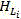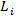CN110690699B - Transformer substation intelligent detection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things - Google Patents
Transformer substation intelligent detection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110690699B CN110690699B CN201910694381.0A CN201910694381A CN110690699B CN 110690699 B CN110690699 B CN 110690699B CN 201910694381 A CN201910694381 A CN 201910694381A CN 110690699 B CN110690699 B CN 110690699B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- sensor
- equipment
- fault
- sensors
- image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J3/00—Circuit arrangements for ac mains or ac distribution networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V20/00—Scenes; Scene-specific elements
- G06V20/50—Context or environment of the image
- G06V20/52—Surveillance or monitoring of activities, e.g. for recognising suspicious objects
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J13/00—Circuit arrangements for providing remote indication of network conditions, e.g. an instantaneous record of the open or closed condition of each circuitbreaker in the network; Circuit arrangements for providing remote control of switching means in a power distribution network, e.g. switching in and out of current consumers by using a pulse code signal carried by the network
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y04—INFORMATION OR COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES HAVING AN IMPACT ON OTHER TECHNOLOGY AREAS
- Y04S—SYSTEMS INTEGRATING TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO POWER NETWORK OPERATION, COMMUNICATION OR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES FOR IMPROVING THE ELECTRICAL POWER GENERATION, TRANSMISSION, DISTRIBUTION, MANAGEMENT OR USAGE, i.e. SMART GRIDS
- Y04S10/00—Systems supporting electrical power generation, transmission or distribution
- Y04S10/16—Electric power substations
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y04—INFORMATION OR COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES HAVING AN IMPACT ON OTHER TECHNOLOGY AREAS
- Y04S—SYSTEMS INTEGRATING TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO POWER NETWORK OPERATION, COMMUNICATION OR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES FOR IMPROVING THE ELECTRICAL POWER GENERATION, TRANSMISSION, DISTRIBUTION, MANAGEMENT OR USAGE, i.e. SMART GRIDS
- Y04S40/00—Systems for electrical power generation, transmission, distribution or end-user application management characterised by the use of communication or information technologies, or communication or information technology specific aspects supporting them
- Y04S40/12—Systems for electrical power generation, transmission, distribution or end-user application management characterised by the use of communication or information technologies, or communication or information technology specific aspects supporting them characterised by data transport means between the monitoring, controlling or managing units and monitored, controlled or operated electrical equipment
- Y04S40/128—Systems for electrical power generation, transmission, distribution or end-user application management characterised by the use of communication or information technologies, or communication or information technology specific aspects supporting them characterised by data transport means between the monitoring, controlling or managing units and monitored, controlled or operated electrical equipment involving the use of Internet protocol
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
- Remote Monitoring And Control Of Power-Distribution Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Hair brushThe intelligent detection system comprises a sensor table and a sensor early warning value table, wherein the sensor table is established; establishing a sensor cooperation table; when the sensor LiDetection valueWhen the safety interval is exceeded, the sensor L is read according to the sensor cooperation tableiOf the cooperative sensor Li‑kDetected value of (2)And judging whether equipment failure occurs or not, and if the equipment failure occurs, sending an alarm. The substantial effects of the invention are as follows: through the sensor early warning value table, faults and abnormity existing in the power grid system can be found in time, and maintainers are guided to carry out inspection and first-aid repair; by establishing an equipment state portrait and an equipment fault early warning portrait, the early warning of equipment faults can be provided, the fault times of power grid equipment are reduced, and the fault shadow loss is reduced; by dividing the sub-network and establishing the edge server, the communication expense can be reduced, and the detection efficiency can be improved.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of power equipment fault detection, in particular to a transformer substation intelligent detection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things.
Background
With the development of economy, the demand of users for electric power is rapidly increasing. At the same time, users have higher requirements for the stability of the power supply. The scale of the power grid is also continuously enlarged, and in order to meet the requirements of users on power and stability, a large number of intelligent devices are used in the construction of the power grid. With the continuous construction of communication networks, the establishment of perfect detection networks has a technical foundation and has been gradually promoted, and an electric power internet of things is gradually formed. The electric power thing networking can be comprehensive each operating condition of detection electric wire netting equipment, has improved the quality and the efficiency of electric wire netting control. However, the fault existing in the power grid is found only by directly detecting and comparing the data, so that certain hysteresis is achieved, and effective early warning cannot be provided. At present, in the power grid fault repairing process, after fault warning information is obtained, firstly, a maintainer is dispatched to carry out on-site confirmation, and the fault is checked on site. The efficiency of field troubleshooting is very dependent on the experience accumulation of the maintainers. Moreover, the maintenance tool is not brought well, and the maintenance personnel is required to return to the warehouse to take the maintenance tool. When the fault is determined, the fault still can not be immediately repaired, and the fault also needs to be returned to a warehouse to take spare parts and repair tools needed to be used. Thus, the efficiency is very low. The reason for such a site is that after the power grid fails, the monitoring system of the power grid can only give the fault location and the fault type, and cannot judge the fault source. Causing the overhaul personnel to need to carry out on-site troubleshooting. Moreover, the monitoring system of the power grid cannot determine the tools and appliances which need to be used during troubleshooting, so that when the overhaul personnel start, the selection of carrying the tools and appliances is not targeted, and whether the tools and appliances are carried completely depends on the experience judgment of the overhaul personnel. When the power grid fails and is powered off, huge loss of the power grid can be caused, and the personal interests and the power consumption experience of users are influenced. Therefore, developing an intelligent power grid fault detection system becomes an important subject for power grid construction.
If chinese patent CN101783530A, publication No. 2010, No. 7, No. 21, an intelligent monitoring and auxiliary control system for a substation based on the internet of things includes a substation management host connected to a plurality of auxiliary systems, the substation management host is connected to a centralized control station management host through a power communication network, the auxiliary systems include a first host, a data transmission base station, a wireless temperature sensor disposed on a primary live device whose operating temperature needs to be monitored, a wireless temperature sensor disposed on a cable in a cable trench, and an environmental temperature sensor disposed in the cable trench; the wireless temperature sensor and the environment temperature sensor are communicated with the data transmission base station through a wireless sensor network, the data transmission base station is connected with a first host through a CAN bus or an RS-485 bus, and the first host is connected with a substation management host. Although monitoring of the transformer substation can be achieved, monitoring data are not mined, fault early warning cannot be effectively carried out, the advantages of the Internet of things cannot be fully played, and safe operation of a power grid is guaranteed. In patent CN105762940A, published 2016, 7, 13, an Internet of things intelligent predicting system for the state of 66kV substation equipment, a piezoelectric induction wireless sensor is adopted to carry out wireless temperature measurement on the 66kV substation equipment, an intelligent electric quantity metering device is adopted to detect the substation equipment, a multi-channel signal collector is used for collecting, and the Internet of things is used for realizing remote monitoring; the system specifically comprises a temperature measuring system, a transponder, a controller and a GPRS wireless Internet of things, wherein the temperature measuring system is communicated with a remote monitoring center through the transponder and the GPRS wireless Internet of things; the temperature measuring system is connected with a controller with a display screen through an electric optical fiber and a field bus; the temperature measurement system comprises piezoelectric induction wireless sensors, multiple signal collectors, 433 transmitter and transceivers, wherein each multiple signal collector is communicated with 8 piezoelectric induction wireless sensors, the multiple signal collectors are connected with the 433 transmitter, and the transceivers are arranged on the multiple signal collectors. Although the monitoring of multiple states of the transformer substation can be realized, the monitoring data cannot be effectively sorted and analyzed, the operation state of the power grid is difficult to master, and the safe and stable operation of the power grid cannot be guaranteed.
Disclosure of Invention
The technical problem to be solved by the invention is as follows: the technical problem that a detection system for effectively monitoring whether a power grid system has a fault is lacked at present. The intelligent transformer substation detection system based on the ubiquitous power internet of things can effectively detect the abnormity and faults of a power grid system.
In order to solve the technical problems, the technical scheme adopted by the invention is as follows: intelligent transformer substation detection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things and used for building ubiquitous power Internet of thingsFault detection of an electrical grid system, comprising a sensor meter which records a sensor LiName of (2), detected device information, and detected value; establishing a sensor early warning value table which records each sensor LiDetected value of (2)The safety interval of (2); establishing a sensor cooperation table recording each sensor LiOf the cooperative sensor Li-kThe list of the cooperative sensors Li-kFor equipment failure, and the sensor LiSensors affected by the fault together; when the sensor LiDetection valueWhen the safety interval is exceeded, the sensor L is read according to the sensor cooperation tableiOf the cooperative sensor Li-kDetected value of (2)And judging whether equipment failure occurs or not, if so, sending an alarm, otherwise, periodically and repeatedly checking whether the sensor L exists or notiDetected value of (2)Beyond its safe range. Through the sensor early warning value table, the faults and the abnormity of the power grid system can be found in time, and the maintainers are guided to carry out inspection and first-aid repair.
Preferably, a device status representation is created, the creation of the device status representation comprising the steps of: enumerating the sensors L that detect the deviceiA sensor LiDetected value of (2)Normalizing and associating the gray value, and associating the gray value with the sensor LiDetected value of (2)The images are arranged in order to form an image as an image of the status of the device. The device state representation can integrally reflect the running state of the device, so that the detection data is not used as single island data any more, and a scheme is provided for discovering the correlation characteristics between the sensor data.
Preferably, the method comprises the following steps of establishing an equipment failure image, wherein the establishment of the equipment failure image comprises the following steps: enumerating the sensors L that detect the devicei(ii) a Acquisition sensor LiDetected value of (2)Historical values of (a) and historical fault data of the device; computing sensor LiDetected value of (2)Correlation with equipment failure, selecting detection valueSeveral sensors L with a fault correlation higher than a set thresholdi(ii) a Will be selected out of the sensors LiDetected value of (2)Normalizing and associating the gray value, and associating the gray value with the sensor LiDetected value of (2)The images are arranged in sequence to form an image of the failure of the equipment. The fault image is used for carrying out fault matching when a power grid fails and locking a device with a fault.
Preferably, the power grid system is divided into a plurality of subnets, an edge server is established for each subnet, and the sensors in the subnets are connected with the corresponding edge servers. The edge server reduces communication cost and improves detection efficiency.
Preferably, the method for dividing the power grid system into sub-networks comprises the following steps: the grid being divided into several zones according to voltage classes, the voltage classes varyingThe nodes are classified as regions with higher voltage levels, and the regions are used as subnets. All the corresponding sensors L of the same power equipment can be classified according to voltage gradesiAssign to the same subnet, avoid the sensor L corresponding to the same equipmentiAnd the detection result is inaccurate due to the fact that the detection result is positioned in the two subnets, and the detection efficiency is reduced.
Preferably, the cooperative sensor Li-kAlso comprises a maneuvering sensor, the maneuvering sensor and the sensor LiThe mobile sensor is arranged on the mobile device and is provided with a plurality of detection stations for detecting a plurality of devices. The moving device is a robot, a rail trolley or a rotary holder.
Preferably, the sensor L is readiOf the cooperative sensor Li-kDetected value of (2)The method for judging whether the equipment failure occurs comprises the following steps: obtaining a sensor LiOf the cooperative sensor Li-kN, each cooperative sensor L is judged in turni-kDetected value of (2)Whether the safety interval is exceeded or not, if the number N of the cooperative sensors which do not exceed the detection value safety interval is less than 0.6 x N, the equipment is judged to be in fault, otherwise, the equipment is judged not to be in fault, and the sensors L of which the detection values exceed the safety interval are used for detecting the sensors Li-kAnd reporting. The accuracy of fault detection is improved, and the sensor L can be providediDetection of (3).
Preferably, an equipment failure early warning portrait is established, and the establishment of the equipment failure early warning portrait comprises the following steps: enumerating the sensors L that detect the devicei(ii) a Acquisition sensor LiDetected value of (2)Historical values of (a) and historical fault data of the device; computing sensor LiDetected value of (2)Correlation with equipment failure, selecting detection valueSeveral sensors L with a fault correlation higher than a set thresholdi(ii) a Will be selected out of the sensors LiTotal detection value at time T1 before equipment failureRespectively normalizing and associating the gray values, and associating the sensors L with the gray valuesiDetected value of (2)Sequentially arranged, and the formed images are used as the early warning images of the equipment faults and read out the selected sensor LiNormalizing and associating the gray values of the real-time detection values, arranging the real-time detection values in the same sequence as the equipment fault early warning portrait, and sending out fault early warning if the formed image is similar to the equipment fault early warning portrait. The early warning of equipment faults is provided, the fault times of the power grid equipment are reduced, and the fault shadow loss is reduced.
Preferably, the method for judging the similarity between the formed image and the equipment failure warning portrait comprises the following steps: obtaining a plurality of failure early warning pictures and the selected sensors L obtained in normal stateiDetected value of (2)The constructed image is used as a sample image; establishing an image recognition neural network, and training by using a sample image until the probability that the image recognition neural network correctly distinguishes the fault early warning portrait is higher than a set threshold value; inputting the latest image into the image recognition neural network, if the image is judged to be a fault early warning portrait by the image recognition neural network, judging that the formed image is similar to the equipment fault early warning portrait, otherwise, judging that the formed image is not similar to the equipment fault early warning portrait. The neural network can realize the rapidness by image recognitionBetter balance of judgment and accurate judgment.
Preferably, the sensors include a primary equipment operation temperature monitoring sensor, a lightning arrester leakage current monitoring sensor, a video monitoring image sensor, a perimeter intrusion prevention sensor, a tower theft prevention monitoring sensor, an SF6 gas density monitoring sensor, a fire smoke detection sensor and a rain sensor.
The substantial effects of the invention are as follows: through the sensor early warning value table, faults and abnormity existing in the power grid system can be found in time, and maintainers are guided to carry out inspection and first-aid repair; by establishing an equipment state portrait and an equipment fault early warning portrait, the early warning of equipment faults can be provided, the fault times of power grid equipment are reduced, and the fault shadow loss is reduced; by dividing the sub-network and establishing the edge server, the communication expense can be reduced, and the detection efficiency can be improved.
Drawings
FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a detection method according to an embodiment.
FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a process of creating an equipment failure picture according to an embodiment.
FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a process of creating an image of an equipment failure warning image according to an embodiment.
Detailed Description
The following provides a more detailed description of the present invention, with reference to the accompanying drawings.
The first embodiment is as follows:
the utility model provides a transformer substation intelligence detecting system based on ubiquitous electric power thing networking for establish the fault detection of electric wire netting system of ubiquitous electric power thing networking, as shown in figure 1, include, establish the sensor table, sensor table record sensor LiName of (2), detected device information, and detected value.
Establishing a sensor early warning value table, wherein the sensor early warning value table records each sensor LiDetected value of (2)The sensors comprise a primary equipment operation temperature monitoring sensor and a lightning arrester leakage current monitoring sensorSensors, video surveillance image sensors, perimeter intrusion prevention sensors, tower theft prevention monitoring sensors, SF6 gas density monitoring sensors, fire smoke detection sensors, and rain sensors.
Establishing a sensor cooperation table, wherein the sensor cooperation table records each sensor LiOf the cooperative sensor Li-kList of (2), collaboration sensor Li-kFor equipment failure, and the sensor LiSensor and mobility sensor affected by fault together, mobility sensor and sensor LiThe mobile sensor is arranged on the mobile device and is provided with a plurality of detection stations for detecting a plurality of devices. The moving device is a robot, a rail trolley or a rotary holder.
Establishing an equipment state portrait, wherein the establishment of the equipment state portrait comprises the following steps: enumerating the sensors L that detect the deviceiA sensor LiDetected value of (2)Normalizing and associating the gray value, and associating the gray value with the sensor LiDetected value of (2)The images are arranged in order to form an image as an image of the status of the device. Establishing an equipment failure image, as shown in fig. 2, the establishing of the equipment failure image comprises the following steps: enumerating the sensors L that detect the devicei(ii) a Acquisition sensor LiDetected value of (2)Historical values of (a) and historical fault data of the device; computing sensor LiDetected value of (2)Correlation with equipment failure, selecting detection valueSeveral sensors with fault correlation higher than set thresholdDevice Li(ii) a Will be selected out of the sensors LiDetected value of (2)Normalizing and associating the gray value, and associating the gray value with the sensor LiDetected value of (2)The images are arranged in sequence to form an image of the failure of the equipment.
When the sensor LiDetection valueWhen the safety interval is exceeded, the sensor L is read according to the sensor cooperation tableiOf the cooperative sensor Li-kDetected value of (2)Obtaining a sensor LiOf the cooperative sensor Li-kN, each cooperative sensor L is judged in turni-kDetected value of (2)If the number N of the cooperative sensors which do not exceed the detection value safety interval is less than 0.6 x N, judging that the equipment has a fault and giving an alarm, otherwise, judging that the equipment has no fault and adding the sensors L of which the detection values exceed the safety intervali-kAnd reporting.
The embodiment has the following beneficial effects: the system can find faults and abnormity existing in the power grid system in time and guide maintainers to carry out inspection and first-aid repair. When the power grid fails, the equipment failure picture is used for fault matching, and the equipment with the fault is locked.
Example two:
the embodiment is further improved on the basis of the first embodiment. The method specifically comprises the steps that a power grid is divided into a plurality of areas according to voltage levels, nodes with changed voltage levels belong to areas with higher voltage levels, and the areas are used as sub-networks. And establishing an edge server for each subnet, wherein the sensors in the subnets are connected with the corresponding edge servers.
An equipment failure early warning portrait is established, as shown in fig. 3, the establishment of the equipment failure early warning portrait comprises the following steps: enumerating the sensors L that detect the devicei(ii) a Acquisition sensor LiDetected value of (2)Historical values of (a) and historical fault data of the device; computing sensor LiDetected value of (2)Correlation with equipment failure, selecting detection valueSeveral sensors L with a fault correlation higher than a set thresholdi(ii) a Will be selected out of the sensors LiTotal detection value at time T1 before equipment failureRespectively normalizing and associating the gray values, and associating the sensors L with the gray valuesiDetected value of (2)Sequentially arranged, and the formed images are used as the early warning images of the equipment faults and read out the selected sensor LiNormalizing and associating the gray values of the real-time detection values, arranging the real-time detection values in the same sequence as the equipment fault early warning portrait, and sending out fault early warning if the formed image is similar to the equipment fault early warning portrait. The method for judging the similarity between the formed image and the equipment fault early warning portrait comprises the following steps: obtaining a plurality of failure warning pictures and the selected sensors L obtained in normal stateiDetected value of (2)The constructed image is used as a sample image; establishing image recognition neural network, and using sample graphTraining until the probability that the neural network correctly distinguishes the fault early warning portrait is higher than a set threshold value; inputting the latest constructed image into the neural network, if the neural network judges that the image is a failure early warning portrait, judging that the constructed image is similar to the equipment failure early warning portrait, otherwise, judging that the constructed image is not similar to the equipment failure early warning portrait. This embodiment can be implemented in real time together with the embodiment.
The embodiment has the following beneficial effects: the early warning of equipment faults is provided, the fault times of the power grid equipment are reduced, and the fault shadow loss is reduced; and the subnetworks are divided and the edge server is established, so that the communication expense can be reduced and the detection efficiency is improved.
The above-described embodiments are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention in any way, and other variations and modifications may be made without departing from the spirit of the invention as set forth in the claims.
Claims (8)
1. An intelligent transformer substation detection system based on the ubiquitous power Internet of things is used for fault detection of a transformer substation with the ubiquitous power Internet of things and is characterized in that,
includes establishing a sensor meter that records sensorsName of (2), detected device information, and detected value;
establishing a sensor early warning value table which records each sensorDetected value of (2)The safety interval of (2);
establishing a sensor cooperation table that records each sensorIn cooperation with the sensorThe cooperative sensor ofIn case of equipment failure, and sensorsSensors affected by the fault together;
when the sensorDetection valueWhen the safety interval is exceeded, the sensor is read according to the sensor cooperation tableIn cooperation with the sensorDetected value of (2)And judging whether equipment failure occurs or not, if so, sending an alarm, otherwise, periodically and repeatedly checking whether a sensor exists or notDetected value of (2)Exceeding its safety interval;
establishing an equipment state representation, wherein the establishment of the equipment state representation comprises the following steps:
enumerating sensors to detect the deviceWill sensorDetected value of (2)Normalizing and associating gray values, and associating gray value sensorsDetected value of (2)Arranging the images in sequence to form an image as an equipment state image;
establishing an equipment failure portrait, wherein the establishment of the equipment failure portrait comprises the following steps:
Acquisition sensorDetected value of (2)Historical values of (a) and historical fault data of the device;
computing sensorDetected value of (2)And equipment failureTo select a detection valueSensor with fault correlation higher than set threshold;
2. The intelligent substation detection system based on the Internet of things of ubiquitous power as claimed in claim 1,
the power grid system is divided into a plurality of subnets, an edge server is established for each subnet, and sensors in the subnets are connected with the corresponding edge servers.
3. The intelligent substation detection system based on the Internet of things of ubiquitous power as claimed in claim 2, wherein,
the method for dividing the power grid system into the sub-networks comprises the following steps:
the power grid is divided into a plurality of areas according to the voltage levels, nodes with changed voltage levels are classified into areas with higher voltage levels, and the areas are used as subnets.
4. The intelligent substation detection system based on the Internet of things of ubiquitous power as claimed in claim 1,
5. The intelligent substation detection system based on the Internet of things of ubiquitous power as claimed in claim 1,
reading sensorIn cooperation with the sensorDetected value of (2)The method for judging whether the equipment fault occurs comprises the following steps:
acquisition sensorIn cooperation with the sensorN, each cooperative sensor is judged in turnDetected value of (2)Whether the safety interval is exceeded or not, if the number N of the cooperative sensors which do not exceed the detection value safety interval is less than 0.6 x N, the equipment is judged to be in fault, otherwise, the equipment is judged not to be in fault, and the sensors of which the detection values exceed the safety interval are used for judging that the equipment is in faultAnd reporting.
6. The intelligent substation detection system based on the Internet of things of ubiquitous power as claimed in claim 1,
establishing an equipment fault early warning portrait, wherein the establishment of the equipment fault early warning portrait comprises the following steps:
Acquisition sensorDetected value of (2)Historical values of (a) and historical fault data of the device;
computing sensorDetected value of (2)Correlation with equipment failure, selecting detection valueSeveral sensors with fault correlation higher than set threshold;
Will be selected out of the sensorTotal detection value at time T1 before equipment failureRespectively normalizing and associating gray values, and associating the gray values with the sensorsDetected value of (2)Sequentially arranged to form an image as an equipment failure warning image,
reading selected sensorsNormalizing and associating the gray values of the real-time detection values, arranging the real-time detection values in the same sequence as the equipment fault early warning portrait, and sending out fault early warning if the formed image is similar to the equipment fault early warning portrait.
7. The intelligent substation detection system based on the Internet of things of ubiquitous power as claimed in claim 6, wherein,
the method for judging the similarity between the formed image and the equipment fault early warning portrait comprises the following steps:
obtaining a plurality of failure warning pictures and the selected sensor obtained in normal stateDetected value of (2)The constructed image is used as a sample image;
establishing an image recognition neural network, and training by using a sample image until the probability that the neural network correctly distinguishes the fault early warning portrait is higher than a set threshold value;
inputting the latest image into the neural network, if the neural network judges the image as a failure early-warning portrait, then judging the image is similar to the failure early-warning portrait, otherwise, judging the image is not similar to the failure early-warning portrait.
8. The intelligent substation detection system based on the Internet of things of ubiquitous power as claimed in claim 1,
the sensor comprises a primary equipment operation temperature monitoring sensor, a lightning arrester leakage current monitoring sensor, a video monitoring image sensor, a perimeter anti-intrusion sensor, a tower anti-theft monitoring sensor, an SF6 gas density monitoring sensor, a fire smoke detection sensor and a rain sensor.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910694381.0A CN110690699B (en) | 2019-07-30 | 2019-07-30 | Transformer substation intelligent detection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910694381.0A CN110690699B (en) | 2019-07-30 | 2019-07-30 | Transformer substation intelligent detection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110690699A CN110690699A (en) | 2020-01-14 |
| CN110690699B true CN110690699B (en) | 2022-03-18 |
Family
ID=69108164
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910694381.0A Active CN110690699B (en) | 2019-07-30 | 2019-07-30 | Transformer substation intelligent detection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110690699B (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112731827B (en) * | 2020-12-11 | 2022-07-08 | 国网宁夏电力有限公司吴忠供电公司 | Monitoring system for intelligent sensor for power equipment |
| CN113340357B (en) * | 2021-07-05 | 2022-09-30 | 山东国稳电气有限公司 | GIS equipment state on-line monitoring system |
| CN113659570B (en) * | 2021-08-13 | 2023-07-04 | 湘潭大学 | Elastic lifting-oriented power distribution network power-communication fault collaborative restoration method |
| CN114007149B (en) * | 2021-11-01 | 2024-04-30 | 国网北京市电力公司 | Monitoring method, device, system, storage medium and processor of power system |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IES20050382A2 (en) * | 2004-06-04 | 2005-12-14 | Fmc Tech Ltd | A method of monitoring line faults in a medium voltage network |
| CN103227839B (en) * | 2013-05-10 | 2016-08-17 | 网宿科技股份有限公司 | The management system of regional autonomy of content distribution network server |
| CN104092305A (en) * | 2014-07-11 | 2014-10-08 | 国家电网公司 | Power distribution network fault handling method |
| CN104483954A (en) * | 2014-12-31 | 2015-04-01 | 蒋长叙 | Internet of things based intelligent diagnosis system of electric transmission and transformation equipment |
| CN105183619B (en) * | 2015-09-29 | 2018-03-27 | 北京奇艺世纪科技有限公司 | A kind of system failure method for early warning and system |
| CN106530114A (en) * | 2016-09-22 | 2017-03-22 | 厦门亿力吉奥信息科技有限公司 | Power grid equipment monitoring method and system |
-
2019
- 2019-07-30 CN CN201910694381.0A patent/CN110690699B/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110690699A (en) | 2020-01-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110690699B (en) | Transformer substation intelligent detection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things | |
| CN112910094B (en) | Remote automatic transformer substation inspection system and method based on ubiquitous power Internet of things | |
| CN108684010B (en) | Cable well running state online monitoring device and monitoring method based on Internet of things | |
| CN109146093A (en) | A kind of electric power equipment on-site exploration method based on study | |
| CN111525697B (en) | Medium and low voltage power distribution network electricity larceny prevention method and system based on current monitoring and line topology analysis | |
| CN108199891B (en) | Cps network attack identification method based on artificial neural network multi-angle comprehensive decision | |
| CN106597231A (en) | GIS fault detection system and method based on multi-source information fusion and deep learning network | |
| CN104753178A (en) | Power grid fault handling system | |
| CN109490713A (en) | A kind of method and system moving inspection and interactive diagnosis for cable run | |
| CN110336379B (en) | Transformer substation online monitoring system based on Internet of things and terminal equipment | |
| CN102354329A (en) | Infrared database intelligent diagnosis management system for charged equipment | |
| CN114383652A (en) | Method, system and device for identifying potential fault online risk of power distribution network | |
| CN116169778A (en) | Processing method and system based on power distribution network anomaly analysis | |
| CN106646110A (en) | Low-voltage distribution network fault positioning system based on GIS and Petri technologies | |
| CN109450084B (en) | Intelligent substation multilayer protocol collaborative analysis method based on information data link | |
| CN115224794A (en) | Power distribution network monitoring method based on Internet of things technology | |
| CN208572446U (en) | Cable shaft operating status on-Line Monitor Device based on Internet of Things | |
| CN112381321A (en) | Power distribution network operation state sensing method based on gridding division | |
| CN111983512A (en) | Line grounding device monitoring system and method | |
| CN116566043A (en) | Power distribution terminal monitoring system and monitoring method | |
| CN115664006A (en) | Increment distribution network intelligence management and control integration platform | |
| CN108872730A (en) | Intelligent management method for low-voltage power failure | |
| CN115618303B (en) | Automatic dispatch monitoring and fault locating system based on information fusion technology | |
| Guo et al. | Realization of Initiative Repair of Power Distribution Network Based on Backpropagation Neural Network Optimization. | |
| CN117639230A (en) | Active service monitoring method based on electric power |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |