CN109668275B - Air conditioning system and control method and device thereof - Google Patents
Air conditioning system and control method and device thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN109668275B CN109668275B CN201811496587.4A CN201811496587A CN109668275B CN 109668275 B CN109668275 B CN 109668275B CN 201811496587 A CN201811496587 A CN 201811496587A CN 109668275 B CN109668275 B CN 109668275B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- temperature
- target
- working temperature
- actual
- conditioning system
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004378 air conditioning Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 83
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 44
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 claims description 28
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 claims description 23
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 20
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000005057 refrigeration Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004134 energy conservation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013307 optical fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/62—Control or safety arrangements characterised by the type of control or by internal processing, e.g. using fuzzy logic, adaptive control or estimation of values
- F24F11/63—Electronic processing
- F24F11/65—Electronic processing for selecting an operating mode
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/62—Control or safety arrangements characterised by the type of control or by internal processing, e.g. using fuzzy logic, adaptive control or estimation of values
- F24F11/63—Electronic processing
- F24F11/64—Electronic processing using pre-stored data
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/70—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof
- F24F11/80—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the temperature of the supplied air
- F24F11/86—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the temperature of the supplied air by controlling compressors within refrigeration or heat pump circuits
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F2110/00—Control inputs relating to air properties
- F24F2110/10—Temperature
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F2140/00—Control inputs relating to system states
- F24F2140/20—Heat-exchange fluid temperature
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Fuzzy Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Air Conditioning Control Device (AREA)
Abstract
The application provides an air conditioning system and a control method and device thereof, wherein the method comprises the following steps: acquiring the current return air temperature of the indoor unit, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time by using the current return air temperature; detecting the current actual working temperature of the indoor unit; and controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature, so that the power of the compressor is dynamically adjusted while the target working temperature is changed according to the return air temperature, the indoor temperature can meet the user requirement as soon as possible, and finally the indoor temperature is maintained in a comfortable range.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of air conditioning systems, in particular to an air conditioning system and a control method and device thereof.
Background
With the progress of air conditioning technology, the requirements of users on energy conservation and comfort of the air conditioner are higher and higher, the air conditioner can quickly refrigerate or heat after being started, and the indoor temperature is required to be kept within a comfortable range in the operation process. However, when the air conditioning system is operating at a variable evaporating temperature or a variable condensing temperature, further optimization of how the air conditioner is controlled is required.
Disclosure of Invention
The present invention is directed to solving, at least to some extent, one of the technical problems in the related art. To this end, a first objective of the present invention is to provide a control method for an air conditioning system, so as to control the power of the compressor according to the target operating temperature and the actual operating temperature while varying the target operating temperature according to the return air temperature.
A second object of the present invention is to provide a control device for an air conditioning system.
A third object of the present invention is to provide an air conditioning system.
A fourth object of the invention is to propose an electronic device.
A fifth object of the invention is to propose a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium.
In order to achieve the above object, an embodiment of a first aspect of the present invention provides a control method for an air conditioning system, including the following steps: acquiring the current return air temperature of the indoor unit, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time by using the current return air temperature; detecting the current actual working temperature of the indoor unit; and controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the updating the target operating temperature of the indoor unit in real time by using the current return air temperature further includes: and determining the target working temperature according to the mapping relation between the return air temperature and the target working temperature.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the updating the target operating temperature of the indoor unit in real time by using the current return air temperature further includes: and identifying the working mode of the air conditioning system, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time according to the working mode and the return air temperature.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the air conditioning system includes at least one indoor unit, and the acquiring current return air temperature of the indoor unit further includes: and acquiring the current return air temperature of at least one indoor unit, and calculating the average value of the at least one return air temperature.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, said controlling the power of the compressor according to said target operating temperature and said actual operating temperature further comprises: acquiring the deviation amount of the target working temperature and the actual working temperature; and determining the power adjustment amount of the compressor according to the deviation amount.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the operation mode is a cooling mode, the target operation temperature is a target evaporation temperature, and the actual operation temperature is an actual evaporation temperature; controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature specifically comprises: judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not; if yes, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity; and if not, reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the operation mode is a heating mode, the target operation temperature is a target condensation temperature, and the actual operation temperature is an actual condensation temperature; controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature specifically comprises: judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not; if yes, controlling and reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity; and if not, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment amount.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the compressor is controlled to maintain the current power when the actual operating temperature is equal to the target operating temperature.
According to the control method of the air conditioning system, the current return air temperature of the indoor unit is obtained in real time, the target working temperature of the indoor unit is updated in real time by using the current return air temperature, and then the power of the compressor is controlled according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature, so that the target working temperature is changed according to the return air temperature, the power of the compressor is dynamically adjusted, the indoor temperature can meet the requirements of users as soon as possible, and the indoor temperature is finally maintained in a comfortable range.
In order to achieve the above object, a second embodiment of the present invention provides a control device for an air conditioning system, including: the target working temperature acquisition module is used for acquiring the current return air temperature of the indoor unit and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time by using the current return air temperature; the actual working temperature acquisition module is used for detecting the current actual working temperature of the indoor unit; and the control module is used for controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the target operating temperature obtaining module is further configured to: and determining the target working temperature according to the mapping relation between the return air temperature and the target working temperature.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the target operating temperature obtaining module is further configured to: and identifying the working mode of the air conditioning system, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time according to the working mode and the return air temperature.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the air conditioning system includes at least one indoor unit, and the target operating temperature obtaining module is further configured to: and acquiring the current return air temperature of at least one indoor unit, and calculating the average value of the at least one return air temperature.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the control module is further configured to: acquiring the deviation amount of the target working temperature and the actual working temperature; and determining the power adjustment amount of the compressor according to the deviation amount.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the operation mode is a cooling mode, the target operation temperature is a target evaporation temperature, and the actual operation temperature is an actual evaporation temperature; the control module is further configured to: judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not; if yes, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity; and if not, reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the operation mode is a heating mode, the target operation temperature is a target condensation temperature, and the actual operation temperature is an actual condensation temperature; the control module is further configured to: judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not; if yes, controlling and reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity; and if not, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment amount.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the control module is further configured to: and controlling the compressor to keep the current power when the actual working temperature is equal to the target working temperature.
According to the control device of the air conditioning system, the current return air temperature of the indoor unit is obtained through the target working temperature obtaining module, the target working temperature of the indoor unit is updated in real time through the current return air temperature, and then the power of the compressor is controlled through the control module according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature, so that the power of the compressor is dynamically adjusted while the target working temperature is changed according to the return air temperature, the indoor temperature can meet the requirements of users as soon as possible, and finally the indoor temperature is maintained in a comfortable range.
In order to achieve the above object, a third embodiment of the present invention provides an air conditioning system, including the control device of the air conditioning system.
In order to achieve the above object, a fourth aspect of the present invention provides an electronic device, including a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and running on the processor, where the processor executes the computer program to implement the control method of the air conditioning system.
In order to achieve the above object, a fifth aspect embodiment of the present invention proposes a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium having stored thereon a computer program that, when executed by a processor, implements the control method of an air conditioning system.
Additional aspects and advantages of the invention will be set forth in part in the description which follows and, in part, will be obvious from the description, or may be learned by practice of the invention.
Drawings
The foregoing and/or additional aspects and advantages of the present invention will become apparent and readily appreciated from the following description of the embodiments, taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings of which:
fig. 1 is a flowchart of a control method of an air conditioning system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a graph of return air temperature versus target evaporating temperature for one embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a graph of return air temperature versus target condensing temperature for one embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 4 is a flowchart of a control method of an air conditioning system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 5 is a flowchart of a control method of an air conditioning system according to another embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 6 is a flowchart of a control method of an air conditioning system according to still another embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 7 is a flowchart of a method for controlling an air conditioning system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 8 is a flowchart of a method for controlling an air conditioning system according to another embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 9 is a block diagram schematically illustrating a control apparatus of an air conditioning system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 10 is a block diagram of an air conditioning system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Detailed Description
Reference will now be made in detail to embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings, wherein like or similar reference numerals refer to the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar function throughout. The embodiments described below with reference to the drawings are illustrative and intended to be illustrative of the invention and are not to be construed as limiting the invention.
An air conditioning system, a control method and apparatus thereof according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
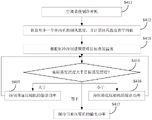
Fig. 1 is a flowchart of a control method of an air conditioning system according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in fig. 1, the control method of the air conditioning system according to the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
s101: and acquiring the current return air temperature of the indoor unit, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time by using the current return air temperature.
It should be noted that, in an inverter air conditioning system, in order to achieve the effect that cooling at startup can be rapidly reduced or heating at startup can be rapidly increased, the target operating temperature (the evaporation temperature during cooling operation and the condensation temperature during heating operation) of the indoor unit needs to be adjusted.
The returnable air temperature can be detected by a return air temperature sensor, and the return air temperature sensor can be arranged at a return air inlet of the indoor unit.
As a possible embodiment, the target operating temperature may be determined according to a mapping relationship between the return air temperature and the target operating temperature.
Specifically, the working mode of the air conditioning system can be identified, and the target working temperature of the indoor unit can be updated in real time according to the working mode and the return air temperature.
For example, as shown in fig. 2, in the embodiment of the present invention, when the air conditioning system performs a cooling operation, the target operating temperature (evaporating temperature) of the indoor unit is inversely proportional to the return air temperature, that is, the higher the return air temperature is, the lower the target evaporating temperature is, and the lower the return air temperature is, the higher the target evaporating temperature is; similarly, as shown in fig. 3, when the air conditioning system is in heating operation, the target operating temperature (condensing temperature) of the indoor unit is also in inverse proportion to the return air temperature.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the air conditioning system can comprise at least one indoor unit, and specifically, the current return air temperature of the at least one indoor unit can be obtained, and the average value of the at least one return air temperature can be calculated.
That is to say, when a plurality of indoor units participate in temperature regulation in the air conditioning system, the current return air temperature of the indoor units participating in temperature regulation can be collected in real time, the average value of the current return air temperatures is used as the return air temperature of the current air conditioning system, and then the target working temperature of the indoor unit is determined according to the return air temperature of the current air conditioning system.
Therefore, the control method provided by the embodiment of the invention can adjust the target working temperature of the indoor unit according to the return air temperature acquired in real time, so as to control the power of the compressor according to the changed target working temperature.
S102: and detecting the current actual working temperature of the indoor unit.
The indoor unit can be provided with an actual working temperature detection device so as to detect the actual evaporation temperature when the air conditioning system works in a refrigerating mode and detect the actual condensation temperature when the air conditioning system works in a heating mode.
S103: and controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature.
That is, when the air conditioning system is in operation, the actual operating temperature of the indoor unit is made to approach the target operating temperature as much as possible by controlling the operating power of the compressor, so that the indoor temperature can meet the user's demand as soon as possible.
As a possible embodiment, as shown in fig. 4, step S103 may specifically include:
s201: and acquiring deviation amount of the target working temperature and the actual working temperature.
S202: and determining the power adjustment amount of the compressor according to the deviation amount.
That is, the deviation amount may be calculated according to the target operating temperature and the actual operating temperature of the indoor unit, and then the power adjustment amount of the compressor may be determined according to the deviation amount, so that the actual operating temperature may reach the target operating temperature by adjusting the operating power of the compressor according to the power adjustment amount.
Specifically, when the operation mode is the cooling mode, as shown in fig. 5, step S103 specifically includes:
s311: and judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature.
S312: if yes, the power of the compressor is increased according to the power adjustment amount.
S313: if not, the power of the compressor is reduced according to the power adjustment amount.
Specifically, when the operation mode is the heating mode, as shown in fig. 6, step S103 specifically includes:
s321: and judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature.
S322: if so, the power of the compressor is reduced according to the power adjustment amount.
S323: if not, the power of the compressor is increased according to the power adjustment amount.
Further, when the actual operating temperature is equal to the target operating temperature, the compressor is controlled to maintain the current power.
That is, in the refrigeration mode of the air conditioning system, the higher the return air temperature is, the lower the target evaporation temperature is, the higher the output power of the compressor is, the better the refrigeration effect of the indoor unit is, so as to realize the rapid cooling of the indoor side, the target evaporation temperature is gradually increased along with the reduction of the return air temperature, the output power of the compressor is reduced, and finally, when the actual evaporation temperature is equal to the target evaporation temperature, the output power of the compressor is kept unchanged; the air conditioning system is under the heating mode, and the return air temperature is lower, and the target condensing temperature is higher, and compressor output is bigger, and indoor set heating effect is better to realize indoor side's rapid heating up, along with the rising of return air temperature, the target condensing temperature reduces gradually, and compressor output reduces, and finally when actual condensing temperature equals the target condensing temperature, compressor output maintains unchangeably.
Therefore, the control method provided by the embodiment of the invention can adjust the compressor in real time according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature, so that the indoor temperature can be rapidly cooled or heated to meet the temperature requirement of a user, and finally the indoor temperature is maintained in a comfortable temperature range, thereby improving the user experience.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in fig. 7, when the air conditioning system performs a cooling operation, the control method specifically includes:
s411: and (5) refrigerating and starting the air conditioning system.
S412: and acquiring the return air temperature of at least one indoor unit, and calculating the average value of the return air temperature.
S413: and acquiring the target evaporation temperature according to the refrigeration control logic.
S414: and judging whether the actual evaporation temperature is greater than the target evaporation temperature.
If so, go to step S415; if so, go to step S416; if so, step S417 is performed.
S415: the control increases the output power of the compressor and returns to step S414.
S416: the control reduces the output power of the compressor and returns to step S414.
S417: the current compressor output is maintained.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in fig. 8, when the air conditioning system is in heating operation, the control method specifically includes:
s421: and the air conditioning system is started up by heating.
S422: and acquiring the return air temperature of at least one indoor unit, and calculating the average value of the return air temperature.
S423: and acquiring the target condensation temperature according to the heating control logic.
S424: and judging whether the actual condensation temperature is greater than the target condensation temperature.
If so, go to step S415; if so, go to step S416; if so, step S417 is performed.
S425: the control reduces the output power of the compressor and returns to step S424.
S426: the control increases the output power of the compressor and returns to step S424.
S427: the current compressor output is maintained.
In summary, according to the control method of the air conditioning system in the embodiment of the present invention, the current return air temperature of the indoor unit is obtained in real time, the target working temperature of the indoor unit is updated in real time by using the current return air temperature, and then the power of the compressor is controlled according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature, so that the power of the compressor is dynamically adjusted while the target working temperature is changed according to the return air temperature, so that the indoor temperature can meet the user requirement as soon as possible, and finally, the indoor temperature is maintained within a comfortable range.
In order to implement the above embodiments, the present invention further provides a control device of an air conditioning system.
Fig. 9 is a block diagram illustrating a control apparatus of an air conditioning system according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in fig. 9, the control device 100 of the air conditioning system includes: a target operating temperature acquisition module 10, an actual operating temperature acquisition module 20, and a control module 30.
The target working temperature acquisition module 10 is used for acquiring the current return air temperature of the indoor unit and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time by using the current return air temperature; the actual working temperature obtaining module 20 is used for detecting the current actual working temperature of the indoor unit; the control module 30 is configured to control the power of the compressor based on the target operating temperature and the actual operating temperature.
Further, the target operating temperature obtaining module 10 is further configured to: and determining the target working temperature according to the mapping relation between the return air temperature and the target working temperature.
Further, the target operating temperature obtaining module 10 is further configured to: and identifying the working mode of the air conditioning system, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time according to the working mode and the return air temperature.
Further, the air conditioning system includes at least one indoor unit, and the target operating temperature obtaining module 10 is further configured to: and acquiring the current return air temperature of at least one indoor unit, and calculating the average value of at least one return air temperature.
Further, the control module 30 is further configured to: acquiring deviation amount of the target working temperature and the actual working temperature; and determining the power adjustment amount of the compressor according to the deviation amount.
Further, when the working mode is the refrigeration mode, the target working temperature is the target evaporation temperature, and the actual working temperature is the actual evaporation temperature; the control module 30 is further configured to: judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not; if yes, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity; if not, the power of the compressor is reduced according to the power adjustment amount.
Further, when the working mode is the heating mode, the target working temperature is the target condensation temperature, and the actual working temperature is the actual condensation temperature; the control module 30 is further configured to: judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not; if yes, reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity; if not, the power of the compressor is increased according to the power adjustment amount.
It should be noted that the foregoing explanation of the embodiment of the control method of the air conditioning system is also applicable to the control device of the air conditioning system of the embodiment, and details are not repeated here.
In order to implement the above embodiment, the present invention further provides an air conditioning system, as shown in fig. 10, an air conditioning system 200 includes the control device 100 of the air conditioning system.
In order to implement the above embodiments, the present invention further provides an electronic device, which includes a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and running on the processor, wherein when the processor executes the computer program, the control method of the air conditioning system is implemented.
In order to implement the above embodiments, the present invention also proposes a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium having stored thereon a computer program which, when executed by a processor, implements the aforementioned control method of an air conditioning system.
In the description herein, references to the description of the term "one embodiment," "some embodiments," "an example," "a specific example," or "some examples," etc., mean that a particular feature, structure, material, or characteristic described in connection with the embodiment or example is included in at least one embodiment or example of the invention. In this specification, the schematic representations of the terms used above are not necessarily intended to refer to the same embodiment or example. Furthermore, the particular features, structures, materials, or characteristics described may be combined in any suitable manner in any one or more embodiments or examples. Furthermore, various embodiments or examples and features of different embodiments or examples described in this specification can be combined and combined by one skilled in the art without contradiction.
Furthermore, the terms "first", "second" and "first" are used for descriptive purposes only and are not to be construed as indicating or implying relative importance or implicitly indicating the number of technical features indicated. Thus, a feature defined as "first" or "second" may explicitly or implicitly include at least one such feature. In the description of the present invention, "a plurality" means at least two, e.g., two, three, etc., unless specifically limited otherwise.
Any process or method descriptions in flow charts or otherwise described herein may be understood as representing modules, segments, or portions of code which include one or more executable instructions for implementing steps of a custom logic function or process, and alternate implementations are included within the scope of the preferred embodiment of the present invention in which functions may be executed out of order from that shown or discussed, including substantially concurrently or in reverse order, depending on the functionality involved, as would be understood by those reasonably skilled in the art of the present invention.
The logic and/or steps represented in the flowcharts or otherwise described herein, e.g., an ordered listing of executable instructions that can be considered to implement logical functions, can be embodied in any computer-readable medium for use by or in connection with an instruction execution system, apparatus, or device, such as a computer-based system, processor-containing system, or other system that can fetch the instructions from the instruction execution system, apparatus, or device and execute the instructions. For the purposes of this description, a "computer-readable medium" can be any means that can contain, store, communicate, propagate, or transport the program for use by or in connection with the instruction execution system, apparatus, or device. More specific examples (a non-exhaustive list) of the computer-readable medium would include the following: an electrical connection (electronic device) having one or more wires, a portable computer diskette (magnetic device), a Random Access Memory (RAM), a read-only memory (ROM), an erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM or flash memory), an optical fiber device, and a portable compact disc read-only memory (CDROM). Additionally, the computer-readable medium could even be paper or another suitable medium upon which the program is printed, as the program can be electronically captured, via for instance optical scanning of the paper or other medium, then compiled, interpreted or otherwise processed in a suitable manner if necessary, and then stored in a computer memory.
It should be understood that portions of the present invention may be implemented in hardware, software, firmware, or a combination thereof. In the above embodiments, the various steps or methods may be implemented in software or firmware stored in memory and executed by a suitable instruction execution system. If implemented in hardware, as in another embodiment, any one or combination of the following techniques, which are known in the art, may be used: a discrete logic circuit having a logic gate circuit for implementing a logic function on a data signal, an application specific integrated circuit having an appropriate combinational logic gate circuit, a Programmable Gate Array (PGA), a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), or the like.
It will be understood by those skilled in the art that all or part of the steps carried by the method for implementing the above embodiments may be implemented by hardware related to instructions of a program, which may be stored in a computer readable storage medium, and when the program is executed, the program includes one or a combination of the steps of the method embodiments.
In addition, functional units in the embodiments of the present invention may be integrated into one processing module, or each unit may exist alone physically, or two or more units are integrated into one module. The integrated module can be realized in a hardware mode, and can also be realized in a software functional module mode. The integrated module, if implemented in the form of a software functional module and sold or used as a stand-alone product, may also be stored in a computer readable storage medium.
The storage medium mentioned above may be a read-only memory, a magnetic or optical disk, etc. Although embodiments of the present invention have been shown and described above, it is understood that the above embodiments are exemplary and should not be construed as limiting the present invention, and that variations, modifications, substitutions and alterations can be made to the above embodiments by those of ordinary skill in the art within the scope of the present invention.
Claims (17)
1. A control method of an air conditioning system is characterized by comprising the following steps:
the method comprises the steps of obtaining the current return air temperature of an indoor unit, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time by utilizing the current return air temperature, wherein the target working temperature is the evaporation temperature during refrigeration work and the condensation temperature during heating work, and is determined according to the mapping relation between the return air temperature and the target working temperature;
detecting the current actual working temperature of the indoor unit, wherein the actual working temperature is the actual evaporation temperature during the refrigeration work and the actual condensation temperature during the heating work;
controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature, wherein the controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature comprises the following steps:
acquiring the deviation amount of the target operating temperature and the actual operating temperature,
and determining the power adjustment amount of the compressor according to the deviation amount.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein the updating the target operating temperature of the indoor unit in real time using the current return air temperature further comprises:
and identifying the working mode of the air conditioning system, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time according to the working mode and the return air temperature.
3. The method for controlling an air conditioning system according to claim 1, wherein the air conditioning system includes at least one indoor unit, and the obtaining of the current return air temperature of the indoor unit further includes:
and acquiring the current return air temperature of at least one indoor unit, and calculating the average value of the at least one return air temperature.
4. The control method of an air conditioning system according to claim 1, wherein when the operation mode is a cooling mode, the target operation temperature is a target evaporation temperature, and the actual operation temperature is an actual evaporation temperature;
controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature specifically comprises:
judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not;
if yes, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity;
and if not, reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity.
5. The control method of an air conditioning system according to claim 1, wherein when the operation mode is a heating mode, the target operation temperature is a target condensation temperature, and the actual operation temperature is an actual condensation temperature;
controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature specifically comprises:
judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not;
if yes, controlling and reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity;
and if not, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment amount.
6. The control method of an air conditioning system according to claim 4 or 5, characterized by further comprising:
and controlling the compressor to keep the current power when the actual working temperature is equal to the target working temperature.
7. A control device of an air conditioning system, characterized by comprising:
the target working temperature acquisition module is used for acquiring the current return air temperature of the indoor unit, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time by using the current return air temperature, wherein the target working temperature is the evaporation temperature during refrigeration work and the condensation temperature during heating work;
the actual working temperature acquisition module is used for detecting the current actual working temperature of the indoor unit, and the actual working temperature is the actual evaporation temperature during the refrigeration work and the actual condensation temperature during the heating work;
and the control module is used for controlling the power of the compressor according to the target working temperature and the actual working temperature.
8. The control device of an air conditioning system according to claim 7, wherein the target operating temperature obtaining module is further configured to:
and determining the target working temperature according to the mapping relation between the return air temperature and the target working temperature.
9. The control device of an air conditioning system according to claim 8, wherein the target operating temperature obtaining module is further configured to:
and identifying the working mode of the air conditioning system, and updating the target working temperature of the indoor unit in real time according to the working mode and the return air temperature.
10. The apparatus of claim 7, wherein the air conditioning system comprises at least one indoor unit, and the target operating temperature obtaining module is further configured to:
and acquiring the current return air temperature of at least one indoor unit, and calculating the average value of the at least one return air temperature.
11. The control device of an air conditioning system according to claim 7, wherein the control module is further configured to:
acquiring the deviation amount of the target working temperature and the actual working temperature;
and determining the power adjustment amount of the compressor according to the deviation amount.
12. The control device of an air conditioning system according to claim 10, wherein when the operation mode is a cooling mode, the target operation temperature is a target evaporation temperature, and the actual operation temperature is an actual evaporation temperature;
the control module is further configured to:
judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not;
if yes, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity;
and if not, reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity.
13. The control device of an air conditioning system according to claim 10, wherein when the operation mode is a heating mode, the target operation temperature is a target condensation temperature, and the actual operation temperature is an actual condensation temperature;
the control module is further configured to:
judging whether the actual working temperature is higher than the target working temperature or not;
if yes, controlling and reducing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment quantity;
and if not, controlling and increasing the power of the compressor according to the power adjustment amount.
14. The control device of an air conditioning system according to claim 12 or 13, wherein the control module is further configured to:
and controlling the compressor to keep the current power when the actual working temperature is equal to the target working temperature.
15. An air conditioning system, characterized by comprising a control device of an air conditioning system according to any of claims 7-14.
16. An electronic device comprising a memory, a processor and a computer program stored on the memory and executable on the processor, wherein the processor, when executing the program, implements the control method of the air conditioning system according to any one of claims 1 to 6.
17. A non-transitory computer-readable storage medium having stored thereon a computer program, characterized in that the program, when executed by a processor, implements the control method of an air conditioning system according to any one of claims 1 to 6.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811496587.4A CN109668275B (en) | 2018-12-07 | 2018-12-07 | Air conditioning system and control method and device thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811496587.4A CN109668275B (en) | 2018-12-07 | 2018-12-07 | Air conditioning system and control method and device thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN109668275A CN109668275A (en) | 2019-04-23 |
| CN109668275B true CN109668275B (en) | 2022-04-19 |
Family
ID=66144187
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811496587.4A Active CN109668275B (en) | 2018-12-07 | 2018-12-07 | Air conditioning system and control method and device thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN109668275B (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107036243A (en) * | 2017-04-24 | 2017-08-11 | 广东美的暖通设备有限公司 | Indoor set points out control method and system, indoor set, multi-connected machine central air-conditioning |
| CN107631436A (en) * | 2017-10-25 | 2018-01-26 | 广东美的暖通设备有限公司 | Control method and system of the multi-connected air conditioner device under cooling condition |
| CN108397853A (en) * | 2018-02-11 | 2018-08-14 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Air conditioning unit control method and device |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104515245B (en) * | 2013-09-26 | 2017-06-30 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | control method and device of air conditioning system |
| JP5831661B1 (en) * | 2014-09-30 | 2015-12-09 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | air conditioner |
| CN108613343A (en) * | 2018-05-28 | 2018-10-02 | 广东美的暖通设备有限公司 | A kind of control method and control system of air conditioner |
-
2018
- 2018-12-07 CN CN201811496587.4A patent/CN109668275B/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107036243A (en) * | 2017-04-24 | 2017-08-11 | 广东美的暖通设备有限公司 | Indoor set points out control method and system, indoor set, multi-connected machine central air-conditioning |
| CN107631436A (en) * | 2017-10-25 | 2018-01-26 | 广东美的暖通设备有限公司 | Control method and system of the multi-connected air conditioner device under cooling condition |
| CN108397853A (en) * | 2018-02-11 | 2018-08-14 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Air conditioning unit control method and device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN109668275A (en) | 2019-04-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107300231B (en) | Heat pump unit and control method and device thereof | |
| CN104613593B (en) | Air-conditioner and its electric heating controlling method | |
| CN113218045B (en) | Method for correcting compressor frequency control logic, air conditioner and storage medium | |
| CN105423489B (en) | The control method of multi-split air conditioner | |
| CN108954709B (en) | Control method and device of air conditioning equipment and air conditioning equipment | |
| CN108019900B (en) | Air conditioner and its control method and device | |
| CN107525229B (en) | Method and device for controlling electric heating of air conditioner | |
| CN107178873A (en) | Transducer air conditioning and its control method | |
| CN105509246A (en) | Humidification control method and device for air conditioner | |
| CN109764473B (en) | Method for preventing air outlet of air conditioning unit from carrying water and air conditioning unit | |
| CN113218047B (en) | Method for correcting compressor frequency control logic, air conditioner and storage medium | |
| CN110940064B (en) | Control method for operating frequency of air conditioner | |
| CN108800428A (en) | Control method, device and the apparatus of air conditioning of the apparatus of air conditioning | |
| CN109059224A (en) | Control method, device and the apparatus of air conditioning of the apparatus of air conditioning | |
| CN110160228A (en) | The control method and air conditioner of heat pump air conditioner | |
| CN108931038B (en) | Air conditioner and method for correcting energy requirement of air conditioner | |
| CN109668267B (en) | Control method and device of air conditioning equipment and air conditioning equipment | |
| CN108131774A (en) | Air conditioner and its control method, device | |
| CN110671783A (en) | Control method and device for dehumidification of air conditioner, air conditioner and storage medium | |
| CN107664368B (en) | Air conditioning system and control method and device of electronic expansion valve of air conditioning system | |
| CN112665162A (en) | Fixed-frequency air conditioner and control method and device of indoor fan of fixed-frequency air conditioner | |
| CN108800470A (en) | Control method, device and the apparatus of air conditioning of the apparatus of air conditioning | |
| CN107655141B (en) | Water cooling unit and control method and control device thereof | |
| CN108800464B (en) | Energy-saving control method and device for air conditioner and air conditioner | |
| CN106016588A (en) | Air conditioner and air speed adjusting method and device thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |
Effective date of registration: 20220922 Address after: No. 66, Shanghai Avenue, Jingzhou Development Zone, Jingzhou City, Hubei Province 434099 Patentee after: Hubei Midea Building Technology Co.,Ltd. Address before: 528311 Industrial Road, Penglai Road, Beijiao Town, Shunde District, Guangdong, Foshan Patentee before: GD MIDEA HEATING & VENTILATING EQUIPMENT Co.,Ltd. Patentee before: MIDEA GROUP Co.,Ltd. |