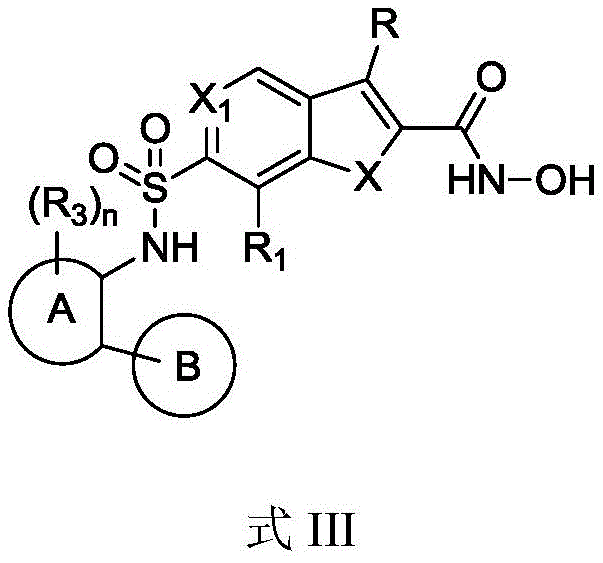
CN111848591B - HDAC inhibitors and methods of making and using the same - Google Patents
HDAC inhibitors and methods of making and using the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111848591B CN111848591B CN201910321788.9A CN201910321788A CN111848591B CN 111848591 B CN111848591 B CN 111848591B CN 201910321788 A CN201910321788 A CN 201910321788A CN 111848591 B CN111848591 B CN 111848591B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- substituted
- halogen
- alkyl
- membered
- independently selected
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000003276 histone deacetylase inhibitor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 12
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title description 9
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 79
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 230000002062 proliferating effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 208000023275 Autoimmune disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 206010061218 Inflammation Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 229940121372 histone deacetylase inhibitor Drugs 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 230000004054 inflammatory process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 208000015122 neurodegenerative disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 230000003612 virological effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 125000000753 cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 227
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 196
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 166
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 166
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 144
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 claims description 144
- 229910003827 NRaRb Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 120
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 102
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 claims description 90
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 75
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 claims description 64
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 52
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 44
- 125000000449 nitro group Chemical group [O-][N+](*)=O 0.000 claims description 40
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 40
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 38
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 28
- 102000003964 Histone deacetylase Human genes 0.000 claims description 24
- 108090000353 Histone deacetylase Proteins 0.000 claims description 24
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 14
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052701 rubidium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- 208000003174 Brain Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 206010006187 Breast cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000026310 Breast neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 206010009944 Colon cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 206010058467 Lung neoplasm malignant Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 206010033128 Ovarian cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 206010061535 Ovarian neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 206010060862 Prostate cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000000236 Prostatic Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000024770 Thyroid neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000029742 colonic neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 201000005202 lung cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000020816 lung neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000004770 neurodegeneration Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 201000002510 thyroid cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- LMBFAGIMSUYTBN-MPZNNTNKSA-N teixobactin Chemical compound C([C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H](CCC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H]1C(N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C[C@@H]2NC(=N)NC2)C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)O[C@H]1C)[C@@H](C)CC)=O)NC)C1=CC=CC=C1 LMBFAGIMSUYTBN-MPZNNTNKSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 abstract description 3
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 abstract 2
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 361
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 276
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 184
- 238000004895 liquid chromatography mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 153
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 140
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 130
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 105
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 73
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 72
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 69
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 68
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-WFGJKAKNSA-N Dimethyl sulfoxide Chemical compound [2H]C([2H])([2H])S(=O)C([2H])([2H])[2H] IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-WFGJKAKNSA-N 0.000 description 56
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 55
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 54
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 51
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 47
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 45
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 44
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 41
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium on carbon Substances [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 41
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 41
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 41
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 38
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 34
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 34
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N trifluoroacetic acid Substances OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 34
- 238000005160 1H NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 33
- AVXURJPOCDRRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydroxylamine Chemical compound ON AVXURJPOCDRRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 33
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 33
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 33
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 32
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 32
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 32
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 description 32
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 32
- 238000002953 preparative HPLC Methods 0.000 description 32
- -1 alicyclic hydrocarbon Chemical class 0.000 description 31
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 31
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 30
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 28
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 description 28
- 125000002023 trifluoromethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)* 0.000 description 25
- 238000010898 silica gel chromatography Methods 0.000 description 24
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 23
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 23
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 23
- SFWYTPZGJMDCNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)Cl Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)Cl SFWYTPZGJMDCNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 22
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 22
- QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen group Chemical group [N] QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- QHKJIJXBJCOABP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzofuran-2-carboxamide Chemical compound C1=CC=C2OC(C(=O)N)=CC2=C1 QHKJIJXBJCOABP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 19
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- KAWQPOUWLVOHKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 1-benzofuran-2-carboxylate Chemical compound C1=CC=C2OC(C(=O)OCC)=CC2=C1 KAWQPOUWLVOHKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 17
- 125000001072 heteroaryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 17
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 16
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 15
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 15
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 15
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 15
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 15
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 14
- BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium carbonate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C([O-])=O BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 14
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 13
- 125000003349 3-pyridyl group Chemical group N1=C([H])C([*])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 12
- DBIRXZYYKAVZBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-chloro-2-(4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound C1CC(OCC)CCN1C1=NC=C(Cl)C=C1N DBIRXZYYKAVZBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- JRNVZBWKYDBUCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-chlorosuccinimide Chemical compound ClN1C(=O)CCC1=O JRNVZBWKYDBUCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 12
- AMZDFTDDIXRTQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-(3-aminopyridin-2-yl)oxypiperidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CCC1OC1=NC=CC=C1N AMZDFTDDIXRTQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- RQENQEWXRLUZKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-(3-nitropyridin-2-yl)oxypiperidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CCC1OC1=NC=CC=C1[N+]([O-])=O RQENQEWXRLUZKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- CXNIUSPIQKWYAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N xantphos Chemical compound C=12OC3=C(P(C=4C=CC=CC=4)C=4C=CC=CC=4)C=CC=C3C(C)(C)C2=CC=CC=1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 CXNIUSPIQKWYAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 125000004397 aminosulfonyl group Chemical group NS(=O)(=O)* 0.000 description 11
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 11
- UUOLETYDNTVQDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CN=C1Cl UUOLETYDNTVQDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 9
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 description 8
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 8
- MSDSXECMRRAJIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-fluoro-2-piperidin-1-ylpyridin-3-amine Chemical compound Nc1cc(F)cnc1N1CCCCC1 MSDSXECMRRAJIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 102000004243 Tubulin Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 108090000704 Tubulin Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 229960000583 acetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 230000021736 acetylation Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000006640 acetylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 7
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 7
- 229910000027 potassium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 229910000104 sodium hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- CYPYTURSJDMMMP-WVCUSYJESA-N (1e,4e)-1,5-diphenylpenta-1,4-dien-3-one;palladium Chemical compound [Pd].[Pd].C=1C=CC=CC=1\C=C\C(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CC=C1.C=1C=CC=CC=1\C=C\C(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CC=C1.C=1C=CC=CC=1\C=C\C(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CC=C1 CYPYTURSJDMMMP-WVCUSYJESA-N 0.000 description 6
- NWZSZGALRFJKBT-KNIFDHDWSA-N (2s)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid;(2s)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O.NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O NWZSZGALRFJKBT-KNIFDHDWSA-N 0.000 description 6
- GVXZWNMVOCXCTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4,4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl)-5-fluoropyridin-3-amine Chemical compound C1CN(CCC1(F)F)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)F)N GVXZWNMVOCXCTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- KOQUBJBSRNMBSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CN=C1N1CCN(CC=2C=CC=CC=2)CC1 KOQUBJBSRNMBSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- BTJXXNXTUKGXLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl)-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound CCOC1CCN(CC1)c1ncccc1[N+]([O-])=O BTJXXNXTUKGXLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- NSZIHEHAEPPESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound C1CC(OCC)CCN1C1=NC=CC=C1N NSZIHEHAEPPESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- ZAERSIHFGFJCGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl)-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound COC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=CC=N2)[N+](=O)[O-] ZAERSIHFGFJCGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- GBKWYQSEBULIGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound C1CC(OC)CCN1C1=NC=CC=C1N GBKWYQSEBULIGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- IDZBAAJJFVMDQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound C1CC(C)CCN1C1=NC=CC=C1[N+]([O-])=O IDZBAAJJFVMDQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- JNBHCONHFUNVNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound C1CC(C)CCN1C1=NC=CC=C1N JNBHCONHFUNVNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- OSMMWFKGKROSHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-propan-2-ylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound C1CN(C(C)C)CCN1C1=NC=CC=C1N OSMMWFKGKROSHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- OPRNQKJWMRQIGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(cyclohexen-1-yl)-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CN=C1C1=CCCCC1 OPRNQKJWMRQIGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- KNMBWRWHUFZCAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(oxan-4-yloxy)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CN=C1OC1CCOCC1 KNMBWRWHUFZCAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- ATKGDSZMGXQFBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)piperidin-1-yl]pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CN=C1N1CC(C(F)(F)F)CCC1 ATKGDSZMGXQFBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- IISKGTANCWTLEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-cyclohexylpyridin-3-amine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CN=C1C1CCCCC1 IISKGTANCWTLEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- DHYQHRDXKCKJAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-morpholin-4-ylpyridin-3-amine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CN=C1N1CCOCC1 DHYQHRDXKCKJAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- JRCLEGSGUUSEGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-nitro-2-(oxan-4-yloxy)pyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CN=C1OC1CCOCC1 JRCLEGSGUUSEGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- OPDRFXXHFKYJAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-nitro-2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)piperidin-1-yl]pyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CN=C1N1CC(C(F)(F)F)CCC1 OPDRFXXHFKYJAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- QMINJWUSSJFQBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3-nitropyridin-2-yl)morpholine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CN=C1N1CCOCC1 QMINJWUSSJFQBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- GSGGHYVLXMJKEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-chloro-2-(4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl)-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)[N+](=O)[O-] GSGGHYVLXMJKEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- WVXSONLIJCFFQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-chloro-2-(4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound C1CC(OC)CCN1C1=NC=C(Cl)C=C1N WVXSONLIJCFFQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- XCTBRKBIWJIXPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-chloro-2-piperidin-1-ylpyridin-3-amine Chemical compound NC1=CC(Cl)=CN=C1N1CCCCC1 XCTBRKBIWJIXPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- NLKNVZYZIIMAJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-chloro-3-nitro-2-piperidin-1-ylpyridine Chemical compound ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCCCC1)[N+](=O)[O-] NLKNVZYZIIMAJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- YEDLILPWCOFEKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC1=C(SC2=C1C=CC(=C2)S(=O)(=O)Cl)C(=O)OC Chemical compound COC1=C(SC2=C1C=CC(=C2)S(=O)(=O)Cl)C(=O)OC YEDLILPWCOFEKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- XBZNNKHVGDRIRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)Cl)[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound COC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)Cl)[N+](=O)[O-] XBZNNKHVGDRIRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- LKTHVMLOXZRXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC1CC1)N Chemical compound ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC1CC1)N LKTHVMLOXZRXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-diisopropylethylamine Substances CCN(C(C)C)C(C)C JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- LGJMMDXTYFGWNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-cyclohexyl-N-ethyl-3-nitropyridin-2-amine Chemical compound N=1C=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=1N(CC)C1CCCCC1 LGJMMDXTYFGWNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- NPXOKRUENSOPAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Raney nickel Chemical compound [Al].[Ni] NPXOKRUENSOPAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical class [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 6
- 125000004429 atom Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- UENWRTRMUIOCKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl thiol Chemical compound SCC1=CC=CC=C1 UENWRTRMUIOCKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 6
- 125000001246 bromo group Chemical group Br* 0.000 description 6
- FJDQFPXHSGXQBY-UHFFFAOYSA-L caesium carbonate Chemical compound [Cs+].[Cs+].[O-]C([O-])=O FJDQFPXHSGXQBY-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 6
- 229910000024 caesium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 125000001309 chloro group Chemical group Cl* 0.000 description 6
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000003810 ethyl acetate extraction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 description 6
- IKDUDTNKRLTJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrazine monohydrate Substances O.NN IKDUDTNKRLTJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 6
- HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;chloride;hydrate Chemical class O.[Na+].[Cl-] HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 6
- WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-Dichloroethane Chemical compound ClCCCl WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- KWWSSWVJUWLPDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydro-1H-cyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound Nc1cccnc1N1CC2CCCC2C1 KWWSSWVJUWLPDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- RKPBMYLHWHQJKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydro-1H-cyclopenta[c]pyrrole Chemical compound C1CC2CN(CC2C1)C3=C(C=CC=N3)[N+](=O)[O-] RKPBMYLHWHQJKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- SOBNUCLWVKUPKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4,4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl)-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)c1cccnc1N1CCC(F)(F)CC1 SOBNUCLWVKUPKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- GGMWOMKCAMWUAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4,4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound FC1(CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1N)F GGMWOMKCAMWUAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- HFVWEJPRXFXZBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl)-5-fluoro-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=C(C=C1[N+](=O)[O-])F HFVWEJPRXFXZBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- KUWQKFIENLFXOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[1-(3-nitropyridin-2-yl)piperidin-4-yl]propan-2-ol Chemical compound [N+](=O)([O-])C=1C(=NC=CC1)N1CCC(CC1)C(C)(C)O KUWQKFIENLFXOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- HFACYWDPMNWMIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-cyclohexylethanamine Chemical compound NCCC1CCCCC1 HFACYWDPMNWMIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- IUAHQKOAIKIXFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(cyclopropylmethoxy)piperidine Chemical compound C1CC1COC1CCNCC1 IUAHQKOAIKIXFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- MLYXHAAWXUGOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-amino-6-(4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl)pyridine-3-carbonitrile Chemical compound CCOC1CCN(CC1)c1ncc(cc1N)C#N MLYXHAAWXUGOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- HUJOFSBFHPQMGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1C)C=CC(=C2)S(NC=2C(=NC=C(C2)Cl)N2CCC(CC2)OCC)(=O)=O Chemical compound C(C)OC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1C)C=CC(=C2)S(NC=2C(=NC=C(C2)Cl)N2CCC(CC2)OCC)(=O)=O HUJOFSBFHPQMGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- XSXZRDHKYCIUHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=C(C#N)C=C1[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=C(C#N)C=C1[N+](=O)[O-] XSXZRDHKYCIUHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- VSROFRJKZKJNFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1CC2(CC2(F)F)CN(C1)C3=C(C=CC=N3)N Chemical compound C1CC2(CC2(F)F)CN(C1)C3=C(C=CC=N3)N VSROFRJKZKJNFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- VJXUIMXPWAXQTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)Cl)C Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)Cl)C VJXUIMXPWAXQTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- ZIOLMTWHFIMRFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C(=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)Cl)F Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C(=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)Cl)F ZIOLMTWHFIMRFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- LUYFKKWIXNUKJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)F)N Chemical compound CCOC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)F)N LUYFKKWIXNUKJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- XJXUXJCTAHJAAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(S1)C=C(C=C2)SCC2=CC=CC=C2)OC Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(S1)C=C(C=C2)SCC2=CC=CC=C2)OC XJXUXJCTAHJAAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- LPMGJWLFKUQUDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N FC1(CC12CN(CCC2)C2=NC=CC=C2[N+](=O)[O-])F Chemical compound FC1(CC12CN(CCC2)C2=NC=CC=C2[N+](=O)[O-])F LPMGJWLFKUQUDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- WZQFBLOQHKQANB-UHFFFAOYSA-N FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)(F)F)[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)(F)F)[N+](=O)[O-] WZQFBLOQHKQANB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- MKPGIKZWARANAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCCCC1)[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCCCC1)[N+](=O)[O-] MKPGIKZWARANAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- JMIVXULHQBDAIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N NC=1C(=NC=CC1)N1CCC(CC1)C(C)(C)O Chemical compound NC=1C(=NC=CC1)N1CCC(CC1)C(C)(C)O JMIVXULHQBDAIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- LEUXJECAJFORAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-(cyclopropylmethoxy)piperidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CCC1OCC1CC1 LEUXJECAJFORAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- OBUGJYJQJWMOQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,5-dichloro-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC(Cl)=CN=C1Cl OBUGJYJQJWMOQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QCFRHISLUKNFQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-cyclohexyl-5-methylpyrazol-3-amine Chemical compound N1=C(C)C=C(N)N1C1CCCCC1 QCFRHISLUKNFQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QDKIYDGHCFZBGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-fluoro-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CN=C1F QDKIYDGHCFZBGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- BCHBVHMSOBXQFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromo-3-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde Chemical compound Oc1c(F)c(Br)ccc1C=O BCHBVHMSOBXQFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- PYWGJFVEOGVKSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromo-3-fluoro-2-methoxybenzaldehyde Chemical compound COC1=C(F)C(Br)=CC=C1C=O PYWGJFVEOGVKSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- PJHAUBFOPBCASB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-ethoxypiperidine;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.CCOC1CCNCC1 PJHAUBFOPBCASB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QUTHIVPADSLFBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-chloro-4-oxo-1h-pyridine-3-carbaldehyde Chemical compound OC1=CC(Cl)=NC=C1C=O QUTHIVPADSLFBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- HHEJVRVQMSCMEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC(=O)C1=CC=2C=NC(=CC2O1)S(NC=1C(=NC=C(C1)Cl)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)(=O)=O Chemical compound C(C)OC(=O)C1=CC=2C=NC(=CC2O1)S(NC=1C(=NC=C(C1)Cl)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)(=O)=O HHEJVRVQMSCMEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CGHFIQNOBCKILN-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1)C=CC(=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC=2C(=NC=CC2)OC2CCN(CC2)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C Chemical compound C(C)OC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1)C=CC(=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC=2C(=NC=CC2)OC2CCN(CC2)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C CGHFIQNOBCKILN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- RMHWQJCPSFPPFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1)C=CC(=C2)S(NC=2C(=NC=CC2)N2CC1C(C2)CCC1)(=O)=O Chemical compound C(C)OC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1)C=CC(=C2)S(NC=2C(=NC=CC2)N2CC1C(C2)CCC1)(=O)=O RMHWQJCPSFPPFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VOHJCFSYALJRQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1)C=CC(=C2F)S(NC=2C(=NC=C(C2)Cl)N2CCC(CC2)OCC)(=O)=O Chemical compound C(C)OC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1)C=CC(=C2F)S(NC=2C(=NC=C(C2)Cl)N2CCC(CC2)OCC)(=O)=O VOHJCFSYALJRQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- WDQNHHAEUQHDQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(=O)NC1=C(N=CC=C1)N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C Chemical compound CC(=O)NC1=C(N=CC=C1)N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C WDQNHHAEUQHDQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- OLYMVORJXOXFBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCNC1(C2CCCCC2)NC=CC=C1N Chemical compound CCNC1(C2CCCCC2)NC=CC=C1N OLYMVORJXOXFBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LHGCNXKUTJQWEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3)C Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3)C LHGCNXKUTJQWEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CVPIYGLYIGAXOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C(=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3)F Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C(=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3)F CVPIYGLYIGAXOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- AWXQXHAFMSRTAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCC(CC4)C Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCC(CC4)C AWXQXHAFMSRTAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- MMQRYCHVHRWACF-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCC(CC4)C(C)(C)O Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCC(CC4)C(C)(C)O MMQRYCHVHRWACF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- YMTKBKQKSRUIFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)Cl)NS(=O)(=O)C3=C(C4=C(C=C3)C=C(O4)C(=O)NO)F Chemical compound CCOC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)Cl)NS(=O)(=O)C3=C(C4=C(C=C3)C=C(O4)C(=O)NO)F YMTKBKQKSRUIFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- KMGYAUQZBSUMKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(S1)C=C(C=C2)S(NC=2C(=NC=C(C2)Cl)N2CCC(CC2)OCC)(=O)=O)OC Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(S1)C=C(C=C2)S(NC=2C(=NC=C(C2)Cl)N2CCC(CC2)OCC)(=O)=O)OC KMGYAUQZBSUMKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- JKEYUAQYMYOOAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound COC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 JKEYUAQYMYOOAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- FDCFWXARSGTULW-UHFFFAOYSA-N ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 FDCFWXARSGTULW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 4
- NKDHZKSZOIPLEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCCCC1)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCCCC1)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 NKDHZKSZOIPLEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 102100022537 Histone deacetylase 6 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108010033040 Histones Proteins 0.000 description 4
- NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperidine Chemical compound C1CCNCC1 NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N Trichloro(2H)methane Chemical compound [2H]C(Cl)(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000004113 cell culture Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- UQLDLKMNUJERMK-UHFFFAOYSA-L di(octadecanoyloxy)lead Chemical compound [Pb+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O UQLDLKMNUJERMK-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 4
- BHQBSMLYZIRFHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 6-bromo-1-benzofuran-2-carboxylate Chemical compound C1=C(Br)C=C2OC(C(=O)OCC)=CC2=C1 BHQBSMLYZIRFHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- WUXXJIYMXCUNTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 6-bromo-3-methyl-1-benzofuran-2-carboxylate Chemical compound BrC1=CC=C2C(C)=C(C(=O)OCC)OC2=C1 WUXXJIYMXCUNTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- IIFOHXFDINFVOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 6-bromo-7-fluoro-1-benzofuran-2-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)c1cc2ccc(Br)c(F)c2o1 IIFOHXFDINFVOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- WHOBGYUENJXBDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 6-chlorosulfonylfuro[3,2-c]pyridine-2-carboxylate Chemical compound ClS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=N1)C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC WHOBGYUENJXBDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- PQJJJMRNHATNKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl bromoacetate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CBr PQJJJMRNHATNKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- XDYVZHUZZZKQOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 5-bromo-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylate Chemical compound BrC1=CC=C2SC(C(=O)OC)=CC2=C1 XDYVZHUZZZKQOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000013642 negative control Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 4
- WWTBZEKOSBFBEM-SPWPXUSOSA-N (2s)-2-[[2-benzyl-3-[hydroxy-[(1r)-2-phenyl-1-(phenylmethoxycarbonylamino)ethyl]phosphoryl]propanoyl]amino]-3-(1h-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid Chemical compound N([C@@H](CC=1C2=CC=CC=C2NC=1)C(=O)O)C(=O)C(CP(O)(=O)[C@H](CC=1C=CC=CC=1)NC(=O)OCC=1C=CC=CC=1)CC1=CC=CC=C1 WWTBZEKOSBFBEM-SPWPXUSOSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OFFSPAZVIVZPHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2OC(C(=O)O)=CC2=C1 OFFSPAZVIVZPHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YSUIQYOGTINQIN-UZFYAQMZSA-N 2-amino-9-[(1S,6R,8R,9S,10R,15R,17R,18R)-8-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-9,18-difluoro-3,12-dihydroxy-3,12-bis(sulfanylidene)-2,4,7,11,13,16-hexaoxa-3lambda5,12lambda5-diphosphatricyclo[13.2.1.06,10]octadecan-17-yl]-1H-purin-6-one Chemical compound NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2[C@@H]2O[C@@H]3COP(S)(=O)O[C@@H]4[C@@H](COP(S)(=O)O[C@@H]2[C@@H]3F)O[C@H]([C@H]4F)N2C=NC3=C2N=CN=C3N)C(=O)N1 YSUIQYOGTINQIN-UZFYAQMZSA-N 0.000 description 3
- TVTJUIAKQFIXCE-HUKYDQBMSA-N 2-amino-9-[(2R,3S,4S,5R)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-7-prop-2-ynyl-1H-purine-6,8-dione Chemical compound NC=1NC(C=2N(C(N(C=2N=1)[C@@H]1O[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]1O)F)CO)=O)CC#C)=O TVTJUIAKQFIXCE-HUKYDQBMSA-N 0.000 description 3
- SVVZGNAZMPSGMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-5-fluoro-3-nitropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC(F)=CN=C1Cl SVVZGNAZMPSGMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QBWKPGNFQQJGFY-QLFBSQMISA-N 3-[(1r)-1-[(2r,6s)-2,6-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl]ethyl]-n-[6-methyl-3-(1h-pyrazol-4-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-8-yl]-1,2-thiazol-5-amine Chemical compound N1([C@H](C)C2=NSC(NC=3C4=NC=C(N4C=C(C)N=3)C3=CNN=C3)=C2)C[C@H](C)O[C@H](C)C1 QBWKPGNFQQJGFY-QLFBSQMISA-N 0.000 description 3
- WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic anhydride Chemical compound CC(=O)OC(C)=O WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- JGHLXSNOEYKQLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(#N)C=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound C(#N)C=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 JGHLXSNOEYKQLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- VVHKBXPAMQPFRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C(C)C)OC(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound C(C(C)C)OC(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 VVHKBXPAMQPFRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- IKPFGYVASAJTMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1NCC(CC1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1)F Chemical compound C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1NCC(CC1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1)F IKPFGYVASAJTMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- LKLVYTNJSIMNBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)OC4CCN(CC4)C Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)OC4CCN(CC4)C LKLVYTNJSIMNBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MQTBAHGZDCIVQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=CN=C(C=C2O1)Cl Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=CN=C(C=C2O1)Cl MQTBAHGZDCIVQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- NSSPIRGWERWYHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)Cl)NS(=O)(=O)C3=CC4=C(C=C3)C(=C(O4)C(=O)NO)C Chemical compound CCOC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)Cl)NS(=O)(=O)C3=CC4=C(C=C3)C(=C(O4)C(=O)NO)C NSSPIRGWERWYHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 108010077544 Chromatin Proteins 0.000 description 3
- RIUWACHEGRYLER-UHFFFAOYSA-N ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC1CC1)[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC1CC1)[N+](=O)[O-] RIUWACHEGRYLER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- XBEVROTUWIRDOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N FC1(CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1)F Chemical compound FC1(CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1)F XBEVROTUWIRDOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102100039996 Histone deacetylase 1 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 102000006947 Histones Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 101001035024 Homo sapiens Histone deacetylase 1 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101000899330 Homo sapiens Histone deacetylase 6 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- WMFOQBRAJBCJND-UHFFFAOYSA-M Lithium hydroxide Chemical compound [Li+].[OH-] WMFOQBRAJBCJND-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- WWGBHDIHIVGYLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-[4-[3-[[[7-(hydroxyamino)-7-oxoheptyl]amino]-oxomethyl]-5-isoxazolyl]phenyl]carbamic acid tert-butyl ester Chemical compound C1=CC(NC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)=CC=C1C1=CC(C(=O)NCCCCCCC(=O)NO)=NO1 WWGBHDIHIVGYLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OPFJDXRVMFKJJO-ZHHKINOHSA-N N-{[3-(2-benzamido-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)-pyrazol-5-yl]carbonyl}-G-dR-G-dD-dD-dD-NH2 Chemical compound S1C(C=2NN=C(C=2)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H](CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(N)=O)=C(C)N=C1NC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 OPFJDXRVMFKJJO-ZHHKINOHSA-N 0.000 description 3
- RYGJATBUYSPTKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N N1(CCNCC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NC(C)=O Chemical compound N1(CCNCC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NC(C)=O RYGJATBUYSPTKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ROLCHNAJOQYQOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-ethyl 6-benzylfuro[3,2-c]pyridine-2-carbothioate Chemical compound C(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC2=C(C=N1)C=C(O2)C(=S)OCC ROLCHNAJOQYQOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910000564 Raney nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006907 apoptotic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- XRWSZZJLZRKHHD-WVWIJVSJSA-N asunaprevir Chemical compound O=C([C@@H]1C[C@H](CN1C(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)C)OC1=NC=C(C2=CC=C(Cl)C=C21)OC)N[C@]1(C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C2CC2)C[C@H]1C=C XRWSZZJLZRKHHD-WVWIJVSJSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KGNDCEVUMONOKF-UGPLYTSKSA-N benzyl n-[(2r)-1-[(2s,4r)-2-[[(2s)-6-amino-1-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)-1,1-dihydroxyhexan-2-yl]carbamoyl]-4-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1CO[C@H]1CN(C(=O)[C@@H](CCC=2C=CC=CC=2)NC(=O)OCC=2C=CC=CC=2)[C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(O)(O)C=2OC3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C1 KGNDCEVUMONOKF-UGPLYTSKSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000003483 chromatin Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 229940125904 compound 1 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940125782 compound 2 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940125810 compound 20 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940126086 compound 21 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940126208 compound 22 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940125833 compound 23 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940125961 compound 24 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940125846 compound 25 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940125851 compound 27 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940126214 compound 3 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940125898 compound 5 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- XLJWAHXKBCDQNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 5-bromo-1-benzofuran-2-carboxylate Chemical compound BrC1=CC=C2OC(C(=O)OCC)=CC2=C1 XLJWAHXKBCDQNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000014509 gene expression Effects 0.000 description 3
- JAXFJECJQZDFJS-XHEPKHHKSA-N gtpl8555 Chemical compound OC(=O)C[C@H](N)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N1CCC[C@@H]1C(=O)N[C@H](B1O[C@@]2(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](C3(C)C)C[C@H]2O1)CCC1=CC=C(F)C=C1 JAXFJECJQZDFJS-XHEPKHHKSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000006195 histone acetylation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000005457 ice water Substances 0.000 description 3
- SFDVDNLBYGHFNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 6-bromo-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylate Chemical compound C1=C(Br)C=C2SC(C(=O)OC)=CC2=C1 SFDVDNLBYGHFNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QGQYTZCACKYMKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 6-bromo-3-hydroxy-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylate Chemical compound BrC1=CC=C2C(O)=C(C(=O)OC)SC2=C1 QGQYTZCACKYMKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OHUFKNSNLQYPFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 6-bromo-3-methoxy-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)c1sc2cc(Br)ccc2c1OC OHUFKNSNLQYPFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- PWQLFIKTGRINFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-hydroxypiperidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)N1CCC(O)CC1 PWQLFIKTGRINFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- AOSZTAHDEDLTLQ-AZKQZHLXSA-N (1S,2S,4R,8S,9S,11S,12R,13S,19S)-6-[(3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-12,19-difluoro-11-hydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-9,13-dimethyl-6-azapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.04,8.013,18]icosa-14,17-dien-16-one Chemical compound C([C@@H]1C[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@]([C@]4(C=CC(=O)C=C4[C@@H](F)C3)C)(F)[C@@H](O)C[C@@]2([C@@]1(C1)C(=O)CO)C)N1CC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 AOSZTAHDEDLTLQ-AZKQZHLXSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GLGNXYJARSMNGJ-VKTIVEEGSA-N (1s,2s,3r,4r)-3-[[5-chloro-2-[(1-ethyl-6-methoxy-2-oxo-4,5-dihydro-3h-1-benzazepin-7-yl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-2-carboxamide Chemical compound CCN1C(=O)CCCC2=C(OC)C(NC=3N=C(C(=CN=3)Cl)N[C@H]3[C@H]([C@@]4([H])C[C@@]3(C=C4)[H])C(N)=O)=CC=C21 GLGNXYJARSMNGJ-VKTIVEEGSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SZUVGFMDDVSKSI-WIFOCOSTSA-N (1s,2s,3s,5r)-1-(carboxymethyl)-3,5-bis[(4-phenoxyphenyl)methyl-propylcarbamoyl]cyclopentane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid Chemical compound O=C([C@@H]1[C@@H]([C@](CC(O)=O)([C@H](C(=O)N(CCC)CC=2C=CC(OC=3C=CC=CC=3)=CC=2)C1)C(O)=O)C(O)=O)N(CCC)CC(C=C1)=CC=C1OC1=CC=CC=C1 SZUVGFMDDVSKSI-WIFOCOSTSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GHYOCDFICYLMRF-UTIIJYGPSA-N (2S,3R)-N-[(2S)-3-(cyclopenten-1-yl)-1-[(2R)-2-methyloxiran-2-yl]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-[[(2S)-2-[(2-morpholin-4-ylacetyl)amino]propanoyl]amino]propanamide Chemical compound C1(=CCCC1)C[C@@H](C(=O)[C@@]1(OC1)C)NC([C@H]([C@@H](C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC)O)NC([C@H](C)NC(CN1CCOCC1)=O)=O)=O GHYOCDFICYLMRF-UTIIJYGPSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QFLWZFQWSBQYPS-AWRAUJHKSA-N (3S)-3-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[5-[(3aS,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoylamino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-[1-bis(4-chlorophenoxy)phosphorylbutylamino]-4-oxobutanoic acid Chemical compound CCCC(NC(=O)[C@H](CC(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](Cc1ccc(O)cc1)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CCCCC1SC[C@@H]2NC(=O)N[C@H]12)C(C)C)P(=O)(Oc1ccc(Cl)cc1)Oc1ccc(Cl)cc1 QFLWZFQWSBQYPS-AWRAUJHKSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IWZSHWBGHQBIML-ZGGLMWTQSA-N (3S,8S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-isoquinolin-7-yl-N,N,10,13-tetramethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-amine Chemical compound CN(C)[C@H]1CC[C@]2(C)C3CC[C@@]4(C)[C@@H](CC[C@@H]4c4ccc5ccncc5c4)[C@@H]3CC=C2C1 IWZSHWBGHQBIML-ZGGLMWTQSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KKHFRAFPESRGGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dimethyl-7-[3-(n-methylanilino)propyl]purine-2,6-dione Chemical compound C1=NC=2N(C)C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C=2N1CCCN(C)C1=CC=CC=C1 KKHFRAFPESRGGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ONBQEOIKXPHGMB-VBSBHUPXSA-N 1-[2-[(2s,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-4,6-dihydroxyphenyl]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1OC1=CC(O)=CC(O)=C1C(=O)CCC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 ONBQEOIKXPHGMB-VBSBHUPXSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QKNYBSVHEMOAJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol;hydron;chloride Chemical compound Cl.OCC(N)(CO)CO QKNYBSVHEMOAJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FWBHETKCLVMNFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4',6-Diamino-2-phenylindol Chemical compound C1=CC(C(=N)N)=CC=C1C1=CC2=CC=C(C(N)=N)C=C2N1 FWBHETKCLVMNFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MPMKMQHJHDHPBE-RUZDIDTESA-N 4-[[(2r)-1-(1-benzothiophene-3-carbonyl)-2-methylazetidine-2-carbonyl]-[(3-chlorophenyl)methyl]amino]butanoic acid Chemical compound O=C([C@@]1(N(CC1)C(=O)C=1C2=CC=CC=C2SC=1)C)N(CCCC(O)=O)CC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 MPMKMQHJHDHPBE-RUZDIDTESA-N 0.000 description 2
- UPCARQPLANFGQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromo-2-fluorobenzaldehyde Chemical compound FC1=CC(Br)=CC=C1C=O UPCARQPLANFGQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HXTWKHXDFATMSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde Chemical compound OC1=CC(Br)=CC=C1C=O HXTWKHXDFATMSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZEYSHALLPAKUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methoxypiperidine Chemical compound COC1CCNCC1 ZEYSHALLPAKUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RSIWALKZYXPAGW-NSHDSACASA-N 6-(3-fluorophenyl)-3-methyl-7-[(1s)-1-(7h-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl]-[1,3]thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidin-5-one Chemical compound C=1([C@@H](NC=2C=3N=CNC=3N=CN=2)C)N=C2SC=C(C)N2C(=O)C=1C1=CC=CC(F)=C1 RSIWALKZYXPAGW-NSHDSACASA-N 0.000 description 2
- MJKBQIXGOHBBFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-chloro-4-methoxypyridine-3-carbaldehyde Chemical compound COC1=CC(Cl)=NC=C1C=O MJKBQIXGOHBBFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XASOHFCUIQARJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-methoxy-6-[7-(2-morpholin-4-ylethoxy)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl]-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1-one Chemical compound C(N1C(=O)C2=C(OC)C=C(C=3N4C(=NC=3)C=C(C=C4)OCCN3CCOCC3)C=C2CC1)C(F)(F)F XASOHFCUIQARJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IZPUDRISPDDIIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C(C)C)OC(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)NO)C=C1 Chemical compound C(C(C)C)OC(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)NO)C=C1 IZPUDRISPDDIIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HAJCQOFAKXTYDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)(C)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NC(C)=O Chemical compound C(C)(C)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NC(C)=O HAJCQOFAKXTYDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XSZTXAQCJNGADH-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)(C)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)NO)C=C1 Chemical compound C(C)(C)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)NO)C=C1 XSZTXAQCJNGADH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HNIKLLICTKSAAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)(C)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound C(C)(C)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 HNIKLLICTKSAAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YJBMUQCKRGQWLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 YJBMUQCKRGQWLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CGISTDKEYRHXKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C1=CC=CC=C1)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NC(C)=O Chemical compound C(C1=CC=CC=C1)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NC(C)=O CGISTDKEYRHXKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XQUNPAOTSKIRSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1(CCCCC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound C1(CCCCC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 XQUNPAOTSKIRSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YHEOZZRVHWHXDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC(=C3)Cl)N4CCCCC4 Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC(=C3)Cl)N4CCCCC4 YHEOZZRVHWHXDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BZDXFDZDFVOIBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCN(CC4)CC5=CC=CC=C5 Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCN(CC4)CC5=CC=CC=C5 BZDXFDZDFVOIBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PERLRRDKCYSFIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCNCC4 Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCNCC4 PERLRRDKCYSFIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JRZKQSMIVYHYGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCOCC4 Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)N4CCOCC4 JRZKQSMIVYHYGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VRKWMCNGFOIDDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)OC4CCNCC4 Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)OC4CCNCC4 VRKWMCNGFOIDDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JFXDDENORYJAPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)OC4CCOCC4 Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC=C3)OC4CCOCC4 JFXDDENORYJAPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VCVRRVFCROGUOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=CC(=NN3C4CCCCC4)C Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=CC(=NN3C4CCCCC4)C VCVRRVFCROGUOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UFIOSITWCWROPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)Cl)NS(=O)(=O)C3=NC=C4C=C(OC4=C3)C(=O)NO Chemical compound CCOC1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C(C=N2)Cl)NS(=O)(=O)C3=NC=C4C=C(OC4=C3)C(=O)NO UFIOSITWCWROPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IAVJEUHTQLBVLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC(=O)C1=CC2=C(S1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC(=C3)F)N4CCCCC4 Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC2=C(S1)C=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(N=CC(=C3)F)N4CCCCC4 IAVJEUHTQLBVLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BKBZYQFCABURQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N CS(=O)(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 BKBZYQFCABURQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000283707 Capra Species 0.000 description 2
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 2
- UKDIPMYHMMQOLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OC)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OC)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 UKDIPMYHMMQOLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CXRFKDNFQQQYEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)NS(=O)(=O)C=1C=CC2=C(SC(=C2OC)C(=O)NO)C1 Chemical compound ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC)NS(=O)(=O)C=1C=CC2=C(SC(=C2OC)C(=O)NO)C1 CXRFKDNFQQQYEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SEGTZEZEPRPVQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC1CC1)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound ClC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OCC1CC1)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 SEGTZEZEPRPVQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940126657 Compound 17 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-MZCSYVLQSA-N Deuterated methanol Chemical compound [2H]OC([2H])([2H])[2H] OKKJLVBELUTLKV-MZCSYVLQSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FWDVSUOAPQYPSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)(F)F)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 Chemical compound FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)(F)F)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 FWDVSUOAPQYPSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NMTHSBZKMFPLHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OC)[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCC(CC1)OC)[N+](=O)[O-] NMTHSBZKMFPLHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YPRJYOPZPKEZOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCCCC1)NS(=O)(=O)C=1C=CC2=C(SC(=C2)C(=O)NO)C1 Chemical compound FC=1C=C(C(=NC1)N1CCCCC1)NS(=O)(=O)C=1C=CC2=C(SC(=C2)C(=O)NO)C1 YPRJYOPZPKEZOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RRSNDVCODIMOFX-MPKOGUQCSA-N Fc1c(Cl)cccc1[C@H]1[C@@H](NC2(CCCCC2)[C@@]11C(=O)Nc2cc(Cl)ccc12)C(=O)Nc1ccc(cc1)C(=O)NCCCCCc1cccc2C(=O)N(Cc12)C1CCC(=O)NC1=O Chemical compound Fc1c(Cl)cccc1[C@H]1[C@@H](NC2(CCCCC2)[C@@]11C(=O)Nc2cc(Cl)ccc12)C(=O)Nc1ccc(cc1)C(=O)NCCCCCc1cccc2C(=O)N(Cc12)C1CCC(=O)NC1=O RRSNDVCODIMOFX-MPKOGUQCSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000003893 Histone acetyltransferases Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000246 Histone acetyltransferases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- PGBFYLVIMDQYMS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl thiophene-2-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=CS1 PGBFYLVIMDQYMS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YNAVUWVOSKDBBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Morpholine Chemical compound C1COCCN1 YNAVUWVOSKDBBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QOVYHDHLFPKQQG-NDEPHWFRSA-N N[C@@H](CCC(=O)N1CCC(CC1)NC1=C2C=CC=CC2=NC(NCC2=CN(CCCNCCCNC3CCCCC3)N=N2)=N1)C(O)=O Chemical compound N[C@@H](CCC(=O)N1CCC(CC1)NC1=C2C=CC=CC2=NC(NCC2=CN(CCCNCCCNC3CCCCC3)N=N2)=N1)C(O)=O QOVYHDHLFPKQQG-NDEPHWFRSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000035195 Peptidases Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108091005804 Peptidases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 239000004365 Protease Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007868 Raney catalyst Substances 0.000 description 2
- KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium Chemical compound [Na] KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium methoxide Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]C WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LNUFLCYMSVYYNW-ZPJMAFJPSA-N [(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-2-[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-6-[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-6-[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-6-[[(3s,5s,8r,9s,10s,13r,14s,17r)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2r)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl]oxy]-4,5-disulfo Chemical compound O([C@@H]1[C@@H](COS(O)(=O)=O)O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1OS(O)(=O)=O)OS(O)(=O)=O)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COS(O)(=O)=O)O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1OS(O)(=O)=O)OS(O)(=O)=O)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](COS(O)(=O)=O)O[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1OS(O)(=O)=O)OS(O)(=O)=O)O[C@@H]1C[C@@H]2CC[C@H]3[C@@H]4CC[C@@H]([C@]4(CC[C@@H]3[C@@]2(C)CC1)C)[C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@H]1O[C@H](COS(O)(=O)=O)[C@@H](OS(O)(=O)=O)[C@H](OS(O)(=O)=O)[C@H]1OS(O)(=O)=O LNUFLCYMSVYYNW-ZPJMAFJPSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000003698 anagen phase Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000008346 aqueous phase Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000002837 carbocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229940125773 compound 10 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940125797 compound 12 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940126543 compound 14 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940125758 compound 15 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940126142 compound 16 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 125000001995 cyclobutyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 125000000113 cyclohexyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 125000001511 cyclopentyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 125000001559 cyclopropyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 238000007405 data analysis Methods 0.000 description 2
- FQYYIPZPELSLDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl pyridine-2-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=N1 FQYYIPZPELSLDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000012065 filter cake Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000012010 growth Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000000592 heterocycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000000959 isobutyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- ZLVXBBHTMQJRSX-VMGNSXQWSA-N jdtic Chemical compound C1([C@]2(C)CCN(C[C@@H]2C)C[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H]2NCC3=CC(O)=CC=C3C2)=CC=CC(O)=C1 ZLVXBBHTMQJRSX-VMGNSXQWSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229930195734 saturated hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012312 sodium hydride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001308 synthesis method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010189 synthetic method Methods 0.000 description 2
- CBTYZJKYXVDWOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-(3-aminopyridin-2-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CCN1C1=NC=CC=C1N CBTYZJKYXVDWOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LIXGIYPYLOVAKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-[3-[(2-ethoxycarbonyl-1-benzofuran-6-yl)sulfonylamino]pyridin-2-yl]piperazine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound C(C)(C)(C)OC(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=CC=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)OCC)C=C1 LIXGIYPYLOVAKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 231100000331 toxic Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 230000002588 toxic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000035897 transcription Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013518 transcription Methods 0.000 description 2
- FFJCNSLCJOQHKM-CLFAGFIQSA-N (z)-1-[(z)-octadec-9-enoxy]octadec-9-ene Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCOCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC FFJCNSLCJOQHKM-CLFAGFIQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KZPYGQFFRCFCPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene Chemical compound [Fe+2].C1=CC=C[C-]1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=C[C-]1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 KZPYGQFFRCFCPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UZHVXJZEHGSWQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3,3a,4,5,6,6a-octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrole Chemical compound C1NCC2CCCC21 UZHVXJZEHGSWQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LQCMMXGKEGWUIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(4-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone Chemical compound CC(=O)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1O LQCMMXGKEGWUIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DXZOGVBFSOBEOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2-difluoro-5-azaspiro[2.5]octane;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.FC1(F)CC11CNCCC1 DXZOGVBFSOBEOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QNZFUMVTUFOLRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(cyclohexen-1-yl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane Chemical compound O1C(C)(C)C(C)(C)OB1C1=CCCCC1 QNZFUMVTUFOLRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YOETUEMZNOLGDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpropyl carbonochloridate Chemical compound CC(C)COC(Cl)=O YOETUEMZNOLGDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KPEKTRARZLEBCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpropyl piperazine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)COC(=O)N1CCNCC1 KPEKTRARZLEBCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PBJWXQXXAGFSOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-n-cyclohexyl-2-n-ethylpyridine-2,3-diamine Chemical compound N=1C=CC=C(N)C=1N(CC)C1CCCCC1 PBJWXQXXAGFSOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IIXYTWTZMGUQPT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-piperidin-4-ylpropan-2-ol Chemical compound CC(C)(O)C1CCNCC1 IIXYTWTZMGUQPT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JOHFJTBDUSVGQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(trifluoromethyl)piperidine Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C1CCCNC1 JOHFJTBDUSVGQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-azaniumyl-2-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound NCC(O)C(O)=O BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OPXYNEYEDHAXOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-oxobutanenitrile Chemical compound CC(=O)CC#N OPXYNEYEDHAXOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OABUKBBBSMNNPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4-difluoropiperidin-1-ium;chloride Chemical compound Cl.FC1(F)CCNCC1 OABUKBBBSMNNPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MJOUJKDTBGXKIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4-difluoropiperidine Chemical compound FC1(F)CCNCC1 MJOUJKDTBGXKIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IMOLPSNRLZLWQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromo-2,3-difluorobenzaldehyde Chemical compound FC1=C(F)C(C=O)=CC=C1Br IMOLPSNRLZLWQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UZOFELREXGAFOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methylpiperidine Chemical compound CC1CCNCC1 UZOFELREXGAFOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MMFGGDVQLQQQRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-bromo-2-fluorobenzaldehyde Chemical compound FC1=CC=C(Br)C=C1C=O MMFGGDVQLQQQRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MKKSTJKBKNCMRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde Chemical compound OC1=CC=C(Br)C=C1C=O MKKSTJKBKNCMRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MOSUYPAVZUSBNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-chloro-5-nitropyridine-3-carbonitrile Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC(C#N)=CN=C1Cl MOSUYPAVZUSBNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7553-56-2 Chemical compound [I] ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WXMOSJJKOOTXLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=C(C=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)NO)C=C1)F Chemical compound C(C)OC1CCN(CC1)C1=NC=C(C=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C(O2)C(=O)NO)C=C1)F WXMOSJJKOOTXLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JDYHSMJZBWATIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1CCC(CC1)C2=C(C=CC=N2)NS(=O)(=O)C3=CC4=C(C=C3)C=C(O4)C(=O)NO Chemical compound C1CCC(CC1)C2=C(C=CC=N2)NS(=O)(=O)C3=CC4=C(C=C3)C=C(O4)C(=O)NO JDYHSMJZBWATIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BJBWJPWTPKWOPB-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1CN(CCC1(F)F)C2=C(C=CC=N2)NS(=O)(=O)C3=CC4=C(C=C3)C=C(O4)C(=O)NO Chemical compound C1CN(CCC1(F)F)C2=C(C=CC=N2)NS(=O)(=O)C3=CC4=C(C=C3)C=C(O4)C(=O)NO BJBWJPWTPKWOPB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DHYDIKPQNBJKMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(C)OC(N(CC1)CCC1OC1=NC=CC=C1NS(C1=CC(OC(C(OO)=O)=C2)=C2C=C1)(=O)=O)=O Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(N(CC1)CCC1OC1=NC=CC=C1NS(C1=CC(OC(C(OO)=O)=C2)=C2C=C1)(=O)=O)=O DHYDIKPQNBJKMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CEOUWFVEHXODGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3 Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3 CEOUWFVEHXODGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QYQSMMZYXVDSHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC(=O)C1=CC2=C(S1)C=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3 Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC2=C(S1)C=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3 QYQSMMZYXVDSHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GJUZJBNCUVYXFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1)C=CC(=C2)SCC2=CC=CC=C2 Chemical compound COC(=O)C=1OC2=C(C1)C=CC(=C2)SCC2=CC=CC=C2 GJUZJBNCUVYXFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KHYHTDZZWGMYMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC(C1=CC(C=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3)=C2S1)=O Chemical compound COC(C1=CC(C=C(C=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3)=C2S1)=O KHYHTDZZWGMYMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KZBUYRJDOAKODT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine Chemical compound ClCl KZBUYRJDOAKODT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000007067 DNA methylation Effects 0.000 description 1
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formaldehyde Chemical compound O=C WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010023925 Histone Deacetylase 6 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100039999 Histone deacetylase 2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102100021455 Histone deacetylase 3 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101001035011 Homo sapiens Histone deacetylase 2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000899282 Homo sapiens Histone deacetylase 3 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012359 Methanesulfonyl chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108091023040 Transcription factor Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000040945 Transcription factor Human genes 0.000 description 1
- OKJPEAGHQZHRQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triiodomethane Natural products IC(I)I OKJPEAGHQZHRQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003042 antagnostic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001093 anti-cancer Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002246 antineoplastic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940041181 antineoplastic drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- NCNRHFGMJRPRSK-MDZDMXLPSA-N belinostat Chemical compound ONC(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CC(S(=O)(=O)NC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 NCNRHFGMJRPRSK-MDZDMXLPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003094 belinostat Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000005605 benzo group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- AGEZXYOZHKGVCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl bromide Chemical compound BrCC1=CC=CC=C1 AGEZXYOZHKGVCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- AEILLAXRDHDKDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromomethylcyclopropane Chemical compound BrCC1CC1 AEILLAXRDHDKDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000484 butyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 208000035269 cancer or benign tumor Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012230 colorless oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- JZRHODNPRNTXKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexylhydrazine;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.NNC1CCCCC1 JZRHODNPRNTXKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 231100000433 cytotoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000001472 cytotoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004069 differentiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009509 drug development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004064 dysfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008482 dysregulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007608 epigenetic mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- PVBRSNZAOAJRKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-sulfanylacetate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CS PVBRSNZAOAJRKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 210000003527 eukaryotic cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000008098 formaldehyde solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012362 glacial acetic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009036 growth inhibition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000004051 hexyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 206010020718 hyperplasia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 125000002883 imidazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000002779 inactivation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011630 iodine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- INQOMBQAUSQDDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodomethane Chemical compound IC INQOMBQAUSQDDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001972 isopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- FMKOJHQHASLBPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N isopropyl iodide Chemical compound CC(C)I FMKOJHQHASLBPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010534 mechanism of action Effects 0.000 description 1
- QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CS(Cl)(=O)=O QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MKIJJIMOAABWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-sulfanylacetate Chemical compound COC(=O)CS MKIJJIMOAABWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DLILIUSWDLJMCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-bromo-2-fluorobenzoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1F DLILIUSWDLJMCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JIBOKBLKZPAVHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 6-benzylsulfanyl-3-methyl-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylate Chemical compound CC1=C(SC2=C1C=CC(=C2)SCC3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)OC JIBOKBLKZPAVHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004702 methyl esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002950 monocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002757 morpholinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004108 n-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- AGVKXDPPPSLISR-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-ethylcyclohexanamine Chemical compound CCNC1CCCCC1 AGVKXDPPPSLISR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000740 n-pentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004123 n-propyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001971 neopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- LMYJGUNNJIDROI-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxan-4-ol Chemical compound OC1CCOCC1 LMYJGUNNJIDROI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- FWZRWHZDXBDTFK-ZHACJKMWSA-N panobinostat Chemical compound CC1=NC2=CC=C[CH]C2=C1CCNCC1=CC=C(\C=C\C(=O)NO)C=C1 FWZRWHZDXBDTFK-ZHACJKMWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960005184 panobinostat Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000001147 pentyl group Chemical group C(CCCC)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004193 piperazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003386 piperidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001436 propyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000003373 pyrazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003226 pyrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002098 pyridazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004076 pyridyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000714 pyrimidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007115 recruitment Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000022532 regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000012321 sodium triacetoxyborohydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003003 spiro group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000565 sulfonamide group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003527 tetrahydropyrans Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- DENPQNAWGQXKCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiophene-2-carboxamide Chemical compound NC(=O)C1=CC=CS1 DENPQNAWGQXKCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QERYCTSHXKAMIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiophene-2-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CS1 QERYCTSHXKAMIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000005758 transcription activity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004881 tumor cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 231100000588 tumorigenic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000000381 tumorigenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/41—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole
- A61K31/415—1,2-Diazoles
- A61K31/416—1,2-Diazoles condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. indazole
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/41—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole
- A61K31/4164—1,3-Diazoles
- A61K31/4178—1,3-Diazoles not condensed 1,3-diazoles and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. pilocarpine, nitrofurantoin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/41—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole
- A61K31/4196—1,2,4-Triazoles
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/41—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole
- A61K31/42—Oxazoles
- A61K31/423—Oxazoles condensed with carbocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/41—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole
- A61K31/4245—Oxadiazoles
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/41—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole
- A61K31/425—Thiazoles
- A61K31/428—Thiazoles condensed with carbocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/4353—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/4355—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems the heterocyclic ring system containing a five-membered ring having oxygen as a ring hetero atom
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/439—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom the ring forming part of a bridged ring system, e.g. quinuclidine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/4427—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/443—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems containing a five-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/4427—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/444—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring heteroatom, e.g. amrinone
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/4965—Non-condensed pyrazines
- A61K31/497—Non-condensed pyrazines containing further heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/498—Pyrazines or piperazines ortho- and peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. quinoxaline, phenazine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/4985—Pyrazines or piperazines ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/50—Pyridazines; Hydrogenated pyridazines
- A61K31/501—Pyridazines; Hydrogenated pyridazines not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/50—Pyridazines; Hydrogenated pyridazines
- A61K31/504—Pyridazines; Hydrogenated pyridazines forming part of bridged ring systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
- A61K31/506—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/535—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. 1,2-oxazines
- A61K31/5375—1,4-Oxazines, e.g. morpholine
- A61K31/5377—1,4-Oxazines, e.g. morpholine not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. timolol
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/28—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system, e.g. nootropic agents, cognition enhancers, drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/12—Antivirals
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D263/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-oxazole or hydrogenated 1,3-oxazole rings
- C07D263/52—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-oxazole or hydrogenated 1,3-oxazole rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D263/54—Benzoxazoles; Hydrogenated benzoxazoles
- C07D263/58—Benzoxazoles; Hydrogenated benzoxazoles with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached in position 2
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D277/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings
- C07D277/60—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D277/62—Benzothiazoles
- C07D277/68—Benzothiazoles with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached in position 2
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D307/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D307/77—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D307/78—Benzo [b] furans; Hydrogenated benzo [b] furans
- C07D307/82—Benzo [b] furans; Hydrogenated benzo [b] furans with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to carbon atoms of the hetero ring
- C07D307/84—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen
- C07D307/85—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen attached in position 2
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D333/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D333/50—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D333/52—Benzo[b]thiophenes; Hydrogenated benzo[b]thiophenes
- C07D333/62—Benzo[b]thiophenes; Hydrogenated benzo[b]thiophenes with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to carbon atoms of the hetero ring
- C07D333/68—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen
- C07D333/70—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen attached in position 2
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D409/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D413/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D413/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D471/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00
- C07D471/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D471/08—Bridged systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D487/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D477/00
- C07D487/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D477/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D487/04—Ortho-condensed systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D487/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D477/00
- C07D487/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D477/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D487/08—Bridged systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D491/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00
- C07D491/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D491/08—Bridged systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D491/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00
- C07D491/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D491/10—Spiro-condensed systems
- C07D491/107—Spiro-condensed systems with only one oxygen atom as ring hetero atom in the oxygen-containing ring
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a compound shown as a formula I, a stereoisomer thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound shown in the formula I and application of the compound in preparing HDAC inhibitor medicines. The compounds of the present invention or pharmaceutical compositions thereof may be used to treat cell proliferative disorders, autoimmune disorders, inflammation, neurodegenerative disorders or viral disorders.
Description
Technical Field
The present invention relates to HDAC inhibitors, methods of making and uses thereof.
Background
Tumor refers to a new organism formed by clonal abnormal hyperplasia caused by the loss of normal regulation and control of local tissue cells on the gene level under the action of various tumorigenic factors. Epigenetic mechanisms that cause gene inactivation mainly include DNA methylation, histone acetylation, and modifications of other components in chromatin higher order structures, which alter chromatin conformation, resulting in changes in gene transcription regulation, and dysregulation of gene transcription causing cell proliferation disorders, resulting in tumor production.
Histone acetylation plays a central role in transcriptional regulation in eukaryotic cells. Its action is regulated by a pair of functionally antagonistic proteases Histone Acetyltransferases (HATs) and Histone Deacetylases (HDACs). In normal cells, the pair of enzymes is in a state of dynamic equilibrium. In general, increased histone acetylation levels are associated with increased gene transcription activity, while too low acetylation levels are associated with suppressed gene expression. Studies have found that HDACs are overexpressed and recruited by transcription factors, leading to abnormal suppression of specific genes, leading to tumors and other diseases; inhibition of HDAC activity will lead to growth inhibition and apoptosis in many cancer cells. Therefore, HDACs have become the newest and most popular target in the current field of antineoplastic drug development.
HDAC inhibitors have the function of interfering with histone deacetylase. There are generally two broad categories: NAD + -dependent enzymes and Zn2+ -dependent enzymes. Zn2+ -dependent proteases include HDACs I (including HDACs 1,2, 3 and 8), II (including HDACs 4,5, 6, 7, 9 and 10), IV (including HDAC 11) subfamily; NAD + -dependent enzymes are mainly of the HDACs subgroup III. The mechanism of action of HDAC inhibitors is to modulate gene expression in the treatment of cancer by inhibiting HDAC, blocking the repression of gene expression due to dysfunction of HDAC recruitment, and altering chromatin structure by altering the degree of acetylation of histones. It has obvious curative effect on treating blood system tumor and solid tumor by inducing growth arrest, differentiation or apoptosis of tumor cell. HDAC inhibitors are tumor specific and cytotoxic to proliferating and quiescent variant cells, whereas normal cells are more than 10-fold tolerant to them and do not cause growth arrest and apoptosis in normal cells.
Five HDAC inhibitors are currently on the market. SAHA marketed in 2006, with a Pan-HDAC as an active target; FK-288 marketed in 2011 has the action targets of HDAC1 and HDAC 2; PXD101 marketed in 2014 has the action targets of HDAC1 and HDAC 2; the effect targets of the cidam amine marketed in 2015 are HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3 and HDAC 10; LBH589 marketed in 2015, the target of action is HDAC (MOLT-4 cells). The five HDAC inhibitors have certain problems in the aspects of anticancer activity, toxic and side effects, subtype selectivity and the like.
Therefore, there is an urgent need for a novel compound having histone deacetylase inhibitory activity.
Disclosure of Invention
The invention provides a compound shown as a formula I, or a stereoisomer or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
X1selected from N, CR2;
R、R1、R2And each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group, a 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl group;
R4is selected from-NRhRi、-ORc、-SRc、-(CH2)rRc4-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
r is 0, 1,2 or 3;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle;
Rh、Riare each independently selected from C1~C10Alkyl, 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted with m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
Rcselected from 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein cycloalkyl and heteroThe ring, spiro ring, heterospiro ring, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I is preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R is hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I1Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, and heteroaryl,3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R1Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I2Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R2Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula I3Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, each R3Is hydrogen, fluorine,Chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, the A ring in formula I is preferably selected from a benzene ring.
In some embodiments of the invention, the A ring in formula I is preferably selected from a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 5-membered aromatic heterocycle are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, the A ring in formula I is preferably selected from a 6-membered heteroaromatic ring. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-membered heteroaromatic ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I4Preferably 4-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, wherein the cycloalkyl may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, R4Selected from 4-6 membered cycloalkyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I4Preferably 4-to 10-membered heterocycle, wherein the heterocycle may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatom in the 4-10 membered heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, R4Is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I4Preferably selected from 6-12 membered spirocyclic ring and 6-12 membered heterospirocyclic ring, wherein the spirocyclic ring and the heterospirocyclic ring can be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-12 membered heterospirocycles are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, R4Is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I4Preferably selected from 6-to 10-membered bridged rings and 6-to 10-membered heterobridged rings, wherein the bridged rings and heterobridged rings can be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-10 membered heterobridged ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, R4Is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula IdIndependently preferably from halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively independently preferably selected from hydrogen and C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently preferably-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle. More preferably, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C4Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I4Is preferably selected from-NRhRi(ii) a Wherein R ish、RiAre respectively independently preferably selected from C1~C10Alkyl, 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle may be substituted with m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, Rh、RiAre each independently selected from C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, and 3-to 6-membered heterocycle. Further preferably, Rh、RiAre each independently selected from C1~C4An alkyl group, a 5-to 6-membered cycloalkyl group, a 5-to 6-membered heterocycle; wherein the heteroatom in the heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula I4Preferably selected from-ORc、-SRc、-(CH2)rRc(ii) a Wherein R iscPreferably selected from 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl and 3-to 10-membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl and heterocycle may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, RcSelected from 3-6 membered cycloalkyl and 3-6 membered heterocycle. Further preferably, RcSelected from 5-6 membered cycloalkyl and 5-6 membered heterocycle; wherein the heteroatom in the heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur.
Further, the compound of formula I is represented by formula II:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
X1selected from N, CR2;
R、R1、R2Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group, a 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl group;
the B ring is selected from 4-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle;
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula II is preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R is hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably isA trifluoromethyl group.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula II1Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R1Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula II2Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R2Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, the A ring in formula II is preferably selected from a benzene ring.
In some embodiments of the invention, the A ring in formula II is preferably selected from a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 5-membered aromatic heterocycle are nitrogen, oxygen,And (3) sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, the a ring in formula II is preferably selected from a 6-membered heteroaromatic ring. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-membered heteroaromatic ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, the B ring in formula II is preferably selected from 4-10 membered cycloalkyl, wherein the cycloalkyl group may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the B ring is selected from 4-6 membered cycloalkyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, the B ring in formula II is preferably selected from 4-to 10-membered heterocyclic rings, wherein the heterocyclic ring may be substituted with m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatom in the 4-10 membered heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, ring B is selected from
In some embodiments of the present invention, the ring B in formula II is preferably selected from 6-12 membered spirocyclic ring, 6-12 membered heterospirocyclic ring, wherein the spirocyclic ring and the heterospirocyclic ring may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-12 membered heterospirocycles are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, ring B is selected from
In some embodiments of the present invention, the ring B in formula II is preferably selected from 6-10 membered bridged rings, 6-10 membered heterobridged rings, wherein the bridged rings, heterobridged rings may be substituted with m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-10 membered heterobridged ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, ring B is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula IIdIndependently preferably from halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively independently preferably selected from hydrogen and C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently preferably-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle. More preferably, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C4Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
Still further, the compound of formula II is:
further, the compound of formula I is represented by formula III:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
X1selected from N, CR2;
R、R1、R2And each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group, a 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl group;
the B ring is selected from 4-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula III is preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R is hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula III1Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R1Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula III2Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R2Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula III3Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, each R3Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, ring a in formula III is preferably selected from a benzene ring.
In some embodiments of the invention, the A ring in formula III is preferably selected from a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 5-membered aromatic heterocycle are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, the a ring in formula III is preferably selected from a 6-membered heteroaromatic ring. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-membered heteroaromatic ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some of the present inventionIn embodiments, the B ring in formula III is preferably selected from 4-to 10-membered cycloalkyl groups, wherein the cycloalkyl group may be substituted with m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the B ring is selected from 4-6 membered cycloalkyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, the B ring in formula III is preferably selected from 4-to 10-membered heterocyclic rings, wherein the heterocyclic ring may be substituted with m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatom in the 4-10 membered heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, ring B is selected from
In some embodiments of the present invention, the ring B in formula III is preferably selected from 6-12 membered spirocyclic ring, 6-12 membered heterospirocyclic ring, wherein the spirocyclic ring and the heterospirocyclic ring may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-12 membered heterospirocycles are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, ring B is selected from
In some embodiments of the present invention, the ring B in formula III is preferably selected from the group consisting of a 6-to 10-membered bridged ring, a 6-to 10-membered heterobridged ring, wherein the bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted with m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-10 membered heterobridged ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, ring B is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula IIIdIndependently preferably from halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively independently preferably selected from hydrogen and C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently preferably-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle. More preferably, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C4Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
Still further, the compound of formula III is:
further, the compound of formula I is represented by formula IV:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
R、R1and each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group, a 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl group;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted by 0 to c3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle;
Rh、Riare each independently selected from C1~C10Alkyl, 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted with m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula IV is preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R is hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula IV1Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R1Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula IV3Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, each R3Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, ring a in formula IV is preferably selected from a benzene ring.
In some embodiments of the invention, the ring a in formula IV is preferably selected from a 6-membered heteroaromatic ring. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-membered heteroaromatic ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. IntoPreferably, ring A is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula IVh、RiAre respectively independently preferably selected from C1~C10Alkyl, 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle may be substituted with m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, Rh、RiAre each independently selected from C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, and 3-to 6-membered heterocycle. Further preferably, Rh、RiAre each independently selected from C1~C4An alkyl group, a 5-to 6-membered cycloalkyl group, a 5-to 6-membered heterocycle; wherein the heteroatom in the heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur.
Still further, the compound of formula IV is:
further, the compound of formula I is represented by formula V:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
R、R1and each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbare each independently selected fromHydrogen, C1~C10An alkyl group, a 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl group;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle;
Rcselected from 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula V is preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R is hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen,C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula V1Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R1Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula V3Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, each R3Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, ring A in formula V is preferably selected from the group consisting of phenyl rings.
In some embodiments of the invention, the ring a in formula V is preferably selected from a 6-membered heteroaromatic ring. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-membered heteroaromatic ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VcPreferably selected from 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl and 3-to 10-membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl and heterocycle may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, RcSelected from 3-6 membered cycloalkyl and 3-6 membered heterocycle. Further preferably, RcSelected from 5-6 membered cycloalkyl and 5-6 membered heterocycle; wherein the heteroatom in the heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur.
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula VdIndependently preferably from halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively independently preferably selected from hydrogen and C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently preferably-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle. More preferably, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C4Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
Still further, the compound of formula V is:
further, the compound of formula I is represented by formula VI:
in the formula,
x is selected from O, S;
R、R1and each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group, a 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl group;
R4selected from 4-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VI is preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R is hydrogen, fluoro, chloro, bromo, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VI1Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, R1Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula VI3Preferably hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl. More preferably, each R3Is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively hydrogen and C1~C4An alkyl group, a 3-to 4-membered cycloalkyl group; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, ring a in formula VI is preferably selected from a benzene ring.
In some embodiments of the invention, ring a in formula VI is preferably selected from a 5-membered heteroaromatic ring. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 5-membered aromatic heterocycle are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, ring a in formula VI is preferably selected from a 6-membered heteroaromatic ring. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-membered heteroaromatic ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, the A ring is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VI4Preferably 4-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, wherein the cycloalkyl may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, R4Selected from 4-6 membered cycloalkyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VI4Preferably 4-to 10-membered heterocycle, wherein the heterocycle may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatom in the 4-10 membered heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, R4Is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VI4Preferably selected from 6-12 membered spirocyclic ring and 6-12 membered heterospirocyclic ring, wherein the spirocyclic ring and the heterospirocyclic ring can be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-12 membered heterospirocycles are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, R4Is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VI4Preferably selected from 6-to 10-membered bridged rings and 6-to 10-membered heterobridged rings, wherein the bridged rings and heterobridged rings can be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, the heteroatoms in the 6-10 membered heterobridged ring are nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur. Further preferably, R4Is selected from
In some embodiments of the invention, each R in formula VIdIndependently preferably from halogen, cyano, C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively independently preferably selected from hydrogen and C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen radicalsSubstituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre preferably hydrogen and C, respectively1~C6Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently preferably-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle. More preferably, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C6Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C6An alkyl group; wherein R ise、RfAre respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 2RgSubstituted C1~C4Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; wherein R isa、RbAre respectively selected from hydrogen and C1~C4Alkyl, 3-6 membered cycloalkyl; wherein each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-6 membered aromatic ring, 5-6 membered aromatic heterocycle; wherein halogen is substituted C1~C4The alkyl group is preferably fluorine-substituted C1~C4An alkyl group; more preferably trifluoromethyl.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VI4Is preferably selected from-NRhRi(ii) a Wherein R ish、RiAre respectively independently preferably selected from C1~C10Alkyl, 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle may be substituted with m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, Rh、RiAre each independently selected from C1~C6Alkyl, 3-to 6-membered cycloalkyl, and 3-to 6-membered heterocycle. Further preferably, Rh、RiAre each independently selected from C1~C4An alkyl group, a 5-to 6-membered cycloalkyl group, a 5-to 6-membered heterocycle; wherein the heteroatom in the heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur.
In some embodiments of the invention, R in formula VI4Preferably selected from-ORc、-SRc、-(CH2)rRc(ii) a Wherein R iscPreferably selected from 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl and 3-to 10-membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl and heterocycle may be substituted by m RdAnd (4) substitution. More preferably, RcSelected from 3-6 membered cycloalkyl and 3-6 membered heterocycle. Further preferably, RcSelected from 5-6 membered cycloalkyl and 5-6 membered heterocycle; wherein the heteroatom in the heterocycle is nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur.
Still further, the compound of formula VI is:
the invention also provides the application of the compound or the stereoisomer thereof or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in preparing the HDAC inhibitor medicines.
Further, the medicament is a medicament for treating a cell proliferative disease, an autoimmune disease, inflammation, a neurodegenerative disease, or a viral disease.
Further, the cell proliferative disease is cancer.
Still further, the cancer includes colon cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, brain cancer, ovarian cancer, thyroid cancer.
Further, the HDAC is HDAC 6.
The invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition, which is a preparation prepared by taking the compound, or the stereoisomer or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as an active ingredient and adding pharmaceutically acceptable auxiliary materials.
Further, the preparation is an oral preparation, a transdermal absorption preparation or an injection preparation.
The invention also provides the application of the pharmaceutical composition in the preparation of HDAC inhibitor medicines.
Further, the medicament is a medicament for treating a cell proliferative disease, an autoimmune disease, inflammation, a neurodegenerative disease, or a viral disease.
Further, the cell proliferative disease is cancer.
Still further, the cancer includes colon cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, brain cancer, ovarian cancer, thyroid cancer.
Further, the HDAC is HDAC 6.
The compounds and derivatives provided in the present invention may be named according to the IUPAC (international union of pure and applied chemistry) or CAS (chemical abstracts service, Columbus, OH) naming system.
Definitions of terms used in connection with the present invention: the initial definitions provided herein for a group or term apply to that group or term throughout the specification unless otherwise indicated; for terms not specifically defined herein, the meanings that would be given to them by a person skilled in the art are to be given in light of the disclosure and the context.
"alkyl" refers to a saturated hydrocarbon chain having the indicated number of member atoms. E.g. C1~C10Alkyl refers to having 1 to 10 member atoms. The alkyl group may be linear or branched. Representative branched alkyl groups have one, two, or three branches. The alkyl group may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents as defined herein. Alkyl groups include methyl, ethyl, propyl (n-propyl and isopropyl), butyl (n-butyl, isobutyl and tert-butyl), pentyl (n-pentyl, isopentyl and neopentyl) and hexyl.
"cycloalkyl" refers to a saturated hydrocarbon ring having the indicated number of member atoms. Cycloalkyl groups may be monocyclic or fused. For example, a 4-10 membered cycloalkyl group refers to a cycloalkyl group having 4 to 10 member atoms, and a 3-10 membered cycloalkyl group refers to a cycloalkyl group having 3 to 10 member atoms. Cycloalkyl groups include cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, and the like. In one embodiment, a cycloalkyl group herein is cyclopropyl. In one embodiment, a cycloalkyl group herein is cyclobutyl. In one embodiment, a cycloalkyl group herein is cyclopentyl. In one embodiment, a cycloalkyl group herein is cyclohexyl.
"heterocycloalkyl", "heterocycle" refers to a saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic monocyclic, fused ring having the indicated number of member atoms, which carries heteroatoms such as nitrogen, oxygen, in place of one or more carbon atoms. The heterocycloalkyl group may be, in particular, a piperidinyl group, a tetrahydropyran group, a morpholinyl group, a piperazinyl group,And the like.
"spirocycloalkyl" and "spirocyclic" refer to alicyclic hydrocarbon molecules in which two carbocyclic rings share a common carbon atom.
"Heterospirocycloalkyl", "heterospirocyclic" refers to an alicyclic hydrocarbon molecule in which two carbocyclic rings share a single carbon atom, with heteroatoms such as nitrogen, oxygen replacing one or more carbon atoms. The hetero-spirocycloalkyl group may be specifically: and the like.
"bridged ring group", bridged ring "refers to a cyclic hydrocarbon in which any two rings share two carbon atoms which are not directly connected.
"Heterocyclyl", "heterobridged ring" refers to cyclic hydrocarbons in which any two rings share two carbon atoms not directly connected, with heteroatoms such as nitrogen, oxygen replacing one or more carbon atoms. The hetero-spirocycloalkyl group may be specifically:and the like.
"aromatic ring" means a single or multiple ring having aromatic character, such as phenyl.
"heteroaryl ring" refers to a single or fused ring having aromatic character with one or more carbon atoms replaced by heteroatoms such as nitrogen and oxygen. The heteroaromatic ring may specifically be pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, isoxazoleA group, a1, 2, 4-triazolyl group, an imidazolyl group,And the like.
"halogen" means fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine.
In the inventionOrRepresents R on the A ring4In the ortho position relative to the sulfonamide group.
In the present invention, "M" means mol/L; "mM" means mmol/L; "μ M" means μmol/L.
The term "room temperature" as used herein means 25. + -. 5 ℃.
The novel compound shown in the formula I shows good HDAC6 inhibition activity, and provides a new choice for clinically treating diseases related to abnormal HDAC6 activity.
Obviously, many modifications, substitutions, and variations are possible in light of the above teachings of the invention, without departing from the basic technical spirit of the invention, as defined by the following claims.
The present invention will be described in further detail with reference to the following examples. This should not be understood as limiting the scope of the above-described subject matter of the present invention to the following examples. All the technologies realized based on the above contents of the present invention belong to the scope of the present invention.
Detailed Description
The raw materials and equipment used in the embodiment of the present invention are known products and obtained by purchasing commercially available products.
The specific embodiments of the present invention are described in the following short form: TEA is triethylamine; DCM is dichloromethane; DMF is N, N-dimethylformamide; EA is ethyl acetate; NaH: sodium hydride; MeOH: methanol; CH (CH)3CN: acetonitrile; TFA: trifluoroacetic acid; PE: stone (stone)Oleyl ether
Synthesis of intermediate 4a and intermediate 4b
Ethyl 6-bromobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (intermediate 2 a):
4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (20g,99.5mmol) and ethyl 2-bromoacetate (18.3g,109.4mmol) were dissolved in 100mL of DMF under nitrogen, potassium carbonate (41.3g,298.5mmol) was added, and the reaction was stirred at 100 ℃ for 18 hours. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture was added to 500g of ice water and extracted 4 times with 500mL of ethyl acetate. The organic layers were combined and washed 1 time with 500mL of saturated sodium chloride. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 50:1 to 20:1) to give intermediate 2a 6-bromobenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (18.6g, yield 69.4%).
MS(ESI)m/z=269.0,271.0[M+1].
Ethyl 5-bromobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (intermediate 2 b):
intermediate 2b ethyl 5-bromobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (42% yield) was obtained following the synthesis of intermediate 2a using 5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde instead of 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde. MS (ESI) M/z 269.0,271.0[ M +1]
Ethyl 6- (benzylthio) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (intermediate 3 a):
ethyl 6-bromobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (18.6g,69.1mmol) was dissolved in 200mL of toluene under nitrogen, benzylthiol (10.3g,82.9mmol), N-diisopropylethylamine (26.8g,207.1mmol), 4, 5-bis (diphenylphosphino) -9, 9-dimethylxanthene (4.0g,6.9mmol) and tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (3.2g,3.5mmol) were added, air was replaced with nitrogen, and the reaction was warmed to reflux for 18 hours. After cooling to room temperature, 500mL of water was added, extraction was performed with ethyl acetate (300 mL. times.3), and the organic layers were combined and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 50:1 to 30:1) to give intermediate 3a 6- (benzylthio) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (19.5g, yield 90.3%).
MS(ESI)m/z=313.1[M+1]。
Ethyl 5- (benzylthio) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (intermediate 3 b):
the procedure for the synthesis of intermediate 3a was followed, using ethyl 5-bromobenzofuran-2-carboxylate instead of ethyl 6-bromobenzofuran-2-carboxylate, to give intermediate 3b ethyl 5- (benzylthio) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (91% yield). MS (ESI) M/z 313.1[ M +1]
Ethyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (intermediate 4 a):
ethyl 6- (benzylthio) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (19.5g,62.3mmol) was dissolved in 45mL of acetic acid and 15mL of water, N-chlorosuccinimide (33.3g,249.3mmol) was added in portions, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. After the reaction was complete, 200mL of water was added. Ethyl acetate extraction (200 mL. times.3) and the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 99:1 to 19:1) to give intermediate 4a 6- (chlorosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester as a yellow solid, (11.0g, yield 61.1%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ7.82(s,1H),7.76(s,1H),7.75(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.63(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),4.36(q,J=6.8Hz,2H),1.34(t,J=6.8,3H).
Ethyl 5- (chlorosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (intermediate 4 b):
using ethyl 5- (benzylthio) benzofuran-2-carboxylate as a starting material instead of ethyl 6- (benzylthio) benzofuran-2-carboxylate, the synthesis of intermediate 4a was followed to give intermediate 4b ethyl 5- (chlorosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (62.0% yield). Synthesis of intermediate 7a and intermediate 7b
Methyl 6-bromobenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate (intermediate 5 a):
4-bromo-2-fluorobenzaldehyde (10g,49.3mmol) and methyl 2-mercaptoacetate (12.0g,113.1mmol) were dissolved in 1.0L DMF, sodium hydride (59.2g,1.48mol, 60%) was added at 0 deg.C, after 3 hours of stirring reaction ice water (500L) was slowly added, ethyl acetate (200mL) was extracted 4 times, and the organic layers were combined and washed 1 time with saturated sodium chloride solution. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 99:1 to 19:1) to give intermediate 5a (10.9g, yield 81.5%). Ms (esi) M/z 271.0,273.0[ M +1].
5-Bromobenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (intermediate 5 b):
the intermediate 5b 5-bromobenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (yield 87%) was obtained according to the synthesis method of intermediate 5a using 5-bromo-2-fluorobenzaldehyde as a starting material instead of 4-bromo-2-fluorobenzaldehyde. Ms (esi) M/z 271.0,273.0[ M +1].
6-Benzylthenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (intermediate 6 a):
methyl 6-bromobenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate 5a (5.4g,19.7mmol) was dissolved in 100mL of toluene under nitrogen, benzylthiol (1.44g,23.6mmol), N-diisopropylethylamine (7.64g,59.1mmol,10.3mL), 4, 5-bis (diphenylphosphino) -9, 9-dimethylxanthene (1.14g,1.97mmol) and tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (902mg,985umol) were added, and the air was replaced with nitrogen, and the mixture was heated to reflux for 18 hours. After cooling to room temperature, 200mL of water was added, extraction was performed with ethyl acetate (200 mL. times.3), and the organic layers were combined and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 80:1 to 30:1) to give intermediate 6a 6- (benzylthio) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester as a pale yellow solid (4.0g, yield 64.6%). Ms (esi) M/z 315.1[ M +1].
5-Benzylthenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (intermediate 6 b):
the synthesis of 6a was performed using 5-bromobenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester 5b as the starting material instead of 6-bromobenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester 5a to give intermediate 6b 5-benzylsulfanylbenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester as a pale yellow solid (yield 76.0%).
Methyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) benzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate (intermediate 7 a):
methyl 6- (benzylthio) benzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate 6a (3.6g,11.5mmol) was dissolved in 21mL of acetic acid and 7mL of water, N-chlorosuccinimide (6.2g,46.0mmol) was added in portions, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. After the reaction was complete, 50mL of water was added. Ethyl acetate extraction (100 mL. times.3) and the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give intermediate 7a methyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) benzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate as a yellow solid (3.1g, 92.7% yield). The product was used in the next reaction without further purification.
Methyl 5- (chlorosulfonyl) benzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate (intermediate 7 b):
an oxidation reaction was carried out according to the synthesis method of 7a using 5-bromobenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester 6b as a starting material instead of 6- (benzylthio) benzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester to give intermediate 7b (yield 91.5%).
Example 14- (3- (2- (Hydroxyloxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (Compound 1)
The first step is as follows: 4- (3-Nitropyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (1A)
N-Boc-4-piperidinol (697mg,3.47mmol) was dissolved in 10mL THF at room temperature, NaH (139mg,3.47mmol, 60%) was added and stirred for 30min, 2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (500mg,3.15mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 30mL water and 50mL ethyl acetate were added, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate again (50mL × 2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spun dry to give 4- (3-nitropyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 1A as a brown oil (1.12g, 109.8%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 4- (3-aminopyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (1B)
At room temperature, 4- (3-nitropyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 1A (1.12g,3.47mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of MeOH, 10% Pd/C (200mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred under hydrogen atmosphere overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was spin dried to give 4- (3-aminopyridin-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 1B as a brown oil (1.02g, 87.4%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (1C)
Tert-butyl 4- (3-aminopyridin-2-yloxy) piperidine-1-carboxylate 1B (500mg,1.7mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, pyridine (0.41mL,5.1mmol) and intermediate 4a (542mg,1.88mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product tert-butyl 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonamido) pyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylate 1C (500mg, 53.8%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: 4- (3- (2- (Hydroxyloxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (Compound 1)
Tert-butyl 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylate 1C (150mg,0.27mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.24mL,4.05mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (54mg,1.35mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 1 as a white solid (5.7mg, 3.5%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ7.95–7.85(m,3H),7.72–7.52(m,3H),6.98(ddd,J=12.7,7.7,5.0Hz,1H),4.96–4.89(m,1H),3.31(dd,J=11.2,7.0Hz,2H),3.18–3.04(m,2H),1.49(td,J=8.7,4.1Hz,2H),1.39(s,9H).1.17-1.15(m,2H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=533[M+1].
Example 2N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (piperidin-4-yloxy) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 2)
The first step is as follows: 4- (3-Nitropyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (2A)
N-Boc-4-piperidinol (697mg,3.47mmol) was dissolved in 10mL THF at room temperature, NaH (139mg,3.47mmol, 60%) was added and stirred for 30min, 2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (500mg,3.15mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 30mL water and 50mL ethyl acetate were added, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate again (50mL × 2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spun dry to give 4- (3-nitropyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 2A as a brown oil (1.12g, 109.8%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 4- (3-aminopyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (2B)
At room temperature, 4- (3-nitropyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 2A (1.12g,3.47mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of MeOH, 10% Pd/C (200mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred under hydrogen atmosphere overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was spin dried to give 4- (3-aminopyridin-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 2B as a brown oil (1.02g, 87.4%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (2C)
Tert-butyl 4- (3-aminopyridin-2-yloxy) piperidine-1-carboxylate 2B (500mg,1.7mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, pyridine (0.41mL,5.1mmol) and intermediate 4a (542mg,1.88mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product tert-butyl 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonamido) pyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylate 2C (500mg, 53.8%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: 6- (N- (2- (piperidin-4-yloxy) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (2D)
Tert-butyl 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridine-2-oxy) piperidine-1-carboxylate 3C (400mg,0.733mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, HCl/EA (4M,5mL) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and after spin-drying the reaction solution the product ethyl 6- (N- (2- (piperidin-4-yloxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 2D (400mg, 113.2%) was obtained as a light brown solid which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fifth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (piperidin-4-yloxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 2)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (piperidin-4-yloxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 2D (200mg,0.415mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.37mL,6.23mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (83mg,2.08mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 2 as a white solid (24mg, 11.9%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ7.95–7.88(m,3H),7.72–7.59(m,2H),7.56(s,1H),6.99(ddd,J=7.7,5.0,1.0Hz,1H),5.02(d,J=5.4Hz,1H),3.20(t,J=11.5Hz,2H),2.98(dd,J=11.8,6.2Hz,2H),1.76(dt,J=11.3,7.1Hz,2H),1.45(dd,J=15.1,4.9Hz,2H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=433[M+1].
Example 3N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 3)
The first step is as follows: 2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (3A)
2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (300mg,1.89mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (0.78mL,5.67mmol) and 4-methylpiperidine (200mg,2.02mmol) were added, and the reaction was allowed to react at 40 ℃ for 1 hour and monitored by LC-MS to show completion. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 3A as a yellow oil (390mg, 93.3%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (3B)
2- (4-Methylpiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 3A (380mg,1.72mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (100mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen protection. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was spin dried to give 2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 3B as an off-white solid (300mg, 91.2%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (3C)
2- (4-Methylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 3B (300mg,1.57mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of DCM, pyridine (0.2mL,2.7mmol) and intermediate 4a (453mg,1.57mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and 100mL dichloromethane was added to the reaction, separated, washed with water (100mL), dried and spun to dryness to give the product 6- (N- (2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 3C (250mg, 35.9%) which was used directly in the next reaction. LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 444[ M +1].
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 3)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 3C (125mg,0.282mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.31mL,5.22mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH solution (56mg,1.39mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) purified to give compound 3 as a white solid (12mg, 9.9%). LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 431.1[ M +1].
Example 4N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2-morpholinopyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 4)
The first step is as follows: 4- (3-Nitropyridin-2-yl) morpholine (4A)
2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (300mg,1.89mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (0.78mL,5.67mmol) and morpholine (181mg,2.08mmol) were added, the reaction was refluxed for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spin-dried to give 4- (3-nitropyridin-2-yl) morpholine 4A as a yellow solid (376mg, 95%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2-morpholinylpyridin-3-amine (4B)
4- (3-Nitropyridin-2-yl) morpholine 4A (376mg,1.8mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (100mg) was added and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spun dry to give 2-morpholinopyridin-3-amine 4B as an off-white solid (300mg, 133%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2-Morpholinopyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (4C)
2-Morpholinylpyridin-3-amine 4B (80mg,0.447mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of DCM, and pyridine (0.1mL,1.34mmol) and intermediate 4a (142mg,0.492mmol) were added and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2-morpholinopyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 4C (150mg, 77.8%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2-morpholinylpyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 4)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2-morpholinopyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 4C (150mg,0.348mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.31mL,5.22mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (56mg,1.39mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS display reverseTo completion, 1M HCl was added to adjust pH to 8, spin dried, and the residue was subjected to prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) purified to give compound 4 as a white solid (4mg, 2.8%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.08–8.00(m,2H),7.95(q,J=9.1,7.8Hz,1H),7.70(dd,J=8.3,1.5Hz,1H),7.58(s,1H),7.38–7.17(m,1H),6.91(dd,J=7.8,4.8Hz,1H),3.52(t,J=4.6Hz,4H),2.98–2.86(m,4H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=419[M+1].
Example 56- (N- (2-Cyclohexylpyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 5)
The first step is as follows: 2- (cyclohexen-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (5A)
Dissolving 2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (300mg,1.89mmol) in 20mL 1, 4-dioxane, adding 1-cyclohexenylboronic acid pinacol ester (472mg,2.27mmol), Pd (dppf) Cl2(138mg,0.189mmol) and Na in sequence under the protection of nitrogen2CO3(601mg,5.67mmol), the reaction was refluxed overnight and monitored by LC-MS to show completion of the reaction. Insoluble matter was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was dried by rotary chromatography on silica gel (PE: EA ═ 8:1) to give 2- (cyclohexen-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 5A (320mg, 82.8%) as a product and a yellow oil.
The second step is that: 2-Cyclohexylpyridin-3-amine (5B)
2- (cyclohexen-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 5A (160mg,0.784mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (80mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen protection. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 2-cyclohexylpyridin-3-amine 5B as a colorless oil (130mg, 94%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2-Cyclohexylpyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (5C)
2-Cyclohexylpyridin-3-amine 5B (130mg,0.739mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, and pyridine (292mg,3.7mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (256mg,0.886mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2-cyclohexylpyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 5C (300mg, 120%) as a yellow oil which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: 6- (N- (2-Cyclohexylpyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 5)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2-cyclohexylpyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 5C (300mg,0.7mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.625mL,10.5mmol) was added, an aqueous NaOH (140mg,3.5mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 5 as a white solid (34mg, 11.5%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.44(dd,J=5.2,1.5Hz,1H),7.99–7.87(m,3H),7.63–7.50(m,2H),7.57(s,1H),2.63(dt,J=12.2,3.2Hz,1H),1.47(t,J=15.4Hz,3H),1.24(tt,J=13.2,7.0Hz,2H),1.02(t,J=12.3Hz,1H),0.93(s,1H),0.91(s,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=416[M+1].
Example 6N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 6)
The first step is as follows: 2- (4-Methoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (6A)
2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (300mg,1.89mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (0.52mL,3.78mmol) and 4-methoxypiperidine (240mg,2.08mmol) were added, the reaction was refluxed for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 6A as a yellow oil (500mg, 111.37%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (4-Methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (6B)
2- (4-Methoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 6A (500mg,2.11mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (200mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen protection. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was spin-dried to give 2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 6B as a black oil (410mg, 93.9%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (6C)
2- (4-Methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 6B (410mg,1.98mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of DCM, and pyridine (0.48mL,5.94mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (560mg,1.98mmol) were added, followed by stirring at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product 6- (N- (2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 6C (909mg, 100%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 6)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 6C (909mg,1.98mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (1.2mL,19.8mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH solution (320mg,7.92mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 6 as a white solid (116mg, 12.9%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.04(s,1H),7.99–7.92(m,2H),7.71–7.63(m,1H),7.58(s,1H),7.29(dd,J=7.8,1.7Hz,1H),6.90(dd,J=7.8,5.4Hz,1H),3.44–3.28(m,3H),3.21(s,3H),3.03–2.92(m,2H),1.82(tt,J=7.1,3.3Hz,2H),1.48(dtd,J=12.7,8.8,3.6Hz,2H)).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=447[M+1].
Example 7N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4-methanesulfonylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 7)
The first step is as follows: 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (7A)
Tert-butyl 4- (3-aminopyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate (1g,3.6mmol) was dissolved in 30mL of DCM, pyridine (0.87mL,10.8mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (1.56g,5.4mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product tert-butyl 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate 7A (1.14g, 59.6%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The second step is that: 6- (N- (2- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (7B)
Tert-butyl 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate 7A (1.14g,2.15mmol) was dissolved in 5mL MeOH at room temperature, HCl in EA (4M,20mL) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction and the solvent was spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (950mg, 94.7%) as a white solid which was used directly in the next reaction.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (4-Methanesulfonylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (7C)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 7B (50mg,0.117mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM at room temperature, pyridine (25mg,0.321mmol) and methanesulfonyl chloride (15mg,0.118mmol) were added sequentially, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was complete as monitored by LCMS and washed with water (50mL), dried and spun to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-methanesulfonylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 7C (54mg, 91.4%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4-methanesulfonylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 7)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-methanesulfonylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 7C (54mg,0.107mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.047mL,1.6mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (21mg,0.53mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 7 as a white solid (6mg, 11.4%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.09–7.99(m,2H),7.95(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.68(dd,J=8.2,1.6Hz,1H),7.58(s,1H),7.42(dd,J=7.9,1.7Hz,1H),6.98(dd,J=7.9,5.0Hz,1H),3.09–3.00(m,8H),2.81(s,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=496[M+1].
Example 8N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 8)
The first step is as follows: 3-Nitro-2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridine (8A)
Tetrahydropyran-4-ol (142mg,1.39mmol) was dissolved in 10mL THF at room temperature, NaH (56mg,1.39mmol, 60%) was added and stirred for 30min, 2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (200mg,1.26mmol) was added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 30mL water and 50mL ethyl acetate were added, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50mL × 2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spin dried to give 3-nitro-2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridine 8A as a brown oil (282mg, 100%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridin-3-amine (8B)
3-Nitro-2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridine 8A (282mg,1.26mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (100mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen protection. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridin-3-amine 8B (180mg, 73.7%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (8C)
2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridin-3-amine 8B (180mg,0.93mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, pyridine (0.22mL,2.79mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (268mg,0.93mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 8C (380mg, 91.8%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 8)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (tetrahydropyran-4-oxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 8C (380mg,0.93mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.76mL,12.8mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (170mg,4.25mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) purification to give compound 8 as a white solid (90mg, 23.4%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ7.95(s,1H),7.89(dt,J=6.7,1.8Hz,2H),7.64(ddt,J=17.0,8.3,1.7Hz,2H),7.55(s,1H),6.95(dd,J=7.6,4.9Hz,1H),4.87(tq,J=8.1,3.9Hz,1H),3.60(dq,J=11.8,4.0Hz,2H),3.26(ddt,J=11.4,8.8,2.5Hz,2H),1.61–1.50(m,2H),1.16(dtt,J=12.5,8.3,3.4Hz,2H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=434[M+1].
Example 96- (N- (2- (4-Benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxy-benzofuran 2-carboxamide (Compound 9)
The first step is as follows: 4- (3-Acetylaminopyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (9A)
Tert-butyl 4- (3-aminopyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate (200mg,0.72mmol) was dissolved in 5mL of pyridine at room temperature, acetic anhydride (147mg,1.44mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 30mL water and 50mL ethyl acetate were added, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate again (50mL × 2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spun dry to give 4- (3-acetamidopyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 9A as a brown solid (270mg, 117.3%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: n- (2- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide (9B)
Tert-butyl 4- (3-acetamidopyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate 9A (270mg,0.84mmol) was dissolved in 5mL of meoh at room temperature, HCl in EA (4M,10mL) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the solvent was spin dried under reduced pressure to give the product, N- (2- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide 9B (280mg, 99.4%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: n- (2- (4-Benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide (9C)
N- (2- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide 9B (185mg,0.84mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of tetrahydrofuran, triethylamine (0.35mL,2.52mmol) and benzyl bromide (287mg,1.68mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 30mL water and 50mL ethyl acetate were added to the reaction, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50mL × 2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spun to give N- (2- (4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide 9C (60mg, 23%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The fourth step: 2- (4-Benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (9D)
N- (2- (4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide 9C (60mg, 0.19mmol) was dissolved in 10mM MyOH at room temperature, NaOH (39mg,0.97mmol) was added and the reaction heated to reflux for 4 h and was monitored by LCMS to show completion. The reaction was spun down, pH adjusted to about 5 with 1M HCl, extracted with ethyl acetate (30mLx3), the organic layers combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spun down to give 2- (4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 9D (51mg, 98%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The fifth step: 6- (N- (2- (4-Benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (9E)
2- (4-Benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 9D (51mg,0.19mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, pyridine (0.053mL,0.57mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (55mg,0.19mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 9E (180mg, 182%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
And a sixth step: 6- (N- (2- (4-Benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxy-benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 9)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 9E (180mg,0.35mmol) was dissolved in 5mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.31mL,5.19mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (70mg,1.75mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 9 as a white solid (25mg, 19%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.06(s,2H),7.93-7.91(m,1H),7.70-7.68(m,1H),7.50-7.49(m,6H),7.39-7.38(m,1H),6.99-6.97(m,1H),4.30-4.28(m,2H),3.235-3.28(m,4H),3.03-2.99(m,4H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=508[M+1].
Example 106- (N- (2-cyclohexylethylamine) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -N-hydroxy-benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 10)
The first step is as follows: N-cyclohexyl-N-ethyl-3-nitropyridin-2-amine (10A)
2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (200mg,1.26mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (0.52mL,3.78mmol) and N-ethylcyclohexylamine (177mg,1.39mmol) were added, the reaction was refluxed for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give N-cyclohexyl-N-ethyl-3-nitropyridin-2-amine 10A as a yellow oil (314mg, 100%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: n is a radical of2-cyclohexyl-N2-ethyl-pyridine-2, 3-diamine (10B)
N-cyclohexyl-N-ethyl-3-nitropyridin-2-amine 10A (314mg,1.26mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (100mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen protection. LCMS shows that the reaction is finished, Pd/C is removed by filtration, and N is obtained after filtrate is dried by rotation2-cyclohexyl-N2Ethyl-pyridine-2, 3-diamine 10B, a black oil (190mg, 68.8%), was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2-cyclohexylethylamine) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (10C)
Will N2-cyclohexyl-N2-Ethyl-pyridine-2, 3-diamine 10B (190mg,0.868mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, and pyridine (0.0.21mL,2.6mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (250mg,0.868mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2-cyclohexylethylamine) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 10C (409mg, 100%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: 6- (N- (2-cyclohexylethylamine) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -N-hydroxy-benzofuran-2-carboxamide (10)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2-cyclohexylethylamine) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 10C (180mg,0.35mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.31mL,5.19mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (70mg,1.75mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 10 as a white solid (25mg, 14%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.08–7.92(m,3H),7.67(tq,J=6.3,1.5Hz,1H),7.59(d,J=2.7Hz,1H),7.27(ddd,J=8.3,5.7,1.7Hz,1H),6.90(dd,J=7.9,5.4Hz,1H),3.58(s,1H),3.42–3.34(m,2H),1.67(dd,J=23.2,12.6Hz,4H),1.50(d,J=12.3Hz,1H),1.32(d,J=12.8Hz,2H),1.06(dq,J=52.5,12.8Hz,3H),0.83(qd,J=6.5,6.0,3.2Hz,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=459[M+1].
Example 11N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 11)
The first step is as follows: 2- (4-Ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (11A)
2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (200mg,1.26mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (0.52mL,3.78mmol) and 4-ethoxypiperidine hydrochloride (250mg,1.51mmol) were added, the reaction was refluxed for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 2- (4 ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 11A as a yellow oil (316mg, 100%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (11B)
2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 11A (316mg,1.26mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (100mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen protection. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 11B (330mg, 118%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (11C)
2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 11B (278mg,1.26mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, and pyridine (0.3mL,3.78mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (264mg,1.26mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 11C (570mg, 95.8%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (11)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 11C (570mg,1.20mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (1.07mL,18.1mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH solution (240mg,6mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 11 as a white solid (114mg, 20.4%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.05–7.94(m,3H),7.72(dd,J=8.4,1.6Hz,1H),7.61(s,1H),7.32(dd,J=7.9,1.7Hz,1H),6.89(dd,J=7.8,5.0Hz,1H),3.49–3.27(m,5H),2.83(ddd,J=12.8,9.7,2.9Hz,2H),1.80(dq,J=12.5,3.7Hz,2H),1.48(ddt,J=13.2,8.9,4.5Hz,2H),1.10(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=461[M+1].
Example 126- (N- (2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxy-benzofuran 2-carboxamide (Compound 12)
The first step is as follows: n- (2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide (12A)
N- (2- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide 9B (300mg,0.895mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of tetrahydrofuran, triethylamine (0.37mL,2.69mmol) and 2-iodopropane (152mg,0.895mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 30mL water and 50mL ethyl acetate were added to the reaction, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50mL × 2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spun to dryness to give N- (2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide 12A (100mg, 28%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (4-Isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (12B)
N- (2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) acetamide 12A (100mg, 0.352mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, NaOH (46mg,1.14mmol) was added and heated to reflux for 16 h and LCMS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction was spun down, pH adjusted to about 5 with 1M HCl, extracted with ethyl acetate (30mLx3), the organic layers combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spun down to give 2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 12B (84mg, 100%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (12C)
2- (4-Isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 12B (84mg,0.382mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, pyridine (0.1mL,1.146mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (110mg,0.382mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 12C (180mg, 100%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: 6- (N- (2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -N-hydroxy-benzofuran 2-carboxamide (12)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-isopropylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 12C (180mg,0.382mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.34mL,5.78mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (76mg,1.91mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to afford compound 12 as a white solid (19mg, 9%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.11–8.03(m,2H),7.97(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.74(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.46(d,J=7.9Hz,1H),7.01(dd,J=8.0,4.8Hz,1H),3.51–3.29(m,5H),3.10–2.92(m,4H),1.24(d,J=6.4Hz,6H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=460[M+1].
Example 134- (3- (2- (hydroxylamine carbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylic acid isobutyl ester (Compound 13)
The first step is as follows: 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylic acid isobutyl ester (13A)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 7B (100mg,0.233mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM at room temperature, pyridine (0.1mL,1.165mmol) and isobutyl chloroformate (32mg,0.233mmol) were added in that order, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was complete as monitored by LCMS, and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product isobutyl 4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonamido) pyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate 13A (123mg, 100%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The second step is that: 4- (3- (2- (hydroxylamine carbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridin-2-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylic acid isobutyl ester (13)
4- (3- (2- (ethoxycarbonyl) benzofuran-6-sulfonylamino) pyridine-2-one at room temperatureYl) piperazine-1-carboxylic acid isobutyl ester 13A (200mg,0.377mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH, aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.34mL,5.66mmol) was added, and an aqueous solution of NaOH (75mg,1.86mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to afford compound 13 as a white solid (22mg, 11%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.69(s,1H),9.67(s,1H),8.07(dd,J=4.8,1.7Hz,1H),8.01–7.94(m,2H),7.71(dd,J=8.2,1.6Hz,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.41(dd,J=7.8,1.7Hz,1H),6.95(dd,J=7.8,4.7Hz,1H),3.79(d,J=6.5Hz,2H),3.34(s,2H)2.92–2.84(m,4H),1.86(hept,J=6.7Hz,1H),0.88(d,J=6.7Hz,6H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=518[M+1].
EXAMPLE 14N-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 14)
The first step is as follows: 5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (14A)
2, 5-dichloro-3-nitropyridine (200mg,1.04mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (0.43mL,3.12mmol) and 4-methoxypiperidine (143mg,1.24mmol) were added, the reaction was refluxed for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 14A as a yellow oil (290mg, 103%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (14B)
5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 14A (500mg,2.11mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of MeOH, Raney's nickel (300mg) was added, and hydrazine hydrate (1mL) was slowly added dropwise with cooling in an ice bath, followed by reaction for 1 hour in an ice bath. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 14B as a yellow oil (258mg, 100%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (14C)
5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 14B (230mg,1.07mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of DCM, and pyridine (0.26mL,3.21mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (310mg,1.07mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 14C (100mg, 21.3%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (14)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 14C (100mg,0.2mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.18mL,3.0mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (40mg,1.0mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 14 as a white solid (1.15mg, 1.2%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.72(s,1H),9.46(s,1H),8.10–7.95(m,3H),7.73(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),7.61(s,1H),7.35(d,J=2.4Hz,1H),3.27–3.12(m,6H),2.68(dd,J=22.4,2.9Hz,2H),1.73(tt,J=7.5,3.4Hz,2H),1.39(dtd,J=12.8,9.2,3.6Hz,2H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=481.0[M+1].
Example 15N-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 15)
The first step is as follows: 5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (15A)
2, 5-dichloro-3-nitropyridine (200mg,1.04mmol) was dissolved in 10mL 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (0.43mL,3.12mmol) and piperidine (106mg,1.24mmol) were added, the reaction was refluxed for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 15A as a yellow oil (270mg, 107.5%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (15B)
5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 15A (270mg,1.12mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of MeOH, Raney-Ni (300mg) was added, and hydrazine hydrate (1mL) was slowly added dropwise with cooling in an ice bath, and the reaction was carried out for 1 hour in an ice bath. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 15B as a yellow oil (236mg, 100%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (15C)
5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 15B (233mg,1.1mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, and pyridine (0.27mL,3.3mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (318mg,1.1mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 15C (50mg, 9.8%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (15)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 15C at room temperature(50mg,0.108mmol) was dissolved in 5mL MeOH, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.1mL,1.62mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH (22mg,0.54mmol) solution was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 15(5.0mg, 8.12%) as a white solid.
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.10–7.98(m,2H),7.97(dd,J=8.3,2.8Hz,1H),7.71(dd,J=8.2,1.8Hz,1H),7.59(d,J=2.8Hz,1H),7.29(dd,J=5.3,2.6Hz,1H),,2.87(t,J=4.2Hz,4H),1.41(s,6H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=451.0[M+1].
Example 16N-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 16)
The first step is as follows: 5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (16A)
2-chloro-3-nitro-5-fluoropyridine (150mg,0.85mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of acetonitrile at room temperature, potassium carbonate (235mg,1.7mmol) and 4, 4-difluoropiperidine hydrochloride (147mg,0.94mmol) were added, the reaction was refluxed for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 5-fluoro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 16A as a yellow oil (190mg, 85.6%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (16B)
5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 16A (190mg,0.73mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (100mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen protection. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 16B as a yellow oil (140mg, 83.2%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (16C)
5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 16B (140mg,0.61mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, and pyridine (0.15mL,1.83mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (176mg,0.61mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 16C (210mg, 68%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (16)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 16C (210mg,0.435mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.39mL,6.52mmol) was added, an aqueous NaOH solution (87mg,2.18mmol) was added dropwise with stirring, and stirring was carried out at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 16(23mg, 9%) as a white solid.
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.70(s,1H),9.94(s,1H),9.45(s,1H),8.14–8.04(m,2H),7.99(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.79(dd,J=8.3,1.6Hz,1H),7.62–7.49(m,2H),2.80(t,J=5.5Hz,4H),1.97(tt,J=14.1,5.5Hz,4H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=471.0[M+1].
Example 17N-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 17)
The first step is as follows: 5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (17A)
2-chloro-3-nitro-5-fluoropyridine (150mg,0.85mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of acetonitrile at room temperature, and potassium carbonate (352mg,2.55mmol) and piperidine (86.9mg,1.02mmol) were added to react at room temperature for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitored to show completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.1), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 5-fluoro-2- (4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 17A as a yellow oil (190mg, 99.2%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (17B)
5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 17A (190mg,0.84mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (19mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under a hydrogen atmosphere. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 17B as a yellow oil (140mg, 85.4%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (17C)
5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 17B (140mg,0.717mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, pyridine (0.78mL,7.17mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (207mg,0.717mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 17C (240mg, 74.8%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (17)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 17C (240mg,0.54mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.48mL,8.12mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH solution (108mg,2.7mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, 1M HCl adjusted pH to 8, spin dried, and residue prep-HPLC(0.5%TFA in CH3CN/H2O) to give compound 17(55mg, 23.6%) as a white solid.
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.70(s,1H),9.51(s,2H),8.12(s,1H),8.06(d,J=2.8Hz,1H),7.97(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.78(dd,J=8.3,1.6Hz,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.44(dd,J=9.6,2.8Hz,1H),2.67(t,J=5.1Hz,4H),1.52–1.36(m,6H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=435[M+1].
EXAMPLE 18N-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 18)
The first step is as follows: 5-chloro-2- (4 ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (18A)
2, 5-dichloro-3-nitropyridine (250mg,1.3mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (0.54mL,3.9mmol) and 4-ethoxypiperidine hydrochloride (236mg,1.42mmol) were added, the reaction was refluxed for 1 hour, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 18A as a yellow oil (430mg, 116%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (18B)
5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 18A (430mg,1.5mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of MeOH, Raney-Ni (300mg) was added, and hydrazine hydrate (1mL) was slowly added dropwise with cooling in an ice bath, and the reaction was carried out for 1 hour in an ice bath. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 18B as a yellow solid (320mg, 83.1%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (18C)
5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 18B (320mg,1.25mmol) was dissolved in 5mL of pyridine, and 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (361mg,1.25mmol) was added, followed by stirring at 80 ℃ overnight. LCMS shows that the reaction is finished, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate are added to the reaction solution to dissolve the residue, an ethyl acetate layer is separated, an aqueous layer is extracted by ethyl acetate again (50mL multiplied by 2), organic layers are combined, and the mixture is dried by anhydrous sodium sulfate and then is dried in a rotary manner to obtain the product, namely 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 18C (453mg, 67.7%) which is directly used for the next reaction. The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (18)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 18C (453mg,0.892mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.8mL,13.4mmol) was added, an aqueous solution of NaOH (179mg,4.47mmol) was added dropwise with stirring, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 18(34mg, 7.4%) as a white solid.
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.10–8.00(m,2H),7.97(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.71(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.29(d,J=2.4Hz,1H),3.38(q,J=7.0Hz,2H),3.31(dq,J=8.5,4.3Hz,1H),3.18(dt,J=12.3,4.3Hz,2H),2.66(ddd,J=12.8,9.8,2.9Hz,2H),,1.70(dq,J=12.3,3.7Hz,2H),1.42–1.29(m,2H),1.05(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=495[M+1].
Example 19N-hydroxy-6- (N- (3-trifluoromethylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 19)
The first step is as follows: 3-Nitro-2- (3-trifluoromethylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridine (19A)
2-chloro-3-nitropyridine (317mg,2.0mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of 1, 4-dioxane at room temperature, TEA (607mg,6.0mmol) and 3-trifluoromethylpiperidine (320mg,2.09mmol) were added, and the reaction was heated at 60 ℃ for 1 hour and monitored by LC-MS to show completion. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the solvent, 30mL of water and 50mL of ethyl acetate were added to dissolve the residue, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spin-dried to give 3-nitro-2- (3-trifluoromethylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridine 19A as a yellow oil (550mg, 99.9%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (3-Trifluoromethylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (19B)
3-Nitro-2- (3-trifluoromethylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridine 19A (550mg,2.0mmol) was dissolved in 30mL MeOH at room temperature, 10% Pd/C (50mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight under hydrogen protection. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Pd/C was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 2- (3-trifluoromethylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 19B (500mg, 102%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (3-trifluoromethyl) -piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (19C)
2- (3-Trifluoromethylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 19B (500mg,2mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of DCM, and pyridine (0.48mL,6mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (584mg,2mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product 6- (N- (2- (3-trifluoromethyl) -piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 19C (430mg, 42.4%) which was used directly in the next reaction.
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (3-trifluoromethylpiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (19)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (3-trifluoromethyl) -piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 19C (430mg,0.865mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.77mL,13mmol) was added, and an aqueous NaOH solution (173mg,4.33mmol) was added dropwise with stirring at room temperatureStirred for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 19(130mg, 30.1%) as a white solid.
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.65(s,1H),8.07(s,1H),7.99–7.87(m,3H),7.76(dd,J=8.2,1.6Hz,1H),7.54(s,1H),7.46(dd,J=8.3,4.5Hz,1H),4.14(t,J=12.2Hz,1H),3.92(td,J=12.7,3.2Hz,1H),3.74(d,J=11.8Hz,1H),3.65–3.56(m,1H),3.41(ddq,J=12.4,8.8,4.1Hz,1H),2.31(qt,J=13.5,3.9Hz,1H),1.97(d,J=12.6Hz,1H),1.89(d,J=14.3Hz,1H),1.66
(qd,J=12.9,4.1Hz,1H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=485[M+1].
Example 20N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- ((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 20)
The first step is as follows: 6- (N- (2- ((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (20A)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (piperidin-4-yloxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (82mg,0.20mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of methanol at room temperature, and 35-40% formaldehyde solution (82mg,1.0mmol), glacial acetic acid (12mg,0.2mmol) and anhydrous sodium sulfate (574mg,4.0mmol) were added, followed by sodium triacetoxyborohydride (214mg,1.0mmol), and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 5 h. 20mL of water was added, extracted with 50mL of dichloromethane (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and dried by spin-drying to give ethyl 6- (N- (2- ((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 20A as a pale yellow solid (75mg, 80.8%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification. LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 460.3[ M +1].
The second step is that: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- ((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 20)
At room temperature, 6- (N- (2- ((1-)Methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 20A (430mg,0.865mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.77mL,13mmol) was added, an aqueous solution of NaOH (173mg,4.33mmol) was added dropwise with stirring, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 20(130mg, 30.1%) as a white solid. LC-MS M/z (ESI) ═ 447.1[ M +1].
Example 21N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- ((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 21)
The first step is as follows: 2- (3-Nitropyridin-2-yl) octahydrocyclopenta [ c ] pyrrole (21A)
2-fluoro-3-nitropyridine (282mg,2.0mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DMF at room temperature and cesium carbonate (1.29mg,3.97mmol) and octahydrocyclopenta [ c ] pyrrole (221mg,2.0mmol) were added and the reaction was allowed to react for 2 h at room temperature with TLC monitoring showing completion. 30mL of water was added, extraction was performed with 50mL of ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, 100 mL. times.2 was washed with saturated brine, and the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then dried by spin-drying to give 21A as a yellow oil (400mg, 86.4%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (hexahydrocyclopenta [ c ] pyrrol-2 (1H) -yl) pyridin-3-amine (21B)
To 2- (3-nitropyridin-2-yl) octahydrocyclopenta [ C ] pyrrole 21A (400mg,1.71mmol) was added 10mL of MeOH and 10mL of dichloromethane, 10% Pd/C (40mg) at room temperature, and the reaction was stirred under a hydrogen atmosphere overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was dried by spinning to give 21B (320mg, 91.8%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (hexahydrocyclopenta [ C ] pyrrol-2 (1H) -yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (21C)
2- (Hexahydrocyclopenta [ c ] pyrrol-2 (1H) -yl) pyridin-3-amine 21B (200mg,0.98mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DCM, pyridine (389mg,4.92mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (426mg,1.48mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was added with 100mL of dichloromethane, washed with water (50mL × 2), the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (dichloromethane: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 1:6 to 1:4) to give 21C as a pale yellow solid (400mg, 89.3%). LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 456.2[ M +1].
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- ((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 21)
Reacting 6- (N- (2- (hexahydrocyclopenta [ c ]) at room temperature]Pyrrol-2 (1H) -yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 21C (400mg,0.878mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.580mg,8.78mmol) was added, and a solution of NaOH (105mg,2.63mmol) in water (0.5mL) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 21 as a white solid (165mg, 42.5%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.69(s,1H),8.07(s,1H),7.99(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.95(dd,J=5.3,1.7Hz,1H),7.87(s,1H),7.63(dd,J=8.3,1.4Hz,1H),6.86(d,J=7.1Hz,1H),6.56(s,1H),3.80-3.66(m,1H),3.34(d,J=10.4Hz,2H),2.69-2.57(m,2H),1.74(dt,J=14.1,7.1Hz,2H),1.68-1.59(m,1H),1.59-1.46(m,1H),1.42-1.30(m,2H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=443.1[M+1].
Example 22N-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4- (2-hydroxyprop-2-yl) piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 22)
The first step is as follows: 2- (1- (3-Nitropyridin-2-yl) piperidin-4-yl) propan-2-ol (22A)
2-fluoro-3-nitropyridine (300mg,2.0mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DMF at room temperature, cesium carbonate (1.29mg,3.97mmol) and 2- (piperidin-4-yl) propan-2-ol (333mg,2.32mmol) were added and the reaction was allowed to react for 2 hours at room temperature with TLC monitoring indicating completion. 30mL of water was added, extraction was performed with 50mL of ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, 100 mL. times.2 was washed with saturated brine, and the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then dried by spin-drying to give 22A as a yellow oil (500mg, 89.3%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (1- (3-Aminopyridin-2-yl) piperidin-4-yl) propan-2-ol (22B)
To 2- (1- (3-nitropyridin-2-yl) piperidin-4-yl) propan-2-ol 22A (500mg,1.88mmol) were added 10mL of DMEOH and 10mL of dichloromethane, 10% Pd/C (100mg) at room temperature, and the reaction was stirred under a hydrogen atmosphere overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was dried by spinning to give 22B (400mg, 90.2%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (4- (2-hydroxypropan-2-yl) piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (22C)
2- (1- (3-Aminopyridin-2-yl) piperidin-4-yl) propan-2-ol 22B (400mg,1.7mmol) was dissolved in 15mL DCM, pyridine (672mg,8.5mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (490mg,1.7mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was added with 100mL of dichloromethane, washed with water (50mL × 2), the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (dichloromethane: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 1:6 to 1:4) to give 22C as a white solid (600mg, 72.4%).1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ8.10(s,1H),8.06(d,J=3.8Hz,1H),7.88(dd,J=8.1,1.4Hz,1H),7.83-7.75(m,2H),7.53(d,J=0.8Hz,1H),7.03(s,1H),4.46(q,J=7.2Hz,2H),2.83-2.60(m,4H),1.86-1.73(m,2H),1.49-1.35(m,3H),1.44(t,J=7.2Hz,3H),1.24(s,6H).
The fourth step: n-hydroxy-6- (N- (2- (4- (2-hydroxyprop-2-yl) piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxamide (compound 22)
Reacting 6- (N- (2- (4- (2-hydroxypropane-))2-Yl) piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 22C (600mg,1.23mmol) was dissolved in 15mL MeOH, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.813mg,12.3mmol) was added, and a solution of NaOH (148mg,3.7mmol) in water (0.5mL) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 22 as a white solid (300mg, 51.4%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.67(s,1H),9.56(s,1H),8.03(dd,J=4.9,1.7Hz,1H),7.99(s,1H),7.95(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.70(dd,J=8.3,1.5Hz,1H),7.58(s,1H),7.33(dd,J=7.8,1.7Hz,1H),6.87(dd,J=7.8,4.9Hz,1H),3.46(d,J=11.7Hz,2H),2.58-2.42(m,2H),1.57(d,J=9.1Hz,2H),1.25-1.14(m,3H),0.99(s,6H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=475.2[M+1].
Example 236- (N- (2- (4, 4-Difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 23)
The first step is as follows: 2- (4, 4-Difluoropiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine (23A)
2-fluoro-3-nitropyridine (300mg,2.1mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DMF at room temperature, cesium carbonate (2.06mg,6.33mmol) and 4, 4-difluoropiperidine (331mg,2.1mmol) were added and the reaction was allowed to react for 10 h at room temperature with TLC monitoring indicating completion. 30mL of water was added, extraction was performed with 50mL of ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, 100 mL. times.2 was washed with saturated brine, and the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then dried by spin-drying to give 23A as a yellow oil (500mg, 97.4%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (4, 4-Difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (23B)
To 2- (4, 4-Difluoropiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 23A (500mg,2.06mmol) was added 10mL of MeOH and 10mL of dichloromethane, 10% Pd/C (100mg) at room temperature, and the reaction was stirred under a hydrogen atmosphere overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was dried by spinning to give 23B (400mg, 91.3%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (4, 4-Difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (23C)
2- (4, 4-Difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 23B (400mg,1.88mmol) was dissolved in 15mL DCM, pyridine (742mg,9.38mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (542mg,1.88mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was added with 100mL of dichloromethane, washed with water (50mL × 2), the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (dichloromethane: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 1:6 to 1:4) to give 23C as a white solid (600mg, 72.4%).
1H NMR(400MHz,CDCl3)δ8.10(d,J=1.0Hz,1H),8.06(dd,J=4.8,1.7Hz,1H),7.86(dd,J=8.1,1.6Hz,1H),7.80(d,J=1.0Hz,2H),7.54(d,J=0.9Hz,1H),7.43(s,1H),7.05(dd,J=7.2,4.8Hz,1H),4.46(q,J=7.2Hz,2H),2.93-2.80(m,4H),2.10-2.00(m,4H),1.44(t,J=7.2Hz,3H),1.24(s,6H).
The fourth step: 6- (N- (2- (4, 4-Difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 23)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4, 4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 23C (400mg,1.40mmol) was dissolved in 15mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.923mg,14.0mmol) was added, and a solution of NaOH (167mg,4.2mmol) in water (0.5mL) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 23 as a white solid (400mg, 63.3%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.68(s,1H),9.71(s,1H),8.05(dd,J=4.8,1.7Hz,1H),8.00(s,1H),7.97(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.73(dd,J=8.3,1.5Hz,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.41(dd,J=7.9,1.6Hz,1H),6.95(dd,J=7.9,4.8Hz,1H),3.10-2.96(m,4H),2.05-1.86(m,4H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=453.1[M+1].
Example 246- (N- (2- (1, 1-difluoro-5-aza [2.5] octan-5-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 24)
The first step is as follows: 1, 1-difluoro-5- (3-nitropyridin-2-yl) -5-azaspiro [2.5] octane (24A)
2-fluoro-3-nitropyridine (130mg,0.914mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of DMF at room temperature, and cesium carbonate (893mg,2.74mmol) and 1, 1-difluoro-5-azaspiro [2.5] octane hydrochloride (135mg,0.914mmol) were added and reacted at room temperature for 10 hours with TLC monitoring showing completion of the reaction. 30mL of water was added and extracted with 50mL of ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, 100 mL. times.2 was washed with saturated brine, and the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then dried by spin-drying to give 24A as a yellow oil (100mg, 40.6%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 2- (1, 1-difluoro-5-azaspiro [2.5] octan-5-yl) pyridin-3-amine (24B)
5mL of MeOH and 5mL of dichloromethane and 10% Pd/C (20mg) were added to 1, 1-difluoro-5- (3-nitropyridin-2-yl) -5-azaspiro [2.5] octane 24A (100mg,371umol) at room temperature, and the reaction was stirred overnight under a hydrogen atmosphere. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was dried by spinning to give 24B (80mg, 90.0%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (1, 1-difluoro-5-aza [2.5] oct-5-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (24C)
2- (1, 1-difluoro-5-azaspiro [2.5] octan-5-yl) pyridin-3-amine 24B (80mg,334umol) was dissolved in 15mL DCM, pyridine (132mg,1.67mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (96.5mg,334umol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was added with 100mL of dichloromethane, washed with water (50mL × 2), the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (dichloromethane: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 1:6 to 1:4) to give 24C as a pale yellow solid (85mg, 51.7%).
The fourth step: 6- (N- (2- (1, 1-difluoro-5-aza [2.5] oct-5-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 24)
Reacting 6- (N- (2- (1, 1-difluoro-5-aza [2.5 ]) at room temperature]Octane-5-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 24C (80mg,163umol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (108mg,1.63mmol) was added, a solution of NaOH (20mg,488umol) in water (0.3mL) was added dropwise with stirring, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 24 as a white solid (20mg, 25.7%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.68(s,1H),9.44(s,1H),8.00(s,1H),7.96(dd,J=8.3,1.3Hz,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.21(dd,J=8.3,1.4Hz,1H),6.82(dd,J=7.7,4.8Hz,1H),3.19(d,J=12.3Hz,1H),3.10-2.97(m,3H),1.69-1.60(m,3H),1.58-1.52(m,1H),0.86-0.82(m,2H).LC-MSm/z(ESI)=479.1[M+1].
Example 256- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-fluoropyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 25)
The first step is as follows: 2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-fluoro-3-nitropyridine (25A)
2-chloro-5-fluoro-3-nitropyridine (250mg,1.42mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DMF at room temperature, cesium carbonate (1.39mg,4.26mmol) and 4-ethoxypiperidine hydrochloride (235mg,1.42mmol) were added and the reaction was allowed to react for 5 hours at room temperature with TLC monitoring showing completion. 30mL of water was added and extracted with 50mL of ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, 100 mL. times.2 was washed with saturated brine, and the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spun dry to give 25A as a yellow oil (300mg, 78.2%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification. The second step is that: 2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-fluoropyridin-3-amine (25B)
10mM LEOH, Raney nickel (20mg) was added to 2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-fluoro-3-nitropyridine 25A (300mg,371umol) under ice-bath, and hydrazine hydrate (179mg,5.57mmol) was added dropwise under nitrogen protection. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was dried by spinning to give 25B (250mg, 93.8%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-fluoropiperidin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (25C)
2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-fluoropyridin-3-amine 25B (250mg,1.04mmol) was dissolved in 15mL DCM, pyridine (826mg,10.5mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (301.6mg,1.04mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was added with 100mL of dichloromethane, washed with water (50mL × 2), the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (dichloromethane: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 1:6 to 1:4) to give 25C as a pale yellow solid (200mg, 39.0%).
The fourth step: 6- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-fluoropyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 25)
Ethyl 6- (N- (2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-fluoropiperidin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 25C (200mg,407umol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, 50% aqueous hydroxylamine solution (4.07mmol) was added, and a solution of NaOH (49mg,1.2mmol) in water (0.2mL) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 25 as a white solid (20mg, 25.7%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.69(s,1H),9.47(s,1H),8.12(s,1H),8.05(d,J=2.5Hz,1H),7.98(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.79(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.44(dd,J=9.5Hz,J=2.5Hz,1H),3.47-3.40(m,3H),2.93-2.90(m,2H),2.57–2.51(m,2H),1.75–1.72(m,2H),1.51–1.44(m,2H),1.09(t,J=7.2Hz,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=479.1[M+1].
Example 266- (N- (5-cyano-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 26)
The first step is as follows: 6- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-nitronicotinonitrile (26A)
6-chloro-5-nitronicotinonitrile (250mg,1.36mmol) was dissolved in 10mL DMF at room temperature, cesium carbonate (1.33mg,4.08mmol) and 4-ethoxypiperidine hydrochloride (225mg,1.42mmol) were added and the reaction was allowed to react for 5h at room temperature with TLC monitoring showing completion. 30mL of water was added and extracted with 50mL of ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL. times.2), the organic layers were combined, 100 mL. times.2 was washed with saturated brine, and the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then dried by spin-drying to give 26A as a yellow oil (300mg, 78.2%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The second step is that: 5-amino-6- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) nicotinonitrile (26B)
Under ice bath, 10mL of LEOH, Raney nickel (20mg) was added to 6- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -5-nitronicotinonitrile 26A (330mg,1.19mmol), and hydrazine hydrate (191mg,5.97mmol) was added dropwise under nitrogen. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction, the catalyst was removed by filtration and the filtrate was dried by spinning to give 26B (280mg, 95.2%) which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
The third step: 6- (N- (5-cyano-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (26C)
5-amino-6- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) nicotinonitrile 26B (250mg,1.01mmol) was dissolved in 15mL DCM, pyridine (803mg,10.2mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (293mg,1.01mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The reaction mixture was added with 100mL of dichloromethane, washed with water (50mL × 2), the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (dichloromethane: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 1:6 to 1:4) to give 26C as a pale yellow solid (250mg, 49.4%).
The fourth step: 6- (N- (5-cyano-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 26)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-cyano-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 26C (250mg,501umol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, 50% aqueous hydroxylamine solution (5.01mmol) was added, and a solution of NaOH (60mg,1.50mmol) in water (0.3mL) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 26 as a white solid (8mg, 3.3%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.70(s,1H),9.91(s,1H),8.41(d,J=2.1Hz,1H),8.00(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.92(s,1H),7.62–7.60(m,2H),7.17(d,J=2.1Hz,1H),3.85(dd,J=8.6,5.3Hz,2H),3.43-3.41(m,3H),3.17-3.14(m,2H),1.83–1.73(m,2H),1.42–1.35(m,2H),1.09(t,J=6.8Hz,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=486.2[M+1].
Example 276- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1 yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 27)
The first step is as follows: 4-Cyclopropylmethoxypiperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (27A)
Tert-butyl 4-hydroxypiperidine-1-carboxylate (1g,4.98mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of N, N-dimethylformamide, cooled in an ice bath under nitrogen, and NaH (60% in content, 219mg,5.48mmol) was added in portions, and stirred in an ice bath for 30 minutes, at which time cyclopropylmethyl bromide (1g,7.46mmol) was added, slowly warmed to room temperature and reacted overnight. LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction, the reaction was poured into water, extracted 3 times with 20mL ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layers were combined, dried and spun dry, and purified by silica gel column chromatography (PE: EA ═ 20:1) to give the product tert-butyl 4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidine-1-carboxylate (870mg,68.. 5%) as a yellow oil.
The second step is that: 4-Cyclopropylmethoxypiperidine (27B)
Tert-butyl 4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidine-1-carboxylate 27A (870mg,3.41mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of dichloromethane, 5mL of trifluoroacetic acid was added and the reaction was allowed to proceed overnight at room temperature, as monitored by LC-MS. The reaction solution was made basic with aqueous sodium carbonate, extracted 3 times with 20mL of dichloromethane, the dichloromethane layers were combined, dried and spin dried to give the product 4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidine 27B (530mg, 100%) as a yellow oil.
The third step: 5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 27C)
2, 5-dichloro-3-nitropyridine (193mg,1.00mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 4-dioxane, and 4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidine (170mg,1.10mmol) and triethylamine (0.41mL,3.00mmol) were added to the solution, and the mixture was reacted at room temperature overnight. LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. The solvent was spun dry, 30mL of water and 20mL of ethyl acetate were added to the residue, the organic layer was separated, the aqueous phase was extracted 2 times with 20mL of ethyl acetate, the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and spun dry to give the product 5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 27C (480mg, 155%) as a yellow oil.
The fourth step: 5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (27D)
5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) -3-nitropyridine 27C (480mg,1.2mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of MeOH at room temperature, Raney-Ni (200mg) was added, and hydrazine hydrate (0.3mL,6.0mmol) was added dropwise with cooling on an ice bath. After the dripping, stirring was continued for 1 hour under ice bath. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, Raney-Ni was removed by filtration and the filtrate was spin dried to give 5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 27D (337mg, 77%) which was used directly in the next step.
The fifth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (27E)
5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 27D (337mg,1.2mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 2-dichloroethane, and pyridine (0.39mL,4.8mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylate (693mg,2.4mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 27E (600mg, 94%) as a yellow oil which was used directly in the next reaction.
And a sixth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1 yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 27)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-cyclopropylmethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate 27E (600mg,1.12mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of methanol at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (1mL,16.9mmol) was added, and an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (224mg,5.6mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 1M HCl was added to adjust pH to 8, the solvent was dried and the residue was purified by prep-HPLC to give the product compound 27(198mg, 33%) as a white solid.
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.11–8.05(m,1H),8.03–7.92(m,2H),7.69(dd,J=8.3,1.6Hz,1H),7.60–7.55(m,1H),7.29(d,J=2.4Hz,1H),3.34(tt,J=8.6,3.9Hz,1H),3.16(t,J=6.2Hz,3H),2.65(ddd,J=12.7,9.8,2.9Hz,2H),2.01(s,1H),1.69(d,J=11.7Hz,2H),1.41–1.27(m,2H),0.90(dddd,J=14.8,6.9,3.2,2.0Hz,1H),0.46–0.35(m,2H),0.15–0.04(m,2H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=521.2[M+1].
Examples 28 to 60
Examples 28-60 were prepared according to the synthetic method of example 14.
Example 626- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxy-furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxamide (Compound 62)
The first step is as follows: 6-chloro-4-hydroxynicotinaldehyde (62A)
6-chloro-4-methoxypyridine-3-carbaldehyde (1g,4.98mmol) was added to 50mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and the mixture was heated to reflux for 18 hours. TLC monitoring indicated completion of the reaction, cooling to room temperature, pouring the reaction into 100mL of water, extracting 5 times with 200mL of dichloromethane, combining the organic layers, drying and spin-drying to give the product 6-chloro-4-hydroxynicotinaldehyde 61A (520mg, 28.3%) as a white solid.
The second step is that: 6-chloro-furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (62B)
6-chloro-4-methoxypyridine-3-carbaldehyde 62A (405mg,2.57mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of DMF, ethyl bromoacetate (537mg,3.22mmol) and potassium carbonate (1.07,7.72mmol) were added, and the reaction was allowed to warm at room temperature for 2 hours overnight. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture was introduced into 100mL of water, and 3 times with 100mL of ethyl acetate, the organic layers were combined, dried and spun to dryness, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (15% ethyl acetate/dichloromethane) to give ethyl 6-chloro-furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylate (300mg, 51.7%) as a white solid. LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 226.0[ M +1].
The third step: 6-Benzylthio-furo [3,2-C ] pyridine-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (62C)
Reacting 6-chloro-furo [3,2-c ]]Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (418mg,185mmol), benzylthiol (345mg,2.78mmol) were dissolved in 15mL toluene, N-diisopropylethylamine (718mg,5.55mmol), 4, 5-bis (diphenylphosphino) -9, 9-dimethylxanthene (214mg,370mmol), and tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium 43mg,185umol were added, air was replaced with nitrogen, and the mixture was heated to reflux for 18 hours. After cooling to room temperature, 50mL of water was added, extraction was performed with ethyl acetate (100 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Purifying the residue by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 50:1 to 30:1) to obtain 6-benzylthio-furo [3, 2-c)]Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (250mg, yield 43.1%). MS (ESI) M/z 314.1[ M +1]].1HNMR(400MHz,DMSO)δ8.96(s,1H),7.82(d,J=0.9Hz 1H),7.78(s,1H),7.45(m,2H),7.35-7.28(m,2H),7.27-7.21(m,1H),4.49(s,2H),4.37(q,J=7.1Hz,2H),1.33(t,J=6.8,J=7.1Hz,3H).
The fourth step: 6-Chlorosulfonyl-furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (62D)
Ethyl 6-benzylthio-furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylate (450mg,1.44mmol) was suspended in 10mL of acetic acid and 5mL of water, N-chlorosuccinimide (575mg,4.31mmol) was added in portions, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 10 hours. After the reaction was complete, 50mL of water was added. Ethyl acetate extraction (100 mL. times.3) and the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylate as a pale yellow solid, (250mg, yield 61.1%). LC-MSm/z (esi) 290.0[ M +1].
The fifth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (62E)
5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (221mg,0.863mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 2-dichloroethane, and pyridine (0.39mL,4.8mmol) and ethyl 6-chlorosulfonyl-furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylate (250mg,0.863mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS indicated the reaction was complete and the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spin dried to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylate (100mg, 22.8%) as a pale yellow solid which was used in the next reaction without further purification.
And a sixth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxy-furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxamide (62)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -furo [3,2-c ] pyridine-2-carboxylate (100mg,0.196mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of methanol at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.12mL,2.03mmol) was added, and an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (24mg,5.6mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 1M HCl was added to adjust pH to 8, the solvent was dried and the residue was purified by prep-HPLC to give example compound 62(6.5mg, 6.7%) as a white solid.
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ9.16(s,1H),8.33(s,1H),8.00(d,J=2.4Hz,1H),7.70(s,1H),7.58(d,J=2.4Hz,1H),3.39(q,J=7.0Hz,1H),3.28(m,1H),2.73(t,J=10.24Hz,2H),1.78-1.74(m,2H),1.38-1.34(m,2H),1.05(t,J=10.24Hz,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=496.2[M+1].
Example 636- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Compound 63)
The first step is as follows: 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (63A)
5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (200mg,1.02mmol) was dissolved in 5mL of 1, 2-dichloroethane, and pyridine (0.576mL,7.15mmol) and methyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) benzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate (1.04mg,3.58mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 50:1 to 30:1) to give methyl 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) benzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate (339mg, 73.8%) as a pale yellow solid. LC-MS M/z (esi) 450.1[ M +1].
The second step is that: 6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxamide (63)
6- (N- (5-fluoro-2- (piperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) benzo [ b ] at room temperature]Thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (170mg,0.377mmol) was dissolved in 5mL MeOH, 50% aqueous hydroxylamine solution (186.7mg,5.66mmol) was added, and 0.5mL aqueous NaOH (45mg,1.13mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1MHCl, spin dried, and residue by prep-HPLC (CH with 0.5% TFA)3CN/H2O) to give compound 63 as a white solid (57.4mg, 33.4%).
1H NMR(400MHz,Methanol-d4)δ8.60–8.55(m,1H),8.05(d,J=8.5Hz,1H),7.95(d,J=2.8Hz,1H),7.91(s,1H),7.83(dd,J=8.5,1.7Hz,1H),7.69(dd,J=9.5,2.9Hz,1H),2.64(t,J=5.3Hz,4H),1.60(q,J=5.2Hz,4H),1.55–1.48(m,2H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=451.0[M+1].
Examples 64 to 66
Compounds 64-66 were prepared according to the synthetic procedure of example 63.
Example 676- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -7-fluoro-N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 67)
The first step is as follows: 4-bromo-3-fluoro-2-methoxybenzaldehyde (67A)
To a solution of 4-bromo-2, 3-difluorobenzaldehyde (4.83g,21.85mmol) in 125mL of methanol was added sodium methoxide (1.77g,32.78mmol) at room temperature. The reaction was heated to reflux for 2 hours. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, 100mL of ethyl acetate and 50mL of water were added to the mixture, the layers were separated, the aqueous phase was extracted 2 times with 100mL of ethyl acetate, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent to give 4-bromo-3-fluoro-2-methoxybenzaldehyde as a pale yellow solid (5.09mg, 91.79%). LC-MSm/z (esi) 233.0,235.0[ M +1].
The second step is that: 4-bromo-3-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (67B)
To 4-bromo-3-fluoro-2-methoxybenzaldehyde (4.67g,20.06mmol) was added 30mL hydrobromic acid (48%) at room temperature. The reaction was heated to reflux for 18 hours. After the reaction, the reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, the residue was diluted with 100mL of water, ethyl acetate (100mL) was added and extracted 2 times, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 20:1 to 10:1) to obtain 4-bromo-3-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (2.8g, 63.7%) as a product, and a pale yellow solid. LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 219.0,221.0[ M +1].
The third step: 6-bromo-7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (67C)
To a solution of 4-bromo-3-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (2.83g,12.9mmol) in 30ml of DMF at room temperature were added ethyl bromoacetate (3.45g,20.7mmol) and potassium carbonate (5.35g,38.8 mmol). The reaction was heated to 90 ℃ for 18 hours. After the reaction is finished, the reaction solution is concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, the residue is diluted by 100mL of water, ethyl acetate 100mL of ethyl acetate is added for extraction for 2 times, organic phases are combined, dried by anhydrous sodium sulfate, the solvent is removed under reduced pressure, and the residue is purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 200: 1-100: 1) to obtain a product, namely 6-bromo-7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (1.81g, 48.8%) and light yellow solid. LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 287.0,289.0[ M +1].
The fourth step: 6- (benzylthio) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (67D)
Ethyl 6-bromo-7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (1.81g,6.30mmol), benzylthiol (940mg,7.57mmol) were dissolved in 30mL of toluene, N-diisopropylethylamine (2.44g,18.9mmol), 4, 5-bis (diphenylphosphino) -9, 9-dimethylxanthene (365mg, 630. mu. mol) and tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (289mg, 315. mu. mol) were added, air was replaced with nitrogen, and the mixture was heated to reflux and reacted for 18 hours. After cooling to room temperature, 50mL of water was added, extraction was performed with ethyl acetate (100 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 100:1 to 20:1) to give ethyl 6- (benzylthio) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (1.65g, yield 79.2%). Ms (esi) M/z 331.0[ M +1].
The fifth step: 6- (Chlorosulfonyl) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (67E)
Ethyl 6- (benzylsulfanyl) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (1.65g,4.99mmol) is suspended in 18mL of acetic acid and 6mL of water. N-chlorosuccinimide (2.67mg,20.0mmol) was added in portions at 0 ℃ and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 10 hours. After the reaction was complete, 50mL of water was added. Ethyl acetate extraction (100 mL. times.3) and the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give ethyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylate as a pale yellow solid, (250mg, 61.1% yield). The reaction mixture was used in the next reaction without further purification.
And a sixth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (67F)
5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine (210mg,0.819mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of 1, 2-dichloroethane, and pyridine (0.46mL,5.7mmol) and ethyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (879mg,2.87mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 49: 1-10:1) to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (234mg, 54.3%) as an off-white solid. LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 526.1[ M +1].
The seventh step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -7-fluoro-N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (67)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (117mg,0.222mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of methanol at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (110mg,3.34mmol) was added, and 0.3mL of an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (27mg,6.7mmol) was added dropwise with stirring and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 1M HCl was added to adjust pH to 8, the solvent was spun off, and the residue was purified by prep-HPLC to give example compound 67 as an off-white solid (54.5mg, 46.9%).
1H NMR(400MHz,Methanol-d4)δ8.02(d,J=2.4Hz,1H),7.73(dd,J=8.3,5.5Hz,1H),7.70–7.65(m,2H),7.61(d,J=2.7Hz,1H),3.54(q,J=7.0Hz,2H),3.42(tt,J=8.5,3.9Hz,1H),3.14(dt,J=9.9,4.1Hz,2H),2.74(ddd,J=12.7,9.9,2.9Hz,2H),1.87(dq,J=12.5,3.8Hz,2H),1.54(dtd,J=12.9,9.4,3.6Hz,2H),1.20(t,J=7.0Hz,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=513.1[M+1].
Examples 68 to 69
Compounds 68-69 were prepared according to the synthetic procedure of example 67.
Examples 70 to 87
Examples 70-87 were prepared according to the synthetic method of example 18.
Example 886- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -7-fluoro-N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 88)
The first step is as follows: 1-cyclohexyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine (88A)
To a solution of cyclohexylhydrazine hydrochloride (500mg,3.32mmol) in 15mL of ethanol was added 3-oxobutanenitrile (414mg,4.98mmol) at room temperature. The reaction was heated to reflux for 18 hours. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 50mL water was added, extracted with ethyl acetate (100mL × 2), the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent to give 1-cyclohexyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine as a brown solid (590mg, 99.2%). LC-MS M/z (esi) 180.1[ M +1].
The second step is that: 6- (N- (1-cyclohexyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (88B)
1-cyclohexyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine (300mg,1.67mmol) was dissolved in 15mL of 1, 2-dichloroethane, and pyridine (662mg,8.4mmol) and ethyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) -7-fluorobenzofuran-2-carboxylate (483mg,1.67mmol) were added, followed by stirring at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, the reaction was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 49:1 to 10:1) to give the product ethyl 6- (N- (1-cyclohexyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (600mg, 83.3%) as an off-white solid. LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 432.1[ M +1].
The third step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -7-fluoro-N-hydroxybenzofuran-2-carboxamide (88)
Ethyl 6- (N- (1-cyclohexyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl) sulfamoyl) benzofuran-2-carboxylate (600mg,1.39mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of methanol at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (919mg,13.9mmol) was added, and 1mL of an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (167mg,4.17mmol) was added dropwise with stirring, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, adjusted to pH8 with 1M HCl and extracted with dichloromethane (200mL × 4). The organic phases are combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, 20mL of dichloromethane are added to the residue, slurried with stirring at room temperature for 1 hour, and filtered under reduced pressure. The above slurry operation was repeated on the filter cake, suction filtered and the filter cake was dried to give example compound 88 as an off-white solid (550mg, 94.6%).
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.70(s,1H),10.40(s,1H),9.44(s,1H),8.00(d,J=8.3,1H),7.93(s,1H),7.68(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),7.61(s,1H),5.52(s,1H),3.87-3.73(m,1H),2.01(s,3H),1.68-1.57(m,2H),1.57-1.45(m,3H),1.35-1.20(m,2H),1.14-0.97(m,3H).LC-MS m/z(ESI)=419.0[M+1].
Examples 89 to 97
Compounds 89-97 were prepared according to the synthetic procedure of example 88.
Example 986- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -N-hydroxy-3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxamide (Compound 98)
The first step is as follows: 6-bromo-3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (98A)
1- (4-bromo-2-hydroxy-phenyl) ethanone (2.0g,9.30mmol) was dissolved in 30mL of DMF at room temperature, potassium carbonate (3.85g,27.9mmol) and ethyl bromoacetate (1.86g,11.2mmol) were added, the mixture was heated to 90 ℃ for reaction for 3 hours, and LC-MS monitoring indicated that the reaction was complete. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture was added to 100g of ice water and the residue was dissolved in 100mL of ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layer was separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (100mL × 2), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then spun, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 99:1 to 49:1) to give 98A pale yellow solid (2.63g, 22.0%). LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 282.9,284.9[ M +1].
The second step is that: 6- (benzylthio) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (98B)
Ethyl 6-bromo-3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylate (580mg,2.05mmol), benzylthiol (150mg,2.46mmol) were dissolved in 15mL of toluene, N-diisopropylethylamine (794.3mg,6.15mmol), 4, 5-bis (diphenylphosphino) -9, 9-dimethylxanthene (237mg,410umol) and tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (188mg,205umol) were added, air was replaced with nitrogen, and the mixture was heated to reflux for 18 hours. After cooling to room temperature, 50mL of water was added, extraction was performed with ethyl acetate (100 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 50:1-30:1) to give ethyl 6- (benzylthio) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylate as an off-white solid (300mg, yield 44.9%). LC-MS M/z (esi) 327.2[ M +1].
The third step: 6- (Chlorosulfonyl) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (98C)
Ethyl 6- (benzylthio) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylate (200mg,613umol) was suspended in 6mL of acetic acid and 2mL of water, and N-chlorosuccinimide (327mg,2.45mmol) was added in portions, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 5 hours. After the reaction was complete, 50mL of water was added. Ethyl acetate extraction (100 mL. times.3) and the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give ethyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylate 98C as a pale yellow solid, (177mg, 95.4% yield). Used in the next step without further purification.
The fourth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (98D)
Ethyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylate (177mg,0.585mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of DCM, and pyridine (139mg,1.75mmol) and 5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 18B (150mg,0.585mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 100mL dichloromethane was added, the layers were separated, the organic phase was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry. Ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylate as a pale yellow solid (200mg, 65.5%) was used directly in the next reaction. LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 522.2[ M +1].
The fifth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxy-3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxamide (98)
Ethyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -3-methylbenzofuran-2-carboxylate 98D (200mg,0.383mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH at room temperature, an aqueous hydroxylamine solution (0.4mL,6.93mmol) was added, 0.3mL of an aqueous NaOH (86mg,2.16mmol) was added dropwise with stirring, and stirring was carried out at room temperature for 2 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 98 as a white solid (50mg, 25.6%). LC-MS M/z (ESI) ═ 509.1[ M +1].
Example 996- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminesulfonyl) -N-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Compound 99)
The first step is as follows: 6-bromo-3-hydroxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (99A)
Methyl 4-bromo-2-fluorobenzoate (2.0g,8.58mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of DMF at room temperature, lithium hydroxide (411mg,17.2mmol) and ethyl thioglycolate (911mg,8.58mmol) were added, the reaction was stirred for 13 hours, and LC-MS monitoring indicated completion of the reaction. Cooled to room temperature, 1M hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to neutralize the reaction and precipitate, which was filtered to give 99A, a white solid (1.57g, 63.7%).
The second step is that: 6-bromo-3-methoxybenzo [ B ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (99B)
Methyl 6-bromo-3-hydroxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate (1.57g,5.47mmol) was dissolved in 15mL of DMF at room temperature, and potassium carbonate (1.51g,10.9mmol) and iodomethane (1.55g,10.9mmol) were added to react at room temperature for 18 hours. 100mL of water was added, extraction was performed with ethyl acetate (100 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 100:1-10:1) to give methyl 6- (benzylthio) -3-methylbenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate as a yellow solid (1.90g, yield 80.6%). LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 301.0,303.0[ M +1].
The third step: 6- (benzylthio) -3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (99C)
Methyl 6-bromo-3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate (1.90g,6.30mmol), benzylthiol (460mg,7.56mmol) were dissolved in 15mL of toluene, N-diisopropylethylamine (2.44g,18.9mmol), 4, 5-bis (diphenylphosphino) -9, 9-dimethylxanthene (729mg,1.26mmol), and tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (576mg, 630. mu. mol) were added, the air was replaced with nitrogen, and the mixture was heated to reflux for 18 hours. After cooling to room temperature, 50mL of water was added, extraction was performed with ethyl acetate (100 mL. times.2), and the organic layers were combined and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (v/v) ═ 20:1-10:1) to give methyl 6- (benzylthio) -3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate as a yellow solid (500mg, yield 23.0%). LC-MS M/z (esi) ═ 344.9[ M +1].
The fourth step: 6- (Chlorosulfonyl) -3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (99D)
Methyl 6- (benzylthio) -3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate 99C (200mg, 581. mu. mol) was suspended in 6mL of acetic acid and 2mL of water, and N-chlorosuccinimide (310mg,2.32mmol) was added in portions, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 5 hours. After the reaction was complete, 50mL of water was added. Ethyl acetate extraction (100 mL. times.3) and the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give methyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) -3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate 99D as a pale yellow solid, (186mg, 99.9% yield). Used in the next step without further purification.
The fifth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (99E)
Methyl 6- (chlorosulfonyl) -3-methoxybenzo [ B ] thiophene-2-carboxylate 99D (167mg,0.520mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of DCM, and pyridine (150mg,1.89mmol) and 5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-amine 18B (133mg,0.52mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature overnight. LCMS showed the reaction was complete, 100mL dichloromethane was added, the layers were separated, the organic phase was washed with water (50mL), dried and spun dry. Methyl 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxylate as a pale yellow solid (170mg, 60.5%) was used directly in the next reaction. LC-MS M/z (esi) 540.1[ M +1].
And a sixth step: 6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) sulfamoyl) -N-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzo [ b ] thiophene-2-carboxamide (99)
6- (N- (5-chloro-2- (4-ethoxypiperidin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl) aminosulfonyl) -3-methoxybenzo [ b ] at room temperature]Thiophene-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester 99E (170mg,0.315mmol) was dissolved in 10mL MeOH, 50% aqueous hydroxylamine solution (300mg,6.8mmol) was added, 0.2mL aqueous NaOH (50mg,1.25mmol) was added dropwise with stirring, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. LCMS showed reaction completion, pH8 adjusted with 1M HCl, spin dried, residue by prep-HPLC (0.5% TFA in CH)3CN/H2O) to give compound 99 as a white solid (32mg, 18.8%). LC-MS M/z (ESI) ═ 541[ M +1]].
The following test examples specifically illustrate the advantageous effects of the present invention:
test example 1 acetylation Activity of alpha-tubulin
HCT116 cells in logarithmic growth phase were seeded in 96-well clear-bottom blackboards (Corning # 3340). After overnight cell culture, compounds were added at different concentrations to treat the cells, with final concentrations of 100, 30, 10, 3, 1, 0.3, 0.1, 0.03, 0.01, 0.003uM, and DMSO controls were provided, with 3 replicates for each compound. The cell culture plate was placed in a carbon dioxide incubator for an additional 6 hours.
After 6 hours of compound treatment, the well plates were discarded and 200ul of 4% (w/v) PFA (dissolved in PBS buffer (aMRESCO # E404-200TABS) and pH adjusted to 7.4) was added to immobilize the cells and incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes. PFA was discarded, 200ul of 0.1% (v/v) TritonX-100 (dissolved in PBS buffer) was added to permeabilize the cells, and incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature. TritonX-100 was discarded and 100ul of 1% (w/v) blocking solution (Roche #11096176001, dissolved in TBS solution (20mM Tris-HCl, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0)) was added to each well. Incubate 30 minutes at room temperature with shaking at 300 rpm. The acetylated tubulin antibody (Sigma-Aldrich # T6793) was diluted 1% (w/v) in blocking solution at a 1:2000 dilution ratio, 50ul of the diluted antibody was pipetted into all wells of the cell plate and incubated overnight at 4 ℃. The following day 200ul wash (0.05% PBST) was pipetted into each well and the plate was washed 4 times. Goat anti-mouse fluorescent secondary antibody (Invitrogen # F-2761) was diluted with 1% (w/v) blocking solution at a 1:500 dilution and DAPI (Themolfisher #62247) at a 1:2000 dilution. 50ul of diluted antibody was pipetted into all wells of the cell plate and incubated with shaking at 300rpm in the dark at room temperature for 120 minutes. Pipette 200ul of wash solution (0.05% PBST) into each well and repeat the plate wash 4 times. And (5) wrapping the plate with tin foil paper to prevent light to be detected after the plate is washed.
Data were acquired using a high content imaging analysis system In Cell Analyzer (GE #2200) and data analysis was performed using In Cell Analyzer work software. Normalized cell grey values obtained after treatment at each concentration of each compound (intensity (N + C) divided by normalized cell grey values after negative control (DMSO treatment) (intensity (N + C), respectively, to obtain fold-changes in acetylated tubulin relative to negative control after treatment with different compounds, and EC relative to log concentration was fitted and calculated in GraphPad Prism software50。
The acetylation activity of α -tubulin of HCT116 cells was measured for the compounds prepared in the previous examples according to the above-described method, and the results of the test are shown in Table 1, in which the EC of each compound was determined50Classified as per the description.
TABLE 1 acetylation activity of compounds on alpha-tubulin
Note: "+" indicates EC50More than 1uM and less than 100 uM; "+ +" indicates EC50Greater than 300nM and less than 1000 nM; "+ + + +" denotes EC50Less than 300 nM.
Test results show that the compound has good deacetylase inhibitory activity on tubulin, and can be effectively used for treating diseases related to tubulin action and diseases related to histone deacetylase 6 abnormity.
Test example 2 acetylation Activity of Histone3
HCT116 cells in logarithmic growth phase were seeded in 96-well clear-bottom blackboards (Corning # 3340). After overnight cell culture, compounds were added at different concentrations to treat the cells, with final concentrations of 100, 30, 10, 3, 1, 0.3, 0.1, 0.03, 0.01, 0.003uM, and DMSO controls were provided, with 3 replicates for each compound. The cell culture plate was placed in a carbon dioxide incubator for further 24 hours.
After 24 hours of compound treatment, the plate was discarded, 200ul of pre-cooled methanol fixed cells were added and incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature. Methanol was discarded, 200ul of 0.1% (v/v) TritonX-100 (dissolved in PBS buffer) was added to permeabilize the cells, and incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature. TritonX-100 was discarded and 100ul of 1% (w/v) blocking solution (Roche #11096176001, dissolved in TBS solution (20mM Tris-HCl, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0)) was added to each well. Incubate 30 minutes at room temperature with shaking at 300 rpm. The acetylated histone H3 antibody (Abcam # ab47915) was diluted with 1% (w/v) blocking solution at a dilution ratio of 1:1000, 50ul of the diluted antibody was pipetted into all wells of the cell plate and incubated overnight at 4 ℃. The following day 200ul wash (0.05% PBST) was pipetted into each well and the plate was washed 4 times. Goat anti-rabbit fluorescent secondary antibody (Invitrogen # A11034) was diluted with 1% (w/v) blocking solution at A1: 500 dilution ratio and DAPI (Themolfisher #62247) at A1: 2000 dilution ratio. 50ul of diluted antibody was pipetted into all wells of the cell plate and incubated with shaking at 300rpm in the dark at room temperature for 120 minutes. Pipette 200ul of wash solution (0.05% PBST) into each well and repeat the plate wash 4 times. And (5) wrapping the plate with tin foil paper to prevent light to be detected after the plate is washed.
Data were acquired using a high content imaging analysis system In Cell Analyzer (GE #2200) and data analysis was performed using In Cell Analyzer work software. Normalized cellular gray values obtained after treatment at each concentration of each compound (intensity (N + C) divided by normalized cellular gray values after negative control (DMSO treatment) (intensity (N + C), respectively, were obtained as fold changes of acetylated histone H3 relative to negative control after treatment with different compounds, and EC50 relative to log concentration was fitted and calculated in GraphPad Prism software.
The acetylation activity of Histone3 of HCT116 cells was measured for the compounds prepared in the previous examples according to the method described above, and the results are shown in Table 1, in which the EC of each compound was determined50Classified as per the description.
The test result shows that the compound has weaker deacetylase inhibitory activity on histone3, so that the compound has higher selectivity on HDAC6, and can avoid or reduce toxic effects related to histone while effectively treating diseases.
Claims (18)
1. A compound represented by formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
X1selected from N, CR2;
R is respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORaHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
R1each independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro;
R2each independently selected from hydrogen;
each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group;
R4is selected from-NRhRi、-ORc、-SRc、-(CH2)rRc4-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
r is 0, 1,2 or 3;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle;
Rh、Riare each independently selected from C1~C10Alkyl, 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle may be substituted with m RdSubstitutionEach RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, ═ O, -ORe、-NReRf0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
Rcselected from 3-10 membered cycloalkyl and 3-10 membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl and heterocycle can be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, ═ O, -ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
2. The compound of claim 1, wherein: a compound of formula I is represented by formula II:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
X1selected from N, CR2;
R is respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORaHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
R1each independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro;
R2each independently selected from hydrogen;
each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group;
the B ring is selected from 4-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle;
4. the compound of claim 1, wherein: a compound of formula I is represented by formula III:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
X1selected from N, CR2;
R is respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORaHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
R1each independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro;
R2each independently selected from hydrogen;
each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group;
the B ring is selected from 4-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle.
6. the compound of claim 1, wherein: a compound of formula I is represented by formula IV:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
r is respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORaHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
R1each independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro;
each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle;
Rh、Riare each independently selected from C1~C10Alkyl, 3-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle may be substituted with m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, ═ O, -ORe、-NReRf0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group.
8. the compound of claim 1, wherein: a compound of formula I is represented by formula V:
wherein,
x is selected from O, S;
r is respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORaHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
R1each independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro;
each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle;
Rcselected from 3-10 membered cycloalkyl and 3-10 membered heterocycle, wherein the cycloalkyl and heterocycle can be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, ═ O, -ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group.
10. the compound of claim 1, wherein: a compound of formula I is represented by formula VI:
in the formula,
x is selected from O, S;
r is respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORaHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
R1each independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro;
each R3Are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro and C1~C10Alkyl, -ORa、-NRaRbHalogen-substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
the ring A is selected from a 5-10-membered aromatic ring and a 5-10-membered aromatic heterocycle;
n is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Ra、Rbeach independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10An alkyl group;
R4selected from 4-10 membered cycloalkyl, 3-10 membered heterocycle, 6-12 membered spirocycle, 6-12 membered heterospirocycle, 6-10 membered bridged ring, 6-10 membered heterobridged ring, wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocycle, spirocycle, heterospirocycle, bridged ring, heterobridged ring may be substituted by m RdSubstituted, each RdIndependently selected from halogen, cyano, nitro, C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, ═ O ORe、-NReRf、-OC(O)Ra、-NRaC(O)Rb、-NRaS(O)2Rb、-S(O)2Rb、-S(O)2NRaRb、-C(O)Rb、-C(O)ORb、-C(O)NRaRb0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
m is 0, 1,2 or 3;
Re、Rfare respectively and independently selected from hydrogen and C1~C10Alkyl, 3-to 10-membered cycloalkyl, substituted with 0 to 3RgSubstituted C1~C10Alkyl, halogen substituted C1~C10An alkyl group;
each RgAre each independently selected from-ORa、-NRaRb5-10 membered aromatic ring, 5-10 membered aromatic heterocycle.
12. use of a compound according to any one of claims 1 to 11, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament for the HDAC inhibitor class.
13. Use according to claim 12, characterized in that: the medicament is a medicament for treating a cell proliferative disease, an autoimmune disease, an inflammation, a neurodegenerative disease, or a viral disease.
14. Use according to claim 13, characterized in that: the cell proliferative disease is cancer.
15. Use according to claim 14, characterized in that: the cancer is selected from colon cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, brain cancer, ovarian cancer, and thyroid cancer.
16. Use according to any one of claims 12 to 15, characterized in that: the HDAC is HDAC 6.
17. A pharmaceutical composition characterized by: the compound or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as an active ingredient, and pharmaceutically acceptable auxiliary materials.
18. The composition of claim 17, wherein: the preparation is an oral preparation, a transdermal absorption preparation or an injection preparation.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910321788.9A CN111848591B (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2019-04-25 | HDAC inhibitors and methods of making and using the same |
| PCT/CN2020/086427 WO2020216298A1 (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2020-04-23 | Hdac inhibitor, preparation method therefor and use thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910321788.9A CN111848591B (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2019-04-25 | HDAC inhibitors and methods of making and using the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111848591A CN111848591A (en) | 2020-10-30 |
| CN111848591B true CN111848591B (en) | 2022-03-18 |
Family
ID=72941493
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910321788.9A Active CN111848591B (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2019-04-25 | HDAC inhibitors and methods of making and using the same |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111848591B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2020216298A1 (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002030879A2 (en) * | 2000-09-29 | 2002-04-18 | Prolifix Limited | Carbamic acid compounds comprising a sulfonamide linkage as hdac inhibitors |
| CN101868446A (en) * | 2007-09-25 | 2010-10-20 | 托波塔吉特英国有限公司 | The synthetic method of some hydroxamic acid compound |
| CN107873023A (en) * | 2015-02-02 | 2018-04-03 | 福马治疗股份有限公司 | Bicyclic [4,5, the 0] hydroxamic acid of the acylamino- of 3 alkyl 4 as hdac inhibitor |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109705071B (en) * | 2017-10-25 | 2020-11-13 | 成都先导药物开发股份有限公司 | HDAC inhibitors and methods of making and using the same |
-
2019
- 2019-04-25 CN CN201910321788.9A patent/CN111848591B/en active Active
-
2020
- 2020-04-23 WO PCT/CN2020/086427 patent/WO2020216298A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002030879A2 (en) * | 2000-09-29 | 2002-04-18 | Prolifix Limited | Carbamic acid compounds comprising a sulfonamide linkage as hdac inhibitors |
| CN101868446A (en) * | 2007-09-25 | 2010-10-20 | 托波塔吉特英国有限公司 | The synthetic method of some hydroxamic acid compound |
| CN107873023A (en) * | 2015-02-02 | 2018-04-03 | 福马治疗股份有限公司 | Bicyclic [4,5, the 0] hydroxamic acid of the acylamino- of 3 alkyl 4 as hdac inhibitor |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| Pharmacophore Identification of Hydroxamate HDAC 1 Inhibitors;YU, Liqin,等;《Chinese Journal of Chemistry》;20091231;第557-564页 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2020216298A1 (en) | 2020-10-29 |
| CN111848591A (en) | 2020-10-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5335932B2 (en) | Disubstituted pyridine derivatives as anticancer agents | |
| US7429603B2 (en) | C-fms kinase inhibitors | |
| CA2772718C (en) | Compounds as tyrosine kinase modulators | |
| JP6466171B2 (en) | Novel amine derivative or salt thereof | |
| WO2006036024A1 (en) | Proton pump inhibitors | |
| AU2003255724A1 (en) | Substituted thienyl-hydroxamic acids as histone deacetylase inhibitors | |
| KR20050065624A (en) | Novel tricyclic compounds useful for the treatment of inflammatory and allergic disorders, process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them | |
| WO2012068589A2 (en) | Modulators of methyl modifying enzymes, compositions and uses thereof | |
| EP2812001A2 (en) | Modulators of methyl modifying enzymes, compositions and uses thereof | |
| WO2006047504A1 (en) | Aromatic amides as inhibitors of c-fms kinase | |
| KR20150127249A (en) | 3-(aryl or heteroaryl)methyleneindolin-2-one derivatives as inhibitors of cancer stem cell pathway kinases for the treatment of cancer | |
| EP1843820A1 (en) | Multicyclic bis-amide mmp inhibitors | |
| EP3004057A1 (en) | Heterocyclic derivatives and use thereof | |
| CN115667216A (en) | (1H-indol-5-yl) acrylamide derivatives as TEAD proteins and inhibitors of the HIPPO-YAP1/TAZ signaling cascade for the treatment of cancer | |
| AU2003301853A1 (en) | Indoles useful in the treatment of androgen- receptor related diseases | |
| CN111196804B (en) | TGF-beta R1 inhibitors and uses thereof | |
| AU2010211583A1 (en) | Dihydroquinolinone derivatives | |
| CA2512502A1 (en) | Indole-phenylsulfonamide derivatives used as ppar-delta activating compounds | |
| WO2008010061A2 (en) | 3-azabicyclo [3.1.0] hexane vanilloid receptor ligands, pharmaceutical compositions containing them, and processes for their preparation | |
| WO2013100672A1 (en) | 3,6-disubstituted indazole derivative having protein kinase inhibiting activity | |
| WO2005077912A1 (en) | Indazole compound and pharmaceutical use thereof | |
| TW201427968A (en) | Aromatic ring compound | |
| JP2015520224A (en) | 1- [m-carboxamide (hetero) aryl-methyl] -heterocyclyl-carboxamide derivatives | |
| WO2006048251A1 (en) | Anthranilamide pyridinureas as vegf receptor kinase inhibitors | |
| JP2012211085A (en) | Hedgehog signal inhibitor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |