CN106440510B - Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump - Google Patents
Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN106440510B CN106440510B CN201610815112.1A CN201610815112A CN106440510B CN 106440510 B CN106440510 B CN 106440510B CN 201610815112 A CN201610815112 A CN 201610815112A CN 106440510 B CN106440510 B CN 106440510B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- heat
- communicated
- medium channel
- compressor
- working medium
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B30/00—Heat pumps
- F25B30/02—Heat pumps of the compression type
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Engine Equipment That Uses Special Cycles (AREA)
Abstract
The invention provides a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump, and belongs to the technical field of power, heat supply and heat pumps. The compressor is communicated with a heat supply device through a circulating working medium channel, the heat supply device is also communicated with the evaporator through a water turbine, the heat supply device is also communicated with an expander through a circulating working medium channel, the expander is also communicated with a condenser through a circulating working medium channel, the condenser is also communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also communicated with the compressor through a circulating working medium channel, the evaporator is also communicated with the outside through a heat source medium channel, the heat supply device is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, the condenser is also communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, the expander and the water turbine are connected with the compressor or the compressor and the booster pump are connected and transmit power, and the second-class heat-driven compression heat pump is formed.
Description
The technical field is as follows:
the invention belongs to the technical field of power, heat supply and heat pumps.
Background art:
heat and power requirements are common in human life and production. The higher the temperature of the heat energy, the higher the possibility of its utilization, and the more convenient the utilization. In reality, people need to adopt necessary technology to increase the temperature of the heat load with lower temperature. In achieving the above objects, various considerations or conditional limitations are faced, including the type, grade and quantity of energy sources, the type, grade and quantity of user demands, ambient temperature, the type of working medium, the flow, structure and manufacturing cost of the equipment, and so on.
A heat energy (temperature difference) utilization technology represented by an absorption heat pump technology, wherein the temperature difference between a heat load and a cold environment is utilized to realize the increase of the temperature of part of the heat load; however, due to the influence of the properties of the working media (solution and refrigerant media), the conversion from heat energy to mechanical energy cannot be realized while supplying heat, and the application field and the application range of the heat pump are greatly limited.
The invention provides a steam compression type second-class heat-driven compression heat pump which has a simple flow and a simple structure and can effectively utilize the temperature difference between the heat load and the cold environment from the starting point of fully realizing the efficient utilization of the temperature difference between the heat load and the cold environment, and also considers the simultaneous utilization of power drive or the consideration of power output.
The invention content is as follows:
the invention mainly aims to provide a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump, and the specific contents of the invention are explained in terms of the following items:
1. the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device and a condenser; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with an expander, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with an evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander is connected with the compressor and transmits power to form a second-class thermally driven compression heat; wherein, or the expander is connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmits power.
2. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a water turbine, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander and the water turbine are connected with the compressor and transmit; wherein, or the expander and the water turbine are connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmit power.
3. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a throttle valve; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a throttle valve, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with an expander, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander is connected with the compressor and transmits power to form; wherein, or the expander is connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmits power.
4. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser through a water turbine, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander and the water turbine are connected with the compressor and; wherein, or the expander and the water turbine are connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmit power.
5. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a throttle valve; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser through a throttle valve, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander is connected with the compressor and transmits power to; wherein, or the expander is connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmits power.
6. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a water turbine, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with an expander, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander and the water turbine are connected with the compressor and transmit power to form; wherein, or the expander and the water turbine are connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmit power.
7. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a throttle valve; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a throttle valve, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with an expander, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander is connected with the compressor and transmits power to form a second-; wherein, or the expander is connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmits power.
8. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supplier, a condenser, a water turbine and a heat regenerator; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with a heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with an evaporator through a heat regenerator and a water turbine, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with an expander through the heat regenerator, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with a condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel which is communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel which is communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel which is communicated with; wherein, or the expander and the water turbine are connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmit power.
9. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supplier, a condenser, a throttle valve and a heat regenerator; the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supply device, the heat supply device is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a heat regenerator and a throttle valve, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with an expander through a heat regenerator, the expander is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a condenser, the condenser is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator through a booster pump, the evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor, the evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander is connected with the compressor and transmits power to form; wherein, or the expander is connected with the compressor and the booster pump and transmits power.
10. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a heat regenerator is added in the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump in items 1-5, the compressor is communicated with a heat supplier through a circulating medium channel and adjusted to be communicated with the heat supplier through the heat regenerator, the heat supplier is communicated with an expander through a circulating medium channel and adjusted to be communicated with the heat supplier through a circulating medium channel and adjusted to be communicated with the expander through the heat regenerator, and the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is formed.
11. A second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a heat regenerator is added in the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump in item 2 or 6, the evaporator is adjusted to be communicated with a compressor through a circulating medium channel, the evaporator is provided with a circulating medium channel, the compressor is communicated through the heat regenerator, the heat supply device is adjusted to be communicated with the evaporator through a water turbine, the heat supply device is provided with a circulating medium channel, the circulating medium channel is communicated with the evaporator through the heat regenerator and the water turbine, and the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump is formed.
12. A second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump is provided in item 3 or 7, wherein a heat regenerator is added, the evaporator is adjusted to be communicated with a compressor through a circulating medium channel, the evaporator is provided with a circulating medium channel, the compressor is communicated through the heat regenerator, the heater is adjusted to be communicated with the evaporator through a throttle valve, the heater is provided with a circulating medium channel, the circulating medium channel is communicated with the evaporator through the heat regenerator and the throttle valve, and the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump is formed.
13. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor is added in the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump in items 1-9, the compressor is adjusted to be communicated with a heat supplier through a circulation medium channel, the compressor is communicated with the second compressor through the heat supplier, the second compressor is communicated with the heat supplier through the circulation medium channel, and an expander is connected with the second compressor and transmits power to form the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump.
14. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly-added water turbine are added in any second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump of items 2-3 and 6-7, the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the heat supplier, the compressor is provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the second heat supplier, the second heat supplier is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the second compressor, the second compressor is further provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the heat supplier, the second heat supplier is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with an evaporator through the newly-added water turbine, the second heat supplier is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, and the expander and the newly-added water turbine are connected with the second compressor and transmit power to form the second kind of heat-driven compression.
15. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly-added throttle valve are added in any second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump of items 2-3 and 6-7, the communication between the compressor and the heat supplier is adjusted to be that the compressor is communicated with the second heat supplier through a circulating medium channel, the second heat supplier is also communicated with the second compressor through a circulating medium channel, the second compressor is also communicated with the heat supplier through a circulating medium channel, the second heat supplier is also communicated with an evaporator through the newly-added throttle valve, the second heat supplier is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, and an expander is connected with the second compressor and transmits power to form the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump.
16. A second-class heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly-added water turbine are added in any one of the second-class heat-driven compression heat pumps in items 2-3 and 6-7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on an evaporator and communicated with the second compressor, the second compressor is also communicated with the second heat supplier through the circulating working medium channel, the second heat supplier is also communicated with the evaporator through the newly-added water turbine, the second heat supplier is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, and an expander and the newly-added water turbine are connected with the second compressor and transmit power to form the second-class heat-driven compression heat pump.
17. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly-added throttle valve are added in any one of the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pumps in items 2-3 and 6-7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on an evaporator and communicated with the second compressor, the second compressor is also communicated with the second heat supplier through the circulating working medium channel, the second heat supplier is also communicated with the evaporator through the newly-added throttle valve, the second heat supplier is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, and an expander is connected with the second compressor and transmits power to form the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump.
18. A second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second evaporator and a second booster pump are additionally arranged in any one of the second type of thermally driven compression heat pumps in items 2-3 and 6-7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on the evaporator and is communicated with the second evaporator through the second booster pump, the second evaporator is also communicated with the second compressor through a circulating working medium channel, the second compressor is also communicated with a heat supply device through a circulating working medium channel, the second evaporator is also communicated with the outside through a heat source medium channel, and an expander is connected with the second compressor and transmits power to form the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
19. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second evaporator and a second booster pump are added in any one of the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump of items-3 and-7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on a condenser and is communicated with the second evaporator through the second booster pump, the second evaporator is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the second compressor, the second compressor is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with a heat supply device, the second evaporator is also provided with a heat source medium channel which is communicated with the outside, and an expander is connected with the second compressor and transmits power to form the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump; and the expander is connected with the second compressor and the second booster pump and transmits power.
20. A second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second booster pump, a second expansion machine and a second condenser are added in any one of the second type of thermally driven compression heat pumps in items 2-3, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on a heat supply device and communicated with the second expansion machine, the second expansion machine is also communicated with the second condenser through a circulating working medium channel, the second condenser is also communicated with an evaporator through the second booster pump through the circulating working medium channel, the second condenser is also communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, the second expansion machine is connected with a compressor and transmits power, or the second expansion machine is connected with the compressor and the second booster pump and transmits power, so that the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is formed.
21. A second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second booster pump, a second expansion machine and a second condenser are added in any one of the second type of thermally driven compression heat pumps in items 6-7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on an evaporator and communicated with the second expansion machine, the circulating working medium channel of the second expansion machine is communicated with the second condenser, the circulating working medium channel of the second condenser is communicated with the evaporator through the second booster pump, the second condenser is also communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, the second expansion machine is connected with a compressor and transmits power, or the second expansion machine is connected with the compressor and the second booster pump and transmits power, so that the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is formed.
22. A second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second booster pump, a second expansion machine and a second condenser are additionally arranged in any one of the second type of thermally driven compression heat pumps in items 2-3 and 6-7, the expansion machine is communicated with the condenser through a circulating working medium channel, the expansion machine is adjusted to be communicated with the second condenser through a circulating working medium channel, the second condenser is also communicated with an evaporator through the second booster pump through the circulating working medium channel, the second condenser is also communicated with the second expansion machine through the circulating working medium channel, the second expansion machine is also communicated with the condenser through the circulating working medium channel, the second expansion machine is connected with a compressor and transmits power, or the second expansion machine is connected with the compressor and the second booster pump and transmits power, so that the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is formed.
23. The second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump is one of the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pumps in items 1-22, and has increased power machine connected to the compressor to provide power to the compressor and to form the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump driven by the added external power.
24. The second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump is one of the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pumps in items 1-22, and has one additional work machine connected to the expander to provide power to the work machine and to form the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump with additional externally provided power load.
Description of the drawings:
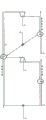
fig. 1 is a diagram of a 1 st principal thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 2 is a diagram of a 2 nd principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 3 is a diagram of a 3 rd principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 4 is a diagram of a 4 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 5 is a diagram of a 5 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 6 is a diagram of a 6 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 7 is a diagram of a 7 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 8 is a diagram of 8 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 9 is a diagram of a 9 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 10 is a diagram of a 10 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 11 is a diagram of a 11 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 12 is a diagram of a 12 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 13 is a 13 th principle thermodynamic system diagram of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump provided in accordance with the present invention.
Fig. 14 is a diagram of a 14 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 15 is a diagram of a 15 th principle thermodynamic system for a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 16 is a diagram of a 16 th principle thermodynamic system for a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump provided in accordance with the present invention.
Fig. 17 is a diagram of a 17 th principle thermodynamic system for a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 18 is a diagram of a 18 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 19 is a diagram of a 19 th principle thermodynamic system for a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to the present invention.
Fig. 20 is a diagram of a 20 th principle thermodynamic system of a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump provided in accordance with the present invention.
In the figure, 1-compressor, 2-expander, 3-booster pump, 4-evaporator, 5-heater, 6-condenser, 7-water turbine, 8-throttle valve, 9-heat regenerator, 10-second compressor, 11-second heater, 12-second evaporator, 13-second booster pump, 14-second expander, 15-second condenser; a-newly-added water turbine and B-newly-added throttle valve.
The specific implementation mode is as follows:
it is to be noted that, in the description of the structure and the flow, the repetition is not necessary; obvious flow is not described. The invention is described in detail below with reference to the figures and examples.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 1 is realized by:
(1) structurally, the system consists of compressor, expander, booster pump, evaporator, heat supplier and condenser; the compressor 1 is communicated with a heat supply device 5 through a circulating working medium channel, the heat supply device 5 is communicated with an expansion machine 2 through a circulating working medium channel, the expansion machine 2 is communicated with a condenser 6 through a circulating working medium channel, the condenser 6 is communicated with an evaporator 4 through a booster pump 3 through a circulating working medium channel, the evaporator 4 is communicated with the compressor 1 through a circulating working medium channel, the evaporator 4 is communicated with the outside through a heat source medium channel, the heat supply device 5 is communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, the condenser 6 is communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, and the expansion machine 2 is connected with the compressor 1 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4 to absorb heat and evaporate into a gaseous circulating working medium, and the gaseous circulating working medium released by the evaporator 4 flows through the compressor 1 to be pressurized and heated and then enters the heat supplier 5; the circulating working medium entering the heat supplier 5 releases heat to the heated medium and partially condenses, and then enters the expander 2 to reduce pressure and do work; the circulating working medium discharged by the expander 2 enters the condenser 6 and releases heat to the cooling medium, and then a liquid circulating working medium is formed; the work output by the expander 2 is provided to the compressor 1 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2 is realized by:
(1) structurally, the system consists of a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier 5, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through a water turbine 7, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander 2, the expander 2 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser 6, the condenser 6 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through a booster pump 3, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor 1, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser 6 is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander 2 and the water turbine 7 are connected with the compressor 1 and the booster pump.
(2) In the process, the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4, the liquid circulating working medium of the heat supply device 5 is depressurized by the water turbine 7 and then enters the evaporator 4, the liquid circulating working medium is absorbed and evaporated in the evaporator 4 into gaseous circulating working medium, and the gaseous circulating working medium released by the evaporator 4 is pressurized by the compressor 1 and heated and then enters the heat supply device 5; the circulating working medium entering the heat supplier 5 releases heat to the heated medium and is partially condensed, then the circulating working medium is divided into two paths, namely, the gaseous circulating working medium enters the expander 2 to reduce pressure and do work and then enters the condenser 6, and the liquid circulating working medium flows through the water turbine 7 to reduce pressure and do work and then enters the evaporator 4; the gaseous circulating working medium entering the condenser 6 releases heat to the cooling medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the work output by the expander 2 and the water turbine 7 is provided for the compressor 1 and the booster pump 3 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 3 is realized by:
(1) structurally, the system consists of compressor, expander, booster pump, evaporator, heater, condenser and throttle valve; the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier 5, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through the throttle valve 8, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander 2, the expander 2 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser 6, the condenser 6 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through the booster pump 3, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor 1, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser 6 is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander 2 is connected with the compressor 1 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4, the liquid circulating working medium of the heat supply device 5 is depressurized by the throttle valve 8 and then enters the evaporator 4, the liquid circulating working medium is absorbed and evaporated in the evaporator 4 into gaseous circulating working medium, and the gaseous circulating working medium released by the evaporator 4 is pressurized by the compressor 1 and heated and then enters the heat supply device 5; the circulating working medium entering the heat supplier 5 releases heat to the heated medium and is partially condensed, then the circulating working medium is divided into two paths, namely, the gaseous circulating working medium enters the expander 2 to be decompressed and work and then enters the condenser 6, and the liquid circulating working medium flows through the throttle valve 8 to be throttled and decompressed and then enters the evaporator 4; the circulating working medium entering the condenser 6 releases heat to the cooling medium, and then a liquid circulating working medium is formed; the work output by the expander 2 is provided to the compressor 1 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 4 is realized by:
(1) structurally, the system consists of a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor 1 is communicated with a heat supplier 5 through a circulating working medium channel, the heat supplier 5 is also communicated with a condenser 6 through a water turbine 7 through a circulating working medium channel, the heat supplier 5 is also communicated with an expander 2 through a circulating working medium channel, the expander 2 is also communicated with the condenser 6 through a circulating working medium channel, the condenser 6 is also communicated with an evaporator 4 through a booster pump 3, the evaporator 4 is also communicated with the compressor 1 through a circulating working medium channel, the evaporator 4 is also communicated with the outside through a heat source medium channel, the heat supplier 5 is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, the condenser 6 is also communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, and the expander 2 and the water turbine 7 are connected with the compressor 1 and transmit power.
(2) In the process, the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4 to absorb heat and evaporate into a gaseous circulating working medium, and the gaseous circulating working medium released by the evaporator 4 flows through the compressor 1 to be pressurized and heated and then enters the heat supplier 5; the circulating working medium entering the heat supplier 5 releases heat to the heated medium and is partially condensed, then the circulating working medium is divided into two paths, namely, the gaseous circulating working medium enters the expander 2 to reduce pressure and do work and then enters the condenser 6, and the liquid circulating working medium flows through the water turbine 7 to reduce pressure and do work and then enters the condenser 6; the gaseous circulating working medium entering the condenser 6 releases heat to the cooling medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the work output by the expander 2 and the water turbine 7 is provided for the compressor 1 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 5 is realized by:
(1) structurally, the system consists of compressor, expander, booster pump, evaporator, heater, condenser and throttle valve; the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heater 5, the heater 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser 6 through the throttle valve 8, the heater 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander 2, the expander 2 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser 6, the condenser 6 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through the booster pump 3, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor 1, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heater 5 is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser 6 is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander 2 is connected with the compressor 1 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4 to absorb heat and evaporate into a gaseous circulating working medium, and the gaseous circulating working medium released by the evaporator 4 flows through the compressor 1 to be pressurized and heated and then enters the heat supplier 5; the circulating working medium entering the heat supplier 5 releases heat to the heated medium and is partially condensed, then the circulating working medium is divided into two paths, namely, the gaseous circulating working medium enters the expander 2 to be decompressed and work and then enters the condenser 6, and the liquid circulating working medium flows through the throttle valve 8 to be throttled and decompressed and then enters the condenser 6; the gaseous circulating working medium entering the condenser 6 releases heat to the cooling medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the work output by the expander 2 is provided for the compressor 1 as power to form a second type of heat-driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 6 is realized by:
(1) structurally, the system consists of a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier 5, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through a water turbine 7, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander 2, the expander 2 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser 6, the condenser 6 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through a booster pump 3, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor 1, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser 6 is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander 2 and the water turbine 7 are connected with the compressor 1 and the booster pump 3.
(2) In the process, a liquid circulating working medium of a condenser 6 is pressurized by a booster pump 3 and then enters an evaporator 4, a liquid circulating working medium of a heat supply device 5 is depressurized by a water turbine 7 and then enters the evaporator 4, the liquid circulating working medium is subjected to heat absorption and evaporation in the evaporator 4 to form a gaseous circulating working medium, the gaseous circulating working medium released by the evaporator 4 is divided into two paths, wherein the first path flows through a compressor 1 to be pressurized and heated and then enters the heat supply device 5, and the second path flows through an expander 2 to be depressurized and work and then enters the condenser 6; the circulating working medium entering the heat supplier 5 releases heat to the heated medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the liquid circulating working medium flows through the water turbine 7 to reduce the pressure and do work and then enters the evaporator 4; the gaseous circulating working medium entering the condenser 6 releases heat to the cooling medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the work output by the expander 2 and the water turbine 7 is provided for the compressor 1 and the booster pump 3 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 7 is realized by:
(1) structurally, the system consists of compressor, expander, booster pump, evaporator, heater, condenser and throttle valve; the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier 5, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through the throttle valve 8, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander 2, the expander 2 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser 6, the condenser 6 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through the booster pump 3, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor 1, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser 6 is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander 2 is connected with the compressor 1 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4, the liquid circulating working medium of the heat supply device 5 is throttled and depressurized by the throttle valve 8 and then enters the evaporator 4, the liquid circulating working medium is thermally evaporated in the evaporator 4 into a gaseous circulating working medium, the gaseous circulating working medium released by the evaporator 4 is divided into two paths, the first path flows through the compressor 1 to be pressurized and heated and then enters the heat supply device 5, and the second path flows through the expander 2 to be depressurized and work and then enters the condenser 6; the circulating working medium entering the heat supplier 5 releases heat to the heated medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the liquid circulating working medium flows through the throttle valve 8 to be throttled and depressurized and then enters the evaporator 4; the gaseous circulating working medium entering the condenser 6 releases heat to the cooling medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the work output by the expander 2 is provided for the compressor 1 as power to form a second type of heat-driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 8 is realized by:
(1) structurally, the system consists of a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser, a water turbine and a heat regenerator; the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier 5, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through a heat regenerator 9 and a water turbine 7, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander 2 through the heat regenerator 9, the expander 2 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser 6, the condenser 6 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through a booster pump 3, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor 1, the evaporator 4 is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier 5 is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser 6 is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander 2 and the water turbine 7 are connected with the compressor.
(2) In the process, the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4, the liquid circulating working medium of the heat supply device 5 enters the evaporator 4 through the heat regenerator 9 and the water turbine 7, the liquid circulating working medium is thermally absorbed and evaporated in the evaporator 4 to form a gaseous circulating working medium, the gaseous circulating working medium released by the evaporator 4 is divided into two paths, the first path flows through the compressor 1 to be pressurized and heated and then enters the heat supply device 5, and the second path flows through the heat regenerator 9 in sequence to absorb heat and flows through the expander 2 to be depressurized and do work and then enters the condenser 6; the circulating working medium entering the heat supplier 5 releases heat to the heated medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the liquid circulating working medium flows through the heat regenerator 9 in sequence, releases heat, flows through the water turbine 7, is decompressed and does work, and then enters the evaporator 4; the gaseous circulating working medium entering the condenser 6 releases heat to the cooling medium to form a liquid circulating working medium, and the work output by the expander 2 and the water turbine 7 is provided for the compressor 1 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 9 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 1, a heat regenerator is added, the compressor 1 is communicated with the heat supplier 5 through a circulating working medium channel, so that the compressor 1 is communicated with the heat supplier 5 through the heat regenerator 9, and the heat supplier 5 is communicated with the expander 2 through the circulating working medium channel, so that the heat supplier 5 is communicated with the expander 2 through the heat regenerator 9.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 1, the increased or changed process is carried out in such a way that the circulating working medium discharged by the compressor 1 flows through the heat regenerator 9 to release heat and then enters the heat supplier 5, and the circulating working medium discharged by the heat supplier 5 flows through the heat regenerator 9 to absorb heat and then enters the expansion machine 2, so as to form the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 10 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2, a heat regenerator is added, the compressor 1 is communicated with the heat supplier 5 through a circulating working medium channel, so that the compressor 1 is communicated with the heat supplier 5 through the heat regenerator 9, and the heat supplier 5 is communicated with the expander 2 through a circulating working medium channel, so that the heat supplier 5 is communicated with the expander 2 through the heat regenerator 9.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 2, the increased or changed process is performed in such a way that the circulating working medium discharged from the compressor 1 flows through the heat regenerator 9 and releases heat, and then enters the heat supplier 5; the circulating working medium discharged by the heat supplier 5 flows through the heat regenerator 9 and absorbs heat, and then enters the expansion machine 2 to form a second type heat-driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 11 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 3, a heat regenerator is added, the evaporator 4 is communicated with the compressor 1 through a circulating working medium channel, so that the evaporator 4 is communicated with the compressor 1 through the heat regenerator 9, the heater 5 is communicated with the evaporator 4 through a circulating working medium channel, so that the heater 5 is communicated with the evaporator 4 through the throttle valve 8, so that the heater 5 is communicated with the evaporator 4 through the heat regenerator 9 and the throttle valve 8.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 3, the increased or changed process is performed in such a way that the circulating working medium discharged by the evaporator 4 enters the compressor 1 after absorbing heat through the heat regenerator 9, the liquid circulating working medium discharged by the heat supplier 5 enters the evaporator 4 after passing through the heat regenerator 9 and releasing heat, and then the liquid circulating working medium is throttled and decompressed through the throttle valve 8 to form the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 12 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 1, a second compressor is added, the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel and a heat supplier 5, the heat supplier 5 is provided with a circulating working medium channel to be communicated with the expander 2, the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel to be communicated with the second compressor 10 through the heat supplier 5, the second compressor 10 is provided with a circulating working medium channel to be communicated with the expander 2 through the heat supplier 5, and the expander 2 is connected with the second compressor 10 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 1, the increased or changed process is performed in such a way that the circulating working medium discharged by the compressor 1 flows through the heat supplier 5 to release heat and then enters the second compressor 10 to be boosted and heated, the circulating working medium discharged by the second compressor 10 flows through the heat supplier 5 to release heat and then enters the expander 2, and the work output by the expander 2 simultaneously provides power for the compressor 1 and the second compressor 10 to form the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 13 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2, a second compressor is added, the compressor 1 is communicated with the heat supplier 5 through a circulating working medium channel, the heat supplier 5 is communicated with the evaporator 4 through a water turbine 7 through a circulating working medium channel, the heat supplier 5 is communicated with the expander 2 through a circulating working medium channel, the compressor 1 is adjusted to be communicated with the second compressor 10 through the heat supplier 5 through the circulating working medium channel, the second compressor 10 is communicated with the second compressor 10 through the heat supplier 5 through the circulating working medium channel, the heat supplier 5 is communicated with the evaporator 4 through the water turbine 7 and communicated with the expander 2 through the circulating working medium channel, and the expander 2 is connected with the second compressor 10 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 2, the increased or changed process is carried out in such a way that the circulating working medium discharged by the compressor 1 flows through the heat supplier 5 to release heat and then enters the second compressor 10 to increase the pressure and raise the temperature, the circulating working medium discharged by the second compressor 10 flows through the heat supplier 5 to release heat and then forms two parts of liquid circulating working medium and gaseous circulating working medium, the liquid circulating working medium flows through the water turbine 7 to reduce the pressure and work and then enters the evaporator 4, the gaseous circulating working medium is provided for the expander 2, and the work output by the expander 2 simultaneously provides power for the compressor 1 and the second compressor 10 to form the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 14 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2, a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly added water turbine are added, the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier 5 and adjusted to be that the compressor 1 is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the second heat supplier 11, the second heat supplier 11 is further provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the second compressor 10, the second compressor 10 is further provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier 5, the second heat supplier 11 is further provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator 4 through the newly added water turbine a, the second heat supplier 11 is further provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander 2 and the newly added water turbine a are connected with the second compressor 10 and transmit power.
(2) In the process, compared with the working process of the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2, the increased or changed process is carried out in such a way that the circulating working medium discharged by the compressor 1 enters the second heat supply device 11 to release heat and then is divided into two paths, the first path enters the evaporator 4 after passing through the newly-added water turbine A to reduce the pressure and do work, and the second path enters the second compressor 10 to increase the pressure and temperature and then is provided for the heat supply device 5; the expander 2 and the additional water turbine a provide power for the second compressor 10 to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 15 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 7, a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly added throttle valve are added, a circulating medium channel is additionally arranged on the evaporator 4 and communicated with the second compressor 10, the second compressor 10 is also communicated with the second heat supplier 11, the second heat supplier 11 is also communicated with the evaporator 4 through the newly added throttle valve B, the second heat supplier 11 is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, and the expander 2 is connected with the second compressor 10 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 7, the increased or changed process is performed in such a way that the circulating working medium discharged by the evaporator 4 is divided into two paths, the first path is provided for the compressor 1, the second path enters the second compressor 10 for boosting and warming, then enters the second heat supply 11 and releases heat to form liquid circulating working medium, the liquid circulating working medium of the second heat supply 11 flows through the newly added throttle valve B for throttling and pressure reduction, then enters the evaporator 4, and the expander 2 provides power for the second compressor 10 to form the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 16 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 3, a second compressor, a second evaporator and a second booster pump are added, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on the evaporator 4 and is communicated with the second evaporator 12 through a second booster pump 13, the second evaporator 12 is also communicated with the second compressor 10 through the circulating working medium channel, the second compressor 10 is also communicated with the heat supply device 5 through the circulating working medium channel, the second evaporator 12 is also communicated with the outside through the heat source medium channel, and the expander 2 is connected with the second compressor 10 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 3, the increased or changed process is carried out in such a way that the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4 to absorb heat and be partially vaporized, the gaseous circulating working medium of the evaporator 4 enters the compressor 1, and the liquid circulating working medium of the evaporator 4 is pressurized by the second booster pump 13 and enters the second evaporator 12 to absorb heat and be vaporized; the circulating working medium released by the second evaporator 12 flows through the second compressor 10 to be boosted and heated, and then enters the heat supply device 5 to release heat; the expander 2 powers the second compressor 10, forming a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 17 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 7, a second compressor, a second evaporator and a second booster pump are added, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on the condenser 6 and is communicated with the second evaporator 12 through a second booster pump 13, the second evaporator 12 is also communicated with the second compressor 10 through the circulating working medium channel, the second compressor 10 is also communicated with the heat supply device 5 through the circulating working medium channel, the second evaporator 12 is also communicated with the outside through the heat source medium channel, and the expander 2 is connected with the second compressor 10 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 7, the increased or changed process is carried out in such a way that the liquid circulating working medium of the condenser 6 is divided into two paths, the first path is pressurized by the booster pump 3 and then enters the evaporator 4 to absorb heat and vaporize, and the second path is pressurized by the second booster pump 13 and then enters the second evaporator 12 to absorb heat and vaporize; the circulating working medium released by the second evaporator 12 flows through the second compressor 10 to be boosted and heated, and then enters the heat supply device 5 to release heat; the expander 2 powers the second compressor 10, forming a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 18 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2, a second booster pump, a second expander and a second condenser are added, a circulation working medium channel is additionally arranged on the heat supply device 5 and communicated with the second expander 14, the second expander 14 is also communicated with the second condenser 15 through a circulation working medium channel, the second condenser 15 is also communicated with the evaporator 4 through a second booster pump 13 through a circulation working medium channel, the second condenser 15 is also communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, and the second expander 14 is connected with the compressor 1 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, compared with the working process of the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2, the increased or changed process is carried out in such a way that the gaseous circulating working medium of the heat supplier 5 is divided into two paths, the first path flows through the expander 2 to work by reducing the pressure, and the second path flows through the second expander 14 to work by reducing the pressure; the circulating working medium discharged by the second expander 14 enters the second condenser 15, releases heat to the cooling medium to form liquid, and then is pressurized by the second booster pump 13 to enter the evaporator 4; the work output by the second expander 14 is provided to the compressor 1 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 19 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 6, a second booster pump, a second expander and a second condenser are added, the evaporator 4 is additionally provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the second expander 14, the second expander 14 is also communicated with the second condenser 15 through a circulating working medium channel, the second condenser 15 is also communicated with the evaporator 4 through a second booster pump 13 through a circulating working medium channel, the second condenser 15 is also communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, and the second expander 14 is connected with the compressor 1 and the second booster pump 13 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, compared with the second type of thermal driving compression heat pump working process shown in fig. 6, the increased or changed process is carried out in such a way that the gaseous circulating working medium of the evaporator 4 is divided into two paths, the first path flows through the expansion machine 2 to work by reducing the pressure, and the second path flows through the second expansion machine 14 to work by reducing the pressure; the circulating working medium discharged by the second expander 14 enters the second condenser 15, releases heat to the cooling medium to form liquid, and then is pressurized by the second booster pump 13 to enter the evaporator 4; the work output by the second expander 14 is provided to the compressor 1 and the second booster pump 13 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 20 is realized by:
(1) structurally, in the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2, a second booster pump, a second expansion machine and a second condenser are added, the expansion machine 2 is adjusted to be communicated with the condenser 6 through a circulating working medium channel, the expansion machine 2 is adjusted to be communicated with the second condenser 15 through a circulating working medium channel, the second condenser 15 is also communicated with the evaporator 4 through a second booster pump 13, the second condenser 15 is also communicated with a circulating working medium channel 14, the second expansion machine 14 is also communicated with the condenser 6 through a circulating working medium channel, and the second expansion machine 14 is connected with the compressor 1 and transmits power.
(2) In the process, compared with the working process of the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump shown in fig. 2, the increased or changed process is carried out in such a way that the circulating working medium discharged by the expander 2 enters the second condenser 15 to release heat and is partially condensed, the liquid circulating working medium of the second condenser 15 is pressurized by the second booster pump 13 and enters the evaporator 4, the gaseous circulating working medium of the second condenser 15 enters the second expander 14 to reduce the pressure and do work, and the circulating working medium discharged by the second expander 14 enters the condenser 6; the work output by the second expander 14 is provided to the compressor 1 as power to form a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
The effect that the technology of the invention can realize-the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump provided by the invention has the following effects and advantages:
(1) the heat energy (temperature difference) is driven to realize the temperature increase of the heat energy, or the heat energy and the temperature can be selected to provide power for the outside at the same time.
(2) The process is reasonable, and the full and efficient utilization of heat energy (temperature difference) can be realized.
(3) When necessary, or realize heat energy temperature with the help of partial external power, the mode is nimble, and the adaptability is good.
(4) The compressor, the expander and the heat exchanger are used as components of the compression heat pump, and the structure is simple.
(5) The working medium has wide selection range, can adapt to heat supply requirements in various temperature ranges, and is flexibly matched with working parameters.
(6) The bidirectional thermodynamic cycle can be completed by using a single working medium, and the operation cost is low.
(7) The conversion between heat energy and mechanical energy is realized while carrying out high-efficient heat supply, and a tractor serves two purposes, the usage is wide.
(8) A plurality of specific technical schemes are provided, so that the method can cope with a plurality of different actual conditions and has a wider application range.
(9) The heat pump technology is expanded, the types of compression heat pumps are enriched, and the high-efficiency utilization of heat energy is better realized.
Claims (24)
1. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device and a condenser; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier (5), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander (2), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through the booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander (2) is connected with the compressor (1) and transmits power to form a second-class heat-driven compression heat pump; wherein, or the expander (2) is connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmits power.
2. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier (5), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through a water turbine (7), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander (2), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through a booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander (2) and the water turbine (7) are connected with the compressor (1) and transmit power, so that a second type heat compression heat; wherein, or the expander (2) and the water turbine (7) are connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmit power.
3. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a throttle valve; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with a heat supply device (5), the heat supply device (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with an evaporator (4) through a throttle valve (8), the heat supply device (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with an expander (2), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with a condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the evaporator (4) through a booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel which is communicated with the outside, the heat supply device (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel which is communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel which is communicated with the outside, and the expander (2); wherein, or the expander (2) is connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmits power.
4. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier (5), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with a condenser (6) through a water turbine (7), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander (2), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with an evaporator (4) through a booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander (2) and the water turbine (7) are connected with the compressor (1) and transmit power, so that a second type heat-; wherein, or the expander (2) and the water turbine (7) are connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmit power.
5. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a throttle valve; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the heat supplier (5), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the condenser (6) through a throttle valve (8), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the expander (2), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the evaporator (4) through a booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel which is communicated with the outside, the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel which is communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel which is communicated with the outside, and the expander (2) is connected with; wherein, or the expander (2) is connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmits power.
6. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a water turbine; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supply device (5), the heat supply device (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through a water turbine (7), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander (2), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through a booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supply device (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander (2) and the water turbine (7) are connected with the compressor (1) and transmit power, so that a second type heat; wherein, or the expander (2) and the water turbine (7) are connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmit power.
7. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supply device, a condenser and a throttle valve; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the heat supply device (5), the heat supply device (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the evaporator (4) through a throttle valve (8), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the expander (2), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the evaporator (4) through a booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel which is communicated with the outside, the heat supply device (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel which is communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel which is communicated with the outside, and the expander (2) is connected; wherein, or the expander (2) is connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmits power.
8. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supplier, a condenser, a water turbine and a heat regenerator; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier (5), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through a heat regenerator (9) and a water turbine (7), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander (2) through the heat regenerator (9), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through a booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, the expander (2) is connected with the compressor (1) and transmits power, forming a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump; wherein, or the expander (2) and the water turbine (7) are connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmit power.
9. The second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump mainly comprises a compressor, an expander, a booster pump, an evaporator, a heat supplier, a condenser, a throttle valve and a heat regenerator; the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the heat supplier (5), the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through a heat regenerator (9) and a throttle valve (8), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the expander (2) through the heat regenerator (9), the expander (2) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the condenser (6), the condenser (6) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the evaporator (4) through a booster pump (3), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel communicated with the compressor (1), the evaporator (4) is also provided with a heat source medium channel communicated with the outside, the heat supplier (5) is also provided with a heated medium channel communicated with the outside, the condenser (6) is also provided with a cooling medium channel communicated with the outside, and the expander (2) is connected with the compressor (1) and transmits power to form a second-type heat-driven; wherein, or the expander (2) is connected with the compressor (1) and the booster pump (3) and transmits power.
10. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a heat regenerator is added in the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump disclosed in claims 1-5, the compressor (1) is communicated with the heat supplier (5) and adjusted to be that the compressor (1) is communicated with the heat supplier (5) through a circulating working medium channel, the heat supplier (5) is communicated with the expander (2) through a circulating working medium channel and adjusted to be that the heat supplier (5) is communicated with the expander (2) through a circulating working medium channel, and the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is formed.
11. A second type of heat-driven compression heat pump is the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump disclosed in claim 2 or claim 6, wherein a heat regenerator is added, the evaporator (4) is communicated with the compressor (1) through a circulating working medium channel and adjusted to be communicated with the compressor (1) through the heat regenerator (9) through the circulating working medium channel of the evaporator (4), the heat supply device (5) is communicated with the evaporator (4) through a water turbine (7) and adjusted to be communicated with the evaporator (5) through the heat regenerator (9) and the water turbine (7) through the circulating working medium channel of the heat supply device (5) and communicated with the evaporator (4) through the heat regenerator (9) and the water turbine (7), and the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump is formed.
12. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump described in claim 3 or claim 7, wherein a heat regenerator is added, the evaporator (4) is communicated with the compressor (1) through a circulation medium channel, the evaporator (4) is adjusted to have a circulation medium channel, the heat regenerator (9) is communicated with the compressor (1), the heat supply device (5) is communicated with the evaporator (4) through a throttle valve (8), the heat supply device (5) is adjusted to have a circulation medium channel, the heat regenerator (9) and the throttle valve (8) are communicated with the evaporator (4), and the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is formed.
13. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is in the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump of claims 1-9, a second compressor is added, the compressor (1) is communicated with the heat supplier (5) through a circulation working medium channel, the compressor (1) is communicated with the second compressor (10) through the heat supplier (5), the second compressor (10) is communicated with the heat supplier (5) through a circulation working medium channel, and the expander (2) is connected with the second compressor (10) and transmits power, so that the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is formed.
14. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly added water turbine are added in any one of the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump of claims 2-3 and 6-7, the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel to be communicated with the heat supplier (5) and adjusted to be that the compressor (1) is provided with a circulating working medium channel to be communicated with the second heat supplier (11), the second heat supplier (11) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel to be communicated with the second compressor (10), the second compressor (10) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel to be communicated with the heat supplier (5), the second heat supplier (11) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel to be communicated with the evaporator (4) through the newly added water turbine (A), the second heat supplier (11) is also provided with a heated medium channel to be communicated with the outside, the expander (2) and the newly added water turbine (A) are connected with the second compressor (10), forming a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
15. A second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to any one of claims 2 to 3 and 6 to 7, the second compressor, the second heat supplier and the newly added throttle valve are added, the compressor (1) is communicated with the heat supplier (5) and adjusted to be the compressor (1) which is communicated with the second heat supplier (11) through a circulating working medium channel, the second heat supplier (11) is also communicated with the second compressor (10) through a circulating working medium channel, the second compressor (10) is communicated with the heat supplier (5) through a circulating working medium channel, the second heat supplier (11) is also communicated with the evaporator (4) through the newly added throttle valve (B), the second heat supplier (11) is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, the expander (2) is connected with the second compressor (10) and transmits power, and a second type heat driving compression heat pump is formed.
16. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly added water turbine are added in any second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump of claims 2-3 and 6-7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on an evaporator (4) and communicated with the second compressor (10), the second compressor (10) is also communicated with a second heat supplier (11) through a circulating working medium channel, the second heat supplier (11) is also communicated with the evaporator (4) through a newly added water turbine (A), the second heat supplier (11) is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, and the expander (2) and the newly added water turbine (A) are connected with the second compressor (10) and transmit power to form the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump.
17. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second compressor, a second heat supplier and a newly-added throttle valve are added in any one of the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump of claims 2-3 and 6-7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on the evaporator (4) and is communicated with the second compressor (10), the second compressor (10) is also communicated with a second heat supplier (11), the second heat supplier (11) is also communicated with the evaporator (4) through the newly-added throttle valve (B), the second heat supplier (11) is also communicated with the outside through a heated medium channel, and the expander (2) is connected with the second compressor (10) and transmits power to form the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump.
18. A second type of heat-driven compression heat pump, which is formed by adding a second compressor, a second evaporator and a second booster pump in any one of the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump of claims 2-3 and 6-7, wherein a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on the evaporator (4) and is communicated with the second evaporator (12) through a second booster pump (13), the second evaporator (12) is also communicated with a second compressor (10) through a circulating working medium channel, the second compressor (10) is also communicated with a heat supply device (5), the second evaporator (12) is also communicated with the outside through a heat source medium channel, and the expander (2) is connected with the second compressor (10) and transmits power to form the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump; wherein the expander (2) is connected with the second compressor (10) and the second booster pump (13) and transmits power.
19. A second type of heat-driven compression heat pump, which is characterized in that a second compressor, a second evaporator and a second booster pump are added in any one of the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump of claims 2-3 and 6-7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on a condenser (6) and is communicated with the second evaporator (12) through a second booster pump (13), the second evaporator (12) is also communicated with the second compressor (10) through a circulating working medium channel, the second compressor (10) is also communicated with a heat supply device (5), the second evaporator (12) is also communicated with the outside through a heat source medium channel, and an expander (2) is connected with the second compressor (10) and transmits power to form the second type of heat-driven compression heat pump; wherein the expander (2) is connected with the second compressor (10) and the second booster pump (13) and transmits power.
20. A second type of thermally driven compression heat pump, which is the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to any one of claims 2 to 3, wherein a second booster pump, a second expander and a second condenser are added, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged in the heat supply device (5) and is communicated with the second expander (14), the second expander (14) is also communicated with a circulating working medium channel and a second condenser (15), the second condenser (15) is also communicated with the evaporator (4) through the second booster pump (13) and the circulating working medium channel, the second condenser (15) is also communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, the second expander (14) is connected with the compressor (1) and transmits power, or the second expander (14) is connected with the compressor (1) and the second booster pump (13) and transmits power, so that the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is formed.
21. A second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second booster pump, a second expansion machine and a second condenser are added in any second type of thermally driven compression heat pump of claims 6 to 7, a circulating working medium channel is additionally arranged on an evaporator (4) and is communicated with the second expansion machine (14), the second expansion machine (14) is also communicated with a second condenser (15) through a circulating working medium channel, the second condenser (15) is also communicated with the evaporator (4) through a second booster pump (13), the second condenser (15) is also communicated with the outside through a cooling medium channel, the second expansion machine (14) is connected with a compressor (1) and transmits power, or the second expansion machine (14) is connected with the compressor (1) and the second booster pump (13) and transmits power, so that the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is formed.
22. A second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump is characterized in that a second booster pump, a second expander and a second condenser are added in any one of the second kind of heat-driven compression heat pump of claims 2-3 and 6-7, the communication between the expander (2) and the condenser (6) is adjusted to be that the expander (2) is provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the second condenser (15), the second condenser (15) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the evaporator (4) through a second booster pump (13), the second condenser (15) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with a second expander (14), the second expander (14) is also provided with a circulating working medium channel which is communicated with the condenser (6), the second expander (14) is connected with the compressor (1) and transmits power or the second expander (14) is connected with the compressor (1) and the second booster pump (13) and transmits power, forming a second type of thermally driven compression heat pump.
23. The second type of thermally driven compression heat pump is the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump according to any one of claims 1 to 22, wherein a power machine is added, the power machine is connected with the compressor (1) and provides power for the compressor (1), and the second type of thermally driven compression heat pump driven by additional external power is formed.
24. The second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump is the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump according to any one of claims 1 to 22, wherein a working machine is added, and the expansion machine (2) is connected with the working machine and provides power for the working machine to form the second kind of thermally driven compression heat pump additionally providing power load to the outside.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610121093 | 2016-02-25 | ||
| CN2016101210932 | 2016-02-25 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN106440510A CN106440510A (en) | 2017-02-22 |
| CN106440510B true CN106440510B (en) | 2020-05-29 |
Family
ID=58167733
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610815112.1A Active CN106440510B (en) | 2016-02-25 | 2016-08-30 | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN106440510B (en) |
Families Citing this family (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111721023B (en) * | 2019-01-07 | 2023-08-29 | 李华玉 | Second type heat driven compression heat pump |
| US20220260285A1 (en) * | 2019-06-13 | 2022-08-18 | Huayu Li | Reversed single-working-medium vapor combined cycle |
| CN115478919A (en) * | 2019-06-13 | 2022-12-16 | 李华玉 | Reverse single working medium steam combined cycle |
| GB2599866B (en) * | 2019-06-14 | 2023-03-29 | Li Huayu | Reversed single-working-medium vapor combined cycle |
| WO2020248588A1 (en) * | 2019-06-14 | 2020-12-17 | 李华玉 | Reverse single working medium steam combined cycle |
| CN111964291A (en) * | 2019-07-21 | 2020-11-20 | 李华玉 | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump |
| CN111964292A (en) * | 2019-07-23 | 2020-11-20 | 李华玉 | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump |
| CN114893924A (en) * | 2019-08-21 | 2022-08-12 | 李华玉 | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump |
| CN110631280A (en) * | 2019-08-23 | 2019-12-31 | 李华玉 | Multidirectional thermodynamic cycle of the second kind |
| WO2021047126A1 (en) * | 2019-09-10 | 2021-03-18 | 李华玉 | Reverse single-working-medium steam combined cycle |
| WO2021047125A1 (en) * | 2019-09-10 | 2021-03-18 | 李华玉 | Reverse single-working-medium steam combined cycle |
| WO2021047127A1 (en) * | 2019-09-11 | 2021-03-18 | 李华玉 | Reverse single-working-medium steam combined cycle |
| CN112344579A (en) * | 2019-10-16 | 2021-02-09 | 李华玉 | Reverse single working medium steam combined cycle |
| CN115355627A (en) * | 2020-03-14 | 2022-11-18 | 李华玉 | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump |
| CN115355628A (en) * | 2020-03-14 | 2022-11-18 | 李华玉 | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump |
| CN115218510A (en) * | 2020-03-15 | 2022-10-21 | 李华玉 | Second-type thermally-driven compression heat pump |
| CN115218515A (en) * | 2020-03-15 | 2022-10-21 | 李华玉 | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump |
| CN113310237A (en) * | 2020-05-11 | 2021-08-27 | 李华玉 | Internal combustion engine type combined cycle heat pump device |
| CN113310236A (en) * | 2020-05-11 | 2021-08-27 | 李华玉 | Internal combustion engine type combined cycle heat pump device |
| CN113310242A (en) * | 2020-05-12 | 2021-08-27 | 李华玉 | Internal combustion engine type combined cycle heat pump device |
| CN113310240A (en) * | 2020-05-19 | 2021-08-27 | 李华玉 | Internal combustion engine type combined cycle heat pump device |
| CN113310244A (en) * | 2020-05-19 | 2021-08-27 | 李华玉 | Internal combustion engine type combined cycle heat pump device |
| CN113310241A (en) * | 2020-05-19 | 2021-08-27 | 李华玉 | Internal combustion engine type combined cycle heat pump device |
| CN113309630A (en) * | 2020-05-20 | 2021-08-27 | 李华玉 | Internal combustion engine type combined cycle heat pump device |
| CN113309628A (en) * | 2020-05-20 | 2021-08-27 | 李华玉 | Internal combustion engine type combined cycle heat pump device |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4342201A (en) * | 1980-02-19 | 1982-08-03 | Kawasaki Jukogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Energy recovery apparatus for a gas compressor plant |
| US5833446A (en) * | 1996-01-31 | 1998-11-10 | Carrier Corporation | Deriving mechanical power by expanding a liquid to its vapour |
| CN1349603A (en) * | 1999-03-05 | 2002-05-15 | 大金工业株式会社 | Air conditioner |
| CN101135504A (en) * | 2006-08-29 | 2008-03-05 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | Refrigerating cycle device |
| CN101298949A (en) * | 2008-05-20 | 2008-11-05 | 洪国伟 | Heat pump |
| CN101701755A (en) * | 2009-10-20 | 2010-05-05 | 李华玉 | Sectionalized heat absorption, sectionalized compression and sectionalized expansion gas compression type heat pump |
| CN103765125A (en) * | 2011-09-01 | 2014-04-30 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Refrigeration cycle device |
| CN103940134A (en) * | 2014-04-03 | 2014-07-23 | 天津大学 | Vapor compression refrigeration cycle expansion work recovery system |
| CN105332747A (en) * | 2015-12-03 | 2016-02-17 | 陈栋 | Ultralow-temperature heat source power generation and heat energy transfer system |
-
2016
- 2016-08-30 CN CN201610815112.1A patent/CN106440510B/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4342201A (en) * | 1980-02-19 | 1982-08-03 | Kawasaki Jukogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Energy recovery apparatus for a gas compressor plant |
| US5833446A (en) * | 1996-01-31 | 1998-11-10 | Carrier Corporation | Deriving mechanical power by expanding a liquid to its vapour |
| CN1349603A (en) * | 1999-03-05 | 2002-05-15 | 大金工业株式会社 | Air conditioner |
| CN101135504A (en) * | 2006-08-29 | 2008-03-05 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | Refrigerating cycle device |
| CN101298949A (en) * | 2008-05-20 | 2008-11-05 | 洪国伟 | Heat pump |
| CN101701755A (en) * | 2009-10-20 | 2010-05-05 | 李华玉 | Sectionalized heat absorption, sectionalized compression and sectionalized expansion gas compression type heat pump |
| CN103765125A (en) * | 2011-09-01 | 2014-04-30 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Refrigeration cycle device |
| CN103940134A (en) * | 2014-04-03 | 2014-07-23 | 天津大学 | Vapor compression refrigeration cycle expansion work recovery system |
| CN105332747A (en) * | 2015-12-03 | 2016-02-17 | 陈栋 | Ultralow-temperature heat source power generation and heat energy transfer system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN106440510A (en) | 2017-02-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN106440510B (en) | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN108679880B (en) | Double-working medium combined cycle compression heat pump | |
| CN106016821B (en) | First-class thermally driven compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106403372B (en) | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN106322828B (en) | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN106225321B (en) | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN106568233B (en) | Third-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN106352601B (en) | Third-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN106225316B (en) | Third-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN106440493B (en) | Fourth type thermal driving compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106247674B (en) | First-class thermally driven compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN105841401B (en) | First-class thermally driven compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106322821B (en) | Fourth type thermal driving compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN105953464B (en) | Fourth type thermal driving compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106403371B (en) | First-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN105953465B (en) | Fourth type thermal driving compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106247653B (en) | First-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN105928246B (en) | Fifth type thermal driving compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106440498B (en) | Fourth type thermal driving compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106440509B (en) | Third-class thermally-driven compression heat pump | |
| CN106196710B (en) | First-class thermally driven compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106440495B (en) | Fourth type thermal driving compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN105953463B (en) | First-class thermally driven compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN106403361B (en) | Fifth type thermal driving compression-absorption heat pump | |
| CN111964292A (en) | Second-class thermally-driven compression heat pump |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |