and TEA (0.32mL,2.3mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) and stirred at room temperature for 17 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (V/V) ═ 10/1), and further chromatographed by preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/NeOH (V/V) ═ 10/1) to give 127-1(31mg, 13%) and 127-2(39mg, 16%) as yellow solids.
127-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=630.1[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.86(t,J=5.7Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.79(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.53(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.03(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),4.55(d,J=5.6Hz,2H),4.15(s,1H),3.82–3.74(m,1H),3.49(s,4H),3.41(s,1H),3.25(d,J=7.3Hz,4H),2.70–2.58(m,1H),2.46(s,1H),2.30(s,2H),2.16(t,J=12.3Hz,2H),1.76(s,3H),1.08(d,J=7.3Hz,3H).
127-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=630.1[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.83(s,1H),7.83(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.69(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.97(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),4.54(d,J=5.5Hz,2H),4.33(s,1H),3.63(d,J=10.5Hz,1H),3.51(s,4H),3.28–3.25(m,2H),3.25–3.21(m,2H),3.03(t,J=12.1Hz,1H),2.91(d,J=11.6Hz,1H),2.81–2.72(m,1H),2.33(s,2H),2.24(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),2.08(d,J=10.4Hz,1H),1.95–1.86(m,1H),1.75(d,J=10.3Hz,2H),1.08(s,3H).
Example 128N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S,5S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide/N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S,5R) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (morpholinomethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (115mg,0.26mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (92mg,0.40mmol), EDCI (224mg,1.17mmol), HOBt (142mg,1.05mmol) and TEA (0.3mL,2mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) and stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel column (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) and silica gel plate (developing solvent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) in this order to give 128-1(43mg, 25%) and 128-2(24mg, 14%) as yellow solids.
128-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=660.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.50(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.82(t,J=9.3Hz,4H),7.64(dd,J=12.3,8.3Hz,4H),7.53(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.03(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),5.14(dd,J=13.4,6.8Hz,1H),5.03(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),4.16(s,1H),3.73(dt,J=11.3,8.5Hz,3H),3.51(s,4H),3.31–3.18(m,4H),2.70–2.60(m,1H),2.50–2.39(m,2H),2.30(s,2H),2.17(s,2H),1.77(t,J=14.7Hz,3H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
128-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=660.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.47(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=9.5Hz,4H),6.97(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.12(dd,J=13.6,6.6Hz,1H),5.01(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),4.34(s,1H),3.78–3.68(m,2H),3.63(d,J=9.6Hz,1H),3.52(s,4H),3.32–3.21(m,3H),3.03(t,J=11.9Hz,1H),2.92(d,J=11.6Hz,1H),2.78(t,J=10.6Hz,1H),2.52(s,1H),2.33(s,2H),2.26–2.18(m,1H),2.10(d,J=13.2Hz,1H),1.91(t,J=12.9Hz,1H),1.77(t,J=13.4Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 129N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (((((R) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxo) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (((((R) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (60mg,2.50mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (208mg,0.58mmol) in DMF (1mL) under nitrogen in ice bath, after 10min addition was completed, (S) -tetrahydrofuran-3-ylmethylsulfonate (270mg,1.62mmol) was slowly added to the reaction system and stirring was continued at room temperature for 24 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (50mL), followed by extraction with DCM (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a yellow oil (104mg, 42%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=431.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (((((R) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.38g,25.50mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (((((R) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (104mg,0.24mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 10 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction solution, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 4, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na 2SO4Drying gave a yellow oil (102mg, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=450.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (((((R) -tetrahydrofuran-3-yl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
Reacting 4- ((2S) -2- ((((R) -tetrahydro)Furan-3-yl) oxo) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (102mg,0.23mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (70mg,0.31mmol), EDCI (174mg,0.91mmol), HOBt (105mg,0.78mmol) and TEA (0.16mL,1.20mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a yellow solid (89mg, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=661.2[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.49(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.79(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.68–7.60(m,4H),6.98(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),5.13(dd,J=13.3,6.6Hz,1H),4.27(s,1H),4.11(s,1H),3.80–3.70(m,3H),3.70–3.62(m,4H),3.59(dd,J=13.0,6.3Hz,2H),3.26(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.20(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),3.09(t,J=12.0Hz,1H),2.92(t,J=11.3Hz,1H),1.98(dd,J=19.5,12.2Hz,2H),1.93–1.84(m,2H),1.78(d,J=12.9Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 130N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (80mg,3.33mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (201mg,0.56mmol) in DMF (1.5mL) under nitrogen protection in ice bath, after which 1-bromo-2-fluoro-ethane (0.24mL,3.20mmol) was slowly added dropwise to the reaction system after 10min and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. The reaction was quenched by adding saturated NaCl solution (50mL) to the reaction solution, followed by extraction with DCM (40 mL. times.2) and anhydrous Na 2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, and collecting the crude product from silica gelColumn chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) gave a yellow oil (83mg, 37%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=406.9[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.16g,21.50mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (83mg,0.20mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 22 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 4, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow oil (73mg, 84%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=426.0[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- ((2-Fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (35mg,0.08mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (34mg,0.17mmol), EDCI (49mg,0.26mmol), HOBt (45mg,0.33mmol) and TEA (0.06mL,0.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a yellow solid (5mg, 10%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=607.3[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.86(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),7.82(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),7.69(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),6.98(d,J=9.0Hz,2H),4.54(dd,J=8.5,4.7Hz,3H),4.43(t,J=4.0Hz,1H),4.22(t,J=6.5Hz,1H),3.83–3.78(m,1H),3.71–3.65(m,2H),3.63–3.60(m,1H),3.54(dd,J=9.7,5.2Hz,2H),3.23(t,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.08(t,J=12.2Hz,1H),1.98(dd,J=10.8,6.0Hz,2H),1.78(d,J=9.4Hz,1H),1.65(d,J=7.1Hz,1H),1.08(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 131N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- ((2-Fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (40mg,0.09mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (34mg,0.15mmol), EDCI (64mg,0.33mmol), HOBt (42mg,0.31mmol) and TEA (0.07mL,0.50mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/6) to give a yellow solid (6mg, 10%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=637.8[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.49(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.1Hz,4H),6.98(d,J=9.0Hz,2H),5.12(dd,J=13.8,7.0Hz,1H),4.56(t,J=4.0Hz,1H),4.44(t,J=4.0Hz,1H),4.31(s,1H),3.81(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),3.77–3.66(m,4H),3.64–3.60(m,1H),3.54(dd,J=11.0,6.5Hz,2H),3.25(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.08(s,1H),2.93(d,J=11.6Hz,1H),2.04–1.95(m,2H),1.84–1.75(m,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1324- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (31mg,1.29mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (131mg,0.36mmol) in DMF (1mL) under nitrogen protection in ice bath, after 10min bromomethylcyclopropane (0.08mL,0.80mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. To the reaction mixture was added a saturated NaCl solution (50mL), extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 8/1) to give a yellow oil (139mg, 92%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=415.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.84g,34.10mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (139mg,0.34mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 14 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 4, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow oil (140mg, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=434.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (73mg,0.17mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (69mg,0.35mmol), EDCI (111mg,0.58mmol), HOBt (80mg,0.59mmol) and TEA (0.12mL,0.86mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and then washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2) over anhydrous Na 2SO4The mixture is dried and then is dried,concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) to give a yellow solid (77mg, 74%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=615.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.84(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.56(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),6.98(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.55(d,J=5.7Hz,2H),4.27(s,1H),3.75(t,J=8.9Hz,1H),3.68(dd,J=12.5,3.1Hz,1H),3.50(dd,J=9.7,5.1Hz,1H),3.28–3.22(m,4H),3.09(t,J=12.2Hz,1H),2.92(t,J=11.5Hz,1H),2.06–1.91(m,2H),1.81(t,J=13.1Hz,2H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),1.01–0.93(m,1H),0.45(d,J=5.4Hz,1H),0.42(dd,J=4.6,3.3Hz,1H),0.14(q,J=4.9Hz,2H).
Example 1334- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- ((cyclopropylmethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (79mg,0.18mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (74mg,0.32mmol), EDCI (112mg,0.58mmol), HOBT (82mg,0.61mmol) and TEA (0.13mL,0.94mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The application was diluted with DCM (60mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (50 mL. times.2) and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/6) to give a yellow solid (72mg, 61%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=645.4[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.47(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.64(dd,J=7.9,4.4Hz,4H),6.98(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),5.13(dd,J=13.6,6.8Hz,1H),5.01(t,J=5.4Hz,1H),4.28(s,1H),3.78–3.65(m,4H),3.49(dd,J=9.6,5.1Hz,1H),3.28–3.23(m,4H),3.09(t,J=12.1Hz,1H),2.92(t,J=11.7Hz,1H),2.06–1.91(m,2H),1.86–1.74(m,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),1.01–0.94(m,1H),0.47–0.41(m,2H),0.14(q,J=4.8Hz,2H).
Example 1344- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
NaH (40mg,1.67mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (154mg,0.43mmol) in DMF (1mL) under nitrogen in ice bath, stirred for 10min, then 1-bromobutane (0.09mL,0.80mmol) was added and after addition, the reaction was stirred at room temperature for a further 13 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (50mL), followed by extraction with DCM (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 6/1) to give a yellow oil (157mg, 88%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=417.4[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (2.04g,37.80mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (157mg,0.38mmol) in EtOH (6mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 18 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (30mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 4, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (158mg, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=436.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (butoxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (158mg,0.36mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (117mg,0.51mmol), EDCI (228mg,1.19mmol), HOBt (176mg,1.30mmol) and TEA (0.27mL,1.9mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (50 mL. times.2), and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/6) to give a yellow solid (176mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=647.2[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.48(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.80(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.70(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.64(t,J=8.8Hz,4H),6.97(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.14(dd,J=13.4,6.7Hz,1H),5.03(t,J=5.2Hz,1H),4.29(s,1H),3.77–3.64(m,4H),3.50–3.41(m,2H),3.28–3.22(m,2H),3.08(t,J=12.1Hz,1H),2.92(t,J=11.3Hz,1H),2.04–1.90(m,2H),1.86–1.75(m,2H),1.48–1.40(m,2H),1.32–1.21(m,3H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.85(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1354- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (7.42g,137mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (508mg,1.41mmol) in EtOH (15mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 20 h. Cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, and adding HCl solution into the reaction solution(15mL,1mol/L), adjusting the pH of the system to about 2, extracting with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), combining the organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow solid (520mg, 97%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=380.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (151mg,0.40mmol) and CuI (87mg,0.46mmol) were dissolved in MeCN (4mL) under nitrogen, warmed to 50 ℃ and stirred, 2-difluoro-2- (fluorosulfonyl) -acetic acid (0.15mL,1.50mmol) was slowly added dropwise, and after addition, stirring with heating continued for 16 h. Cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, adding NaHCO into the reaction solution 3(15mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove acetonitrile, then extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the combined organic phases were Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow oil (39mg, 23%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=430.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (39mg,0.09mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (34mg,0.15mmol), EDCI (56mg,0.29mmol), HOBt (42mg,0.31mmol) and TEA (0.08mL,0.57mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) to give a white solid (27mg, 46%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=641.0[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.50(d,J=6.9Hz,1H),7.81(dd,J=13.2,8.3Hz,4H),7.71(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.69–7.60(m,4H),7.00(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),6.69(t,J=76.1Hz,1H),5.13(d,J=6.3Hz,1H),5.02(s,1H),4.41(s,1H),4.18(t,J=8.9Hz,1H),4.05–3.95(m,1H),3.70(d,J=11.7Hz,3H),3.26(d,J=7.2Hz,2H),3.13(s,1H),2.93(s,1H),2.02–1.92(m,2H),1.91–1.79(m,2H),1.10(t,J=7.2Hz,3H).
