CN108076495B - Method, system and device for realizing cross-cell switching in wireless network - Google Patents
Method, system and device for realizing cross-cell switching in wireless network Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN108076495B CN108076495B CN201611005647.9A CN201611005647A CN108076495B CN 108076495 B CN108076495 B CN 108076495B CN 201611005647 A CN201611005647 A CN 201611005647A CN 108076495 B CN108076495 B CN 108076495B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- user
- station
- new
- address
- user station
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/08—Reselecting an access point
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/24—Reselection being triggered by specific parameters
- H04W36/32—Reselection being triggered by specific parameters by location or mobility data, e.g. speed data
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a method, a system and a device for realizing cross-cell switching in a wireless network, comprising the following steps: when a user station accesses a new cell, a new AP sends user information of the user station to a user manager to which the new AP belongs; the user manager determines and stores the position information of the user site according to the user information; when the user manager determines that the user station is a cross-cell switching station, sending a change signaling to an original AP (access point), and informing the original AP of updating and configuring a first forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station; and sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station. Therefore, the user station in the wireless network can realize cross-school zone switching, communication interruption caused by cross-cell movement of the user station is avoided, cross-cell connection of communication is better realized, and user communication experience is improved.
Description
Technical Field
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and particularly relates to a method, a system and a device for realizing cross-cell switching in a wireless network.
Background
With the continuous development of wireless communication technology and network technology, wireless networks are increasingly applied, and besides mobile communication technology, various wireless network technologies suitable for different scenes have been proposed and applied in corresponding scenes, such as: a Wireless Fidelity (WiFi) technology capable of implementing fast data communication in a small coverage area, a ZigBee (ZigBee) technology capable of implementing Access of a plurality of nodes, a Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) technology capable of implementing fast Wireless internet Access of users in a wider area, and an Ultra High speed Wireless local area network (enhanced Ultra High Throughput, EUHT) technology, where the EUHT technology can provide a higher data rate than the WiFi technology, can provide support for a user's moving speed, has a larger coverage than the WiFi technology, supports a higher moving speed, provides a higher data rate, and is currently applied to internet Access of a High-speed railway system, Wireless broadband Access in rural areas, and the like. In addition, it is expected that as wireless communication and network technologies develop, more wireless network technologies suitable for a specific scenario will emerge.
The above-described wireless network techniques, while enabling wireless users in a coverage area to achieve corresponding communication performance, generally do not support cross-cell handover of users between wireless networks. Such as: when a WiFi user station leaves the current WiFi cell and enters the adjacent WiFi cell, the current WiFi standard does not support the cross-cell handover of the user station between WiFi cells, so when the user station is transmitting data with the network station in the internet through the Access Point (AP) of the original WiFi cell, the data connection is interrupted, and the connection after the cross-cell cannot be realized. This will affect the user experience when the user is using the wireless network in a mobile state, which may result in a poor user experience when the user station moves frequently in the cells of the wireless network.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above, an object of the present invention is to provide a method, a system and a device for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network, so as to solve the problem in the prior art that the cross-cell handover of a user station cannot be implemented in the wireless network. The following presents a simplified summary in order to provide a basic understanding of some aspects of the disclosed embodiments. This summary is not an extensive overview and is intended to neither identify key/critical elements nor delineate the scope of such embodiments. Its sole purpose is to present some concepts in a simplified form as a prelude to the more detailed description that is presented later.
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for realizing cross-cell switching in a wireless network, when a user station accesses a new cell, the method comprises the following steps:
the new AP sends the user information of the user station to the user manager;
the user manager determines and stores the position information of the user site according to the user information;
when the user manager determines that the user station is a cross-cell switching station, sending a change signaling to an original AP (access point), and informing the original AP of updating and configuring a first forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station; and sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station.
In some optional embodiments, the sending, by the new AP, the user information of the user station to the user manager to which the new AP belongs specifically includes:
the new AP acquires a user station name reported by a user station and allocates an IP address for the user station;
and sending the acquired user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site to the affiliated user manager as user information.
In some optional embodiments, the determining, by the user manager, and storing the location information of the user site according to the user information specifically includes:
the user manager acquires the name of the user site and the IP address allocated to the user site according to the received user information; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP;
and establishing a triple group of the user station by using the user station name, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP, and storing the triple group.
In some optional embodiments, the determining, by the user manager, that the user station is a cross-cell handover station specifically includes:
the user manager searches a locally stored user station position information list according to the user station name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, determining the user site as a site of a new access network.
In some optional embodiments, the first transfer table comprises: a roll-out table used for the original AP to forward the received data of the user station to the new AP and a roll-out backtracking table used for the original AP to forward the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to an external network station;
the second forwarding table comprises: a transfer-in table for the new AP to transfer the user data forwarded by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a transfer-in backtracking table for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the original AP.
An embodiment of the present invention further provides a user manager, including:
the first receiving module is used for receiving the user information of the user station sent by the new AP when the user station accesses the new cell;
the information processing module is used for determining the position information of the user station according to the user information;
the information storage module is used for storing the position information of the user station;
the switching judging module is used for determining whether the user site is a cross-cell switching site;
a first sending module, configured to send a change signaling to an original AP when determining that the user station is a cross-cell handover station, and notify the original AP to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station; and sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station.
In some optional embodiments, the information processing module is specifically configured to:
according to the received user information, acquiring a user site name and an IP address distributed to a user site; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP;
and establishing a triple group of the user station by using the user station name, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP.
In some optional embodiments, the handover discrimination module is specifically configured to:
searching a locally stored user station position information list according to the user station name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, determining the user site as a site of a new access network.
An embodiment of the present invention further provides an AP, including:
the second sending module is used for sending the user information of the user site to the user manager when the user site is accessed to the cell;
the second receiving module is used for receiving the change signaling sent by the user manager; and/or receiving configuration signaling sent by a user manager;
a first configuration module, configured to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station according to the received change signaling; and/or configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station according to the received configuration signaling.
In some optional embodiments, the second sending module is specifically configured to:
acquiring a user station name reported by a user station, and allocating an IP address for the user station;
and sending the acquired user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site to the affiliated user manager as user information.
In some optional embodiments, the first configuration module is specifically configured to:
configuring a first forwarding table which comprises a forwarding-out table used for forwarding the received data of the user station to the new AP by the original AP and a forwarding-out backtracking table used for forwarding the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to the external network station by the original AP;
the configuration comprises a transfer-in table used for the new AP to transfer the user data transferred by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a second transfer table used for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the transfer-in backtracking table of the original AP.
The embodiment of the invention also provides a system for realizing cross-cell switching in the wireless network, which comprises a user manager, an Access Point (AP) and a user site;
the AP is used as a new AP and is used for sending the user information of the user station to the user manager when the user station is accessed into the cell; configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user site according to the received change signaling sent by the user manager;
the AP is used as an original AP and is used for updating and configuring a first forwarding table used for forwarding the data of the user station according to a received change signaling sent by a user manager;
the user manager is used for determining and storing the position information of the user site according to the user information; when the user station is determined to be a cross-cell switching station, sending a change signaling to the original AP, and informing the original AP to update and configure a first forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station; and sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station.
The method, the system and the device for realizing cross-cell switching in the wireless network provided by the embodiment of the invention have the advantages that when a user station accesses a new cell, the new AP reports the user information to a user manager, the user manager indicates the original AP to change the information of the user station and configures a forwarding table, and instructing the new AP to configure a forwarding table so as to correctly forward the communication data of the user station in the original cell to the user station through the original AP and the new AP, thereby enabling the user station in the wireless network to realize cross-school zone switching, avoiding communication interruption caused by the cross-cell movement of the user station, avoiding the loss of data forwarded by the original cell, better realizing cross-cell connection of communication, improving the communication experience of users, even if the user station moves frequently and switches the cell, the effective and timely receiving and replying of the data can be ensured, and the communication continuity of the user station switched across the cell is ensured.
For the purposes of the foregoing and related ends, the one or more embodiments include the features hereinafter fully described and particularly pointed out in the claims. The following description and the annexed drawings set forth in detail certain illustrative aspects and are indicative of but a few of the various ways in which the principles of the various embodiments may be employed. Other benefits and novel features will become apparent from the following detailed description when considered in conjunction with the drawings and the disclosed embodiments are intended to include all such aspects and their equivalents.
Drawings
The accompanying drawings, which are included to provide a further understanding of the invention and are incorporated in and constitute a part of this specification, illustrate embodiments of the invention and together with the description serve to explain the principles of the invention and not to limit the invention. In the drawings:
fig. 1 is a flowchart of a method for implementing a cross-cell handover in a wireless network according to an embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network according to a first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a structure of a user manager according to an embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of an access point according to a first embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 5 is a flowchart of a method for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network according to a second embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network according to a second embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 7 is a schematic structural diagram of a user information summarizing server according to a second embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating a structure of a user manager according to a second embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 9 is a schematic structural diagram of an access point according to a second embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 10 is a flowchart of a data transmission method across cell handover in a wireless network according to a third embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 11 is a schematic structural diagram of a data transmission system switched across cells in a wireless network according to a third embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 12 is a schematic structural diagram of an access point in the third embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 13 is a schematic structural diagram of a user station in the third embodiment of the present invention.
Detailed Description
The following description and the drawings sufficiently illustrate specific embodiments of the invention to enable those skilled in the art to practice them. Other embodiments may incorporate structural, logical, electrical, process, and other changes. The examples merely typify possible variations. Individual components and functions are optional unless explicitly required, and the sequence of operations may vary. Portions and features of some embodiments may be included in or substituted for those of others. The scope of embodiments of the invention encompasses the full ambit of the claims, as well as all available equivalents of the claims. Embodiments of the invention may be referred to herein, individually or collectively, by the term "invention" merely for convenience and without intending to voluntarily limit the scope of this application to any single invention or inventive concept if more than one is in fact disclosed.
In the application of the wireless network, if the cross-cell switching among the cells of the same wireless network can be realized, the user experience of a user of the wireless network when the user uses the wireless network to surf the internet in the moving process can be greatly improved.
Further, if handover is performed between these heterogeneous wireless networks that achieve area coverage, namely: when a user station leaves a cell of one wireless network and crosses into a cell of another wireless network, the cross-cell switching of the current data of the user can be realized, and the user experience of the user when surfing the internet by using a wire network in a mobile state can be greatly improved.
Although existing wireless networks such as those using WiFi technology, ZigBee technology, WiMAX technology, and EUHT technology have their respective features, they have the following common features: all need to be connected to a common external network, the most typical application of which is the internet, and in which communication with external network sites is achieved using IP protocols; there is a component that implements IP routing in both the wireless network and the Access Point (AP), which constitutes a wireless router.
Based on the above characteristics of the wireless network, to solve the problem in the prior art that the wireless network communication technology cannot support cross-cell handover of a user station between wireless networks, embodiments of the present invention provide a method for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network, where a user manager manages handover to implement cross-cell handover of a user station between cells covered by different Access Points (APs) in a wireless network, so as to ensure continuity of communication after a cell change is caused by a movement of the user station position.
The method is suitable for the situation that all wireless network cells are the same wireless network, such as WiFi wireless network cells or EUHT wireless network cells, so that cross-cell switching of user stations among all the same wireless network cells can be realized; the method is also suitable for the situation that all wireless network cells are not the same wireless network, and when the user station accesses any wireless network cell, the cross-cell switching of the user station among the same or different wireless network cells can be realized according to the method provided by the invention.
In the method of the invention, a wireless network cell refers to a cell covered by an Access Point (AP) through a wireless communication technology under the wireless communication technology, and the coverage of the AP on a user station not only comprises the situation that the AP is used as a central base station and all the user stations and the AP can realize one-hop communication, but also comprises the situation that the user station can be connected to the AP through one-hop or more connections in a wireless mesh (mesh) network, thereby realizing the communication between the user stations and an external network.
In the method of the present invention, the AP comprises a component for realizing the IP routing function, and the AP forms a wireless router.
In the method of the invention, the wireless network cells considered are all accessed to a common external network through the AP, and the external network supports IP functions, namely: the AP of the wireless network cell and the station of the external network may communicate via an IP protocol. Among them, the most typical example of the common external network is the internet.
In the method of the present invention, the wireless technologies adopted by the wireless network cells are considered to be different wireless communication technologies in principle, that is, different types of wireless network cells are considered in principle; as a specific example, it can also be considered that all wireless network cells are wireless network cells using the same wireless technology, where the same wireless technology refers to: when the user station accesses any wireless network cell, the same Media Access Control (MAC) network card and MAC address are used.
In the method, when a user station accesses a certain wireless network cell, an IP address is allocated to the user station by an AP or an upper station point of the AP through the AP, and the IP address configured by the user station is divided into a global IP address and a local IP address. Generally, the AP configures a global IP address or a local IP address for all the affiliated user stations, and accordingly, the wireless network cell can be divided into two types, i.e., a cell configured with a global IP address and a cell configured with a local IP address. In a special case, the AP may also configure a global IP address for a part of the user stations to which the AP belongs, and configure a local IP address for other user stations, in which case, if the current user station is configured with the global IP address, the cell is a cell configured with the global IP address for the user, and if the current user station is configured with the local IP address, the cell is a cell configured with the local IP address for the user.
For a cell configured with a local IP Address, an AP of the cell must support a Network Address Translation (NAT) protocol, and communication between a subscriber station and an external Network station in the cell is achieved through Address Translation of the NAT protocol.
When a user station leaves a cell of a wireless network and enters a cell of another wireless network, for convenience of description, the original wireless network cell may be referred to as an original cell, a corresponding AP may be referred to as an original AP, the newly entered wireless network cell may be referred to as a new cell, and the corresponding AP may be referred to as a new AP.
In the method provided by the invention, the effect of the user station for realizing the cross-cell switching of the wireless network is as follows: the user station leaves the original cell and enters a new cell, and if the user station transmits data with the station of the external network through the AP of the original cell before leaving the original cell, the user station can continue to transmit between the user station and the external network station as before without interrupting the current data transmission after entering the new cell until finishing the current data transmission. In this case, user-unaware data switching will be achieved.
The following is a detailed description by way of specific examples.
Example one
The method for implementing cross-cell switching in a wireless network provided by the embodiment of the invention implements cross-cell switching of a user station among different wireless network cells by the following modes: (1) adding a station for managing user position information in a common external network, which can be called a user manager, wherein the user manager is connected with a plurality of APs; (2) and a forwarding table supporting user data to realize cross-cell switching is additionally arranged in a routing component of the AP.
In the method provided in the first embodiment of the present invention, only one user manager is added to the entire system, and when a user station moves between cells covered by APs connected to the user manager, the following method is used to implement cross-cell handover of user data.
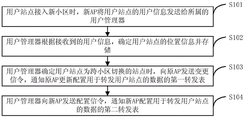
In the method for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network according to an embodiment of the present invention, in order to set a user manager to implement cross-cell handover, a flow of the method is shown in fig. 1, and includes the following steps:
step S101: when the user station accesses the new cell, the new AP sends the user information of the user station to the user manager.
When the position of a user station moves and enters a new wireless network cell, an AP (access point) of the new cell acquires a user station name reported by the user station and allocates an IP (Internet protocol) address for the user station; and the obtained user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site are used as user information and sent to the user manager.
Generally, when a user station accesses an AP, the AP allocates a global IP address and/or a local IP address to the user station; the cell configured with the local IP address needs to support a network address translation protocol, so that communication with a station of an external network is realized through address translation of the protocol.
When the user station accesses the AP, the user station reports the user station name of the user station to the AP; the AP packages the user information of the user station in an IP packet and sends the user information to the user manager; wherein, the user information includes: user site name, user site IP address (global IP address or local IP address).
Step S102: and the user manager determines and stores the position information of the user site according to the received user information.
The user manager acquires the name of the user site and the IP address allocated to the user site according to the received user information; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; and establishing a triple group of the user station by using the name of the user station, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP, and storing the triple group.
After receiving the user site IP packet, the user manager acquires a user site name and a user site IP address which are included in user information; acquiring a source IP address of the IP packet to obtain a global IP address of an AP (access point) to which the user station belongs; the user manager builds the triplets and stores them.
Step S103: and when the user manager determines that the user station is a cross-cell switching station, sending a change signaling to the original AP, and informing the original AP to update and configure a first forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station.
The user manager needs to determine whether the user site is a site for cross-cell switching, and at this time, the user manager searches a locally stored user site position information list according to the user site name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, determining the user station as the station of the new access network.
For a user station switched across cells, a user manager needs to send a change signaling to an original AP and establish a data forwarding table, so that when the original AP receives data of the user station, the received data can be timely forwarded to the user station through a new AP, and reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP is forwarded to a corresponding data receiving station.
After the original AP receives the change signaling, a first forwarding table is established or updated; wherein the first transfer table comprises: and the roll-out table is used for forwarding the received data of the user station to the new AP by the original AP and the roll-out backtracking table is used for forwarding the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to the external network station by the original AP.
Step S104: and the user manager sends a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP of configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station.
For a user station switched across cells, a user manager needs to send a configuration signaling to a new AP and establish a data forwarding table, so that the new AP can correctly forward user data forwarded by an original AP to the user station and forward reply data of the user station to the original AP.
After receiving the configuration signaling, the new AP establishes and updates a second forwarding table, where the second forwarding table includes: a transfer-in table for the new AP to transfer the user data forwarded by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a transfer-in backtracking table for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the original AP.
Based on the same inventive concept, a system for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network is further provided in an embodiment of the present invention, and the structure of the system is shown in fig. 2, where the system includes: a user manager 201, an Access Point (AP)202, and a user station 203. There may be a plurality of APs 202, and each AP202 may cover a cell with access to a plurality of user stations 203, and only one AP202 and one user station 203 are schematically indicated in fig. 2 by reference numerals.
The AP202 is used as a new AP, and is configured to send user information of the user station 203 to the user manager 201 when the user station 203 accesses the cell; and configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding data of the user site 203 according to the received change signaling sent by the user manager 201.
AP202, as an original AP, is configured to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of subscriber station 203 according to the received change signaling sent by subscriber manager 201.
The user manager 201 is used for determining and storing the position information of the user site 203 according to the user information; when the user station 203 is determined to be a cross-cell switching station, sending a change signaling to the original AP, and notifying the original AP to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station 203; and sending a configuration signaling to the new AP, informing the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station 203.
Preferably, the AP202 is used as a new AP, and is specifically configured to obtain a name of a user station reported by the user station, and allocate an IP address to the user station; and sending the acquired user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site to the affiliated user manager as user information.
Preferably, the user manager 201 is specifically configured to obtain a name of a user site and an IP address allocated to the user site according to the received user information; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; and establishing a triple group of the user station by using the name of the user station, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP, and storing the triple group.
Preferably, the user manager 201 is specifically configured to search a locally stored user station location information list according to a user station name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, determining the user station as the station of the new access network.
In an alternative embodiment, the structure of the user manager 201 is shown in fig. 3, and includes: a first receiving module 301, an information processing module 302, an information storage module 303, a switching discrimination module 304 and a first sending module 305.
A first receiving module 301, configured to receive user information of a user station sent by a new AP when the user station accesses a new cell;
an information processing module 302 for determining the location information of the user site according to the received user information
An information storage module 303 for storing the location information of the user station
A handover discrimination module 304, configured to determine whether a user station is a cross-cell handover station;
a first sending module 305, configured to send a change signaling to an original AP when determining that a user station is a cross-cell handover station, and notify the original AP to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station; and sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station.
Preferably, the information processing module 302 is specifically configured to obtain a name of a user site and an IP address assigned to the user site according to the received user information; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; and establishing a triple group of the user station by using the name of the user station, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP.
Preferably, the switching determination module 304 is specifically configured to search a locally stored user station location information list according to the user station name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, determining the user station as the station of the new access network.
In an alternative embodiment, the structure of AP202 is shown in fig. 4, and includes: a second sending module 401, a second receiving module 402 and a first configuration module 403.
The second sending module 401 is configured to send the user information of the user station to the user manager to which the user station belongs when the user station accesses the cell.
A second receiving module 402, configured to receive a change signaling sent by a user manager; and/or receiving configuration signaling sent by a user manager.
A first configuration module 403, configured to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station according to the received change signaling; and/or configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station according to the received configuration signaling.
Preferably, the second sending module 401 is specifically configured to obtain a name of a user station reported by the user station, and allocate an IP address to the user station; and sending the acquired user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site to the affiliated user manager as user information.
Preferably, the first configuration module 403 is specifically configured to configure a first forwarding table that includes a forwarding table for forwarding, by the original AP, the received data of the user station to the new AP and a forwarding table for forwarding, by the original AP, the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to the external network station; the configuration comprises a transfer-in table used for the new AP to transfer the user data transferred by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a second transfer table used for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the transfer-in backtracking table of the original AP.
Example two
In order to expand the range of the switchable cell, in the method provided in the second embodiment of the present invention, it may be considered that a plurality of user managers are added in a common external network, each user manager is connected to a plurality of APs, and a user information summarizing server is further added in the common external network, and the user information summarizing server is connected to each user manager.
In the method for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network provided in the second embodiment of the present invention, in order to set a multi-user manager to implement cross-cell handover, in this case, a user information summarizing server is further set to connect to each user manager, so as to implement unified information management. The flow is shown in fig. 5, and comprises the following steps:
step S201: when the user station accesses the new cell, the new AP sends the user information of the user station to the user manager.
In this embodiment, a plurality of user managers are provided, each of which can manage a plurality of APs, and when an AP managed by the user manager has a user station switched to access, the AP managed by the user manager is used as a new AP to obtain a user station name reported by the user station and allocate an IP address to the user station; and sending the acquired user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site to the affiliated user manager as user information.
Step S202: and the user manager determines and stores the position information of the user site according to the user information.
Referring to step S102 specifically, details are not repeated here.
Step S203: and the user manager reports the position information of the user site to the user information summarizing server for storage.
Because a plurality of user managers are arranged, a user information summarizing server is further arranged and connected with each user manager for storing the position information of the user sites reported by each user manager.
Step S204: and when the user manager determines that the user station is a cross-cell switching station according to the judgment result of the user information summarizing server, the user manager sends a change signaling to the original AP to inform the original AP to update and configure a first forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station.
Referring specifically to step S102, the same processing is not described here again. In this step, the user manager may determine whether the user site is a site for cross-cell handover, or the user information summarizing server may determine whether the user site is a site for cross-cell handover, and notify the user manager. Especially, for the case that the AP before the user site is switched does not belong to the AP managed by the user manager, it is necessary to obtain the relevant information from the user information summarizing server to determine whether the user site is a site switched across cells.
Specifically, the user manager searches a locally stored user station position information list according to the user station name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; if the position information table item matched with the user station name cannot be searched, sending a switching judgment signaling to a user information summarizing server; the user information summarizing server searches a locally stored user station position information list according to the switching judging signaling, and if a position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, the user station is determined to be a cross-cell switching station, and a user manager is informed; otherwise, determining the user station as the station of the new access network.
In the step, whether corresponding items of the user site exist in other user managers or not is searched by sending a switching judgment signaling to a user information summarizing server; if yes, extracting original position information of the user through a user information summarizing server, and sending a change signaling to the original AP; if not, the description is a new user.
Step S205: and the user manager sends a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP of configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station.
Referring to step S104 specifically, details are not repeated here.
Based on the same inventive concept, a second embodiment of the present invention further provides a system for implementing cross-cell handover in a wireless network, where the structure of the system is shown in fig. 6, and the system includes: a user information summary server 604, a user manager 602, an Access Point (AP)603, and a user station 604. There may be a plurality of user managers 602 and APs 603, each AP603 may access a plurality of user stations 604 in a cell covered by the AP, and only the reference numerals of one user manager 602, one AP202 and one user station 203 are schematically shown in fig. 6.
The AP603 serves as a new AP, and is configured to send the user information of the user station 604 to the belonging user manager 602 when the user station 604 accesses the cell; and configure a second forwarding table for forwarding data of subscriber site 604 according to the received change signaling sent by subscriber manager 602.
AP603 is configured to update, as an original AP, a first forwarding table configured to forward data of subscriber station 604 according to the received change signaling sent by subscriber manager 602.
A user manager 602, configured to determine and store location information of the user site 604 according to the user information; when the user station 604 is determined to be a cross-cell switching station, sending a change signaling to the original AP, and notifying the original AP to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station 604; and send configuration signaling to the new AP informing the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding data of the subscriber station 604.
The user information summarizing server 601 is configured to receive and store the location information of the user site 604 reported by the user manager 602, and determine whether the user site 604 is a site for cross-cell handover according to a request of the user manager 602.
Preferably, the AP603 is used as a new AP, and is specifically configured to obtain a user station name reported by the user station 604 and allocate an IP address to the user station 604; the acquired user site name and the IP address assigned to the user site are sent to the user manager 602 to which the user site belongs, as user information.
Preferably, the user manager 602 is specifically configured to obtain a name of a user site and an IP address assigned to the user site according to the received user information; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; and establishing a triple group of the user station by using the name of the user station, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP, and storing the triple group.
Preferably, the user manager 602 is specifically configured to search a locally stored user station location information list according to a user station name; if the location information table entry matching the user station name is searched, determining the user station 604 as a cross-cell handover station; if the position information table item matched with the user station name cannot be searched, a switching judgment signaling is sent to the user information summarizing server 601; if the user information summarizing server 601 searches a locally stored user station location information list according to the switching judgment signaling, and searches a location information table item matched with the user station name, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, the user station 604 is determined to be a station of the new access network.
Correspondingly, the user information summarizing server 601 is specifically configured to search a locally stored user station location information list according to the switching discrimination signaling, determine that the user station is a cross-cell switching station if a location information entry matching the user station name is searched, and notify the user manager 602;
as shown in fig. 7, the user information aggregating server 601 includes: an information receiving module 701, an information storing module 702, and a handover determining module 703.
An information receiving module 701, configured to receive location information of a user station reported by a user manager.
And an information storage module 702 for storing the received location information of the user station.
A handover determining module 703, configured to determine whether the user station is a cross-cell handover station according to a request of the user manager.
Preferably, the receiving module 701 is configured to receive a handover discrimination signaling sent by a user manager.
Correspondingly, the switching determining module 703 is specifically configured to search a locally stored user station location information list according to the received switching discrimination signaling, determine that the user station is a cross-cell switching station if a location information entry matching the user station name is searched, and notify the user manager;
the structure of the user manager 602 is shown in fig. 8, and includes: a first receiving module 801, an information processing module 802, an information storage module 803, a switching discrimination module 804 and a first sending module 805.
A first receiving module 801, configured to receive user information of a user station sent by a new AP when the user station accesses a new cell.
An information processing module 802, configured to determine location information of the user station according to the user information.
An information storage module 803, configured to store location information of the user station.
A switching determining module 804, configured to determine whether the user site is a site for cross-cell switching, or determine whether the user site is a site for cross-cell switching according to a determination result of the user information summarizing server.
A first sending module 805, configured to report location information of the user station to a user information summary server for storage, and send a change signaling to an original AP when the user station is determined to be a cross-cell handover station, to notify the original AP to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station; and sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station.
Preferably, the information processing module 802 is specifically configured to obtain a name of a user site and an IP address allocated to the user site according to the received user information; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; and establishing a triple group of the user station by using the name of the user station, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP.
Preferably, the switching determining module 804 is specifically configured to search a locally stored subscriber station location information list according to a subscriber station name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; if the position information table item matched with the user station name cannot be searched, sending a switching judgment signaling to a user information summarizing server; if the user information summarizing server searches a locally stored user station position information list according to the switching judging signaling, and a position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, determining the user station as the station of the new access network.
The structure of the AP603 is shown in fig. 9, and includes: a second sending module 901, a second receiving module 902 and a first configuring module 903.
A second sending module 901, configured to send the user information of the user station to the affiliated user manager when the user station accesses the cell.
A second receiving module 902, configured to receive a change signaling sent by a user manager; and/or receiving configuration signaling sent by a user manager.
A first configuration module 903, configured to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station according to the received change signaling; and/or configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station according to the received configuration signaling.
Preferably, the second sending module 901 is specifically configured to obtain a name of a user station reported by the user station, and allocate an IP address to the user station; and sending the acquired user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site to the affiliated user manager as user information.
Preferably, the first configuration module 903 is specifically configured to configure a first forwarding table including a forwarding table for forwarding, by the original AP, the received data of the user station to the new AP and a forwarding table for forwarding, by the original AP, the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to the external network station; the configuration comprises a transfer-in table used for the new AP to transfer the user data transferred by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a second transfer table used for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the transfer-in backtracking table of the original AP.
In the above-mentioned embodiment, the connection relationship between the common external network, the AP of the wireless network cell, and the user manager shown in fig. 2 in the first embodiment and the connection relationship between the common external network, the AP of the wireless network cell, the user manager, and the user information summarizing server shown in fig. 6 in the second embodiment, a thick line segment between the AP and the common external network represents a connection for transmitting data, and a thin line segment between the AP and the user manager represents a connection for transmitting signaling. It should be noted that the connections shown in fig. 2 and 6 refer to logical connections, not physical connections, such as: the AP's connection to data connections in a common external network and to the signalling connection of the user manager can be implemented with the same physical connection.
The following is further illustrated for the first and second embodiments:
in the method of the present invention, a system including a user manager, a user information aggregating server, and a connection therebetween is referred to as a user management system. And a system formed by a common external network and all wireless network cells is called a wireless network system.
In the method of the invention, a user manager is used for managing the latest position information of a user station and sending the updated position information to an original AP under the condition that the user station has access to a user management system, wherein the position information of a user is two items of information, namely the information of the AP to which the user station belongs and the IP address of the user station under the current AP, and the station in a wireless network system can uniquely determine the position of the user station through the two items of information. The user manager uniformly registers the location information of the user through the user location information list shown in table 1. Each subscriber manager maintains location information for subscriber stations subordinate to all its subordinate APs.
TABLE 1
The user information summarizing server is provided with a user position information summarizing table which is used for summarizing the position information of all user stations in the wireless network. The structure of the user location information summary table is shown in table 2, and compared with the user location information list, the user location information summary table has an additional IP address of the user manager to which the AP of the user site belongs, that is, the IP address of the user manager to which the user site belongs.
TABLE 2
Generally, the user site names in the user location information list and the user location information summary table are generated by a user management system by uniformly compiling user sites in advance, and each user site name uniquely corresponds to one user site. Each user station knows the name of the user station in the wireless network system before accessing the wireless network system.
Under the condition of only preparing to realize cross-cell switching in the same type of wireless network, all wireless network cells are the same type of wireless network cells, namely, when a user station enters the cells, the user station accesses the AP of the wireless network cells by the same network card. In such a cross-cell switching of the user station in the same wireless network, the MAC address of the wireless network card of the user station can be used as the name of the user station, and the user management system does not need to uniformly compile the user stations.
In the above method of the present invention, there is a wireless routing table in the AP of each wireless network cell, and the specific format is shown in table 3.
TABLE 3
| IP address of user site | MAC address of user station |
When a user station accesses a certain wireless network cell AP, the user station informs the AP of the name of the user station, and under the condition that cross-cell switching of the same wireless network is only realized, the AP can directly obtain the name of the user station by using the MAC address of the wireless network card as the name of the user station. Then, the AP of the wireless network cell encapsulates the information of the user station in an IP packet and sends the IP packet to the user manager to which the AP belongs, and the user information sent by the AP includes: the name of the user site, the IP address (global address or local address) newly assigned to the user site. After receiving the IP packet of the AP, the user manager may extract the source IP address of the IP packet to obtain the global IP address of the AP to which the user station belongs, in addition to obtaining the user station name of the user station and the IP address newly allocated to the user station, thereby obtaining the triplet of the user station information.
The user manager searches in the user position information list by taking the user site name as a matching item, and if a corresponding item is searched, the user site is indicated to have cross-cell switching under the same user manager; if the corresponding table entry is not searched, it sends signaling to the user information summarizing server, and searches the user information in it, if it is not yet searched, it indicates that the user station is newly accessed to the whole wireless network system, and the user manager only registers the information of the new user in its user information list and reports it to the user information summarizing server, but does not do other processing.
After the user management server searches the user information in the user position information list of the user management server or the user information summary list of the user information summary server, the user management server extracts the original position information of the user, namely: the global IP address of the original AP of the user station and the IP address of the user station in the original cell. Then, the user manager sends signaling to the original AP (if the original AP belongs to another user manager, the current user manager sends a change signaling to the original user manager, and the original user manager sends a corresponding signaling to the original AP), including the following information: the IP address of the user site in the original cell; and if the new cell is the cell configured with the global IP address, the address is the global IP address of the user station in the new cell, and if the new cell is the cell configured with the local IP address, the address is the global IP address of the new AP.
After the original AP receives the signaling, the original AP finds the routing table item of the user station in the cell from the wireless routing table (namely, the IP address: MAC address comparison table) of the user station in the original cell by using the IP address of the user station in the original cell. The original AP configures a virtual roll-out port number for the switching forwarding connection, and replaces the original MAC address with the virtual roll-out port number in the wireless routing table. In the method of the invention, the AP of the wireless network cell can distinguish the MAC address and the virtual roll-out port number in the wireless routing table, when the routing table indicates to turn the corresponding IP packet to a certain virtual roll-out port number, the AP searches the virtual roll-out port number in the roll-out table of the AP and forwards the data packet according to the corresponding global IP address. After the original AP is configured with the virtual roll-out port number, a table entry is added in a roll-out list of the original AP by the virtual roll-out port number and the roll-out global IP address binary group, and then all IP packets (in a cell configured with a local IP address, the IP packets are IP packets processed by an NAT protocol) to be sent to the corresponding MAC address are transferred to the table entry of the roll-out list corresponding to the virtual roll-out port number and are forwarded according to the global IP address shown by the table entry.
And then, the original AP adds a corresponding table entry on the backtracking table of the roll-out table by using the forwarded global IP address and the IP address binary group of the user station in the original cell, thereby completing the configuration of the backtracking table.
And under the condition that the user site is switched across the user managers, the original user manager deletes the corresponding user information table entry after finishing the configuration of the original AP transfer-out table. After that, the user information summarizing server also sends an inquiry signaling to the user information summarizing server again to confirm whether the user table entry is deleted or not, and if the corresponding table entry is not deleted in response to a certain fault, the table entry is forcibly deleted.
If the new AP cell is the cell configured with the local IP address, a transfer-in table exists in the new AP. In this case, the user manager must send signaling to the new AP to complete the configuration of the forwarding table. Specifically, in a response frame to the new AP, the user manager sends two items of information, namely, the global IP address of the original AP of the user site and the IP address of the user site in the original cell, to the new AP, and the new AP adds a new entry in the transfer table according to the triple of the global IP address of the original AP, the IP address of the user site in the original cell and the IP address of the user site in the new cell, thereby completing configuration of the transfer table.
And then, the new AP adds entries in the backtracking table of the transfer-in table by using the triple group of the IP address of the user site in the new cell, the IP address of the user site in the original cell and the global IP address of the original AP, thereby completing the configuration of the backtracking table.
When the user manager searches the original position information of the user site, it will update or add the position information of the user in its own user information list and report the information to the user information summarizing server, which updates the corresponding user information list item in its own user information list and compares the IP address of the user manager, if the IP address of the new user manager is not consistent with the IP address of the original user manager, the user information summarizing server sends signaling to the original user manager to determine whether it has deleted the corresponding user information list item, if not, it is required to delete the corresponding list item.
After the user station leaves a cell covered by the original AP and enters a cell covered by a new AP, the user manager completes configuration of a wireless routing table, a roll-out table and a backtracking table of the roll-out table in the original AP, and the user manager completes configuration of a roll-in table and a backtracking table of the roll-in table in the new AP under the condition that the new cell is the cell configured with a local IP address, the user station is connected with an external network station through data transmission of the IP address in the original cell until the data transmission is completed.
EXAMPLE III
After entering the new cell from the original cell, the user station can transmit data through the new cell, but in order to ensure seamless switching and continuous data transmission, the user station needs to process the data transmitted by the original cell, so that the data can be smoothly transmitted to the user station, and the reply data of the user station is transmitted to the sender. Based on the above, the embodiment of the invention also provides a data transmission method after the cell switching of the user site.
The flow of the data transmission method for cross-cell handover in a wireless network provided by the third embodiment of the present invention is shown in fig. 10, and after a user station is handed over from an original cell to a new cell, the method includes the following steps:
step S301: and the original AP receives the data packet sent to the user station by other stations.
After the user station is switched from the original cell to the new cell, due to the communication connection established between the original cell and other stations, other stations can also send data packets to the user station through the original cell AP, but at this time, the user station has left the original cell, so that the original AP is required to forward the data packets to maintain the continuity of communication.
Step S302: and the original AP determines the address of the new AP to which the user station is switched, and forwards the data packet to the new AP.
When the first forwarding table comprises a forwarding table and a forwarding backtracking table, the address of the new AP is determined according to the forwarding table, so that the new AP to which the received data packet needs to be forwarded is determined.
And the original AP determines the global IP address of the new AP according to the transfer-out table, takes the data packet as an inner IP packet, takes the IP address of the original AP as the source IP address of the outer IP packet and takes the global IP address of the new AP as the target IP address of the outer IP packet, encapsulates the source IP address and the target IP address into a first transfer data packet, and transfers the first transfer data packet to the new AP.
Step S302: and the new AP analyzes the received data packet to acquire the address information of the user station.
And after receiving the first forwarding data packet, the new AP analyzes the first forwarding data packet, analyzes the data packet contained in the first forwarding data packet and sent to the user station, and acquires the address information of the user station so as to send the address information to the user station. And the new AP determines the address information of the user station to be forwarded according to the first forwarding table, thereby determining the user station to which the data packet is forwarded.
Specifically, after receiving the first forwarding data packet, the new AP obtains a data packet of the inner IP packet from the first forwarding data packet; and determining the IP address of the user site in the cell according to the transfer table.
Step S304: and the new AP sends the data packet to the user station according to the analyzed address information.
And the new AP takes the data packet as an inner IP packet, takes the IP address of the new AP as a source IP address and takes the IP address of the new AP in the cell as a target IP address, encapsulates the IP address into a second forwarding data packet and sends the second forwarding data packet to the user station.
Step S305: and the new AP receives a reply data packet returned by the user station.
In the step, the user station encapsulates the reply data packet into a reply forwarding data packet by taking the reply data packet as an inner IP packet, the IP address of the user station as a source IP address and the IP address of the new AP as a target IP address, and sends the reply forwarding data packet to the new AP. And when the new AP receives the reply forwarding data packet, analyzing the reply forwarding data packet to obtain the reply data packet contained in the reply forwarding data packet.
After receiving the second forwarding data packet, the user station may obtain the data packet therein, and reply information to other stations that send datagrams, where the replied data packet is transferred to the original AP through the new AP and then transferred to the corresponding other stations by the original AP, and the replied data packet in replying information may be encapsulated into a reply frame form.
After the user station receives the second forwarding data packet, decapsulating the data packet to obtain an IP packet therein, namely, a data packet sent by other stations; and comparing the target address of the extracted IP packet with the IP address of the IP packet in the original cell, if the target address of the extracted IP packet is the same as the IP address of the IP packet in the original cell, indicating that the data packet is a data packet forwarded after switching, and saving the source address of the received data packet as the IP address of the next hop station when the source address of the data packet is used for sending the complex data packet back to other stations, wherein the IP address can also be called the backtracking IP address of the user station.
Step S306: and the new AP determines the original AP address before the user station is switched, and sends the received reply data packet to the original AP.
The new AP determines the global IP address of the original AP according to the backtracking table of the transferred table; and the new AP packages the reply data packet into a third forwarding data packet by taking the IP address of the new AP as a source IP address and the global IP address of the original AP as a target IP address, and sends the third forwarding data packet to the original AP.
Step S307: and the original AP receives the reply data packet sent by the new AP.
Step S308: and the original AP analyzes the received reply data packet and sends the reply data packet to the corresponding other sites.
After receiving the third forwarding data packet, the original AP acquires a reply data packet of the inner IP packet from the third forwarding data packet; and when the analyzed reply data packet from the user site of the external cell is determined according to the backtracking table of the roll-out table, the analyzed reply data packet is sent to other corresponding sites.
Based on the same inventive concept, a third embodiment of the present invention further provides a data transmission system for cross-cell handover in a wireless network, where the structure of the data transmission system is shown in fig. 11, and the data transmission system includes: an Access Point (AP)111 and a user station 112.
The AP111, serving as an original AP, is configured to determine a new AP address to which the user station 112 is switched and forward the data packet to the new AP when the user station 112 receives a data packet sent to the user station 112 by another station after switching from the local cell to the new cell; and when receiving the reply data packet sent by the new AP, analyzing the reply data packet and sending the reply data packet to the corresponding other sites.
The AP111, as a new AP, is configured to parse the data packet, obtain address information of the user station 112, and send the data packet to the user station 112 according to the address information; and when receiving a reply data packet returned by the user station 112, determining the original AP address before the user station 112 switches, and sending the reply data packet to the original AP.
And the user station 112 is configured to receive the data packet sent by the new AP and send the data packet back to the new AP.
Preferably, the AP111 is used as the original AP, and is specifically configured to determine a global IP address of the new AP according to the roll-out table, encapsulate the data packet as an inner IP packet, the IP address of the AP as a source IP address of an outer IP packet, and the global IP address of the new AP as a target IP address of the outer IP packet into a first forwarding data packet, and forward the first forwarding data packet to the new AP.
Preferably, the AP111 is used as a new AP, and is specifically configured to obtain a data packet of an inner IP packet from a first forwarding data packet after receiving the first forwarding data packet; determining the IP address of the user station 112 in the cell according to the transfer table; and encapsulating the data packet serving as an inner IP packet into a second forwarding data packet by taking the IP address of the data packet as a source IP address and the IP address of the user station in the cell serving as a target IP address, and sending the second forwarding data packet to the user station 112.
Preferably, the AP111 is used as a new AP, and is specifically configured to determine a global IP address of an original AP according to a backtracking table transferred to the table; and packaging a third forwarding data packet by taking the reply data packet as an inner IP packet, taking the IP address of the reply data packet as a source IP address and the global IP address of the original AP as a target IP address, and sending the third forwarding data packet to the original AP.
Preferably, the AP111 is used as an original AP, and is specifically configured to obtain a reply data packet of the inner IP packet from the third forwarding data packet after receiving the third forwarding data packet; and when the analyzed reply data packet from the user site of the external cell is determined according to the backtracking table of the roll-out table, the analyzed reply data packet is sent to other corresponding sites.
As shown in fig. 12, the AP111 includes: a first forwarding module 121, a second forwarding module 122, a third forwarding module 123 and a fourth forwarding module 124.
The first forwarding module 121 is configured to, when receiving a data packet sent by another station to a user station that has been switched to a new cell, determine a new AP address to which the user station is switched, and forward the data packet to the new AP.
The second forwarding module 122 is configured to, when receiving a data packet sent by the original AP to the user station that has been switched to the current cell, parse the data packet, obtain address information of the user station, and send the data packet to the user station according to the address information.
The third forwarding module 123 is configured to, when receiving a reply data packet returned by a user station that has been switched to the current cell, determine an original AP address before the user station is switched, and send the reply data packet to the original AP.
The fourth forwarding module 124 is configured to, when receiving a reply data packet sent by a user station that has been switched to a new cell through a new AP, parse the reply data packet, and send the reply data packet to another corresponding station.
Preferably, the first forwarding module 121 is specifically configured to determine a global IP address of the new AP according to the forwarding table, encapsulate the data packet as an inner IP packet, the IP address of the first forwarding module as a source IP address of an outer IP packet, and the global IP address of the new AP as a target IP address of the outer IP packet, and forward the first forwarding data packet to the new AP.
Preferably, the second forwarding module 122 is specifically configured to, after receiving the first forwarding data packet, obtain a data packet of the inner IP packet from the first forwarding data packet; determining the IP address of the user site in the cell according to the transfer table; and encapsulating the data packet serving as an inner IP packet into a second forwarding data packet by taking the IP address of the data packet as a source IP address and the IP address of the user station in the cell serving as a target IP address, and sending the second forwarding data packet to the user station.
Preferably, the third forwarding module 123 is specifically configured to determine the global IP address of the original AP according to the backtracking table of the transfer-to table; and packaging the reply data packet serving as an inner IP packet into a third forwarding data packet by taking the IP address of the reply data packet as a source IP address and the global IP address of the original AP as a target IP address, and sending the third forwarding data packet to the original AP.
Preferably, the fourth forwarding module 124 is specifically configured to, after receiving the third forwarding data packet, obtain a reply data packet of the inner IP packet from the third forwarding data packet; and when the analyzed reply data packet from the user site of the external cell is determined according to the backtracking table of the roll-out table, the analyzed reply data packet is sent to other corresponding sites.
The structure of the user site 112 is shown in fig. 13, and includes: a data transmitting module 131 and a data receiving module 132.
A data sending module 131, configured to receive a data packet sent by the new AP.
A data receiving module 132, configured to send the complex data packet back to the new AP.
The data receiving module 132 is specifically configured to encapsulate the reply data packet as an inner IP packet, use the IP address of the data receiving module as a source IP address, and use the IP address of the new AP as a destination IP address to form a reply forwarding data packet, and send the reply forwarding data packet to the new AP.
With respect to the methods of the first, second, and third embodiments, some specific configurations and implementation processes are described below.
Optionally, in the method of the present invention, the connection between the user manager and the AP is a connection that guarantees a bandwidth, and in this case, signaling information between the user manager and the AP can be quickly transmitted, so that when a user station is switched between different APs under the same user manager, real-time switching of user data can be supported.
Optionally, in the method of the present invention, the connection between the user information summarizing server and the user manager is a connection that guarantees a bandwidth, and in this case, the signaling information between the user information summarizing server and the user manager can be quickly transmitted, so that when a user site is switched between two APs under different user managers, real-time switching of user data can be supported.
The connection of the guaranteed bandwidth refers to: when a station needs to send data, the station can send the data to the corresponding station through the corresponding connection, and the data cannot be transmitted in time due to network congestion. In the method provided by the invention, no matter between the user manager and the AP or between the user information summarizing server and the user manager, the transmitted data is only signaling data with small data volume, and if broadband optical fiber and other connections are configured in an external network, the connection of bandwidth is ensured to be easily realized. In addition, this can be achieved by some protocols that reserve bandwidth, such as: bandwidth can be reserved for stations along a connection line by Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP), so as to ensure connection of bandwidth. Because the bandwidth required for transmitting the signaling between the user manager and the AP or between the user information summarizing server and the user manager is limited, the bandwidth is reserved for the connections through the bandwidth reservation protocol, and the influence on other data transmission is small.
In the method provided by the present invention, for each AP in the wireless network system, in order to implement the above-mentioned data forwarding after cell switching access, a forwarding table and a backtracking table (forwarding backtracking table) of the forwarding table are added in its routing component. The roll-out table is used to indicate to the AP: for a user station which has left the local cell and accessed to a new cell, after receiving a data packet sent to the user station, the AP how to forward the data packet. The backtracking table of the roll-out table is used to indicate to the AP: for a user station that has left the local cell and accessed to the new cell, how to forward the reply frame from the user station of the external cell to the station in the external network after the AP receives the reply frame.
The format of the roll-out table added to the AP is shown in table 4. The virtual roll-out port number is compiled and maintained by the AP, and corresponds to the connection between the AP and the user station entering a new cell when the user station is switched across the cells. The diverted global IP address in table 4 means: if the newly accessed cell of the user site is the cell configured with the global IP address, the IP address is the global IP address newly allocated by the user, otherwise, the IP address is the global IP address of the newly accessed AP.
TABLE 4
| Virtual roll-out port number | Diverted Global IP Address |
The format of the trace-back table of the roll-out table added to the AP is shown in table 5 below. Here, the "rolled out global IP address" is also the "diverted global IP address" in table 4.
TABLE 5
For the AP of the wireless network cell configured with the local IP address, a transfer-in table and a backtracking table (transfer-in backtracking table) of the transfer-in table are added in the routing component. After the user station is switched to a new AP, when the new cell is a cell configured with a local IP address, the original AP forwards a data packet sent to the user station by an external network station to the new AP, and a transfer-in table additionally arranged in the AP has the following functions: instructing the current AP to which subscriber station to forward these packets. The backtracking table of the transfer-in table is used for: when the subscriber station sends a reply frame back to a station in the external network, it instructs the current AP to which AP the reply frame is forwarded.
The format of the transfer-in table in the AP of the wireless network cell configured with the local IP address is shown in table 6.
TABLE 6
The format of the look-back table of the roll-in table in the AP of the wireless network cell configured with the local IP address is shown in table 7.
TABLE 7
For a wireless network cell with a part of users configured with global IP addresses and a part of users configured with local IP addresses, the AP still needs to maintain the above-mentioned forwarding table and the backtracking table of the forwarding table, but only needs to use the forwarding table and the backtracking table thereof for newly accessed user sites configured with local IP addresses.
Comparing table 6 and table 7, it can be seen that, for each user site, the contents of its triplet entry are the same in both tables, which differ primarily in the match field and the find field in each triplet entry. In table 6, the first entry and the second entry are matching fields, and the AP finds the corresponding entry according to the matching of the two fields, thereby finding the content of the third field. In table 7, the first and second entries are also matching fields, and the third entry is what the AP needs to find. Therefore, in practical use, only one table merging the branch-in and backtracking functions, for example, the first branch-in table, may be set, but the table may be used as the branch-in table or the backtracking table of the branch-in table respectively by different definitions of the matching field and the finding field. Such as: table 6 may be used as a table where the first two fields are match fields and the third field is a find field when used as a transfer-in table; and when it is used as a trace-back table into the table, the latter two fields are match fields and the first field is a find field.
In the method of the invention, when the AP of the wireless network cell sends the data packet to the next hop station according to the roll-out table and the roll-in table, the data packet is encapsulated in an IP in IP (IP nesting) mode and then sent to the next hop station, namely: and the data packet sent to the user station by the external network station is an internal IP packet, and the data packet is sent by taking the IP address of the data packet as the source IP address of the external IP packet and the IP address of the next hop station as the target IP address. Specifically, when the AP of the wireless network cell sends a switching data packet according to the roll-out table, the source address and the destination address of the external IP packet are the global IP address of the AP and the global IP address of the next hop station indicated by the roll-out table, respectively; when the AP of the wireless network cell configured with the local IP address sends a switching data packet according to the switching-in table, the source address and the target address of the external IP packet are the local IP address of the AP and the local IP address of the user station indicated by the switching-in table respectively.
In the method, when the AP of the wireless network cell sends the data packet to the next hop station according to the roll-out table and the roll-in table, the data packet is encapsulated in an IP in IP mode, the next hop station decapsulates the IP in IP after receiving the IP packet to obtain the switching data packet sent to the user station, and then the next step of processing is carried out.
In the method of the invention, after a user site receives an IP in IP packet and decapsulates the IP packet to obtain the IP packet therein, the user site compares the target address of the extracted IP in packet with the IP address of the user site in the original cell, if the target address of the extracted IP in packet is the same as the IP address of the user site, the user site indicates that the data packet is a switching data packet, the user site saves the source address of the IP in IP packet as the IP address of the next hop site when the user site sends a reply frame back to the external site, and the IP address can also be called the backtracking IP address of the user site.
In the method of the invention, when the user station sends the data packet to the next hop station according to the backtracking IP address and the AP of the wireless network cell configured with the local IP address and the backtracking table of the transfer-in table, the data packet is encapsulated in an IP in IP mode and then sent to the next hop station, namely: and taking a data packet sent by the user site to the external network site as an internal IP packet, and sending the data packet by taking the IP address of the user site as the source IP address of the external IP packet and the IP address of the next hop site as a target IP address. Specifically, when the user site sends a data packet according to the backtracking IP address, the source address and the target address of the external IP packet are the IP address and the backtracking IP address of the user site respectively; when the AP of the wireless network cell configured with the local IP address sends a switching data packet according to the backtracking table of the switching-in table, the source address and the target address of the external IP packet are the global IP address of the AP and the global IP address of the next hop station (namely the global IP address of the original AP) indicated by the backtracking table of the switching-in table respectively.
In the method provided by the invention, when a user station sends a data packet to a next hop station according to a backtracking address of the user station and a backtracking table of a transfer table by an AP of a wireless network cell configured with a local IP address, the data packet is encapsulated in an IP in IP mode, the next hop station decapsulates the IP in IP after receiving the IP packet to obtain a switching data packet sent to an external network station (other stations) by the user station, and then the next step of processing is carried out.
In the data transmission between the AP and the user station, when it receives a data packet encapsulated in an IP in IP manner, it considers that the IP packet carries a handover forwarding packet, and after matching successfully with a matching entry in the forwarding table (for the AP) or matching successfully between the target address of the inner IP packet and the IP address of its own original cell (for the user station), it confirms that it is a handover data packet, and then performs further processing.
The following two cases specifically provide a switching process for switching the current data stream of the user station from the original cell to the new cell.
The first condition is as follows: the new AP cell is a cell configured with a global IP address
At this time, the field of the "diverted global IP address" of the table entry related to the current user station in the original AP roll-out table configures the global IP address of the user station in the new cell. When a data packet sent to a user station by an external network station is sent to an original AP, the original AP obtains an IP address of the user station according to a source IP address of the data packet (for a cell configured with a local IP address, the original AP obtains the IP address of the user station through an NAT protocol at first), and then the IP address is used as a matching field to search in a wireless routing table, so that a virtual transfer-out port number is obtained; the AP searches the global IP address of the user station in the transfer table by the virtual transfer port number, and at the moment, the original AP packages the IP packet which is sent to the user station through the wireless MAC address in an IP in IP mode and directly sends the IP packet to the user station.
After the user station receives the IP packet encapsulated in the IP in IP mode in the new cell, considering that the IP packet may be a data packet for switching forwarding, the IP in IP decapsulation is carried out in the new cell, and the user station confirms that the IP packet is a switching forwarding packet by comparing that the target IP address of the inner IP packet is the IP address of the original cell, and places the switching forwarding packet into the original data stream for processing to obtain corresponding data information. Meanwhile, the user site also uses the obtained source IP address of the external IP packet as a backtracking IP address for sending a reply frame back to the external network site according to the original connection.
In the above data transmission process, if the user station wants to send a reply frame back to the external network station, it will use the same way as sending the reply frame back when it is in the original cell to encapsulate the frame, i.e. the source IP address of the reply frame is the IP address of the user station in the original cell, the destination IP address is the IP address of the external network station, then it uses the global IP address of itself in the new cell as the source address of the external IP packet, uses the backtracking IP address as the destination address of the external IP packet, encapsulates the reply frame by IP in IP, and sends it to the original AP.
After receiving the IP packet, the original AP performs IP in IP decapsulation, considering that this may be a reply frame, and it uses the source address of the outer IP packet and the source address of the inner IP packet as matching fields, searches for corresponding entries in the trace-back table of the roll-out table, if the search is successful, it indicates that this is a reply frame, and then the original AP will send the reply frame back to the external network station in the same manner as when the user station is still in the original cell (if the original cell is a cell configured with a local IP address, the original AP needs to convert the source IP address of the reply frame by using the NAT protocol first).
Alternatively, if the IP address of the user station in the original cell is also the global IP address, it may also send a reply frame with the source address of its own IP address in the original cell directly to the external network station.
Thus, the flow of user data switching is completed.
Case two: the new AP cell is a cell configured with a local IP address
At this time, the "diverted global IP address" field of the table entry related to the current user station in the original AP roll-out table configures the global IP address of the AP of the new cell. When a data packet sent to a user station by an external network station is sent to an original AP, the original AP obtains an IP address of the user station according to a source IP address of the data packet (for a cell configured with a local IP address, the original AP obtains the IP address of the user station through an NAT protocol at first), and then the IP address is used as a matching field to search in a wireless routing table, so that a virtual transfer-out port number is obtained; the AP searches the global IP address of the new AP in the roll-out table by the virtual roll-out port number, and at the moment, the original AP packages the IP data packet which is sent to the user station by the wireless MAC address in an IP in-IP mode and directly sends the IP data packet to the new AP.
And after receiving the IP in IP packet, the new AP carries out IP in IP decapsulation, extracts the source IP address of the outer IP packet and the target IP address of the inner IP packet, searches in a transfer-in table of the new AP as a matching field, finds out a corresponding table entry and obtains the local IP address of the user site. And the new AP encapsulates the switching data packet by IP in IP by taking the local IP address of the new AP as the source address of the outer IP packet and taking the local IP address of the user site as the target address of the outer IP packet, and sends the IP packet to the user site.
After the user site receives the IP packet encapsulated in the mode of IP in the new cell, considering that the IP packet may be a data packet for switching forwarding, the IP in IP is decapsulated in the new cell, and the user site confirms that the IP packet is a switching forwarding packet by comparing that the target IP address of the inner IP packet is the IP address of the original cell, and places the switching forwarding packet into the original data stream for processing to obtain corresponding data information. Meanwhile, the user site also uses the obtained source IP address of the external IP packet as a backtracking IP address for sending a reply frame back to the external network site according to the original connection.
In the above data transmission process, if the user station wants to send a reply frame back to the external network station, it will encapsulate the frame in the same way as sending the reply frame back when it is in the original cell, i.e. the source IP address of the reply frame is the IP address of the user station in the original cell, the destination IP address is the IP address of the external network station, then it encapsulates the reply frame in the way of IP in IP with its own local IP address in the new cell as the source address of the external IP packet, with the backtracking IP address as the destination address of the external IP packet, and sends it to the new AP. And the new AP carries out IP in IP decapsulation on the data packet, and takes the possible reply frame as consideration, the new AP searches corresponding table items in a backtracking table of a switching-in table by taking the source address of the outer IP packet and the source address of the inner IP packet as matching fields to obtain the global IP address of the original AP. And then, the new AP encapsulates the reply frame by using the global IP address of the new AP as the source address of the outer IP packet, using the global IP address of the original AP as the target address of the outer IP packet and using an IP in IP mode, and sends the reply frame to the original AP.
The original AP decapsulates the data packet and then performs IP in IP decapsulation, considering that this may be a reply frame, which uses the source address of the outer IP packet and the source address of the inner IP packet as matching fields, searches for a corresponding entry in the trace-back table of the roll-out table, if the search is successful, it indicates that this is a reply frame, and then the original AP sends the reply frame back to the external network site in the same manner as when the user site is still in the original cell (if the original cell is a cell configured with a local IP address, the original AP needs to convert the source IP address of the reply frame by using the NAT protocol first).
Thus, the flow of user data switching is completed.
In the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, when the cross-cell switching of the user station is realized in the wireless network, the user manager is additionally arranged in the common external network connected with the wireless network cells, the user manager is connected to the APs of the plurality of wireless network cells, and the user manager manages the position information of the user station; a forwarding table related to data switching is additionally arranged in a routing component of an AP of a wireless network cell; and the data of the user station is switched from the original cell to the new cell by the configuration of the forwarding table in the AP by the user manager. Therefore, communication can not be interrupted and data can not be lost when the user site moves to cause cell switching, data packets sent to the user site by other sites can be timely and accurately sent to the user site, and the data packets replied by the user site are sent to other sites.
Unless specifically stated otherwise, terms such as processing, computing, calculating, determining, displaying, or the like, may refer to an action and/or process of one or more processing or computing systems or similar devices that manipulates and transforms data represented as physical (e.g., electronic) quantities within the processing system's registers and memories into other data similarly represented as physical quantities within the processing system's memories, registers or other such information storage, transmission or display devices. Information and signals may be represented using any of a variety of different technologies and techniques. For example, data, instructions, commands, information, signals, bits, symbols, and chips that may be referenced throughout the above description may be represented by voltages, currents, electromagnetic waves, magnetic fields or particles, optical fields or particles, or any combination thereof.
It should be understood that the specific order or hierarchy of steps in the processes disclosed is an example of exemplary approaches. Based upon design preferences, it is understood that the specific order or hierarchy of steps in the processes may be rearranged without departing from the scope of the present disclosure. The accompanying method claims present elements of the various steps in a sample order, and are not intended to be limited to the specific order or hierarchy presented.
In the foregoing detailed description, various features are grouped together in a single embodiment for the purpose of streamlining the disclosure. This method of disclosure is not to be interpreted as reflecting an intention that the claimed embodiments of the subject matter require more features than are expressly recited in each claim. Rather, as the following claims reflect, invention lies in less than all features of a single disclosed embodiment. Thus, the following claims are hereby expressly incorporated into the detailed description, with each claim standing on its own as a separate preferred embodiment of the invention.
Those of skill would further appreciate that the various illustrative logical blocks, modules, circuits, and algorithm steps described in connection with the embodiments disclosed herein may be implemented as electronic hardware, computer software, or combinations of both. To clearly illustrate this interchangeability of hardware and software, various illustrative components, blocks, modules, circuits, and steps have been described above generally in terms of their functionality. Whether such functionality is implemented as hardware or software depends upon the particular application and design constraints imposed on the overall system. Skilled artisans may implement the described functionality in varying ways for each particular application, but such implementation decisions should not be interpreted as causing a departure from the scope of the present disclosure.
The steps of a method or algorithm described in connection with the embodiments disclosed herein may be embodied directly in hardware, in a software module executed by a processor, or in a combination of the two. A software module may reside in RAM memory, flash memory, ROM memory, EPROM memory, EEPROM memory, registers, hard disk, a removable disk, a CD-ROM, or any other form of storage medium known in the art. An exemplary storage medium is coupled to the processor such the processor can read information from, and write information to, the storage medium. Of course, the storage medium may also be integral to the processor. The processor and the storage medium may reside in an ASIC. The ASIC may reside in a user terminal. Of course, the processor and the storage medium may reside as discrete components in a user terminal.
For a software implementation, the techniques described herein may be implemented with modules (e.g., procedures, functions, and so on) that perform the functions described herein. The software codes may be stored in memory units and executed by processors. The memory unit may be implemented within the processor or external to the processor, in which case it can be communicatively coupled to the processor via various means as is known in the art.
What has been described above includes examples of one or more embodiments. It is, of course, not possible to describe every conceivable combination of components or methodologies for purposes of describing the aforementioned embodiments, but one of ordinary skill in the art may recognize that many further combinations and permutations of various embodiments are possible. Accordingly, the embodiments described herein are intended to embrace all such alterations, modifications and variations that fall within the scope of the appended claims. Furthermore, to the extent that the term "includes" is used in either the detailed description or the claims, such term is intended to be inclusive in a manner similar to the term "comprising" as "comprising" is interpreted when employed as a transitional word in a claim. Furthermore, any use of the term "or" in the specification of the claims is intended to mean a "non-exclusive or".
Claims (6)
1. A method for realizing cross-cell switching in a wireless network is characterized in that when a user station accesses a new cell, the method comprises the following steps:
the new AP sends the user information of the user station to the user manager; the new AP acquires a user station name reported by a user station and allocates an IP address for the user station; the acquired user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site are used as user information and sent to the user manager to which the user site belongs;
the user manager determines and stores the position information of the user site according to the user information; the user manager acquires the name of the user site and the IP address allocated to the user site according to the received user information; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; establishing a triple group of the user station by using the user station name, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP, and storing the triple group;
when the user manager determines that the user station is a cross-cell switching station, sending a change signaling to an original AP (access point), and informing the original AP of updating and configuring a first forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station; sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station;
the first transfer table includes: a roll-out table used for the original AP to forward the received data of the user station to the new AP and a roll-out backtracking table used for the original AP to forward the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to an external network station; the second forwarding table comprises: a transfer-in table for the new AP to transfer the user data forwarded by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a transfer-in backtracking table for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the original AP.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein the determining, by the user manager, that the user station is a cross-cell handover station specifically comprises:
the user manager searches a locally stored user station position information list according to the user station name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, determining the user site as a site of a new access network.
3. A user manager, comprising:
the first receiving module is used for receiving the user information of the user station sent by the new AP when the user station accesses the new cell;
the information processing module is used for determining the position information of the user station according to the user information; according to the received user information, acquiring a user site name and an IP address distributed to a user site; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; establishing a triple group of the user station by using the user station name, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP;
the information storage module is used for storing the position information of the user station;
the switching judging module is used for determining whether the user site is a cross-cell switching site;
a first sending module, configured to send a change signaling to an original AP when determining that the user station is a cross-cell handover station, and notify the original AP to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station; sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station;
the first transfer table includes: a roll-out table used for the original AP to forward the received data of the user station to the new AP and a roll-out backtracking table used for the original AP to forward the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to an external network station; the second forwarding table comprises: a transfer-in table for the new AP to transfer the user data forwarded by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a transfer-in backtracking table for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the original AP.
4. The user manager according to claim 3, wherein the handover discrimination module is specifically configured to:
searching a locally stored user station position information list according to the user station name; if the position information table item matched with the user station name is searched, determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station; otherwise, determining the user site as a site of a new access network.
5. An access point, AP, comprising:
the second sending module is used for sending the user information of the user site to the user manager when the user site is accessed to the cell; acquiring a user station name reported by a user station, and allocating an IP address for the user station; the acquired user site name and the IP address distributed to the user site are used as user information and sent to the user manager to which the user site belongs; the user manager acquires the name of the user site and the IP address allocated to the user site according to the received user information; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; establishing a triple group of the user station by using the user station name, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP, and storing the triple group;
the user manager sends a change signaling to the original AP when determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station, and informs the original AP of updating and configuring a first forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station; sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station; the second forwarding table comprises: a transfer-in table for the new AP to transfer the user data transferred from the original AP to the corresponding user station and a transfer-in backtracking table for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the original AP;
the second receiving module is used for receiving the change signaling sent by the user manager; and/or receiving configuration signaling sent by a user manager;
a first configuration module, configured to update a first forwarding table configured to forward data of the user station according to the received change signaling; and/or configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station according to the received configuration signaling; configuring a first forwarding table which comprises a forwarding-out table used for forwarding the received data of the user station to the new AP by the original AP and a forwarding-out backtracking table used for forwarding the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to the external network station by the original AP; the configuration comprises a transfer-in table used for the new AP to transfer the user data transferred by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a second transfer table used for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the transfer-in backtracking table of the original AP.
6. A system for realizing cross-cell switching in a wireless network is characterized by comprising a user manager, an Access Point (AP) and a user site;
the AP is used as a new AP and is used for sending the user information of the user station to the user manager when the user station is accessed into the cell; configuring a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user site according to the received change signaling sent by the user manager;
the AP is used as an original AP and is used for updating and configuring a first forwarding table used for forwarding the data of the user station according to a received change signaling sent by a user manager; the first transfer table includes: a roll-out table used for the original AP to forward the received data of the user station to the new AP and a roll-out backtracking table used for the original AP to forward the reply data of the user station forwarded by the new AP to an external network station;
the user manager is used for determining and storing the position information of the user site according to the user information; according to the received user information, acquiring a user site name and an IP address distributed to a user site; extracting a source IP address for sending the user information to obtain a global IP address of the new AP; establishing a triple group of the user station by using the user station name, the IP address distributed to the user station and the global IP address of the new AP, and storing the triple group;
the user manager sends a change signaling to the original AP when determining that the user station is a cross-cell switching station, and informs the original AP of updating and configuring a first forwarding table for forwarding data of the user station; sending a configuration signaling to the new AP to inform the new AP to configure a second forwarding table for forwarding the data of the user station; the second forwarding table comprises: a transfer-in table for the new AP to transfer the user data forwarded by the original AP to the corresponding user station and a transfer-in backtracking table for the new AP to transfer the reply data of the user station to the original AP.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201611005647.9A CN108076495B (en) | 2016-11-16 | 2016-11-16 | Method, system and device for realizing cross-cell switching in wireless network |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201611005647.9A CN108076495B (en) | 2016-11-16 | 2016-11-16 | Method, system and device for realizing cross-cell switching in wireless network |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN108076495A CN108076495A (en) | 2018-05-25 |
| CN108076495B true CN108076495B (en) | 2022-03-25 |
Family
ID=62162731
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201611005647.9A Active CN108076495B (en) | 2016-11-16 | 2016-11-16 | Method, system and device for realizing cross-cell switching in wireless network |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN108076495B (en) |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1282167A (en) * | 1999-07-27 | 2001-01-31 | 财团法人资讯工业策进会 | Wireless network roaming method of cross IP domain |
| CN1756412A (en) * | 2004-09-30 | 2006-04-05 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Station switching method in WLAN |
| CN101141493A (en) * | 2007-10-11 | 2008-03-12 | 杭州华三通信技术有限公司 | Address analysis method and access point of wireless LAN |
| CN101312571A (en) * | 2007-05-24 | 2008-11-26 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for idle terminal to update location thereof after movement across wireless control point |
| CN100441043C (en) * | 2004-06-08 | 2008-12-03 | 株式会社Ntt都科摩 | Mobile communication system, access router, management device and mobile communication method |
| CN101656993A (en) * | 2009-09-16 | 2010-02-24 | 华为技术有限公司 | Access point switching method and device |
| US8121126B1 (en) * | 2006-09-08 | 2012-02-21 | Juniper Networks, Inc. | Layer two (L2) network access node having data plane MPLS |
| CN103621133A (en) * | 2011-05-03 | 2014-03-05 | 瑞典爱立信有限公司 | Physical cell identifier (pci) adaptation to mitigate interference in heterogeneous cellular network |
| CN105744575A (en) * | 2014-12-11 | 2016-07-06 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Method, wireless network SDN controller and system for switching cells |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7350077B2 (en) * | 2002-11-26 | 2008-03-25 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | 802.11 using a compressed reassociation exchange to facilitate fast handoff |
| JP4702110B2 (en) * | 2006-03-03 | 2011-06-15 | 日本電気株式会社 | RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, RADIO BASE STATION, RADIO COMMUNICATION CONTROL DEVICE, PROGRAM, AND ROUTING CONTROL METHOD |
| US9258702B2 (en) * | 2006-06-09 | 2016-02-09 | Trapeze Networks, Inc. | AP-local dynamic switching |
| US8446876B2 (en) * | 2010-05-04 | 2013-05-21 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Maintaining point of presence at access switch for roaming clients in distributed wireless controller system |
| CN102164368B (en) * | 2011-03-07 | 2016-09-07 | 北京新岸线移动多媒体技术有限公司 | A kind of method accessing WLAN and communication system |
| US8693478B2 (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2014-04-08 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Multiple shortest-path tree protocol |
| CN103945471B (en) * | 2013-01-21 | 2019-01-22 | 电信科学技术研究院 | A kind of cell switching method and device |
| CN105142189B (en) * | 2015-08-11 | 2018-10-23 | 华讯方舟科技有限公司 | The roam control method and device of website |
-
2016
- 2016-11-16 CN CN201611005647.9A patent/CN108076495B/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1282167A (en) * | 1999-07-27 | 2001-01-31 | 财团法人资讯工业策进会 | Wireless network roaming method of cross IP domain |
| CN100441043C (en) * | 2004-06-08 | 2008-12-03 | 株式会社Ntt都科摩 | Mobile communication system, access router, management device and mobile communication method |
| CN1756412A (en) * | 2004-09-30 | 2006-04-05 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Station switching method in WLAN |
| US8121126B1 (en) * | 2006-09-08 | 2012-02-21 | Juniper Networks, Inc. | Layer two (L2) network access node having data plane MPLS |
| CN101312571A (en) * | 2007-05-24 | 2008-11-26 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for idle terminal to update location thereof after movement across wireless control point |
| CN101141493A (en) * | 2007-10-11 | 2008-03-12 | 杭州华三通信技术有限公司 | Address analysis method and access point of wireless LAN |
| CN101656993A (en) * | 2009-09-16 | 2010-02-24 | 华为技术有限公司 | Access point switching method and device |
| CN103621133A (en) * | 2011-05-03 | 2014-03-05 | 瑞典爱立信有限公司 | Physical cell identifier (pci) adaptation to mitigate interference in heterogeneous cellular network |
| CN105744575A (en) * | 2014-12-11 | 2016-07-06 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Method, wireless network SDN controller and system for switching cells |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN108076495A (en) | 2018-05-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP4044557B1 (en) | Device and method for providing information of application server in mobile communication system | |
| CN103152787B (en) | Local agent, mobile node and control method | |
| US9787497B2 (en) | Network apparatus and method using link layer routing | |
| CN107172666A (en) | The method and device of its local service is kept when mobile terminal switches communication cell | |
| US7406064B2 (en) | Communication system, server, router, and mobile communications terminal | |
| US8782172B2 (en) | Method of controlling mobile terminal, home hub, and visited hub in virtual group for content sharing | |
| CN102025702A (en) | Network based on identity and position separation frame, and backbone network and network element thereof | |
| US12028932B2 (en) | Communication service transmission method and apparatus, storage medium and electronic apparatus | |
| KR20080075306A (en) | Method of lossless mobile ip packet delivery and system thereof | |
| CN104254110A (en) | Wireless Mesh network inter-domain switching method | |
| CN101803299A (en) | Policy routing in a communications network | |
| CN102026318B (en) | Switching management method and system and user data management method and system during switching as well as AGR (Access gateway Router) | |
| US20080205393A1 (en) | System and Method for Routing Packets in Portable Internet System | |
| US9629059B2 (en) | Mobile node registration method, intercommunication method, switching method and network element | |
| CN102984813B (en) | Data straight through processing method, equipment and system | |
| CN109275172B (en) | Method, device, computer storage medium and system for establishing communication route | |
| CN112533236B (en) | Communication method and device | |
| CN112449382B (en) | Data transmission method and server | |
| CN108076495B (en) | Method, system and device for realizing cross-cell switching in wireless network | |
| JP2006005607A (en) | Network system and mobile router | |
| CN108076496B (en) | Method, system and device for realizing cross-cell switching in wireless network | |
| CN106658479B (en) | Method for realizing wireless network convergence | |
| CN103167463B (en) | Update the processing method and system, mapping server and mobile node of message | |
| US11375412B2 (en) | Method for realizing continued transmission of user data during handover crossing multiple cells | |
| KR101433380B1 (en) | MANEMO(MANET for NEMO;Mobile Ad-hoc Network for Network Mobility) System and Method based on Anchor Point |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |