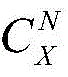CN111163506B - Energy saving method and device, computer equipment and storage medium - Google Patents
Energy saving method and device, computer equipment and storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111163506B CN111163506B CN201911336755.8A CN201911336755A CN111163506B CN 111163506 B CN111163506 B CN 111163506B CN 201911336755 A CN201911336755 A CN 201911336755A CN 111163506 B CN111163506 B CN 111163506B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- remote
- remote unit
- remote units
- cell
- resource utilization
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 83
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 claims description 26
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 abstract description 7
- 238000005265 energy consumption Methods 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 12
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000010295 mobile communication Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000002776 aggregation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004220 aggregation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004422 calculation algorithm Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007405 data analysis Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010261 cell growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0203—Power saving arrangements in the radio access network or backbone network of wireless communication networks
- H04W52/0206—Power saving arrangements in the radio access network or backbone network of wireless communication networks in access points, e.g. base stations
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/04—TPC
- H04W52/18—TPC being performed according to specific parameters
- H04W52/28—TPC being performed according to specific parameters using user profile, e.g. mobile speed, priority or network state, e.g. standby, idle or non transmission
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/04—TPC
- H04W52/30—TPC using constraints in the total amount of available transmission power
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/08—Access point devices
- H04W88/085—Access point devices with remote components
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
The application relates to an energy-saving method, an energy-saving device, computer equipment and a storage medium, wherein the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started are determined based on the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in a cell, the signal coverage area of the remote units under the target bandwidth is determined, a list of the remote units to be turned off and a list of the remote units to be turned on of the cell are further determined, and then energy-saving operation is performed. In the method, the flexible adjustment of the working bandwidth of the remote units in the cell is realized, the remote units which are started are flexibly selected, the turn-off and the turn-on of each remote unit are controlled, the reasonable use of hardware resources is realized, and the equipment energy consumption of the whole set of base station system is reduced. The energy-saving method does not need to completely close the cell, does not need to interact with the adjacent cell, does not affect the communication quality of the terminal of the cell to be energy-saved, and is more flexible and wide in applicability.
Description
Technical Field
The present application relates to the field of mobile communications technologies, and in particular, to an energy saving method and apparatus, a computer device, and a storage medium.
Background
With the rapid spread of mobile networks and mobile terminal intelligence, mobile networks have spread throughout every corner of human social life, and the demand for mobile communication services has grown exponentially. To cope with the explosively increasing traffic demands, the development of mobile communication base station systems tends to higher data rates and lower system delays. However, the accompanying system power consumption will also be higher.
For the problem of high energy consumption of a mobile communication base station system, various energy-saving methods are proposed in the industry, and the main stream method is to interact with an adjacent cell when the traffic of the cell is small, access each terminal in the cell to the adjacent cell and close the cell, thereby achieving the purpose of reducing the power consumption of the mobile communication base station system.
However, in order to achieve better system coverage, coverage intersection areas of adjacent cells are generally few, and the communication quality of the terminal is often reduced by handing over the terminal of the cell to be closed to the adjacent cell. Therefore, the conventional energy saving method is not flexible enough, and the communication quality of some users is often sacrificed.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above, it is necessary to provide a power saving method, apparatus, computer device and storage medium for solving the above technical problems.
In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an energy saving method, where the method includes:
acquiring the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, wherein the resource utilization rate represents the proportion of the total resource quantity of the cell occupied by the resources required by the remote unit;
determining the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit;
determining a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on of a cell according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the signal coverage area of each remote unit under a target bandwidth and the number of the remote units to be turned on;
and executing energy-saving operation according to the list of the remote units to be turned off, the list of the remote units to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on.
In one embodiment, the determining the number of remote units to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit includes:
acquiring the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to a preset mapping rule and the total cell resource utilization rate; the total resource utilization rate of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization rates of the remote units, and the mapping rule comprises the corresponding relation among the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be started and the number of the remote units to be started.
In one embodiment, the determining the number of remote units to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit includes:
when the preset conditions are met, acquiring the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to a preset mapping rule and the total cell resource utilization rate; the total resource utilization rate of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization rates of the remote units, and the mapping rule comprises the corresponding relation among the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be started and the number of the remote units to be started.
In one embodiment, the preset conditions include:
the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is less than the preset number, the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset high threshold, or the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset high threshold and the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is less than the preset number.
In one embodiment, the total resource utilization of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on, and the number of the remote units to be turned on in the mapping rule are in a direct proportion.
In one embodiment, the proportional relationship includes:
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset low threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is the first target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N1;
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the low threshold and less than the preset middle threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a second target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N2;
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the medium threshold and less than the preset high threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a third target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N3;
wherein the first target bandwidth < the second target bandwidth < the third target bandwidth; n1< N2< N3.
In one embodiment, the determining a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on in a cell according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the signal coverage area of each remote unit in the target bandwidth, and the number of remote units to be turned on includes:
determining a plurality of remote unit combination results from all remote units in the cell according to the number of the remote units to be started;
acquiring a resource evaluation value of a combination result of each remote unit according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit and a signal coverage area of each remote unit under a target bandwidth; the resource evaluation value represents the utilization degree of the combination result of each remote unit to the resources in the cell;
determining the remote unit corresponding to the remote unit combination result with the maximum resource evaluation value as the remote unit in the remote unit list to be started; and determining remote units in the cell other than the remote units in the list of remote units to be turned on as the remote units in the list of remote units to be turned off.
In one embodiment, the obtaining a resource evaluation value of a combination result of each remote unit according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit and the signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth includes:
acquiring the capacity ratio of the resource utilization rate of the remote units in the combined result of the remote units in the total resource utilization rate of the cell, and the coverage ratio of the signal coverage area of the remote units under the target bandwidth in the total signal coverage area of the cell in the combined result of the remote units;
the weighted sum of the capacity and coverage ratios is determined as the resource assessment value for the combined result of the remote units.
In one embodiment, the executing the energy saving operation according to the list of remote units to be turned off, the list of remote units to be turned on, and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on includes:
keeping the remote units in the remote unit list to be started, and adjusting the bandwidth of each remote unit in the remote unit list to be started to be a target bandwidth; wherein, the power of each remote unit in the remote unit list to be started is kept unchanged;
and turning off the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned off.
In one embodiment, the obtaining the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell includes:
receiving signal transmission quality data of each terminal reported by each remote unit;
for any terminal, according to the transmission quality data of the terminal reported by each remote unit, determining the remote unit with the strongest signal transmission quality as the corresponding remote unit of the terminal;
and determining the ratio of the resource quantity required by the corresponding terminal of each remote unit to the total resource quantity of the cell as the resource utilization rate of each remote unit.
In one embodiment, after obtaining the resource utilization of each remote unit in the cell, the method further includes:
when the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than a preset high threshold and the number of the remote units with the resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is greater than a preset number, turning off all the remote units with the resource utilization rate of 0; the total resource utilization of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization of each remote unit.
In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an energy saving device, including:
the system comprises an acquisition module, a processing module and a processing module, wherein the acquisition module is used for acquiring the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in a cell, and the resource utilization rate represents the proportion of the total resource quantity of the cell occupied by the resources required by the remote units;
the first determining module is used for determining the number of the remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit;
a second determining module, configured to determine a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on in a cell according to a resource utilization rate of each remote unit, a signal coverage area of each remote unit in a target bandwidth, and a number of remote units to be turned on;
and the energy-saving module is used for executing energy-saving operation according to the remote unit list to be turned off, the remote unit list to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be turned on.
In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a computer device, including a memory and a processor, where the memory stores a computer program, and the processor implements the steps of any one of the methods provided in the embodiments of the first aspect when executing the computer program.
In a fourth aspect, the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, where the computer program, when executed by a processor, implements the steps of any one of the methods provided in the embodiments of the first aspect.
According to the energy saving method, the energy saving device, the computer equipment and the storage medium, the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started are determined based on the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in a cell, the signal coverage area of the remote units under the target bandwidth is determined, the list of the remote units to be turned off and the list of the remote units to be turned on of the cell are further determined, and then energy saving operation is performed. According to the method, based on the resource occupation condition of each remote unit in the cell, the flexible adjustment of the working bandwidth of the remote unit in the cell is realized, and the turned-on remote unit is flexibly selected according to the signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth to control the turning-off and turning-on of each remote unit, so that the reasonable use of hardware resources is realized, and the equipment energy consumption of the whole base station system is reduced. The energy-saving method does not need to completely close the cell, does not need to interact with the adjacent cell, does not affect the communication quality of the terminal of the cell to be energy-saved, and is more flexible and wide in applicability.
Drawings
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an exemplary embodiment of an application environment of a power saving method;
FIG. 2 is a schematic flow chart of an energy saving method according to an embodiment;
FIG. 3 is a schematic flow chart of a method for saving energy according to another embodiment;
fig. 3a is a schematic diagram illustrating relative positions of remote units and signal coverage areas of cells according to an embodiment;
fig. 3b is a schematic diagram of relative location and cell signal coverage area of a remote unit according to another embodiment;
FIG. 4 is a schematic flow chart of a method for saving energy according to another embodiment;
FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram illustrating an application flow of an energy saving method according to another embodiment;
FIG. 5a is a schematic diagram of an energy saving module according to an embodiment;
fig. 6 is a diagram illustrating remote unit operating conditions prior to power saving according to an exemplary embodiment;
fig. 7 is a diagram illustrating an operating state of a remote unit after power saving is performed according to an embodiment;
fig. 8 is a schematic diagram illustrating an operating state of a remote unit after power saving is performed according to another embodiment;
fig. 9 is a schematic diagram illustrating an operating state of a remote unit after power saving is performed according to another embodiment;
fig. 10 is a schematic diagram illustrating an operating state of a remote unit after power saving is performed according to another embodiment;
fig. 11 is a block diagram illustrating an energy saving device according to an embodiment;
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an internal structure of a computer device according to an embodiment.
Detailed Description
In order to make the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the present application more apparent, the present application is described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are merely illustrative of the present application and are not intended to limit the present application.
The energy saving method provided by the present application can be applied to a distributed base station system as shown in fig. 1, where the system includes a host Unit (Access Unit), at least one expansion Unit (Switch), and at least one Remote Unit (Remote Unit), where the host Unit is responsible for protocol stack processing and operation and maintenance functions of a base station, and is composed of a general X86 server and an FPGA Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) board; the expansion unit is responsible for IQ data downlink distribution, uplink aggregation, clock synchronization, active Ethernet (POE) Power supply and the like of the remote unit, and comprises a Central Processing Unit (CPU) processing module of a Central Processing Unit (CPU), an FPGA aggregation and distribution module and a Power Supply Equipment (PSE) Power supply and peripheral circuit module; the remote unit is a low-power RRU device, has a Radio Frequency transceiving function, and comprises a CPU control module, a transmission interface module, a POE power supply and peripheral circuit module, and a Radio Frequency (RF) transceiving module. The distributed base station shown in fig. 1 has a host unit connected to a plurality of extension units, which can be connected to a plurality of remote units, so that a coverage effect of a common cell or a plurality of cells can be realized, the architecture supports digital connection of Internet Protocol (IP), has the advantages of high performance, large capacity, easy deployment, flexible cell expansion and splitting, and the like, and is suitable for various indoor coverage scenes such as office buildings, markets, supermarkets, hotels and dormitory houses.
The embodiment of the application provides an energy saving method, an energy saving device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and aims to provide an energy saving method and related equipment of a distributed base station system to solve the problem that the traditional energy saving method is not flexible enough. The following describes in detail the technical solutions of the present application and how the technical solutions of the present application solve the above technical problems by embodiments and with reference to the drawings. The following several specific embodiments may be combined with each other, and details of the same or similar concepts or processes may not be repeated in some embodiments. It should be noted that, in the energy saving method provided in the present application, the execution main body in fig. 2 to fig. 5 is a host unit, where the execution main body may also be an energy saving device, where the device may be implemented as part or all of the host unit by software, hardware, or a combination of software and hardware.
In order to make the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present application clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present application, and it is obvious that the described embodiments are some embodiments of the present application, but not all embodiments.
In an embodiment, fig. 2 provides an energy saving method, where the embodiment relates to a specific process in which a host unit determines a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on according to resource utilization rates of the remote units in a cell, signal coverage areas of the remote units under a target bandwidth, and a number of remote units to be turned on, and further performs an energy saving operation, as shown in fig. 2, the method includes:
s101, acquiring resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, wherein the resource utilization rate represents the proportion of the total resource quantity of the cell occupied by the resource required by the remote unit.
In this embodiment, the resource utilization of the remote unit indicates a ratio of the total resource amount of the cell occupied by the resource required by the remote unit, that is, a ratio of the total resource occupied by the resource required by all terminals of the remote unit, where the resource includes but is not limited to a PRB resource utilization, a number of connected terminals, and the like.
Generally, a terminal can be simultaneously covered by a plurality of remote units, one terminal sends uplink signals to the plurality of remote units, and sends uplink information to a host unit through the plurality of remote units, and likewise, the host unit sends downlink signals to the terminal through the plurality of remote units to communicate downlink information. We switch views and for a remote unit, it connects multiple terminals, communicating with multiple terminals both uplink and downlink. The above-mentioned obtaining the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell may be to count the resource amount required by all terminals connected to each terminal, and then to compare the resource amount required by all terminals connected to each terminal with the total resource amount in the cell.
However, in the above-mentioned connection communication method, the same terminal is usually connected to a plurality of remote units, and the plurality of remote units all need to transmit uplink and downlink data of the terminal, which causes resource waste.
Since one host unit can cover a plurality of cells in the distributed base station, the energy saving operation can be performed in units of cells when performing the energy saving operation. In this step, the host unit needs to obtain the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in each cell, and specifically, the host unit determines the corresponding terminal of each remote unit in the cell first, that is, after it is determined that the terminals covered by each remote unit are not repeated, calculates the proportion of the resource required by the corresponding terminal of the remote unit in the total resource amount of the cell, where the proportion is the resource utilization rate of the remote unit.
For example, taking the resource utilization rate of the remote unit as the PRB resource utilization rate as an example, the resource utilization rate of the remote unit is a ratio of the amount of PRB resources occupied by the terminal corresponding to the remote unit to the total amount of PRB resources of the cell in which the remote unit is located.
S102, determining the number of the remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit.
The remote unit to be started is the remote unit which is still kept started after the base station system enters the energy-saving mode. The target bandwidth is the working bandwidth of each remote unit to be started after the base station system enters the energy-saving mode.
Based on the determined resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, the host unit determines the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started.
For example, the host unit may use the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell as an input of the model according to a pre-trained algorithm model, and directly obtain the number of remote units to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on after inputting the resource utilization rate into the algorithm model; the host unit may also determine the total resource utilization rate of the cell, and then determine the number of the remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the total resource utilization rate of the cell, for example, determine a specific numerical value according to big data distribution, determine a specific numerical value according to a preset mapping relationship table, and the like.
And S103, determining a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on of the cell according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth and the number of the remote units to be turned on.
The signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth may be defined by starting from the remote unit position and using attenuation reaching a certain preset power as a coverage area boundary according to a signal attenuation model.
For example, the host unit needs to determine which remote units to be turned on are specifically which remote units in the cell according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, the signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth, and the number of remote units to be turned on, determine the determined remote units to be turned on as the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned on, and determine the other remote units in the cell except the remote units to be turned on as the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned off.
In practical applications, all or part of the processes in steps S101 to S103 may not be executed by the host unit, that is, the processes in steps S101 to S103 may be implemented by another server, and after the processes are implemented by another server, the processes may be transmitted to the host unit to execute step S104. Besides the two execution methods listed currently, the method may also be implemented in other ways, and this embodiment is not limited to this.
And S104, executing energy-saving operation according to the remote unit list to be turned off, the remote unit list to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be turned on.
Optionally, the energy-saving operation mode comprises: keeping the remote units in the remote unit list to be started on, turning off the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned off, and adjusting the bandwidth of all the remote units in the remote unit list to be started to be the target bandwidth; wherein the power at which each remote unit in the list of remote units to be turned on is maintained constant. This is because when the operating power of a single remote unit is not changed, the bandwidth is reduced, and the coverage area is increased, so that the adjustment can ensure that the signal service quality of the whole cell is not deteriorated after the power-saving operation is performed.
Compared with the prior art, the energy saving method provided by this embodiment realizes flexible adjustment of the working bandwidth of the remote units in the cell based on the resource occupation of each remote unit in the cell, flexibly selects the remote units to be turned on according to the signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth, controls turn-off and turn-on of each remote unit, realizes reasonable use of hardware resources, and reduces the energy consumption of the equipment of the whole base station system. The energy-saving method does not need to completely close the cell, does not need to interact with the adjacent cell, does not affect the communication quality of the terminal of the cell to be energy-saved, and is more flexible and wide in applicability.
In addition, when the energy-saving method is applied to a Small Cell (Small Cell) distributed system, the method can bring greater advantages compared with the traditional energy-saving technology.
The application scene of the small base station is mainly matched with the 'blind compensation' or 'heat compensation' of the macro base station. The conventional energy-saving technology can only be applied to the small base station in a heat compensation scene (for example, when the traffic of the small base station is small, the small base station is closed, and the macro base station takes over the access of the terminal of the small base station), but cannot be applied in a blind compensation scene. Moreover, in the conventional energy saving technology, the small base station interacts with the macro base station based on an air interface protocol (such as an X2 interface), but air interface protocol processing mechanisms of different manufacturers are different, which may affect terminal communication service transfer.
The energy-saving method provided by the application does not need air interface interaction among base stations, can be widely applied to blind-supplementary scenes and heat-supplementary scenes of small base stations, and flexibly adjusts the number of the remote units to be started, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started and the positions of the remote units to be started according to the resource occupation condition of each remote unit in a cell, thereby achieving the purpose of energy saving and optimizing the system coverage of the small base stations.
Based on the above embodiments, the following describes how each step in the above fig. 2 embodiment can be implemented by several embodiments. One possible implementation is provided for S102 described above. Optionally, S102 includes: acquiring the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to a preset mapping rule and the total cell resource utilization rate; wherein, the total resource utilization rate of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization rates of the remote units. The mapping rules include a correspondence between a total resource utilization of the cell, a target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on, and a number of the remote units to be turned on.
Wherein the mapping rule is preset. When setting the mapping rule, the total resource utilization rate of the cell is divided into different grades, and the different grades correspond to different target bandwidths and the number of remote units to be started. For example, a high threshold, a medium threshold, and a low threshold are preset, and the total resource utilization of the cell is classified into different levels according to the thresholds. For example, when the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the high threshold, the energy saving scheme provided by the present application is executed, and if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the high threshold, the energy saving operation provided by the present application is executed, otherwise, the energy saving operation is not performed.
In one embodiment, the total resource utilization of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on, and the number of the remote units to be turned on in the mapping rule are in a direct proportion relationship. Optionally, the proportional relationship includes: if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset low threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is the first target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N1; if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the low threshold and less than the preset middle threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a second target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N2; if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the medium threshold and less than the preset high threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a third target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N3; wherein the first target bandwidth < the second target bandwidth < the third target bandwidth; n1< N2< N3.
For example, a result of setting a mapping rule is provided, taking resource utilization as PRB utilization as an example, as shown in table 1 below:
TABLE 1
Optionally, the host unit may obtain the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to a preset mapping rule and a total cell resource utilization rate under a preset condition, and in another embodiment, when the preset condition is met, obtain the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the preset mapping rule and the total cell resource utilization rate. Optionally, the preset condition includes: the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is less than the preset number, the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset high threshold, or the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset high threshold and the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is less than the preset number.
The preset high threshold is a preset critical value of the total resource utilization rate of the cell, if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the high threshold, the current cell is not suitable for an energy-saving scheme, and only if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the high threshold, the subsequent energy-saving steps are continuously executed. The preset high threshold may refer to the high threshold in the third case in table 1.
If the host unit determines that the number of the remote units with the resource utilization rate equal to 0 is smaller than the preset number, which indicates that most of the remote units are in a working state, and the total resource utilization rate of the cell is smaller than the high threshold value, which is a condition suitable for energy saving, the host unit needs to acquire the number of the remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the total resource utilization rate of the cell, so as to perform energy saving operation on the cell.
In this embodiment, when the host unit determines, according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the number of remote units to be opened and the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be opened, the number of remote units whose resource utilization rate is equal to 0 in each remote unit is smaller than a preset number, or the total resource utilization rate of a cell is smaller than a preset high threshold and the number of remote units whose resource utilization rate is equal to 0 in each remote unit is smaller than a preset number, where any one of the three preset conditions is satisfied. That is, the total resource utilization rate of the cell and the number of remote units in the cell whose resource utilization rate is equal to 0 are divided into several different cases, and some of the cases are used as preset conditions, and when the current total resource utilization rate of the cell or the number of remote units whose current resource utilization rate is equal to 0 satisfy the preset conditions, the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started are determined according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit.
Based on this, an embodiment is provided to explain operations that the host unit needs to execute if the current total resource utilization rate of the cell or the number of remote units whose current resource utilization rate is equal to 0 does not satisfy the preset condition. Optionally, when the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset high threshold and the number of remote units with resource utilization rates equal to 0 in each remote unit is greater than the preset number, turning off all remote units with resource utilization rates of 0;
wherein, the total resource utilization rate of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization rates of the remote units.
If the number of the remote units with the resource utilization rate equal to 0 in the cell is larger than the preset number, the most of the remote units in the cell are in an idle state, in this case, the host unit turns off all the remote units with the resource utilization rate of 0, and the remote units with the resource utilization rate different from 0 are reserved to continue working according to the original bandwidth and the original power, so that the energy-saving scheme is completed.
For example, suppose a cell is covered by X remote units, if the number of remote units with resource utilization rate of 0 exceeds M, the remote units with resource utilization rate of 0 are turned off, and the remote units with resource utilization rate not 0 are reserved to provide coverage; where M is a preset number, and may be determined according to the total number X of remote units in the cell, for example, where M is 80% X.
The mapping rule provided by this embodiment presets the corresponding relationship between the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started, and the number of the remote units to be started, and after the host unit obtains the resource utilization rates of the remote units of a certain cell, and further obtains the resource utilization rates of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started and the number of the remote units to be started of the cell can be determined according to the mapping rule, so that the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started and the number of the remote units to be started of the cell can be conveniently, quickly, and accurately determined, and the energy-saving efficiency and accuracy are improved.
In another embodiment, an energy saving method is provided, which is described with respect to the process of determining the list of remote units to be turned off and the list of remote units to be turned on in the foregoing S103, as shown in fig. 3, where the foregoing S103 includes:
s201, according to the number of remote units to be started, determining a plurality of remote unit combination results from all remote units in the cell.
Based on the number of remote units to be turned on determined in step S102, the host unit may determine a plurality of remote unit combination results from all the remote units in the cell according to the number of remote units to be turned on.
For example, if the cell has a total of X remote units and the number of remote units to be turned on is N, the combination result can be expressed asI.e. selecting N remote units from among X remote units, there being a total ofAnd (4) combination.
S202, acquiring a resource evaluation value of a combination result of each remote unit according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit and a signal coverage area of each remote unit under a target bandwidth; the resource assessment value represents the degree of utilization of the resources in the cell by each remote unit combination result.
Based on the aboveAnd combining the results to obtain resource evaluation values of various remote unit combination results.
The resource evaluation value indicates the utilization degree of the combination result of each remote unit to the resource in the cell, which is the secondary objective in this embodimentThe best combination is selected from the combinations, which of course is the combination that best serves the terminals in the cell, but may also be understood as the combination that makes the highest use of the resources in the cell.
The host unit determines resource evaluation values of various remote unit combination results according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit and the signal coverage area of each remote unit.
Optionally, an implementable manner is provided: and acquiring the capacity ratio of the resource utilization rate of the remote unit in the cell total resource utilization rate in the remote unit combination result and the coverage ratio of the signal coverage area of the remote unit under the target bandwidth in the cell total signal coverage area in the remote unit combination result, and determining the weighted sum of the capacity ratio and the coverage ratio as the resource evaluation value of the remote unit combination result.
The capacity occupation ratio is the occupation ratio of the resource utilization ratio of the remote units in the combination result of each remote unit to the total resource utilization ratio of the cell, and the coverage occupation ratio represents the occupation ratio of the signal coverage area of all the remote units in the combination result of each remote unit to the total signal coverage area of the cell when the remote units work in the target bandwidth with the current power. Where the total signal coverage area of a cell is the union of the coverage areas of all remote units in the cell at the current power and current bandwidth, and the current bandwidth refers to the bandwidth before the remote unit is adjusted to the target bandwidth. That is, the coverage area of the remote unit at the current bandwidth is different from the coverage area of the remote unit at the target bandwidth based on the premise that the coverage area of the remote unit increases as the bandwidth of the remote unit becomes smaller. It should be noted that the meaning of the total signal coverage area of the cell referred to in this application is a union area of coverage areas of all remote units in the cell under the current power and the current bandwidth, and repeated descriptions will not be repeated.
For example, Cell _ resource usage represents the total resource utilization of a Cell, Cell _ Coverage represents the total Coverage area of a Cell, and RU _ resource usageiIndicates the resource utilization, RU _ Coverage, of remote unit iiRepresents the coverage area, w, of the remote unit i operating at the current power at the target bandwidth1And w2Respectively, a capacity weighting factor and a coverage weighting factor, and f represents a resource assessment value of a combination result of each remote unit, the resource assessment value can be represented as:
wherein, in the formula (1),the function represents the union of coverage areas of the N remote units operating at the current power and the target bandwidth, and the intersection area of the total signal coverage area of the cell. And the coverage area of the remote unit is obtained by calculation by taking-100 dBm as the boundary judgment power of the coverage area of the remote unit based on a signal attenuation model according to the position information of the remote unit.
The calculation process of the total signal coverage area of the cell may be that, firstly, the coverage area of each remote unit is obtained based on a signal attenuation model according to the current working power, the current bandwidth and the coverage area boundary determination power (-100dbm) of each remote unit, and then the coverage area of each remote unit is determined by summing the coverage areas.
For example, as shown in fig. 3a and 3b, taking N-3 as an example, the outer edge curve of each remote unit is a coverage curve of-100 dBm downlink received power;
wherein, in the 3 remote units in fig. 3a, there is no coverage overlap area with downlink received power greater than-100 dBm, and the union set of the 3 remote units in fig. 3a is SRU and=SRU1+SRU2+SRU3wherein RU denotes a remote unit; the total cell coverage area is denoted S in fig. 3aCell;
in the 3 remote units of fig. 3b, there is an overlap area of coverage for remote unit 1 and remote unit 2 with downlink received power greater than-100 dBm, assuming that the overlap area coverage area is SoverlapThe union of 3 remote units in FIG. 3b is SRU and=SRU1+SRU2+SRU3-Soverlap(ii) a The total coverage area of the cell is again denoted S in fig. 3bCell;
s203, determining the remote unit corresponding to the remote unit combination result with the maximum resource evaluation value as the remote unit in the remote unit list to be started; and determining remote units in the cell other than the remote units in the list of remote units to be turned on as the remote units in the list of remote units to be turned off.
Based on the resource evaluation value of each remote unit combination result determined in the above step, the host unit determines the remote unit combination result with the largest resource evaluation value as the finally selected resource combination.
Based on this, the host unit determines the remote unit corresponding to the remote unit combination result with the largest resource evaluation value as the remote unit in the remote unit list to be turned on, and then the remaining remote units in the cell except the remote unit in the remote unit list to be turned on are determined as the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned off.
In the energy saving method provided by this embodiment, the remote unit level resource utilization rate, the signal coverage area of each remote unit, and the total coverage area of the cell determined by the relative position relationship of the remote units are selected from the X remote units, and finally, the N combinations of the remote units that are finally needed are selected, so as to determine the list of the remote units to be turned on and the list of the remote units to be turned off, and the resource evaluation value is used as the selection standard, thereby ensuring that the selected remote units to be turned on have better service quality for each terminal in the cell, and ensuring the effectiveness of the energy saving scheme.
In an embodiment, an energy saving method is provided, which relates to a specific process in which a host unit determines a terminal corresponding to each remote unit according to signal transmission quality data reported by the terminal, as shown in fig. 4, where the step S101 includes:
s301, receiving the signal transmission quality data of each terminal reported by each remote unit.
The signal transmission quality data is a signal indicating the condition of signal quality between the remote unit and the terminal, i.e., data indicating the strength of signal quality.
For example, the Signal transmission quality data is a measurement value of a terminal Uplink Reference Signal or a Physical Uplink Shared Channel (PUSCH) Channel, or preamble data obtained through a Physical random access Channel, that is, Sounding Reference Signal (SRS), or the like.
In this step, each remote unit receives signal transmission quality data reported by all terminals within the coverage area, and as described above, the coverage areas of the remote units overlap, that is, different remote units receive signal transmission quality data reported by the same terminal.
S302, for any terminal, according to the transmission quality data of the terminal reported by each remote unit, the remote unit with the strongest signal transmission quality is determined as the corresponding remote unit of the terminal.
Based on the signal transmission quality data, for any terminal, the host unit compares the signal transmission quality data reported by the same terminal, and determines a corresponding remote unit with larger signal transmission quality data as the home remote unit of the terminal, wherein the larger the signal transmission quality data is, the stronger the signal transmission quality is.
By adopting the method, an attributive remote unit is determined for the overlapped terminals, and the corresponding terminal of each remote unit is finally determined, so that the situation that one terminal belongs to two remote units does not occur in the determined corresponding terminals of each remote unit can be naturally obtained.
S303, determining a ratio of the resource amount required by the terminal corresponding to each remote unit to the total resource amount of the cell as the resource utilization rate of each remote unit.
And determining the ratio of the resource quantity required by the corresponding terminal of each remote unit to the total resource quantity of the cell as the resource utilization rate of each remote unit.
In the energy saving method provided by this embodiment, before the host unit obtains the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the host unit screens the corresponding terminal of each remote unit to determine that no terminal is repeatedly calculated, so that the finally determined resource utilization rate of the remote unit can be more accurate.
In addition, for the embodiments of all the energy saving methods described above, two examples of application scenarios are provided.
In one embodiment, as shown in fig. 5, an application scenario provides an energy-saving suggestion for energy saving according to the energy-saving method, and the process of the embodiment of the application scenario includes:
s401, acquiring comprehensive data information of a cell; the comprehensive data information at least comprises the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, the total signal coverage area of the cell and the signal coverage area of each remote unit in the cell under the target bandwidth.
Illustratively, several energy saving modules are arranged in the distributed base station, such as an energy saving module interaction diagram of the distributed base station system shown in fig. 5 a. The following steps in this embodiment will be described with reference to the energy saving module illustrated in fig. 5 a.
Based on each energy saving module in fig. 5a, in this step, the monitoring module may obtain the comprehensive data information of the cell; the comprehensive data information reflects relevant data such as resources, flow and the like in a cell, the data can be averaged for a long time, and the granularity can be set to be on the hour level when the data are acquired, so that the average level of the data can be reflected.
The comprehensive data information at least includes the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, the total signal coverage area of the cell, and the signal coverage area of each remote unit in the cell under the target bandwidth.
S402, generating an energy-saving suggestion table according to the comprehensive data information; the energy-saving suggestion table is used for representing the energy-saving strategy of the cell.
In this step, a non-real-time data analysis module generates a far-end unit energy-saving suggestion table of the cell according to the comprehensive data information acquired by the monitoring module, wherein the energy-saving suggestion table is used for representing an energy-saving strategy of the cell, and the energy-saving suggestion table may include on and off suggestions of each far-end unit in each time period. For example, as shown in table 2 below, remote units 1\2\3 are recommended to be in the off state from 12 pm to 7 am and in the on state after 7 am.
TABLE 2
And S403, judging whether the resource utilization rate and the signal coverage area of each current remote unit of the cell meet the energy-saving strategy in the energy-saving suggestion table.
Illustratively, through the real-time energy-saving decision module in fig. 5a, it is determined whether the energy-saving policy in the energy-saving suggestion table matches the current cell resource data. Specifically, the real-time energy-saving decision module may determine an energy-saving decision result by using the energy-saving method provided in the foregoing embodiment according to the resource utilization rate and the signal coverage area of each remote unit of the cell at the current time, and compare the decision result with the energy-saving policy in the energy-saving suggestion table provided by the non-real-time data analysis module to determine whether the resource utilization rate and the signal coverage area of each remote unit at the current time satisfy the energy-saving policy in the energy-saving suggestion table.
And S404, if the energy-saving strategy in the energy-saving suggestion table is met, executing energy-saving operation according to the energy-saving suggestion table.
And if the judgment result is that the energy-saving strategy in the energy-saving suggestion table is met, the real-time energy-saving judgment module sends an instruction to the real-time energy-saving execution module to inform the real-time energy-saving execution module to execute the energy-saving operation of the remote unit. Of course, if the energy-saving strategy in the energy-saving suggestion table is not satisfied, the real-time energy-saving execution module is notified to execute the energy-saving exit action.
The energy-saving method provided by the embodiment can give an energy-saving suggestion according to the counted resource comprehensive data of the cell, if the resource data of the cell at the current moment conforms to the energy-saving suggestion, the energy-saving operation is executed, and if the resource data of the cell does not conform to the energy-saving suggestion, the energy-saving operation is quitted.
In another scenario, an example of the result of performing the energy saving method provided herein is provided. Specifically, as shown in fig. 6, a diagram of the operating state of the remote unit before power saving is performed is shown.
Wherein, the cell totally has 8 remote units to jointly complete continuous coverage of a region, and the default bandwidth is set to be 100 MHz. Table 3 below shows statistical results of resource utilization rates (PRB utilization rates are used as examples) of 8 remote units in the cell at a certain time period, and CASE 1-CASE 4 represent cell resource occupation conditions of different degrees. Wherein the set low, medium and high thresholds are respectively 10%, 20% and 25%.
TABLE 3
The results of performing the remote unit power saving methods according to CASE 1-CASE 4 in the above table are shown in fig. 7-10, respectively. Wherein,
fig. 7 corresponds to CASE1, where most remote units in CASE1 have resource utilization of 0%, and the decision is to keep only remote unit 1 working, and the initial bandwidth is not adjusted.
Fig. 8 corresponds to CASE2, where the resource utilization of most remote units in CASE2 is 1%, and the cell resource utilization is lower than the low threshold, it is determined that only remote unit 5 is reserved for operation, and the initial bandwidth is adjusted to 10 MHz. Because the working bandwidth of the remote unit 5 is reduced and the power is unchanged, the remote unit 5 with the adjusted bandwidth can achieve the best effect that a single remote unit works on the bandwidth of 10MHz and compensates the coverage hole after other remote units are switched off.
Fig. 9 corresponds to CASE3, where the utilization rate of cell resources in CASE3 is higher than the low threshold and lower than the medium threshold, and it is determined to keep remote unit 4 and remote unit 6 working, and the initial bandwidth is adjusted to 20 MHz. The remote units 4 and 6 with adjusted bandwidth can achieve the best effect of compensating coverage holes after other remote units are turned off.
Fig. 10 corresponds to CASE4, where the utilization rate of cell resources in CASE4 is higher than the medium threshold and lower than the high threshold, and it is determined to keep remote unit 1, remote unit 5, and remote unit 7 working, and the initial bandwidth is adjusted to 40 MHz. The remote unit 1, the remote unit 5 and the remote unit 7 after bandwidth adjustment can achieve the best effect of compensating coverage holes after other remote units are turned off.
According to the application embodiment of the energy saving method provided by the embodiment, it can be seen that the energy saving method provided by the application can flexibly control the turning-off and turning-on of the resources of each remote unit, and realize the reasonable use of hardware resources, thereby reducing the energy consumption of the equipment of the whole set of distributed base station system.
It should be understood that although the various steps in the flow charts of fig. 2-5 are shown in order as indicated by the arrows, the steps are not necessarily performed in order as indicated by the arrows. The steps are not performed in the exact order shown and described, and may be performed in other orders, unless explicitly stated otherwise. Moreover, at least some of the steps in fig. 2-5 may include multiple sub-steps or multiple stages that are not necessarily performed at the same time, but may be performed at different times, and the order of performance of the sub-steps or stages is not necessarily sequential, but may be performed in turn or alternating with other steps or at least some of the sub-steps or stages of other steps.
In one embodiment, as shown in fig. 11, there is provided an energy saving device including: an obtaining module 10, a first determining module 11, a second determining module 12 and an energy saving module 13, wherein,
an obtaining module 10, configured to obtain a resource utilization rate of each remote unit in a cell, where the resource utilization rate indicates a ratio of resources required by the remote unit to a total resource amount of the cell;
a target determining module 11, configured to determine, according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the number of remote units to be started and a target bandwidth of the remote units to be started;
a list determining module 12, configured to determine a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on in a cell according to a resource utilization rate of each remote unit, a signal coverage area of each remote unit in a target bandwidth, and the number of remote units to be turned on;
and the energy saving module 13 is configured to execute energy saving operation according to the list of remote units to be turned off, the list of remote units to be turned on, and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on.
In an embodiment, the target determining module 11 is configured to obtain the number of remote units to be turned on and a target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on according to a preset mapping rule and a total cell resource utilization rate; the total resource utilization rate of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization rates of the remote units, and the mapping rule comprises the corresponding relation among the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be started and the number of the remote units to be started.
In an embodiment, the target determining module 11 is further configured to, when a preset condition is met, obtain the number of remote units to be started and a target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to a preset mapping rule and a total cell resource utilization rate; the total resource utilization rate of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization rates of the remote units, and the mapping rule comprises the corresponding relation among the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be started and the number of the remote units to be started.
In one embodiment, the preset conditions include: the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is less than the preset number, the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset high threshold, or the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset high threshold and the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is less than the preset number.
In one embodiment, the total resource utilization of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on, and the number of the remote units to be turned on in the mapping rule are in a direct proportion relationship.
In one embodiment, the proportional relationship comprises:
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than the preset low threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is the first target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N1;
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the low threshold and less than the preset middle threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a second target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N2;
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the medium threshold and less than the preset high threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a third target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N3;
wherein the first target bandwidth < the second target bandwidth < the third target bandwidth; n1< N2< N3.
In one embodiment, the list determining module 12 comprises: a combination determination unit, a resource evaluation unit, and a list determination unit, wherein,
a combination determining unit, configured to determine a combination result of multiple remote units from all remote units in a cell according to the number of remote units to be started;
the resource evaluation unit is used for acquiring a resource evaluation value of a combination result of each remote unit according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit and the signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth; the resource evaluation value represents the utilization degree of the combination result of each remote unit to the resources in the cell;
the list determining unit is used for determining the remote unit corresponding to the remote unit combination result with the largest resource evaluation value as the remote unit in the remote unit list to be started; and determining remote units in the cell other than the remote units in the list of remote units to be turned on as the remote units in the list of remote units to be turned off.
In an embodiment, the resource evaluating unit is specifically configured to obtain a capacity occupancy of a resource utilization rate of the remote unit in the combined result of each remote unit in the total resource utilization rate of the cell, and a coverage occupancy of a signal coverage area of the remote unit in the combined result of each remote unit in the target bandwidth in the total signal coverage area of the cell; the weighted sum of the capacity and coverage ratios is determined as the resource assessment value for the combined result of the remote units.
In one embodiment, the root energy saving module is specifically configured to keep the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned on, and adjust the bandwidth of each remote unit in the remote unit list to be turned on to the target bandwidth; wherein, the power of each remote unit in the remote unit list to be started is kept unchanged; and turning off the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned off.
In one embodiment, there is provided an energy saving device, and the obtaining module 10 includes: a receiving unit, a first determining unit and a second determining unit, wherein,
a receiving unit, configured to receive signal transmission quality data of each terminal reported by each remote unit;
a terminal determining unit, configured to determine, for any one terminal, a remote unit with the strongest signal transmission quality as a remote unit corresponding to the terminal according to the transmission quality data of the terminal reported by each remote unit;
and the resource utilization determining unit is used for determining the ratio of the resource quantity required by the corresponding terminal of each remote unit to the total resource quantity of the cell as the resource utilization rate of each remote unit.
In an embodiment, the target determining module 11 is further configured to turn off all remote units with resource utilization rate of 0 when the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than a preset high threshold and the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is greater than a preset number; the total resource utilization of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization of each remote unit.
The implementation principle and technical effect of all the energy saving devices provided by the above embodiments are similar to those of the above embodiments, and are not described herein again.
For specific limitations of the energy saving device, reference may be made to the above limitations of the energy saving method, which are not described herein again. The modules in the energy saving device can be wholly or partially realized by software, hardware and a combination thereof. The modules can be embedded in a hardware form or independent from a processor in the computer device, and can also be stored in a memory in the computer device in a software form, so that the processor can call and execute operations corresponding to the modules.
In one embodiment, a computer device is provided, which may be a terminal, and its internal structure diagram may be as shown in fig. 12. The computer device includes a processor, a memory, a network interface, a display screen, and an input device connected by a system bus. Wherein the processor of the computer device is configured to provide computing and control capabilities. The memory of the computer device comprises a nonvolatile storage medium and an internal memory. The non-volatile storage medium stores an operating system and a computer program. The internal memory provides an environment for the operation of an operating system and computer programs in the non-volatile storage medium. The network interface of the computer device is used for communicating with an external terminal through a network connection. The computer program is executed by a processor to implement a power saving method. The display screen of the computer equipment can be a liquid crystal display screen or an electronic ink display screen, and the input device of the computer equipment can be a touch layer covered on the display screen, a key, a track ball or a touch pad arranged on the shell of the computer equipment, an external keyboard, a touch pad or a mouse and the like.
Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the architecture shown in fig. 12 is merely a block diagram of some of the structures associated with the disclosed aspects and is not intended to limit the computing devices to which the disclosed aspects apply, as particular computing devices may include more or less components than those shown, or may combine certain components, or have a different arrangement of components.
In one embodiment, a computer device is provided, comprising a memory and a processor, the memory having a computer program stored therein, the processor implementing the following steps when executing the computer program:
acquiring the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, wherein the resource utilization rate represents the proportion of the total resource quantity of the cell occupied by the resources required by the remote unit;
determining the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit;
determining a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on of a cell according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the signal coverage area of each remote unit under a target bandwidth and the number of the remote units to be turned on;
and executing energy-saving operation according to the list of the remote units to be turned off, the list of the remote units to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on.
The implementation principle and technical effect of the computer device provided by the above embodiment are similar to those of the above method embodiment, and are not described herein again.
In one embodiment, a computer-readable storage medium is provided, having a computer program stored thereon, which when executed by a processor, performs the steps of:
acquiring the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, wherein the resource utilization rate represents the proportion of the total resource quantity of the cell occupied by the resources required by the remote unit;
determining the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit;
determining a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on of a cell according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the signal coverage area of each remote unit under a target bandwidth and the number of the remote units to be turned on;
and executing energy-saving operation according to the list of the remote units to be turned off, the list of the remote units to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on.
The implementation principle and technical effect of the computer-readable storage medium provided by the above embodiments are similar to those of the above method embodiments, and are not described herein again.
It will be understood by those skilled in the art that all or part of the processes of the methods of the embodiments described above can be implemented by hardware instructions of a computer program, which can be stored in a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium, and when executed, can include the processes of the embodiments of the methods described above. Any reference to memory, storage, database, or other medium used in the embodiments provided herein may include non-volatile and/or volatile memory, among others. Non-volatile memory can include read-only memory (ROM), Programmable ROM (PROM), Electrically Programmable ROM (EPROM), Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM), or flash memory. Volatile memory can include Random Access Memory (RAM) or external cache memory. By way of illustration and not limitation, RAM is available in a variety of forms such as Static RAM (SRAM), Dynamic RAM (DRAM), Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), Double Data Rate SDRAM (DDRSDRAM), Enhanced SDRAM (ESDRAM), Synchronous Link DRAM (SLDRAM), Rambus Direct RAM (RDRAM), direct bus dynamic RAM (DRDRAM), and memory bus dynamic RAM (RDRAM).
The technical features of the above embodiments can be arbitrarily combined, and for the sake of brevity, all possible combinations of the technical features in the above embodiments are not described, but should be considered as the scope of the present specification as long as there is no contradiction between the combinations of the technical features.
The above-mentioned embodiments only express several embodiments of the present application, and the description thereof is more specific and detailed, but not construed as limiting the scope of the invention. It should be noted that, for a person skilled in the art, several variations and modifications can be made without departing from the concept of the present application, which falls within the scope of protection of the present application. Therefore, the protection scope of the present patent shall be subject to the appended claims.
Claims (13)
1. A method for conserving energy, the method comprising:
acquiring the resource utilization rate of each remote unit in the cell, wherein the resource utilization rate represents the proportion of the total resource quantity of the cell occupied by the resources required by the remote unit;
determining the number of remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit;
determining a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on of the cell according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit, the signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth and the number of the remote units to be turned on;
executing energy-saving operation according to the remote unit list to be turned off, the remote unit list to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be turned on;
wherein the executing of the energy-saving operation according to the remote unit list to be turned off, the remote unit list to be turned on, and the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be turned on includes:
keeping the remote units in the remote unit list to be started on, and adjusting the bandwidth of each remote unit in the remote unit list to be started to the target bandwidth; wherein the power of each remote unit in the list of remote units to be turned on remains unchanged;
and turning off the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned off.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein said determining a number of remote units to be turned on and a target bandwidth for said remote units to be turned on based on resource utilization of each of said remote units comprises:
acquiring the number of the remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to a preset mapping rule and the total cell resource utilization rate; the total resource utilization rate of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization rates of the remote units, and the mapping rule comprises the corresponding relation among the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be started and the number of the remote units to be started.
3. The method of claim 1, wherein said determining a number of remote units to be turned on and a target bandwidth for said remote units to be turned on based on resource utilization of each of said remote units comprises:
when a preset condition is met, acquiring the number of the remote units to be started and the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started according to a preset mapping rule and the total utilization rate of the cell resources; the total resource utilization rate of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization rates of the remote units, and the mapping rule comprises the corresponding relation among the total resource utilization rate of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be started and the number of the remote units to be started.
4. The energy saving method according to claim 3, wherein the preset condition comprises:
the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is less than a preset number, the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than a preset high threshold, or the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than a preset high threshold and the number of remote units with resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is less than a preset number.
5. The method according to any of claims 2 to 4, wherein the mapping rule is proportional to the total resource utilization of the cell, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be turned on, and the number of remote units to be turned on.
6. The energy saving method according to claim 5, wherein the proportional relationship comprises:
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than a preset low threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a first target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N1;
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the low threshold and less than a preset middle threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a second target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N2;
if the total resource utilization rate of the cell is greater than the medium threshold and less than a preset high threshold, the target bandwidth of the remote units to be started is a third target bandwidth, and the number of the remote units to be started is N3;
wherein the first target bandwidth < the second target bandwidth < the third target bandwidth; the N1< N2< N3.
7. The method according to any of claims 1-4, wherein determining the list of remote units to be turned off and the list of remote units to be turned on for the cell according to the resource utilization of each remote unit, the signal coverage area of each remote unit in the target bandwidth, and the number of remote units to be turned on comprises:
determining a plurality of remote unit combination results from all remote units of the cell according to the number of the remote units to be started;
acquiring a resource evaluation value of a combination result of each remote unit according to the resource utilization rate of each remote unit and a signal coverage area of each remote unit under the target bandwidth; the resource evaluation value represents the utilization degree of the combination result of each remote unit to the resource in the cell;
determining the remote unit corresponding to the remote unit combination result with the maximum resource evaluation value as the remote unit in the remote unit list to be started; and determining remote units in the cell other than the remote units in the list of remote units to be turned on as the remote units in the list of remote units to be turned off.
8. The method of claim 7, wherein said obtaining a resource assessment value of a combination result of each remote unit according to a resource utilization of each remote unit and a signal coverage area of each remote unit at the target bandwidth comprises:
obtaining a capacity occupation ratio of the resource utilization rate of the remote unit in the combined result of the remote units in the total resource utilization rate of the cell, and a coverage occupation ratio of a signal coverage area of the remote unit in the combined result of the remote units in the target bandwidth in the total signal coverage area of the cell;
determining a weighted sum of said capacity and coverage ratios as a resource assessment value for a combined result of each of said remote units.
9. The method of claim 1, wherein the obtaining resource utilization of each remote unit in the cell comprises:
receiving signal transmission quality data of each terminal reported by each remote unit;
for any one of the terminals, determining the remote unit with the strongest signal transmission quality as the corresponding remote unit of the terminal according to the transmission quality data of the terminal reported by each remote unit;
and determining the ratio of the resource quantity required by the corresponding terminal of each remote unit to the total resource quantity of the cell as the resource utilization rate of each remote unit.
10. The method according to any of claims 1-4, wherein after said obtaining resource utilization of each remote unit in the cell, the method further comprises:
when the total resource utilization rate of the cell is less than a preset high threshold and the number of the remote units with the resource utilization rate equal to 0 in each remote unit is greater than a preset number, turning off all the remote units with the resource utilization rate of 0; the total resource utilization of the cell is the sum of the resource utilization of each of the remote units.
11. An energy saving device, characterized in that the device comprises:
an obtaining module, configured to obtain a resource utilization rate of each remote unit in a cell, where the resource utilization rate indicates a ratio of resources required by the remote unit to a total resource amount of the cell;
a first determining module, configured to determine, according to a resource utilization rate of each remote unit, a number of remote units to be started and a target bandwidth of the remote unit to be started;
a second determining module, configured to determine a list of remote units to be turned off and a list of remote units to be turned on in the cell according to a resource utilization rate of each remote unit, a signal coverage area of each remote unit in the target bandwidth, and the number of remote units to be turned on;
the energy-saving module is used for executing energy-saving operation according to the remote unit list to be turned off, the remote unit list to be turned on and the target bandwidth of the remote unit to be turned on;
the energy saving module is specifically configured to keep the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned on, and adjust the bandwidth of each remote unit in the remote unit list to be turned on to the target bandwidth; turning off the remote units in the remote unit list to be turned off; wherein the power at which each remote unit in the list of remote units to be turned on is kept constant.
12. A computer device comprising a memory and a processor, the memory storing a computer program, characterized in that the processor, when executing the computer program, implements the steps of the energy saving method of any one of claims 1 to 10.
13. A computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, which, when being executed by a processor, carries out the steps of the energy saving method of one of claims 1 to 10.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911336755.8A CN111163506B (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2019-12-23 | Energy saving method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| PCT/CN2020/079021 WO2021128596A1 (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2020-03-12 | Energy-saving method and apparatus, computer device and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911336755.8A CN111163506B (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2019-12-23 | Energy saving method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111163506A CN111163506A (en) | 2020-05-15 |
| CN111163506B true CN111163506B (en) | 2021-05-28 |
Family
ID=70557823
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911336755.8A Active CN111163506B (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2019-12-23 | Energy saving method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111163506B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2021128596A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111770503B (en) * | 2020-07-01 | 2023-03-28 | 重庆邮电大学 | System, method and storage medium for closing and opening micro base station |
| CN114173400B (en) * | 2020-09-11 | 2023-05-16 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Energy saving method, device and equipment of network equipment |
| CN112929951B (en) * | 2021-01-25 | 2023-06-30 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Energy saving method and equipment |
| CN112702753B (en) * | 2021-03-24 | 2021-06-08 | 四川创智联恒科技有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and storage medium for automatic configuration recovery of communication radio frequency unit |
| CN113242592B (en) * | 2021-05-12 | 2022-05-03 | 江苏亨鑫众联通信技术有限公司 | Method, device and storage medium for energy conservation of distributed base station |
| CN113329515A (en) * | 2021-05-13 | 2021-08-31 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Method and device for determining remote unit to which user equipment belongs and storage medium |
| CN115696517A (en) * | 2021-07-29 | 2023-02-03 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Communication method, apparatus and storage medium |
| CN113727294B (en) * | 2021-08-12 | 2023-03-24 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Communication method and device |
| CN116193550B (en) * | 2023-04-24 | 2023-06-30 | 广州世炬网络科技有限公司 | Energy-saving method and device for 5G (fourth generation) extension pico-base station |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102378323A (en) * | 2010-08-13 | 2012-03-14 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Energy-saving compensation method and base station |
| CN103269511A (en) * | 2013-04-23 | 2013-08-28 | 北京邮电大学 | Method for energy conservation for wireless access network |
| CN104105151A (en) * | 2013-04-01 | 2014-10-15 | 华为技术有限公司 | Base station processing method and device, and base station |
| CN104509178A (en) * | 2013-07-23 | 2015-04-08 | 华为技术有限公司 | Base station state processing method and apparatus |
| WO2015103772A1 (en) * | 2014-01-10 | 2015-07-16 | 华为技术有限公司 | Energy-saving system, device and method of distributed base station |
| CN105407520A (en) * | 2015-10-13 | 2016-03-16 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | Centralized base station dormancy decision method and dormancy system |
| US10070375B2 (en) * | 2014-08-08 | 2018-09-04 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Adapting the number of cells to measure in a network with on/off cells |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101702822B (en) * | 2009-10-23 | 2014-12-10 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for realizing carrier control and system |
| CN102340853A (en) * | 2010-07-20 | 2012-02-01 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Mobile communication system base station energy-saving method and device |
| CN102740326B (en) * | 2011-04-07 | 2015-02-04 | 中国移动通信集团公司 | Managing method and device for processing resources in BBU |
| CN103188713B (en) * | 2011-12-28 | 2016-06-22 | 华为技术有限公司 | The method of wireless communication networks capacity management and base station |
| CN102984742B (en) * | 2012-11-14 | 2015-07-08 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device and system for base station energy consumption monitoring |
| WO2014168336A1 (en) * | 2013-04-11 | 2014-10-16 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method and user equipment for transmitting uplink signal |
| CN103648112A (en) * | 2013-12-20 | 2014-03-19 | 中国移动通信集团江苏有限公司无锡分公司 | Method for converting opening/closing state of base stations in micro cell in cellular network |
| CN104661241B (en) * | 2015-01-05 | 2018-05-22 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | A kind of cell dormancy decision-making technique, realization method and system |
| CN107567077B (en) * | 2016-07-01 | 2021-02-19 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Base station energy saving method and device |
| EP3769582A4 (en) * | 2018-03-19 | 2022-03-16 | Mavenir Networks, Inc. | System and method for reduction in fronthaul interface bandwidth for cloud ran |
| CN110099400B (en) * | 2019-06-05 | 2022-10-14 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Energy saving method and device for communication base station and computer readable storage medium |
-
2019
- 2019-12-23 CN CN201911336755.8A patent/CN111163506B/en active Active
-
2020
- 2020-03-12 WO PCT/CN2020/079021 patent/WO2021128596A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102378323A (en) * | 2010-08-13 | 2012-03-14 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Energy-saving compensation method and base station |
| CN104105151A (en) * | 2013-04-01 | 2014-10-15 | 华为技术有限公司 | Base station processing method and device, and base station |
| CN103269511A (en) * | 2013-04-23 | 2013-08-28 | 北京邮电大学 | Method for energy conservation for wireless access network |
| CN104509178A (en) * | 2013-07-23 | 2015-04-08 | 华为技术有限公司 | Base station state processing method and apparatus |
| WO2015103772A1 (en) * | 2014-01-10 | 2015-07-16 | 华为技术有限公司 | Energy-saving system, device and method of distributed base station |
| US10070375B2 (en) * | 2014-08-08 | 2018-09-04 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Adapting the number of cells to measure in a network with on/off cells |
| CN105407520A (en) * | 2015-10-13 | 2016-03-16 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | Centralized base station dormancy decision method and dormancy system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2021128596A1 (en) | 2021-07-01 |
| CN111163506A (en) | 2020-05-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN111163506B (en) | Energy saving method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| RU2502188C2 (en) | Apparatus and method of controlling wireless communication node | |
| CN111212463B (en) | Energy saving method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN101352059B (en) | Method for planning honeycomb mobile telecom network | |
| Hossain et al. | Distributed inter-BS cooperation aided energy efficient load balancing for cellular networks | |
| US9544858B2 (en) | Channel power adjustment based on positional information of area restricted self-organizing subnets | |
| CN104272857A (en) | Methods and apparatus for intelligent wireless technology selection | |
| WO2021109746A1 (en) | Method for controlling active room distribution system, electronic device, and storage medium | |
| JP2014523159A5 (en) | ||
| JP5189244B2 (en) | Channel assignment to wireless LAN | |
| WO2013056394A1 (en) | Determination of ue location in a cell | |
| WO2021083230A1 (en) | Power adjusting method and access network device | |
| Suárez et al. | Energy-efficient BS switching-off and cell topology management for macro/femto environments | |
| Akter et al. | Distributed approach for power and rate allocation to secondary users in cognitive radio networks | |
| CN106332203B (en) | The method that green energy conservation in a kind of framework of floored community LTE calculates | |
| CN115066006A (en) | Base station dormancy method, equipment and medium based on reinforcement learning | |
| Yao et al. | Data-driven resource allocation with traffic load prediction | |
| CN117528744A (en) | Cell power configuration method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| Wang et al. | Base station sleeping strategy for on-grid energy saving in cellular networks with hybrid energy supplies in IoT environment | |
| CN111556574A (en) | Management method and management device for wireless local area network work and access controller | |
| CN110461048A (en) | A kind of method and user equipment adjusting traffic handling capability | |
| Yuan et al. | A QoE-orientated base station sleeping strategy for multi-services in cellular networks | |
| CN109151972B (en) | Uplink power control method, device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114980282A (en) | Power adjustment method and network management server | |
| US9591654B2 (en) | Wireless communication apparatus for reducing interference with neighboring cell and method of reducing interference thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |
Effective date of registration: 20210729 Address after: 510663 Shenzhou Road 10, Guangzhou Science City, Guangzhou economic and Technological Development Zone, Guangzhou, Guangdong Patentee after: Jingxin Network System Co.,Ltd. Address before: 510730, No. 6, Jin Lu, Guangzhou economic and Technological Development Zone, Guangdong, Guangzhou Patentee before: COMBA TELECOM TECHNOLOGY (GUANGZHOU) Ltd. |