Example 1364- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (260mg,0.69mmol), MeOH (0.15mL,3.70mmol), HOBT (278mg,2.06mmol), EDCI (398mg,2.08mmol) and TEA (0.50mL,3.58mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a yellow oil (198mg, 73%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=394.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
NaH (223mg,5.67mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (318mg,0.81mmol) and 3-bromo-3, 3-difluoro-propyl-1-ene (1.16mL,11.30mmol) in DMF (2mL) under nitrogen protection in ice bath, stirred at this temperature for 10min and then displaced to room temperature for 20 h. Adding saturated NH to the reaction solution4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (50mL) and then extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2)Combining organic phases and anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 6/1) to give a yellow oil (139mg, 37%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=470.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
Pd/C (261mg, 10%) was added to a solution of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (220mg,0.47mmol) in MeOH/THF (5mL/5mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Celite was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless oil (197mg, 89%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=472.3[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (64mg,1.53mmol) methyl 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (197mg,0.42mmol) in THF/MeOH/H was added2O (4mL/2mL/1.5mL), and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. Adding HCl solution (8mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting pH to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure, extracting the rest solution with EtOAc (40mL × 2), combining organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a colorless oil (78mg, 41%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=458.1[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
A mixture of 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (60mg,0.13mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (50mg,0.22mmol), HOBt (77mg,0.57mmol), EDCI (115mg,0.60 mmol)mmol) and TEA (0.2mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (12mg, 14%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=669.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.50(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.81(dd,J=14.6,8.4Hz,4H),7.71(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.68–7.62(m,4H),6.99(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.13(dd,J=13.3,6.6Hz,1H),5.04(t,J=5.5Hz,1H),4.40(dd,J=11.5,7.7Hz,1H),4.17–4.11(m,1H),4.01(dd,J=10.3,6.2Hz,1H),3.77–3.66(m,3H),3.26(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.12(t,J=12.2Hz,1H),2.94(t,J=10.5Hz,1H),2.00(d,J=11.1Hz,1H),1.91(dd,J=18.5,11.0Hz,4H),1.80(d,J=9.7Hz,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.88(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 137N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
DAST (0.6mL,5.00mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (83mg,0.23mmol) in DCM (3mL) under nitrogen on an ice bath, and after addition, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (15mL) and then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a colorless oil (75mg, 90%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 363.1[ M +1 ═ M ]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.21g,22.40mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (75mg,0.21mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 2, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (72mg, 91%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=382.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (72mg,0.19mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (75mg,0.33mmol), HOBt (85mg,0.63mmol), EDCI (113mg,0.59mmol) and TEA (0.15mL,1.10mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (40mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was successively subjected to silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (49mg, 44%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=593.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.46(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.79(s,2H),7.71(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.62(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),6.87(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.15–5.09(m,1H),4.42–4.27(m,1H),4.01(d,J=12.1Hz,1H),3.80–3.65(m,3H),3.25(s,2H),3.15(d,J=16.0Hz,2H),3.04(s,1H),2.15(dd,J=24.7,11.4Hz,2H),2.00(dd,J=16.6,6.7Hz,1H),1.70(d,J=11.5Hz,1H),1.53(dd,J=26.7,14.1Hz,1H),1.09(d,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1384- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
DAST (0.22mL,1.70mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (147mg,0.41mmol) in DCM (3mL) under nitrogen in ice bath, then warmed to room temperature and stirred for 24 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (30mL) and then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a yellow oil (80mg, 51%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 381.3[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.12g,20.70mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (80mg,0.21mmol) in EtOH (4mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 2, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (78mg, 93%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=400.0[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (difluoromethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (78mg,0.20mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (73mg,0.32mmol), HOBt (100mg,0.74mmol), EDCI (118mg,0.62mmol) and TEA (0.15mL,1.10mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (39mg, 33%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=611.0[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.51(d,J=7.2Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.79(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=7.7Hz,4H),7.05(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),6.58(td,J=55.6,5.5Hz,1H),5.13(d,J=6.3Hz,1H),4.48(s,1H),3.73(d,J=8.1Hz,3H),3.29–3.20(m,4H),2.95(s,1H),2.05(d,J=11.2Hz,1H),2.00–1.90(m,2H),1.85(d,J=9.6Hz,1H),1.10(t,J=7.2Hz,3H).
Example 139(2S,5S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (93mg,2.22mmol) was added to methyl (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylate (308mg,0.79mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (3mL/1.5mL/1mL) was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Adding HCl solution (30mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, extracting with EtOAc (30mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (218mg, 73%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=375.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
(2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (221mg,0.59mmol), NH4Cl (77mg,1.44mmol) and HATU (171)mg,1.27mmol) was dissolved in DMF (5mL) and TEA (0.25mL,1.80mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 22 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), followed by extraction with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow oil (165mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=373.9[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2-carbamoyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (2.40g,44.00mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide (165mg,0.44mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 13 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 2, the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (168mg, 97%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=393.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2-carbamoyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (78mg,0.20mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (75mg,0.38mmol), HOBt (84mg,0.62mmol), EDCI (115mg,0.60mmol) and TEA (0.15mL,1.08mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (20mg, 18%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=574.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.86(t,J=5.9Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.1Hz,4H),7.45(s,1H),7.12(s,1H),6.96(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.64(d,J=4.2Hz,1H),4.55(d,J=5.7Hz,2H),3.82(dd,J=12.4,3.9Hz,1H),3.44(d,J=8.0Hz,1H),3.27–3.22(m,2H),2.95(t,J=11.7Hz,1H),2.27(d,J=12.3Hz,1H),1.99–1.89(m,1H),1.85–1.72(m,2H),1.08(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 140(2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2-carbamoyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (90mg,0.23mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (81mg,0.35mmol), HOBt (113mg,0.84mmol), EDCI (154mg,0.80mmol) and TEA (0.18mL,1.30mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (7mg, 5%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=603.9[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.49(d,J=7.5Hz,1H),7.82(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.46(s,1H),7.10(s,1H),6.95(d,J=9.0Hz,2H),5.14–5.09(m,1H),4.64(d,J=4.1Hz,1H),3.79(d,J=11.9Hz,1H),3.74–3.68(m,2H),3.38(s,2H),3.27–3.22(m,2H),2.93(d,J=11.2Hz,1H),2.03–1.92(m,2H),1.83–1.72(m,2H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 141(2S,5S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
(2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (218mg,0.58mmol), methylamine hydrochloride (87mg,1.29mmol), EDCI (230mg,1.20mmol) and HOBt (158mg,1.17mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) and TEA (0.42mL,3.01mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), followed by extraction with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a colorless oil (111mg, 49%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=388.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (methylcarbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.59g,29.40mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide (111mg,0.29mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 15 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 2, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na 2SO4Drying gave a yellow oil (112mg, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=407.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (methylcarbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (50mg,0.12mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (53mg,0.27mmol), HOBt (55mg,0.41mmol), EDCI (80mg,0.42mmol) and TEA (0.09mL,0.65mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, purifying the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1), and purifying by column chromatographySeparation by preparative chromatography (developer: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) gave a white solid (11mg, 15%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=588.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.89(t,J=6.1Hz,1H),7.88(dd,J=8.8,4.2Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.66(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.2Hz,4H),6.92(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.55(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),4.13(d,J=4.9Hz,1H),3.81(dd,J=12.1,4.3Hz,1H),3.51(s,1H),3.25(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.56(d,J=4.5Hz,3H),2.00(d,J=5.7Hz,2H),1.94(s,1H),1.91(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),1.73(d,J=7.2Hz,1H),1.09(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
EXAMPLE 142(2S,5R) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide/(2S, 5S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carboxamide) phenyl) -N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (methylcarbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (61mg,0.15mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (59mg,0.26mmol), HOBt (89mg,0.66mmol), EDCI (114mg,0.59mmol) and TEA (0.12mL,0.86mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, and sequentially passing the crude product through siliconGel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) and preparative chromatography (developer: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) gave white solids 142-1(10mg, 11%) and 142-2(18mg, 19.41%).
142-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=618.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.50(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),7.95(dd,J=8.2,3.6Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.96(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.12(dd,J=13.6,6.9Hz,1H),4.65(d,J=4.3Hz,1H),3.80(d,J=8.7Hz,1H),3.76–3.67(m,2H),3.51(s,1H),3.48(d,J=5.9Hz,1H),3.28–3.22(m,2H),2.94(t,J=11.0Hz,1H),2.62(d,J=4.3Hz,3H),2.23(d,J=12.4Hz,1H),1.94–1.85(m,1H),1.83–1.73(m,2H).
142-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=618.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.52(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.88(d,J=4.5Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),7.65(t,J=8.6Hz,4H),7.55(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.92(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),5.12(dd,J=13.7,6.8Hz,1H),5.03(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),4.13(s,1H),3.81(dd,J=12.2,4.4Hz,1H),3.72(dd,J=14.2,6.4Hz,2H),3.51(s,1H),3.48(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),3.25(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),2.60–2.52(m,3H),2.00(d,J=5.7Hz,2H),1.94–1.87(m,1H),1.76–1.68(m,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 143(2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
Reacting (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-methylThe acid (455mg,1.22mmol), dimethylamine (309mg,3.79mmol), EDCI (468mg,2.44mmol), HOBt (343mg,2.54mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) and TEA (0.85mL,6.10mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), followed by extraction with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a yellow solid (328mg, 67%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=402.5[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (dimethylcarbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.11g,20.50mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide (91mg,0.23mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 90 ℃ and stirred for 15 h. HCl solution (15mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction solution to adjust the pH of the system to about 2, and then extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (80mg, 84%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=421.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N, N-dimethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (dimethylcarbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (112mg,0.27mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (93mg,0.41mmol), HOBt (130mg,0.96mmol), EDCI (172mg,0.90mmol) and TEA (0.20mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (18mg, 11%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=632.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.49(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),7.82(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.94(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),5.19(s,1H),5.11(d,J=7.0Hz,1H),3.73(dd,J=19.4,10.4Hz,3H),3.60(t,J=11.7Hz,1H),3.25(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.13(s,3H),2.99(s,1H),2.81(s,3H),2.10(d,J=12.3Hz,1H),2.05–1.93(m,2H),1.81(s,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 144(2S,5S) -N, N-diethyl-1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide/(2S, 5R) -N, N-diethyl-1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N, N-diethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
(2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (246mg,0.66mmol), diethylamine (0.14mL,1.40mmol), EDCI (315mg,1.64mmol) and HOBt (186mg,1.38mmol) were dissolved in DCM (10mL) and TEA (0.48mL,3.50mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. To the reaction mixture was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v)1/1) to give a yellow oil (199mg, 71%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=430.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (diethylaminoformyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (2.52g,46.6mmol) was added to a solution of (2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -N, N-diethyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide (199mg,0.46mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the temperature was raised to 100 ℃ and stirred for 12 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 2, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na 2SO4Drying gave a yellow oil (200mg, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=449.0[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -N, N-diethyl-1- (4- ((4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (diethylaminoformyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (95mg,0.21mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (88mg,0.44mmol), HOBt (123mg,0.91mmol), EDCI (129mg,0.67mmol) and TEA (0.16mg,0.16mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) and further chromatographed by preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give 144-1(64mg, 68%) and 144-2(14mg, 11%) as white solids.
144-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=630.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(s,1H),7.83(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=6.2Hz,4H),6.98(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),5.12(s,1H),4.54(d,J=4.1Hz,2H),3.77(d,J=8.5Hz,1H),3.62–3.50(m,2H),3.25(d,J=7.0Hz,4H),3.16–3.09(m,1H),2.94(s,1H),2.01(s,2H),1.93–1.76(m,2H),1.15(s,3H),1.08(t,J=6.8Hz,3H),0.99(s,3H).
144-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=630.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.88(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.76(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.66(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.60–7.52(m,4H),6.94(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),4.71(d,J=5.5Hz,1H),4.55(d,J=5.6Hz,2H),3.97(dd,J=12.4,4.3Hz,1H),3.66(dd,J=12.4,5.8Hz,1H),3.51(dd,J=12.7,8.6Hz,2H),3.29–3.22(m,4H),3.17(dd,J=13.4,7.0Hz,1H),1.99(dd,J=16.2,7.0Hz,2H),1.81(d,J=17.3Hz,2H),1.14(t,J=6.9Hz,3H),1.09(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.95(t,J=6.9Hz,3H).
Example 145(2S,5S) -N, N-diethyl-1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide/(2S, 5R) -N, N-diethyl-1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (diethylaminoformamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (105mg,0.23mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (85mg,0.37mmol), HOBt (111mg,0.82mmol), EDCI (298mg,1.55mmol) and TEA (0.18mL,1.30mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 101) and then separated by preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give 145-1(64mg, 61%) and 145-2(14mg, 9%) as white solids.
145-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=659.9[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.49(d,J=7.5Hz,1H),7.80(dd,J=16.5,8.1Hz,4H),7.71(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),6.98(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),5.13(s,2H),5.03(s,1H),3.79–3.67(m,3H),3.59(d,J=11.5Hz,1H),3.52–3.47(m,1H),3.31(d,J=14.3Hz,2H),3.27–3.22(m,2H),3.12(dd,J=12.9,6.7Hz,1H),2.95(s,1H),2.02(s,2H),1.95–1.87(m,1H),1.81(s,1H),1.15(s,3H),1.09(t,J=7.2Hz,3H),1.00(s,3H).
145-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=659.9[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.50(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.65(t,J=6.8Hz,4H),7.55(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.94(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),5.12(d,J=6.4Hz,1H),4.71(s,1H),3.97(dd,J=12.3,3.9Hz,1H),3.73(dd,J=17.7,9.0Hz,2H),3.66(d,J=10.6Hz,1H),3.52(t,J=10.9Hz,2H),3.31(d,J=7.3Hz,1H),3.25(dd,J=14.7,7.3Hz,4H),3.18(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),2.04–1.93(m,2H),1.81(d,J=16.3Hz,2H),1.15(t,J=6.9Hz,3H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.96(t,J=6.1Hz,3H).
Example 146(2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
Mixing (2S) -1- (4- (methoxy formyl) phenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (178 m)g,0.44mmol), N, O-dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride (105mg,1.08mmol), HOBt (198mg,1.47mmol), EDCI (261mg,1.36mmol) and TEA (0.40mL,2.87mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow oil (150mg, 76%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=451.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (81mg,1.93mmol) methyl 4- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (150mg,0.33mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (5mL/2.5mL/2mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Adding HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting pH to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure, removing organic solvent, extracting the rest solution with EtOAc (30mL × 2), combining organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10:1) to give a yellow oil (122mg, 84%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=437.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -1- (4- (((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl) phenyl) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
4- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (122mg,0.28mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (87mg,0.38mmol), HOBt (136mg,1.00mmol), EDCI (258mg,1.35mmol) and TEA (0.2mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (50mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (5)0mg,28%)。
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=648.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.50(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),7.82(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.79(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.57(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.97(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.18(d,J=5.4Hz,1H),5.12(dd,J=13.4,6.7Hz,1H),3.79(s,3H),3.76–3.71(m,2H),3.71–3.65(m,1H),3.60(t,J=11.7Hz,1H),3.52–3.45(m,1H),3.25(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.10(s,3H),3.04–2.97(m,1H),2.20(d,J=12.5Hz,1H),2.10(d,J=12.0Hz,1H),1.87–1.73(m,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 147N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile
(2S) -1- (4-cyanophenyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (204mg,0.54mmol), morpholine (0.12mL,1.40mmol), EDCI (231mg,1.20mmol), HOBt (158mg,1.17mmol) were dissolved in DCM (8mL) and TEA (0.40mL,2.87mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 22 h. To the reaction mixture was added a saturated NaCl solution (30mL), extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a colorless oil (138mg, 57%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=444.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
MeONa (1.76g,32.6mmol) was added to a solution of 4- ((2S) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzonitrile (138mg,0.31mmol) in EtOH (5mL) and the reaction was heated to reflux in a 100 ℃ oil bath for 12 h. Will be provided with The reaction was cooled to room temperature, HCl solution (20mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH of the system was adjusted to about 4, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (140mg, 97%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=463.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of N- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) benzyl) -4- ((2S) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (70mg,0.15mmol), (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) methylamine (52mg,0.26mmol), HOBt (71mg,0.53mmol), EDCI (90mg,0.47mmol) and TEA (0.12mL,0.86mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL), stirred at room temperature for 24h, the reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a white solid (8mg, 8%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=643.9[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(t,J=6.0Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.77(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.2Hz,4H),6.96(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),5.24(d,J=3.8Hz,1H),4.54(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),3.80(dd,J=11.8,4.8Hz,1H),3.68(d,J=9.9Hz,2H),3.63–3.50(m,6H),3.47(d,J=13.0Hz,1H),3.24(t,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.00–2.93(m,1H),2.05–1.96(m,2H),1.81(s,2H),1.08(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 148N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S,5S) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide/N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -4- ((2S,5R) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzamide
4- ((2S) -2- (morpholine-4-formyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (70mg,0.15mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (54mg,0.24mmol), HOBt (73mg,0.54mmol), EDCI (102mg,0.53mmol) and TEA (0.12mL,0.86mmol) were dissolved in DCM (6mL) and stirred at room temperature for 14 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) and chromatographed on silica gel preparative chromatography (developing solvent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give 148-1(18mg, 18%) and 148-2(4mg, 4%) as white solids.
148-1:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=674.2[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.49(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),7.82(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.78(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.55(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),6.96(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),5.24(d,J=4.0Hz,1H),5.12(dd,J=13.4,6.4Hz,1H),5.02(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),3.79(dd,J=11.8,4.5Hz,1H),3.72(td,J=11.3,5.1Hz,4H),3.56(d,J=10.4Hz,5H),3.52–3.47(m,1H),3.31(d,J=3.2Hz,1H),3.25(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.98(ddd,J=15.7,10.9,4.6Hz,1H),2.01(dd,J=17.9,10.5Hz,2H),1.80(t,J=11.6Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
148-2:
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=674.2[M+1]+.
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.51(d,J=7.9Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.80(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.65(t,J=7.1Hz,4H),7.54(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),6.96(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),5.13(dd,J=13.0,7.0Hz,1H),5.02(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),4.80(t,J=4.9Hz,1H),3.92(dd,J=12.3,4.5Hz,1H),3.78–3.64(m,5H),3.51(t,J=7.4Hz,4H),3.48–3.44(m,2H),3.27(s,1H),3.24(d,J=7.2Hz,2H),2.00(dd,J=16.3,8.3Hz,2H),1.84–
1.76(m,2H),1.10(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 149N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate
((2S) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-yl) methanol (294mg,1.13mmol), methyl 6-fluoropyridine-3-carboxylate (198mg,1.28mmol) and K2CO3(489mg,3.54mmol) was dissolved in DMSO (3mL) and the reaction was heated in a 50 ℃ oil bath for 24 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, saturated NaCl solution (50mL) was added to the reaction, extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a colorless oil (166mg, 37%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=395.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate
NaH (80mg,3.33mmol) was added to a solution of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate (166mg,0.42mmol) in DMF (2mL) under nitrogen protection in ice bath, after 10min 1-bromo-2-fluoro-ethane (0.17mL,2.30mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. To the reaction mixture was added a saturated NaCl solution (20mL), extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Drying, concentrating under reduced pressure, and collecting the crude product from silica gelColumn chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 6/1) gave a yellow oil (92mg, 50%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=441.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (80mg,1.91mmol) methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate (96mg,0.22mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (3mL/1.5mL/1mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 15 h. Adding HCl solution (5mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure, removing the organic solvent, extracting with EtOAc (20mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a white solid (84mg, 90%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=427.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -6- ((2S) -2- ((2-fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinamide
6- ((2S) -2- ((2-Fluoroethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (84mg,0.20mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (57mg,0.25mmol), HOBt (88mg,0.65mmol), EDCI (144mg,0.75mmol) and TEA (0.2mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/6) to give a white solid (60mg, 48%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=638.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.67(s,1H),8.58(d,J=6.3Hz,1H),8.00(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.64(t,J=8.3Hz,4H),6.92(d,J=9.0Hz,1H),5.22–4.97(m,2H),4.87(s,1H),4.58(s,1H),4.45(s,2H),3.86–3.79(m,1H),3.73(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),3.68(d,J=10.8Hz,3H),3.26(d,J=7.2Hz,2H),3.06(d,J=12.3Hz,1H),2.83(t,J=11.1Hz,1H),2.00(t,J=10.8Hz,2H),1.83–1.71(m,2H),1.10(t,J=7.1Hz,3H).
Example 1506- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate
Mixing TMSCF 2Br (0.40mL,3.00mmol) was added methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate (256mg,0.65mmol) and KOAc (258mg,2.63mmol) in DCM/H2O (0.5mL/0.5mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The solution (10mL) was then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined and washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a colorless oil (30mg, 10%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=445.1[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (38mg,0.91mmol) methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate (30mg,0.07mmol) in THF/MeOH/H was added2O (2mL/1mL/0.7mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 20 h. Adding HCl solution (5mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, extracting with EtOAc (25mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) to give a colorless oil (18mg, 62%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=431.1[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (18mg,0.04mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (21mg,0.09mmol), HOBt (52mg,0.38mmol), EDCI (66mg,0.34mmol) and TEA (0.10mL,0.71mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a yellow solid (13mg, 48%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=642.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.68(s,1H),8.60(d,J=7.5Hz,1H),8.01(d,J=9.0Hz,1H),7.83(t,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.61(dd,J=34.4,8.1Hz,4H),6.95(d,J=9.1Hz,1H),6.70(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.13(dd,J=13.6,6.9Hz,1H),5.03(d,J=16.3Hz,2H),4.41(d,J=12.5Hz,1H),4.16(p,J=10.4Hz,2H),3.71(dd,J=12.8,6.9Hz,2H),3.24(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),3.14–3.08(m,1H),2.84(t,J=12.1Hz,1H),1.97(d,J=12.5Hz,2H),1.81(d,J=9.8Hz,2H),1.09(d,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 151N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) carbamoyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -1- (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (236mg,4.07mmol) was added to (2S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1, 2-dimethylAcid ester (876mg,2.26mmol) in THF/MeOH/H 2O (6mL/3mL/2mL) was stirred at room temperature for 16 h. Adding NaHCO into the reaction liquid3The solution (80mL) was then extracted with DCM (60 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow oil (670mg, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=274.3[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (methoxy (methyl) aminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
(2S) -1- (tert-Butoxycarbonyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (254mg,0.68mmol), N-methoxymethanamine hydrochloride (107mg,1.10mmol), HATU (544mg,1.43mmol) and TEA (0.6mL,4.00mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction solution was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a yellow oil (279mg, 98%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 439.3[ M +23 ═ M]+.
Step three: synthesis of (2S) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide
(2S) -tert-butyl 2- (methoxy (methyl) aminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (628mg,1.51mmol) was dissolved in DCM (5mL) and TFA (0.90mL,10mmol) was slowly added dropwise under ice-bath and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution 3The solution (20mL) was adjusted to about pH 8, extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases combined over anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (313mg, 66%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=317.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) aminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
(2S) -N-methoxy-N-methyl-5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-2-carboxamide (135mg,0.43mmol), ethyl 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (87mg,0.47mmol) and K2CO3(191mg,1.38mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (3mL) and reacted at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure, and a saturated NaCl solution (30mL) was added to the residue, followed by extraction with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a colorless oil (102mg, 51%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=467.1[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) aminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (45mg,1.07mmol) was added 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) aminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (102mg,0.22mmol) in THF/MeOH/H 2O (3mL/1.5mL/1mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 15 h. Adding HCl solution (8mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, extracting with EtOAc (20mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/3) to give a white solid (85mg, 89%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=439.0[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) -2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) aminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
Dissolve 2- ((2S) -2- (methoxy (methyl) aminocarboxamide) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (85mg,0.19mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (57mg,0.25mmol), HOBt (94mg,0.70mmol), EDCI (127mg,0.66mmol) and TEA (0.15mL,1.10mmol) in DCM (5mL) and stir at RT for 21 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/6) to give a white solid (66mg, 52%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=650.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.88(d,J=27.8Hz,2H),8.76(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),5.75(d,J=5.8Hz,1H),5.13(dd,J=13.4,6.5Hz,1H),5.05(t,J=5.1Hz,1H),4.75(dd,J=12.7,3.9Hz,1H),3.89(s,3H),3.75–3.65(m,2H),3.52(t,J=12.6Hz,1H),3.29–3.23(m,2H),3.16(s,3H),2.96(t,J=12.0Hz,1H),2.22(d,J=13.7Hz,1H),2.07–1.99(m,1H),1.87(d,J=10.2Hz,1H),1.82–1.71(m,1H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1522- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (156mg,0.38mmol) and CuI (82mg,0.43mmol) were dissolved in MeCN (5mL) under nitrogen, warmed to 50 deg.C, and 2, 2-difluoro-2- (fluorosulfonyl) -acetic acid (0.16mL,1.50mmol) was added slowly dropwise, followed by stirring for 18 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and then extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a yellow oil (32mg, 18%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=460.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (40mg,0.95mmol) Ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (32mg,0.07mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (2mL/1mL/0.7mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Adding HCl solution (5mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, extracting with EtOAc (25mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a white solid (20mg, 67%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=432.0[M+1]+.
Step three: 2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (28mg,0.07mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (26mg,0.11mmol), HOBt (52mg,0.38mmol), EDCI (53mg,0.28mmol) and TEA (0.08mL,0.57mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (28mg, 67%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=643.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(s,2H),8.76(s,1H),7.84(d,J=6.5Hz,2H),7.72(d,J=6.5Hz,2H),7.66(d,J=9.1Hz,4H),6.70(t,J=76.0Hz,1H),5.32(s,1H),5.14(s,1H),4.83(d,J=11.7Hz,1H),4.21(s,2H),3.72(s,3H),3.27(d,J=6.5Hz,2H),3.16(d,J=10.6Hz,1H),2.83(s,1H),1.98(d,J=11.3Hz,2H),1.80(s,2H),1.14–1.07(m,3H).
Example 1536- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate
NaH (360mg,9.00mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate (600mg,1.52mmol) in DMF (3mL) under nitrogen protection in ice bath, after 10min 3-bromo-3, 3-difluoro-propyl-1-ene (1.8mL,18mmol) was added and the reaction warmed to room temperature for 24 h. Adding saturated NH to the reaction solution4The reaction was quenched with Cl solution (50mL) and then extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), the organic phases combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 6/1) to give a yellow oil (125mg, 17%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=471.0[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate
Pd/C (191mg, 10%) was added to a solution of methyl 6- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxo) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate (163mg,0.35mmol) in THF/MeOH (5mL/5mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. Filtration through celite, and concentration under reduced pressure gave a colorless oil (159mg, 97%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=473.3[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid
Reacting LiOH & H 2O (83mg,1.98mmol) methyl 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinate (159mg,0.34mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (2mL/1mL/0.8mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 20 h. Adding HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, and adjusting the pH of the system to about 4Concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, then extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) to give a colorless oil (92mg, 60%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=459.1[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (51mg,0.11mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (38mg,0.17mmol), HOBt (75mg,0.56mmol), EDCI (86mg,0.45mmol) and TEA (0.16mL,1.20mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), and the organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (13mg, 17%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=670.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.68(s,1H),8.59(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),8.01(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.65(d,J=8.1Hz,4H),6.93(d,J=9.2Hz,1H),5.13(dd,J=13.6,7.0Hz,1H),5.05(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),5.00–4.92(m,1H),4.41(d,J=12.0Hz,1H),4.19–4.09(m,2H),3.71(ddd,J=14.4,11.4,5.1Hz,2H),3.26(dd,J=14.6,7.3Hz,2H),3.08(t,J=12.5Hz,1H),2.85(t,J=11.9Hz,1H),1.95(ddd,J=15.4,14.5,8.0Hz,4H),1.81(d,J=10.9Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.86(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 1542- ((2R,5S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2R) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Will K2CO3(224mg,1.62mmol) was added to a solution of ((2R) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-yl) methanol (132mg,0.51mmol) and ethyl 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (113mg,0.61mmol) in MeCN (2mL) and reacted at room temperature for 11 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (50mL), followed by extraction with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a colorless oil (156mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=410.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2R) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
NaH (475mg,11.87mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of ethyl 2- ((2R) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (880mg,2.15mmol) in DMF (10mL) under nitrogen protection in an ice bath, after 10min 3-bromo-3, 3-difluoro-propyl-1-ene (3mL,29.49mmol) was added and the reaction warmed to room temperature for 12 h. Adding saturated NH to the reaction solution 4Cl solution (80mL), extracted with EtOAc (60 mL. times.2), and the combined organic phases anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 6/1) to give a yellow oil (230mg, 22%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=486.4[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2R) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Pd/C (421mg, 10%) was added to a solution of ethyl 2- ((2R) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (378mg,0.78mmol) in MeOH/THF (5mL/5mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Celite was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless oil (300mg, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=488.4[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 2- ((2R,5S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (57mg,1.36mmol) Ethyl 2- ((2R) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (300mg,0.62mmol) in THF/MeOH/H was added2O (4mL/2mL/1.5mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 20 h. Adding HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, extracting with EtOAc (20mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) and subjected to chiral resolution to give a colorless oil (20mg, 7%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=460.4[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- ((2R,5S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
2- ((2R,5S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (20mg,0.044mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (16mg,0.070mmol), HOBt (33mg,0.24mmol), EDCI (40mg,0.21mmol) and TEA (0.08mL,0.60mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (5mg, 17%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=671.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.88(s,2H),8.75(d,J=7.5Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.66(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.49(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),5.17–5.08(m,2H),5.01(d,J=13.2Hz,2H),4.22(t,J=6.5Hz,1H),4.17–4.11(m,1H),4.05(dd,J=9.8,6.3Hz,1H),3.71(dd,J=14.1,6.4Hz,2H),3.31–3.23(m,3H),1.96(ddd,J=37.0,18.5,7.4Hz,4H),1.64(dt,J=14.3,7.3Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.87(d,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 1552- ((2S,5S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Will K2CO3(224mg,1.62mmol) was added to a solution of ((2S) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-yl) methanol (132mg,0.51mmol) and ethyl 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (113mg,0.61mmol) in MeCN (2mL) and reacted at room temperature for 11 h. To the reaction solution was added a saturated NaCl solution (50mL), followed by extraction with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), and the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a colorless oil (156mg, 75%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=410.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
NaH (475mg,11.87mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (880mg,2.15mmol) in DMF (10mL) under nitrogen protection in an ice bath, after 10min 3-bromo-3, 3-difluoro-propyl-1-ene (3mL,29.49mmol) was added and the reaction warmed to room temperature for 12 h. Adding saturated NH to the reaction solution4Cl solution (80mL) and then extracted with EtOAc (60 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 6/1) to give a yellow oil As (230mg, 22%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=486.4[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
Pd/C (421mg, 10%) was added to a solution of ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- (((1, 1-difluoroallyl) oxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (378mg,0.78mmol) in MeOH/THF (5mL/5mL) under hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Celite was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless oil (300mg, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=488.4[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of 2- ((2S,5S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (57mg,1.36mmol) Ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (300mg,0.62mmol) in THF/MeOH/H was added2O (4mL/2mL/1.5mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 20 h. Adding HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, extracting with EtOAc (20mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) and subjected to chiral resolution to give a colorless oil (56mg, 20%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=460.4[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 2- ((2S,5S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
2- ((2S,5S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (56mg,0.12mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (44mg,0.19mmol), HOBt (85mg,0.63mmol), EDCI (96mg,0.50mmol) and TEA (0.20mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction solution was washed with DCM (2)0mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (48mg, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=671.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(s,2H),8.75(d,J=7.4Hz,1H),7.85(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.67(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.61(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),7.49(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),5.12(dd,J=13.1,5.9Hz,2H),5.00(d,J=12.5Hz,2H),4.18–4.11(m,1H),4.09–4.02(m,1H),3.76–3.66(m,2H),3.56(d,J=14.2Hz,1H),3.31–3.24(m,3H),2.23(s,1H),1.98–1.82(m,3H),1.69(d,J=27.5Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.2Hz,3H),0.86(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1562- ((2S,5R) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of 2- ((2S,5R) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid
Reacting LiOH & H2O (57mg,1.36mmol) Ethyl 2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylate (300mg,0.62mmol) in THF/MeOH/H was added 2O (4mL/2mL/1.5mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 20 h. Adding HCl solution (10mL,1mol/L) into the reaction solution, adjusting the pH of the system to about 4, concentrating under reduced pressure to remove the organic solvent, extracting with EtOAc (20mL × 2), combining the organic phases, and adding anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) and subjected to chiral resolution to give a colorless oil (45mg, 16%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=460.4[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of 2- ((2S,5R) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
2- ((2S,5R) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (45mg,0.10mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (35mg,0.15mmol), HOBt (54mg,0.40mmol), EDCI (83mg,0.43mmol) and TEA (0.15mL,1.10mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The reaction solution was diluted with DCM (20mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (33mg, 50%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=671.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(s,2H),8.75(d,J=6.7Hz,1H),7.84(d,J=6.3Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=7.1Hz,2H),7.68–7.58(m,4H),5.29(s,1H),5.12(dd,J=12.8,5.2Hz,2H),4.82(d,J=11.9Hz,1H),4.23–4.10(m,2H),3.70(s,2H),3.27(d,J=6.6Hz,2H),3.12(t,J=12.7Hz,1H),2.83(t,J=14.8Hz,1H),2.04–1.90(m,4H),1.87–1.75(m,2H),1.10(t,J=6.1Hz,3H),0.86(d,J=5.7Hz,3H).
Example 1574- ((2S,5S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethanesulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- ((2S,5S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (195mg,0.45mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (5-ethylsulfonyl-2-pyridine) ethanol (220mg,0.73mmol), HOBt (250mg,1.85mmol), EDCI (340mg,1.77mmol) and TEA (0.7mL,5.02mmol) were dissolved in DCM (20mL) and stirred at room temperature for 20 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (40 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent:PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/6) to give a white solid (170mg, 58%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=642.4[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.79(s,1H),8.57(d,J=7.5Hz,1H),8.12(d,J=7.3Hz,1H),8.03(d,J=8.0Hz,1H),7.78(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.66(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.01(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),6.70(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.15(dt,J=10.8,5.1Hz,2H),4.42(dd,J=11.1,6.1Hz,1H),4.21–4.15(m,1H),4.00(dd,J=10.3,6.1Hz,1H),3.82–3.73(m,2H),3.69(d,J=15.9Hz,1H),3.29(s,1H),3.16–3.07(m,2H),2.91(d,J=10.3Hz,1H),1.98(d,J=12.6Hz,2H),1.83(d,J=24.0Hz,2H),1.13(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1586- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethanesulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
A50 mL round bottom flask was charged with 6- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (22mg,0.05mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (5-ethylsulfonyl-2-pyridine) ethanol (31mg,0.10mmol), HOBt (45mg,0.33mmol), EDCI (51mg,0.27mmol) and TEA (0.10mL,0.70mmol) dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL) and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2) and the organic phase was Na-free 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a yellow solid (26mg, 79%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=643.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.79(s,1H),8.74(s,1H),8.67(s,1H),8.12(d,J=7.4Hz,1H),8.06–7.97(m,2H),7.71(d,J=7.6Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=7.9Hz,2H),6.94(d,J=9.3Hz,1H),6.69(t,J=76.0Hz,1H),5.16(dd,J=12.6,6.4Hz,1H),4.99(s,1H),4.40(s,1H),4.16(s,2H),3.81–3.71(m,3H),3.17(d,J=5.9Hz,2H),3.09(d,J=12.3Hz,1H),2.83(t,J=11.6Hz,1H),1.96(d,J=12.2Hz,2H),1.80(d,J=11.1Hz,2H),1.15(s,3H).
Example 1592- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethanesulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
2- ((2S) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (65mg,0.15mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (5-ethylsulfonyl-2-pyridine) ethanol (82mg,0.27mmol), HOBt (69mg,0.51mmol), EDCI (84mg,0.44mmol) and TEA (0.20mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 21 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (30mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (74mg, 76%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=644.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.81(t,J=13.6Hz,4H),8.14(d,J=7.5Hz,1H),8.04(d,J=8.0Hz,1H),7.72(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.63(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),6.69(t,J=76.0Hz,1H),5.33(s,1H),5.22–5.13(m,2H),4.82(d,J=11.4Hz,1H),4.20(s,2H),3.82–3.70(m,2H),3.44(s,2H),3.14(t,J=12.6Hz,1H),2.83(t,J=10.5Hz,1H),1.98(d,J=11.7Hz,2H),1.81(d,J=10.6Hz,2H),1.14(t,J=7.1Hz,3H).
Example 1604- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethanesulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
Mixing 4- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid(90mg,0.20mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (91mg,0.30mmol), HOBt (110mg,0.81mmol), EDCI (153mg,0.80mmol) and TEA (0.30mL,2.02mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (15mg, 11%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=670.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.79(s,1H),8.57(s,1H),8.11(s,1H),8.04(s,1H),7.78(d,J=6.4Hz,2H),7.68(d,J=12.2Hz,4H),7.00(s,2H),5.15(d,J=16.0Hz,2H),4.39(s,1H),4.14(s,1H),4.01(s,1H),3.89–3.61(m,4H),3.12(s,1H),2.93(s,1H),2.08–1.71(m,7H),1.13(s,3H),0.87(s,3H).
Example 1616- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethanesulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) nicotinamide
6- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) nicotinic acid (50mg,0.11mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (52mg,0.17mmol), HOBt (84mg,0.62mmol), EDCI (87mg,0.45mmol) and TEA (0.18mL,1.30mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a white solid (19mg, 26%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=671.3[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.80(s,1H),8.65(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),8.13(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),8.02(dd,J=15.6,8.5Hz,2H),7.71(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.64(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.93(d,J=9.1Hz,1H),5.22–5.16(m,1H),5.14(t,J=5.7Hz,1H),4.96(s,1H),4.42(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),4.24–4.06(m,2H),3.84–3.70(m,2H),3.52–3.43(m,2H),3.09(t,J=12.5Hz,1H),2.85(t,J=11.3Hz,1H),2.05–1.89(m,4H),1.81(d,J=10.6Hz,2H),1.14(t,J=7.3Hz,3H),0.86(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
Example 1622- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (5- (ethanesulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) -2-hydroxyethyl) pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
2- ((2S) -2- ((1, 1-Difluoropropoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid (52mg,0.11mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (5-ethylsulfonyl-2-pyridine) ethanol (55mg,0.18mmol), HOBt (68mg,0.50mmol), EDCI (92mg,0.48mmol) and TEA (0.2mL,1.43mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (20mL), washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/8) to give a yellow solid (29mg, 38%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=672.5[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.86(s,2H),8.81(s,2H),8.15(d,J=6.4Hz,1H),8.04(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.61(d,J=6.9Hz,2H),7.48(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),5.19(dd,J=6.1,5.1Hz,1H),4.99(d,J=11.9Hz,2H),4.18–4.09(m,1H),4.09–3.99(m,1H),3.76(dd,J=11.4,6.2Hz,2H),3.55(d,J=14.0Hz,1H),3.29(s,2H),3.16(s,1H),2.22(t,J=14.5Hz,1H),2.02–1.80(m,4H),1.75–1.61(m,2H),1.15–1.11(m,3H),0.86(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).
Example 1634- ((6S) -6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
NaH (81mg,2.03mmol, 60%) was slowly added to a solution of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (550mg,1.53mmol) and BnBr (0.20mL,1.70mmol) in DMF (10mL) under ice-bath, after 10min, it was transferred to room temperature and stirred for 8 h. EtOAc (80mL) is added to the reaction solution, followed by saturated NH4Cl solution (20 mL. times.5) washing, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1) to give a pale yellow oily liquid (478mg, 69%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=472.4[M+23]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S) -tert-butyl 2- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
Ruthenium trichloride (12mg,0.06mmol) was slowly added to (2S) -tert-butyl 2- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (478mg,1.06mmol) and NaIO at room temperature 4(683mg,3.19mmol) of CCl4/MeCN/H2O (2mL/2mL/3mL) solution was stirred at room temperature for 5 h. Adding H to the reaction solution2O (50mL) was then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v/v) ═ 10/1/1) to give a pale yellow oil (425mg, 86%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=486.2[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of (6S) -tert-butyl 6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
(6S) -tert-butyl 6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (425mg,0.92mmol) was dissolved in HCl in MeOH (10mL, 20%) and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. Saturated NaHCO was slowly added to the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (30mL) and then washed withDCM (30 mL. times.3) extracted the aqueous phase, the organic phases were combined and washed with saturated NaCl solution (20mL) anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oily liquid (287mg, 86%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=364.2[M+1]+.
Step four: synthesis of methyl 4- ((6S) -6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, (6S) -6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-2-one (287mg,0.79mmol), methyl 4-bromobenzoate (344mg.,1.58mmol), Pd 2(dba)3(38mg,0.04mmol), XantPhos (34mg,0.06mmol) and Cs2CO3(782mg,2.38mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (6mL) and the reaction was stirred in a 100 ℃ oil bath with heating for 28 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1/1) to give a yellow solid (147mg, 37%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 498.4[ M +1 ═ M]+.
Step five: synthesis of 4- ((6S) -6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- ((6S) -6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (77mg,0.19mmol) was dissolved in a HBr solution (48%)/AcOH/1, 4-dioxane (1mL/1mL/3mL) mixed solvent, and the reaction was stirred with heating in a 100 ℃ oil bath for 2 h. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, and saturated Na was added2CO3The solution was adjusted to pH about 10 and then extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.2), HCl solution (1mol/L) was added to the aqueous phase, the solution pH was adjusted to about 3 and then extracted with DCM (30 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and extracted with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow solid (30mg, 33%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=484.2[M+1]+.
Step six: synthesis of 4- ((6S) -6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
Mixing 4- ((6S) -6- ((benzyloxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (30mg,0.06mmol), (R) -2-amino-2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) ethanol (30mg,0.13mmol), EDCI (56mg,0.29mmol) and HOBt (42mg,0.31mmol) were dissolved in DCM (4mL) and TEA (0.10mL,0.72mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction was diluted with DCM (60mL) and saturated NaHCO3Solution (20mL) washed with anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a yellow solid (12mg, 28%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=695.2[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.66(d,J=6.9Hz,1H),7.97–7.91(m,1H),7.88(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),7.85(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.74–7.61(m,6H),7.55–7.35(m,6H),7.01(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),5.14(dd,J=7.8Hz,1H),5.04(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),4.64-4.56(m,1H),4.51-4.42(m,1H),4.24-4.19(m,1H),4.19–4.08(m,1H),3.80–3.67(m,2H),3.27(d,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.11-3.00(m,1H),3.00-2.89(m,1H),2.03–1.97(m,2H),1.91-1.79(m,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1642- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of (2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine
NaH (10mg,0.25mmol, 60%) was added to a solution of ((2R) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl) methanol (80mg,0.22mmol) in THF (32mL) with stirring in a cold bath at-20 ℃ under nitrogen, after 2h MeI (0.10mL,2.00mmol) was added slowly and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Adding NaHCO into the reaction system3The reaction was quenched with solution (20mL), concentrated under reduced pressure to remove organic solvent, the residue was extracted with DCM (20 mL. times.3), the organic phases were combined and Na anhydrous 2SO4Drying, and subjecting the crude product to silica gel column chromatographyIsolation (eluent: PET/EtOAv (v/v) ═ 5/1) gave a yellow solid (70mg, 84%).
Step two: synthesis of 4- ((2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline
Pd/C (860mg, 5%) was added to a solution of (2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -1- (4-nitrophenyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidine (80mg,0.21mmol) in MeOH (50mL) under hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/DCM (v/v) ═ 1/10) to give a yellow solid (70mg, 95%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=351.2[M+1]+.
Step three: synthesis of 2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -N- (4- ((2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) phenyl) acetamide
4- ((2R) -2- (methoxymethyl) -4- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) pyrrolidin-1-yl) aniline (80mg,0.23mmol),2- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) acetic acid (100mg,0.44mmol), EDCI (100mg,0.34mmol) and HOBt (80mg,0.51mmol) were dissolved in DCM (50mL) under nitrogen and stirred at room temperature for 8 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3The reaction was quenched with solution (30mL), separated, and the organic phase was successively treated with H2O (50mL) and saturated NaCl solution (50mL) washed with anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: DCM/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1) to give a pale yellow solid (50mg, 39%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z=561.1[M+1]+;
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ(ppm):7.88(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.66–7.58(m,2H),7.54(t,J=11.1Hz,2H),7.48–7.42(m,2H),7.37(d,J=15.3Hz,1H),7.34–7.28(m,2H),6.64(s,2H),4.07(s,1H),3.90(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),3.84–3.71(m,3H),3.70–3.62(m,1H),3.58(s,1H),3.43(s,1H),3.20–3.05(m,3H),2.68–2.49(m,1H),2.36(dd,J=19.6,11.8Hz,1H),1.30(t,J=7.5Hz,3H).
Example 1654- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl (2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylate
(2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid (20.40g,141mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (200mL) and SOCl is slowly added dropwise in an ice bath2(18mL,248mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 22 h. Concentration under reduced pressure gave a white solid (21g, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:160.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S,5S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-hydroxypiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate
(2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (21.10g,131.93mmol) is dissolved in THF (240mL) and K is then added2CO3(46.60g,337mmol) was dissolved in H2O (120mL), adding the mixture into a flask in ice bath, and slowly dropwise adding Boc in ice bath until the reaction solution is uniformly mixed2O (45mL,200mmol), stirred at room temperature for 24 h. EtOAc (200 mL. times.3) extraction, combined organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (33g, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:282.3[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of 1-tert-butyl (S) -2-methyl-5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate
(2S,5S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-hydroxypiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (32.01g,123.41mmol) was dissolved in DCM (400mL), and DMP (105.01g,247.60mmol) was added portionwise under ice-bath and stirred at room temperature for 21 h. Filtering with diatomite, adding saturated NaHCO into reaction liquid3Solution (600mL), adjusting system pH to about 8, DCM (200 mL. times.3) extraction, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow oil (30g, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:280.1[M+23]+.
Step four: synthesis of (S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2- (2H) -dicarboxylic acid ester
1-tert-butyl (S) -2-methyl-5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (5.10g,20.01mmol) and P (OPh)3) (18.08g,58.27mmol) in DCM (50mL) at-20 deg.C TEA (14mL,101.10mmol) was added followed by Br2(2.8mL,55.03mmol) was diluted with DCM (25mL), added dropwise slowly to the reaction system, and after addition over 40min, the temperature was raised to room temperature and stirred for 16 h. DCM (80mL), saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction3Washing with solution (150 mL. times.2), washing with saturated NaCl (100 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (3.77g, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:222.0[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 6'- (trifluoromethyl) -5, 6-dihydro- [3,3' -bipyridine ] -1,6(4H) -dicarboxylic acid 6-tert-butyl ester
(S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylate (2.51g,7.84mmol), (6- (trifluoromethyl) -3-pyridinyl) boronic acid (2.22g,11.60mmol), Pd (dppf) Cl under nitrogen2(620mg,0.85mmol),Cs2CO3(2.62g,8.04mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (30mL) and the reaction was allowed to warm to 70 ℃ for 21 h. Celite was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow oil (1.7g, 56%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:387.1[M+1]+
Step six: synthesis of 6- (hydroxymethyl) -6'- (trifluoromethyl) -5, 6-dihydro- [3,3' -bipyridine ] -1(4H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
Mixing 6'- (trifluoromethyl) -5, 6-dihydro- [3,3' -bipyridine]-6-tert-butyl 1,6(4H) -dicarboxylate (421mg,1.09mmol) was dissolved in THF (10mL) and LiBH was dissolved in ice bath4A solution of (100mg,4.59mmol) in MeOH (5mL) was slowly added dropwise to the reaction and stirred at room temperature for 21 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (30mL), quench reaction, EtOAc (60 mL. times.2) extract, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was separated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent:PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/1), yielding a colorless oil (254mg, 65%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:359.2[M+1]+
Step seven: synthesis of tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
6- (hydroxymethyl) -6'- (trifluoromethyl) -5, 6-dihydro- [3,3' -bipyridine ] -1(4H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (254mg,0.71mmol), Pd/C (390mg, 10%) was dissolved in THF (10mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 12H. Celite was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (234mg, 92%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:361.1[M+1]+
Step eight: synthesis of tert-butyl 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
Tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (234mg,0.65mmol), KOAc (380mg,3.88mmol) were dissolved in DCM/H2O (1.5mL/1.5mL), then (bromo (difluoro) methyl) -trimethyl-silane (0.31mL,2.00mmol) was slowly added dropwise and stirred at room temperature for 17 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (10mL), quench reaction, DCM (30 mL. times.2) extract, Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a colorless oil (185mg, 69%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 411.2[ M +1 ]]+
Step nine: synthesis of 5- (6- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidin-3-yl) -2- (trifluoromethyl) pyridine
Tert-butyl 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (185mg,0.45mmol) was dissolved in DCM (2mL), TFA (0.3mL,4.01mmol) was slowly added dropwise under ice bath, and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. The mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove part of DCM and TFA, and saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction mixture3Solution (20mL), adjusted to about pH 8, extracted with DCM (60 mL. times.2) and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (125mg, 89%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 311.1[ M +1 ]]+
Step ten: synthesis of methyl 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
5- (6- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidin-3-yl) -2- (trifluoromethyl) pyridine (164mg,0.53mmol), methyl 4-iodobenzoate (268mg,1.02mmol), Pd under nitrogen2(dba)3(62mg,0.07mmol),XantPhos(67mg,0.12mmol),Cs2CO3(356mg,1.09mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-Dioxane (10mL) and heated to 100 ℃ for 24 h. Celite was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow oil (55mg, 23%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:445.1[M+1]+
Step eleven: synthesis of 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Methyl 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (55mg,0.12mmol), lioh2O (30mg,0.72mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (1mL/0.5mL/0.3mL), and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. HCl solution (8mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH was adjusted to about 4, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a yellow oil (29mg, 54%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:431.1[M+1]+
Step twelve: synthesis of 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (6- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-3-yl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (29mg,0.07mmol), (2R) -2-amino-2- (4-ethylsulfonylphenyl) ethanol (28mg,0.12mmol), HOBt (30mg,0.22mmol), EDCI (42mg,0.22mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and TEA (0.05mL,0.40mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. DCM (50mL) was added to the reaction solution, followed by saturated NaCl solution (30)mL. times.2) washing, anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentration under reduced pressure and chromatography of the crude product on silica gel column (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/4) followed by preparative isolation gave 165-1 (9mg, 21%, Rt ═ 7.75min) as a white solid and 165-2 (4mg, 9%, Rt ═ 13.52min) as a yellow solid.
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:642.2[M+1]+
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):δ8.72(s,1H),8.55(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.99(d,J=7.2Hz,1H),7.83(t,J=6.3Hz,5H),7.65(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.08(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),6.67(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.13(dd,J=14.0,6.9Hz,1H),5.03(t,J=5.6Hz,1H),4.22–4.14(m,1H),4.07–4.00(m,1H),3.88(dd,J=10.2,4.7Hz,1H),3.84–3.78(m,1H),3.77–3.68(m,2H),3.50–3.45(m,1H),3.45–3.40(m,1H),3.28–3.22(m,2H),2.20(s,1H),1.87–1.72(m,3H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.84(s,1H),8.51(d,J=8.0Hz,1H),8.18(d,J=8.1Hz,1H),7.90(d,J=8.1Hz,1H),7.81(dd,J=13.0,8.4Hz,4H),7.64(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.03(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),6.69(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.35–5.30(m,1H),5.13(d,J=7.2Hz,1H),5.02(t,J=6.0Hz,1H),4.61–4.56(m,1H),4.41(s,1H),4.23–4.18(m,1H),4.04–3.99(m,1H),3.78–3.67(m,3H),3.27(s,2H),2.00(dd,J=15.1,8.0Hz,4H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1664- [5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -1-piperidinyl ] -N- [ (1R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxy-ethyl ] benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl (2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylate
(2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid (20.40g,141mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (200mL) and SOCl is slowly added dropwise in an ice bath2(18mL,248mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 22 h. Concentration under reduced pressure gave a white solid (21g, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:160.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S,5S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl 5-hydroxypiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate
(2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (21.10g,131.93mmol) is dissolved in THF (240mL) and K is then added2CO3(46.60g,337mmol) was dissolved in H2O (120mL), adding the mixture into a flask in ice bath, and slowly dropwise adding Boc in ice bath until the reaction solution is uniformly mixed2O (45mL,200mmol), stirred at room temperature for 24 h. EtOAc (200 mL. times.3) extraction, combined organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (33g, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:282.3[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of (S) -2-methyl-5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid-1-tert-butyl ester
(2S,5S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-5-hydroxypiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (32.01g,123.41mmol) was dissolved in DCM (400mL), and DMP (105.01g,247.60mmol) was added portionwise under ice-bath and stirred at room temperature for 21 h. Filtering with diatomite, adding saturated NaHCO into reaction liquid 3The solution (600mL) is adjusted to about pH 8, and DCM (200 mL. times.3) is used for extraction, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow oil (30g, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:280.1[M+23]+.
Step four: synthesis of (S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl 5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2- (2H) -dicarboxylic acid ester
1-tert-butyl (S) -2-methyl-5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (5.10g,20.01mmol) and P (OPh)3) (18.08g,58.27mmol) in DCM (50mL) at-20 deg.C TEA (14mL,101.10mmol) was added followed by Br2(2.8mL,55.03mmol) was diluted with DCM (25mL), added dropwise slowly to the reaction system, and after addition over 40min, the temperature was raised to room temperature and stirred for 16 h. DCM (80mL), saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction3Washing with solution (150 mL. times.2), washing with saturated NaCl (100 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (3.77g, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:222.0[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl ester
(S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylate (1.52g,4.76mmol), (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) boronic acid (1.07g,5.30mmol), Pd (dppf) Cl 2(351mg,0.48mmol),Cs2CO3(1.57g,4.82mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (20mL) and allowed to warm to 80 ℃ for 17 h. Celite was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow oil (800mg, 42%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:420.0[M+23]+
Step six: synthesis of tert-butyl 5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate
5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl ester (0.75g,1.90mmol) was dissolved in THF (10mL) and LiBH was dissolved in ice bath4(445mg,20.43mmol) was added portionwise to the reaction and stirred at room temperature for 17 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (50mL), quench reaction, EtOAc (100 mL. times.2) extract, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a colorless oil (600mg, 86%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:314.0([M+1-56]+
Step seven: synthesis of tert-butyl 5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- (hydroxymethyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxolan-5-yl) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (717mg,1.94mmol), Pd/C (1.16g, 10%) was dissolved in THF (10mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 24H. Celite was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless oil (712mg, 99%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:394.1[M+23]+
Step eight: synthesis of tert-butyl 5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxolan-5-yl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
Tert-butyl 5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- (hydroxymethyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (712mg,1.93mmol), KOAc (1.16g,11.80mmol) was dissolved in DCM/H2O (2.3mL/2.3mL) and then (bromo (difluoro) methyl) -trimethyl-silane (0.9mL,6.01mmol) was slowly added dropwise with stirring at room temperature for 18H. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (30mL), quench reaction, DCM (80 mL. times.2) extract, Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a colorless oil (667mg, 82%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:444.3[M+23]+
Step nine: synthesis of 5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidine
Tert-butyl-5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (667mg,1.58mmol) was dissolved in EtOAc (5mL), and a solution of HCl in EtOAc (5.5mL,17mmol,3mol/L) was added slowly dropwise over an ice bath and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Concentrating under reduced pressure to remove part of EtOAc and HCl, adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (30mL), adjusting the pH of the system to about 8, and DCM (60 mL. times.2) extraction Taking anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (460mg, 90%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:322.2[M+1]+
Step ten Synthesis of methyl 4- [ (5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- (difluoromethoxymethyl) -1-piperidinyl ] benzoate
Under the protection of nitrogen, 5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidine (319mg,0.10mmol), methyl 4-iodobenzoate (802mg,3.06mmol), Pd2(dba)3(93mg,0.10mmol),XantPhos(123mg,0.21mmol),Cs2CO3(672mg,2.06mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-Dioxane (8mL) and heated to 100 ℃ for reaction for 48 h. Celite was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a brown oil (265mg, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:456.1[M+1]+
Step eleven: synthesis of 4- [5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- (difluoromethoxymethyl) -1-piperidinyl ] benzoic acid
Coupling 4- [ (5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- (difluoromethoxymethyl) -1-piperidinyl group]Methyl benzoate (300mg,0.66mmol), LiOH2O (121mg,2.88mmol) was dissolved in THF/MeOH/H2O (2mL/1mL/0.8mL) and stirred at room temperature for 15H. HCl solution (8mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH was adjusted to about 4, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (30 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow oil (180mg, 62%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:442.1[M+1]+
Step twelve: synthesis of 4- [5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxolan-5-yl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -1-piperidinyl ] -N- [ (1R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxy-ethyl ] benzamide
4- [5- (2, 2-difluoro-1, 3-benzodioxol-5-yl) -2- (difluoromethoxymethyl) -1-Piperidinyl group]Benzoic acid (180mg,0.41mmol), (2R) -2-amino-2- (4-ethylsulfonylphenyl) ethanol (126mg,0.55mmol), HOBt (182mg,1.35mmol), EDCI (252mg,1.31mmol) was dissolved in DCM (10mL) and TEA (0.3mL,2.01mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. DCM (50mL) was added to the reaction solution, which was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/5) to give 168mg of a white solid; chiral resolution was then prepared to give 166-1 as a white solid (82mg, 31%, Rt 16.22min) and 166-2 as a yellow solid (36mg, 14%, Rt 19.09 min).
MS(ESI,neg.ion)m/z:651.7[M-1]–
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.55(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.83(d,J=8.1Hz,4H),7.66(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.35(s,1H),7.29(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.14(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),7.06(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),6.66(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.14(dd,J=13.0,6.2Hz,1H),5.03(t,J=5.6Hz,1H),4.07(d,J=4.3Hz,1H),4.02–3.94(m,1H),3.85(dd,J=10.0,4.4Hz,1H),3.80–3.67(m,2H),3.62(dd,J=12.7,5.3Hz,1H),3.40(s,1H),3.26(q,J=7.3Hz,2H),3.21–3.14(m,1H),2.16–2.06(m,1H),1.94–1.84(m,1H),1.77–1.68(m,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):δ8.50(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.81(dd,J=15.3,8.5Hz,4H),7.64(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.58(s,1H),7.36(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.25(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),6.99(d,J=8.9Hz,2H),6.68(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.12(dd,J=13.7,7.0Hz,1H),5.01(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),4.39(d,J=5.0Hz,1H),4.22–4.14(m,1H),3.99(dd,J=10.2,6.2Hz,1H),3.77–3.62(m,3H),3.28–3.23(m,2H),3.07(t,J=12.2Hz,1H),2.86(t,J=11.2Hz,1H),2.01–1.89(m,2H),1.80(dd,J=35.9,13.6Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1674- (6- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -2-oxy-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl (2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylate
(2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid (20.40g,141mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (200mL) and SOCl is slowly added dropwise in an ice bath2(18mL,248mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 22 h. Concentration under reduced pressure gave a white solid (21g, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:160.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S,5S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-hydroxypiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate
(2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (21.10g,131.93mmol) is dissolved in THF (240mL) and K is then added2CO3(46.60g,337mmol) was dissolved in H2O (120mL), adding the mixture into a flask in ice bath, and slowly dropwise adding Boc in ice bath until the reaction solution is uniformly mixed2O (45mL,200mmol), stirred at room temperature for 24 h. EtOAc (200 mL. times.3) extraction, combined organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (33g, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:282.3[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of 1-tert-butyl (S) -2-methyl-5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate
(2S,5S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-hydroxypiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (32.01g,123.41mmol) was dissolved in DCM (400mL), and DMP (105.01g,247.60mmol) was added portionwise under ice-bath and stirred at room temperature for 21 h. DiatomiteFiltering, adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction liquid3The solution (600mL) is adjusted to about pH 8, and DCM (200 mL. times.3) is used for extraction, anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow oil (30g, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:280.1[M+23]+.
Step four: synthesis of (S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2- (2H) -dicarboxylic acid ester
1-tert-butyl (S) -2-methyl-5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (5.10g,20.01mmol) and P (OPh)3) (18.08g,58.27mmol) in DCM (50mL) at-20 deg.C TEA (14mL,101.10mmol) was added followed by Br2(2.8mL,55.03mmol) was diluted with DCM (25mL), added dropwise slowly to the reaction system, and after addition over 40min, the temperature was raised to room temperature and stirred for 16 h. DCM (80mL), saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction3Washing with solution (150 mL. times.2), washing with saturated NaCl (100 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (3.77g, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:222.0[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of 5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl ester
(S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylate (3.77g,11.80mmol), (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) boronic acid (3.57g,18.80mmol), Pd (dppf) Cl under nitrogen2(887mg,1.21mmol),Cs2CO3(7.63g,23.40mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (30mL) and stirred at 100 ℃ for 12 h. Celite was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (2.6g, 58%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:408.2[M+23]+.
Step six: synthesis of 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl ester (800mg,2.08mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous THF (10mL) and LiBH was added under ice bath4(520mg,23.88mmol) was slowly added to the reaction system, warmed to room temperature and stirred for 17 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (30mL), quench, EtOAc (50 mL. times.2) extract, combine organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 2/1) to give a white solid (630mg, 85%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 302.1[ M +1-56 ]]+.
Step seven: synthesis of tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
Under a hydrogen atmosphere, tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (630mg,1.76mmol), Pd/C (907mg, 10%) was dissolved in THF (8mL) and stirred at room temperature for 17H. Celite was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a colorless oil (602mg, 98%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:382.2[M+23]+.
Step eight: synthesis of tert-butyl 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
Tert-butyl 2- (hydroxymethyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (602mg,1.66mmol), KOAc (978mg,9.97mmol) were dissolved in DCM/H2O (1.8mL/1.8mL), then (bromo (difluoro) methyl) -trimethyl-silane (0.80mL,5mmol) was slowly added dropwise and stirred at room temperature for 19 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (30mL), quench reaction, DCM (50 mL. times.2) extract, Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a colorless oil (546mg, 80%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 432.5[ M +23 ]]+
Step nine: synthesis of 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine
Tert-butyl 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (266mg,0.65mmol) was dissolved in EtOAc (2mL), a solution of HCl in EtOAc (2mL) was added slowly and dropwise over an ice bath,stir at rt for 16 h. Concentrating under reduced pressure to remove part of HCl and EtOAc, adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (20mL), adjusted to pH around 8, extracted with DCM (40 mL. times.2) and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (192mg, 96%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 310.1[ M +1 ] ]+
Step ten: synthesis of methyl 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, 2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidine (192mg,0.62mmol), methyl 4-iodobenzoate (492mg,1.88mmol), Pd2(dba)3(74mg,0.08mmol), XantPhos (93mg,0.16mmol), Cs2CO3(426mg,1.31mmol) were dissolved in 1,4-Dioxane (10mL) and heated to 100 ℃ for reaction for 32 h. Celite was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a brown oil (146mg, 53%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:444.1[M+1]+
Step eleven: synthesis of methyl 4- (6- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
Methyl 4- (2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -5- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate (146mg,0.33mmol), RuCl3(66mg,0.32mmol), dissolved in CCl4/CH3CN/H2O (2mL/1mL/1mL), and NaIO was added4(221mg,1.03mmol), stirred at room temperature for 21 h. Filtering with diatomaceous earth, concentrating under reduced pressure, and removing CH3CN and CCl4EtOAc (15 mL. times.2) extraction, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow oil (40mg, 27%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:458.6[M+1]+
Step twelve: synthesis of 4- (6- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
Reacting 4- (6- ((difluoro)Methoxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid methyl ester (97mg,0.21mmol), LiOH2O (61mg,1.45mmol) in THF/MeOH/H2O (1mL/0.5mL/0.4mL), and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. HCl solution (5mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH was adjusted to about 4, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (20 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried, concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (26mg, 28%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:444.1[M+1]+
Step thirteen: synthesis of 4- (6- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- (6- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) -2-oxo-3- (4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (26mg,0.06mmol), (2R) -2-amino-2- (4-ethylsulfonylphenyl) ethanol (21mg,0.09mmol), HOBt (50mg,0.37mmol), EDCI (39mg,0.20mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and TEA (0.05mL,0.40mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 12 h. DCM (50mL) was added to the reaction solution, which was washed with saturated NaCl solution (20 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na 2SO4Drying, concentration under reduced pressure and separation of the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: DCM/MeOH (v/v) ═ 10/1), further preparative chiral resolution gave 167-1 (4mg, 10%) and 167-2 (6mg, 16%) yellow solids.
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:655.1[M+1]+
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.97(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.84(d,J=7.7Hz,2H),7.67(d,J=8.4Hz,4H),7.50(d,J=8.3Hz,2H),7.43(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),6.63(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.18–5.13(m,1H),5.07(t,J=5.0Hz,1H),4.32(s,1H),3.93(s,1H),3.73(d,J=6.6Hz,3H),3.26(d,J=7.8Hz,3H),2.20(dd,J=12.5,5.0Hz,2H),2.00(dd,J=15.9,7.4Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.87(d,J=7.8Hz,1H),7.97(d,J=8.1Hz,2H),7.85(d,J=8.2Hz,2H),7.69(t,J=9.3Hz,4H),7.57(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),7.44(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),6.68(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.19–5.14(m,1H),5.07(t,J=5.0Hz,1H),4.28(s,1H),3.94(d,J=7.4Hz,1H),3.86(d,J=8.0Hz,1H),3.78(dd,J=10.9,3.6Hz,2H),3.72(d,J=5.2Hz,1H),3.28–3.23(m,2H),2.18–2.12(m,2H),2.03(dd,J=20.0,12.2Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.3Hz,3H).
Example 1684- (5- (4, 4-Difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of methyl (2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylate
(2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid (20.40g,141mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (200mL) and SOCl is slowly added dropwise in an ice bath2(18mL,248mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 22 h. Concentration under reduced pressure gave a white solid (21g, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:160.2[M+1]+.
Step two: synthesis of (2S,5S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-hydroxypiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate
(2S,5S) -5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (21.10g,131.93mmol) is dissolved in THF (240mL) and K is then added2CO3(46.60g,337mmol) was dissolved in H2O (120mL), added to the flask in ice bath,after the reaction solution is mixed evenly, the Boc is slowly dripped under ice bath2O (45mL,200mmol), stirred at room temperature for 24 h. EtOAc (200 mL. times.3) extraction, combined organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil (33g, 96%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:282.3[M+23]+.
Step three: synthesis of 1-tert-butyl (S) -2-methyl-5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate
(2S,5S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-hydroxypiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (32.01g,123.41mmol) was dissolved in DCM (400mL), and DMP (105.01g,247.60mmol) was added portionwise under ice-bath and stirred at room temperature for 21 h. Filtering with diatomite, adding saturated NaHCO into reaction liquid3Solution (600mL), adjusting system pH to about 8, DCM (200 mL. times.3) extraction, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow oil (30g, 94%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:280.1[M+23]+.
Step four: synthesis of (S) -1-tert-butyl-2-methyl-5-bromo-3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2- (2H) -dicarboxylic acid ester
1-tert-butyl (S) -2-methyl-5-oxopiperidine-1, 2-dicarboxylate (5.10g,20.01mmol) and P (OPh)3) (18.08g,58.27mmol) in DCM (50mL) at-20 deg.C TEA (14mL,101.10mmol) was added followed by Br2(2.8mL,55.03mmol) was diluted with DCM (25mL), added dropwise slowly to the reaction system, and after addition over 40min, the temperature was raised to room temperature and stirred for 16 h. DCM (80mL), saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction3Washing with solution (150 mL. times.2), washing with saturated NaCl (100 mL. times.2), anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 10/1) to give a yellow oil (3.77g, 59%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:222.0[M+1]+.
Step five: synthesis of (4, 4-difluorocyclohex-1-en-1-yl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl ester
Under the protection of nitrogen, (S) -1-tert-butyl 2-methyl 5-bromo-34-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylate (3.02g,4.72mmol), 2- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexen-1-yl) -4,4,5, 5-tetramethyl-1, 3, 2-dioxaborolane (1.24g,5.08mmol), Pd (dppf) Cl2(364mg,0.50mmol),Cs2CO3(1.54g,4.73mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (20mL) and stirred at 70 ℃ for 16 h. Celite was filtered, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 5/1) to give a yellow oil (900mg, 53%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z 258.2[ M +1-100 ]]+
Step six: synthesis of 5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohex-1-en-1-yl) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
LiBH is added under ice bath4(105mg,4.82mmol), added slowly to a solution of (4, 4-difluorocyclohex-1-en-1-yl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1, 2(2H) -dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl 2-methyl ester (307mg,0.86mmol) in THF (6mL), then warmed to room temperature for 16H. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (20mL), quench, EtOAc (50 mL. times.2) extract, combine organic phases, anhydrous Na2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a colorless oil (239mg, 84%).
MS:(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:274.2[M+1-56]+
Step seven: synthesis of tert-butyl 5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- (hydroxymethyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
5- (4, 4-Difluorocyclohex-1-en-1-yl) -2- (hydroxymethyl) -3, 4-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (689mg,2.09mmol), Pd/C (1.17g, 10%) was dissolved in THF (10mL) under a hydrogen atmosphere and stirred at room temperature for 11H. Filtration through celite, and concentration under reduced pressure gave a colorless oil (690mg, 99%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:356.3[M+23]+
Step eight: synthesis of tert-butyl 5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
5- (4, 4-Difluorocyclohexyl) -2- (hydroxymethyl) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (443mg,1.33mmol), KOAc (751mg,7.65mmol) were dissolved in DCM/H2O (1.5mL/1.5mL), howeverThen (bromo (difluoro) methyl) -trimethyl-silane (0.6mL,4mmol) was slowly added dropwise and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Adding saturated NaHCO into the reaction solution3Solution (50mL), quench reaction, DCM (80 mL. times.2) extract, Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 4/1) to give a colorless oil (391mg, 77%). MS (ESI, pos. ion) M/z 406.3[ M +23 ]]+)。
Step nine: synthesis of 5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidine
Tert-butyl 5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (391mg,1.02mmol) was dissolved in DCM (5mL), TFA (0.6mL,8mmol) was slowly added dropwise under ice bath, and stirred at room temperature for 18 h. The mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove part of DCM and TFA, and saturated NaHCO was added to the reaction mixture 3Solution (20mL), adjusted to about pH 8, extracted with DCM (60 mL. times.2) and Na anhydrous2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/2) to give a yellow oil (197mg, 68%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:284.1[M+1]+.
Step ten: synthesis of methyl 4- (5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoate
Under nitrogen protection, 5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidine (197mg,0.70mmol), methyl 4-iodobenzoate (306mg,1.17mmol), Pd2(dba)3(142mg,0.16mmol),XantPhos(191mg,0.33mmol),Cs2CO3(779mg,2.39mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-Dioxane (10mL) and heated to 100 ℃ for 48 h. Celite was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow solid (100mg, 34%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:418.2[M+1]+
Step eleven: synthesis of 4- (5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid
4- (5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzylAcid methyl ester (100mg,0.24mmol), LiOH2O (37mg,0.88mmol) was dissolved in THF/MeOH/H2O (1.5mL/0.8mL/0.5mL) and stirred at room temperature for 16H. HCl solution (8mL,1mol/L) was added to the reaction, the pH was adjusted to about 4, the aqueous phase was extracted with EtOAc (40 mL. times.2), the organic phases were combined, anhydrous Na 2SO4Dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was isolated by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 3/1) to give a yellow oil (37mg, 38%). MS (ESI, pos.ion) M/z:404.2[ M +1 ]]+
Step twelve: synthesis of 4- (5- (4, 4-difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidin-1-yl) -N- ((R) -1- (4- (ethylsulfonyl) phenyl) -2-hydroxyethyl) benzamide
4- (5- (4, 4-Difluorocyclohexyl) -2- ((difluoromethoxy) methyl) piperidin-1-yl) benzoic acid (37mg,0.09mmol), (2R) -2-amino-2- (4-ethylsulfonylphenyl) ethanol (30mg,0.13mmol), HOBt (58mg,0.43mmol), EDCI (78mg,0.41mmol) were dissolved in DCM (5mL) and TEA (0.08mL,0.60mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature for 16 h. DCM (50mL) was added to the reaction solution, which was washed with saturated NaCl solution (30 mL. times.2) and anhydrous Na2SO4Drying, concentration under reduced pressure and further preparative isolation of the crude product by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: PET/EtOAc (v/v) ═ 1/5) gave a yellow solid (9mg, 16%).
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:615.2[M+1]+
1H NMR(400MHz,d6-DMSO)δ(ppm):8.49(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),7.81(dd,J=16.1,8.4Hz,4H),7.65(d,J=7.8Hz,2H),6.96(d,J=8.4Hz,2H),6.65(t,J=76Hz,1H),5.12(dd,J=13.3,6.9Hz,1H),5.02(t,J=5.2Hz,1H),4.09–4.02(m,1H),3.97–3.91(m,1H),3.83(dd,J=10.1,4.2Hz,1H),3.76–3.68(m,2H),3.53–3.44(m,2H),3.26(dd,J=14.8,7.6Hz,3H),3.14(dd,J=13.4,3.0Hz,1H),1.98(s,2H),1.81(dd,J=25.9,13.5Hz,5H),1.66(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),1.57–1.42(m,3H),1.10(t,J=7.2Hz,3H).
Biological activity assay
In vitro ROR γ Binding activity assay for compounds of the invention
1. Test method
(1) ROR gamma experiment buffer and 10mM DTT are prepared
100mL of 1 Xbasic assay buffer (HEPES (pH 7.4), 100mM NaCl, 0.01% BSA) was prepared, and 154.25mg of DTT was added and mixed well.
(2) Formulation of gradient concentrations of Compounds
a. Standard compounds were prepared, diluted to 2.5mM with 100% DMSO, then 3-fold diluted, 11-step dilutions to a final concentration of 42.34 nM;
b. experimental compounds were prepared with reference to standard compounds.
(3) Preparation of 1x protein solution mixture
a. The required amount of 2x B-ROR gamma LBD/SA-APC protein mixture was formulated. The concentration of B-ROR γ LBD was 40nM and the concentration of SA-APC was 20nM, mixed by gentle inversion and incubated for 15 min at room temperature. Then adding 400nM biotin, mixing by gentle inversion, and incubating for 10 min at room temperature;
b. the required amount of 2X Biotin-SRC1/SA-eu protein mixture was formulated. Bioin-SRC1 was 40nM and SA-eu was 20nM, mixed by gentle inversion and incubated for 15 min at room temperature. Then adding 200nM biotin, mixing by gentle inversion, and incubating for 10 min at room temperature;
c.1:1(v: v) mixing the protein mixture prepared in the step a and the step b uniformly, and incubating for 5 minutes at room temperature;
d. adding 25 μ L of the mixture of step c to a 384 well plate containing the test compound;
e.1000rpm for one minute;
f. incubate at room temperature for 1 hour.
(4) Data collection and computation
After 1 hour of incubation at room temperature, the fluorescence values at 665nm and 615nm were measured with an EnVision plate reader, respectively, and the inhibition was calculated to obtain the IC 50The values are shown in Table 1;
the inhibition ratio (%) [ (X-Min)/(Max-Min) ]. times.100%
X is the value of "665/615" for the test compound; min is the average of "665/615" for DMSO blank; max is the average of "665/615" for 10 μ M SRC.
2. Results of the experiment
Table 1: evaluation of the Compound of the present invention on ROR γ Binding Activity
And (4) conclusion: the compound of the invention has good inhibitory activity on ROR gamma.
Pharmacokinetic evaluation
1. Test method
ICR mice were fasted overnight for 15 hours and then weighed, and randomly grouped according to body weight, and the test compound was formulated with 5% DMSO + 5% Solutol + 90% Saline as the vehicle. For the test group administered intravenously, the test animals were given a dose of 1 mg/kg; for the orally administered test group, the test animals were given a dose of 5 mg/kg. Venous blood (approximately 0.2mL) was then removed at time points of 0, 0.083 (intravenous only group), 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 7.0 and 24 hours and placed in the EDTAK2In an anticoagulation tube, centrifuge at 11000rpm for 2 minutes, collect plasma, and store at-20 ℃ or-70 ℃ until LC/MS/MS analysis. The drug concentration in plasma was measured at each time point and pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated from the drug concentration-time curve.
The pharmacokinetic properties of the compounds of the invention were tested by the above assay.
2. Test results
Table 2: pharmacokinetic parameters in mice
| Example numbering | AUCpo(h*μM) | Fpo(%) |
| 78 | 13.8 | 94% |
| 105 | 60.5 | 74% |
And (4) conclusion: the compound of the invention has good pharmacokinetic characteristics in ICR mice after oral administration.
Finally, it should be noted that there are other ways of implementing the invention. Accordingly, the embodiments of the present invention will be described by way of illustration, but not limitation to the description of the present invention, and modifications made within the scope of the present invention or equivalents added to the claims are possible. All publications or patents cited herein are incorporated by reference.
Claims (26)
1. A compound which is a compound represented by formula (I) or a stereoisomer, a geometric isomer, a tautomer, a nitrogen oxide, a hydrate, a solvate, a metabolite, an ester, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of a compound represented by formula (I), or a prodrug thereof,
wherein:
r is C1-4Alkyl radical, C1-4Alkoxy radical, C1-4Alkylamino radical, C1-4Haloalkyl or C1-4A haloalkoxy group;
Z1、Z2、Z3、Z4、Z5、Z6、Z7and Z8Each independently is CR1Or N;
each R1Independently of one another is hydrogen, deuterium, C1-6Alkyl, cyano, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Hydroxyalkyl, -C1-6alkylene-C 1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl or 3-8 membered heterocyclyl;
ring A is a 3-12 membered heterocyclic ring, said 3-12 membered heterocyclic ring optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5R2Substitution;
each R2Independently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydroxyl, oxo, amino, nitro, cyano, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, -C0-6alkylene-ORa、-C0-4Alkylene- (C ═ O)m-Rb、-C0-4Alkylene- (O)n-(C=O)p-NRcRd5-10 membered heteroaryl, -C0-4Alkylene- (3-12 membered heterocyclyl), -C0-4Alkylene- (5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl) or-C0-4Alkylene- (4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl); the R is2Optionally substituted by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RfSubstitution;
each RaIndependently of one another is hydrogen, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 5-10 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl or 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl; each Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 4-12 membered fused ring group, 5-12 membered spiro ring group, 5-10 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiro heterocyclyl or 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl; or Rc、RdAnd the N atom to which they are attached together form a 4-8 membered heterocyclic ring; each of said Ra、Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RgSubstitution;
Each RfAnd RgIndependently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, oxo, hydroxyl, amino, nitro, cyano、C1-6Alkyl radical, C1-6Hydroxyalkyl radical, C1-6Haloalkyl, C6-10Aryl radical, C3-8Cycloalkyl, 4-12 membered fused ring group, 5-12 membered spiro ring group, 3-12 membered heterocyclic group, 5-12 membered spiro heterocyclic group, 4-12 membered fused heterocyclic group, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylamino or C1-6A haloalkoxy group;
ring B is C6-10Aryl, 5-12 membered heteroaryl, 3-12 membered heterocyclyl, 4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl, 5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl, 4-12 membered fused cyclic, 5-12 membered spirocyclic or C3-8Cycloalkyl, wherein said B ring is optionally substituted with 1, 2, 3 or 4ReSubstitution;
each ReIndependently hydrogen, deuterium, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, cyano, nitro, hydroxyl, amino, C1-4Alkyl radical, C1-4Alkoxy radical, C3-6Cycloalkyl radical, C1-4Haloalkyl or C1-4A haloalkoxy group; or, any two adjacent ReAnd together with the atom to which they are attached form C3-8A carbocyclic ring or a 3-8 membered heterocyclic ring; or, optionally, two R's attached to the same carbon atomeAnd together with the atom to which they are attached form C3-8A carbocyclic ring or a 3-8 membered heterocyclic ring;
L1is-S (O)2-NH-、-NH-S(O)2-, -s (O) -NH-, -NH-s (O) -, -C (═ O) NH-, or-NHC (═ O) -;
L2is a bond or-CR3R4-;
Each R3And R4Independently is hydrogen or C 1-6A hydroxyalkyl group;
m is independently 0, 1 or 2;
n is independently 0 or 1;
p is independently 0, 1 or 2.
2. The compound of claim 1, wherein R is methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, or isopropoxy.
3. A compound according to claim 1 or 2, wherein each R is1Independently hydrogen, cyano, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, methoxymethylene, ethoxymethylene, n-propoxymethylene, isopropoxymethylene, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl.
4. A compound according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein each R is3And R4Independently hydrogen, hydroxymethyl, hydroxyethyl or hydroxy-n-propyl.
5. The compound of any one of claims 1-4, wherein ring B is phenyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, azetidinyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, pyrrolidinyl, azetidinyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, thiazolyl, or the like, Said B ring being optionally substituted with 1,2, 3 or 4ReAnd (4) substitution.
6. The compound of any one of claims 1-5, wherein each ReIndependently hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, cyano, nitro, hydroxy, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, monofluoromethoxy, difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy, or 1, 2-difluoroethoxy;
or, any two adjacent ReAnd together with the atom to which they are attached form C3-6Carbocyclic ring or 3-6 membered heteroA ring;
or, optionally, two R's attached to the same carbon atomeAnd together with the atom to which they are attached form C3-6Carbocyclic or 3-6 membered heterocyclic.
11. The compound according to any one of claims 1-10, wherein each R is2Independently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydroxyl, oxo, amino, nitro, cyano, C1-4Alkyl radical, C1-4Haloalkyl, C1-4Alkoxy radical, C3-6Cycloalkyl, -C0-4alkylene-ORa、-C0-4Alkylene- (C ═ O)m-Rb、-C0-4Alkylene- (O)n-(C=O)p-NRcRd5-6 membered heteroaryl, -C0-4Alkylene- (3-to 8-membered heterocyclic group), -C0-4Alkylene- (5-12 membered spiroheterocyclyl) or-C0-4Alkylene- (4-12 membered fused heterocyclyl);
wherein, R is2Optionally substituted by 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RfAnd (4) substitution.
12. The compound according to any one of claims 1-11, wherein each R is2Independently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydroxyl, oxo, amino, nitro, cyano, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclohexyl, -C 0-4alkylene-ORa、-C0-4Alkylene- (C ═ O)m-Rb、-C0-4Alkylene- (O)n-(C=O)p-NRcRdOxazolyl, thiazolyl, thienyl, imidazolyl, pyridazinyl, pyridyl,
Wherein, R is2Optionally substituted by 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RfAnd (4) substitution.
13. The compound of any one of claims 1-12, wherein each R isaIndependently hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1,1, 1-trifluoroethyl, oxirane, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, oxepanyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl; each Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, monofluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, 1,1, 1-trifluoroethyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, oxiranyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, oxepanyl, Cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl; or R c、RdAnd with themThe linked N atoms together form a 4-8 membered heterocyclic ring;
wherein each R isa、Rb、RcAnd RdIndependently optionally substituted with 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or 6RgAnd (4) substitution.
14. The compound of any one of claims 1-13, wherein each RfAnd RgIndependently hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, oxo, hydroxyl, amino, nitro, cyano, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, -CH2OH, fluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, monofluoroethyl, 1-difluoroethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, phenyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, oxiranyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, oxa-ethyl, 1, 2-difluoroethyl, phenyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, oxiranyl, oxa-cyclobutyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, trifluoromethyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclohexyl, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, isopropoxy, monofluoromethoxy, difluoromethoxy or trifluoromethoxy.
16. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of any one of claims 1-15, and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, carrier, adjuvant, or combination thereof.
17. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16, wherein the pharmaceutical composition further comprises other drugs or any combination thereof for preventing or treating inflammatory syndrome or autoimmune disease.
18. Use of a compound of any one of claims 1-15 or a pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 16-17 in the manufacture of a medicament for preventing or treating a disease, disorder or syndrome mediated by roryt in a mammal.
19. The use according to claim 18, wherein the roryt mediated disease, disorder or syndrome is an inflammatory or autoimmune disease.
20. The use of claim 18, wherein the roryt mediated disease, disorder or syndrome is psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ocular disease, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, crohn's disease or kawasaki disease.
21. A compound according to any one of claims 1 to 15 or a pharmaceutical composition according to any one of claims 16 to 17 for use in the manufacture of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of a disease, disorder or syndrome mediated by roryt in a mammal.
22. The compound or pharmaceutical composition of claim 21, wherein said roryt mediated disease, disorder or syndrome is an inflammatory or autoimmune disease.
23. The compound or pharmaceutical composition of claim 21, wherein the roryt-mediated disease, disorder or syndrome is psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ocular disease, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, crohn's disease or kawasaki disease.
24. A method of preventing or treating a roryt mediated disease, disorder or syndrome in a mammal, comprising administering to the mammal an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 1-15 or a pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 16-17.
25. The method of claim 24, wherein the roryt mediated disease, disorder or syndrome is an inflammatory or autoimmune disease.
26. The method of claim 24, wherein the roryt mediated disease, disorder or syndrome is psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune ocular disease, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoarthritis, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, crohn's disease or kawasaki disease.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810749760 | 2018-07-10 | ||
| CN2018107497600 | 2018-07-10 | ||
| PCT/CN2019/095203 WO2020011147A1 (en) | 2018-07-10 | 2019-07-09 | RORγ ANTAGONIST AND APPLICATION THEREOF IN MEDICINE |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112513021A true CN112513021A (en) | 2021-03-16 |
| CN112513021B CN112513021B (en) | 2023-06-27 |
Family
ID=69143152
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201980045075.2A Active CN112513021B (en) | 2018-07-10 | 2019-07-09 | ROR gamma antagonist and application thereof in medicines |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112513021B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2020011147A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115521233A (en) * | 2021-06-08 | 2022-12-27 | 复旦大学 | ROR gamma agonist and application thereof in preparation of drugs for treating tumor diseases and promotion of Type17 cell differentiation |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW202136238A (en) * | 2020-01-06 | 2021-10-01 | 大陸商廣東東陽光藥業有限公司 | ROR[gamma]T inhibitor, preparation method therefor and use thereof |
| TW202136237A (en) * | 2020-01-06 | 2021-10-01 | 大陸商廣東東陽光藥業有限公司 | ROR[gamma]T inhibitor, preparation method therefor and use thereof |
| CN111658651B (en) * | 2020-06-08 | 2021-08-03 | 重庆医科大学附属第一医院 | Application of CQMU151 in preparing medicament for treating Th17 cell-mediated autoimmune disease |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106061947A (en) * | 2014-01-06 | 2016-10-26 | 百时美施贵宝公司 | Cyclohexyl sulfone ror [gamma] modulators |
| WO2017024018A1 (en) * | 2015-08-05 | 2017-02-09 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Modulators of ror-gamma |
| CN107531679A (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2018-01-02 | 江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司 | Aromatic amides analog derivative, its preparation method and its application in medicine |
| WO2018116285A1 (en) * | 2016-12-23 | 2018-06-28 | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals S.A. | Substituted morpholine derivatives as ror gamma modulators |
-
2019
- 2019-07-09 WO PCT/CN2019/095203 patent/WO2020011147A1/en active Application Filing
- 2019-07-09 CN CN201980045075.2A patent/CN112513021B/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106061947A (en) * | 2014-01-06 | 2016-10-26 | 百时美施贵宝公司 | Cyclohexyl sulfone ror [gamma] modulators |
| WO2017024018A1 (en) * | 2015-08-05 | 2017-02-09 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Modulators of ror-gamma |
| CN107531679A (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2018-01-02 | 江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司 | Aromatic amides analog derivative, its preparation method and its application in medicine |
| WO2018116285A1 (en) * | 2016-12-23 | 2018-06-28 | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals S.A. | Substituted morpholine derivatives as ror gamma modulators |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115521233A (en) * | 2021-06-08 | 2022-12-27 | 复旦大学 | ROR gamma agonist and application thereof in preparation of drugs for treating tumor diseases and promotion of Type17 cell differentiation |
| CN115521233B (en) * | 2021-06-08 | 2024-02-09 | 复旦大学 | ROR gamma agonist and application thereof in preparing medicament for treating tumor diseases and promoting Type17 cell differentiation |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN112513021B (en) | 2023-06-27 |
| WO2020011147A1 (en) | 2020-01-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI811353B (en) | Pyridazinones as parp7 inhibitors | |
| CN104619709B (en) | Imidazopyridine derivatives as TNF active regulator | |
| CN108473498B (en) | Pyrazolo [1,5a ] pyrimidine derivatives as IRAK4 modulators | |
| CN104693193B (en) | Aryl methoxy isoindoline derivative and composition and their application method including it | |
| TWI657076B (en) | Substituted sulfonamide compounds | |
| CN112105385A (en) | IRAK degrading agents and uses thereof | |
| CN107253963B (en) | Pyridone and azapyridone compounds and methods of use | |
| CN109970743B (en) | 5-chloro-2-difluoromethoxyphenyl pyrazolopyrimidine compounds as JAK inhibitors | |
| CN114615981A (en) | KRAS G12D inhibitors | |
| CN114502158A (en) | IRAK degradation agent and application thereof | |
| KR20210111252A (en) | IRAK disintegrants and uses thereof | |
| CN111601799A (en) | Fused imidazole derivatives as Il-17 modulators | |
| CN112513021A (en) | ROR gamma antagonist and application thereof in medicine | |
| CN107011348A (en) | It is used as the heteroaryl pyridines ketone and azepine pyridinone compounds of the inhibitor of BTK activity | |
| TW201602109A (en) | Imidazopyridazines useful as inhibitors of the PAR-2 signaling pathway | |
| CN113072542B (en) | ROR gamma t inhibitor and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN108026105A (en) | Tgf beta receptor antagonists | |
| CN103709151B (en) | Spiro-compound as hepatitis c inhibitor and its application in medicine | |
| CN106187838B (en) | Aryl alkynes compound and its preparation method and application | |
| WO2020169058A1 (en) | Pd-l1 antagonist compound | |
| TWI689497B (en) | Heteroaromatic derivatives and parmaceutical applications thereof | |
| CN113563244A (en) | Substituted aza five-membered ring compound and application thereof in medicine | |
| CN113072476B (en) | ROR gamma t inhibitor and preparation method and application thereof | |
| TW201932470A (en) | Pyrazolopyrimidines having activity against RSV | |
| CN114075139A (en) | Five-membered heteroaromatic ring compound and application thereof in medicines |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CP01 | Change in the name or title of a patent holder |
Address after: 523808 No.1, Gongye North Road, Songshanhu Park, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province Patentee after: Guangdong Dongyangguang Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd. Address before: 523808 No.1, Gongye North Road, Songshanhu Park, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province Patentee before: SUNSHINE LAKE PHARMA Co.,Ltd. |
|
| CP01 | Change in the name or title of a patent holder |