CN111376841B - Calibration method and device of lane departure system and storage medium - Google Patents
Calibration method and device of lane departure system and storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111376841B CN111376841B CN201811625128.1A CN201811625128A CN111376841B CN 111376841 B CN111376841 B CN 111376841B CN 201811625128 A CN201811625128 A CN 201811625128A CN 111376841 B CN111376841 B CN 111376841B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- angle
- camera
- height
- image
- lane departure
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R11/00—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for
- B60R11/04—Mounting of cameras operative during drive; Arrangement of controls thereof relative to the vehicle
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/80—Analysis of captured images to determine intrinsic or extrinsic camera parameters, i.e. camera calibration
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R11/00—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for
- B60R2011/0001—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for characterised by position
- B60R2011/0003—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for characterised by position inside the vehicle
- B60R2011/0026—Windows, e.g. windscreen
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R11/00—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for
- B60R2011/0042—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for characterised by mounting means
- B60R2011/008—Adjustable or movable supports
- B60R2011/0092—Adjustable or movable supports with motorization
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Abstract
The present disclosure provides a calibration method and apparatus for a lane departure system, and a storage medium, to solve the problems of complicated calibration process and low calibration precision of the lane departure system in the related art. The calibration method of the lane departure system comprises the following steps: after a vehicle stops on a horizontal ground, standing a calibration plate in front of the vehicle; acquiring height images which are shot by cameras of a lane departure device in the vehicle at different heights and contain the calibration plate; determining the installation height of the camera according to the height image; according to the installation height of the camera, obtaining angle images which are shot by the camera of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different shooting angles and contain the calibration plate; and determining the installation angle of the camera according to the angle image.
Description
Technical Field
The present disclosure relates to the field of lane departure systems, and in particular, to a method and an apparatus for calibrating a lane departure system, and a storage medium.
Background
The lane departure early warning system is a system for assisting a driver to reduce traffic accidents caused by lane departure by a vehicle in an alarming mode. The method comprises the steps of collecting lane marking line image information in a road through a camera arranged on a front windshield, taking the lane marking line information collected by a large number of road test tests in the early stage as reference and judgment basis, determining the position and direction information of a vehicle in the lane through calculation, and determining whether alarming is necessary in the current state through an early warning model preset in software according to the current speed and the distance of deviating from the lane line. In order to confirm the position relation and the direction information between the vehicle and the lane line, the accurate installation position of a camera of the lane departure warning system needs to be confirmed firstly, however, because of the error of a part mould and the error generated during installation, the actual installation position and the theoretical installation position of a front-view camera of the lane departure warning system have certain deviation, and therefore compensation needs to be carried out through calibration.
The calibration in the prior art is complicated and has low precision. In the field aspect, a horizontal ground is needed, and a four-wheel positioning mechanism is needed; in the aspect of lighting, the requirement on lighting is high, the lighting can be neither too bright nor too dark, and meanwhile, the lighting can not be directly projected to the camera, so that the requirement of illuminating a field can be met, and the normal work of the camera cannot be influenced; in the aspect of precision, the calibration of the camera is completely manually realized, the precision is not high, and the error is large.
Disclosure of Invention
The present disclosure provides a calibration method and apparatus for a lane departure system, and a storage medium, to solve the problems of complicated calibration process and low calibration precision of the lane departure system in the related art.
In order to achieve the above object, in a first aspect of the embodiments of the present disclosure, a calibration method of a lane departure system is provided, including:
after a vehicle stops on a horizontal ground, standing a calibration plate in front of the vehicle;
acquiring height images which are shot by cameras of a lane departure device in the vehicle at different heights and contain the calibration plate;
determining the installation height of the camera according to the height image;
according to the installation height of the camera, obtaining angle images which are shot by the camera of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different shooting angles and contain the calibration plate;
and determining the installation angle of the camera according to the angle image.
Optionally, the lane departure device comprises a vertical rail mounted above the center of the windshield, and the camera is slidably arranged on the vertical rail;
the acquiring height images which are shot by cameras of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different heights and contain the calibration plate comprises the following steps:
controlling the camera to slide on the vertical rail;
the camera shoots a height image containing the calibration plate when sliding.
Optionally, the determining the installation height of the camera according to the height image includes:
selecting a target height image from a plurality of height images, wherein a specified calibration block on a calibration plate contained in the target height image is positioned in a specified area of the target height image;
and taking the shooting height corresponding to the target height image as the mounting height.
Optionally, the acquiring angle images of the calibration board captured by the camera of the lane departure device at different capturing angles includes:
sliding the camera to the mounting height;
controlling the camera to rotate a shooting angle;
the camera shoots an angle image containing the calibration plate when rotating.
Optionally, before controlling the camera to rotate the shooting angle, the method further includes:
determining a shooting angle range of the camera according to the curvature of a front window glass of the vehicle;
control camera rotation shooting angle includes:
and controlling the camera to rotate a shooting angle within the shooting angle range.
Optionally, the determining the installation angle of the camera according to the angle image includes:
selecting a target angle image from a plurality of angle images, wherein a designated block on a calibration plate contained in the target angle image is consistent with the shape of a designated block in the front view of the calibration plate;
and taking the shooting angle corresponding to the target angle image as the installation angle.
In a second aspect of the embodiments of the present disclosure, a calibration apparatus for a lane departure system is provided, including:
a preparation work module configured to stand a calibration board in front of a vehicle after the vehicle is stopped on a horizontal ground;
a height image acquisition module configured to acquire height images including the calibration plate, which are taken by cameras of lane departure devices in the vehicle at different heights;
a mounting height determination module configured to determine a mounting height of the camera according to the height image;
the angle image acquisition module is configured to acquire angle images which are shot by a camera of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different shooting angles and contain the calibration plate according to the installation height of the camera;
and the installation angle determining module is configured to determine the installation angle of the camera according to the angle image.
Optionally, the lane departure device comprises a vertical rail mounted above the center of the windshield, and the camera is slidably arranged on the vertical rail;
the height image acquisition module includes:
a first sliding control submodule configured to control the camera to slide on the vertical rail;
the first shooting sub-module is configured to shoot a height image containing the calibration plate when the camera slides.
Optionally, the installation height determining module comprises:
a first image determination sub-module configured to select a target height image from a plurality of height images, wherein a designated calibration block on a calibration plate included in the target height image is located in a specified area of the target height image;
and the mounting height determining submodule is configured to take the shooting height corresponding to the target height image as the mounting height.
Optionally, the angle image obtaining module includes:
the second sliding control submodule is configured to slide the camera to the installation height;
a third sliding control submodule configured to control the camera to rotate a shooting angle;
and the second shooting sub-module is configured to shoot an angle image containing the calibration plate when the camera rotates.
Optionally, the angle image obtaining module further includes:
a photographing angle range determination submodule configured to determine a photographing angle range of the camera according to a curvature of a windshield of the vehicle;
the third slip control submodule includes:
and controlling the camera to rotate a shooting angle within the shooting angle range.
Optionally, the installation angle determining module includes:
a second image determination sub-module configured to select a target angle image from a plurality of angle images, wherein a designated block on a calibration plate included in the target angle image is consistent with a shape of a designated block in the calibration plate front view;
and the installation angle determining submodule is configured to take the shooting angle corresponding to the target angle image as the installation angle.
In a third aspect of the embodiments of the present disclosure, a computer-readable storage medium is provided, on which a computer program is stored, which when executed by a processor implements the steps of the method of any one of the above first aspects.
In a fourth aspect of the embodiments of the present disclosure, a calibration apparatus for a lane departure system is provided, including:
the computer-readable storage medium recited in the third aspect above; and
one or more processors to execute the program in the computer-readable storage medium.
By adopting the technical scheme, four-wheel positioning is not needed to be established in calibration preparation work; the adjustment of the installation height and the installation angle is realized through the lane departure system without manual adjustment, and the problems of complicated calibration process and low calibration precision of the lane departure system in the related technology are solved.
Additional features and advantages of the disclosure will be set forth in the detailed description which follows.
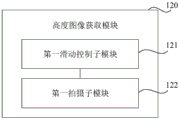
Drawings
The accompanying drawings, which are included to provide a further understanding of the disclosure and are incorporated in and constitute a part of this specification, illustrate embodiments of the disclosure and together with the description serve to explain the disclosure without limiting the disclosure. In the drawings:
fig. 1 is a model diagram of a track of a lane departure device according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
Fig. 2 is a view of an installation position of a rail of the lane departure device of fig. 1.
Fig. 3 is a front view of a vertical rail of a lane departure device of fig. 1.
Fig. 4 is a side view of a vertical rail of a lane departure device of fig. 1.
Fig. 5 is a side view of a slide rail of one of the lane departure devices of fig. 1.
FIG. 6 is a flow chart illustrating a method of calibration of a lane departure system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 7 is a flow chart illustrating the acquisition of a height image according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 8 is a flowchart illustrating the determination of the installation height according to one exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating the acquisition of an angle image according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating the determination of an installation angle according to one exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 11 is a block diagram illustrating a calibration arrangement for a lane departure system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 12 is a block diagram of a height image acquisition module shown in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 13 is a block diagram illustrating an installation height determination module according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 14 is a block diagram illustrating an angular image acquisition module according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
FIG. 15 is another block diagram of an angular image acquisition module shown in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
Fig. 16 is a block diagram illustrating an installation angle determination module according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
Fig. 17 is a block diagram illustrating a calibration arrangement for a lane departure system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure.
Detailed Description
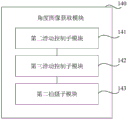
The following detailed description of specific embodiments of the present disclosure is provided in connection with the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the detailed description and specific examples, while indicating the present disclosure, are given by way of illustration and explanation only, not limitation.
The vehicle in the present disclosure may be a car, a truck, a bus, or the like, and the present disclosure is not limited thereto. In this disclosure, the description of the embodiments is made using a truck.
The lane departure device described in this disclosure includes, but is not limited to, a control chip, a driving circuit, a motor, and a camera, and further includes a track, which is not limited in this disclosure. The track is an auxiliary tool in the calibration process of the embodiment of the disclosure, and the track is not used after the calibration is completed.
Fig. 1 is a model view of a track of a lane departure device according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in fig. 1, the track includes a vertical rail 330 and a sliding rail 320, the camera 310 is mounted in the sliding rail 320, and the sliding rail 320 is mounted on the vertical rail 330. The height of the camera 310 is adjusted by adjusting the camera 310 and the slide rail 320 up and down on the vertical rail 330. The angle adjustment of the camera 310 is to adjust the angle of the camera 310 in the slide rail 320.
The head of the camera 310 is fixed to the vertical rail 330, and the tail of the camera 310 is fixed to the slide rail 320.
The vertical rail 330 and the slide rail 320 respectively include a first motor and a second motor therein.
In the present disclosure, in an initial state, the camera 310 is installed in the sliding rail 320 in a state perpendicular to the vertical rail 330 by default, that is, an included angle between the camera 310 and the vertical rail 330 is ninety degrees, and the camera 310 is located at the top of the vertical rail 330. Subsequent adjustment of the mounting height and mounting angle is performed on the basis of the initial state.
Fig. 2 is a view showing an installation position of a rail of a lane departure device of fig. 1, and as shown in fig. 2, the lane departure device 300 is installed at an upper portion of a center of a front window 400 of the vehicle.
Fig. 3 is a front view of a vertical rail of the lane departure device in fig. 1, as shown in fig. 3, the camera 310 and the belt 331 are visible from a front view of the vertical rail 330, the camera 310 moves up and down on the vertical rail 330 by the belt 331, further, the camera 310 and the sliding rail 320 move up and down on the vertical rail 330 by the belt 331, and the sliding rail 320 is not shown in fig. 3. The belt 331 is driven by the first motor, and the operation of the first motor is controlled by the lane departure system. In this disclosure, the tool for driving the camera 310 and the slide rail 320 to move may be the belt 331, a chain, or other tools, which is not limited in this disclosure.
Fig. 4 is a side view of a vertical rail of a lane departure device of fig. 1, and as shown in fig. 4, a side view of the vertical rail 330 shows a path along which the camera 310 and the slide rail 320 move.
Fig. 5 is a side view of a slide rail of a lane departure device of fig. 1, as shown in fig. 5, the slide rail 320 being used to adjust the angle of the camera 310.
Fig. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a method of calibrating a lane departure system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in fig. 6, the method of calibrating a lane departure system comprising:
and S10, standing the calibration board in front of the vehicle after the vehicle stops on the horizontal ground.
And S20, acquiring height images containing the calibration board, which are shot by the cameras of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different heights.
And S30, determining the installation height of the camera according to the height image.
And S40, acquiring angle images which are shot by the camera of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different shooting angles and contain the calibration plate according to the installation height of the camera.
And S50, determining the installation angle of the camera according to the angle image.
In S10, preparation before calibration is required. The vehicle is first stopped on a horizontal ground straightly, and the vehicle may be operated manually or controlled without any control, which is not limited in this disclosure.
After the vehicle is stably stopped, the calibration plate is placed according to the model of the vehicle, if the vehicle is a truck, the height of the truck is about 2 meters, the calibration plate can be erected at the position of a distance of 2.5 meters to 3 meters from the center of a window right in front of the truck, the height of the calibration plate is related to the height of a front window of the truck, and the height of the calibration plate is in direct proportion to the height of the front window of the truck, so that the calibration plate can be completely seen when the calibration plate is seen through the front window of the truck to the right front. The calibration plate is provided with a plurality of calibration blocks, and the calibration blocks are related to the adjustment of the subsequent camera mounting height and mounting angle.
And after the calibration plate is placed, the calibration preparation work is completed.
In S20, height images including the calibration plate taken by the cameras of the lane departure device at different heights in the vehicle are acquired.
FIG. 7 is a flowchart illustrating a method of acquiring a height image according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, including the steps of:
and S21, controlling the camera to slide on the vertical rail.
At S21, the camera is mounted on the rail, and the rail is mounted above the center of the front window of the vehicle, and the adjustment of the height of the camera is the adjustment of the vertical position of the whole of the camera and the slide rail on the vertical rail. The vertical rail drives the camera and the sliding rail to move through the belt or the chain, the belt or the chain moves under the control of the first motor, and the first motor is controlled by the lane departure system.
The lane departure system needs to acquire vehicle type information of the vehicle, writes the vehicle type information into an algorithm, and calculates according to the vehicle type information and outputs a height control result to control the first motor.
The vehicle type information of the vehicle includes, but is not limited to, the height of the entire vehicle, the width of the vehicle, the range of the wiper track, and the curvature of the front window glass.
The vehicle type information CAN be acquired through a CAN bus or manually input, and if a manufacturer of the vehicle stores the vehicle type information of the vehicle in the CAN bus, the vehicle type information of the vehicle CAN be acquired by directly reading the CAN bus.
The track is connected with the lane departure system through a data line, and the height control result is transmitted to the first motor in the track through the data line.
The data transmission in this disclosure may be a data line, and may also be a wireless transmission, such as 4G, bluetooth, WIFI, and the like, which this disclosure does not limit.
And S22, shooting a height image containing the calibration board through the camera when the camera slides.
In S22, the camera performs a camera shooting operation during a sliding process, i.e., a height adjustment process, and transmits a camera video including the calibration board in front of the lens to the lane departure system in real time, and data may be transmitted through a data line or wirelessly, such as 4G, bluetooth, WIFI, and the like, which is not limited by the present disclosure.
In S30, the installation height of the camera is determined based on the height image.
FIG. 8 is a flowchart illustrating the determination of the installation height of the present disclosure according to an exemplary embodiment, including the steps of:
and S31, selecting a target height image from the height images, wherein the designated calibration block on the calibration plate included in the target height image is positioned in the specified area of the target height image.
In S31, the lane departure system analyzes the height image acquired in step S22. The lane departure system has a preset standard area, firstly, a plurality of calibration blocks are required to be appointed on the calibration plate as appointed calibration blocks, and when the appointed calibration blocks in the height image are all in the standard area of the lane departure system, the height image is appointed as the target height image.
The lane departure system firstly analyzes the received camera videos to obtain the height images, namely, the camera videos at different moments are subjected to screenshot processing and converted into static height images. The acquisition of the static height image can also be carried out by other operations.
Assuming that four calibration blocks at the center of the calibration plate are designated as the designated calibration blocks, the lane departure system analyzes the static height image obtained by screenshot, judges whether the height image contains the designated calibration blocks, further judges whether the calibration blocks are completely located in the standard area if the height image contains the designated calibration blocks, and designates the height image meeting the two requirements as the target height image. And if a plurality of height images meeting the requirements appear, selecting the height image which contains the designated positioning block and has the clearest imaging and the position closest to the center of the standard area as the target height image.
And S32, taking the shooting height corresponding to the target height image as the installation height.
In S32, it is necessary to determine the shooting height corresponding to the target height image obtained in step S31 as the mounting height of the camera. And after the target height image is obtained, the lane departure system controls the first motor to stop working, stops the camera at a shooting height corresponding to the target height image, determines the shooting height as the installation height, and records the data of the installation height in the lane departure system.
In S40, angle images including the calibration plate, which are captured by the camera of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different capturing angles, are acquired according to the mounting height of the camera.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating the acquisition of an angle image according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure. The method comprises the following steps:
and S41, sliding the camera to the installation height.
In S41, the camera needs to be moved and fixed at the mounting height, which is described in detail in step S32.
And S42, controlling the camera to rotate by a shooting angle.
In S42, the second motor controls the camera and the tail of the slide rail to slide on the slide rail to adjust the shooting angle.
It should be noted that before controlling the camera to rotate the shooting angle, the shooting angle range of the camera needs to be determined according to the curvature of the windshield of the vehicle. And controlling the camera to rotate the shooting angle is to control the camera to rotate the shooting angle within the shooting angle range.
The lane departure system writes the curvature of the front window glass of the vehicle into an algorithm, the algorithm obtains a preliminary angle position and a shooting angle range through calculation, and the second motor is controlled to operate through the preliminary angle position, so that the tail part of the camera connected with the sliding rail is driven to move to the preliminary angle position. The transmission of preliminary angular position and the data of shooting angle scope can be through the data line, also can transmit through wireless, like 4G, bluetooth and WIFI etc. this disclosure does not limit this
When the tail of the camera reaches the initial angle position, the second motor is controlled to operate according to the shooting angle range, so that the second motor drives the tail of the camera to operate within the shooting angle range.
And S43, shooting an angle image containing the calibration board through the camera when the camera rotates.
In S43, the camera performs a camera shooting operation during a rotation process, i.e., a shooting angle adjustment process, and transmits a camera video including the calibration board in front of the lens to the lane departure system in real time, and data may be transmitted through a data line or wirelessly, such as 4G, bluetooth, WIFI, and the like, which is not limited by the present disclosure.
In S50, the installation angle of the camera is determined based on the angle image.
FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating the determination of an installation angle according to one exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure. The method comprises the following steps:
and S51, selecting a target angle image from the angle images, wherein the designated block on the calibration board contained in the target angle image is consistent with the shape of the designated block in the front view of the calibration board.
In S51, the lane departure system analyzes the angle image acquired in step S43. The lane departure system presets the size ratio of a designated block in the angle image to the designated block in the calibration plate front view, and when the size ratio of the designated block in the angle image to the designated block in the calibration plate front view reaches a preset size ratio, the angle image is designated as the target angle image.
The lane departure system firstly analyzes the received camera videos to obtain the angle images, namely, the camera videos at different moments are subjected to screenshot processing and converted into static angle images. The acquisition of the static angle image can also be carried out by other operations.
Assuming that four calibration blocks at the center of the calibration plate are designated as the designated calibration blocks, the size ratio preset by the lane departure system is 1:1, that is, the designated calibration blocks in the angle image are the same as the designated calibration blocks in the calibration plate front view and are also the same as the shape ratio, that is, the shape of the designated calibration blocks in the angle image is not skewed.
And the lane departure system analyzes the static angle image obtained by screenshot, judges whether the size ratio of the designated scaling block in the angle image to the designated scaling block in the front view of the scaling plate is 1:1 or not, and designates the angle image meeting the requirements as the target angle image. And if a plurality of angle images meeting the requirements appear, selecting the included angle image which is most clear in imaging of the designated positioning block as the target angle image.
And S52, taking the shooting angle corresponding to the target angle image as the installation angle.
In S52, it is necessary to determine the shooting angle corresponding to the target angle image obtained in step S51 as the mounting angle of the camera. And after the target angle image is obtained, the lane departure system controls the second motor to stop working, stops the camera at a shooting angle corresponding to the target angle image, determines the shooting angle as the installation angle, and records the data of the installation angle in the lane departure system.
Through the steps, the lane departure system can accurately acquire the data information of the installation height and the installation angle of the camera, transmit the data information to the lane departure device, and then install and fix the camera and the rest parts of the lane departure device at the installation height and the installation angle, so that calibration is completed.
Fig. 11 is a block diagram illustrating a calibration apparatus 100 for a lane departure system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, and as shown in fig. 11, the calibration apparatus 100 for a lane departure system includes:
a preparation module 110 configured to stand the calibration board in front of the vehicle after the vehicle is stopped on a horizontal ground.
A height image acquiring module 120 configured to acquire height images including the calibration plate taken by cameras of lane departure devices in the vehicle at different heights.
A mounting height determination module 130 configured to determine a mounting height of the camera according to the height image.
An angle image obtaining module 140 configured to obtain angle images including the calibration plate, which are captured by a camera of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different capturing angles, according to the installation height of the camera.
A mounting angle determining module 150 configured to determine a mounting angle of the camera according to the angle image.
Fig. 12 is a block diagram illustrating a height image acquisition module 110 according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in fig. 12, the height image acquisition module 110 including:
and a first sliding control submodule 111 configured to control the camera to slide on the vertical rail.
A first photographing sub-module 112 configured to photograph a height image including the calibration plate by the camera while sliding.
Fig. 13 is a block diagram of a mounting height determination module 120 shown in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, the mounting height determination module 120 including, as shown in fig. 13:
the first image determining sub-module 121 is configured to select a target height image from a plurality of height images, where a designated calibration block on a calibration plate included in the target height image is located in a specified area of the target height image.
A mounting height determination sub-module 122 configured to take a shooting height corresponding to the target height image as the mounting height.
Fig. 14 is a block diagram illustrating an angle image acquisition module 140 according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in fig. 14, the angle image acquisition module 140 including:
and a second sliding control submodule 141 configured to slide the camera to the mounting height.
And a third sliding control submodule 142 configured to control the camera to rotate a shooting angle.
And a second photographing sub-module 143 configured to photograph an angle image including the calibration plate by the camera while rotating.
The third sliding control sub-module 142 is further configured to control the camera to rotate a shooting angle within the shooting angle range.
Fig. 15 is another block diagram of the angle image acquisition module 140 shown in the present disclosure according to an exemplary embodiment, and as shown in fig. 15, the angle image acquisition module 140 further includes:
a photographing angle range determination submodule 144 configured to determine a photographing angle range of the camera according to a curvature of a windshield of the vehicle.
Fig. 16 is a block diagram of a mounting angle determination module 150 shown in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in fig. 16, the mounting angle determination module 150 including:
a second image determination sub-module 151 configured to select a target angle image among a plurality of angle images, the target angle image including a designated block on a calibration plate having a shape identical to a shape of the designated block in the calibration plate front view.
And an installation angle determining submodule 152 configured to take a shooting angle corresponding to the target angle image as the installation angle.
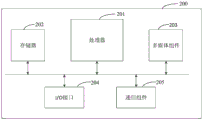
Fig. 17 is a block diagram illustrating a calibration arrangement for a lane departure system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown in fig. 17, the apparatus 200 may include: a processor 201, a memory 202, a multimedia component 203, an input/output (I/O) interface 204, and a communication component 205.
The processor 201 is configured to control the overall operation of the apparatus 200 to complete all or part of the steps of the calibration method of the lane departure system. The memory 202 is used to store various types of data to support operation of the device 200, which may include, for example, instructions for any application or method operating on the device 200, as well as application-related data. The Memory 202 may be implemented by any type of volatile or non-volatile Memory device or combination thereof, such as Static Random Access Memory (SRAM), Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM), Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EPROM), Programmable Read-Only Memory (PROM), Read-Only Memory (ROM), magnetic Memory, flash Memory, magnetic disk or optical disk. The multimedia components 203 may include screen and audio components. Wherein the screen may be, for example, a touch screen and the audio component is used for outputting and/or inputting audio signals. For example, the audio component may include a microphone for receiving external audio signals. The received audio signal may further be stored in the memory 202 or transmitted through the communication component 205. The audio assembly also includes at least one speaker for outputting audio signals. The I/O interface 204 provides an interface between the processor 201 and other interface modules, such as a keyboard, mouse, buttons, etc. These buttons may be virtual buttons or physical buttons. The communication component 205 is used for wired or wireless communication between the apparatus 200 and other devices. Wireless Communication, such as Wi-Fi, bluetooth, Near Field Communication (NFC), 2G, 3G, or 4G, or a combination of one or more of them, so that the corresponding Communication component 205 may include: Wi-Fi module, bluetooth module, NFC module.
In an exemplary embodiment, the apparatus 200 may be implemented by one or more Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), Digital Signal Processors (DSPs), Digital Signal Processing Devices (DSPDs), Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs), Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), controllers, microcontrollers, microprocessors, or other electronic components, for performing the above-mentioned lane departure system calibration method.
In another exemplary embodiment, a computer readable storage medium, such as a memory 202, comprising program instructions executable by a processor 201 of the apparatus 200 to perform the above-described method of calibrating a lane departure system is also provided.
The preferred embodiments of the present disclosure are described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, however, the present disclosure is not limited to the specific details of the above embodiments, and various simple modifications may be made to the technical solution of the present disclosure within the technical idea of the present disclosure, and these simple modifications all belong to the protection scope of the present disclosure.
It should be noted that the various features described in the above embodiments may be combined in any suitable manner without departing from the scope of the invention. In order to avoid unnecessary repetition, various possible combinations will not be separately described in this disclosure.
In addition, any combination of various embodiments of the present disclosure may be made, and the same should be considered as the disclosure of the present disclosure, as long as it does not depart from the spirit of the present disclosure.
Claims (12)
1. A method for calibrating a lane departure system, comprising:
after a vehicle stops on a horizontal ground, standing a calibration plate in front of the vehicle;
acquiring height images which are shot by cameras of a lane departure device in the vehicle at different heights and contain the calibration plate;
determining the installation height of the camera according to the height image;
according to the installation height of the camera, obtaining angle images which are shot by the camera of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different shooting angles and contain the calibration plate;
determining the installation angle of the camera according to the angle image;
the lane departure device comprises a vertical rail arranged above the center of the windshield, and the camera is arranged on the vertical rail in a sliding manner;
the acquiring height images which are shot by cameras of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different heights and contain the calibration plate comprises the following steps:
controlling the camera to slide on the vertical rail;
the camera shoots a height image containing the calibration plate when sliding.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein determining the mounting height of the camera from the height image comprises:
selecting a target height image from a plurality of height images, wherein a specified calibration block on a calibration plate contained in the target height image is positioned in a specified area of the target height image;
and taking the shooting height corresponding to the target height image as the mounting height.
3. The method of claim 1, wherein the obtaining of the angle images of the calibration plate taken by the camera of the lane departure device at different taking angles comprises:
sliding the camera to the mounting height;
controlling the camera to rotate a shooting angle;
the camera shoots an angle image containing the calibration plate when rotating.
4. The method of claim 3, wherein before controlling the camera to rotate the shooting angle, further comprising:
determining a shooting angle range of the camera according to the curvature of a front window glass of the vehicle;
control camera rotation shooting angle includes:
and controlling the camera to rotate a shooting angle within the shooting angle range.
5. The method of claim 1, wherein determining the mounting angle of the camera from the angle image comprises:
selecting a target angle image from a plurality of angle images, wherein a designated block on a calibration plate contained in the target angle image is consistent with the shape of a designated block in the front view of the calibration plate;
and taking the shooting angle corresponding to the target angle image as the installation angle.
6. A calibration apparatus for a lane departure system, comprising:
the preparation working module is used for standing the calibration plate in front of the vehicle after the vehicle stops on the horizontal ground;
the height image acquisition module is used for acquiring height images which are shot by cameras of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different heights and contain the calibration plate;
the installation height determining module is used for determining the installation height of the camera according to the height image;
the angle image acquisition module is used for acquiring angle images which are shot by the cameras of the lane departure device in the vehicle at different shooting angles and contain the calibration plate according to the installation height of the cameras;
the installation angle determining module is used for determining the installation angle of the camera according to the angle image;
the lane departure device comprises a vertical rail arranged above the center of the windshield, and the camera is arranged on the vertical rail in a sliding manner;
the height image acquisition module includes:
the first sliding control submodule is used for controlling the camera to slide on the vertical rail;
the first shooting submodule is used for shooting a height image containing the calibration plate when the camera slides.
7. The apparatus of claim 6, wherein the installation height determination module comprises:
the first image determining submodule is used for selecting a target height image from a plurality of height images, and a specified calibration block on a calibration plate contained in the target height image is positioned in a specified area of the target height image;
and the mounting height determining submodule is used for taking the shooting height corresponding to the target height image as the mounting height.
8. The apparatus of claim 6, wherein the angular image acquisition module comprises:
the second sliding control submodule is used for sliding the camera to the mounting height;
the third sliding control submodule is used for controlling the camera to rotate a shooting angle;
and the second shooting submodule is used for shooting the angle image containing the calibration plate when the camera rotates.
9. The apparatus of claim 8, wherein the angular image acquisition module further comprises:
the shooting angle range determining submodule is used for determining the shooting angle range of the camera according to the curvature of the front window glass of the vehicle;
the third slip control submodule includes:
and controlling the camera to rotate a shooting angle within the shooting angle range.
10. The apparatus of claim 6, wherein the mounting angle determining module comprises:
a second image determination submodule, configured to select a target angle image from a plurality of angle images, where a designated block on a calibration plate included in the target angle image is consistent with a shape of a designated block in a front view of the calibration plate;
and the mounting angle determining submodule is used for taking the shooting angle corresponding to the target angle image as the mounting angle.
11. A computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored which, when being executed by a processor, carries out the steps of the method according to any one of claims 1 to 5.
12. A calibration apparatus for a lane departure system, comprising:
a memory having a computer program stored thereon; and
a processor for executing the computer program in the memory to carry out the steps of the method of any one of claims 1 to 5.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811625128.1A CN111376841B (en) | 2018-12-28 | 2018-12-28 | Calibration method and device of lane departure system and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811625128.1A CN111376841B (en) | 2018-12-28 | 2018-12-28 | Calibration method and device of lane departure system and storage medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111376841A CN111376841A (en) | 2020-07-07 |
| CN111376841B true CN111376841B (en) | 2021-09-17 |
Family
ID=71213352
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811625128.1A Active CN111376841B (en) | 2018-12-28 | 2018-12-28 | Calibration method and device of lane departure system and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111376841B (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113942458B (en) * | 2021-10-29 | 2022-07-29 | 禾多科技(北京)有限公司 | Control method, device, equipment and medium for vehicle-mounted camera adjusting system |
| CN115100299B (en) * | 2022-08-29 | 2023-02-10 | 广州镭晨智能装备科技有限公司 | Calibration method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4820221B2 (en) * | 2006-06-29 | 2011-11-24 | 日立オートモティブシステムズ株式会社 | Car camera calibration device and program |
| EP2767846B1 (en) * | 2013-02-18 | 2017-01-11 | Volvo Car Corporation | Method for calibrating a sensor cluster in a motor vehicle |
| CN104268884B (en) * | 2014-09-30 | 2017-11-17 | 苏州智华汽车电子有限公司 | A kind of calibration system and method for the lane departure warning based on car networking |
| DE102016006615A1 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2016-11-17 | Daimler Ag | Method for determining calibration parameters of a vehicle camera and calibration device |
| CN207809249U (en) * | 2018-02-05 | 2018-09-04 | 南昌比亚迪电子部品件有限公司 | A kind of liftable vehicle-mounted camera |
-
2018
- 2018-12-28 CN CN201811625128.1A patent/CN111376841B/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111376841A (en) | 2020-07-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110706282B (en) | Automatic calibration method and device for panoramic system, readable storage medium and electronic equipment | |
| CN110796711B (en) | Panoramic system calibration method and device, computer readable storage medium and vehicle | |
| CN110520707B (en) | Multifunctional unit for analyzing and calibrating devices and components of a vehicle | |
| US10227032B2 (en) | Vehicle headlamp alignment system and method | |
| CN107249922B (en) | Display device for vehicle | |
| US9500339B2 (en) | Method and a device for testing a lighting driving assistance system | |
| KR100888721B1 (en) | Gis system | |
| EP3816967A1 (en) | Automatic parking method, apparatus and system, and vehicle | |
| JP4461091B2 (en) | Position detection apparatus and correction method thereof | |
| JPH07280704A (en) | Method and equipment for testing headlight for vehicle | |
| CN111376841B (en) | Calibration method and device of lane departure system and storage medium | |
| CN110827358A (en) | Camera calibration method applied to automatic driving automobile | |
| CN110930462A (en) | Vehicle camera external parameter calibration method, device, system and computer equipment | |
| CN109509231A (en) | Panorama system calibration facility | |
| US12112583B2 (en) | Automotive sensor calibration system and related methodology | |
| AU2020249324A1 (en) | Method, apparatus, server and system for calibrating at least one camera of a driver assistance system | |
| KR20080010768A (en) | A position move equipment using the position detection method and its method | |
| US20160353032A1 (en) | Camera apparatus and method for generating image signal for viewfinder | |
| WO2016179798A1 (en) | A system and a computer-implemented method for calibrating at least one senser | |
| KR100892443B1 (en) | Gis system | |
| CN105721773A (en) | Video acquisition system and method | |
| JP2020010123A (en) | On-vehicle photographing apparatus, photographing system and photographing method | |
| JP2006074329A (en) | Optical axis adjustment apparatus for on-vehicle camera | |
| EP3945300A1 (en) | Adas calibration system for calibrating at least one headlamp of a vehicle | |
| JP2014235022A (en) | Navigation device and navigation method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| EE01 | Entry into force of recordation of patent licensing contract | ||
| EE01 | Entry into force of recordation of patent licensing contract |
Application publication date: 20200707 Assignee: Beijing Zhike chelian Technology Co.,Ltd. Assignor: BEIQI FOTON MOTOR Co.,Ltd. Contract record no.: X2022980018253 Denomination of invention: Calibration method, device and storage medium of lane departure system Granted publication date: 20210917 License type: Common License Record date: 20221013 |