CN111233198A - Industrial wastewater treatment method and device - Google Patents
Industrial wastewater treatment method and device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111233198A CN111233198A CN202010087589.9A CN202010087589A CN111233198A CN 111233198 A CN111233198 A CN 111233198A CN 202010087589 A CN202010087589 A CN 202010087589A CN 111233198 A CN111233198 A CN 111233198A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- industrial wastewater
- wastewater
- reaction
- tank
- treated
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F9/00—Multistage treatment of water, waste water or sewage
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/28—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by sorption
- C02F1/281—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by sorption using inorganic sorbents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/28—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by sorption
- C02F1/283—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by sorption using coal, charred products, or inorganic mixtures containing them
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/52—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by flocculation or precipitation of suspended impurities
- C02F1/5236—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by flocculation or precipitation of suspended impurities using inorganic agents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/72—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by oxidation
- C02F1/722—Oxidation by peroxides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F2101/00—Nature of the contaminant
- C02F2101/30—Organic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F2305/00—Use of specific compounds during water treatment
- C02F2305/02—Specific form of oxidant
- C02F2305/026—Fenton's reagent
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Hydrology & Water Resources (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Water Supply & Treatment (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Treatment Of Water By Oxidation Or Reduction (AREA)
- Separation Of Suspended Particles By Flocculating Agents (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses an industrial wastewater treatment method and device, and relates to the technical field of water treatment. The industrial wastewater treatment method comprises the following steps: s10, carrying out contact flocculation pretreatment on the industrial wastewater, and then carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain supernatant, namely the wastewater to be treated; s20, adding patina into the wastewater to be treated, mixing and adsorbing, adding a hydrogen peroxide solution to perform a Fenton-like reaction until organic matters in the wastewater to be treated are completely oxidized, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain clear water; s30, further removing organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water, and finishing the treatment of the industrial wastewater; the patina is prepared by fully mixing and reacting sodium carbonate, ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and iron powder and then performing efficient gravity concentration. The invention has simple flow, high processing efficiency, convenient operation and management and high system operation stability.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to a method and a device for treating industrial wastewater.
Background
With the increasing requirements for environmental protection, the requirements for wastewater treatment are becoming more and more strict, and the requirements for environment for people are also increasing and more, on the other hand, the environmental bearing capacity is also becoming weaker and weaker due to the continuous erosion of human production and living activities, so that the nation puts forward higher requirements for the discharge of various industrial wastewater. Such as Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) in industrial water pollutant discharge standard of pulping and papermaking (GB3544-2008) and Chinese medicine pharmacy (GB21906-2008)cr) The minimum emission requirements of three characteristic pollutant indexes of chromaticity and suspended matter (SS) are 100mg/L, 50 times and 50mg/L respectively.
At present, the common traditional industrial wastewater treatment methods such as coagulation, adsorption, chemical oxidation and the like generally have the problems of low decolorization efficiency, incapability of meeting the emission requirement and easiness in generating secondary pollution; advanced oxidation technologies such as ozone oxidation and photo-oxidation and advanced separation technologies such as membrane filtration and reverse osmosis have the problems of limited use environment, high cost and difficulty in large-scale engineering application.
Disclosure of Invention
The invention mainly aims to provide an industrial wastewater treatment method and an industrial wastewater treatment device, and aims to provide the industrial wastewater treatment method which is high in treatment efficiency, mild in condition and good in stability.
In order to achieve the purpose, the invention provides an industrial wastewater treatment method, which comprises the following steps:
s10, carrying out contact flocculation pretreatment on the industrial wastewater, and then carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain supernatant, namely the wastewater to be treated;
s20, adding patina into the wastewater to be treated, mixing and adsorbing, adding a hydrogen peroxide solution to perform a Fenton-like reaction until organic matters in the wastewater to be treated are completely oxidized, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain clear water;
s30, further removing organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water, and finishing the treatment of the industrial wastewater;
the patina is prepared by fully mixing and reacting sodium carbonate, ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and iron powder and then performing efficient gravity concentration.
Optionally, in step S20, the mass ratio of the patina to the wastewater to be treated is 1: (5-20); and/or the presence of a gas in the gas,
in step S20, the mass ratio of the hydrogen peroxide to the wastewater to be treated is (3-15): 10000.
optionally, step S30 includes:
and enabling the clarified water to flow through an activated carbon adsorption filter bed, and removing organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water through the adsorption action of the activated carbon to finish the treatment of the industrial wastewater.
Optionally, the industrial wastewater is one or more of pulping and papermaking black liquor, textile dyeing and finishing wastewater and traditional Chinese medicine pharmaceutical wastewater.
Optionally, step S10 specifically includes:
s101, adding a flocculating agent into the industrial wastewater, and stirring to enable the industrial wastewater to be fully contacted with the flocculating agent;
s102, standing for 1-2 hours to obtain supernatant, namely wastewater to be treated.
Optionally, before step S10, the industrial wastewater treatment method further includes: homogenizing and uniformly measuring the industrial wastewater, and staying for 6-24 hours.
The present invention further provides an industrial wastewater treatment apparatus as described above, comprising:
the pretreatment system is used for pretreating industrial wastewater, so that solid and liquid are separated into layers, and supernatant is collected to obtain wastewater to be treated;
the adsorption reaction system is arranged at the downstream of the pretreatment system and comprises an adsorption tank and a reaction sedimentation tank positioned at the downstream of the adsorption tank, the adsorption tank is used for mixing the wastewater to be treated with the patina, the reaction sedimentation tank is used for carrying out Fenton-like reaction on the mixture of the wastewater to be treated and the patina and a hydrogen peroxide solution, and after the reaction is finished, solid-liquid separation is carried out and supernatant is collected to obtain clarified water; and the number of the first and second groups,
the advanced treatment system is arranged at the downstream of the adsorption reaction system and comprises an activated carbon adsorption filter bed for treating the clarified water so as to remove organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water;
the patina is prepared by fully mixing and reacting sodium carbonate, ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and iron powder and then performing efficient gravity concentration.
Optionally, the pretreatment system comprises a contact flocculation tank and a first sedimentation tank arranged at the downstream of the contact flocculation tank, the contact flocculation tank is used for mixing industrial wastewater and a flocculating agent, stirring is carried out to enable the industrial wastewater to be fully contacted with the flocculating agent, and the first sedimentation tank is used for allowing the fully contacted industrial wastewater and the flocculating agent to stand to obtain a supernatant.
Optionally, the reaction sedimentation tank comprises a reaction tank and a second sedimentation tank arranged at the downstream of the reaction tank, the reaction tank is used for allowing the mixture of the wastewater to be treated and the patina to perform a Fenton-like reaction with a hydrogen peroxide solution, and the second sedimentation tank is used for separating solid from liquid and collecting the liquid after the reaction is finished to obtain clarified water.
Optionally, the pretreatment system further comprises a regulating tank, wherein the regulating tank is arranged at the upstream of the contact flocculation tank and is used for homogenizing and homogenizing the industrial wastewater before the industrial wastewater enters the contact flocculation tank.
In the technical scheme provided by the invention, on one hand, the combination-state ferrous iron with high reactivity in the green rust and the hydrogen peroxide form the Fenton-like reagent, and compared with other commonly adopted traditional Fenton reagents formed by free-state ferrous iron and hydrogen peroxide, the Fenton-like reagent has stronger capacity of degrading organic matters, has no strict requirement on the pH value of the reaction, and can achieve a good reaction effect under a neutral condition; on the other hand, by utilizing the large specific surface area and the high adsorption performance of the patina, a large amount of high-chroma substances in the industrial wastewater are adsorbed on the surface of the patina, so that the concentration of the subsequent organic matters participating in the Fenton-like reaction is greatly improved, and the reaction rate is obviously improved. In addition, the high iron green rust generated after the Fenton-like reaction has good precipitation performance and still has high contact flocculation activity, and the precipitate is concentrated and then is recycled for adsorbing impurities in raw water, so that the pretreatment effect can be realized, the burden of subsequent treatment is greatly reduced, and the cyclic utilization is realized. Finally, after the Fenton-like reaction, the complex macromolecular organic matters are changed into relatively simple micromolecules, and can easily penetrate through the surface of the adsorbent to enter the internal pores. The invention has simple flow, high processing efficiency, convenient operation and management and high system operation stability.
Drawings
In order to more clearly illustrate the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art, the drawings used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art will be briefly described below, it is obvious that the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present invention, and for those skilled in the art, other related drawings can be obtained according to the drawings without creative efforts.
FIG. 1 is a schematic flow diagram of an embodiment of a method for treating industrial wastewater according to the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a process flow diagram of FIG. 1;
FIG. 3 is a process flow diagram of the industrial wastewater treatment method of example 1 of the present invention.
The implementation, functional features and advantages of the objects of the present invention will be further explained with reference to the accompanying drawings.
Detailed Description
In order to make the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below. It is to be understood that the described embodiments are merely a few embodiments of the invention, and not all embodiments.
It should be noted that those whose specific conditions are not specified in the examples were performed according to the conventional conditions or the conditions recommended by the manufacturer. The reagents or instruments used are not indicated by the manufacturer, and are all conventional products available commercially. In addition, the meaning of "and/or" appearing throughout includes three juxtapositions, exemplified by "A and/or B" including either A or B or both A and B. In addition, technical solutions between various embodiments may be combined with each other, but must be realized by a person skilled in the art, and when the technical solutions are contradictory or cannot be realized, such a combination should not be considered to exist, and is not within the protection scope of the present invention. All other embodiments, which can be derived by a person skilled in the art from the embodiments given herein without making any creative effort, shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
The existing industrial wastewater treatment method generally has the problems of low decolorization efficiency, high cost and easy generation of secondary pollution.
In view of this, the invention provides an industrial wastewater treatment method, and aims to provide an industrial wastewater treatment method with high treatment efficiency, mild conditions and good stability.
Referring to fig. 1, the method for treating industrial wastewater of the present invention comprises the following steps:
s10, carrying out contact flocculation pretreatment on the industrial wastewater, and then carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain supernatant, namely the wastewater to be treated;
preferably, step S10 specifically includes:
s101, adding a flocculating agent into the industrial wastewater, and stirring to enable the industrial wastewater to be fully contacted with the flocculating agent;
s102, standing for 1-2 hours to obtain supernatant, namely wastewater to be treated.
The type of the flocculant is not limited in the present invention, and preferably, in the embodiment of the present invention, the flocculant is high iron green rust (described in detail below) obtained by the reaction in step S20, the high iron green rust has strong contact flocculation activity, the high iron green rust is used as the flocculant to pretreat the industrial wastewater, suspended matters, colloidal impurities and colored substances in the industrial wastewater are pre-adsorbed, then the mud-water mixture is left for 1-2 hours, and a supernatant is obtained to serve as a pretreatment for the wastewater to be treated, so as to greatly reduce the burden of subsequent treatment.
Preferably, before the step S10, the industrial wastewater treatment method further includes: and homogenizing and uniformly measuring the industrial wastewater, and staying for 6-24 hours.
The regulating reservoir has the functions of regulating the water quantity and stabilizing the water quality, and the industrial wastewater stays in the regulating reservoir for 6-24 hours before being pretreated, for example, stays for 20 hours, so that the water quality, the flow and the like are uniform, and the impact load on subsequent treatment facilities is greatly reduced.
In the embodiment of the invention, the lower layer sludge obtained after pretreatment and solid-liquid separation is subjected to concentration, dehydration and landfill. The sludge is sequentially concentrated and dehydrated to form a sludge cake, so that the volume of the sludge is greatly reduced, the sludge is convenient to transport and bury, and the occupied space is reduced. In addition, water inevitably occurs during concentration and dehydration, and the water contains impurities such as organic substances and can be treated by the industrial wastewater treatment method proposed by the present invention.
S20, adding patina into the wastewater to be treated, mixing and adsorbing, adding a hydrogen peroxide solution to perform a Fenton-like reaction until organic matters in the wastewater to be treated are completely oxidized, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain clear water; the patina is prepared by fully mixing and reacting sodium carbonate, ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and iron powder and then performing efficient gravity concentration.
In the embodiment of the invention, the preparation method of the patina is prepared according to the method in patent 201811559445.8, and the patina is prepared by fully mixing and reacting sodium carbonate, ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and iron powder and then performing efficient gravity concentration. Fully contacting the wastewater to be treated with the patina, adsorbing a large amount of organic matters in the wastewater to be treated on the surface of the patina, and then adding a hydrogen peroxide solution into the wastewater, wherein the system generates a Fenton-like reaction: under the catalytic action of high-reactivity combined-state ferrous iron in the green rust, hydrogen peroxide is decomposed to generate a large amount of hydroxyl radicals, and the hydroxyl radicals rapidly degrade adsorbed organic matters into inorganic small molecules, so that wastewater decolorization and COD (chemical oxygen demand) are realizedcrAnd (4) removing. And carrying out solid-liquid separation on the mixture after the reaction to obtain clear water.
Because the sludge concentrated at the bottom is the high-iron green rust generated by oxidation, has good contact flocculation activity and good sedimentation performance, the sludge is used as a flocculating agent for the pretreatment of the industrial wastewater in the step S101, so that the recycling is realized, and the sustainable development requirement is met.
The invention is not limited with respect to the ratio of the mass of patina to the wastewater to be treated in this step, and preferably, in the embodiment of the invention, the ratio of the mass of patina to the wastewater to be treated is 1: (5-20), more preferably 1: 10, when the mass ratio of the patina to the wastewater to be treated is 1: when 10, the effect of treating industrial wastewater is the best.
Likewise, the present invention is not limited with respect to the mass ratio of hydrogen peroxide to wastewater to be treated in this step, and preferably, in the embodiment of the present invention, the mass ratio of hydrogen peroxide to wastewater to be treated is (3-15): 10000, more preferably 12: 10000, the reaction is more complete in the above proportion. Wherein the hydrogen peroxide solution is a hydrogen peroxide solution with an effective hydrogen peroxide content of 30%.
The clear water obtained in step S20, wherein suspended matter can stably reach the discharge requirement and CODcrAnd the color intensity is greatly reduced, therefore, the clarified water obtained in the step can be directly used in certain unit operations with low requirements on water quality in a factory, and further treatment is needed in the step S30 if the clarified water is discharged.
S30, further removing organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water, and finishing the treatment of the industrial wastewater;
after the wastewater is subjected to the green rust adsorption-Fenton-like reaction, complex macromolecular organic matters are changed into relatively simple micromolecules and are easier to remove, the invention is not limited to the method for removing the organic matters and the chromaticity in the clarified water, and preferably, in the embodiment of the invention, the method for removing the organic matters and the chromaticity in the clarified water is to pass the clarified water through an activated carbon adsorption filter bed, so that the micromolecular organic matters can easily penetrate through the surface of an adsorbent to enter internal pores, the deep adsorption process is higher in adsorption efficiency and larger in saturated adsorption capacity compared with the traditional adsorption process, and the regeneration period is greatly prolonged.
The invention is not limited for the type of the waste water to be treated, and preferably, the industrial waste water is one or more of pulping and papermaking black liquor, textile dyeing and finishing waste water and traditional Chinese medicine pharmaceutical waste water. The industrial wastewater has high organic matter content, deep chromaticity, complex components and difficult degradation, and in the invention, under the catalytic action of high-reactivity combined-state ferrous iron in the patina, hydrogen peroxide is decomposed to generate a large amount of hydroxyl radicals, and after the patina is subjected to adsorption reaction, a large amount of organic matters are adsorbed to the surface of the patina, so that the generated hydroxyl radicals can rapidly degrade the organic matters in situ, thereby greatly reducing the invalid decomposition proportion of the hydroxyl radicals and improving the instantaneous utilization rate of the hydroxyl radicals.
In the technical scheme provided by the invention, on one hand, the combination-state ferrous iron with high reactivity in the green rust and the hydrogen peroxide form the Fenton-like reagent, and compared with other commonly adopted traditional Fenton reagents formed by free-state ferrous iron and hydrogen peroxide, the Fenton-like reagent has stronger capacity of degrading organic matters, has no strict requirement on the pH value of the reaction, and can achieve a good reaction effect under a neutral condition; on the other hand, by utilizing the large specific surface area and the high adsorption performance of the patina, a large amount of high-chroma substances in the industrial wastewater are adsorbed on the surface of the patina, so that the concentration of the subsequent organic matters participating in the Fenton-like reaction is greatly improved, and the reaction rate is obviously improved. In addition, the high iron green rust generated after the Fenton-like reaction has good precipitation performance and still has high contact flocculation activity, and the precipitate is concentrated and then is recycled for adsorbing impurities in raw water, so that the pretreatment effect can be realized, the burden of subsequent treatment is greatly reduced, and the cyclic utilization is realized. Finally, after the Fenton-like reaction, the complex macromolecular organic matters are changed into relatively simple micromolecules, and can easily penetrate through the surface of the adsorbent to enter the internal pores. The invention has simple flow, high processing efficiency, convenient operation and management and high system operation stability.
The present invention further provides an industrial wastewater treatment apparatus as described above, referring to fig. 2, the industrial wastewater treatment apparatus includes:
the pretreatment system is used for pretreating industrial wastewater, so that solid and liquid are separated into layers, and supernatant is collected to obtain wastewater to be treated;
the adsorption reaction system is arranged at the downstream of the pretreatment system and comprises an adsorption tank and a reaction sedimentation tank positioned at the downstream of the adsorption tank, the adsorption tank is used for mixing the wastewater to be treated with the patina, the reaction sedimentation tank is used for carrying out Fenton-like reaction on the mixture of the wastewater to be treated and the patina and a hydrogen peroxide solution, and after the reaction is finished, solid-liquid separation is carried out and supernatant is collected to obtain clarified water; and the number of the first and second groups,
the advanced treatment system is arranged at the downstream of the adsorption reaction system and comprises an activated carbon adsorption filter bed for treating the clarified water so as to remove organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water;
the patina is prepared by mixing sodium carbonate and ferrous chloride tetrahydrate, fully mixing the mixture with iron powder, reacting, and performing efficient gravity concentration.
Preferably, the pretreatment system comprises a contact flocculation tank and a first sedimentation tank arranged at the downstream of the contact flocculation tank, the contact flocculation tank is used for mixing industrial wastewater and a flocculating agent and stirring to ensure that the industrial wastewater and the flocculating agent are fully contacted, and the first sedimentation tank is used for standing the fully contacted industrial wastewater and the flocculating agent to obtain supernatant.
The contact flocculation tank utilizes a flocculating agent to pre-adsorb suspended matters, colloidal impurities and colored substances in the industrial wastewater so as to reduce the load of subsequent treatment facilities. Preferably, the flocculant is high-iron green rust generated after subsequent green rust adsorption-Fenton-like reaction and still has strong contact flocculation activity. The contact flocculation tank can adopt the types of a mechanical stirring mixing reaction tank, a perforation rotational flow reaction tank, a folded plate flocculation tank, a fluidized bed and the like, and can ensure that the wastewater and the reflowing high iron green rust sludge are fully contacted and flocculated. In addition, the contact flocculation tank and the first sedimentation tank can be combined into a whole, and the contact flocculation and sedimentation functions are combined into a whole by adopting a mechanical stirring clarification tank.
Preferably, the pretreatment system further comprises a regulating tank, wherein the regulating tank is arranged at the upstream of the contact flocculation tank and is used for homogenizing and homogenizing the industrial wastewater before the industrial wastewater enters the contact flocculation tank. Before the industrial wastewater enters the contact flocculation tank, the industrial wastewater enters the regulating tank to regulate the water quantity and stabilize the water quality, so that the impact load on subsequent treatment facilities can be greatly reduced.
Preferably, as shown in fig. 2, the industrial wastewater treatment apparatus further includes a sludge treatment system for treating the precipitated sludge obtained in the pretreatment system. The sludge treatment system comprises a sludge concentration tank and a sludge dewatering room. The sludge concentration tank can greatly reduce the water content of the sludge and the volume of the sludge, and the concentrated sludge enters the sludge dewatering room to be dewatered so as to further reduce the volume of the sludge and reduce the subsequent cost of outward transport landfill or disposal. Because the discharged sludge is mainly high iron green rust, the high iron green rust has good sedimentation performance, the generated floc is compact, a gravity concentration tank is adopted, and the sludge filter pressing can be realized by a plate-and-frame filter press or a belt filter press.
The adsorption reaction system is arranged at the downstream of the pretreatment system and comprises an adsorption tank and a reaction sedimentation tank positioned at the downstream of the adsorption tank, the adsorption tank is used for mixing the wastewater to be treated and the patina, the reaction sedimentation tank is used for carrying out Fenton-like reaction on the mixture of the wastewater to be treated and the patina and a hydrogen peroxide solution, and after the reaction is finished, solid-liquid separation is carried out and supernatant liquid is collected to obtain clarified water.
In the adsorption tank, high-chroma substances in the wastewater are effectively adsorbed by utilizing the large specific surface area and high adsorption performance of the concentrated patina, then hydrogen peroxide is added into the reaction sedimentation tank, and the adsorbed substances are efficiently degraded by utilizing a Fenton-like reagent formed by high-reactivity combined-state ferrous iron and the hydrogen peroxide in the patina, so that the chroma and COD (chemical oxygen demand) of the wastewater are reducedcrThe function of (1).
The adsorption tank can adopt a fluidized bed, a jet flow mixed reaction, a perforated rotational flow reaction and other tank types, and concentrated patina is easy to oxidize when meeting air, so that the adsorption reaction is carried out when the wastewater is fully contacted with the concentrated patina, and strong contact convection with the air is avoided as much as possible.
The reaction sedimentation tank can be a tank, and adopts a high-density clarification tank to integrate two functions of mixing reaction and solid-liquid separation. The reaction sedimentation tank can also be two tanks, namely a reaction tank and a second sedimentation tank which are respectively used for adding hydrogen peroxide solution for reaction and solid-liquid separation. Because the Fenton-like reaction is rapid, generates heat and is accompanied with the generation of a large amount of gas, the reaction tank is required to be open, and is accompanied with the rapid stirring and mixing function, so that the Fenton-like reaction tank is suitable for being mechanically stirred.
The low reaches of adsorption reaction system are located to the advanced treatment system, and the advanced treatment system includes the active carbon adsorption filter bed for handling clarified water, with organic matter and the colourity of detaching in the clarified water, adsorb the simple micromolecule that complicated macromolecule generated after class Fenton reaction, simple micromolecule is changeed and is passed the adsorbent surface and enter into inside hole this moment, makes this degree of depth adsorption process compare with traditional adsorption technology, and its adsorption efficiency is higher, and saturated adsorption capacity is bigger, prolongs regeneration cycle greatly.
The activated carbon adsorption filter bed can be in the form of a traditional activated carbon adsorption packed bed, and the regeneration period of the activated carbon is 3-5 years.
The technical solutions of the present invention are further described in detail below with reference to specific examples and drawings, it should be understood that the following examples are merely illustrative of the present invention and are not intended to limit the present invention.
Example 1
Referring to fig. 3, the dye wastewater stays for 20 hours through the regulating reservoir, is lifted to a mechanical stirring clarification tank after being homogenized and equalized, is stirred for reaction and is precipitated for 2 hours, is subjected to contact flocculation reaction with high iron green rust (namely sludge generated by an adsorption reaction system) flowing back from the bottom of the high-density clarification tank, pre-adsorbs suspended matters, colloidal impurities and colored substances in the dye wastewater, then is subjected to sludge-water separation, the supernatant enters a subsequent adsorption reaction system, and the bottom precipitate is discharged into a sludge treatment system.
The pretreated wastewater is discharged into a fluidized bed and is contacted with incoming patina (the preparation method of the patina is prepared according to the method in patent 201811559445.8) for 1h, and the mass ratio of the patina to the wastewater to be treated is 1: 10, and then according to the mass ratio of hydrogen peroxide to wastewater to be treated of 12: 10000, adding hydrogen peroxide solution into a reaction area at the front part of the high-density clarification tank, allowing a mixture after 0.5h of reaction to enter a clarification area at the rear part through a plug flow channel at the middle part of the high-density clarification tank for solid-liquid separation, allowing sludge concentrated at the bottom to be high iron green rust to be used as a flocculating agent to flow back to the mechanical stirring clarification tank, and allowing supernatant to be directly recycled in a factory or enter an activated carbon adsorption filter bed for adsorption and then to be discharged after reaching the standard.
Example 2
The dye wastewater is subjected to homogenization and uniform amount after staying for 6 hours in the regulating reservoir, then is lifted to a mechanical stirring clarification tank, is subjected to stirring reaction and sedimentation for 2 hours, is subjected to contact flocculation reaction with high-iron green rust (namely sludge generated by an adsorption reaction system) flowing back from the bottom of the high-density clarification tank, is subjected to pre-adsorption on suspended matters, colloidal impurities and colored substances in the dye wastewater, then is subjected to sludge-water separation, the supernatant enters a subsequent adsorption reaction system, and the bottom sediment is discharged into a sludge treatment system.
The pretreated wastewater is discharged into a fluidized bed and is contacted with incoming patina (the preparation method of the patina is prepared according to the method in patent 201811559445.8) for 1h, and the mass ratio of the patina to the wastewater to be treated is 1: and 5, according to the mass ratio of the hydrogen peroxide to the wastewater to be treated being 3: 10000, adding hydrogen peroxide solution into a reaction area at the front part of the high-density clarification tank, allowing a mixture after 0.5h of reaction to enter a clarification area at the rear part through a plug flow channel at the middle part of the high-density clarification tank for solid-liquid separation, allowing sludge concentrated at the bottom to be high iron green rust to be used as a flocculating agent to flow back to the mechanical stirring clarification tank, and allowing supernatant to be directly recycled in a factory or enter an activated carbon adsorption filter bed for adsorption and then to be discharged after reaching the standard.
Example 3
The dye wastewater is subjected to homogenization and uniform amount after being retained for 24 hours by the regulating reservoir, then is lifted to a mechanical stirring clarification tank, is subjected to stirring reaction and sedimentation for 2 hours, is subjected to contact flocculation reaction with high-iron green rust (namely sludge generated by an adsorption reaction system) flowing back from the bottom of the high-density clarification tank, is subjected to pre-adsorption on suspended matters, colloidal impurities and colored substances in the dye wastewater, then is subjected to sludge-water separation, the supernatant enters a subsequent adsorption reaction system, and the bottom sediment is discharged into a sludge treatment system.
The pretreated wastewater is discharged into a fluidized bed and is contacted with incoming patina (the preparation method of the patina is prepared according to the method in patent 201811559445.8) for 1h, and the mass ratio of the patina to the wastewater to be treated is 1: and 20, then according to the mass ratio of the hydrogen peroxide to the wastewater to be treated being 15: 10000, adding hydrogen peroxide solution into a reaction area at the front part of the high-density clarification tank, allowing a mixture after 0.5h of reaction to enter a clarification area at the rear part through a plug flow channel at the middle part of the high-density clarification tank for solid-liquid separation, allowing sludge concentrated at the bottom to be high iron green rust to be used as a flocculating agent to flow back to the mechanical stirring clarification tank, and allowing supernatant to be directly recycled in a factory or enter an activated carbon adsorption filter bed for adsorption and then to be discharged after reaching the standard.
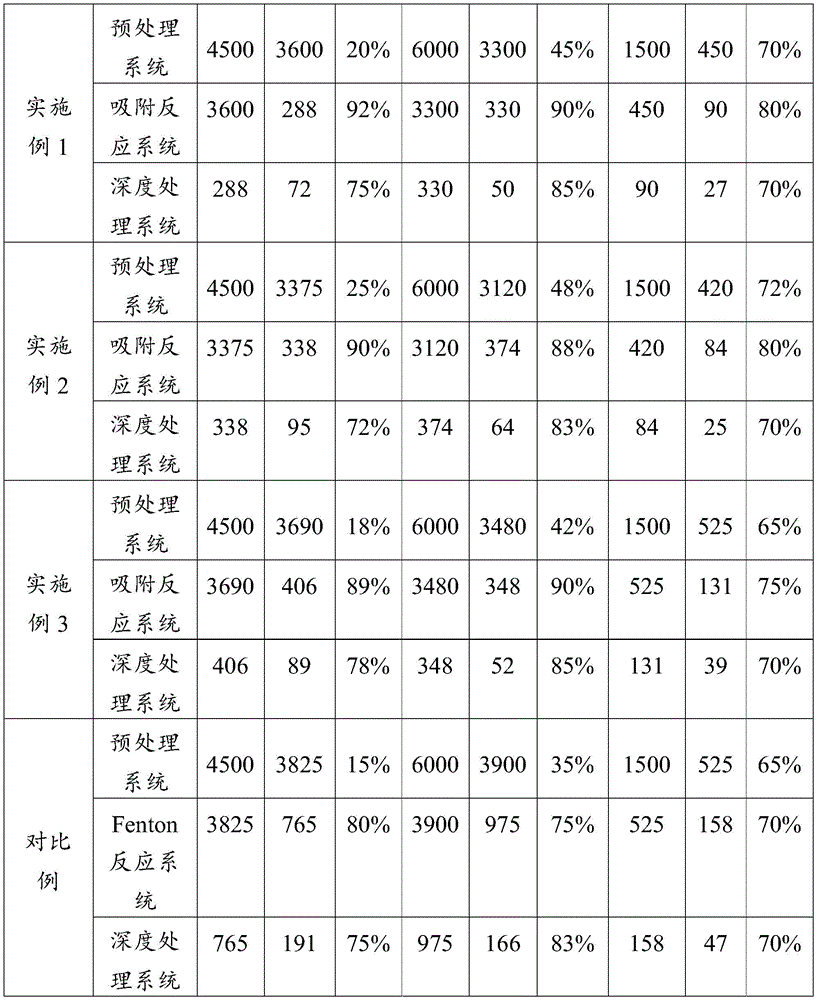
Aluminum trichloride is used as a flocculating agent in a pretreatment system, a traditional Fenton reagent consisting of ferrous sulfate and hydrogen peroxide is used as a reagent of a reaction system to form a comparative example, the dye wastewater which is the same as that in the examples 1, 2 and 3 is treated under the same condition, and main water quality indexes of inlet and outlet water in the three examples and the comparative example at each treatment stage are measured by taking various indexes directly discharged in the GB 4287 + 2012 textile dyeing and finishing industry water pollutant discharge standard as requirements, so that the table 1 is obtained.
TABLE 1 Main Water quality index and removal Rate in each Process stage
As can be seen from table 1, the three characteristic pollutant indexes of the clean water obtained by the industrial wastewater treatment methods in embodiments 1, 2 and 3 of the present application all meet the corresponding requirements in the direct emission standard of the pollutants in the textile dyeing and finishing industry water of GB 4287-. In addition, under the same conditions, all indexes of clean water obtained by the industrial wastewater treatment methods of examples 1, 2 and 3 are superior to those of comparative examples, which shows that the industrial wastewater treatment method provided by the invention has great advantages in treatment efficiency, conditions and stability, has a wide market and can be widely used for treating industrial wastewater.
The above is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and it is not intended to limit the scope of the invention, and various modifications and changes will occur to those skilled in the art. Any modification, equivalent replacement, or improvement made within the spirit and principle of the present invention shall be included in the scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
1. The industrial wastewater treatment method is characterized by comprising the following steps:
s10, carrying out contact flocculation pretreatment on the industrial wastewater, and then carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain supernatant, namely the wastewater to be treated;
s20, adding patina into the wastewater to be treated, mixing and adsorbing, adding a hydrogen peroxide solution to perform a Fenton-like reaction until organic matters in the wastewater to be treated are completely oxidized, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain clear water;
s30, further removing organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water, and finishing the treatment of the industrial wastewater;
the patina is prepared by fully mixing and reacting sodium carbonate, ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and iron powder and then performing efficient gravity concentration.
2. The industrial wastewater treatment method according to claim 1, wherein in step S20, the mass ratio of the patina to the wastewater to be treated is 1: (5-20); and/or the presence of a gas in the gas,
the mass ratio of the hydrogen peroxide to the wastewater to be treated is (3-15): 10000.
3. the industrial wastewater treatment method according to claim 1, wherein the step S30 includes:
and enabling the clarified water to flow through an activated carbon adsorption filter bed, and removing organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water through the adsorption action of the activated carbon to finish the treatment of the industrial wastewater.
4. The method for treating industrial wastewater according to claim 1, wherein the industrial wastewater is one or more of black liquor from pulping and papermaking, wastewater from textile dyeing and finishing, and pharmaceutical wastewater from traditional Chinese medicine.
5. The industrial wastewater treatment method according to claim 1, wherein the step S10 specifically comprises:
s101, adding a flocculating agent into the industrial wastewater, and stirring to enable the industrial wastewater to be fully contacted with the flocculating agent;
s102, standing for 1-2 hours to obtain supernatant, namely wastewater to be treated.
6. The industrial wastewater treatment method according to claim 1, wherein before step S10, the industrial wastewater treatment method further comprises: and homogenizing and uniformly measuring the industrial wastewater, and staying for 6-24 hours.
7. An industrial wastewater treatment apparatus, comprising:
the pretreatment system is used for pretreating industrial wastewater, so that solid and liquid are separated into layers, and supernatant is collected to obtain wastewater to be treated;
the adsorption reaction system is arranged at the downstream of the pretreatment system and comprises an adsorption tank and a reaction sedimentation tank positioned at the downstream of the adsorption tank, the adsorption tank is used for mixing the wastewater to be treated with the patina, the reaction sedimentation tank is used for carrying out Fenton-like reaction on the mixture of the wastewater to be treated and the patina and a hydrogen peroxide solution, and after the reaction is finished, solid-liquid separation is carried out and supernatant is collected to obtain clarified water; and the number of the first and second groups,
the advanced treatment system is arranged at the downstream of the adsorption reaction system and comprises an activated carbon adsorption filter bed for treating the clarified water so as to remove organic matters and chromaticity in the clarified water;
the patina is prepared by fully mixing and reacting sodium carbonate, ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and iron powder and then performing efficient gravity concentration.
8. The industrial wastewater treatment device according to claim 7, wherein the pretreatment system comprises a contact flocculation tank and a first sedimentation tank arranged at the downstream of the contact flocculation tank, the contact flocculation tank is used for mixing the industrial wastewater with the flocculant and stirring to fully contact the industrial wastewater with the flocculant, and the first sedimentation tank is used for standing the fully contacted industrial wastewater and the flocculant to obtain a supernatant.
9. The industrial wastewater treatment device according to claim 7, wherein the reaction sedimentation tank comprises a reaction tank and a second sedimentation tank arranged at the downstream of the reaction tank, the reaction tank is used for allowing the mixture of the wastewater to be treated and the patina to perform a Fenton-like reaction with a hydrogen peroxide solution, and the second sedimentation tank is used for separating solid from liquid and collecting the liquid after the reaction is finished to obtain clarified water.
10. The industrial wastewater treatment plant of claim 8 wherein the pretreatment system further comprises a conditioning tank disposed upstream of the contact flocculation tank for homogenizing the industrial wastewater prior to entering the contact flocculation tank.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010087589.9A CN111233198B (en) | 2020-02-11 | 2020-02-11 | Industrial wastewater treatment method and device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010087589.9A CN111233198B (en) | 2020-02-11 | 2020-02-11 | Industrial wastewater treatment method and device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111233198A true CN111233198A (en) | 2020-06-05 |
| CN111233198B CN111233198B (en) | 2022-09-23 |
Family
ID=70876481
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010087589.9A Active CN111233198B (en) | 2020-02-11 | 2020-02-11 | Industrial wastewater treatment method and device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111233198B (en) |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5641470A (en) * | 1995-07-17 | 1997-06-24 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Process for making goethite |
| JP2003340467A (en) * | 2002-05-28 | 2003-12-02 | Ebara Corp | Method for treating sulfide-containing waste water and facility therefor |
| US20090169470A1 (en) * | 2007-12-28 | 2009-07-02 | Tdk Corporation | Process for production of iron oxyhydroxide particles |
| CN102060334A (en) * | 2010-11-22 | 2011-05-18 | 同济大学 | Preparation of ferrous compound in polyhydroxy structural state and application of ferrous compound in wastewater reduction pretreatment |
| CN105271606A (en) * | 2014-07-16 | 2016-01-27 | 鞍钢股份有限公司 | Coking wastewater treatment method |
| CN105293771A (en) * | 2015-11-10 | 2016-02-03 | 南京润中生物技术有限公司 | Rubbish penetrating fluid treatment method |
| CN107572593A (en) * | 2017-09-15 | 2018-01-12 | 北京三聚环保新材料股份有限公司 | A kind of γ FeOOH preparation method |
| US20180297864A1 (en) * | 2017-04-18 | 2018-10-18 | King Abdulaziz University | AZO DYE INTERCALATED Fe(II)/Fe(III) LAYERED DOUBLE HYDROXIDE FOR WATER PURIFICATION |
| CN208394939U (en) * | 2018-05-01 | 2019-01-18 | 何俊贤 | A kind of printing and dyeing wastewater treatment system |
| CN109589901A (en) * | 2018-12-20 | 2019-04-09 | 武汉轻工大学 | A kind of the preparation of industrialization system and industrialized process for preparing of patina |
-
2020
- 2020-02-11 CN CN202010087589.9A patent/CN111233198B/en active Active
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5641470A (en) * | 1995-07-17 | 1997-06-24 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Process for making goethite |
| JP2003340467A (en) * | 2002-05-28 | 2003-12-02 | Ebara Corp | Method for treating sulfide-containing waste water and facility therefor |
| US20090169470A1 (en) * | 2007-12-28 | 2009-07-02 | Tdk Corporation | Process for production of iron oxyhydroxide particles |
| CN102060334A (en) * | 2010-11-22 | 2011-05-18 | 同济大学 | Preparation of ferrous compound in polyhydroxy structural state and application of ferrous compound in wastewater reduction pretreatment |
| CN105271606A (en) * | 2014-07-16 | 2016-01-27 | 鞍钢股份有限公司 | Coking wastewater treatment method |
| CN105293771A (en) * | 2015-11-10 | 2016-02-03 | 南京润中生物技术有限公司 | Rubbish penetrating fluid treatment method |
| US20180297864A1 (en) * | 2017-04-18 | 2018-10-18 | King Abdulaziz University | AZO DYE INTERCALATED Fe(II)/Fe(III) LAYERED DOUBLE HYDROXIDE FOR WATER PURIFICATION |
| CN107572593A (en) * | 2017-09-15 | 2018-01-12 | 北京三聚环保新材料股份有限公司 | A kind of γ FeOOH preparation method |
| CN208394939U (en) * | 2018-05-01 | 2019-01-18 | 何俊贤 | A kind of printing and dyeing wastewater treatment system |
| CN109589901A (en) * | 2018-12-20 | 2019-04-09 | 武汉轻工大学 | A kind of the preparation of industrialization system and industrialized process for preparing of patina |
Non-Patent Citations (8)
| Title |
|---|
| ALEJANDRO M.SENN等: "Treatment of wastewater from an alkaline cleaning solution by combined coagulation and photo-Fenton processes", 《SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGY》 * |
| K. BARTHÉLÉMY等: "Carbonated ferric green rust as a new material for efficient phosphate removal", 《JOURNAL OF COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE》 * |
| PH.REFAIT等: "Formation of ‘ferric green rust’ and/or ferrihydrite by fast oxidation of iron(II–III) hydroxychloride green rust", 《CORROSION SCIENCE》 * |
| ROGERMATTA等: "Oxidation of phenol by green rust and hydrogen peroxide at neutral pH", 《SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGY》 * |
| 柳儒等: "磁性绿锈吸附固定厌氧水体磷酸盐及其影响因素", 《环境科学与技术》 * |
| 王伟等: "绿锈去除难降解有机物研究", 《大连交通大学学报》 * |
| 赵丹等: "Fe(Ⅱ)/针铁矿复合系统对水中橙黄G的吸附-还原脱色研究", 《岩石矿物学杂志》 * |
| 邹卫东: "绿锈混凝沉淀处理隧洞施工污水的研究", 《中国环境科学学会2019年科学技术年会——环境工程技术创新与应用分论坛论文集(四)》 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111233198B (en) | 2022-09-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN100457654C (en) | Printing-dyeing waste water treatment process | |
| CN102260009B (en) | Method for processing dye wastewater | |
| WO2010133151A1 (en) | Organic wastewater recycling treatment method | |
| CN102295359B (en) | Treatment method for deep-well polysulfide slurry drilling waste water | |
| CN107117767B (en) | Petrochemical wastewater treatment method | |
| CN106554126A (en) | A kind of reverse osmosis concentrated water depth standard processing method and system | |
| CN103588318A (en) | Processing method used for multiple recycling of fur dyeing effluent | |
| CN107417017A (en) | A kind of oil-gas field fracturing returns the processing method of discharge opeing sewage | |
| CN108821473A (en) | A kind of dyeing and printing sewage treatment process | |
| CN102942281A (en) | Treatment method of high-concentration mixing organic acid waste water | |
| CN114524536B (en) | Pretreatment process of landfill leachate | |
| CN102674639A (en) | Treatment process and treatment device of mink skin tanning waste water | |
| CN105692967B (en) | A kind of processing method of PVA process units waste water | |
| CN106186565A (en) | A kind of dyeing waste water zero-emission recycling system and method | |
| CN113480089A (en) | Advanced treatment method of petrochemical wastewater | |
| CN111233198B (en) | Industrial wastewater treatment method and device | |
| CN108726773A (en) | A kind of chemical wastewater treatment technique | |
| CN104926033A (en) | Efficient treatment method for printing and dyeing wastewater | |
| CN209113686U (en) | A kind of combination unit handling hc effluent with high salt | |
| CN104310696A (en) | Method for treating and recycling leather wastewater by electro-adsorption | |
| CN207210203U (en) | A kind of wood-based plate advanced waste treatment system | |
| CN107399879A (en) | A kind of wood-based plate advanced waste treatment system and technique | |
| CN110482683B (en) | Sewage advanced treatment method and equipment based on activated carbon technology | |
| CN203960004U (en) | A kind of printing ink wastewater iron carbon treatment facility | |
| CN106007070A (en) | Treatment method for high-concentration water-based cutting waste liquor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |