CN112494104A - Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof - Google Patents
Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112494104A CN112494104A CN202011480880.9A CN202011480880A CN112494104A CN 112494104 A CN112494104 A CN 112494104A CN 202011480880 A CN202011480880 A CN 202011480880A CN 112494104 A CN112494104 A CN 112494104A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- basket
- catheter
- self
- thrombus
- expandable
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 208000007536 Thrombosis Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 76
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 230000003446 memory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000002861 polymer material Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000003698 laser cutting Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000002792 vascular Effects 0.000 abstract description 7
- 238000007790 scraping Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 210000004204 blood vessel Anatomy 0.000 description 27
- 230000017531 blood circulation Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000013156 embolectomy Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000010339 dilation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001575 pathological effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000009941 weaving Methods 0.000 description 3
- 201000001429 Intracranial Thrombosis Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 2
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N cholesterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000004 hemodynamic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013151 thrombectomy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 201000001320 Atherosclerosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241001391944 Commicarpus scandens Species 0.000 description 1
- 206010019280 Heart failures Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010021143 Hypoxia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000031481 Pathologic Constriction Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000010378 Pulmonary Embolism Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000036770 blood supply Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000012000 cholesterol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000035602 clotting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001747 exhibiting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000295 expanded polytetrafluoroethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000013467 fragmentation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006062 fragmentation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007954 hypoxia Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000014674 injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000053 physical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920006254 polymer film Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001343 polytetrafluoroethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004810 polytetrafluoroethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002685 pulmonary effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000452 restraining effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000036262 stenosis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000037804 stenosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000002537 thrombolytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008736 traumatic injury Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000019553 vascular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000005166 vasculature Anatomy 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/22—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/22—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for
- A61B17/221—Gripping devices in the form of loops or baskets for gripping calculi or similar types of obstructions
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/22—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for
- A61B2017/22079—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for with suction of debris
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/22—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for
- A61B2017/22094—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for for crossing total occlusions, i.e. piercing
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/22—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for
- A61B17/221—Gripping devices in the form of loops or baskets for gripping calculi or similar types of obstructions
- A61B2017/2212—Gripping devices in the form of loops or baskets for gripping calculi or similar types of obstructions having a closed distal end, e.g. a loop
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Surgical Instruments (AREA)
- Media Introduction/Drainage Providing Device (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a catheter device for intravascular thrombus aspiration and a basket assembly thereof, belonging to the field of vascular interventional medical treatment. The device comprises a three-way connecting seat, a conduit, a connecting seat, a conveying sheath tube, an expandable guide head end and a self-expansion basket component; the self-expansion basket component comprises a basket conveying pipe, a hammer-shaped guide cap, a basket supporting pipe and a self-expansion basket, wherein the basket conveying pipe is inserted into the guide pipe, the far end of the basket conveying pipe is provided with a hollow hammer-shaped guide cap, the basket supporting pipe is inserted into the basket conveying pipe, and the far end of the basket supporting pipe is fixed with the self-expansion basket. A hammer-shaped guide cap serving as a thrombus crushing separator is arranged at the suction opening at the distal end of the catheter and is used for crushing and separating thrombus blocked at the suction opening of the suction catheter; a self-expanding basket is disposed at the distal end of the diseased thrombus for scraping and collecting thrombus tissue adhering to the vessel wall while the collected thrombus tissue is pushed toward the suction opening at the proximal end of the suction catheter.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to a catheter device for intravascular thrombus aspiration and a basket assembly thereof, belonging to the technical field of vascular interventional medical treatment.
Background
Abnormal blood flow in blood vessels is caused by abnormal blood vessel passages, and the hemodynamic abnormality can cause a series of adverse effects such as tissue hypoxia, abnormal intravascular pressure, heavy heart load and even heart failure, so that the blood flow in the abnormal blood vessel passages in the blood vessels generally needs to be recovered or rebuilt through a catheter intervention technology. Stenosis or blockage of a blood vessel can cause a number of adverse consequences: turbulent blood flow, a slow flow rate, can lead to blood clot formation, resulting in a restricted blood supply to the downstream regions of the vascular system. Stroke may be initiated when a blood clot is located in the neurovascular system; when a blood clot is located in the pulmonary vasculature, pulmonary embolism can occur, leading to death of the patient. Atherosclerosis and its plaque and other obstructions can also become dangerous as they restrict blood flow, causing abnormal blood flow, causing various vascular diseases. Accordingly, there is a need for an obstruction removal device and system to reduce the likelihood of an obstruction and its fragmented obstructions from remaining in the vascular system while maximizing the probability of capturing the obstruction to reduce the risk of blood flow abnormalities in the blood vessel.
With the development of technology, in recent years, a mechanical thrombus removal (PMT) device has appeared, which is a group of devices for removing blockages in blood vessels, and removes blockages such as thrombus and plaque in blood vessels by dissolving, crushing, aspiration, stent or basket thrombolysis, so as to restore blood circulation function.
A variety of devices and procedures have been used to remove obstructions from blood vessels. For example, a catheter with a balloon on the proximal end may be inserted into a blood vessel and passed through the clot, after which the balloon is inflated, and then the balloon may be withdrawn from the blood vessel to clear the clot. Another example of an endovascular occlusion clearing device is a stent having a helical segment or tubular mesh at its proximal end that can be delivered to a site of a clot within a blood vessel, and then self-expand to embed within the clot to remove the clot. For example, a segmented intracranial thrombus removal stent structure disclosed in patent CN106580397A, a stent structure with a basket at the tail end of the thrombus removal stent for capturing disclosed in patent CN107198554B, a cerebral thrombus removal device disclosed in patent CN209203427U and the like all adopt a physical method of stent embedding and capturing blood clots in blood vessels to remove the blood clots. Also encompassed are embolectomy techniques that employ a combination of stent and aspiration techniques, including the aspiration detachment embolectomy technique described in US patent 08366735B2, as well as the aspiration catheter embolectomy technique with a self-expanding tip described in US patent 5011488, the obstruction removal system described in patent cn201780084363.x, and the like.
Still further interventional obstruction removal techniques include embedding a thrombectomy stent within the thrombus and then completing the thrombus capture and aspiration removal by pulling the thrombus within the aspiration catheter. The method for capturing thrombus by the stent and removing thrombus by suction (namely negative pressure) of the suction catheter is generally safe and effective, but when the self-expanding thrombus-taking stent embedded in the thrombus passes through a suction opening of the suction catheter, the diameter of the stent is gradually narrowed from a self-expanding large-diameter state through the suction opening of the catheter, the thrombus is easily cut and broken by the edge of the opening at the head end of the suction catheter, and the thrombus easily escapes to the far end to block other blood vessel branches. In addition, the diameter of the suction catheter is smaller than that of a blood vessel, after the suction catheter passes through a tortuous vascular system to reach a designated position, the suction opening at the distal end of the suction catheter is usually attached to the wall of the blood vessel, and the position of the suction catheter in the blood vessel is not fixed, so that the suction catheter is not beneficial to the entering of obstructions such as thrombus and the like into the suction opening of the catheter. Moreover, when blood flows towards the distal end of the thrombus, the captured thrombus and other obstructions are easy to break and fall off in the process of transferring the thrombus removal stent, flow to the distal end along the blood flow direction, and accumulate at other parts to block other branch blood vessels. There is therefore a need for a balloon-like catheter that inflates, temporarily blocks or slows down blood flow to reduce the hemodynamic impact on the obstruction and reduce the risk of the obstruction breaking and escaping distally.
One risk with conventional occlusion removal devices is that the clot or plaque may rupture and escape during removal, which may traverse the vascular system and cause traumatic injury elsewhere. Thus, there is also a need to deploy the removal of the obstruction distally beyond the non-involved obstruction, reducing the risk that a portion of the clot or plaque may escape during removal, creating further risk to the patient.
With respect to the known medical devices and methods, each has certain advantages and disadvantages. There is a continuing need to provide alternative medical devices and alternative methods for making and using medical devices. This technique has proposed a novel suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof, and this suction catheter distal end head suction opening part sets up a self-expanding expandable direction head end, and this self-expanding expandable direction head end can block temporarily or reduce the impact of blood flow power, and its toper expansion head end guide bold thrombus gets into suction catheter tube intracavity simultaneously. Meanwhile, a thrombus crushing separator is arranged at the suction opening at the distal end of the catheter and used for crushing and separating thrombus blocked at the suction opening of the suction catheter and further discharging the cracked thrombus out of the body under the action of negative pressure suction. Furthermore, a self-expandable basket assembly formed by weaving metal wires or cutting metal tubes by laser is arranged at the distal end of the pathological thrombus and used for scraping and collecting thrombus tissue attached to the vessel wall, and the collected thrombus tissue is pushed to the vicinity of the distal head end of the suction catheter. Meanwhile, a basket component is arranged at the far end of the pathological thrombus, so that the risk of the thrombus escaping to the far end can be effectively reduced.
Embodiments of the intravascular thrombus-breaking separation device, self-expandable basket assembly, and negative pressure aspiration catheter system presented herein reduce the instances or risks of occlusion during use of the aspiration lumen of the system, while the basket assembly attached to the aspiration opening of the aspiration catheter can remove and collect thrombus adhering to the vessel wall and also prevent distal escape of thrombus. Thus, the aspiration catheter embodiments presented herein can significantly improve patient safety and aspiration effectiveness.
Disclosure of Invention
The technical problem to be solved by the invention is as follows: the utility model provides a be used for thrombus suction catheter device in blood vessel and basket subassembly thereof, it has solved present thrombectomy catheter device and has had the thrombus that adheres to the vascular wall to be difficult for getting rid of, and the suction opening is easy to be blockked up to and the thrombus easily takes place the problem of escaping.
The technical problem to be solved by the invention is realized by adopting the following technical scheme:
a catheter device for intravascular thrombus aspiration and a basket assembly thereof comprise a three-way connecting seat, a catheter, a connecting seat and a conveying sheath tube, wherein the far end of the three-way connecting seat is connected with the catheter in a sealing manner, the far end of the connecting seat is connected with the conveying sheath tube, a sealing valve for dynamic sealing is arranged at the near end of the connecting seat, the catheter penetrates through the sealing valve from the far end and is inserted into the connecting seat and the conveying sheath tube, and the catheter device also comprises an expandable guide head end and a self-expanding basket assembly;
the expandable guide head end is an umbrella-shaped mesh enclosure made of a material with a shape memory effect, and comprises a thin neck part fixed at a suction port at the far end of the catheter, a conical expansion part positioned in the middle and an opening part positioned at the far end;
the guide tube is sleeved with an auxiliary expansion tube, the auxiliary expansion tube moves and is sleeved at the expandable guide head end in an initial state, and after the expandable guide head end is inserted into the connecting seat, the auxiliary expansion tube is blocked outside the near end of the connecting seat;
the self-expansion basket component comprises a basket conveying pipe, a hammer-shaped guide cap, a basket supporting pipe and a self-expansion basket, wherein the basket conveying pipe is inserted into the guide pipe, the far end of the basket conveying pipe is provided with a hollow hammer-shaped guide cap, the basket supporting pipe is inserted into the basket conveying pipe, and the far end of the basket supporting pipe is fixed with the self-expansion basket.
As a preferred example, the expandable guide tip is constructed using a full or partial membrane covering.
As a preferred example, the expandable guiding tip is an umbrella-shaped mesh made of a metal tube with shape memory effect by laser cutting and thermal expansion.
As a preferred example, the expandable guide tip is an umbrella-shaped mesh cover woven from a wire having a shape memory effect.
Preferably, the expandable guide head end is an umbrella-shaped mesh cover woven or injection-molded from a high-elasticity polymer material.
As a preferred example, the self-expandable basket may be any one of a single-layered umbrella-shaped basket, a double-layered woven disk-shaped basket, and a double-layered double-tapered basket.
As a preferable example, the surface of the pseudo-hammer-shaped guide cap (1102) is provided with a plurality of spiral grooves which are uniformly distributed along the circumference.
The invention has the beneficial effects that:
(1) a self-expanding expandable guide head is arranged at the suction opening at the proximal end of the catheter, the expandable guide head can temporarily block or reduce the impact of blood flow force, and the conical expandable head can guide massive thrombus into the catheter cavity;
(2) meanwhile, a hammer-shaped guide cap serving as a thrombus crushing separator is arranged at the suction opening at the distal end of the catheter and is used for crushing and separating thrombus blocked at the suction opening of the suction catheter and further discharging the cracked thrombus out of the body under the action of negative pressure suction;
(3) furthermore, a self-expanding basket is arranged at the far end of the lesion thrombus and is used for scraping and collecting thrombus tissue attached to the vessel wall, and the collected thrombus tissue is pushed to the vicinity of the suction opening at the near end of the suction catheter;
(4) the self-expanding basket is arranged at the far end of the pathological thrombus, so that the risk of the thrombus escaping to the far end can be effectively reduced.
Drawings
FIG. 1 is a schematic structural view of the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a schematic perspective view of the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a schematic structural view of an expandable pilot tip;
FIG. 4 is a schematic view of the structure of the direction of the end of the expandable guide head;
FIG. 5 is a side view of an expandable leading end of the covering;
FIG. 6 is a perspective view of an expandable leading end of the covering;
FIG. 7 is a schematic view of the connection structure of the basket delivery pipe and the hammer-shaped guide cap;
FIG. 8 is a sectional view showing a coupling structure of a basket delivery pipe and a hammer-shaped guide cap;
FIG. 9 is a schematic view showing a connection structure of a basket delivery pipe and a hammer-like guide cap with a spiral groove;
FIG. 10 is a perspective view of a self-expanding basket;
FIG. 11 is a schematic side view of a self-expanding basket;
FIG. 12 is a perspective view of a self-expanding basket in the form of a double layer woven disk basket;
FIG. 13 is a side view of a self-expanding basket employing a double layer woven disk basket structure;
FIG. 14 is a schematic structural view of a double conical basket with a larger cavity for the self-expandable basket;
FIG. 15 is a schematic structural view of a double-cone basket with a flat cavity for self-expanding basket;
FIG. 16 is a schematic view of an auxiliary dilation tube restraining an expandable guide tip leading into a delivery sheath in an initial state;
FIG. 17 is a schematic structural view of the self-expanding basket assembly in an initial state;
FIG. 18 is a schematic view of the present invention being advanced into a blood vessel by a guidewire puncture;
FIG. 19 is a schematic view of the catheter of the present invention delivering an expandable guide tip along a delivery sheath to the proximal end of an obstruction;
FIG. 20 is a schematic representation of the expandable leading end of the present invention after release;
FIG. 21 is a schematic view of the self-expanding basket assembly being delivered through a catheter to the distal end of an obstruction;
FIG. 22 is a schematic view of the self-expanding basket of the present invention after release;
FIG. 23 is a schematic view of the thrombus removal state according to the present invention.
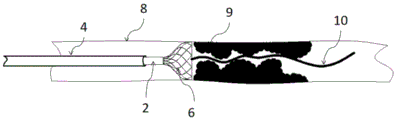
In the figure: 1. a three-way connecting seat; 2. a conduit; 3. a connecting seat; 4. a delivery sheath; 5. a sealing valve; 6. an expandable leading end; 601. a thin neck portion; 602. a tapered expanding portion; 603. an opening part; 7. an auxiliary dilation tube; 8. a blood vessel; 9. thrombosis; 10. a guide wire; 11. a self-expanding basket assembly; 1101. a basket delivery pipe; 1102. a hammer-shaped guide cap; 1103. a basket supporting tube; 1104. a self-expanding basket; 1105. a spiral groove.
Detailed Description
In order to make the technical means, the original characteristics, the achieved purpose and the efficacy of the invention easy to understand, the invention is further described with reference to the specific drawings.
The term occlusion herein may include a blood clot, plaque, cholesterol, thrombus 9, naturally occurring foreign matter (i.e., a portion of self tissue left within a lumen), non-naturally occurring foreign matter (i.e., a portion of a medical device or other non-naturally occurring foreign matter left within a lumen). However, the present apparatus is not limited to such applications and may be applied to any number of medical applications including the removal or reduction of the number of obstructions within the blood vessel 8, such as thrombus 9, plaque, etc., that are desired to obstruct blood flow or impair the blood medical mechanism within the blood vessel 8.
For ease of description, the following description uses the terms "proximal" and "distal", where "proximal" refers to the end proximal to the operative end and "distal" refers to the end distal to the operative end.
Examples
The following is further illustrated with reference to specific figures:
as shown in fig. 1 and 2, the device mainly comprises a three-way connecting base 1, a catheter 2 connected with one end of the three-way connecting base 1, an auxiliary expanding tube 7, a connecting base 3, a delivery sheath 4 and an expandable guiding head 6 located at the proximal end of the catheter 2. The three-way connecting seat 1 and the connecting seat 3 are both provided with inner cavities, and one side ends of the three-way connecting seat are both provided with sealing valves 5 to keep the inlet of the apparatus sealed.
The catheter 2 can enter the tube of the delivery sheath 4 through a sealing valve 5 at one end of the connecting base 3 and reach the distal end of the delivery sheath 4. The luer of the three-way connection base 1 can be connected to an external negative or positive pressure generating device to provide positive or negative pressure to the lumen of its catheter 2.
The self-expansion basket component 11 comprises a basket conveying pipe 1101, a hammer-shaped guide cap 1102, a basket supporting pipe 1103 and a self-expansion basket 1104, wherein the basket conveying pipe 1101 is inserted into the conduit 2, the distal end of the basket conveying pipe 1101 is provided with the hollow hammer-shaped guide cap 1102, the basket supporting pipe 1103 is inserted into the basket conveying pipe 1101, and the distal end of the basket supporting pipe 1103 is fixed with the self-expansion basket 1104.
As shown in fig. 3-15, the expandable guiding tip 6 at the proximal end of the catheter 2 is an expandable mesh skeleton, which may be covered with a film, and the expandable guiding tip 6 is formed by laser cutting and thermal expansion of a metal tube with shape memory effect, or by weaving a metal wire with shape memory effect, or by weaving or injection molding a high-elasticity polymer material. The film is made of polymer materials such as PTFE, ePTFE, PU, TPU and TPE and is covered on the expandable guide head end 6 through the film covering process on the surface of the stent. Fig. 3 and 4 show no coating, and fig. 5 and 6 show coating.
As shown in fig. 7 and 8, a basket delivery pipe 1101 and a pseudo-hammer-shaped guide cap 1102 located at the proximal end of the basket delivery pipe 1101 are disposed at the proximal end of the basket delivery pipe 1101 shown in fig. 8 by injection molding, heat melting, bonding, and the like; the material of the guiding cap 1102 may be polymer material or metal material, and its configuration is shown as hollow guiding pseudo-hammer shape.
As shown in FIG. 9, the surface of the pseudo-hammer-shaped guiding cap 1102 may have a plurality of spiral grooves 1105 uniformly distributed on the circumference, which is beneficial to the fragmentation of thrombus.
As shown in fig. 10 and 11, the basket support tube 1103 and the self-expanding basket 1104 are shown, the self-expanding basket 1104 is similar to the expandable guide head end 6 described above, and the closed end (similar to the thin neck 601) of the self-expanding basket 1104 is connected to the basket support tube 1103 near the distal head end thereof by injection molding, heat melting, bonding, and the like.
As shown in fig. 11 and 13, the self-expandable basket 10 may also be a double-woven disk-shaped basket structure as shown, in which the central partial area of the double-woven disk-shaped basket is recessed to a certain depth.
As shown in fig. 14 and 15, the self-expanding basket 1104 may be a disk-like symmetrical double-tapered basket structure as shown, with the disk-like head end exhibiting a circular arc or cylindrical shape.
The self-expandable basket 1104 may be any one of a single-layer umbrella basket (fig. 10 and 11), a double-layer woven disk basket (fig. 11 and 13), and a double-layer double-cone basket (fig. 14 and 15).
As shown in fig. 16, the expandable guide head end 6 is initially pressed into the lumen of the auxiliary expansion tube 7, and one end of the auxiliary expansion tube 7 passes through the sealing sheet on the sealing valve 5 (connecting seat 3), so that the lumen of the auxiliary expansion tube 7 can communicate with the lumen of the delivery sheath 4; the expandable guide tip 6 can be pushed through the sealing valve 5 by the auxiliary dilation tube 7 under the push of the catheter 2, and thus can enter the lumen of the delivery sheath 4 to the distal end of the delivery sheath 4.
As shown in FIG. 17, the initial state of the self-expanding basket 1104 is crimped within the lumen of the basket delivery tube 1101 and is located near the proximal end of the basket delivery tube 1101.
As shown in fig. 18-23, during the procedure, the blood vessel 8 is punctured and a guidewire 10 (otherwise available) is introduced to completely traverse the lesion (thrombus 9) site. The proximal end of the delivery sheath tube 4 is delivered to the position close to the thrombus 9 under the guidance of the guide wire 10, the delivery sheath tube 4 is kept fixed, at the moment, the expandable guide head end 6 is pressed and held in the lumen of the auxiliary expansion tube 7 in the initial state, one end of the auxiliary expansion tube 7 passes through a sealing sheet on the sealing valve 5 (connecting seat 3), and the auxiliary expansion tube 7 is pushed to be in lap joint communication with the lumen of the delivery sheath tube 4; catheter 2 is then advanced to deliver the distal expandable guide tip 6 of catheter 2 through the lumen of delivery sheath 4 near its proximal end (fig. 18).
As shown in fig. 19, the holding catheter 2 and its proximal end are held stationary and the delivery sheath 4 is withdrawn a distance such that the expandable guide tip 6 self-expands into the deployed state.
As shown in fig. 20, the basket delivery tube 1101 with the hammer-like guiding cap 1102 at the proximal end and the basket support tube 1103 and its self-expanding basket 1104 serve as a self-expanding basket assembly 11 for embolectomy, and the basket support tube 1103 is lumen-wise threaded over the guidewire 10 into the catheter 2, so that the entire self-expanding basket assembly 11 passes through the lumen of the catheter 2 into the blood vessel 8 and through the obstruction to the other end of the obstruction.
As shown in fig. 21, the basket support tube 1103 is then held stationary and the basket delivery tube 1101 is retracted rearwardly adjacent the opening of the expandable guide head end 6.
As shown in fig. 22, the basket support tube 1103 is slowly moved with the self-expanding basket 1104 toward the proximal end of the obstruction, thereby moving and displacing the obstruction into the lumen of the expandable guide tip 6; simultaneously, the external negative pressure suction device is started to provide continuous negative pressure in the suction tube cavity, and the blockage such as thrombus 9 is sucked into the suction opening or the cavity of the catheter 2 under the action of the negative pressure at the suction opening at the near end of the device. When the thrombus 9 and other obstructions block the suction opening of the catheter 2, the basket conveying pipe 1101 reciprocates back and forth near the suction opening of the catheter 2 at the moment, so that the hammer-shaped guide cap 1102 at the proximal end of the basket conveying pipe 1101 is driven to reciprocate back and forth, the thrombus 9 obstructions blocked at the suction opening are crushed into small blocks of obstructions, and the obstructions can more easily enter the lumen of the catheter 2 and are transferred out of the human body. The distal end of the hammer-shaped guide cap 1102 is a highly angled flow-type tip to facilitate passage of the thrombus 9, while its proximal end is less angled to facilitate crushing of the thrombus 9 obstruction within the aspiration opening or lumen of the catheter 2.
Finally, the thrombus 9 entering the lumen of the catheter 2 is conveyed to the outlet end of the three-way connecting seat 1 by negative pressure and is discharged out of the human body. After the thrombus 9 is sucked, all the devices are removed from the human body together.
The foregoing illustrates and describes the principles, general features, and advantages of the present invention. It will be understood by those skilled in the art that the present invention is not limited to the embodiments described above, and that various changes and modifications may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined in the appended claims. The scope of the invention is defined by the appended claims and equivalents thereof.
Claims (7)
1. A catheter device for intravascular thrombus aspiration and a basket assembly thereof comprise a three-way connecting seat (1), a catheter (2), a connecting seat (3) and a conveying sheath tube (4), wherein the distal end of the three-way connecting seat (1) is connected with the catheter (2) in a sealing manner, the distal end of the connecting seat (3) is connected with the conveying sheath tube (4), a sealing valve (5) for dynamic sealing is arranged at the proximal end of the connecting seat (3), and the catheter (2) penetrates through the sealing valve (5) from the distal end and is inserted into the connecting seat (3) and the conveying sheath tube (4), and the catheter device is characterized by further comprising an expandable guide head end (6) and a self-expandable basket assembly (11;
the expandable guide head end (6) is an umbrella-shaped mesh cover made of materials with shape memory effect, and the expandable guide head end (6) comprises a thin neck part (601) fixed at a suction port at the far end of the catheter (2), a conical expansion part (602) positioned in the middle and an opening part (603) positioned at the far end;
the self-expansion basket component (11) is composed of a basket conveying pipe (1101), an approximately hammer-shaped guide cap (1102), a basket supporting pipe (1103) and a self-expansion basket (1104), wherein the basket conveying pipe (1101) is inserted into a guide pipe (2), the far end of the basket conveying pipe (1101) is provided with a hollow approximately hammer-shaped guide cap (1102), the basket supporting pipe (1103) is inserted into the basket conveying pipe (1101), and the far end of the basket supporting pipe (1103) is fixed with the self-expansion basket (1104).
2. The catheter device and basket assembly for intravascular thrombus aspiration according to claim 1 wherein the expandable leading end (6) is in a full or partial membrane configuration.
3. The catheter device and the basket assembly thereof for intravascular thrombus aspiration according to claim 1, wherein the expandable guiding tip (6) is an umbrella-shaped mesh cover made of a metal tube material with shape memory effect by laser cutting and thermal expansion.
4. The catheter device and basket assembly for intravascular thrombus aspiration according to claim 1 wherein the expandable guiding tip (6) is an umbrella shaped mesh cap woven from a metal wire with shape memory effect.
5. The catheter device and the basket assembly thereof for intravascular thrombus aspiration according to claim 1, wherein the expandable guiding tip (6) is an umbrella-shaped mesh cover woven or injection-molded from a high-elasticity polymer material.
6. The catheter device and basket assembly for intravascular thrombus aspiration according to claim 1 wherein the self-expandable basket (1104) is any one of a single-layered umbrella basket, a double-layered braided disk basket and a double-layered double-tapered basket.
7. The catheter device and the basket assembly thereof for intravascular thrombus aspiration according to claim 1 wherein the surface of the pseudo-hammer-shaped guide cap (1102) is provided with a plurality of spiral grooves (1105) uniformly distributed along the circumference.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011480880.9A CN112494104A (en) | 2020-12-15 | 2020-12-15 | Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011480880.9A CN112494104A (en) | 2020-12-15 | 2020-12-15 | Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112494104A true CN112494104A (en) | 2021-03-16 |
Family
ID=74972102
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011480880.9A Pending CN112494104A (en) | 2020-12-15 | 2020-12-15 | Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112494104A (en) |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113180914A (en) * | 2021-04-28 | 2021-07-30 | 河南科技大学第一附属医院 | Cerumen embolism softening and removing device |
| CN113208770A (en) * | 2021-04-12 | 2021-08-06 | 聚辉医疗科技(深圳)有限公司 | Conveying device |
| CN113425373A (en) * | 2021-07-30 | 2021-09-24 | 江苏朴芃医疗科技有限公司 | Blood vessel thrombus taking device |
| CN113855159A (en) * | 2021-09-29 | 2021-12-31 | 北京泰杰伟业科技有限公司 | Combined type regulation and control bolt taking device |
| CN113855164A (en) * | 2021-11-11 | 2021-12-31 | 上海融脉医疗科技有限公司 | Net disc type mechanical thrombus removing catheter device |
| CN114052830A (en) * | 2021-12-21 | 2022-02-18 | 启晨(上海)医疗器械有限公司 | Thrombus removing device |
| CN114081579A (en) * | 2021-11-29 | 2022-02-25 | 上海市第十人民医院 | Mechanical thrombus taking device for cerebral apoplexy and application thereof |
| CN114098904A (en) * | 2021-11-10 | 2022-03-01 | 北京泰杰伟业科技有限公司 | Thrombus collection device |
| CN114983647A (en) * | 2022-06-16 | 2022-09-02 | 晨兴(南通)医疗器械有限公司 | Plastic expander for expanding arterial stent |
| CN115317077A (en) * | 2022-10-13 | 2022-11-11 | 成都百瑞恒通医疗科技有限公司 | Thrombus taking device |
| CN115429387A (en) * | 2022-09-19 | 2022-12-06 | 心凯诺医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Delivery system of thrombectomy support |
| CN115737060A (en) * | 2022-11-14 | 2023-03-07 | 上海中医药大学 | Device for conducting cardiovascular and cerebrovascular vessels |
| CN115919405A (en) * | 2022-11-02 | 2023-04-07 | 上海玮琅医疗科技有限公司 | Blood vessel foreign matter extraction auxiliary device and extraction device |
| CN116138844A (en) * | 2023-04-04 | 2023-05-23 | 杭州亿科医疗科技有限公司 | Thrombus taking device capable of capturing various types of thrombus |
| CN116712135A (en) * | 2023-07-28 | 2023-09-08 | 北京管桥医疗科技有限公司 | Thrombolysis device |
| CN117562622A (en) * | 2023-11-24 | 2024-02-20 | 广东博迈医疗科技股份有限公司 | Thrombus removing and crushing device and thrombus remover |
| CN117731362A (en) * | 2024-01-09 | 2024-03-22 | 苏州中天医疗器械科技有限公司 | Distal thrombus remover |
| CN117562622B (en) * | 2023-11-24 | 2024-11-12 | 广东博迈医疗科技股份有限公司 | Thrombus removing and crushing device and thrombus remover |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5011488A (en) * | 1988-12-07 | 1991-04-30 | Robert Ginsburg | Thrombus extraction system |
| US20060058836A1 (en) * | 2004-09-10 | 2006-03-16 | Arani Bose | System and method for treating ischemic stroke |
| US20060155305A1 (en) * | 2002-09-11 | 2006-07-13 | Franz Freudenthal | Extraction device |
| US20060253145A1 (en) * | 2005-05-05 | 2006-11-09 | Lucas Paul R | Multi-functional thrombectomy device |
| US20070135832A1 (en) * | 2002-03-12 | 2007-06-14 | Wholey Michael H | Vascular catheter with aspiration capabilities and expanded distal tip |
| US20100204672A1 (en) * | 2009-02-12 | 2010-08-12 | Penumra, Inc. | System and method for treating ischemic stroke |
| US20110202088A1 (en) * | 2008-10-24 | 2011-08-18 | Rapid Medical Ltd. | Embolectomy Device With Optional Vibrator |
| US20150150589A1 (en) * | 2013-12-03 | 2015-06-04 | Kawasumi Laboratories, Inc. | Catheter for removing foreign body in blood vessel |
| US20160113662A1 (en) * | 2014-10-27 | 2016-04-28 | Terumo Kabushiki Kaisha | Collection method |
| CN107440763A (en) * | 2017-08-16 | 2017-12-08 | 北京赛铂医药科技有限公司 | A kind of blood vessel near-end protector |
| CN214342507U (en) * | 2020-12-15 | 2021-10-08 | 上海融脉医疗科技有限公司 | Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof |
-
2020
- 2020-12-15 CN CN202011480880.9A patent/CN112494104A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5011488A (en) * | 1988-12-07 | 1991-04-30 | Robert Ginsburg | Thrombus extraction system |
| US20070135832A1 (en) * | 2002-03-12 | 2007-06-14 | Wholey Michael H | Vascular catheter with aspiration capabilities and expanded distal tip |
| US20060155305A1 (en) * | 2002-09-11 | 2006-07-13 | Franz Freudenthal | Extraction device |
| US20060058836A1 (en) * | 2004-09-10 | 2006-03-16 | Arani Bose | System and method for treating ischemic stroke |
| US20060253145A1 (en) * | 2005-05-05 | 2006-11-09 | Lucas Paul R | Multi-functional thrombectomy device |
| US20110202088A1 (en) * | 2008-10-24 | 2011-08-18 | Rapid Medical Ltd. | Embolectomy Device With Optional Vibrator |
| US20100204672A1 (en) * | 2009-02-12 | 2010-08-12 | Penumra, Inc. | System and method for treating ischemic stroke |
| US20150150589A1 (en) * | 2013-12-03 | 2015-06-04 | Kawasumi Laboratories, Inc. | Catheter for removing foreign body in blood vessel |
| US20160113662A1 (en) * | 2014-10-27 | 2016-04-28 | Terumo Kabushiki Kaisha | Collection method |
| CN107440763A (en) * | 2017-08-16 | 2017-12-08 | 北京赛铂医药科技有限公司 | A kind of blood vessel near-end protector |
| CN214342507U (en) * | 2020-12-15 | 2021-10-08 | 上海融脉医疗科技有限公司 | Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof |
Cited By (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113208770A (en) * | 2021-04-12 | 2021-08-06 | 聚辉医疗科技(深圳)有限公司 | Conveying device |
| CN113208770B (en) * | 2021-04-12 | 2021-11-16 | 聚辉医疗科技(深圳)有限公司 | Conveying device |
| CN113180914A (en) * | 2021-04-28 | 2021-07-30 | 河南科技大学第一附属医院 | Cerumen embolism softening and removing device |
| CN113425373B (en) * | 2021-07-30 | 2024-11-05 | 江苏朴芃医疗科技有限公司 | Blood vessel thrombus taking device |
| CN113425373A (en) * | 2021-07-30 | 2021-09-24 | 江苏朴芃医疗科技有限公司 | Blood vessel thrombus taking device |
| CN113855159A (en) * | 2021-09-29 | 2021-12-31 | 北京泰杰伟业科技有限公司 | Combined type regulation and control bolt taking device |
| CN113855159B (en) * | 2021-09-29 | 2024-04-09 | 北京泰杰伟业科技股份有限公司 | Combined type regulation and control thrombus taking device |
| WO2023050521A1 (en) * | 2021-09-29 | 2023-04-06 | 北京泰杰伟业科技有限公司 | Combined control thrombectomy device |
| CN114098904A (en) * | 2021-11-10 | 2022-03-01 | 北京泰杰伟业科技有限公司 | Thrombus collection device |
| CN113855164A (en) * | 2021-11-11 | 2021-12-31 | 上海融脉医疗科技有限公司 | Net disc type mechanical thrombus removing catheter device |
| CN114081579A (en) * | 2021-11-29 | 2022-02-25 | 上海市第十人民医院 | Mechanical thrombus taking device for cerebral apoplexy and application thereof |
| CN114052830A (en) * | 2021-12-21 | 2022-02-18 | 启晨(上海)医疗器械有限公司 | Thrombus removing device |
| CN114983647A (en) * | 2022-06-16 | 2022-09-02 | 晨兴(南通)医疗器械有限公司 | Plastic expander for expanding arterial stent |
| CN115429387A (en) * | 2022-09-19 | 2022-12-06 | 心凯诺医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Delivery system of thrombectomy support |
| CN115317077A (en) * | 2022-10-13 | 2022-11-11 | 成都百瑞恒通医疗科技有限公司 | Thrombus taking device |
| CN115919405A (en) * | 2022-11-02 | 2023-04-07 | 上海玮琅医疗科技有限公司 | Blood vessel foreign matter extraction auxiliary device and extraction device |
| CN115737060A (en) * | 2022-11-14 | 2023-03-07 | 上海中医药大学 | Device for conducting cardiovascular and cerebrovascular vessels |
| CN116138844A (en) * | 2023-04-04 | 2023-05-23 | 杭州亿科医疗科技有限公司 | Thrombus taking device capable of capturing various types of thrombus |
| CN116138844B (en) * | 2023-04-04 | 2023-07-14 | 杭州亿科医疗科技有限公司 | Thrombus taking device capable of capturing various types of thrombus |
| CN116712135A (en) * | 2023-07-28 | 2023-09-08 | 北京管桥医疗科技有限公司 | Thrombolysis device |
| CN117562622A (en) * | 2023-11-24 | 2024-02-20 | 广东博迈医疗科技股份有限公司 | Thrombus removing and crushing device and thrombus remover |
| CN117562622B (en) * | 2023-11-24 | 2024-11-12 | 广东博迈医疗科技股份有限公司 | Thrombus removing and crushing device and thrombus remover |
| CN117731362A (en) * | 2024-01-09 | 2024-03-22 | 苏州中天医疗器械科技有限公司 | Distal thrombus remover |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112494104A (en) | Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof | |
| CN112890915A (en) | Intravascular multi-segment embolectomy support and conveying device thereof | |
| CN112568967A (en) | Multi-section basket type bolt taking support and bolt taking device thereof | |
| CN109906058B (en) | Clot retrieval device for removing an occluded clot from a blood vessel | |
| CN113143405A (en) | Intravascular thrombus taking net disk support and conveying device thereof | |
| CN108348267B (en) | Thrombus removal device with blood flow restriction and related methods | |
| AU2018226388B2 (en) | Devices and systems for thrombus treatment | |
| EP2736425B1 (en) | Intravascular thromboembolectomy device | |
| CN112472210A (en) | Thrombus crushing and collecting mechanism of thrombus capturing and removing catheter device | |
| US11944327B2 (en) | Expandable mouth aspirating clot retrieval catheter | |
| CN112568968A (en) | Double-layer net cage type embolectomy support and assembly thereof | |
| US20160354099A1 (en) | Methods, devices, and systems for postconditioning with clot removal | |
| AU2019363274B2 (en) | A device and a thrombectomy apparatus for extraction of thrombus from a blood vessel | |
| US11376028B1 (en) | Devices, systems, and methods for removing obstructive material from body lumens | |
| JP2003505216A (en) | Vascular device for removing emboli, thrombus and foreign matter and method of use | |
| CN113180781A (en) | Winding type net disc support and conveying device thereof | |
| CN214342506U (en) | Thrombus crushing and collecting mechanism of thrombus capturing and removing catheter device | |
| CN112118795A (en) | Thrombectomy device | |
| CN216495499U (en) | Net disc type mechanical thrombus removing catheter device | |
| CN214342507U (en) | Be used for endovascular thrombus suction catheter device and basket subassembly thereof | |
| CN113993464A (en) | Thrombus removal device | |
| CN214342505U (en) | Catheter device with expandable guide head end | |
| CN214966296U (en) | Multi-section basket type bolt taking support and bolt taking device thereof | |
| US20240016505A1 (en) | Systems, apparatus and methods for removing and filtering vessel occlusions to isolate blood for reinfusion into a patient | |
| CN112472211A (en) | Catheter device with expandable guide head end |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |