CN101141172B - Transmission method and transmission system of wireless relay system - Google Patents
Transmission method and transmission system of wireless relay system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101141172B CN101141172B CN2006101268658A CN200610126865A CN101141172B CN 101141172 B CN101141172 B CN 101141172B CN 2006101268658 A CN2006101268658 A CN 2006101268658A CN 200610126865 A CN200610126865 A CN 200610126865A CN 101141172 B CN101141172 B CN 101141172B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- control
- unit
- node
- information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 108
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 84
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 200
- 230000011218 segmentation Effects 0.000 claims description 35
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 claims description 19
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- SJWPTBFNZAZFSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N pmpp Chemical compound C1CCSC2=NC=NC3=C2N=CN3CCCN2C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C1=C2 SJWPTBFNZAZFSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 description 5
- 101100011863 Arabidopsis thaliana ERD15 gene Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 206010010099 Combined immunodeficiency Diseases 0.000 description 4
- 101100191082 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) GLC7 gene Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101100274406 Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) cid1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 238000001360 collision-induced dissociation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 101150021084 CID2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101150052985 cids-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002407 reforming Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 208000012503 Bathing suit ichthyosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009365 direct transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010295 mobile communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006855 networking Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/08—Load balancing or load distribution
- H04W28/086—Load balancing or load distribution among access entities
- H04W28/0861—Load balancing or load distribution among access entities between base stations
- H04W28/0862—Load balancing or load distribution among access entities between base stations of same hierarchy level
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/02—Diversity systems; Multi-antenna system, i.e. transmission or reception using multiple antennas
- H04B7/022—Site diversity; Macro-diversity
- H04B7/026—Co-operative diversity, e.g. using fixed or mobile stations as relays
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/24—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts
- H04B7/26—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile
- H04B7/2603—Arrangements for wireless physical layer control
- H04B7/2606—Arrangements for base station coverage control, e.g. by using relays in tunnels
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/04—TPC
- H04W52/18—TPC being performed according to specific parameters
- H04W52/24—TPC being performed according to specific parameters using SIR [Signal to Interference Ratio] or other wireless path parameters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
- H04W40/02—Communication route or path selection, e.g. power-based or shortest path routing
- H04W40/22—Communication route or path selection, e.g. power-based or shortest path routing using selective relaying for reaching a BTS [Base Transceiver Station] or an access point
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/02—Terminal devices
- H04W88/04—Terminal devices adapted for relaying to or from another terminal or user
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
The present invention discloses a transmission method in a wireless relay system, which jointly transmits data between a source node and a destination node through a plurality of relay stations. These relay stations transmit same data on the same time frequency resources and transmit different data on varied time frequency resources. The destination node demodulates and decodes received superposed signals of the same data transmitted by the RS on the same time frequency resource. In addition, the destination node demodulates and decodes different data transmitted by the RS on the varied time frequency resource and matches demodulated and decoded data on demand and finally acquires the transmitted data. Moreover, the present invention discloses a wireless relay transmission system. The transmission method and the transmission system provided by the present invention can improve link transmission reliability, realize load balance amongst a plurality of relay stations, avoid overload of single relay station and enhance service quality for the destination node.
Description
Technical Field
The present invention relates to mobile communication technologies, and in particular, to a transmission method and a transmission system in a wireless relay system.
Background
With the increasing demand for wireless communication, Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) technology is becoming one of the hot spots in the current communication technology. However, in the wireless communication system, there are areas where the wireless communication signal strength is low due to the path attenuation of electromagnetic waves, the obstruction of buildings, and the like, and the communication quality of mobile terminals located in these areas is poor. As the demand for broadband wireless communication is increasing, the demand for wireless bandwidth is becoming greater and higher carrier frequencies are used in new protocols and systems, but attenuation of radio waves increases as the frequency increases. Therefore, high carrier frequencies inevitably face the problem of high attenuation, further limiting the coverage of the Base Station (BS). In order to solve the coverage problem of the BS, a Relay Station (RS) is generally required to enhance a wireless communication signal between the BS and a Mobile Station (MS). The RS and the BS do not need to be in wired transmission and only communicate through a wireless link, so that the method has the advantages of low network deployment cost and simplicity in deployment.
The working principle of the RS is as follows: considering the link between the BS and the RS as a virtual connection, the connection is directional, i.e. the uplink connection and the downlink connection are different. Each connection may be distinguished using a Connection Identification (CID), different connections having different CIDs, the CIDs being uniformly assigned by the BS. And each RS maintains a CID binding table managed by the RS, and forwards data corresponding to the managed connection according to the maintained CID binding table. In the process of establishing the connection between the BS and the MS, the BS informs the RS and the MS of the corresponding CID. The BS broadcasts the corresponding relationship between the CID and the time frequency resource to all terminals within the coverage range of the BS in the frame header of the data frame, and the terminals can extract data belonging to the BS from the downlink service frame of the BS and send the data in the uplink service frame after acquiring the corresponding relationship between the CID and the time frequency resource from the frame header. The RS corresponds to one terminal for the BS, and corresponds to one base station for the terminal. One BS and a plurality of RSs are arranged in one area, and the BS and each RS can orthogonally multiplex the same time-frequency resource in an allowed interference range and can also non-orthogonally multiplex the same time-frequency resource. Before the relay function is started, the RS applies for starting the relay function to the BS, and after obtaining the approval of the BS, returns a response to the BS and starts the relay function. The process of forwarding data by using the RS is as follows: the BS or the MS carries out coding modulation on data to be sent and then sends the data out; the RS which starts the relay function demodulates and decodes the received data, then carries out coding modulation again, and then forwards the data; and after receiving the data forwarded by the RS, the MS or the BS estimates the channel coefficient of the data and demodulates and decodes the data to obtain the transmitted data.
However, in a wireless communication system including a relay forwarding station, such as a Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) system with RS introduced, besides the handover between different BSs, there are also handover problems between RS and BS, and between RS and RS. In a wireless communication system including a relay forwarding station, generally, only one RS most suitable for serving a current MS is selected for the MS to serve, and when relay handover is performed, a BS reassigns one RS for the MS, and if the MS is located at a boundary of multiple RSs at this time, a most suitable RS may not be found for serving the MS, or other situations causing degradation of link quality between the currently serving RS and the MS occur, the defects of reduction of service quality of the current MS, even disconnection and the like are caused.
In addition, if several relay RS forwarding stages exist between the BS and the MS, there are many situations involved in the transmission between two nodes, that is, there are various situations such as BS → RS, RS → MS, BS → MS or MS → RS, RS → BS, MS → BS, etc. in the transmission between the source node and the target node, if only one relay RS is selected for forwarding between two nodes, the same problem as above will occur, that is, the service quality to the MS will be reduced, and even the defect of disconnection will be caused.
In addition, when a certain MS has a plurality of traffic flows with large data volume, a single RS serving the MS may greatly increase the load of the RS and increase the processing load, and in a severe case, the quality of service of the RS to other users may be affected, or even the performance of the entire system may be affected.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above, a first objective of the present invention is to provide a transmission method in a wireless relay system, which can effectively improve the quality of service for an MS and prevent disconnection.
A second main objective of the present invention is to provide a transmission method in a wireless relay system, which can effectively adjust the load balance of the RS and avoid the overload of a single RS.
A third main object of the present invention is to provide a wireless relay transmission system, which can effectively improve the quality of service for the MS and avoid overloading of a single RS.
The first main purpose of the invention is realized by the following technical scheme:
a transmission method in a wireless relay system, in which data between a source node and a target node is collectively forwarded by a plurality of relay nodes RS, the method comprising the steps of:
A. the source node generates a sending signal after coding and modulating the information of the service flow to be sent and sends the sending signal out;
B. the RS participating in relay forwarding demodulates and decodes the received signals sent by the source node, then performs coded modulation again, and forwards the coded and modulated signals to the target node on the same time-frequency resource together according to the indication information of the control node;
C. and the target node receives signals forwarded by a plurality of RSs at the same time, the signals are superposition of the signals forwarded by the plurality of RSs, the channel coefficient is estimated, and the received signals are demodulated and decoded to obtain the transmitted information.
Wherein, the indication information of the control node in step B includes: time frequency resource information used by the transmitted service flow; the RS participating in relay forwarding forwards the data on the same time-frequency resource according to the time-frequency resource information.
Wherein, the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B is: the control node sends a control message to designate the RS serving as a relay forwarding station and serving the service flow of the designated characteristic identifier, and then the RSs forward the signals with the same characteristic identifier on the same time-frequency resource together according to the service flow characteristic identifier carried in the correctly received signal;
or the RS participating in relay forwarding is: and if the channel quality between the RS and the target node meets the RS with a preset value, each RS determines whether to forward correctly received signals with the same characteristic identifier on the same time-frequency resource according to the channel quality information between the RS and the target node.
Wherein, the control node in step B is: base station BS or control capable RS.
The sending signal in step a carries a feature identifier of the transmitted service flow, and the sending signal is a single service flow signal; or the sending signal is a plurality of service flow signals, and each service flow signal corresponds to a different feature identifier.
If the RS maintains the CID list of the connection identifier of the service flow, the feature identifier of the service flow includes: the connection identifier CID of the service flow; the RS participating in relay forwarding is: and receiving a control message which is sent by the control node and adds the CID of a certain service flow, and adding the RS of the CID in the CID list.
Preferably, if participating in relay-forwarded RSiKnowing the channel coefficient h from itself to the target nodeiIf i is greater than or equal to 0, the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B performs re-coding modulation on the correctly received signal sent by the source node, and then further includes: using the channel coefficient hiSignal to be transmittedAnd carrying out pre-equalization processing, and then forwarding the processed data. And the pre-equalization process is: multiplying the signal to be transmitted by the channel coefficient hiConjugation of (a) to (b)i *。
Wherein, the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B is: all or part of the RSs in the set of all relay RSs capable of receiving the signal of the source node and capable of serving the target node.
And, the set of all relay RSs capable of receiving the signal of the source node and serving the target node further includes: a source node itself capable of directly serving a target node; the RS participating in relay forwarding further includes a source node itself, and the source node directly sends a signal to a target node; or the RS participating in relay forwarding does not include the source node itself.
If the RS participating in relay forwarding includes a source node, then:
the step B further comprises the following steps: after the source node performs coding modulation on the information of the service flow to be transmitted by adopting the same coding modulation mode as the RS participating in relay forwarding, the RS participating in relay forwarding transmits a signal subjected to coding modulation on the same time-frequency resource, and when pre-equalization processing is adopted, the source node multiplies a coefficient h by the source node before transmitting the signal0 *,h0 *Is the channel coefficient h between the source node and the target node0Conjugation of (1);
the superposed signal received in step C includes: and directly receiving the data sent by the source node.
If the RS participating in relay forwarding comprises a source node and the RS participating in relay forwarding adopts the same coding modulation mode as the source node, then:
the step B further comprises the following steps: the target node receives signals sent by the source node at the same time;
the step C further comprises the following steps: the target node combines the directly received signal of the source node with the received multiple RsS, accumulating the forwarded superposed signals, and if pre-equalization processing is adopted, multiplying the directly received signals of the source node by a coefficient h before accumulation0 *,h0 *Is the channel coefficient h between the source node and the target node0Conjugation of (1).
If the RS participating in relay forwarding comprises a source node and the RS participating in relay forwarding adopts a different coding modulation mode from that of the source node, then:
the step B further comprises the following steps: the target node receives signals sent by the source node at the same time;
in the step C, the target node firstly demodulates and decodes the received superposed signals forwarded by the multiple RSs, checks the check bit, judges whether the superposed signals are correct or not, and finishes the judgment if the superposed signals are correct, and then demodulates and decodes the signals directly received from the source node if the superposed signals are incorrect; or in the step C, the target node firstly demodulates and decodes the signal directly received from the source node, checks the check bit, judges whether the signal is correct or not, and finishes the judgment if the signal is correct, and then demodulates and decodes the received superposed signal forwarded by the plurality of RSs if the signal is incorrect.
In step B, the RS performs coding modulation on the received signal again as follows: the RS performs coding modulation on the received signal again by adopting a coding modulation mode which is the same as that of the source node, or the RS performs coding modulation on the received signal again by adopting a coding modulation mode which is different from that of the source node; the demodulation and decoding method corresponding to the step C is adopted.
The second main purpose of the invention is realized by the following technical scheme:
a transmission method in a wireless relay system, in which data between a source node and a target node is collectively forwarded by a plurality of relay nodes RS, the method comprising the steps of:
A. the source node transmits the information to be transmitted after coding modulation;
B. the RS participating in relay forwarding demodulates and decodes the received signal sent by the source node, then intercepts a specific bit stream according to the indication information of the control node for recoding and modulating, and then forwards the specific bit stream to the target node on different time-frequency resources together;
C. and the target node receives different data signals jointly forwarded by the multiple RSs, demodulates and decodes the received signals according to the indication information of the control node, and then splices the demodulated and decoded data to obtain transmitted information.
Wherein, the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B is: all or part of all sets of relay RSs capable of receiving signals of the source node and capable of serving the target node.
And, the set of all relay RSs capable of receiving the signal of the source node and serving the target node further includes: a source node itself capable of directly serving a target node; the RS participating in relay forwarding further includes a source node itself, and the source node directly sends a signal to a target node; or the RS participating in relay forwarding does not include the source node itself.
If the RS participating in relay forwarding includes a source node, and the source node is a control node, step B further includes: the source node intercepts data which are the same as a certain RS, and after the intercepted data are coded and modulated in a coding modulation mode which is the same as that of the RS, the source node and the RS send out signals to a target node on the same time-frequency resource; or the source node intercepts data different from all RSs, then carries out coding modulation on the intercepted data, and sends out signals to the target node on different time-frequency resources.
If the RS participating in relay forwarding includes a source node, and the source node is not a control node, the step B further includes: the control node sends the indication information to a source node, the source node intercepts data which are the same as a certain RS according to the received indication information, and after the intercepted data are coded and modulated in a coding modulation mode which is the same as that of the RS, the source node sends out signals to a target node on the same time-frequency resource with the RS; or the source node intercepts data different from all RSs, then carries out coding modulation on the intercepted data, and sends out signals to the target node on different time-frequency resources.
Wherein, the indication information of the control node in step B or step C includes: time-frequency resource information used by each segment of data stream and segmentation characteristics of the data;
the RS participating in relay forwarding in the step B intercepts the bit stream according to the segmentation characteristics in the indication information, and transmits the intercepted bit stream after carrying out coding modulation on the corresponding time frequency resources according to the time frequency resource information used by each segment in the indication information;
and C, the target node demodulates and decodes the received bit streams of the specific data forwarded by the RSs respectively, and then splices the demodulated and decoded data according to the segmentation characteristics in the indication information.
Wherein the segmentation features comprise: CID, segmentation start stop bit and segmentation sequence number of the data stream;
the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B intercepts the received data bit stream of the CID according to the segment start stop bit and the segment sequence number in the segment feature in the indication information;
and C, splicing the received bit streams containing the same CID and each segment of data by the target node according to the segment serial number in the segment characteristics in the indication information.
Wherein, the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B is: the control message is sent by the control node to specify the RS as a relay forwarding station.
And, the control node is: BS or control capable RS.
Preferably, if participating in relay-forwarded RSiKnowing the channel coefficient h from itself to the target nodeiIf i is not less than 0, the participation in the relay in the step BThe retransmitted RS performs re-coding modulation on the correctly received signal transmitted by the source node, and then further includes: using the channel coefficient hiAnd carrying out pre-equalization processing on the signal to be transmitted, and then forwarding the processed data. And the pre-equalization processing is as follows: multiplying the signal to be transmitted by the channel coefficient hiConjugation of (a) to (b)i *。
The third main purpose of the invention is realized by the following technical scheme:
a wireless relay transmission system, the system comprising: a source node, a plurality of RSs participating in relay forwarding, a target node and a control node, wherein,
the source node is used for generating a sending signal after the information to be sent is coded and modulated, and sending the sending signal out;
the control node is used for sending command information to the RS and the target node;
the multiple RSs participating in forwarding are used for demodulating and decoding the received signals sent by the source node, then carrying out coded modulation again, and then forwarding the coded and modulated signals to the target node together according to the indication information of the control node;
and the target node is used for receiving the signals sent by the RSs participating in forwarding, demodulating and decoding the received signals according to the indication information of the control node, and obtaining the transmitted information.
Wherein, the source node and the target node are respectively: BS and MS, or MS and BS, or BS and RS, or RS and MS, or MS and RS, or RS and BS, or RS and RS.
Wherein the RS includes: a control capable RS or a non-control capable RS.
Wherein, the RS participating in forwarding is: the control message is sent by the control node to specify the RS as a relay forwarding station.
Wherein the control node is: BS or control capable RS; for uplink transmission, the control node is an RS or BS directly controlling the target node, and if the target node has control capability, the control node is the target node; for downlink transmission, the control node is an RS or BS directly controlling the source node, and if the source node has control capability, the control node is the source node.
Wherein the RS includes: a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer and an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module and a control module, wherein,
the duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna;
a receiver for receiving data transmitted from the source node through an antenna of the duplexer, and converting the received data from a radio frequency signal to a baseband signal;
the downlink data processing module is used for processing downlink data received by the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data, extracting a control command of a control node from the received data, sending the control command to the control module, and then sending the demodulated and decoded data on a specified time-frequency resource position after carrying out coding modulation on the demodulated and decoded data according to the indication information of the control command under the control of the control module, or sending the demodulated and decoded data on the specified time-frequency resource position after carrying out interception and coding modulation on the demodulated and decoded data, or splicing the demodulated and decoded data;
the uplink data processing module is used for processing uplink data received by the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data, and then coding and modulating the demodulated and decoded data according to a control command of a control node extracted from the downlink data processing module under the control of the control module and then sending the demodulated and decoded data at a specified time-frequency resource position through the transmitter, or intercepting and coding and modulating the demodulated and decoded data and then sending the demodulated and decoded data at the specified time-frequency resource position through the transmitter, or splicing the demodulated and decoded data; measuring the quality of the received uplink signal to generate quality information, and generating reporting information of the quality information to be reported and sending the reporting information through a transmitter;
the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner;
the transmitter is used for receiving the data output by the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal and transmitting the radio frequency signal to a target node through an antenna of the duplexer;
and the control module is used for finishing the control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and for the RS with control capability, generating a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node.
The uplink data processing module in the RS comprises:
the uplink demodulation decoding unit is used for demodulating, de-mapping symbols, de-interleaving and channel decoding the uplink baseband signals received by the receiver to obtain uncoded original information data and outputting the obtained original information data;
the uplink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the uplink demodulation and decoding unit, outputting the whole data to the uplink coding and modulation unit according to a control command under the control of the control module, or intercepting a certain section of the data according to the control command and outputting the certain section of the data to the uplink coding and modulation unit, or splicing and outputting the stored sections of data to the uplink coding and modulation unit according to the control command;
an uplink channel measuring unit, configured to measure the quality of a received uplink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the uplink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
a feedback signal generating unit, configured to generate reporting information for the quality information output by the uplink channel measuring unit, and generate reporting information for the load condition of the RS determined to be reported by the control module;
a feedback information extraction unit, configured to extract feedback information from the data output by the uplink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the extracted feedback information to the control module;
the uplink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data output by the uplink data caching unit;
and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the reporting information generated by the feedback information generating unit and the uplink forwarding data generated by the uplink coding and modulating unit and sending the multiplexed information and the uplink forwarding data to the transmitter.
The downlink data processing module in the RS comprises:
a downlink demodulation decoding unit, configured to demodulate, de-symbol map, de-interleave, and channel decode a downlink baseband signal received by the receiver to obtain uncoded original information data, and output the obtained original information data;
a control command extracting unit, configured to extract a control command sent by a control node from original information data output by the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the control command to the control module;
a downlink data caching unit, configured to cache the downlink original information data processed by the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and output the entire data to the downlink code modulation unit according to the control command under the control of the control module, or intercept a certain section of the data according to the control command and output the intercepted data to the downlink code modulation unit, or splice stored sections of data according to the control command and output the spliced data to the downlink code modulation unit;
a downlink channel measuring unit, configured to measure the quality of a received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
the downlink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data output by the downlink data cache unit;
and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the control message generated by the control module and the downlink forwarding data generated by the downlink coding modulation unit together and sending the multiplexed data to the transmitter.
The control module in the RS comprises:
the analysis unit is used for receiving the control command sent by the control command extraction unit in the downlink data processing module, analyzing the received command and sending the analyzed control command to the control unit; receiving feedback information sent by a feedback information extraction unit in the uplink data processing module, analyzing the received information, and sending the analyzed feedback information to a control unit;
a control unit, configured to complete control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module, and the downlink data processing module, including: receiving a control command sent by the analysis unit, and controlling the downlink data cache unit and the uplink data cache unit to directly output, output after segmentation or output after splicing the data according to the control command; receiving quality information sent by an uplink channel measuring unit or a downlink channel measuring unit, judging whether reporting is needed according to the received quality information, outputting the quality information needing reporting to a feedback information generating unit, and controlling the feedback information generating unit to generate reporting information; after receiving the feedback information sent by the analysis unit, the RS with control capability combines the measurement result sent by the uplink channel measurement unit or the downlink channel measurement unit to control the control command generation unit to generate a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node;
the control command generating unit is used for generating a control message containing indication information for controlling a lower node under the control of the control unit for the RS with control capability and sending the control message to the multiplexer; for the RS without control capability, the control command generating unit is used for forwarding the control command sent by the RS with control capability or the BS at the upper level and sending the control command to the multiplexer.
Wherein the BS includes: a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer and an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module and a control module, wherein,
the duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna;
a receiver for receiving data transmitted from the source node through an antenna of the duplexer, and converting the received data from a radio frequency signal to a baseband signal;
the uplink data processing module is used for receiving data sent to the BS by the MS through the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data or demodulating, decoding and splicing the received data under the control of the control module to obtain transmitted data, extracting feedback information from the demodulated and decoded data and sending the feedback information to the control module;
the control module is used for finishing the control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, generating a control message containing indication information according to the feedback information received from the uplink data processing module and sending the control message to the downlink data processing module;
the downlink data processing module is used for carrying out coding modulation on the data to be sent under the control of the control module, and sending out the data subjected to coding modulation and the control message sent by the control module through the transmitter at the time-frequency resource position allocated to the data to be sent;
the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner;
and the transmitter is used for receiving the data of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal, and transmitting the radio frequency signal to the target node through the antenna of the duplexer.
The uplink data processing module in the BS comprises:
the uplink demodulation decoding unit is used for demodulating, de-mapping symbols, de-interleaving and channel decoding a baseband signal which is sent to the BS by the MS and received by the receiver to obtain uncoded original information data and outputting the obtained original information data;
the uplink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the uplink demodulation decoding unit and directly outputting the data under the control of the control module or splicing the data and then outputting the data;
an uplink channel measuring unit, configured to measure the quality of the received uplink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the uplink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
and the feedback information extraction unit is used for extracting feedback information from the data output by the uplink demodulation and decoding unit and sending the extracted feedback information to the control module.
The downlink data processing module in the BS comprises:
a downlink data caching unit, configured to cache original information data to be sent;
the downlink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data in the downlink data cache unit;
and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the control message generated by the control module and the downlink sending data generated by the downlink coding unit together and sending the multiplexed data to the transmitter.
The control module in the BS includes: an analyzing unit, a control command generating unit and a control unit, wherein,
the analysis unit is used for receiving the feedback information sent by the feedback information extraction unit in the uplink data processing module, analyzing the received information and sending the analyzed feedback information to the control unit;
a control command generating unit for generating a control message containing indication information for controlling a lower node under the control of the control unit and transmitting the control message to the multiplexer;
a control unit, configured to complete control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module, and the downlink data processing module, including: and the control command generating unit generates a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node according to the feedback information and the quality information control command.
Wherein the MS includes: a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer and an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module and a control module, wherein,
the duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna;
a receiver for receiving data transmitted from the source node through an antenna of the duplexer, and converting the received data from a radio frequency signal to a baseband signal;
a downlink data processing module, configured to receive data sent by the BS to the MS through the receiver, demodulate and decode the received data or demodulate and decode and splice the received data under the control of the control module to obtain transmitted data, extract a control command from the demodulated and decoded data, send the control command to the control module, measure the quality of a received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
the control module is used for controlling the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and controlling the downlink data processing module to demodulate and decode the data or splice the data after demodulating and decoding according to a control command sent by the received downlink data processing module; receiving quality information sent by a downlink data processing module, and controlling an uplink data processing module to generate reporting information;
the uplink data processing module is used for performing coding modulation on data to be sent under the control of the control module, and sending the data subjected to coding modulation and the generated report information out through a transmitter at a time-frequency resource position allocated to the data to be sent;
the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner;
and the transmitter is used for receiving the data of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal, and transmitting the radio frequency signal to the target node through the antenna of the duplexer.
The downlink data processing module in the MS comprises:
a downlink demodulation decoding unit, configured to demodulate, de-symbol map, de-interleave, and channel decode a baseband signal sent to the MS by the BS received by the receiver to obtain uncoded original information data, and output the obtained original information data;
the downlink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the downlink demodulation decoding unit and directly outputting the data under the control of the control module or splicing the data and then outputting the data;
a downlink channel measuring unit, configured to measure the quality of a received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
and the control command extracting unit is used for extracting a control command from the data processed by the downlink demodulation and decoding unit and sending the control command to the control module.
The uplink data processing module in the MS comprises:
the uplink data caching unit is used for caching original information data to be sent;
the uplink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data in the uplink data cache unit;
the feedback information generating unit is used for generating reporting information from the quality information which is sent by the control module and needs to be reported;
and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the reporting information generated by the feedback information generating unit and the uplink sending data generated by the uplink coding and modulating unit together and sending the multiplexed information to the transmitter.
The control module in the MS comprises:
the analysis unit is used for receiving the control command sent by the control command extraction unit in the downlink data processing module, analyzing the received command and sending the analyzed control command to the control unit;
a control unit, configured to complete control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module, and the downlink data processing module, including: receiving a control command sent by the analysis unit, and controlling the downlink data cache unit to directly output the data according to the control command or output the data after splicing; receiving the quality information sent by the downlink channel measuring unit, judging whether reporting is needed according to the received quality information, if so, sending the quality information needed to be reported to a feedback information generating unit in the uplink data processing module, and generating reporting information by the feedback information unit.
According to the method and the system, data between a source node and a target node are jointly forwarded by a plurality of relay nodes RS, the RSs can forward the same data on the same time-frequency resource and also can forward different data on different time-frequency resources, and the target node demodulates and decodes received superposed signals of the same data forwarded by the RSs on the same time-frequency resource; the target node demodulates and decodes the received different data forwarded by the RS on different time frequency resources respectively, splices the demodulated and decoded data according to needs, and finally obtains the transmitted data, thereby improving the reliability of link transmission, realizing the load balance among a plurality of RSs, improving the quality of service for the terminal, achieving the performance which cannot be obtained by a single service RS, and providing the transmission with higher speed and lower bit error rate for the target node.
Drawings
Fig. 1 is a relationship diagram of a transmission method in a wireless relay system according to the present invention.
Fig. 2 is a flowchart of a transmission method in a first wireless relay system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 3 is a flowchart of an embodiment in which a source node sends a signal twice and a target node receives a signal once when a direct connection from the source node to the target node is included in a transmission method in a first wireless relay system according to the present invention.
Fig. 4 is a flowchart of an embodiment in which a source node sends a signal once and a target node receives a signal twice when a direct connection from the source node to the target node is included in a transmission method in a first wireless relay system according to the present invention.
Fig. 5 is a flowchart of an embodiment of a transmission method in a second wireless relay system according to the present invention.
Fig. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of an RS in an embodiment of a wireless relay transmission system according to the present invention.
Fig. 7 is a schematic diagram of an internal structure of an RS in an embodiment of a wireless relay transmission system according to the present invention.
Fig. 8 is a schematic diagram of an internal structure of a BS in an embodiment of a wireless relay transmission system of the present invention.
Fig. 9 is a schematic diagram of an internal structure of an MS in an embodiment of a wireless relay transmission system according to the invention.
Detailed Description
In order to better understand the technical solution of the present invention, the following will further describe the technical solution of the present invention with reference to the embodiments and the accompanying drawings.
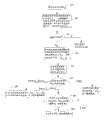
The basic idea of the invention is: the data between the source node and the target node are jointly forwarded by a plurality of RSs, the RSs can forward the same data on the same time-frequency resource and also can forward different data on different time-frequency resources, and the target node demodulates and decodes the received superposed signals of the same data forwarded by the RSs on the same time-frequency resource; the target node demodulates and decodes the received different data forwarded by the RS on different time frequency resources respectively, splices the demodulated and decoded data according to the requirement, and finally obtains the transmitted data, thereby improving the reliability of link transmission and realizing the load balance among a plurality of RSs. Since the transmission of data in this method is from point-to-multipoint to point mode, this transmission mode is called PMPP transmission mode. The plurality of RSs refer to one or more RSs, and for simplicity of description, the plurality of RSs refer to one or more RSs hereinafter.
Referring to fig. 1, fig. 1 is a schematic diagram illustrating a relationship between PMPP transmission modes in the present invention. As shown in the figure, there are k RSs participating in relay forwarding between the source node and the target node, and if the source node can also directly contact with the target node, there may also be direct connection between the source node and the target node, as shown by the dashed dotted line in the figure. H in the figureiIs the channel coefficient of RSi to the target node, where h0Is the channel coefficient between the source node and the target node. In the downlink transmission process, i.e. data starts from the BS and stops in the MS, the PMPP mode can be subdivided into four cases, i.e. the source node → the target node can represent BS → RS, RS → MS, BS → MS; during uplink transmission, i.e. from dataStarting at the MS and ending at the BS, the PMPP mode can be subdivided into four cases, i.e., the source node → the target node can represent MS → RS, RS → BS, MS → BS.
Referring to fig. 1, the present invention provides two methods, in the first method, the relay RS forwards the same data on the same time frequency resource, and in the second method, the relay RS forwards different data on different time frequency resources. The following are detailed below.
The first method will be described first.
The first method is described in detail below with reference to three embodiments, where there is a traffic flow between the source node and the destination node.
The first embodiment is as follows:
referring to fig. 2, fig. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a first embodiment of a transmission method in a first wireless relay system according to the present invention. In this embodiment, the BS or the RS with control function maintains an active set of RSs for the target node, that is, a set of relay RSs capable of receiving the signal of the source node and serving the target node. The judgment standard for entering or exiting the active set is that all relay RSs monitor the quality of uplink signals of the source node or the target node, and the quality information of the received uplink signals is judged whether to meet the reporting requirement or not, or whether to reach a preset threshold value, and if so, the quality information is reported to a BS or an RS with control capability, and the RS active set is required to enter or exit. For the sake of clarity, the present embodiment does not include the case where the source node directly sends a signal to the target node. As shown in fig. 2:
In this step, the source node may be a base station BS, an RS with control capability, an RS without control capability, or an MS.
The sending signal carries information related to the signal, such as a connection identifier CID.
In this step, the indication information of the control node means: and directly sending a control message containing the indication information by the BS or the RS with control capability or sending the control message containing the indication information of the BS or the RS with control capability forwarded by other RSs to the relay RS at the current stage, wherein the indication information contains time-frequency resource information used by the current service flow.
The RS participating in relay forwarding determines whether the received signal needs to be forwarded according to CID information carried in the signal, and if the signal needs to be forwarded, the RS forwards the signal at the time-frequency resource position according to the time-frequency resource position information in the indication information of the control node, because CIDs carried by the same signal are the same and the time-frequency resource information allocated to the signal is the same, it can be ensured that all the RSs participating in relay forwarding forward the received same signal at the same time-frequency resource.
All RSs in the RS active set receive signals sent by the source node, demodulate and decode the received signals and judge whether the RS needs to participate in forwarding, wherein the judgment condition is as follows: firstly, a signal from a source node is correctly received, and then whether the channel quality between the source node and a target node meets a preset threshold value or not is judged, wherein the control node designates the channel quality as a relay forwarding station. If the relay RS meets the forwarding condition after judgment, the relay RS performs re-coding modulation on the demodulated and decoded data, and the coding modulation mode can be the same as that of the source node or different from that of the source node. If the channel information between itself and the target node is known at this time, namely RS is knowniChannel coefficient h to target nodeiIf i is greater than or equal to 0, the signal to be transmitted is multiplied by the conjugate h of the channel coefficienti *And then sent out, i.e. the forwarded data at that time <math>
<mrow>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
</msub>
<mo>=</mo>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>RS</mi>
</msub>
<mo>×</mo>
<msubsup>
<mi>h</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
<mo>*</mo>
</msubsup>
<mo>,</mo>
</mrow>
</math> The situation is called as adopting a pre-equalization technology; if the channel information is unknown, the data after code modulation is directly sent out, namely the forwarding data X at the momenti=XRS(ii) a If the relay RS does not meet the forwarding condition after the judgment, the relay RS discards the demodulated and decoded data, and the process is ended.
The method for the control node to designate the RS as the relay forwarding station comprises the following steps: and directly sending the control message by the BS or the RS with control capability or sending the control message of the BS or the RS with control capability forwarded by other RSs to the relay RS at the current stage, and informing the RS to serve as the relay forwarding station. The method can be as follows: the control node informs the RS of the CID of the signal to be forwarded, and the RS forwards the service flow of the CID. If the system is a WiMAX system, the relay RS can add the CID in the CID list maintained by the relay RS, and when the control node informs the RS to stop relay forwarding of the service flow of a certain CID, the RS deletes the CID of the service flow from the maintained CID list.
In this step, the target node may be an RS with control capability, an RS without control capability, an MS, a BS, or the like.
In this embodiment, it can be found that by using the pre-equalization technique, diversity gain of multiple forwarding RSs can be obtained, and reliability of transmission is higher. Of course, if the channel information between the RS participating in forwarding and the target node is not known, the pre-equalization technique may not be used.
The following describes in detail a case where the transmission method in the first wireless relay system includes direct data transmission from the source node to the target node. When there is a direct connection of the source node to the target node, there may be four transmission strategies. Strategy 1: the source node sends signals twice, the target node only receives signals for 1 time, namely the source node sends signals once first, the RS receives the signals, the target node does not receive the signals, the source node sends signals to the target node once again while the RS forwards the signals to the target node, namely the source node sends signals for the second time, only the signals for the current time are sent to the target node, and at the moment, the target node simultaneously receives the signals forwarded by the RS and the signals directly sent to the target node by the BS; strategy 2: the source node only sends a signal once, the target node receives signals twice, namely the source node only sends a signal once, and simultaneously the RS and the target node receive the signals, namely the target node receives the first signal, the source node does not send a signal to the target node any longer while the RS forwards the signal to the target node, and the target node receives a second signal, namely the signal forwarded by the RS; strategy 3: the source node sends signals twice, and the target node receives the signals twice, namely the target node receives the first signals under the condition of the strategy 1; strategy 4: in this case, the target node does not perform any processing on the signal sent by the source node, and the processing flow is the same as that in the first embodiment, so that the following description is not given for the case in the policy 4, but only for the first three cases.
Example two:
referring to fig. 3, fig. 3 is a flowchart of an embodiment of a PMPP transmission method in which a source node transmits a signal twice and a target node receives a signal once in policy 1. Suppose the signal sent by the source node is XN1Generating a signal X to be transmitted by RS re-encoding modulationRSWherein, the code modulation mode can adopt a code modulation mode different from the source node, or adopt the same code modulation mode as the source node, and the RS is knowniChannel coefficient to target node is hiWherein h isiIs a reaction of with XRSVectors with the same dimensions:
In this step, the control node designates the RSiThe method for forwarding is that the BS or the RS with control capability directly sends a control message or a control message of the BS or the RS with control capability forwarded by other RS to the relay RS of the current stage, and informs the RS to be used as a relay station for forwarding. The control message may include a CID that informs the RS of the signal to be forwarded.
In this step, the indication information of the control node refers to that the BS or the RS with control capability directly sends a control message containing the indication information or a control message containing the indication information of the BS or the RS with control capability forwarded by another RS to the relay RS of the current stage, where the indication information contains a coding and modulation scheme to be adopted by the relay RS, or the relay RS of the current stage decides which coding and modulation scheme should be adopted by itself.
And step 306, the target node receives signals simultaneously transmitted from a plurality of RSs and the source node, estimates equivalent synthesized channel coefficients, and demodulates and decodes the received signals. In this step, because the source node adopts the same code modulation mode as the RS participating in forwarding and transmits data on the same time-frequency resource as the RS participating in forwarding at the same time, the processing method in this step is the same as that in the case where no data from the source node to the target node is directly transmitted, and no other special processing is required.
When the transmission is finished, if the signal transmission is wrong, the retransmission is carried out by a corresponding retransmission mechanism.
The method of the present invention is further described below in conjunction with one specific application of this embodiment.
Taking the case that the source node is the BS and the target node is the MS as an example, the PMPP transmission method is described in detail as follows:
suppose the data transmitted by the BS is XBSAfter RS re-coding modulation, form data X to be transmittedRSWherein the code modulation mode can adopt code modulation different from BSAlternatively, the same code modulation scheme as the BS can be used, and the RS is knowniChannel coefficient to MS is hiWherein h isiIs a reaction of with XRSWith vectors of the same dimension, there is a BS-to-MS direct data transfer, and pre-equalization techniques are enabled:
1) BS transmits data X in downlink relay subframe by broadcasting or multicasting modeBS。
2) Correctly received data X transmitted by BS in downlink relay subframe by RS in RS active setBSAnd demodulating and decoding, and the RS participating in relay forwarding continues to execute the step 3), and the RS not participating in relay forwarding discards the demodulated and decoded data, thereby ending the process.
3) The RS participating in forwarding recodes and modulates the demodulated and decoded bit stream according to the indication of the BS to obtain data XRSThen, the transmission data is formed <math>
<mrow>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
</msub>
<mo>=</mo>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>RS</mi>
</msub>
<mo>·</mo>
<msubsup>
<mi>h</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
<mo>*</mo>
</msubsup>
</mrow>
</math> And sending out the subframe of the downlink terminal, wherein the used time-frequency resource is specified by the BS.
4) BS transmits data on same time frequency resource of downlink terminal subframe <math>
<mrow>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mn>0</mn>
</msub>
<mo>=</mo>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>RS</mi>
</msub>
<mo>·</mo>
<msubsup>
<mi>h</mi>
<mn>0</mn>
<mo>*</mo>
</msubsup>
<mo>,</mo>
</mrow>
</math> h0Is the channel coefficient, X, of the BS to the MSRSTo convert data XBSAnd data generated according to the same coding modulation mode as the RS.
5) The MS receives data forwarded by the BS and the multiple RSs at the same time in a downlink terminal subframe, estimates an equivalent composite channel coefficient, and demodulates and decodes the equivalent composite channel coefficient.
When the transmission is finished, if the data transmission is in error, the retransmission is carried out by a corresponding retransmission mechanism.
Example three:
referring to fig. 4, fig. 4 is a flowchart of a PMPP transmission method in which a source node transmits a signal once and a target node receives a signal twice in policy 2. Suppose the signal sent by the source node is XN1After RS re-encoding modulation, a different encoding modulation method or the same encoding modulation method as the source node may be used, and then the transmission signal X is formedRSAnd RS is knowniChannel coefficient to target node is hiWherein h isiIs a reaction of with XRSVectors with the same dimensions:
In this step, the control node designates the RSiThe relay means that the BS or the RS with control capability directly transmits a control message or a control message of the BS or the RS with control capability forwarded by another RS to the relay RS of the current stage, and notifies the relay RS to forward as a relay station. Wherein the control message may includeIncluding the CID that tells the RS that the signal is to be forwarded.
In this step, the indication information of the control node refers to that the BS or the RS with control capability directly sends a control message containing the indication information or a control message containing the indication information of the BS or the RS with control capability forwarded by another RS to the relay RS of the current stage, where the indication information contains a coding and modulation scheme to be adopted by the relay RS, or the relay RS of the current stage decides which coding and modulation scheme should be adopted by itself.
Step 405-406, the target node receives a signal Y simultaneously transmitted by multiple RSsRSDetermining if there is a direct data transfer from the source node to the target node, if so, XRSIs equal to XN1That is, the RS and the source node adopt the same coding modulation mode, step 407 is executed; if present and XRSIs not equal to XN1If the RS and the source node use different coding modulation modes, step 408 is executed; if there is no direct data transfer from the source node to the target node, the target node estimates the equivalent composite channel, for YRSDemodulation decoding is performed, and then the process is ended.
Wherein the order of step 408 and step 409 may be reversed. That is, the target node can first pair YN1Demodulating and decoding, checking CRC, judging if it is correct, finishing, if it is incorrect, estimating equivalent synthetic channel, and for YRSAnd performing demodulation and decoding.
When the transmission is finished, if the signal transmission is wrong, the retransmission is carried out by a corresponding retransmission mechanism.
The method of the present invention is further described below in conjunction with one specific application of this embodiment.
Taking the case that the source node is the MS and the target node is the BS as an example, the PMPP transmission method is described in detail:
suppose the data transmitted by the MS is XMSRe-encoding and modulating by RS, wherein the encoding and modulating mode can adopt a different encoding and modulating mode from MS or the same encoding and modulating mode as MS, and then forming data X to be transmittedRS,RSiChannel coefficients to BSIs hiWherein h isiAnd XRSVectors with the same dimensionality, there is a direct data transfer from the MS to the BS, and the pre-equalization technique is enabled:
1) MS transmits data X in uplink terminal subframeMSWherein the time-frequency resources used are specified by the BS.
2) The RS in the RS active set receives data X from MS in the uplink terminal subframeMSAnd demodulating and decoding, and meanwhile, the BS also receives the data in the uplink terminal subframe, and the data received by the BS is set as YMS。
3) The RS participating in forwarding recodes and modulates the demodulated and decoded bit stream according to the indication of the BS to obtain data XRSTo reform the forwarding data <math>
<mrow>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
</msub>
<mo>=</mo>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>RS</mi>
</msub>
<mo>·</mo>
<msubsup>
<mi>h</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
<mo>*</mo>
</msubsup>
</mrow>
</math> Sending out the uplink relay subframe, wherein the used time-frequency resource is appointed by the BS; and the RS which does not participate in relay forwarding discards the demodulated and decoded data, and the process is ended.
4) The BS receives a composite signal Y forwarded by a plurality of RSs at the same time on an uplink relay subframeRSThe following cases are respectively processed:
case 1: RS and MS use the same code modulation mode, namely XRSIs equal to XMS:
4.1) BS construction of the composite Signal <math>
<mrow>
<mi>Y</mi>
<mo>=</mo>
<mrow>
<mo>(</mo>
<msub>
<mi>Y</mi>
<mi>RS</mi>
</msub>
<mo>+</mo>
<msub>
<mi>Y</mi>
<mi>MS</mi>
</msub>
<mo>·</mo>
<msubsup>
<mi>h</mi>
<mn>0</mn>
<mo>*</mo>
</msubsup>
<mo>)</mo>
</mrow>
<mo>,</mo>
</mrow>
</math> Wherein h is0Is the MS to BS channel coefficient.
4.2) the BS estimates the equivalent composite channel and demodulates and decodes Y.
Case 2: RS and MS use different code modulation modes, i.e. XRSIs not equal to XMS:
4.1) BS estimates the equivalent composite channel, for YRSAnd demodulating and decoding, checking CRC, judging whether the CRC is correct or not, finishing if the CRC is correct, and entering 4.2 if the CRC is incorrect).
4.2) BS to YMSAnd performing demodulation and decoding.
Wherein the order of 4.1) and 4.2) can be reversed. I.e. BS may first pair YMSDemodulating and decoding, checking CRC, judging if it is correct, finishing, if it is incorrect, estimating equivalent synthetic channel, and for YRSAnd performing demodulation and decoding.
When the transmission is finished, if the data transmission is in error, the retransmission is carried out by a corresponding retransmission mechanism.
For policy 3, i.e. the PMPP transmission method in which the source node sends a signal twice and the target node receives a signal twice, in the third embodiment, step 305 in the second embodiment is further included between step 404 and step 405, i.e. if there is direct data transmission from the source node to the target node, the source node needs to send a signal on the same time-frequency resource at the same time <math>
<mrow>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mn>0</mn>
</msub>
<mo>=</mo>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>RS</mi>
</msub>
<mo>·</mo>
<msubsup>
<mi>α</mi>
<mn>0</mn>
<mo>*</mo>
</msubsup>
<mo>,</mo>
</mrow>
</math> X in the formulaRSThe data generated by coding and modulating the transmitted signal by adopting the same coding and modulation mode as the relay RS participating in forwarding is adopted for the source node, so that the data is in the same phase with the data generated by coding and modulating the RS participating in forwardingAnd when the pre-equalization technique is enabled0=h0Alpha is the channel coefficient from the source node to the target node when the pre-equalization technique is not enabled01. And signal Y in step 305RSThe method includes simultaneously receiving signals sent by the source node, and other processing flows are the same as those in the third embodiment.
In the case where the target node is a conventional MS, the MS does not receive data directly sent by the source node, the processing method applies the policy 4, that is, the same as the case where there is no direct transmission from the source node to the target node, and the method flow is the same as the first embodiment.
In addition, in the first PMPP transmission method, there is a case that a plurality of different service flows exist between the source node and the destination node, at this time, each service flow may be treated as an independent process, that is, there exists a respective superposition of a plurality of different service flows. Two examples of this case are given below for further description.
Example four:
taking the case that the source node is the BS and the target node is the MS as an example:
suppose a certain MS has two downlink traffic streams, such as video and voice, at the same time, two different traffic streams correspond to two different connection identifiers CID, and the BS is connected to the MS through two different RSs. For traffic flow 1, the connection identifier is CID1, and the signal sent by BS is XBS1For traffic flow 2 connection identification is CID2, and the signal sent by BS is XBS2. The BS tells CID of service flow to be forwarded by each RS through control message, so that each RS knows which CID data to forward. In the present embodiment, RS1 is responsible for forwarding data of CID1, and RS2 is responsible for forwarding data of CID 2. Of course, there may be multiple RS forwarding CIDs 1, 2.
Suppose that the signal to be forwarded after the ith RS is subjected to recoding modulation isRSiChannel coefficient to MS is hiWherein h isiAndvectors with the same dimensions and enable pre-equalization techniques:
1) BS simultaneously transmits signal X in downlink relay subframeBS1And XBS2。
2) RS1/RS2 receives signal X transmitted by BS in downlink relay subframeBS1/XBS2And demodulates and decodes.
3)RSiJudging whether the signal needs to be forwarded according to the CID table managed by the RS, wherein the frame header of the received data contains CID information, if the RS does not contain CID information, the RS sends the CID information to the receiveriIf the signal does not need to be forwarded, the signal is discarded, the process is ended, and if the signal needs to be forwarded, the process enters 4).
4) RS1/RS2 recodes and modulates the demodulated and decoded bit stream according to the indication of BS to obtain a signalReforming the transmission signal And sending out the subframe of the downlink terminal, wherein the used time-frequency resource is specified by the BS.
5) The MS receives the forwarded signals from RS1 and RS2 in the downlink terminal subframe according to the indication of the downlink channel MAP message DL-MAP information, which may be generated by the BS, RS1 or RS2, and demodulates and decodes the received signals according to the estimated channel coefficients.
When the transmission is finished, if the signal transmission is wrong, the retransmission is carried out by a corresponding retransmission mechanism.
Example five:
taking the case that the source node is the MS and the target node is the BS as an example:
suppose a MS has two uplink traffic streams, e.g., video and voice, at the same time, two different traffic streams correspond to two different CIDs, and the BS is connected to the MS through two different RSs. For traffic flow 1, the connection identifier is CID1, and the MS sends a signal XMS1For service flow 2, the connection identifier is CID2, and the MS sends a signal XMS2. The BS tells CID of service flow to be forwarded by each RS through control message, so that each RS knows which CID data to forward. In the present embodiment, RS1 is responsible for forwarding data of CID1, and RS2 is responsible for forwarding data of CID 2. Of course, there may be multiple RS forwarding CIDs 1, 2.
Suppose that the signal to be forwarded after the ith RS is subjected to recoding modulation isRSiChannel coefficient to BS is hiWherein h isiAndvectors with the same dimensions and enable pre-equalization techniques:
1) MS simultaneously sends signal X in uplink terminal subframeMS1And XMS2Wherein the time-frequency resources used are specified by the BS.
2) RS1/RS2 receives signal X from MS in uplink terminal subframeMS1/XMS2And demodulates and decodes.
3)RSiJudging whether the signal needs to be forwarded according to the CID table managed by the RS, wherein the frame header of the received data contains CID information, if the RS does not contain CID information, the RS sends the CID information to the receiveriIf it does not need to be forwarded, the signal is discarded, the process is ended, and if it needs to be forwardedAnd 4) is entered.
4)RSiRecoding and modulating the demodulated and decoded bit stream according to the indication of the BS to obtain a signalReforming the transmission signal <math>
<mrow>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
</msub>
<mo>=</mo>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mrow>
<mi>R</mi>
<msub>
<mi>S</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
</msub>
</mrow>
</msub>
<mo>·</mo>
<msubsup>
<mi>h</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
<mo>*</mo>
</msubsup>
</mrow>
</math> And sending out the uplink relay subframe, wherein the used time-frequency resource is designated by the BS.
5) The BS receives the signals forwarded from RS1 and RS2 in the uplink relay subframe, and demodulates and decodes the received signals according to the estimated channel coefficients.
When the transmission is finished, if the signal transmission is wrong, the retransmission is carried out by a corresponding retransmission mechanism.
The second PMPP transmission method of the present invention, that is, the case where data between the source node and the target node is forwarded by multiple relay RSs at different time-frequency resources, is described in detail below. If the direct connection from the source node to the target node exists, the source node can send other different signals to the target node on different time-frequency resources or does not send signals to the target node while the RS transmits signals to the target node.
Referring to fig. 5, fig. 5 is a flowchart of a PMPP transmission method according to a second embodiment of the present invention, that is, a PMPP transmission method in which multiple relay RSs forward different data in different time-frequency resources between a source node and a target node.
Suppose the signal sent by the source node is XN1After RS re-coding modulation, each RS forms different signals X to be forwardedRS_iThe difference of the signals to be forwarded may be caused by the difference of the code modulation modes, or caused by the difference of the source signal bit streams, and because the signals to be forwarded are different, each RS needs to use different time-frequency resources to forward the signals. Let RSiChannel coefficient to target node is hiWherein h isiAnd XRS_iVectors with the same dimensions.
In this step, the source node may be an MS, an RS, or a BS; if the source node is an MS, a direct control node of the MS, that is, the node may be an RS with control capability or a BS, decides to concurrently send a control message containing indication information to the RS, indicate which RSs forward, and forward which data, such as: firstly, the connection identification CID of the data stream to be forwarded is informed to the RS to be forwarded, then the time-frequency resource information of each data stream of each RS is informed, and the segmentation characteristics for data interception are informed, wherein the segmentation characteristics can be the start bit and the end bit of the data bit stream, or the start bit of the data bit stream and the length of the bit stream to be intercepted, and then the RS is indicated to mark the serial number of the intercepted data bit stream. And simultaneously, sending a corresponding signaling containing indication information to the target node to inform the target node of the time-frequency resource information of each data stream and the segmentation characteristics for data splicing, wherein the segmentation characteristics for splicing can be the connection identifiers and the segmentation serial numbers used by each data bit stream. If the source node is the BS, the BS decides which RSs are instructed by the concurrency control command to execute forwarding and which data are forwarded, forwards corresponding signaling to the target node through one or more RSs, and informs time-frequency resource information of each data stream and segmentation characteristics for data splicing of the target node; if the source node is an RS with control capability, the RS makes a relevant decision; otherwise, if the source node does not have the control capability, the RS or BS with the control capability at the upper stage is used for making a decision.
Step 504, for the demodulated and decoded bit stream, the RS participating in forwarding intercepts the specific bit stream according to the indication information of the control node, and re-encodes and modulates the bit stream to obtain a signal XRS_iThen, a transmission signal is formed <math>
<mrow>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
</msub>
<mo>=</mo>
<msub>
<mi>X</mi>
<mrow>
<mi>RS</mi>
<mo>_</mo>
<mi>i</mi>
</mrow>
</msub>
<mo>·</mo>
<msubsup>
<mi>α</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
<mo>*</mo>
</msubsup>
<mo>,</mo>
</mrow>
</math> Wherein, when the pre-equalization technique is activated, αi=hiAlpha without using pre-equalization techniquesiWhen the RS sends a signal, if there is a direct connection from the source node to the target node and the source node is not the control node, the source node may send a signal to the target node on different time-frequency resources according to the indication information of the control node, where the signal may be data that is the same as that of a certain RS and is sent on the same time-frequency resources in the same code modulation manner as that of the RS; the source node and all the RSs can intercept different data, do not overlap and omit, send the data on different time-frequency resources, and also can not send signals to the target node; if the source node is the control node, the sending mode is decided by the source node.
In this step, the indication information of the control node refers to that the BS or the RS with control capability directly sends a control message containing the indication information or a control message containing the indication information of the BS or the RS with control capability forwarded by other RSs to the relay RS of this stage, where the indication information contains time-frequency resource information used by each segment of data stream and segment characteristics of data interception; and the RS participating in relay forwarding intercepts the bit stream according to the segmentation characteristics in the indication information and marks a serial number, and then codes and modulates the intercepted bit stream on the corresponding time frequency resource according to the time frequency resource information used by each segment in the indication information and sends the bit stream out.
And 505, receiving, by the target node, signals simultaneously transmitted on different time-frequency resources from multiple RSs or including the source node, estimating respective equivalent channel coefficients, then respectively demodulating and decoding the signals from the different RSs according to the indication information of the control node, and finally splicing into a bit stream transmitted to the target node by the source node.
In this step, the indication information of the control node refers to that the BS or the RS with control capability directly sends a control message containing the indication information or a control message containing the indication information of the BS or the RS with control capability forwarded by other RSs to the relay RS of this stage, where the indication information contains time-frequency resource information used by each segment of data stream and segment characteristics of the data; and the target node demodulates and decodes the received bit streams of the specific data forwarded by the RSs respectively, and then splices the bit streams according to the segmentation characteristics in the indication information. If the segment characteristics comprise CID and segment serial number of the data stream, the target node demodulates and decodes the received data forwarded by each RS containing the same CID, determines the splicing relation among the data streams according to the segment serial number of each data stream, and then splices the data streams.
When the transmission is finished, if the signal transmission is wrong, the retransmission is carried out by a corresponding retransmission mechanism. As can be seen from the above flow, the signal received by the target node in step 505 is transmitted by multiple units in parallel, so that the load can be balanced among multiple RSs.
In addition, the segmentation features in the indication information sent by the control node to the RS and the target node in this embodiment may be the same, that is, the segmentation features all include: CID, segmentation start stop bit and segmentation sequence number of the data stream; the RS participating in relay forwarding intercepts the received data bit stream of the CID according to the segment start stop bit and the segment sequence number in the segment feature in the indication information in step 504; in step 505, the target node splices the received bit streams of each segment of specific data containing the same CID according to the segment sequence number in the segment characteristics in the indication information.
The following describes the transmission system of the wireless relay according to the present invention in further detail with reference to the embodiments.
The system in this embodiment is composed of a source node, a target node, multiple RSs participating in relay forwarding, and a control node, where a networking structure among the source node, the target node, and the multiple RSs participating in relay forwarding is shown in fig. 1. The source node → target node may represent BS → RS, RS → MS, BS → MS, and MS → RS, RS → BS, MS → BS, wherein RS includes control capable RS and non-control capable RS.
Wherein the control node is a BS or an RS with control capability; for uplink transmission, the control node is an RS or BS directly controlling the target node, and if the target node has control capability, the control node is the target node; for downlink transmission, the control node is an RS or BS directly controlling the source node, and if the source node has control capability, the control node is the source node.
The RS in the above system is composed of a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer and an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module, and a control module, as shown in fig. 6.
The duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna.
And the receiver is used for receiving the data transmitted by the source node through the antenna of the duplexer and converting the data from the radio frequency signal into a baseband signal.
And the downlink data processing module is used for processing the downlink data received by the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data, extracting a control command of the control node from the received data, sending the control command to the control module, then carrying out coding modulation on the demodulated and decoded data according to the indication information of the control command under the control of the control module, and then sending the demodulated and decoded data on a specified time-frequency resource position, or intercepting and carrying out coding modulation on the demodulated and decoded data and then sending the demodulated and decoded data on the specified time-frequency resource position, or splicing the demodulated and decoded data.
If the indication information of the control command contains time-frequency resource information required to be used by the current data and a characteristic identifier of the data, the downlink data processing module performs coding modulation on the data of the characteristic identifier and sends the data out at the time-frequency resource position indicated in the indication information through the transmitter.
If the indication information of the control command contains the segmentation feature for intercepting the current data, the time-frequency resource information needed by the intercepted data and the feature identifier of the data, the downlink data processing module intercepts the data of the feature identifier according to the segmentation feature indicated in the indication information, then carries out coding modulation on the intercepted data, and sends the data out at the time-frequency resource position in the indication information through the transmitter.
If the indication information of the control command contains the segmentation characteristics for intercepting the current data, the time-frequency resource information used by the intercepted data, the characteristic identification of the data and the time-frequency resource information needed to be used by the spliced data, the downlink data processing module splices each segment of data received at the corresponding time-frequency resource position according to the segmentation characteristics, then performs coding modulation, and sends the data out at the time-frequency resource position indicated by the control node through the transmitter.
The uplink data processing module is used for processing the uplink data received by the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data, and then coding and modulating the demodulated and decoded data according to a control command of a control node extracted from the downlink data processing module under the control of the control module and then sending the demodulated and decoded data on a specified time-frequency resource position through the transmitter, or intercepting and coding and modulating the demodulated and decoded data and then sending the demodulated and decoded data on the specified time-frequency resource position through the transmitter, or splicing the demodulated and decoded data; and measuring the quality of the received uplink signal to generate quality information, and sending the quality information to be reported out through a transmitter.
If the indication information of the control command includes time-frequency resource information required to be used by the current data and a feature identifier of the data, the uplink data processing module performs coding modulation on the data of the feature identifier and sends the data out at a time-frequency resource position indicated in the indication information through the transmitter.
If the indication information of the control command comprises the segmentation feature for intercepting the current data, the time-frequency resource information needed by the intercepted data and the feature identifier of the data, the uplink data processing module intercepts the data of the feature identifier according to the segmentation feature indicated in the indication information, then carries out coding modulation on the intercepted data, and sends the data out at the time-frequency resource position in the indication information through the transmitter.
If the indication information of the control command contains the segmentation characteristics for intercepting the current data, the time-frequency resource information used by the intercepted data, the characteristic identification of the data and the time-frequency resource information needed to be used by the spliced data, the uplink data processing module splices each segment of data received at the corresponding time-frequency resource position according to the segmentation characteristics, then performs coding modulation, and sends the data out at the time-frequency resource position indicated by the control node through the transmitter.
The uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner.
And the transmitter is used for receiving the data of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal, and transmitting the radio frequency signal to the target node through the antenna of the duplexer.
And the control module is used for finishing the control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and for the RS with control capability, generating a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node.
The internal structures of the uplink data processing module, the downlink data processing module, and the control module of the RS are shown in fig. 7, and referring to fig. 7, the uplink data processing module of the RS specifically includes: the device comprises an uplink demodulation decoding unit, an uplink data caching unit, an uplink channel measuring unit, a feedback information generating unit, a feedback information extracting unit, an uplink coding modulation unit and a multiplexer; the RS downlink data processing module specifically includes: the device comprises a downlink demodulation decoding unit, a downlink data caching unit, a control command extracting unit, a downlink channel measuring unit, a downlink coding modulation unit and a multiplexer; the control module of the RS specifically includes: the device comprises an analysis unit, a control command generation unit and a control unit. In order to clarify the signal flow relationship between other modules in the drawing, the control signal lines connecting the control unit and each of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module are collectively represented by two thick arrows.
The uplink demodulation decoding unit is used for demodulating, de-mapping symbols, de-interleaving and channel decoding the uplink baseband signal received by the receiver under the control of the control module to obtain uncoded original information data and outputting the obtained original information data.
And the uplink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the uplink demodulation and decoding unit, outputting the whole data to the uplink coding and modulation unit according to the control command under the control of the control module, or intercepting a certain section of the data according to the control command and outputting the certain section of the data to the uplink coding and modulation unit, or splicing the stored sections of data according to the control command and outputting the spliced sections of data to the uplink coding and modulation unit.
And the uplink channel measuring unit is used for measuring the quality of the received uplink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the uplink demodulation decoding unit under the control of the control module, sending the measured quality information to the control module, judging whether the uplink signal needs to be reported or not by the control module according to the received quality information, if the uplink signal needs to be reported, outputting the quality information needing to be reported to the feedback signal generating unit by the control module, and if the uplink signal does not need to be reported, discarding the quality information which does not need to be reported by the control module.
And the feedback signal generating unit is used for generating reporting information according to the quality information output by the uplink channel measuring unit under the control of the control module, and generating reporting information according to the load condition of the RS determined to be reported by the control module.
And the feedback information extraction unit is used for extracting the feedback information from the data output by the uplink demodulation and decoding unit and sending the extracted feedback information to the control module.
And the uplink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data output by the uplink data buffer unit under the control of the control module.
And the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the reporting information generated by the feedback information generating unit and the uplink forwarding data generated by the uplink coding and modulating unit and sending the multiplexed information and the uplink forwarding data to the transmitter.
And the downlink demodulation decoding unit is used for demodulating, de-mapping symbols, de-interleaving and channel decoding the downlink baseband signals received by the receiver under the control of the control module to obtain uncoded original information data and outputting the obtained original information data.
And the control command extraction unit is used for extracting the control command sent by the control node from the original information data processed by the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, sending the control command to the control module, and generating a corresponding control message containing the indication information by the control module.
And the downlink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the downlink demodulation decoding unit, outputting the whole data to the downlink coding modulation unit according to the control command under the control of the control module, or intercepting a certain section of the data according to the control command and outputting the intercepted data to the downlink coding modulation unit, or splicing the stored sections of data according to the control command and outputting the spliced data to the downlink coding modulation unit.
A downlink channel measuring unit used for measuring the quality of the received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation decoding unit under the control of the control module, and sending the measured quality information to the control module, the control module judging whether reporting is needed according to the received quality information, if reporting is needed, the control module sending the quality information needed to be reported to a feedback information generating unit in the uplink data processing module, the feedback information unit generating reporting information and sending the reporting information to a multiplexer in the uplink data processing module, and the multiplexer multiplexing the reporting information and the uplink data together to send to the transmitter.
And the downlink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data output by the downlink data buffer unit under the control of the control module.
And the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the control message generated by the control module and the downlink forwarding data generated by the downlink coding modulation unit together and sending the multiplexed data to the transmitter.
The analysis unit is used for receiving the control command sent by the control command extraction unit in the downlink data processing module, analyzing the received command and sending the analyzed control command to the control unit; and receiving the feedback information sent by the feedback information extraction unit in the uplink data processing module, analyzing the received information, and sending the analyzed feedback information to the control unit.
The control unit is used for controlling the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and comprises: receiving a control command sent by the analysis unit, and controlling the downlink data cache unit and the uplink data cache unit to directly output, output after segmentation or output after splicing the data according to the control command; receiving quality information sent by an uplink channel measuring unit or a downlink channel measuring unit, judging whether reporting is needed according to the received quality information, if so, outputting the quality information needed to be reported to a feedback information generating unit, controlling the feedback information generating unit to generate reporting information, and sending the reporting information to a multiplexer in an uplink data processing module, wherein the multiplexer multiplexes the reporting information generated by the feedback information generating unit and uplink forwarding data generated by an uplink coding modulation unit together and sends the multiplexing information and the uplink forwarding data out; after receiving the feedback information sent by the analysis unit, the RS with control capability combines the measurement result sent by the uplink channel measurement unit or the downlink channel measurement unit to generate a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node.
The control command generating unit is used for generating a control message containing indication information for controlling a lower node under the control of the control unit for the RS with control capability and sending the control message to the multiplexer, and the multiplexer multiplexes the control command generated by the control command generating unit and the downlink forwarding data generated by the downlink coding modulation unit and sends the multiplexed data; for the RS without control capability, the control command generating unit is used for forwarding the control command sent by the RS with control capability or the BS at the upper level and sending the control command to the multiplexer, and the multiplexer multiplexes the control command generated by the control command generating unit and the downlink forwarding data generated by the downlink coding modulation unit and sends the multiplexed data.
Wherein, the internal structure of the BS is as shown in fig. 8, referring to fig. 8, the BS includes: the device comprises a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer, an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module and a control module.
The duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna.
And the receiver is used for receiving the data transmitted by the source node through the antenna of the duplexer and converting the data from the radio frequency signal into a baseband signal.
And the uplink data processing module is used for receiving the data sent to the BS by the MS through the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data or demodulating, decoding and splicing the received data under the control of the control module to obtain the transmitted data, extracting feedback information from the demodulated and decoded data and sending the feedback information to the control module.
And the control module is used for finishing the control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, generating a control message containing indication information according to the feedback information received from the uplink data processing module, and sending the control message to the downlink data processing module.
And the downlink data processing module is used for performing coding modulation on the data to be sent under the control of the control module, and sending the data subjected to coding modulation and the control message sent by the control module out through the transmitter at the time-frequency resource position allocated to the data to be sent.
The uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner.
And the transmitter is used for receiving the data of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal, and transmitting the radio frequency signal to the target node through the antenna of the duplexer.
As shown in fig. 8, the uplink data processing module of the BS specifically includes: the device comprises an uplink demodulation decoding unit, an uplink data caching unit, an uplink channel measuring unit and a feedback information extracting unit; the downlink data processing module of the BS specifically includes: a downlink data buffer unit, a downlink code modulation unit and a multiplexer; the control module of the BS specifically includes: the device comprises an analysis unit, a control unit and a control command generation unit. The control unit in the control module is respectively connected with each module in the uplink data processing module and each module in the downlink data processing module through control signal lines except that the control unit is not connected with the downlink data cache unit.
The uplink demodulation decoding unit is used for demodulating, de-symbol mapping, de-interleaving and channel decoding the baseband signal which is sent to the BS by the MS and received by the receiver under the control of the control module to obtain uncoded original information data and outputting the obtained original information data.
And the uplink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the uplink demodulation decoding unit and directly outputting the data or splicing the data and outputting the data under the control of the control module.
And the uplink channel measuring unit is used for measuring the quality of the received uplink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the uplink demodulation decoding unit under the control of the control module and sending the measured quality information to the control module.
And the feedback information extraction unit is used for extracting the feedback information from the data output by the uplink demodulation and decoding unit and sending the extracted feedback information to the control module.
And the downlink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data to be sent.
And the downlink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data in the downlink data buffer unit under the control of the control module.
And the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the control message generated by the control module and the downlink sending data generated by the downlink coding unit together to the transmitter under the control of the control module.
And the analysis unit is used for receiving the feedback information sent by the feedback information extraction unit in the uplink data processing module, analyzing the received information and sending the analyzed feedback information to the control unit.
And a control command generating unit for generating a control message containing indication information for controlling the lower node under the control of the control unit and transmitting the control message to the multiplexer.
The control unit is used for controlling the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and comprises: and the control command generating unit generates a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node according to the feedback information and the quality information control command.
Wherein, the internal structure of the MS is as shown in fig. 9, referring to fig. 9, the MS includes: the device comprises a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer, an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module and a control module.
The duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna.
And the receiver is used for receiving the data transmitted by the source node through the antenna of the duplexer and converting the data from the radio frequency signal into a baseband signal.
And the downlink data processing module is used for receiving the data sent to the MS by the BS through the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data or demodulating, decoding and splicing the data under the control of the control module to obtain the transmitted data, extracting a control command from the demodulated and decoded data, sending the control command to the control module, measuring the quality of the received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and sending the measured quality information to the control module.
The control module is used for controlling the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and controlling the downlink data processing module to demodulate and decode the data or splice the data after demodulating and decoding according to a control command sent by the received downlink data processing module; and receiving the quality information sent by the downlink data processing module, and controlling the uplink data processing module to generate the report information.
And the uplink data processing module is used for performing coding modulation on the data to be sent under the control of the control module, and sending the data subjected to coding modulation and the generated report information out through the transmitter at the time-frequency resource position allocated to the data to be sent.
The uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner.
And the transmitter is used for receiving the data of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal, and transmitting the radio frequency signal to the target node through the antenna of the duplexer.
As shown in fig. 9, the downlink data processing module of the MS specifically includes: a downlink demodulation decoding unit, a downlink data caching unit, a control command extracting unit and a downlink channel measuring unit; the uplink data processing module of the MS specifically includes: the device comprises an uplink data caching unit, a feedback information generating unit, an uplink coding modulation unit and a multiplexer; the control module of the MS specifically includes: an analysis unit and a control unit. In order to clarify the signal flow relationship between other modules in the drawing, the control signal lines connecting the control unit and each of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module are collectively represented by two thick arrows.
The downlink demodulation and decoding unit is used for demodulating, de-mapping symbols, de-interleaving and channel decoding the baseband signal sent to the MS by the BS received by the receiver under the control of the control module to obtain uncoded original information data, and outputting the obtained original information data.
And the downlink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the downlink demodulation decoding unit and directly outputting the data or splicing the data and outputting the data under the control of the control module.
And the downlink channel measuring unit is used for measuring the quality of the received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation decoding unit under the control of the control module and sending the measured quality information to the control module.
And the control command extracting unit is used for extracting the control command from the data obtained after the processing of the downlink demodulation and decoding unit and sending the control command to the control module.
And the uplink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data to be sent.
And the uplink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data in the uplink data buffer unit under the control of the control module.
And the feedback information generating unit is used for generating the quality information which is sent by the control module and needs to be reported into reporting information under the control of the control module.
And the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the reporting information generated by the feedback information generating unit and the uplink sending data generated by the uplink coding and modulating unit together and sending the multiplexed information to the transmitter.
And the analysis unit is used for receiving the control command sent by the control command extraction unit in the downlink data processing module, analyzing the received command and sending the analyzed control command to the control unit.
The control unit is used for controlling the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and comprises: receiving a control command sent by the analysis unit, and controlling the downlink data cache unit to directly output the data according to the control command or output the data after splicing; and receiving the quality information sent by the downlink channel measuring unit, judging whether reporting is needed according to the received quality information, if so, sending the quality information needed to be reported to a feedback information generating unit in the uplink data processing module, and generating reporting information by the feedback information unit.
The above-mentioned embodiments are intended to illustrate the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention in further detail, and it should be understood that the above-mentioned embodiments are only exemplary embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, and any modifications, equivalent substitutions, improvements and the like made within the spirit and principle of the present invention should be included in the scope of the present invention.
Claims (39)
1. A transmission method in a wireless relay system, wherein data between a source node and a target node is jointly forwarded by a plurality of relay nodes RS, the method comprising the steps of:
the source node generates a sending signal after coding and modulating the information of the service flow to be sent and sends the sending signal out;
the RS participating in relay forwarding demodulates and decodes the received signal sent by the source node, then carries out coding modulation again, and then forwards the coded and modulated signal to the target node on the same time frequency resource together according to the time frequency resource information, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding serves the service flow of the specified characteristic identifier;
and the target node receives signals forwarded by a plurality of RSs at the same time, the signals are superposition of the signals forwarded by the plurality of RSs, the channel coefficient is estimated, and the received signals are demodulated and decoded to obtain the transmitted information.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein a transmission signal sent by the source node carries a feature identifier of a transmitted service flow, and the transmission signal is a single service flow signal; or the sending signal is a plurality of service flow signals, and each service flow signal corresponds to a different feature identifier.
3. The method according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the RS maintains a list of connection identities CID for the traffic flows,
the feature identifier of the service flow includes: the connection identifier CID of the service flow;
the RS participating in relay forwarding is: and receiving a control message which is sent by the control node and adds the CID of a certain service flow, and adding the RS of the CID in the CID list.
4. The method of claim 1, wherein the RS participates in relay forwardingiKnowing the channel coefficient h from itself to the target nodeiAnd if i is greater than or equal to 0, the RS participating in relay forwarding performs recoding modulation on the correctly received signal sent by the source node, and then further includes: using the channel coefficient hiAnd carrying out pre-equalization processing on the signal to be transmitted, and then forwarding the processed data.
5. The method of claim 4, wherein the pre-equalization process is: multiplying the signal to be transmitted by the channel coefficient hiConjugation of (2)
6. The method of claim 1, 2 or 5, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding is: all or part of the RSs in the set of all relay RSs capable of receiving the signal of the source node and capable of serving the target node.
7. The method of claim 6, wherein the set of all relay RSs capable of receiving a signal of a source node and serving a target node further comprises: a source node itself capable of directly serving a target node; or,
and in the set of all relay RSs capable of receiving the signal of the source node and serving the target node, the RSs participating in relay forwarding do not include the source node.
8. The method of claim 7, wherein a source node is included in the RS participating in relay forwarding, the method further comprising:
after the source node performs coding modulation on the information of the service flow to be transmitted by adopting the same coding modulation mode as the RS participating in relay forwarding, the source node transmits a signal subjected to coding modulation on the same time-frequency resource as the RS participating in relay forwarding, and when pre-equalization processing is adopted, the source node multiplies a coefficient before transmitting the signal by the source nodeIs the channel coefficient h between the source node and the target node0Conjugation of (1);
the superposed signal received by the target node comprises: and directly receiving the data sent by the source node.
9. The method according to claim 7, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding includes a source node, and the RS participating in relay forwarding adopts the same coding modulation scheme as that of the source node, then the method further includes:
the target node simultaneously receives signals sent by a source node;
the target node accumulates the directly received signal of the source node and the received superposed signal forwarded by the multiple RSs, and if the pre-equalization processing is adopted, the directly received signal of the source node is multiplied by a coefficient before the accumulationIs the channel coefficient h between the source node and the target node0Conjugation of (1).
10. The method according to claim 7, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding includes a source node, and the RS participating in relay forwarding adopts a different coding modulation scheme than the source node, and then the method further includes:
the target node simultaneously receives signals sent by a source node;
the target node receives signals forwarded by a plurality of RSs at the same time, the signals are superposition of the signals forwarded by the plurality of RSs, and estimating channel coefficients and demodulating and decoding the received signals comprise: the target node firstly demodulates and decodes the received superposed signals forwarded by the multiple RSs, checks the check bit, judges whether the superposed signals are correct or not, ends the judgment if the superposed signals are correct, and then demodulates and decodes the signals directly received from the source node if the superposed signals are incorrect; or, the target node firstly demodulates and decodes the signal directly received from the source node, checks the check bit, judges whether the signal is correct or not, and finishes the judgment if the signal is correct, and then demodulates and decodes the received superposed signal forwarded by the multiple RSs if the signal is incorrect.
11. The method of claim 1, wherein the RS re-code-modulates the received signal as: the RS performs coding modulation on the received signal again by adopting a coding modulation mode which is the same as that of the source node, or the RS performs coding modulation on the received signal again by adopting a coding modulation mode which is different from that of the source node;
and the target node demodulates and decodes the received signal by adopting a demodulation and decoding method corresponding to the RS for coding and modulating again.
12. A transmission method in a wireless relay system, wherein data between a source node and a target node is jointly forwarded by a plurality of relay nodes RS, the method comprising the steps of:
A. the source node transmits the information to be transmitted after coding modulation;
B. after demodulating and decoding the received signal sent by the source node by the RS participating in relay forwarding, intercepting a specific bit stream according to the indication information of the control node to perform recoding modulation, and then forwarding the specific bit stream to the target node on different time-frequency resources together;
C. and the target node receives different data signals jointly forwarded by the multiple RSs, demodulates and decodes the received signals according to the indication information of the control node, and then splices the demodulated and decoded data to obtain transmitted information.
13. The method of claim 12, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B is: all or part of all sets of relay RSs capable of receiving signals of the source node and capable of serving the target node.
14. The method of claim 12, wherein the set of all relay RSs capable of receiving signals of a source node and serving a target node further comprises: a source node itself capable of directly serving a target node; or,
and in the set of all RSs capable of receiving the signal of the source node and serving the target node, the RSs participating in relay forwarding do not include the source node.
15. The method of claim 14, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding includes a source node, and the source node is a control node, then the step B further includes: the source node intercepts data which are the same as a certain RS, and after the intercepted data are coded and modulated in a coding modulation mode which is the same as that of the RS, the source node and the RS send out signals to a target node on the same time-frequency resource; or the source node intercepts data different from all RSs, then carries out coding modulation on the intercepted data, and sends out signals to the target node on different time-frequency resources.
16. The method of claim 14, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding includes a source node, and the source node is not a control node, then step B further includes: the control node sends the indication information to a source node, the source node intercepts data which are the same as a certain RS according to the received indication information, and after the intercepted data are coded and modulated in a coding modulation mode which is the same as that of the RS, the source node sends out signals to a target node on the same time-frequency resource with the RS; or the source node intercepts data different from all RSs, then carries out coding modulation on the intercepted data, and sends out signals to the target node on different time-frequency resources.
17. The method according to claim 12, 15 or 16, wherein the indication information of the control node in step B or step C comprises: time-frequency resource information used by each segment of data stream and segmentation characteristics of the data;
the RS participating in relay forwarding in the step B intercepts the bit stream according to the segmentation characteristics in the indication information, and transmits the intercepted bit stream after carrying out coding modulation on the corresponding time frequency resources according to the time frequency resource information used by each segment in the indication information;
and C, the target node demodulates and decodes the received bit streams of the specific data forwarded by the RSs respectively, and then splices the demodulated and decoded data according to the segmentation characteristics in the indication information.
18. The method of claim 17, wherein the segmentation features comprise: CID, segmentation start stop bit and segmentation sequence number of the data stream;
the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B intercepts the received data bit stream of the CID according to the segment start stop bit and the segment sequence number in the segment feature in the indication information;
and C, splicing the received bit streams containing the same CID and each segment of data by the target node according to the segment serial number in the segment characteristics in the indication information.
19. The method of claim 12, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B is: the control message is sent by the control node to specify the RS as a relay forwarding station.
20. The method according to claim 12 or 19, wherein the control node is: BS or control capable RS.
21. The method of claim 12, wherein the RSi participating in relay forwarding knows the channel coefficient h from itself to the target nodeiIf i is greater than or equal to 0, the RS participating in relay forwarding in step B performs re-coding modulation on the correctly received signal sent by the source node, and then further includes: using the channel coefficient hiAnd carrying out pre-equalization processing on the signal to be transmitted, and then forwarding the processed data.
23. A wireless relay transmission system, comprising: a source node, a plurality of RSs participating in relay forwarding, a target node and a control node, wherein,
the source node is used for generating a sending signal after the information to be sent is coded and modulated, and sending the sending signal out;
the control node is used for sending command information to the RS and the target node;
the multiple RSs participating in relay forwarding are used for demodulating and decoding the received signal sent by the source node and then coding and modulating the signal again, and then forwarding the coded and modulated signal to the target node on the same time-frequency resource according to the time-frequency resource information, wherein the multiple RSs participating in relay forwarding serve the service flow of the specified characteristic identifier;
and the target node is used for receiving signals sent by the RSs participating in relay forwarding, demodulating and decoding the received signals according to the indication information of the control node, and obtaining the transmitted information.
24. The system of claim 23, wherein the source node and the destination node are respectively: BS and MS, or MS and BS, or BS and RS, or RS and MS, or MS and RS, or RS and BS, or RS and RS.
25. The system of claim 24, wherein the RS is: a control capable RS or a non-control capable RS.
26. The system of claim 23, wherein the RS participating in relay forwarding is: the control message is sent by the control node to specify the RS as relay forwarding.
27. The system of claim 23 or 26, wherein the control node is: BS or control capable RS; for uplink transmission, the control node is an RS or BS directly controlling the target node, and if the target node has control capability, the control node is the target node; for downlink transmission, the control node is an RS or BS directly controlling the source node, and if the source node has control capability, the control node is the source node.
28. The system of claim 25, wherein the RS comprises: a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer and an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module and a control module, wherein,
the duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna;
a receiver for receiving data transmitted from the source node through an antenna of the duplexer, and converting the received data from a radio frequency signal to a baseband signal;
the downlink data processing module is used for processing downlink data received by the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data, extracting a control command of a control node from the received data, sending the control command to the control module, and then sending the demodulated and decoded data on a specified time-frequency resource position after carrying out coding modulation on the demodulated and decoded data according to the indication information of the control command under the control of the control module, or sending the demodulated and decoded data on the specified time-frequency resource position after carrying out interception and coding modulation on the demodulated and decoded data, or splicing the demodulated and decoded data;
the uplink data processing module is used for processing uplink data received by the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data, and then coding and modulating the demodulated and decoded data according to a control command of a control node extracted from the downlink data processing module under the control of the control module and then sending the demodulated and decoded data at a specified time-frequency resource position through the transmitter, or intercepting and coding and modulating the demodulated and decoded data and then sending the demodulated and decoded data at the specified time-frequency resource position through the transmitter, or splicing the demodulated and decoded data; measuring the quality of the received uplink signal to generate quality information, and generating reporting information of the quality information to be reported and sending the reporting information through a transmitter;
the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner;
the transmitter is used for receiving the data output by the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal and transmitting the radio frequency signal to a target node through an antenna of the duplexer;
and the control module is used for finishing the control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and for the RS with control capability, generating a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node.
29. The system of claim 28, wherein the uplink data processing module in the RS comprises:
the uplink demodulation decoding unit is used for demodulating, de-mapping symbols, de-interleaving and channel decoding the uplink baseband signals received by the receiver to obtain uncoded original information data and outputting the obtained original information data;
the uplink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the uplink demodulation decoding unit, outputting the whole original information data to the uplink coding modulation unit according to a control command under the control of the control module, or intercepting a certain section of the original information data according to the control command and outputting the certain section of the original information data to the uplink coding modulation unit, or splicing all sections of the stored original information data according to the control command and outputting the spliced original information data to the uplink coding modulation unit;
an uplink channel measuring unit, configured to measure the quality of a received uplink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the uplink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
a feedback signal generating unit, configured to generate reporting information for the quality information output by the uplink channel measuring unit, and generate reporting information for the load condition of the RS determined to be reported by the control module;
a feedback information extraction unit, configured to extract feedback information from the data output by the uplink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the extracted feedback information to the control module;
the uplink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data output by the uplink data caching unit;
and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the reporting information generated by the feedback information generating unit and the uplink forwarding data generated by the uplink coding and modulating unit and sending the multiplexed information and the uplink forwarding data to the transmitter.
30. The system according to claim 28 or 29, wherein the downlink data processing module in the RS comprises:
a downlink demodulation decoding unit, configured to demodulate, de-symbol map, de-interleave, and channel decode a downlink baseband signal received by the receiver to obtain uncoded original information data, and output the obtained original information data;
a control command extracting unit, configured to extract a control command sent by a control node from original information data output by the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the control command to the control module;
a downlink data caching unit, configured to cache the original information data output by the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and output the entire original information data to the downlink code modulation unit according to a control command under the control of the control module, or intercept a certain segment of the original information data according to the control command and output the certain segment of the original information data to the downlink code modulation unit, or splice stored segments of original information data according to the control command and output the spliced original information data to the downlink code modulation unit;
a downlink channel measuring unit, configured to measure the quality of a received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
the downlink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data output by the downlink data cache unit;
and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the control message generated by the control module and the downlink forwarding data generated by the downlink coding modulation unit together and sending the multiplexed data to the transmitter.
31. The system of claim 30, wherein the control module in the RS comprises:
the analysis unit is used for receiving the control command sent by the control command extraction unit in the downlink data processing module, analyzing the received command and sending the analyzed control command to the control unit; receiving feedback information sent by a feedback information extraction unit in the uplink data processing module, analyzing the received feedback information, and sending the analyzed feedback information to a control unit;
a control unit, configured to complete control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module, and the downlink data processing module, including: receiving a control command sent by the analysis unit, and controlling a downlink data cache unit and an uplink data cache unit to directly output, output after segmentation or output after splicing the original information data according to the control command; receiving quality information sent by an uplink channel measuring unit or a downlink channel measuring unit, judging whether reporting is needed according to the received quality information, and outputting the quality information needing reporting to a feedback information generating unit; after receiving the feedback information sent by the analysis unit, the RS with control capability combines the measurement result sent by the uplink channel measurement unit or the downlink channel measurement unit to control the control command generation unit to generate a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node;
the control command generating unit is used for generating a control message containing indication information for controlling a lower node under the control of the control unit for the RS with control capability and sending the control message to the multiplexer; for the RS without control capability, the control command generating unit is used for forwarding the control command sent by the RS with control capability or the BS at the upper level and sending the control command to the multiplexer.
32. The system of claim 25, wherein the BS comprises: a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer and an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module and a control module, wherein,
the duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna;
a receiver for receiving data transmitted from the source node through an antenna of the duplexer, and converting the received data from a radio frequency signal to a baseband signal;
the uplink data processing module is used for receiving data sent to the BS by the MS through the receiver, demodulating and decoding the received data or demodulating, decoding and splicing the received data under the control of the control module to obtain transmitted data, extracting feedback information from the demodulated and decoded data and sending the feedback information to the control module;
the control module is used for finishing the control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, generating a control message containing indication information according to the feedback information received from the uplink data processing module and sending the control message to the downlink data processing module;
the downlink data processing module is used for carrying out coding modulation on the data to be sent under the control of the control module, and sending out the data subjected to coding modulation and the control message sent by the control module through the transmitter at the time-frequency resource position allocated to the data to be sent;
the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner;
and the transmitter is used for receiving the data of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal, and transmitting the radio frequency signal to the target node through the antenna of the duplexer.
33. The system of claim 32, wherein the uplink data processing module in the BS comprises:
the uplink demodulation decoding unit is used for demodulating, de-mapping symbols, de-interleaving and channel decoding a baseband signal which is sent to the BS by the MS and received by the receiver to obtain uncoded original information data and outputting the obtained original information data;
the uplink data caching unit is used for caching the original information data output by the uplink demodulation decoding unit and directly outputting the original information data or splicing and outputting the original information data under the control of the control module;
an uplink channel measuring unit, configured to measure the quality of the received uplink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the uplink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
and the feedback information extraction unit is used for extracting feedback information from the original information data output by the uplink demodulation and decoding unit and sending the extracted feedback information to the control module.
34. The system of claim 32 or 33, wherein the downlink data processing module in the BS comprises:
a downlink data caching unit, configured to cache original information data to be sent;
the downlink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data in the downlink data cache unit;
and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the control message generated by the control module and the downlink sending data generated by the downlink coding unit together and sending the multiplexed data to the transmitter.
35. The system of claim 34, wherein the control module in the BS comprises: an analyzing unit, a control command generating unit and a control unit, wherein,
the analysis unit is used for receiving the feedback information sent by the feedback information extraction unit in the uplink data processing module, analyzing the received feedback information and sending the analyzed feedback information to the control unit;
a control command generating unit for generating a control message containing indication information for controlling a lower node under the control of the control unit and transmitting the control message to the multiplexer;
a control unit, configured to complete control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module, and the downlink data processing module, including: and the control command generating unit generates a control message containing indication information for controlling the subordinate node according to the feedback information and the quality information control command.
36. The system of claim 25, wherein the MS comprises: a transmitter, a receiver, a duplexer and an antenna, an uplink data processing module, a downlink data processing module and a control module, wherein,
the duplexer is connected with the antenna and used for realizing time-sharing sending and receiving of the antenna;
a receiver for receiving data transmitted from the source node through an antenna of the duplexer, and converting the received data from a radio frequency signal to a baseband signal;
a downlink data processing module, configured to receive data sent by the BS to the MS through the receiver, demodulate and decode the received data or demodulate and decode and splice the received data under the control of the control module to obtain transmitted data, extract a control command from the demodulated and decoded data, send the control command to the control module, measure the quality of a received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
the control module is used for controlling the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, and controlling the downlink data processing module to demodulate and decode the data or splice the data after demodulating and decoding according to a control command sent by the received downlink data processing module; receiving quality information sent by a downlink data processing module, and controlling an uplink data processing module to generate reporting information;
the uplink data processing module is used for performing coding modulation on data to be sent under the control of the control module, and sending the data subjected to coding modulation and the generated report information out through a transmitter at a time-frequency resource position allocated to the data to be sent;
the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module share the transmitter and the receiver in a time-sharing manner;
and the transmitter is used for receiving the data of the uplink data processing module and the downlink data processing module, converting the data from a baseband signal into a radio frequency signal, and transmitting the radio frequency signal to the target node through the antenna of the duplexer.
37. The system of claim 36, wherein the downlink data processing module in the MS comprises:
a downlink demodulation decoding unit, configured to demodulate, de-symbol map, de-interleave, and channel decode a baseband signal sent to the MS by the BS received by the receiver to obtain uncoded original information data, and output the obtained original information data;
a downlink data caching unit, configured to cache the original information data output by the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and directly output the original information data under the control of the control module, or output the original information data after splicing;
a downlink channel measuring unit, configured to measure the quality of a received downlink signal according to the output of the receiver and the output of the downlink demodulation and decoding unit, and send the measured quality information to the control module;
and the control command extracting unit is used for extracting a control command from the original information data processed by the downlink demodulation and decoding unit and sending the control command to the control module.
38. The system of claim 36 or 37, wherein the uplink data processing module in the MS comprises:
the uplink data caching unit is used for caching original information data to be sent;
the uplink coding modulation unit is used for carrying out channel coding, interleaving, symbol mapping and modulation on the original information data in the uplink data cache unit;
the feedback information generating unit is used for generating reporting information from the quality information which is sent by the control module and needs to be reported;
and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing the reporting information generated by the feedback information generating unit and the uplink sending data generated by the uplink coding and modulating unit together and sending the multiplexed information to the transmitter.
39. The system of claim 38, wherein the control module in the MS comprises:
the analysis unit is used for receiving the control command sent by the control command extraction unit in the downlink data processing module, analyzing the received command and sending the analyzed control command to the control unit;
a control unit, configured to complete control of the transmitter, the receiver, the uplink data processing module, and the downlink data processing module, including: receiving a control command sent by the analysis unit, and controlling a downlink data cache unit to directly output original information data according to the control command or output the original information data after splicing; receiving the quality information sent by the downlink channel measuring unit, judging whether reporting is needed according to the received quality information, if so, sending the quality information needed to be reported to a feedback information generating unit in the uplink data processing module, and generating reporting information by the feedback information unit.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006101268658A CN101141172B (en) | 2006-09-07 | 2006-09-07 | Transmission method and transmission system of wireless relay system |
| PCT/CN2007/070659 WO2008031360A1 (en) | 2006-09-07 | 2007-09-07 | The method, system and device for transmitting in the wireless relay system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006101268658A CN101141172B (en) | 2006-09-07 | 2006-09-07 | Transmission method and transmission system of wireless relay system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101141172A CN101141172A (en) | 2008-03-12 |
| CN101141172B true CN101141172B (en) | 2012-08-15 |
Family
ID=39183394
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006101268658A Active CN101141172B (en) | 2006-09-07 | 2006-09-07 | Transmission method and transmission system of wireless relay system |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101141172B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2008031360A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2237452B1 (en) * | 2008-01-17 | 2012-10-10 | Alcatel Lucent | Method and device for data relay transmission in wireless relay network |
| CN101616418A (en) * | 2008-06-25 | 2009-12-30 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A kind of method of resource reuse |
| CN101729122B (en) * | 2008-10-24 | 2012-07-25 | 普天信息技术研究院有限公司 | Method for transmitting control information by distributed relay system |
| CN101772086B (en) * | 2009-01-04 | 2014-02-05 | 夏普株式会社 | Method for realizing coexistence of transparent transmission and non-transparent transmission of relay nodes |
| CN101772029B (en) * | 2009-01-05 | 2016-03-23 | 上海贝尔股份有限公司 | Frequency resource allocation method and equipment and wireless communication system |
| CN101582709A (en) * | 2009-06-17 | 2009-11-18 | 北京蓝波视讯科技有限公司 | Transmission method for wireless multipoint receiving and system |
| CN101932007B (en) * | 2009-06-22 | 2014-02-26 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and wireless relay system for realizing service flow transmission of mobile terminal |
| CN102316127B (en) | 2010-06-29 | 2014-04-23 | 阿尔卡特朗讯 | Document transmission method based on distributed storage in wireless communication system |
| CN103546304B (en) * | 2012-07-11 | 2017-08-25 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for processing business, equipment and system |
| CN102892142B (en) * | 2012-08-31 | 2015-03-04 | 宋清洋 | Relay transmission system and method capable of adaptively selecting relay schemes |
| TWI461013B (en) * | 2012-10-30 | 2014-11-11 | Inst Information Industry | Data processing apparatus and data processing method thereof for use in power line communications |
| CN103561237B (en) * | 2013-11-07 | 2017-02-08 | 山西科达自控股份有限公司 | Video monitoring system for laser imaging of mining equipment |
| CN106559837B (en) * | 2015-09-29 | 2020-06-02 | 王维加 | Fission type message transmission system and method between wireless nodes |
| CN108233993B (en) * | 2017-01-22 | 2021-03-30 | 南京邮电大学 | Wireless relay transmission implementation optimization method based on USRPN200 |
| CN107196711B (en) * | 2017-05-02 | 2019-05-07 | 中国人民解放军信息工程大学 | The method and device of signal transmission |
| CN110087212A (en) * | 2018-01-25 | 2019-08-02 | 矢崎总业株式会社 | Wireless communication terminal and communication control method |
| CN108445455A (en) * | 2018-04-03 | 2018-08-24 | 芜湖泰贺知信息系统有限公司 | A kind of portable passive Radar Electromagnetic Environment test device |
| CN110809054B (en) * | 2019-11-11 | 2021-10-29 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Data transmission method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN113079539B (en) * | 2020-01-03 | 2023-07-18 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Information transmission method, terminal and network equipment |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1795651A (en) * | 2003-05-28 | 2006-06-28 | 艾利森电话股份有限公司 | Method and system for wireless communication networks using relaying |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20050013023A (en) * | 2003-07-26 | 2005-02-02 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for transmitting of high rate frame in a wireless local area network |
| US7400856B2 (en) * | 2003-09-03 | 2008-07-15 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for relay facilitated communications |
| JP4754906B2 (en) * | 2004-08-31 | 2011-08-24 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・ドコモ | Communication system, communication node, and communication method |
-
2006
- 2006-09-07 CN CN2006101268658A patent/CN101141172B/en active Active
-
2007
- 2007-09-07 WO PCT/CN2007/070659 patent/WO2008031360A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1795651A (en) * | 2003-05-28 | 2006-06-28 | 艾利森电话股份有限公司 | Method and system for wireless communication networks using relaying |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2008031360A1 (en) | 2008-03-20 |
| CN101141172A (en) | 2008-03-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101141172B (en) | Transmission method and transmission system of wireless relay system | |
| US10063279B2 (en) | Communication system, relay device, communication terminal, and base station | |
| JP4657290B2 (en) | Wireless communication system | |
| JP5608656B2 (en) | Techniques for uplink cooperation of access nodes | |
| US8090310B2 (en) | Radio base station, relay station, and relay method | |
| CN103053201B (en) | Communication setting method, wireless base station, travelling carriage | |
| EP2088814B1 (en) | Radio relay station and radio terminal | |
| US8345587B2 (en) | Relay station, base station and method for extending a coverage area of a base station in a radio network | |
| US20230031794A1 (en) | Selection of decoding level at signal forwarding devices | |
| US20090034447A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for allocating peer-to-peer resource in relay-based wireless communication system | |
| US20090219854A1 (en) | Radio Base Station, Relay Station And Communication Control Method | |
| US20070190934A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for selecting relay mode of relay station in multihop relay broadband wireless communication system | |
| US8811339B2 (en) | Handover schemes for wireless systems | |
| KR101597667B1 (en) | radio base station device and mobile terminal device | |
| KR20110079853A (en) | Transferring data in a mobile telephony network | |
| JP5249983B2 (en) | Radio base station apparatus, mobile terminal apparatus and cell selection method | |
| KR101391847B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for determining time to response of retransmission in multi-hop relay wireless communication system | |
| US11177873B2 (en) | Adaptive relaying in a non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) communication system | |
| US11233586B2 (en) | Providing user equipment feedback via signal forwarding device | |
| JPWO2009040928A1 (en) | Wireless terminal and base station | |
| US11177871B2 (en) | Control signaling for the relay scenarios | |
| WO2010134188A1 (en) | Adaptive modulation control method, communication system and relay device | |
| Tekbıyık et al. | The usage of relay-aided communication techniques in LTE networks: Layer 3 relaying | |
| WO2011020290A1 (en) | Relay method and apparatus thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |