CN110769493A - Electromagnetic radiation control method and related equipment - Google Patents
Electromagnetic radiation control method and related equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110769493A CN110769493A CN201810830376.3A CN201810830376A CN110769493A CN 110769493 A CN110769493 A CN 110769493A CN 201810830376 A CN201810830376 A CN 201810830376A CN 110769493 A CN110769493 A CN 110769493A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- user equipment
- user
- millimeter waves
- separation distance
- electromagnetic radiation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/04—TPC
- H04W52/18—TPC being performed according to specific parameters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B17/00—Monitoring; Testing
- H04B17/10—Monitoring; Testing of transmitters
- H04B17/11—Monitoring; Testing of transmitters for calibration
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/04—TPC
- H04W52/30—TPC using constraints in the total amount of available transmission power
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
The embodiment of the application discloses an electromagnetic radiation control method, which comprises the following steps: acquiring a spacing distance between user equipment and a user; and according to the spacing distance, adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment, so that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity. The embodiment of the application also discloses an electromagnetic radiation control device, and by implementing the embodiment of the application, the transmitting power and the transmitting efficiency of millimeter waves can be improved.
Description
Technical Field
The present application relates to the field of antenna technologies, and in particular, to an electromagnetic radiation control method and related device.
Background
The fifth generation mobile communication specification includes millimeter waves, for example, the millimeter wave band specified by the third generation partnership project (3 GPP) has 28GHz and 38GHz in the united states and 26GHz in europe. However, when the user equipment transmits millimeter waves, electromagnetic radiation is generated, which endangers user safety and health, and therefore, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) of the united states stipulates the maximum allowable dose (MPE) of electromagnetic radiation, which can be allowed only when the transmitted millimeter waves generate electromagnetic radiation smaller than MPE. The electromagnetic radiation generated by the emitted millimeter waves is closely related to the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves, and in the prior art, on the premise of meeting the maximum allowable radiation quantity, the equivalent access radiation power cannot be guaranteed, so that the emission efficiency of the millimeter waves is influenced.
Disclosure of Invention
The embodiment of the application provides an electromagnetic radiation control method and related equipment, which can improve the transmitting power and transmitting efficiency of millimeter waves on the premise of ensuring the safety of users.
In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an electromagnetic radiation control method, including: firstly, acquiring a spacing distance between user equipment and a user; and then according to the spacing distance, adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment, so that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity. The equivalent access radiation power of the transmitted millimeter waves is adjusted according to different spacing distances between the user equipment and the user, so that the transmission power and the transmission efficiency of the millimeter waves are improved on the premise of guaranteeing the safety of the user.
In one possible design, a power value corresponding to the separation distance is looked up from a preset target calibration table, wherein the target calibration table comprises a corresponding relation between the separation distance and the power value; and adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment to the power value, thereby ensuring that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the user equipment does not influence the user at the spacing distance.
In another possible design, on the premise that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity, when the spacing distance is increased, the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment can be improved, so that the transmission efficiency of the millimeter waves is improved. When the spacing distance is reduced, the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment can be reduced, and the user is protected from the influence of electromagnetic radiation.
In another possible design, an antenna used by the ue to transmit the millimeter wave may be determined first, and then the target calibration table may be selected from a plurality of preset calibration tables according to the antenna used to transmit the millimeter wave, so as to achieve the accuracy of adjusting the equivalent access radiation power.
In another possible design, since the antenna used for transmitting millimeter waves in 5G applications varies according to the network environment, the electromagnetic radiation generated by the antenna is different. Therefore, the calibration table corresponding to each antenna in all antennas of the user terminal can be configured in advance. In a network environment of practical application, a received signal strength of each antenna in a plurality of antennas of the user equipment may be obtained first; and determining an antenna used by the user equipment for transmitting the millimeter wave according to the received signal strength.
In another possible design, the separation distance between the user equipment and the user is measured by a ranging sensor within a preset distance range.
In another possible design, the separation distance between the ue and the user is measured according to a preset period, and the measured separation distance is reported to a core processor of the ue for processing.
In another possible design, a plurality of measured distances between the user equipment and the user obtained through a plurality of measurements may be obtained; taking an average of the plurality of measurement distances as the separation distance.
In a second aspect, the present application provides an electromagnetic radiation control apparatus, configured to implement the method and the functions performed by the user equipment in the first aspect, and implemented by hardware/software, where the hardware/software includes units corresponding to the functions.
In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a user equipment, including: the electromagnetic radiation control method comprises a processor, a memory and a communication bus, wherein the communication bus is used for realizing connection communication between the processor and the memory, and the processor executes a program stored in the memory for realizing the steps in the electromagnetic radiation control method provided by the first aspect.
In one possible design, the user equipment provided in the embodiment of the present application may include a module corresponding to the behavior of the electromagnetic radiation control apparatus in the design for executing the method described above. The modules may be software and/or hardware.
In a fourth aspect, embodiments of the present application provide a computer-readable storage medium having stored therein instructions, which, when executed on a computer, cause the computer to perform the methods of the above-mentioned aspects.
In a fifth aspect, embodiments of the present application provide a computer program product comprising instructions which, when run on a computer, cause the computer to perform the method of the above aspects.
Drawings
In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments or the background art of the present application, the drawings required to be used in the embodiments or the background art of the present application will be described below.
Fig. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of an electromagnetic radiation control system provided in an embodiment of the present application;
fig. 2 is a schematic flowchart of an electromagnetic radiation control method provided in an embodiment of the present application;
FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of a calibration table provided in an embodiment of the present application;
fig. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of an electromagnetic radiation control apparatus according to an embodiment of the present application;
fig. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a user equipment according to an embodiment of the present application.
Detailed Description
The embodiments of the present application will be described below with reference to the drawings.
Referring to fig. 1, fig. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of an electromagnetic radiation control system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. As shown, the system in the embodiment of the present application includes a user device and a user. The user equipment may be any equipment with wireless transceiving function, and may refer to equipment providing voice and/or data connection to a user, may be connected to a computing device such as a laptop computer or desktop computer, or may be a stand-alone device such as a Personal Digital Assistant (PDA). A user equipment may also be called a system, subscriber unit, subscriber station, mobile, remote station, access point, remote terminal, access terminal, user agent, or user device. The user equipment may be a device generating (5-generation, 5G) millimeter waves of a fifth generation mobile communication technology, such as a notebook, a router, a watch, and the like. A ranging sensor may be included in the user equipment, and a separation distance between the user and the user equipment is measured by the ranging sensor. Based on the system, the embodiment of the application provides the following solution.
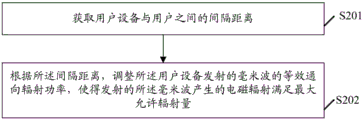
Referring to fig. 2, fig. 2 is a schematic flow chart of an electromagnetic radiation control method provided in an embodiment of the present application, where the method includes, but is not limited to, the following steps:
s201, acquiring the spacing distance between the user equipment and the user.
In specific implementation, the distance measuring sensor may include a laser distance measuring sensor, an infrared distance measuring sensor, an ultrasonic distance measuring sensor, a millimeter wave distance measuring sensor, and the like, and may measure the distance between the user equipment and the user through the laser distance measuring sensor, the infrared distance measuring sensor, the ultrasonic distance measuring sensor, or the millimeter wave distance measuring sensor. The ranging sensor can be arranged inside the user equipment, and the ranging sensor can also be placed on the user equipment for use. For example, a laser ranging sensor arranged in the user equipment can be used for transmitting a laser signal to the user and recording a time point of transmitting the laser signal, the laser signal returns to the laser ranging sensor after being reflected by a human body, the time point of receiving the laser signal is recorded at the moment, the transmission time length of the laser signal is determined according to the time point of transmitting the laser signal and the time point of receiving the laser signal, and then the spacing distance between the user equipment and the user is determined according to the transmission time length. Alternatively, the separation distance between the user equipment and the user may be measured by using the principle that the infrared ranging sensor emits an infrared signal and the intensity of the reflected infrared signal received is different due to the difference in separation distance. The separation distance between the user equipment and the user can also be measured by other methods, which are not described herein.
The influence degree of the electromagnetic radiation on the user is related to the spacing distance between the user equipment and the user, the closer the spacing distance is, the greater the influence degree of the electromagnetic radiation on the user is, the farther the spacing distance is, the smaller the influence degree of the electromagnetic radiation on the user is, and when the spacing distance exceeds the preset distance range, the influence degree of the electromagnetic radiation on the user is almost 0. The separation distance between the user equipment and the user may be measured by a ranging sensor within a preset distance range. The predetermined distance range may be a distance, such as 20cm, at which the electromagnetic radiation has an effect on the user. Within the preset distance range, the electromagnetic radiation generated by the millimeter waves emitted by the user equipment needs to be controlled within the range of the maximum allowable radiation amount.
Optionally, the separation distance between the ue and the user may be measured according to a preset period, and the separation distance measured each time is reported to a core processor of the ue for processing. The preset period may be 1 second or 2 seconds, etc.
Optionally, a plurality of measurement distances between the user equipment and the user obtained through a plurality of measurements may be obtained; taking an average of the plurality of measurement distances as the separation distance.
S202, according to the spacing distance, the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves emitted by the user equipment is adjusted, so that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the emitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity. The millimeter wave is an electromagnetic wave with the wavelength of 1-10 mm, and has the characteristics of high bandwidth and narrow beam. The equivalent access radiation power is the radiation power in a certain specified direction, and is ideally equal to the transmission power of the power amplifier multiplied by the gain of the antenna.
In the specific implementation, on the premise that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity, when the spacing distance is increased, the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment can be improved, so that the transmission efficiency of the millimeter waves is improved. When the spacing distance is reduced, the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment can be reduced, and the user is protected from the influence of electromagnetic radiation.
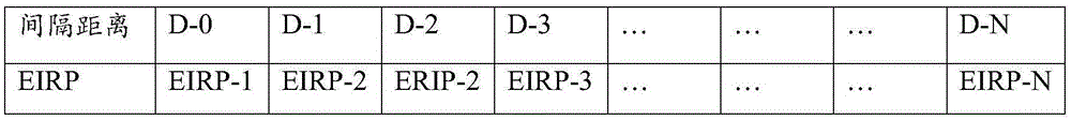
Further, a power value corresponding to the separation distance may be searched from a preset target calibration table, where the target calibration table includes a corresponding relationship between the separation distance and the power value; and adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment to the power value, thereby ensuring that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the user equipment does not influence the user at the spacing distance. For example, as shown in fig. 3, fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of a calibration table provided in an embodiment of the present application, where the calibration table is a calibration table for EIRP and separation distance that meet the maximum allowable radiation requirement. When the distance between the user and the user equipment is D-0, the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves emitted by the user equipment can be adjusted to EIRP-1, and the electromagnetic radiation generated by the millimeter waves emitted by the user equipment in the range of D-0 can not influence the user. When the distance between the user and the user equipment is D-3, the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves emitted by the user equipment can be adjusted to EIRP-3, and the electromagnetic radiation generated by the millimeter waves emitted by the user equipment within the range of D-3 can not influence the user.
In addition, before the adjustment of the equivalent lead-to radiation power of the millimeter wave transmitted by the user equipment, the calibration table of the EIRP and the separation distance may be configured in advance for use in adjusting the equivalent lead-to radiation power. The method specifically comprises the following steps: the method comprises the steps of placing ranging sensors on the front side, the back side and the frame of the user equipment, completely covering a radiation space of an antenna used by the user equipment for transmitting millimeter waves, measuring the distance between the user equipment and a user through the ranging sensors, measuring the current electromagnetic radiation size, and recording the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment at the moment when the electromagnetic radiation size meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity. Then, the distance between the user equipment and the user is changed, and a plurality of tests are carried out according to the method, so that the calibration table of the EIRP and the spacing distance can be generated.
Optionally, since an antenna used for transmitting the millimeter waves in the 5G application may be changed according to a change of a network environment, electromagnetic radiation generated by the antenna is different. Therefore, the calibration table corresponding to each antenna in all antennas of the user terminal can be configured in advance. In a network environment of practical application, a received signal strength of each antenna in a plurality of antennas of the user equipment may be obtained first; according to the received signal strength, determining an antenna used by the user equipment to transmit the millimeter wave, for example, an antenna with the highest received signal strength may be used as the antenna used to transmit the millimeter wave, or an antenna with the received signal strength greater than a preset threshold may be used as the antenna used to transmit the millimeter wave. And then selecting the target calibration table from a plurality of preset calibration tables according to the antenna used for transmitting the millimeter waves, thereby realizing the accuracy of adjusting the equivalent access to the radiation power.
In the embodiment of the application, firstly, the spacing distance between user equipment and a user is obtained; and then according to the spacing distance, adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment, so that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity. The equivalent access radiation power of the transmitted millimeter waves is adjusted according to different spacing distances between the user equipment and the user, so that the transmission power and the transmission efficiency of the millimeter waves are improved on the premise of guaranteeing the safety of the user.
The method of the embodiments of the present application is set forth above in detail and the apparatus of the embodiments of the present application is provided below.
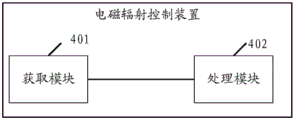
Referring to fig. 4, fig. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of an electromagnetic radiation control apparatus provided in an embodiment of the present application, and the electromagnetic radiation control apparatus may include an obtaining module 401 and a processing module 402, where details of each module are described below.
An obtaining module 401, configured to obtain a separation distance between a user equipment and a user;
a processing module 402, configured to adjust, according to the separation distance, an equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment, so that electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets a maximum allowable radiation amount.
Optionally, the processing module 402 is further configured to search a preset target calibration table for a power value corresponding to the separation distance, where the target calibration table includes a corresponding relationship between the separation distance and the power value; adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment to the power value.
Optionally, the processing module 402 is further configured to determine an antenna used by the user equipment to transmit the millimeter wave; and selecting the target calibration table from a plurality of preset calibration tables according to the antenna used for transmitting the millimeter waves.
An obtaining module 401, configured to obtain a received signal strength of each antenna in a plurality of antennas of the ue;
the processing module 402 is further configured to determine, according to the received signal strength, an antenna used by the user equipment to transmit the millimeter wave.
Optionally, the obtaining module 401 is further configured to measure the separation distance between the ue and the user through a ranging sensor within a preset distance range.
Optionally, the obtaining module 401 is further configured to measure the separation distance between the user equipment and the user according to a preset period.
Optionally, the obtaining module 401 is further configured to obtain a plurality of measurement distances between the user equipment and the user, which are obtained through multiple measurements; taking an average of the plurality of measurement distances as the separation distance.
It should be noted that, the implementation of each module may also correspond to the corresponding description of the method embodiment shown in fig. 2, and execute the method and the function executed by the user equipment in the foregoing embodiment.
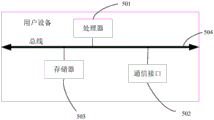
Please refer to fig. 5, fig. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a ue according to the present application. As shown in fig. 5, the user equipment may include: at least one processor 501, at least one communication interface 502, at least one memory 503, and at least one communication bus 504.
The processor 501 may be, for example, a central processing unit, a general purpose processor, a digital signal processor, an application specific integrated circuit, a field programmable gate array or other programmable logic device, a transistor logic device, a hardware component, or any combination thereof. Which may implement or perform the various illustrative logical blocks, modules, and circuits described in connection with the disclosure. The processor may also be a combination of computing functions, e.g., comprising one or more microprocessors, a digital signal processor and a microprocessor, or the like. The communication bus 504 may be a peripheral component interconnect standard PCI bus or an extended industry standard architecture EISA bus, or the like. The bus may be divided into an address bus, a data bus, a control bus, etc. For ease of illustration, only one thick line is shown in FIG. 5, but this is not intended to represent only one bus or type of bus. A communication bus 504 is used to enable connection communications between these components. The communication interface 502 of the device in the embodiment of the present application is used for performing signaling or data communication with other node devices. The Memory 503 may include a volatile Memory, such as a Nonvolatile dynamic Random Access Memory (NVRAM), a phase change Random Access Memory (PRAM), a Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory (MRAM), and the like, and may further include a Nonvolatile Memory, such as at least one magnetic Disk Memory device, an electrically erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM), a flash Memory device, such as a nor flash Memory (NORflash Memory) or a nor flash Memory (NAND flash Memory), a semiconductor device, such as a Solid State Disk (SSD), and the like. The memory 503 may optionally be at least one storage device located remotely from the processor 501. A set of program codes may optionally be stored in the memory 503 and the processor 501 may optionally execute the program executed in the memory 503.
Acquiring a spacing distance between user equipment and a user;
and according to the spacing distance, adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment, so that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity.
Optionally, the processor 501 is further configured to perform the following operations:
searching a power value corresponding to the spacing distance from a preset target calibration table, wherein the target calibration table comprises a corresponding relation between the spacing distance and the power value;
adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment to the power value.
Optionally, the processor 501 is further configured to perform the following operations:
determining an antenna used by the user equipment for transmitting the millimeter wave;
and selecting the target calibration table from a plurality of preset calibration tables according to the antenna used for transmitting the millimeter waves.
Optionally, the processor 501 is further configured to perform the following operations:
acquiring the received signal strength of each antenna in a plurality of antennas of the user equipment;
and determining an antenna used by the user equipment for transmitting the millimeter wave according to the received signal strength.
Optionally, the processor 501 is further configured to perform the following operations:
measuring the separation distance between the user equipment and the user through a ranging sensor within a preset distance range.
Optionally, the processor 501 is further configured to perform the following operations:
and measuring the spacing distance between the user equipment and the user according to a preset period.
Optionally, the processor 501 is further configured to perform the following operations:
obtaining a plurality of measurement distances between the user equipment and the user, which are obtained through a plurality of measurements;
taking an average of the plurality of measurement distances as the separation distance.
Further, the processor may cooperate with the memory and the communication interface to perform the operations of the electromagnetic radiation control apparatus in the embodiments of the above-mentioned application.
In the above embodiments, the implementation may be wholly or partially realized by software, hardware, firmware, or any combination thereof. When implemented in software, may be implemented in whole or in part in the form of a computer program product. The computer program product includes one or more computer instructions. When loaded and executed on a computer, cause the processes or functions described in accordance with the embodiments of the application to occur, in whole or in part. The computer may be a general purpose computer, a special purpose computer, a network of computers, or other programmable device. The computer instructions may be stored in a computer readable storage medium or transmitted from one computer readable storage medium to another, for example, from one website site, computer, server, or data center to another website site, computer, server, or data center via wired (e.g., coaxial cable, fiber optic, Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)) or wireless (e.g., infrared, wireless, microwave, etc.). The computer-readable storage medium can be any available medium that can be accessed by a computer or a data storage device, such as a server, a data center, etc., that incorporates one or more of the available media. The usable medium may be a magnetic medium (e.g., floppy Disk, hard Disk, magnetic tape), an optical medium (e.g., DVD), or a semiconductor medium (e.g., Solid State Disk (SSD)), among others.
The above-mentioned embodiments further explain the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the present application in detail. Any modification, equivalent replacement, improvement and the like made within the spirit and principle of the present application shall be included in the protection scope of the present application.
Claims (16)
1. A method of electromagnetic radiation control, the method comprising:
acquiring a spacing distance between user equipment and a user;
and according to the spacing distance, adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment, so that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein said adjusting the equivalent radiated power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user device based on the separation distance comprises:
searching a power value corresponding to the spacing distance from a preset target calibration table, wherein the target calibration table comprises a corresponding relation between the spacing distance and the power value;
adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment to the power value.
3. The method of claim 2, wherein prior to looking up the power value corresponding to the separation distance to the equivalent radiated power from a preset target calibration table, further comprising:
determining an antenna used by the user equipment for transmitting the millimeter wave;
and selecting the target calibration table from a plurality of preset calibration tables according to the antenna used for transmitting the millimeter waves.
4. The method of claim 3, wherein the determining an antenna used by the user device to transmit the millimeter waves comprises:
acquiring the received signal strength of each antenna in a plurality of antennas of the user equipment;
and determining an antenna used by the user equipment for transmitting the millimeter wave according to the received signal strength.
5. The method of any one of claims 1-4, wherein the obtaining a separation distance between a user device and a user comprises:
measuring the separation distance between the user equipment and the user through a ranging sensor within a preset distance range.
6. The method of any one of claims 1-5, wherein the obtaining a separation distance between a user device and a user comprises:
and measuring the spacing distance between the user equipment and the user according to a preset period.
7. The method of any one of claims 1-6, wherein the obtaining a separation distance between a user device and a user comprises:
obtaining a plurality of measurement distances between the user equipment and the user, which are obtained through a plurality of measurements;
taking an average of the plurality of measurement distances as the separation distance.
8. An electromagnetic radiation control apparatus, comprising:
the acquisition module is used for acquiring the spacing distance between the user equipment and the user;
and the processing module is used for adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment according to the spacing distance so that the electromagnetic radiation generated by the transmitted millimeter waves meets the maximum allowable radiation quantity.
9. The apparatus of claim 8,
the processing module is further configured to search a preset target calibration table for a power value corresponding to the separation distance, where the target calibration table includes a corresponding relationship between the separation distance and the power value; adjusting the equivalent access radiation power of the millimeter waves transmitted by the user equipment to the power value.
10. The apparatus of claim 9,
the processing module is further configured to determine an antenna used by the user equipment to transmit the millimeter wave; and selecting the target calibration table from a plurality of preset calibration tables according to the antenna used for transmitting the millimeter waves.
11. The apparatus of claim 10,
the obtaining module is further configured to obtain a received signal strength of each antenna of a plurality of antennas of the user equipment;
the processing module is further configured to determine, according to the received signal strength, an antenna used by the user equipment to transmit the millimeter wave.
12. The apparatus of any one of claims 8-11,
the acquisition module is further configured to measure the separation distance between the ue and the user through a ranging sensor within a preset distance range.
13. The apparatus of any one of claims 8-12,
the obtaining module is further configured to measure the separation distance between the user equipment and the user according to a preset period.
14. The apparatus of any one of claims 8-13,
the obtaining module is further configured to obtain a plurality of measurement distances between the user equipment and the user, which are obtained through a plurality of measurements; taking an average of the plurality of measurement distances as the separation distance.
15. A user device, comprising: a memory for storing program code, a communication bus, and a processor for invoking the program code to perform the method of any one of claims 1-7.
16. A computer-readable storage medium having stored therein instructions which, when executed on a computer, cause the computer to perform the method of any one of claims 1-7.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810830376.3A CN110769493A (en) | 2018-07-25 | 2018-07-25 | Electromagnetic radiation control method and related equipment |
| PCT/CN2019/097566 WO2020020251A1 (en) | 2018-07-25 | 2019-07-24 | Electromagnetic radiation control method and related device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810830376.3A CN110769493A (en) | 2018-07-25 | 2018-07-25 | Electromagnetic radiation control method and related equipment |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110769493A true CN110769493A (en) | 2020-02-07 |
Family
ID=69181258
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810830376.3A Pending CN110769493A (en) | 2018-07-25 | 2018-07-25 | Electromagnetic radiation control method and related equipment |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110769493A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2020020251A1 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021189281A1 (en) * | 2020-03-25 | 2021-09-30 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Techniques for maximum permissible exposure reporting |
| CN113973363A (en) * | 2020-07-22 | 2022-01-25 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Method and device for sending and receiving P-MPR report and electronic equipment |
| CN114440426A (en) * | 2022-03-09 | 2022-05-06 | 青岛海信日立空调系统有限公司 | Air conditioner |
| WO2022237752A1 (en) * | 2021-05-11 | 2022-11-17 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Method for transmitting information of terminal antenna panel, and terminal and network side device |
| WO2023116048A1 (en) * | 2021-12-22 | 2023-06-29 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Transmission power adjustment method, millimeter-wave terminal and storage medium |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102325365A (en) * | 2011-08-23 | 2012-01-18 | 华为终端有限公司 | Method for adjusting terminal emission power and apparatus thereof |
| US20140307704A1 (en) * | 2013-04-12 | 2014-10-16 | Broadcom Corporation | Dynamic eirp constraint for a cellular communication system using a large number of base station antennas |
| EP2814292A1 (en) * | 2013-06-13 | 2014-12-17 | BlackBerry Limited | Method and device for dynamic control of RF power emissions |
| CN104581896A (en) * | 2013-10-15 | 2015-04-29 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Terminal transmitting power adjusting method and device as well as terminal |
| WO2018111844A1 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2018-06-21 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Reporting power limit and corresponding constraint |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106332132B (en) * | 2015-07-03 | 2021-05-04 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Communication terminal and method for self-adaptive Bluetooth performance adjustment |
| CN105704745A (en) * | 2016-04-29 | 2016-06-22 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | Mobile terminal antenna transmit-receive state control method and device |
| CN205792650U (en) * | 2016-05-11 | 2016-12-07 | 大连工业大学 | A kind of distributed intelligence household wireless network system |
| CN107231682A (en) * | 2017-05-25 | 2017-10-03 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | Reduce terminal SAR processing method, device and terminal |
-
2018
- 2018-07-25 CN CN201810830376.3A patent/CN110769493A/en active Pending
-
2019
- 2019-07-24 WO PCT/CN2019/097566 patent/WO2020020251A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102325365A (en) * | 2011-08-23 | 2012-01-18 | 华为终端有限公司 | Method for adjusting terminal emission power and apparatus thereof |
| US20140307704A1 (en) * | 2013-04-12 | 2014-10-16 | Broadcom Corporation | Dynamic eirp constraint for a cellular communication system using a large number of base station antennas |
| EP2814292A1 (en) * | 2013-06-13 | 2014-12-17 | BlackBerry Limited | Method and device for dynamic control of RF power emissions |
| CN104581896A (en) * | 2013-10-15 | 2015-04-29 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Terminal transmitting power adjusting method and device as well as terminal |
| WO2018111844A1 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2018-06-21 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Reporting power limit and corresponding constraint |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| ERICSSON等: "《TSG-RAN Working Group 4 (Radio) meeting #82bis R4-1703060》", 7 April 2017 * |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021189281A1 (en) * | 2020-03-25 | 2021-09-30 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Techniques for maximum permissible exposure reporting |
| CN113973363A (en) * | 2020-07-22 | 2022-01-25 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Method and device for sending and receiving P-MPR report and electronic equipment |
| WO2022017355A1 (en) * | 2020-07-22 | 2022-01-27 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | P-mpr report sending method and apparatus, p-mpr report receiving method and apparatus, and electronic device |
| CN113973363B (en) * | 2020-07-22 | 2023-09-12 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Method and device for sending and receiving P-MPR report and electronic equipment |
| WO2022237752A1 (en) * | 2021-05-11 | 2022-11-17 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Method for transmitting information of terminal antenna panel, and terminal and network side device |
| WO2023116048A1 (en) * | 2021-12-22 | 2023-06-29 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Transmission power adjustment method, millimeter-wave terminal and storage medium |
| CN114440426A (en) * | 2022-03-09 | 2022-05-06 | 青岛海信日立空调系统有限公司 | Air conditioner |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2020020251A1 (en) | 2020-01-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110769493A (en) | Electromagnetic radiation control method and related equipment | |
| JP6505116B2 (en) | Transmission power adjustment method and electronic device | |
| CN110636516B (en) | Method and device for determining signal propagation model | |
| JP7016303B2 (en) | Radiation power estimation method | |
| CN112448732B (en) | Radio frequency exposure control method and device of wireless equipment and wireless equipment | |
| US20140269384A1 (en) | Through Wall Sensing System Using WiFi/Cellular Radar | |
| US10992393B1 (en) | System, test setup as well as method for performing MIMO tests | |
| CN112069713B (en) | Near-field scattering characteristic modeling method, electronic device and storage medium | |
| KR20210108378A (en) | Mitigating Intercoupling Leakage in Small Form Factor Devices | |
| CN110708702A (en) | Method and device for determining signal propagation model | |
| CN113940011B (en) | Preconfigured antenna beamforming | |
| Bird et al. | Improved finite‐range gain formula for open‐ended rectangular waveguides and pyramidal horns | |
| US20240072836A1 (en) | Transmission power control at a radio terminal | |
| CN109714105B (en) | Communication link determining method and device | |
| WO2023116048A1 (en) | Transmission power adjustment method, millimeter-wave terminal and storage medium | |
| KR102536005B1 (en) | Method and Apparatus for Setting Reception Threshold in Backscatter Communication | |
| US10461869B1 (en) | Method for downlink power tests, test system as well as test setup | |
| Min et al. | Spatial and temporal characterization of indoor millimeter wave propagation at 24 GHz | |
| CN116800360A (en) | Channel path loss estimation method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| KR101626867B1 (en) | Radio altimeter using adaptive threshold value and operating method thereof | |
| CN117406206A (en) | Distance measurement method of UWB (ultra Wide band) equipment, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| WO2019191951A1 (en) | Network planning method and device | |
| CN118226444A (en) | Microwave imaging method and system, transmitting and receiving terminal, and computer readable medium | |
| CN117318859A (en) | Sensing signal transmission method and device | |
| JP2024064870A (en) | Server, control method, and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |
Application publication date: 20200207 |
|
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |