CN100486981C - Compound possessing function for preventing and curing atherosclerosis and its application in biologic pharmacological science - Google Patents
Compound possessing function for preventing and curing atherosclerosis and its application in biologic pharmacological science Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN100486981C CN100486981C CNB011372737A CN01137273A CN100486981C CN 100486981 C CN100486981 C CN 100486981C CN B011372737 A CNB011372737 A CN B011372737A CN 01137273 A CN01137273 A CN 01137273A CN 100486981 C CN100486981 C CN 100486981C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- piperazinyl
- substituted
- hydrocarbyl
- radical
- group
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 title claims abstract description 76
- 201000001320 Atherosclerosis Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 36
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 title 1
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 33
- 208000029078 coronary artery disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- -1 4-methylpiperazinyl Chemical group 0.000 claims description 188
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 claims description 51
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 claims description 28
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 208000031226 Hyperlipidaemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 20
- 230000002526 effect on cardiovascular system Effects 0.000 claims description 19
- 208000026106 cerebrovascular disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 18
- 208000006011 Stroke Diseases 0.000 claims description 17
- 208000024172 Cardiovascular disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 15
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000004423 acyloxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000000449 nitro group Chemical group [O-][N+](*)=O 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000004193 piperazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000006700 (C1-C6) alkylthio group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K Citrate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 3
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen bromide Chemical compound Br CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004177 diethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 3
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M D-gluconate Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M 0.000 claims description 2
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Lactate Chemical compound CC(O)C([O-])=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940050410 gluconate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000002688 maleic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- ABLZXFCXXLZCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphonic acid group Chemical group P(O)(O)=O ABLZXFCXXLZCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L succinate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCC([O-])=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940095064 tartrate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000002029 aromatic hydrocarbon group Chemical group 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 abstract description 25
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 abstract description 14
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 abstract description 11
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 9
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 118
- 125000001476 phosphono group Chemical group [H]OP(*)(=O)O[H] 0.000 description 97
- 235000002639 sodium chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 34
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N cholesterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N 0.000 description 31
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 26
- 125000005499 phosphonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 26
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- 125000005708 carbonyloxy group Chemical group [*:2]OC([*:1])=O 0.000 description 20
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 19
- 125000002755 pyrazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 19
- 206010008190 Cerebrovascular accident Diseases 0.000 description 16
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 16
- 229940125782 compound 2 Drugs 0.000 description 16
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 16
- FQUYSHZXSKYCSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-diazepane Chemical group C1CNCCNC1 FQUYSHZXSKYCSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- 230000002490 cerebral effect Effects 0.000 description 15
- 235000012000 cholesterol Nutrition 0.000 description 15
- 108010007622 LDL Lipoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 14
- 102000007330 LDL Lipoproteins Human genes 0.000 description 14
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 14
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 14
- 125000003917 carbamoyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 14
- 125000002636 imidazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 14
- 125000002769 thiazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 14
- YNAVUWVOSKDBBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Morpholine Chemical group C1COCCN1 YNAVUWVOSKDBBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 241000283973 Oryctolagus cuniculus Species 0.000 description 11
- 235000019441 ethanol Nutrition 0.000 description 11
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical group 0.000 description 11
- 125000004356 hydroxy functional group Chemical group O* 0.000 description 11
- 150000002632 lipids Chemical class 0.000 description 11
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- ZNGWEEUXTBNKFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-oxazepane Chemical group C1CNCCOC1 ZNGWEEUXTBNKFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- ZSIQJIWKELUFRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N azepane Chemical group C1CCCNCC1 ZSIQJIWKELUFRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 10
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 10
- 239000012453 solvate Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000005160 1H NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 9
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N Trichloro(2H)methane Chemical compound [2H]C(Cl)(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 description 8
- 125000003386 piperidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 8
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 8
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 7
- GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperazine Chemical compound C1CNCCN1 GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 6
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical class OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000002552 dosage form Substances 0.000 description 6
- 125000005968 oxazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 125000002971 oxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 125000003226 pyrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 6
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 125000003831 tetrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 125000000335 thiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 125000001425 triazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 125000006651 (C3-C20) cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 108010028554 LDL Cholesterol Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 239000000524 Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substance Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000001338 aliphatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 125000002915 carbonyl group Chemical group [*:2]C([*:1])=O 0.000 description 5
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 5
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 5
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 150000002462 imidazolines Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000004885 piperazines Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000003236 pyrrolines Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005303 weighing Methods 0.000 description 5
- HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(1-cyclopropylpyrazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl]-3-methyl-3,8-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-2-one Chemical class C1(CC1)N1N=CC(=C1)C1=NNC2=C1N=C(N=C2)N1C2C(N(CC1CC2)C)=O HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 4
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 4
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperidine Chemical compound C1CCNCC1 NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 description 4
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 description 4
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000000921 elemental analysis Methods 0.000 description 4
- 235000019197 fats Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 235000001727 glucose Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000009200 high fat diet Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000002540 macrophage Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 150000002825 nitriles Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 235000021590 normal diet Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 4
- LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N (2r,3r,4s,5r,6s)-4,5-dimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)-3-[(2s,3r,4s,5r,6r)-3,4,5-trimethoxy-6-(methoxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-4,5,6-trimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxyoxane Chemical compound CO[C@@H]1[C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)[C@@H](COC)O[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](OC)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)O[C@@H]2COC)OC)O[C@@H]1COC LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N 0.000 description 3
- PVOAHINGSUIXLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Methylpiperazine Chemical compound CN1CCNCC1 PVOAHINGSUIXLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WNWHHMBRJJOGFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 16-methylheptadecan-1-ol Chemical class CC(C)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCO WNWHHMBRJJOGFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical class CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Furan Chemical compound C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 3
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical group OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium laurylsulphate Chemical compound [Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCOS([O-])(=O)=O DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 244000299461 Theobroma cacao Species 0.000 description 3
- 235000005764 Theobroma cacao ssp. cacao Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 235000005767 Theobroma cacao ssp. sphaerocarpum Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 208000007536 Thrombosis Diseases 0.000 description 3
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 230000029936 alkylation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005804 alkylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003064 anti-oxidating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003143 atherosclerotic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N beta-D-glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000014121 butter Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 235000001046 cacaotero Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000003511 endothelial effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 210000003038 endothelium Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- LBAQSKZHMLAFHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethoxyethane;hydron;chloride Chemical class Cl.CCOCC LBAQSKZHMLAFHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 125000002883 imidazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 3
- 235000010981 methylcellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000008055 phosphate buffer solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000006187 pill Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000002381 plasma Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000001422 pyrrolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002390 rotary evaporation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000003335 secondary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000019333 sodium laurylsulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 3
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ZWEHNKRNPOVVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Butanone Chemical compound CCC(C)=O ZWEHNKRNPOVVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RSEBUVRVKCANEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-pyrroline Chemical compound C1CC=CN1 RSEBUVRVKCANEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NPOAOTPXWNWTSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid Chemical class OC(=O)CC(O)(C)CC(O)=O NPOAOTPXWNWTSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acrylonitrile Chemical compound C=CC#N NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001817 Agar Polymers 0.000 description 2
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N Alpha-Lactose Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005995 Aluminium silicate Substances 0.000 description 2
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N D-Glucitol Natural products OC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-N D-gluconic acid Chemical class OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001353 Dextrin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004375 Dextrin Substances 0.000 description 2
- XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethoxyethane Chemical compound COCCOC XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001856 Ethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl cellulose Chemical compound CCOCC1OC(OC)C(OCC)C(OCC)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC)C(CO)O1 ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen peroxide Chemical compound OO MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydroquinone Chemical compound OC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N Lactose Natural products OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@@H]2CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 240000007472 Leucaena leucocephala Species 0.000 description 2
- 235000010643 Leucaena leucocephala Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000006683 Mannich reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- BAPJBEWLBFYGME-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl acrylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C=C BAPJBEWLBFYGME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methylamine Chemical compound NC BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N SJ000286063 Natural products C12C(OC(=O)C(C)(C)CC)CC(C)C=C2C=CC(C)C1CCC1CC(O)CC(=O)O1 RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bicarbonate Chemical compound [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N Sucrose Chemical compound O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229930006000 Sucrose Natural products 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Chemical compound NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000008272 agar Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010419 agar Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 235000012211 aluminium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000000879 anti-atherosclerotic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000000709 aorta Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010216 calcium carbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- OSGAYBCDTDRGGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium sulfate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O OSGAYBCDTDRGGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 125000006297 carbonyl amino group Chemical group [H]N([*:2])C([*:1])=O 0.000 description 2
- KXZJHVJKXJLBKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N chembl1408157 Chemical compound N=1C2=CC=CC=C2C(C(=O)O)=CC=1C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 KXZJHVJKXJLBKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000015165 citric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229940125904 compound 1 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- LADCKIXFXIKHQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohepta-2,4,6-triene-1-carbonitrile Chemical compound N#CC1C=CC=CC=C1 LADCKIXFXIKHQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003405 delayed action preparation Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019425 dextrin Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethanolamine Chemical compound OCCNCCO ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000032050 esterification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005886 esterification reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 201000005577 familial hyperlipidemia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- HYBBIBNJHNGZAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N furfural Chemical compound O=CC1=CC=CO1 HYBBIBNJHNGZAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000012907 honey Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000000260 hypercholesteremic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- MTNDZQHUAFNZQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazoline Chemical compound C1CN=CN1 MTNDZQHUAFNZQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000011534 incubation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000007529 inorganic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N kaolin Chemical compound O.O.O=[Al]O[Si](=O)O[Si](=O)O[Al]=O NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N lactic acid Chemical compound CC(O)C(O)=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000008101 lactose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000008176 lyophilized powder Substances 0.000 description 2
- TWXDDNPPQUTEOV-FVGYRXGTSA-N methamphetamine hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.CN[C@@H](C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 TWXDDNPPQUTEOV-FVGYRXGTSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000001160 methoxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])OC(*)=O 0.000 description 2
- 210000001616 monocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- ZCFOBLITZWHNNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N oct-3-en-2-one Chemical compound CCCCC=CC(C)=O ZCFOBLITZWHNNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019198 oils Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 108010071584 oxidized low density lipoprotein Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000001575 pathological effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940124531 pharmaceutical excipient Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 150000008301 phosphite esters Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229940023488 pill Drugs 0.000 description 2
- SATCULPHIDQDRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N piperonal Chemical compound O=CC1=CC=C2OCOC2=C1 SATCULPHIDQDRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001267 polyvinylpyrrolidone Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 2
- FYPMFJGVHOHGLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N probucol Chemical compound C=1C(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=CC=1SC(C)(C)SC1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 FYPMFJGVHOHGLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229960003912 probucol Drugs 0.000 description 2
- BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCO BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DNXIASIHZYFFRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrazoline Chemical compound C1CN=NC1 DNXIASIHZYFFRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZVJHJDDKYZXRJI-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrroline Natural products C1CC=NC1 ZVJHJDDKYZXRJI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000002966 serum Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000010898 silica gel chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229960002855 simvastatin Drugs 0.000 description 2
- RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N simvastatin Chemical compound C([C@H]1[C@@H](C)C=CC2=C[C@H](C)C[C@@H]([C@H]12)OC(=O)C(C)(C)CC)C[C@@H]1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1 RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000000329 smooth muscle myocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940083575 sodium dodecyl sulfate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000000600 sorbitol Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000005720 sucrose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000003871 sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000000829 suppository Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- KCDXJAYRVLXPFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N syringaldehyde Chemical compound COC1=CC(C=O)=CC(OC)=C1O KCDXJAYRVLXPFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- COBXDAOIDYGHGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N syringaldehyde Natural products COC1=CC=C(C=O)C(OC)=C1O COBXDAOIDYGHGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- CBDKQYKMCICBOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiazoline Chemical compound C1CN=CS1 CBDKQYKMCICBOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-M trans-cinnamate Chemical class [O-]C(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CC=C1 WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-M 0.000 description 2
- LWIHDJKSTIGBAC-UHFFFAOYSA-K tripotassium phosphate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[K+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O LWIHDJKSTIGBAC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- DCXXMTOCNZCJGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N tristearoylglycerol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)COC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC DCXXMTOCNZCJGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 2
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-VKHMYHEASA-N (+)-propylene glycol Chemical compound C[C@H](O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- VCGRFBXVSFAGGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N (1,1-dioxo-1,4-thiazinan-4-yl)-[6-[[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]methoxy]pyridin-3-yl]methanone Chemical compound CC=1ON=C(C=2C=CC(F)=CC=2)C=1COC(N=C1)=CC=C1C(=O)N1CCS(=O)(=O)CC1 VCGRFBXVSFAGGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QFLWZFQWSBQYPS-AWRAUJHKSA-N (3S)-3-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[5-[(3aS,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoylamino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-[1-bis(4-chlorophenoxy)phosphorylbutylamino]-4-oxobutanoic acid Chemical compound CCCC(NC(=O)[C@H](CC(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](Cc1ccc(O)cc1)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CCCCC1SC[C@@H]2NC(=O)N[C@H]12)C(C)C)P(=O)(Oc1ccc(Cl)cc1)Oc1ccc(Cl)cc1 QFLWZFQWSBQYPS-AWRAUJHKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001764 (E)-oct-3-en-2-one Substances 0.000 description 1
- WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-Dichloroethane Chemical compound ClCCCl WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-propanediol Substances OCCCO YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940035437 1,3-propanediol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UICMCANVSAQMRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-dibenzylpiperazine-2-carbonitrile Chemical compound C1CN(CC=2C=CC=CC=2)C(C#N)CN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 UICMCANVSAQMRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YLNGZLZOKPVKON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-dioxane;propan-2-ol Chemical compound CC(C)O.C1COCCO1 YLNGZLZOKPVKON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QUMRLXXCRQWODL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methylpiperazin-1-ium;chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].C[NH+]1CCNCC1 QUMRLXXCRQWODL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IIZPXYDJLKNOIY-JXPKJXOSSA-N 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)CCC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC IIZPXYDJLKNOIY-JXPKJXOSSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ARRIEYYNOLTVTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dibromopropanenitrile Chemical compound BrCC(Br)C#N ARRIEYYNOLTVTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QJNKDAPKWVOYBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)acetonitrile Chemical compound C1CN(C)CCN1C(C#N)C1=CC=C(OCO2)C2=C1 QJNKDAPKWVOYBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BKMFGRAENTYKFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(furan-2-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)acetonitrile;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.C1CN(C)CCN1C(C#N)C1=CC=CO1 BKMFGRAENTYKFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000022 2-aminoethyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000002941 2-furyl group Chemical group O1C([*])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000000954 2-hydroxyethyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])O[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000006228 2-isobutoxyethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004200 2-methoxyethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- NBCHCVZQNIHOBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-morpholin-4-yl-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)acetic acid Chemical compound N1(CCOCC1)C(C(=O)O)C1=CC(=C(C(=C1)OC)OC)OC NBCHCVZQNIHOBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ALIDLKNCYTZCGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-morpholin-4-yl-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)acetonitrile;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.COC1=C(OC)C(OC)=CC(C(C#N)N2CCOCC2)=C1 ALIDLKNCYTZCGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005809 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C(OC([H])([H])[H])C(OC([H])([H])[H])=C(OC([H])([H])[H])C([H])=C1* 0.000 description 1
- BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-azaniumyl-2-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound NCC(O)C(O)=O BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QOXOZONBQWIKDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-hydroxypropyl Chemical group [CH2]CCO QOXOZONBQWIKDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QCQCHGYLTSGIGX-GHXANHINSA-N 4-[[(3ar,5ar,5br,7ar,9s,11ar,11br,13as)-5a,5b,8,8,11a-pentamethyl-3a-[(5-methylpyridine-3-carbonyl)amino]-2-oxo-1-propan-2-yl-4,5,6,7,7a,9,10,11,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3h-cyclopenta[a]chrysen-9-yl]oxy]-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxobutanoic acid Chemical compound N([C@@]12CC[C@@]3(C)[C@]4(C)CC[C@H]5C(C)(C)[C@@H](OC(=O)CC(C)(C)C(O)=O)CC[C@]5(C)[C@H]4CC[C@@H]3C1=C(C(C2)=O)C(C)C)C(=O)C1=CN=CC(C)=C1 QCQCHGYLTSGIGX-GHXANHINSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FHVDTGUDJYJELY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-{[2-carboxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(phosphanyloxy)oxan-3-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-3-phosphanyloxane-2-carboxylic acid Chemical compound O1C(C(O)=O)C(P)C(O)C(O)C1OC1C(C(O)=O)OC(OP)C(O)C1O FHVDTGUDJYJELY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010063746 Accidental death Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000416162 Astragalus gummifer Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000037260 Atherosclerotic Plaque Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000005711 Benzoic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000019034 Chemokines Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010012236 Chemokines Proteins 0.000 description 1
- RENMDAKOXSCIGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroacetonitrile Chemical compound ClCC#N RENMDAKOXSCIGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004381 Choline salt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002261 Corn starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000004127 Cytokines Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000695 Cytokines Proteins 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N D-Mannitol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N D-gluconic acid Chemical class OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N EDTA Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000034826 Genetic Predisposition to Disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108010023302 HDL Cholesterol Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000035150 Hypercholesterolemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010020772 Hypertension Diseases 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 102100025306 Integrin alpha-IIb Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101710149643 Integrin alpha-IIb Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000002841 Lewis acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002879 Lewis base Substances 0.000 description 1
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium sulfate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 description 1
- 229930195725 Mannitol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 229920000168 Microcrystalline cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylacetamide Chemical compound CN(C)C(C)=O FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LIMFPAAAIVQRRD-BCGVJQADSA-N N-[2-[(3S,4R)-3-fluoro-4-methoxypiperidin-1-yl]pyrimidin-4-yl]-8-[(2R,3S)-2-methyl-3-(methylsulfonylmethyl)azetidin-1-yl]-5-propan-2-ylisoquinolin-3-amine Chemical compound F[C@H]1CN(CC[C@H]1OC)C1=NC=CC(=N1)NC=1N=CC2=C(C=CC(=C2C=1)C(C)C)N1[C@@H]([C@H](C1)CS(=O)(=O)C)C LIMFPAAAIVQRRD-BCGVJQADSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 240000007594 Oryza sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000007164 Oryza sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 240000007711 Peperomia pellucida Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000199919 Phaeophyceae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000286209 Phasianidae Species 0.000 description 1
- TUZYXOIXSAXUGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pravastatin Natural products C1=CC(C)C(CCC(O)CC(O)CC(O)=O)C2C(OC(=O)C(C)CC)CC(O)C=C21 TUZYXOIXSAXUGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propanedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)CC(O)=O OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000700159 Rattus Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920001800 Shellac Polymers 0.000 description 1
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- DWAQJAXMDSEUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bisulfite Chemical compound [Na+].OS([O-])=O DWAQJAXMDSEUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229930182558 Sterol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Succinic acid Chemical class OC(=O)CCC(O)=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OUUQCZGPVNCOIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Superoxide Chemical compound [O-][O] OUUQCZGPVNCOIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tartaric acid Natural products [H+].[H+].[O-]C(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001615 Tragacanth Polymers 0.000 description 1
- YKTSYUJCYHOUJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N [O--].[Al+3].[Al+3].[O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] Chemical compound [O--].[Al+3].[Al+3].[O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] YKTSYUJCYHOUJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZVQOOHYFBIDMTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N [methyl(oxido){1-[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]ethyl}-lambda(6)-sulfanylidene]cyanamide Chemical compound N#CN=S(C)(=O)C(C)C1=CC=C(C(F)(F)F)N=C1 ZVQOOHYFBIDMTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000003187 abdominal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003655 absorption accelerator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000011054 acetic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- DPXJVFZANSGRMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid;2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal;sodium Chemical compound [Na].CC(O)=O.OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C=O DPXJVFZANSGRMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003377 acid catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005903 acid hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 206010000891 acute myocardial infarction Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 150000001263 acyl chlorides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000443 aerosol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940008126 aerosol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000003741 agents affecting lipid metabolism Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940072056 alginate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001342 alkaline earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000009435 amidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007112 amidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000005557 antagonist Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002785 anti-thrombosis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000006708 antioxidants Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940127218 antiplatelet drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940127217 antithrombotic drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000000702 aorta abdominal Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000002376 aorta thoracic Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000012736 aqueous medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000006615 aromatic heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005161 aryl oxy carbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 235000014590 basal diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- JUHORIMYRDESRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzathine Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1CNCCNCC1=CC=CC=C1 JUHORIMYRDESRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010233 benzoic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001558 benzoic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000000941 bile Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000017531 blood circulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004204 blood vessel Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 1
- KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N boric acid Chemical compound OB(O)O KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004327 boric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006189 buccal tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940046011 buccal tablet Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-NUQCWPJISA-N butanedioic acid Chemical class O[14C](=O)CC[14C](O)=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-NUQCWPJISA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000484 butyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 235000011132 calcium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004202 carbamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013877 carbamide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001768 carboxy methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001735 carboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000004663 cell proliferation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- HRYZWHHZPQKTII-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloroethane Chemical compound CCCl HRYZWHHZPQKTII-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UXTMROKLAAOEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloroform;ethanol Chemical compound CCO.ClC(Cl)Cl UXTMROKLAAOEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N choline Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CCO OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001231 choline Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019417 choline salt Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940114081 cinnamate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000002808 connective tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008120 corn starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006184 cosolvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 1
- XRAVYESZTUBEBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexane;propan-2-ol Chemical compound CC(C)O.C1CCCCC1 XRAVYESZTUBEBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YKGMKSIHIVVYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N dabrafenib mesylate Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O.S1C(C(C)(C)C)=NC(C=2C(=C(NS(=O)(=O)C=3C(=CC=CC=3F)F)C=CC=2)F)=C1C1=CC=NC(N)=N1 YKGMKSIHIVVYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000034994 death Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000517 death Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 238000001212 derivatisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- LXCYSACZTOKNNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethoxy(oxo)phosphanium Chemical compound CCO[P+](=O)OCC LXCYSACZTOKNNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004821 distillation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008298 dragée Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012377 drug delivery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010828 elution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005538 encapsulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000002889 endothelial cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000008753 endothelial function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002662 enteric coated tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010931 ester hydrolysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- PSLIMVZEAPALCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethanol;ethoxyethane Chemical compound CCO.CCOCC PSLIMVZEAPALCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YKWNUSJLICDQEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethoxyethane;propan-2-ol Chemical compound CC(C)O.CCOCC YKWNUSJLICDQEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019325 ethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001249 ethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960004667 ethyl cellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 235000010944 ethyl methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 239000007941 film coated tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012467 final product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019634 flavors Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 210000000497 foam cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 235000003599 food sweetener Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000007903 gelatin capsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000174 gluconic acid Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000012208 gluconic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000005456 glyceride group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003102 growth factor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000005826 halohydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000007902 hard capsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000019622 heart disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 150000004677 hydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008172 hydrogenated vegetable oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005457 ice water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002757 inflammatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000968 intestinal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000000959 isobutyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 150000003893 lactate salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000004310 lactic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000014655 lactic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000787 lecithin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010445 lecithin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940067606 lecithin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000007517 lewis acids Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000007527 lewis bases Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108010022197 lipoprotein cholesterol Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010021337 lipoprotein triglyceride Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000002502 liposome Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940057995 liquid paraffin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 159000000003 magnesium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000011976 maleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000594 mannitol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010355 mannitol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000030159 metabolic disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229940098779 methanesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000011987 methylation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007069 methylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960002900 methylcellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920003087 methylethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000003094 microcapsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008108 microcrystalline cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940016286 microcrystalline cellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019813 microcrystalline cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011859 microparticle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005012 migration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013508 migration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000002757 morpholinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 210000002200 mouth mucosa Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000010125 myocardial infarction Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 150000006636 nicotinic acid Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000006408 oxalic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- AICOOMRHRUFYCM-ZRRPKQBOSA-N oxazine, 1 Chemical compound C([C@@H]1[C@H](C(C[C@]2(C)[C@@H]([C@H](C)N(C)C)[C@H](O)C[C@]21C)=O)CC1=CC2)C[C@H]1[C@@]1(C)[C@H]2N=C(C(C)C)OC1 AICOOMRHRUFYCM-ZRRPKQBOSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000008506 pathogenesis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004303 peritoneum Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000825 pharmaceutical preparation Substances 0.000 description 1
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenol group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=C1)O ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002989 phenols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940081310 piperonal Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000007505 plaque formation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000106 platelet aggregation inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000166 polytrimethylene carbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000013641 positive control Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000160 potassium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011009 potassium phosphates Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 159000000001 potassium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- TUZYXOIXSAXUGO-PZAWKZKUSA-N pravastatin Chemical compound C1=C[C@H](C)[C@H](CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O)[C@H]2[C@@H](OC(=O)[C@@H](C)CC)C[C@H](O)C=C21 TUZYXOIXSAXUGO-PZAWKZKUSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960002965 pravastatin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001376 precipitating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003449 preventive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035755 proliferation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000001436 propyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- WGYKZJWCGVVSQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylamine Chemical group CCCN WGYKZJWCGVVSQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- GZRKXKUVVPSREJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridinylpiperazine Chemical compound C1CNCCN1C1=CC=CC=N1 GZRKXKUVVPSREJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000003242 quaternary ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003248 quinolines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000664 rectum Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000009566 rice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004208 shellac Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZLGIYFNHBLSMPS-ATJNOEHPSA-N shellac Chemical compound OCCCCCC(O)C(O)CCCCCCCC(O)=O.C1C23[C@H](C(O)=O)CCC2[C@](C)(CO)[C@@H]1C(C(O)=O)=C[C@@H]3O ZLGIYFNHBLSMPS-ATJNOEHPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940113147 shellac Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000013874 shellac Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- XGVXKJKTISMIOW-ZDUSSCGKSA-N simurosertib Chemical compound N1N=CC(C=2SC=3C(=O)NC(=NC=3C=2)[C@H]2N3CCC(CC3)C2)=C1C XGVXKJKTISMIOW-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 210000003491 skin Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000000391 smoking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015590 smooth muscle cell migration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000017557 sodium bicarbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000019812 sodium carboxymethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001027 sodium carboxymethylcellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000010267 sodium hydrogen sulphite Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000007901 soft capsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940032147 starch Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000000707 stereoselective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003432 sterols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000003702 sterols Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000007920 subcutaneous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003890 succinate salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000007940 sugar coated tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004083 survival effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003765 sweetening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000020357 syrup Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000006188 syrup Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011975 tartaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000002906 tartaric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000003892 tartrate salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003512 tertiary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000115 thoracic cavity Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 235000010487 tragacanth Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000196 tragacanth Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940116362 tragacanth Drugs 0.000 description 1
- UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N triformin Chemical compound O=COCC(OC=O)COC=O UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MWOOGOJBHIARFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N vanillin Chemical compound COC1=CC(C=O)=CC=C1O MWOOGOJBHIARFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FGQOOHJZONJGDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N vanillin Natural products COC1=CC(O)=CC(C=O)=C1 FGQOOHJZONJGDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000012141 vanillin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000002792 vascular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003556 vascular endothelial cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000002227 vasoactive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003462 vein Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000080 wetting agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
A compound for preventing and treating atherosclerosis, its derivative, isomer, racemate or optical isomer, medical salt and solvated substance, the medical composition containing them, its preparing process, and its application in preparing medicines for treating atherosclerosis, hyperlipomia, coronary heart disease, etc are disclosed.
Description
The present invention relates to novel substituted alpha-amino nitriles, alpha-amino carboxylic acids, alpha-amino phosphonic acids, derivatives thereof, stereoisomers thereof, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof or solvates thereof, a preparation method thereof, applications thereof in preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, cerebral apoplexy, etc., and a pharmaceutical composition containing the compounds.
Atherosclerosis is the pathological basis of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, cerebral apoplexy and the like, and has high mortality rate and high disability rate. Coronary heart disease accounts for half of 100 million deaths in the United states annually due to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, and is the only important disease in Western countries. The pathological examination result of the 19-35 year old accidental death patient in Beijing area in 1995 shows that the detection rate of coronary heart disease is 71%, the later-stage lesion patient is up to 23%, and the incidence rate is on the increasing trend along with the improvement of the social and economic levels. 2/3 survived in acute myocardial infarction patients, but 2/3 failed to recover completely. The medical and payroll losses incurred in the united states alone are up to 500-.
Epidemiological studies have revealed that several major environmental factors and genetic predisposition factors are associated with atherosclerosis. Its pathogenesis is rather complex, and numerous growth factors, cytokines and vascular regulatory molecules are involved in its process. For example, various factors (changes in hemorheology in hyperlipidemia, smoking and hypertension) can activate endothelial cells to alter their function (e.g., expression of a number of adhesion molecules, chemokines, inflammatory factors, metabolic disorders of vasoactive substances, increased endothelial permeability, and changes in surface antithrombotic properties). As a result, monocyte adhesion to endothelium increases and localizes across the endothelial space to endothelial down-conversion to macrophages; the low density lipoprotein entering under the endothelium is increased and oxidized into oxidized low density lipoprotein under the action of excessive superoxide anion locally generated by damaged endothelium, and macrophages engulf the oxidized low density lipoprotein to become foam cells in a large quantity, so that lipid stripe change in the early stage of atherosclerosis is formed. As the accumulation of cells in the lesion area gradually increases, some macrophages which engulf lipids re-enter the blood stream, and then thrombus is formed at the branch and bifurcation parts of irregular blood flow such as vortex, reflux and the like. Platelets in the thrombus release various growth regulating factors, and the growth regulating factors and various regulating factors released by activated macrophages in the blood vessel wall act on smooth muscle cells together to stimulate the migration and proliferation of the smooth muscle cells and form new connective tissues, so that the atherosclerotic lesion is developed into a progressive complex lesion. The elimination of any influencing factor leading to the development and development of the lesion can prevent the development and development of atherosclerosis and can make the lesion regress. Such as regulating blood lipid; preventing oxidation of low density lipoprotein; improving endothelial function; preventing monocyte adhesion; preventing platelet adhesion and thrombosis, and inhibiting smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation. The compound of the general formula I and the derivative thereof play roles in preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, cerebral apoplexy and the like through two links of regulating blood fat and preventing low-density lipoprotein oxidation.
The types of drugs clinically used for preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, cerebral apoplexy and the like at present comprise: lipid regulating drugs, antioxidant drugs, antiplatelet drugs, antithrombotic drugs, etc. The medicines are not certain in the aspects of curative effect, safety and specificity of resisting atherosclerosis. In recent years, with the deep understanding of the mechanism of atherosclerosis, anti-atherosclerosis drugs such as anti-oxidation and anti-cell adhesion (such as GPIIb/IIIa antagonists) become hot spots of research in the international pharmaceutical industry, but no drug with definite curative effect is available on the market.
The application of the compound of the general formula I and the derivative thereof in preventing and treating atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases is not reported.
The invention aims to find and develop a new medicine for preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and the like.
The inventor of the invention has extensively and deeply researched, and has found that the novel compound shown in the formula I or the formula Ia has exact anti-atherosclerosis, blood fat regulation and antioxidation effects, and the compound can be used for preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and the like. Research shows that the compound shown in the formula I or the formula Ia has the functions of resisting atherosclerosis, regulating blood fat and resisting oxidation. Further synthesis and research show that the derivative and proper inorganic acid or organic acid or medicinal salt formed by the derivative and inorganic base or organic base also have the effects of treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and the like. The present invention has been completed based on the above finding.
The invention relates to application of a compound shown in a general formula I, a derivative, an isomer, a racemate or an optical isomer, a medicinal salt or a solvate thereof in preparing a medicament for preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and the like or as a tool medicament for researching cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and the like,
wherein:
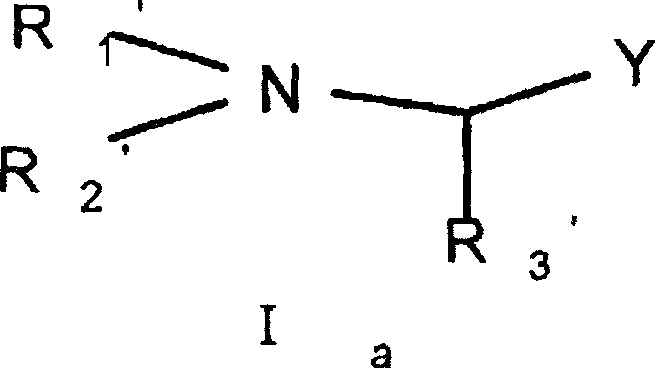
R1、R2、R3each represents a hydrogen atom, C1-20Saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched aliphatic hydrocarbons, C3-20Cycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Cycloalkyl radical, C4-20Aromatic hydrocarbon group of (1), substituted C5-20Aromatic hydrocarbon group, C3-20Heterocycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Heterocyclic hydrocarbon radicals, beta-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1 -10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkoxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C1-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10A hydrocarbyl group; or
R1And R2Or R3Generating a 3-to 9-membered cyclic structure, in particular a morpholine ring, a piperazine ring, a piperidine ring, a pyrroline ring, an imidazoline ring, a pyrazoline ring, a thiazoline ring, a homomorpholine ring, a homopiperazine ring, a homopiperidine ring, a substituted piperazine ring, an N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) piperazine ring, substituted piperidine ring, substituted pyrroline ring, substituted imidazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aralkyl) imidazoline ring, substituted pyrazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl group) pyrazoline ring, substituted thiazoline ring, substituted homomorpholine ring, substituted homopiperazine ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) homopiperazine rings, substituted homopiperidine rings, in which each group bears a substituentThe substituents are selected from: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-10Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Hydrocarbylamino, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group;
y represents cyano, carboxy, phosphonic acid, C1-10Alkoxycarbonyl group, C3-10Heterocyclyloxycarbonyl, substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxycarbonyl radical, C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, substituted C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, C1-10Alkylamino carbonyl, C3-10Heterocyclic aminocarbonyl, substituted C3-10Heterocyclic aminocarbonyl group, C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl, substituted C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl, mono C1-10Alkoxyphosphono, mono C3-10Heterocyclyloxyphosphono, mono (substituted C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, mono C4-10Aryloxyphosphonyl, mono (substituted C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, di (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphono, di (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, di (substituted C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, di (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, di (substituted C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, mono C1-10Alkylamino phosphono, mono C4-10Heterocyclic aminophosphonyl, mono (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) phosphonyl, mono C4-10Arylaminophosphonyl, mono (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, di (C)1-10Alkylamino) phosphono, di (C)4 -10Heterocyclic amino) phosphono, di (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) phosphono, di (C)4-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, di (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C1 -10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphonoRadical (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4 -10Heterocyclic amino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Arylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Arylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolinyl, pyrazolinyl, oxazolinyl, thiazolinyl, wherein the substituents in said "disubstituted phosphono" may be the same or different, and the heterocycle refers to a mono-or fused heterocycle containing 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, O or S, and the substituents of each substituent-bearing group are selected from: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-6Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-5Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Alkylamino radical, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group.
The second aspect of the invention relates to the general formula I for preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and the likeaThe new compound, the derivative, the isomer, the racemate or the optical isomer, the medicinal salt or the solvate thereof,
wherein:
R1’、R2’、R3' independently represent a hydrogen atom, C1-20Saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched aliphatic hydrocarbons, C3-20Cycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Cycloalkyl radical, C4-20Aromatic hydrocarbon group of (1), substituted C5- 20Aromatic hydrocarbon group, C3-20Heterocycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Heterocyclic hydrocarbon radicals, beta-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkoxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C1-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10A hydrocarbyl group; or
R1' and R2' or R3' Generation of 3-to 9-membered cyclic structures, in particular morpholine, piperazine, piperidine, pyrroline, imidazoline, pyrazoline, thiazoline, homomorpholine, homopiperazine, homopiperidine, substituted piperazine, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) piperazine ring, substituted piperidine ring, substituted pyrroline ring, substituted imidazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aralkyl) imidazoline ring, substituted pyrazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl group) pyrazoline ring, substituted thiazoline ring, substituted homomorpholine ring, substituted homopiperazine ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) homopiperazine rings, substituted homopiperidine rings, wherein the substituents for each substituent-bearing group are selected from the group consisting of: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-10Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Hydrocarbylamino, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group;
y represents cyano, carboxy, phosphonic acid, C1-10Alkoxycarbonyl group, C3-10Heterocyclyloxycarbonyl, substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxycarbonyl radical, C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, substituted C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, C1-10Alkylamino carbonyl, C3-10Heterocyclic aminocarbonyl, substituted C3-10Heterocyclic aminocarbonyl group, C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl, substituted C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl, mono C1-10Alkoxyphosphono, mono C3-10Heterocyclyloxyphosphono, mono (substituted C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, mono C4-10Aryloxyphosphonyl, mono (substituted C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, di (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphono, di (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, di (substituted C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, di (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, di (substituted C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, mono C1-10Alkylamino phosphono, mono C4-10Heterocyclic aminophosphonyl, mono (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) phosphonyl, mono C4-10Arylaminophosphonyl, mono (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, di (C)1-10Alkylamino) phosphono, di (C)4 -10Heterocyclic amino) phosphono, di (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) phosphono, di (C)4-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, di (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C1 -10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4 -10Heterocyclic amino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Arylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Arylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolinyl, pyrazolinyl, oxazolinyl, thiazolinyl, wherein the substituents in said "disubstituted phosphono" may be the same or different, and the heterocycle refers to a mono-or fused heterocycle containing 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, O or S, and the substituents of each substituent-bearing group are selected from: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-6Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Alkylamino radical, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group.
The invention also relates to a compound shown in the general formula I, a derivative, an isomer, a racemate or an optical isomer, a medicinal salt or a solvate thereof for preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and the like,
wherein:
R1、R2、R3each represents a hydrogen atom, C1-20Saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched aliphatic hydrocarbons, C3-20Cycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Cycloalkyl radical, C4-20Aromatic hydrocarbon group of (1), substituted C5-20Aromatic hydrocarbon group, C3-20Heterocycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Heterocyclic hydrocarbon radicals, beta-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1 -10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkoxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C1-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10A hydrocarbyl group; or
R1And R2Or R3Generating a 3-to 9-membered cyclic structure, in particular a morpholine ring, a piperazine ring, a piperidine ring, a pyrroline ring, an imidazoline ring, a pyrazoline ring, a thiazoline ring, a homomorpholine ring, a homopiperazine ring, a homopiperidine ring, a substituted piperazine ring, an N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) piperazine ring, substituted piperidine ring, substituted pyrroline ring, substituted imidazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aralkyl) imidazoline ring, substituted pyrazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl group) pyrazoline ring, substituted thiazoline ring, substituted homomorpholine ring, substituted homopiperazine ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) homopiperazine rings, substituted homopiperidine rings, wherein the substituents for each substituent-bearing group are selected from the group consisting of: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-10Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Hydrocarbylamino, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group;
y represents cyano, carboxy, phosphonic acid, C1-10Alkoxycarbonyl group, C3-10Heterocyclyloxycarbonyl, substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxycarbonyl radical, C4-10An aryloxycarbonyl group,Substituted C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, C1-10Alkylamino carbonyl, C3-10Heterocyclic aminocarbonyl, substituted C3-10Heterocyclic aminocarbonyl group, C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl, substituted C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl, mono C1-10Alkoxyphosphono, mono C3-10Heterocyclyloxyphosphono, mono (substituted C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, mono C4-10Aryloxyphosphonyl, mono (substituted C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, di (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphono, di (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, di (substituted C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, di (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, di (substituted C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, mono C1-10Alkylamino phosphono, mono C4-10Heterocyclic aminophosphonyl, mono (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) phosphonyl, mono C4-10Arylaminophosphonyl, mono (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, di (C)1-10Alkylamino) phosphono, di (C)4 -10Heterocyclic amino) phosphono, di (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) phosphono, di (C)4-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, di (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) phosphonyl, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C1 -10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)1-10Alkoxy) phosphonyl, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4 -10Heterocyclic amino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)4-10Arylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (substituted C3-10Heterocyclyloxy) phosphono, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Arylamino) (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (C)4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)1-10Alkylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)4-10Heterocyclic amino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono group, (C)4-10Arylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, (substituted C)5-10Arylamino) (substituted C4-10Aryloxy) phosphono, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolinyl, pyrazolinyl, oxazolinyl, thiazolinyl, wherein the substituents in said "disubstituted phosphono" may be the same or different, and the heterocycle refers to a mono-or fused heterocycle containing 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, O or S, and the substituents of each substituent-bearing group are selected from: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-6Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Alkylamino radical, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group.
In a further aspect, the invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising at least one compound of formula IaOr a compound shown in the formula I, a derivative, an isomer, a racemate or an optical isomer, a medicinal salt or a solvate thereof, and a medicinal carrier or excipient.
The invention also relates to a method for preventing or treating atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, which comprises the step of administering a preventive or therapeutic effective amount of a compound shown in formula I or formula I to a patient suffering from the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseasesaA derivative, isomer, racemate or optical isomer thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a solvate thereof.
The invention also relates to the preparation of the above formula IaMethods of Compounds: first, the present inventors have discovered a novel class of Mannich-like reactions, i.e., when R is involved3When HO-Ar, Y-PO (OR) OR',
the phenolic aldehyde, the secondary amine and the phosphite ester are reacted by heating to 40-300 ℃ and/or pressurizing to 0.1-20Mpa in the presence/absence of an organic solvent and a catalyst, wherein R1’、R2' and R3'As defined above, R and R' are C0-10A hydrocarbyl group; the organic solvent is methanol, ethanol, propanol, isopropanol, butanol, acetone, butanone, toluene, xylene, 1, 2-dichloroethane, methyl hydrogen furan, 1, 4-dioxane, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, N-dimethylformamide, N-dimethylacetamide, N-methylpyrrolidone and dimethyl sulfoxide; the catalyst is acid or/and alkali catalyst, the acid catalyst is Lewis acid comprising organic acid or inorganic acid, and the alkali catalyst is Lewis base comprising organic alkali tertiary amine and inorganic alkali. The discovery and application of this reaction have enabled the present inventors to prepare novel α -aminophosphonic acids and derivatives thereof with high activity in large quantities.
The amides may be prepared by preparing the acid halides from the corresponding acids and condensing with the corresponding amines, or by reacting the corresponding acids with the corresponding amines in the presence of condensing agents, as is well known in the art.
Secondly, when Y ═ CN, the following ternary Mannich reaction can be applied,
When Y ═ COOH, it can be prepared by hydrolysis of the corresponding nitrile by acid hydrolysis, base hydrolysis or hydrogen peroxide hydrolysis methods well known in the art; or by hydrolysis of the corresponding amide by acid or base hydrolysis methods well known in the art.
When Y ═ COOR, CONHR or CONRR', they can be prepared from the corresponding carboxylic acids by esterification and amidation methods well known in the art.
And, again, also from the corresponding amines with the corresponding halohydrocarbons or sulfonates by alkylation,
The method also comprises the step of preparing an isomer or an optical isomer from a product obtained by the reaction through asymmetric reaction or further resolution; further comprising reacting the product obtained by the reaction with an inorganic or organic acid to form a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, i.e., a salt of an inorganic acid such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, and hydrobromic acid; or organic acid salts, i.e., salts of acetic acid, oxalic acid, citric acid, gluconic acid, succinic acid, tartaric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, methanesulfonic acid, benzoic acid, lactic acid, and maleic acid; also included are pharmaceutically acceptable salts formed by reacting the product of the reaction with an inorganic or organic base, i.e., an alkali metal such as Li, Na and K; with alkaline earth metals such as Ca and Mg; with organic bases such as diethanolamine, choline and the like; or with chiral bases such as alkylphenylamine and the like.
Drawings
FIG. 1 shows the effect of the invention on TBARS of a compound of formula I or formula Ia: the drug concentration is 25 mu mol-1(ii) a B: the drug concentration is 250 mu mol-1。
According to the invention, atherosclerosis-related diseases refer to diseases related to atherosclerosis formation, such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
According to the invention, compounds of the general formula I R1Or R2Preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, 2-hydroxyethyl, 2-methoxyethyl, 2-ethoxyethyl, 2-propoxyethyl, 2-isopropoxyethyl, 2-butoxyethyl, 2-isobutoxyethyl, 2-tert-butoxyethyl, 2-aminoethyl, 2-methylaminoethyl, 2-ethylaminoethyl, 2-propylaminoethyl, 2-isopropylaminoethyl, 2-butylaminoethyl, 2-isobutylaminoethyl, 2-tert-butylaminoethyl, 2- (dimethylamino) ethyl, 2- (diethylamino) ethyl, 2- (dipropylamino) ethyl, 2- (dibutylamino) ethyl, tert-butyl, 2-hydroxyethylamino, 2-dimethylaminoethyl, 2- (dipropylamino) ethyl, 2- (diisobutylamino) ethyl, 2- (di-tert-butylamino) ethyl, 2-morpholinoethyl, 2-piperidinylethyl, 2-piperazinylethyl, 2- (4-methylpiperazino) ethyl, 3-hydroxypropyl, 3-methoxypropyl, 3-ethoxypropyl, 3-propoxypropyl, 3-isopropoxypropyl, 3-butoxypropyl, 3-isobutoxypropyl, 3-tert-butoxypropyl, 3-aminopropyl, 3-methylaminopropyl, 3-ethylaminopropyl, 3-propylaminopropyl, 3-isopropylaminopropyl, 3-butylaminopropyl, 3-isobutylaminopropyl, 3-tert-butylaminopropyl, 3- (dimethylamino) propyl, 3- (dipropylamino) propyl, 2- (di-tert-butylamino) propyl, 2-morpholinoethyl, 2-piperidinylethyl, 2-piperazinylethyl, 2-piperazinylpropyl, 3- (dipropylamino) propyl, 3- (dibutylamino) propyl, 3- (diisobutylamino) propyl, 3-, (Di-tert-butylamino) propyl, 3-morpholinopropyl, 3-piperidinopropyl, 3-piperazinopropyl, 3- (4-methylpiperazino) propyl; or,
R1R2n is preferably morpholinyl, piperazinyl, 4-methylpiperazinyl, 4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-methyl-2-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-piperidinylmethyl-2-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-pyrimidinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-pyrimidinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (5-pyrimidinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (6-pyrimidinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-pyridazinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4, 6-dimethoxy-2-triazinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-chlorophenyl) piperazinyl, piperazinyl, 4- (3-chlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-chlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-fluorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3-fluorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-fluorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-chlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3, 4-dichlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (5-chloro-2-methylphenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-methoxyphenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3-methoxyphenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-methoxyphenyl) piperazinyl, 4-bis (4-fluorophenyl) methylpiperazinyl, 4-carbamoyl-4-piperidinyl;
R3preferably a hydrogen atom, methyl group, C2-12A hydrocarbon group of3-8Cycloalkyl radical, C6-12Aryl, substituted C6-12Aryl radical, C4-12Heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon radicals, substituted C4-12A heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon group, wherein the substituent of each substituent-bearing group is selected from: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-6Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Alkylamino radical, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarboxamide group, the substituent can have one, two, three or four, and can be the same or different;
y is preferably cyano, carboxyl, C1-10Alkoxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, C1-10Hydrocarbyl aminocarbonyl, phosphonic acid, mono C1-10Hydrocarbyloxyphosphonyl, di-C1-10Hydrocarbyloxyphosphonyl radical, C1-10Hydrocarbyloxy group C1-10Hydrocarbylaminophosphonyl radical, C1-10Hydrocarbylaminophosphonyl, di-C1-10Hydrocarbylaminophosphonyl, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolinyl, pyrazolinyl, oxazolinyl, thiazolinyl.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, said R is1R2N is 4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl, R3Is 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl and Y is diethoxyphosphonyl.
According to the invention, acid addition salts of the compounds of formula I or formula Ia are illustrated by inorganic acid salts such as hydrochloride, sulfate, phosphate, hydrobromide; or organic acid salts such as acetate, oxalate, citrate, gluconate, succinate, tartrate, p-toluenesulfonate, methanesulfonate, benzoate, lactate and maleate; salts of compounds of formula I with bases are illustrated by alkali metal salts such as lithium, sodium and potassium salts; alkaline earth metal salts such as calcium and magnesium salts; organic base salts such as diethanolamine salts, choline salts and the like; or chiral base salts such as alkylphenylamine salts.
Solvates of the compounds of the invention may be hydrates or contain other crystallization solvents such as alcohols.
The invention further relates to a novel general formula I for preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, cerebral apoplexy and the like or used as a tool medicine for researching diseases related to atherosclerosisaThe new compound, the derivative, the isomer, the racemate or the optical isomer, the medicinal salt or the solvate thereof,
wherein:
R1’、R2’、R3' independently represent a hydrogen atom, C1-20Saturated or unsaturated straight chain ofOr branched aliphatic hydrocarbons, C3-20Cycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Cycloalkyl radical, C4-20Aromatic hydrocarbon group of (1), substituted C5- 20Aromatic hydrocarbon group, C3-20Heterocycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Heterocyclic hydrocarbon radicals, beta-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkoxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C1-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide groupC2-10A hydrocarbyl group; or
R1' and R2' or R3' Generation of 3-to 9-membered cyclic structures, in particular morpholine, piperazine, piperidine, pyrroline, imidazoline, pyrazoline, thiazoline, homomorpholine, homopiperazine, homopiperidine, substituted piperazine, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) piperazine ring, substituted piperidine ring, substituted pyrroline ring, substituted imidazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aralkyl) imidazoline ring, substituted pyrazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl group) pyrazoline ring, substituted thiazoline ring, substituted homomorpholine ring, substituted homopiperazine ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) homopiperazine rings, substituted homopiperidine rings, wherein the substituents for each substituent-bearing group are selected from the group consisting of: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-10Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Hydrocarbylamino, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group;
y represents cyano, carboxy, phosphonic acid, C1-10Alkoxycarbonyl group, C3-10Heterocyclyloxycarbonyl radical, C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, substituted C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, C1-10Alkylamino carbonyl, C3-10Heterocyclic aminocarbonyl group, C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl, substituted C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl group, C1-10Alkoxyphosphono group, C3-10Heterocycleoxyphosphonyl radical, C4-10Aryloxyphosphonyl, substituted C4-10Aryloxy phosphono group, C1-10Alkylamino phosphono group, C4-10Heterocyclic aminophosphonyl radical, C4-10Arylaminophosphonyl group, substituted C5-10Arylaminophosphonyl, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolinyl, pyrazolinyl, oxazolinyl, thiazolinyl, wherein the heterocycle means a mono-or fused heterocycle containing 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, O or S, each withSubstituents of the group of substituents are selected from: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-6Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1 -6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Alkylamino radical, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group.
Preferably, the compound of formula Ia of the present invention may be selected from any one of the group consisting of:
2- (3, 5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl) -2- [4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl ] methylphosphonic acid diethyl ester;
2- (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) -2- [4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl ] methylphosphonic acid diethyl ester;
2- (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazinyl) methylphosphonic acid diethyl ester;
2- (3, 4-methylenedioxyphenyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazinyl) acetonitrile;
2- (2-furyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazinyl) acetonitrile;
2-cyano-1, 4-dibenzylpiperazine
2-cyano-1-methyl-1-azabicyclo [3, 2, 1] -2-heptene (2-cyano-2-tropene)
8-benzyl-6 β -cyano-8-azabicyclo [3, 2, 1] oct-3-en-2-one; and
2-morpholinyl-2- (3, 4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl) acetic acid.
According to the invention, formula IaThe amine derivative, isomer, racemate or optical isomer, medicinal salt or solvate thereof also has the function of preventing or treating and regulating the function of vascular endothelial cells. Wherein formula IaAcid addition salts of amine derivatives are exemplified by inorganic acid salts such as hydrochloride, sulfate, phosphate, hydrobromide; or organic acid salt such as acetate, oxalate, citrate, and grapeA sugar acid salt, a succinate salt, a tartrate salt, a p-toluenesulfonate salt, a methanesulfonate salt, a benzoate salt, a lactate salt, a maleate salt, a nicotinate salt, a cinnamate salt or a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarate salt. Preference is given to formula IaHydrochloride, maleate, p-toluenesulfonate, cinnamate and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarate of the amine derivative. Furthermore, salts of compounds of formula Ia with bases and solvates thereof are as defined above for compounds of formula I.
More specifically, in the derivatives of the general formula I of the present invention, R1、R2、R3May be the same or different and each represents a hydrogen atom, C1-20Saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched aliphatic hydrocarbons, C3-20Cycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Cycloalkyl radical, C4-20Aromatic hydrocarbon group of (1), substituted C5-20Aromatic hydrocarbon group, C3-20Heterocycloalkyl, substituted C3-20Heterocyclic hydrocarbon radicals, beta-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkoxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, beta-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C1-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-hydroxy C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylcarbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aryl carbonyloxy C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Aryloxy radicalC2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Aryloxy radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-mercapto C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylthio group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-10Arylthio radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-amino C2-20Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamino radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C4-14Arylamino group C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C1-10Alkylamido C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10Hydrocarbyl, gamma-substituted C5-14Aromatic amide radical C2-10A hydrocarbyl group; or
R1And R2Or R3Generating a 3-to 9-membered cyclic structure, in particular a morpholine ring, a piperazine ring, a piperidine ring, a pyrroline ring, an imidazoline ring, a pyrazoline ring, a thiazoline ring, a homomorpholine ring, a homopiperazine ring, a homopiperidine ring, a substituted piperazine ring, an N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) piperazine ring, substituted piperidine ring, substituted pyrroline ring, substituted imidazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aralkyl) imidazoline ring, substituted pyrazoline ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl group) pyrazoline ring, substituted thiazoline ring, substituted homomorpholine ring, substituted homopiperazine ring, N- (substituted C)4-6Aryl) homopiperazine rings, substituted homopiperidine rings, wherein the substituents for each substituent-bearing group are selected from the group consisting of: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-10Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Hydrocarbylamino, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C5-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group;
y represents cyano, carboxy, phosphonic acid, C1-10Alkoxycarbonyl group, C3-10Heterocyclyloxycarbonyl radical, C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, substituted C4-10Aryloxycarbonyl, carbamoyl, C1-10Alkylamino carbonyl, C3-10Heterocyclic aminocarbonylsBase, C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl, substituted C4-10Arylaminocarbonyl group, C1-10Alkoxyphosphono group, C3-10Heterocycleoxyphosphonyl radical, C4-10Aryloxyphosphonyl, substituted C4-10Aryloxy phosphono group, C1-10Alkylamino phosphono group, C4-10Heterocyclic aminophosphonyl radical, C4-10Arylaminophosphonyl group, substituted C5-10Arylaminophosphonyl, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolinyl, pyrazolinyl, oxazolinyl, thiazolinyl, wherein the heterocycle refers to a mono-or fused heterocycle containing 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, O or S, and the substituent of each substituent-bearing group is selected from: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-6Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1 -6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Alkylamino radical, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarbon amide group;
when Y is PO (OEt)2Preferred compounds of formula I are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Y ═ PO (OEt)2Preferred compounds of formula I and substituents thereof
When Y is cyano, preferred compounds of formula I and substituents thereof are shown in Table 1.
Table 2 preferred compounds of formula I and substituents thereof when Y ═ CN
When Y is CONH2Preferred compounds and substituents are shown in Table 3
Table 3 preference is given to compounds of the formula I, where Y ═ CONH in formula I2
When Y is CO2H, preferred compounds and substituents are shown in Table 4
Table 4 preference is given to compounds of the formula I in which Y ═ CO2H
When Y is CO2Me, preferred compounds and substituents are shown in Table 5
Table 5 preference is given to compounds of the formula I in which Y ═ CO2Me
Further, formula IaIf the compound has a modifiable group, the compound can be reacted with a proper derivatization reagent to prepare a corresponding derivative. Such as alkylation of phenolic hydroxyl groups (e.g., methylation, carboxymethylation, and alkoxycarbonylmethylation), esterification, ester hydrolysis, and the like.
According to the invention, formula IaWhen Y ═ PO (OR') OR "in the compound, the general preparation method is a new type of Mannich reaction found by the present inventors, and the general conditions are as follows: phenolic aldehyde, secondary amine and phosphite ester are heated and reacted in the presence/absence of an organic solvent, and unlike the previous reaction, the reaction does not need acyl chloride as a catalyst.
When Y ═ CN in the compounds represented by general formula I according to the present invention, the general procedure can be prepared according to methods known in the art, see Houben-weyl. 282-283.
When Y ═ CONH in the compounds represented by formula I2General procedures can be prepared from the corresponding nitrile by hydrolysis according to methods known in the art, see Houben-weyl. 661-; j Am Chem Soc, 1960, 82: 4642-4644.
When Y ═ COOH in the compounds represented by formula I, the general procedure can be prepared from the corresponding nitrile by hydrolysis according to methods known in the art, see Houben-weyl. 428-431; or from the corresponding amides, see Houben-weyl. meth Org Chem, 1952, 8: 432.
when Y ═ COOR' in the compounds represented by formula I, the general procedure can be prepared from the corresponding nitriles according to methods known in the art, see Houben-weyl. 536-; or from the corresponding acids, see Houben-weyl. meth Org Chem, 1952, 8: 542-547.
The compounds represented by formula I can also be prepared via alkylation methods well known in the art, i.e. from the corresponding secondary amines or phenols with appropriate halides or sulfonates, see Org Synth, 1955, col Vol 3: 256-258.
According to the invention, formula I or formula IaThe compounds may exist in stereoisomeric forms. The asymmetric centers present in the compounds of formula (I) may have the R configuration or the S configuration. The present invention includes all possible stereoisomers such as enantiomers or diastereomers, as well as mixtures of two or more stereoisomers, for example mixtures of enantiomers and/or diastereomers, in any desired ratio. The invention therefore relates to enantiomers, for example the levo-and dextro-enantiomers in enantiomerically pure form, and mixtures or racemates of the two enantiomers in different ratios. If cis/trans isomers are present, the present invention relates to the cis form and the trans form as well as mixtures of these forms. If desired, the single stereoisomers may be prepared by resolution of a mixture according to conventional methods, or by, for example, stereoselective synthesis. The invention also relates to tautomeric forms of the compounds of the formula I, if motorized hydrogen atoms are present.
According to the invention, formula I or IaThe compound and its stereoisomer have effects of resisting atherosclerosis, resisting oxidation, and regulating blood lipid. Can be used for preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipemia, and apoplexy. Therefore, can be used for preventing or treating atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, and hypertensionBlood lipid, cerebral apoplexy, etc., and can be used in animals, preferably mammals, especially human.
The invention therefore also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing, as active ingredient, an effective amount of at least one compound of formula I or of formula IaPharmaceutical compositions of the compounds, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts and/or stereoisomers thereof, and conventional pharmaceutical excipients or adjuvants. Typically, the pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention comprise 0.1 to 90% by weight of formula I or formula IaA compound and/or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof. The pharmaceutical compositions may be prepared according to methods known in the art. For this purpose, if desired, formula I or formula IaThe compounds and/or stereoisomers are combined with one or more solid or liquid pharmaceutical excipients and/or adjuvants and formulated into a suitable administration form or dosage form for human use.
The invention is of formula I or formula IaThe compound or pharmaceutical composition containing it can be administered in unit dosage form, and the administration route can be intestinal or parenteral, such as oral, muscle, subcutaneous, nasal, oral mucosa, skin, peritoneum or rectum. The administration dosage forms include tablet, capsule, dripping pill, aerosol, pill, powder, solution, suspension, emulsion, granule, liposome, transdermal agent, buccal tablet, suppository, lyophilized powder for injection, etc. Can be common preparation, sustained release preparation, controlled release preparation and various microparticle drug delivery systems. In order to prepare the unit dosage form into tablets, various carriers well known in the art can be widely used. Examples of the carrier are, for example, diluents and absorbents such as starch, dextrin, calcium sulfate, lactose, mannitol, sucrose, sodium chloride, glucose, urea, calcium carbonate, kaolin, microcrystalline cellulose, aluminum silicate and the like; wetting agents and binders such as water, glycerin, polyethylene glycol, ethanol, propanol, starch slurry, dextrin, syrup, honey, glucose solution, acacia slurry, gelatin slurry, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, shellac, methyl cellulose, potassium phosphate, polyvinylpyrrolidone and the like; disintegrating agents, e.g. dried starch, alginates, agar powder, brown algae starch, sodium bicarbonate and citric acid, calcium carbonate, polyoxyethylene sorbitol esterFatty acid esters, sodium dodecylsulfate, methyl cellulose, ethyl cellulose, and the like; disintegration inhibitors such as sucrose, glyceryl tristearate, cacao butter, hydrogenated oil and the like; absorption accelerators such as quaternary ammonium salts, sodium lauryl sulfate and the like; lubricants, for example, talc, silica, corn starch, stearate, boric acid, liquid paraffin, polyethylene glycol, and the like. The tablets may be further formulated into coated tablets, such as sugar-coated tablets, film-coated tablets, enteric-coated tablets, or double-layer and multi-layer tablets. For making the administration units into pills, a wide variety of carriers well known in the art can be used. Examples of the carrier are, for example, diluents and absorbents such as glucose, lactose, starch, cacao butter, hydrogenated vegetable oil, polyvinylpyrrolidone, Gelucire, kaolin, talc and the like; binders such as acacia, tragacanth, gelatin, ethanol, honey, liquid sugar, rice paste or batter, etc.; disintegrating agents, such as agar powder, dried starch, alginate, sodium dodecylsulfate, methylcellulose, ethylcellulose, etc. For making the administration unit into a suppository, various carriers well known in the art can be widely used. As examples of the carrier, there may be mentioned, for example, polyethylene glycol, lecithin, cacao butter, higher alcohols, esters of higher alcohols, gelatin, semisynthetic glycerides and the like. For the encapsulation of the administration units, the active ingredient is of the formula I or of the formula IaThe compound or its stereoisomer is mixed with the above-mentioned various carriers, and the mixture thus obtained is placed in hard gelatin capsules or soft capsules. The effective component can also be represented by formula I or formula IaThe compound or the stereoisomer thereof is prepared into microcapsules, is suspended in an aqueous medium to form a suspension, and can also be filled into hard capsules or prepared into injections for application. For preparing the administration unit into preparations for injection, such as solutions, emulsions, lyophilized powders and suspensions, all diluents commonly used in the art can be used, for example, water, ethanol, polyethylene glycol, 1, 3-propanediol, ethoxylated isostearyl alcohol, polyoxylated isostearyl alcohol, polyoxyethylene sorbitol fatty acid esters, and the like. In addition, for the preparation of isotonic injection, can be added to the preparation for injection of appropriate amount of sodium chloride, glucose or glycerol, in addition, can also be added with conventional cosolvent, buffer, pH adjustmentAgents, and the like.
In addition, colorants, preservatives, flavors, flavorings, sweeteners or other materials may also be added to the pharmaceutical preparation, if desired.
The invention is represented by formula I or formula IaThe dosage of the compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or stereoisomer thereof, to be administered depends on many factors, such as the nature and severity of the disease to be prevented or treated, the sex, age, body weight and individual response of the patient or animal, the particular compound used, the route of administration and the number of administrations, etc. The above-mentioned dosage may be administered in a single dosage form or divided into several, e.g. two, three or four dosage forms.
Examples
The invention is further illustrated by the following examples, which are not intended to be limiting in any way.
EXAMPLE 12 preparation of diethyl (3, 5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl) -2- [4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl ] methylphosphonate, Compound 1
26.60g (0.146mol) of 3, 5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, 23.20g (0.141mol) of 1- (2-pyridyl) piperazine and 21.10g (0.153mol) of diethyl phosphite are weighed, 50ml of absolute ethyl alcohol is added for dissolution, the mixture is stirred for 3.5 days at the bath temperature of about 60 ℃, a solvent is evaporated, silica gel column chromatography is carried out, excessive raw materials are washed away by chloroform, then the chloroform-ethanol (4:1) is used for elution, the solvent is recovered, and then isopropanol-1, 4-dioxane is used for crystallization, thus obtaining 46.8g of colorless crystals, the yield is 71.3 percent, and the mp is 125-127 ℃. Elemental analysis C22H32N3O6P (%) calcd for C56.76, H6.93, N9.02, found C56.80, H6.92, N8.88.1H-NMR(CDCl3,ppm)1.05-1.12(t,J=7.04Hz,3H),1.35-1.38(t,J=7.04Hz,3H),2.60-2.70(m,2H),2.90-3.00(m,2H),3.45-3.75(m,4H),3.7853.821(d,J=20.33Hz,1H),3.902(s,6H),3.90-4.00(m,2H),4.20-4.30(m,2H),5.542(s,1H),6.60-6.70(m,2H),6.739(s,2H),7.50-7.60(m,1H),8.15-8.17(dd,1H)。MS(FAB+,m/z)466.2(M+1),328.1(B,M-PO(OEt)2). Dissolving Compound 1 in isopropanol, and adding HCl-Et2And O, salifying to obtain hydrochloride: mp 135-136 deg.c,1H-NMR(D2O,ppm)1.00-1.20(m,6H),3.40-3.50(m,4H),3.65-4.05(m,16H),4.3855.007(dd,J=11-15Hz,1H),6.726(d,J=2.20Hz,1H),6.874(s,1H),7.021(t,J=6.59Hz,1H),7.23-7.28(m,1H),8.013(d,J=2.20Hz,1H),8.025(m→d,J=2.20Hz,1H)。MS(FAB+,m/z)466.2(M+1),328.1(B,M-PO(OEt)2)。
EXAMPLE 22 preparation of diethyl- (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) -2- [4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl ] methylphosphonate Compound 2
Prepared according to the method of example 1, vanillin instead of 3, 5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and recrystallized from isopropanol-cyclohexane to obtain white granular crystals with a yield of 64.9% and mp 130-. Elemental analysis C21H30N3O5P (%) calcd for C57.92, H6.94, N9.65; found C57.86, H7.01, N9.48;1H-NMR(CO(CD3)2,ppm)0.97-1.00(t,J=7.17Hz,3H),1.27-1.30(t,J=7.02Hz,3H),2.48-2.53(m,2H),2.88-2.92(m,2H),3.071(s,1H),3.45-3.49(t,J=5.04Hz,2H),3.66-3.74(m,1H),3.785(s,3H),3.81-3.92(m,1H),3.9403.978(d,J=23.19Hz,1H),4.15-4.26(m,2H),6.50-6.52(m,1H),6.6686.683(d,J=8.85Hz,1H),6.7576.770(d,J=7.94Hz,1H),6.90-6.93(d,J=7.94Hz,1H),7.138(s,1H),7.39-7.43(m,1H),8.00-8.02(dd,1H).MS(EI,m/z)435.1(M+),298.1(B,M-PO(OEt)2). Hydrochloride salt: mp 208 and 209,1H-NMR(D2O,ppm)1.00-1.25(m,6H),3.38-3.50(m,4H),3.65-4.05(m,13H),4.4055.004(dd,J=11-14Hz,1H),6.84-6.92(m,1H),6.96-7.04(m,2H),7.10-7.30(m,2H),7.774(m→s,J=2.20Hz,1H),8.025(m,1H)。MS(FAB+,m/z)436.2(M+1),298.1(B,M-PO(OEt)2)。
EXAMPLE 32 preparation of diethyl (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazinyl) methylphosphonate Compound 11
Prepared by the method of example 1, by reaction of N-methylpiperazine, crystallization from ether-ethanol, yield 94.1%,1H-NMR(CDCl3,ppm)1.05-1.09(t,J=7.08Hz,3H),1.34-1.38(t,J=7.08Hz,3H),2.25(s,3H),2.38-2.53(m,4H),2.80-2.94(m,2H),3.62-3.74(m,2H),3.7453.801(d,J=22.46Hz,1H),3.862(s,3H),3.80-3.98(m,2H),4.08-4.32(m,2H),6.7656.786(d,J=8.30Hz,1H),6.8306.849(d,J=7.81Hz,1H),7.034(s,1H).MS(EI+,m/z)372.2(M+),274.1(M-MP)+,235.1(B,M-PO(OEt)2)。
EXAMPLE 4 preparation of N- (cyanomethyl) morpholine-compound 133
Weighing 8.30g (0.11mol) of chloroacetonitrile, adding 50ml of anhydrous ether, stirring, cooling with ice water, dropwise adding 17.50g (0.20mol) of morpholine and 20ml of anhydrous ether, standing overnight after dropwise adding, filtering the mixture, fully washing with the anhydrous ether, combining ether solutions, and rotationally evaporating a low-boiling-point part to obtain 12.20g (96.8%) of light red liquid, namely the compound 1. 2.60g (0.020mol) of the liquid are taken, dissolved in 20ml of anhydrous ether and added with HCl-Et2O salt formation to give 3.20g (95.4%) of a white solid, i.e.N- (cyanoethyl) morpholine hydrochloride, mp, elemental analysis C6H11ClN2Theoretical values of O (%) C44.32, H6.82, N17.23; found C44.36, H6.83, N17.31.1H-NMR(D2O,ppm)3.37-3.46(m,4H),3.95-4.02(t,J=4.58Hz,4H),4.37-4.43(m,2H).
EXAMPLE 51 preparation of- (cyanomethyl) -4-methylpiperazine-Compound 134
Prepared according to the method of example 1, substituting N-methylpiperazine for morpholine, compound 2 yield 98.1%; the salt formation yield is 97.2%.1H-NMR(D2O,ppm)2.70-2.80(m,2H),2.92-2.93(d,J=1.10Hz,3H),3.12-3.24(m,4H),3.55-3.64(m,2H),3.82-3.84(d,J=1.10Hz,2H).
EXAMPLE 62- (3, 4-methylenedioxyphenyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazinyl) acetonitrile-preparation of Compound 150
Weighing 1.10g (0.0224mol) of sodium cyanide, 2.21g (0.0213mol) of sodium bisulfite and 3.10g (0.0206mol) of piperonal, adding 20ml of water, shaking up, adding 2.10g (0.0210mol) of N-methylpiperazine and 10ml of ethanol, reacting for 40 hours at about 50 ℃ while stirring, cooling, adding water, extracting for 3 times with diethyl ether, drying with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, recovering the solvent, crystallizing with diethyl ether-petroleum ether to obtain 3.50g (65.8%) of white crystals, and mp87-88 ℃. Elemental analysis C14H17N3O2(%) theoretical C64.85, H6.61, N16.20; found C64.88, H6.59, N16.27. IR (KBr pellet, cm)-1)3457.92,2905.61,2244.99,2220.27,2187.02,1504.49,1504.49,1496.79,1460.03,1452.37,1258.70,1113.09,932.23,825.46;1H-NMR(CDCl3,ppm)2.293(s,3H),2.40-2.55(m,4H),2.55-2.64(m,4H),4.721(s,1H),5.993(s,2H),6.7936.814(d,J=8.30Hz,1H),6.994(s,1H),7.0057.025(d,J=8.30Hz,1H);MS(FAB+,m/z)260.2(M+1)+,259.2(M+),258.2(M-1)+,233.2(M-CN)+,160.0(B,(M-MP)+)。
EXAMPLE 72 preparation of- (2-furyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazinyl) acetonitrile-Compound 152
Weighing 1.40g (0.0103mol) of N-methylpiperazine hydrochloride, 1.01g (0.0105mol) of furaldehyde and 0.52g (0.0106mol) of sodium cyanide, dissolving in 10ml of water and 20ml of ethanol, stirring at about 55 ℃ for reaction for about 6 hours, cooling, adding 50ml of water, extracting with ethyl acetate (70ml × 2), drying with anhydrous sodium sulfate, recovering solvent to obtain a residue, namely compound 2, and extracting with EtOH-AcOEt-Et2O dissolution, HCl-Et2O salification to obtain 2- (2-furyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazinyl) acetonitrile hydrochloride 2.05g (84.7%), mp 174 and 175 ℃. IR (KBr pellet, cm)-1)3435.79(br),2800-2400(m),1460.65,1184.56,1143.60,1111.70,1015.64,983.75,878.48,752.43;1H-NMR(CDCl3,ppm)2.826 2.837(d,J=4.39Hz,3H),2.90-3.05(m,4H),3.06-3.24(m,2H),3.50-3.62(m,2H),4.945(s,1H),6.42-6.44(m,1H),6.6046.611(d,J=2.93Hz,1H),7.483(s,1H),12.925(br,1H);MS(FAB+,m/z)447.2(2M-Cl-1)+,206.1(M-Cl-1)+,179.1(B,(B-CN)+)。
EXAMPLE 82 preparation of cyano-1, 4-dibenzylpiperazine-compound 182
Weighing 10.65g (0.050mol) of 2, 3-dibromopropionitrile, adding 40ml of dry benzene, dripping 20ml of dry benzene solution in which 10.20g (0.101mol) of triethylamine and 12.05g (0.050mol) of N, N' -dibenzylethylenediamine are dissolved at 40 ℃ under stirring, refluxing for 3 hours after dripping, cooling, filtering, washing solids with benzene, combining benzene liquid, recovering benzene, and performing silica gel column chromatography to obtain light yellow thick liquid, namely a compound; dissolving 1.0g product in 20ml diethyl ether, salifying with hydrochloric ether, precipitating to obtain thick solid, discarding solvent, crystallizing with isopropanol-diethyl ether to obtain hydrochloride 0.90g (80.0%), mp170-171 deg.C.
EXAMPLE 92 preparation of cyano-1-methyl-1-azabicyclo [3, 2, 1] -2-heptene (2-cyano-2-tropene) -Compound 183
Weighing 30.20g (0.258mol) of 2, 4, 6-cycloheptatrienenitrile, putting the weighed 2, 4, 6-cycloheptatrienenitrile into a reaction kettle, adding 200ml of methylamine alcohol solution, putting the mixture into an oil bath at 85-90 ℃, heating for reaction for 28 hours, cooling, opening the kettle, performing rotary evaporation to remove a low boiling point part, and then performing reduced pressure distillation to obtain 33.80g (88.5%) of light yellow liquid, bp95-98 ℃/2-3mmHg, and using HCl-Et2O salifying to obtain a white solid, and carrying out mp 181-184 ℃.
EXAMPLE 108 preparation of benzyl-6 β -cyano-8-azabicyclo [3, 2, 1] oct-3-en-2-one-Compound 184
11.20g (0.050mol) of N-benzyl-3-hydroxypyridine chloride and 0.10g of hydroquinone were weighed, and 25ml of acrylonitrile, 10ml of triethylamine and 65ml of tetrahydrofuran were added thereto, and the mixture was stirred under reflux overnight. The next day, filtration was carried out, the solvent was evaporated off by rotary evaporation, 100ml of diethyl ether was added, filtration was carried out, the solvent was recovered, and the residue was recrystallized from ethanol to give 6.35g (53.4%) of yellow crystals, mp 87-89 ℃.
EXAMPLE 112 preparation of carbamoyl-1-methyl-1-azabicyclo [3, 2, 1] -2-heptene (anhydroecgonine amide) -Compound 250
3.05g (0.0206mol) of 2-cyano-2-tropine is taken and dissolved in 20ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid, reflux reaction is carried out for 6 hours, water is evaporated under reduced pressure, and anhydrous ethanol is used for crystallization to obtain 3.46g (82.5%) of white solid, and mp218-221 ℃ is carried out.
Example 122 preparation of morpholinyl-2- (3, 4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl) acetic acid-compound 254
Referring to the method of example 11, 2-morpholinyl-2- (3, 4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl) acetonitrile hydrochloride 1.80g (6.46mmol) is dissolved in 25ml concentrated hydrochloric acid and 15ml water, the reflux reaction is carried out overnight, the next day, the rotary evaporation is carried out, the residue is dissolved in absolute ethyl alcohol, ether is added for precipitation, the filtration is carried out, the solid is washed by ether, and the recrystallization is carried out by absolute ethyl alcohol.
EXAMPLE 138 preparation of benzyl-6 β -methoxycarbonyl-8-azabicyclo [3, 2, 1] oct-3-en-2-one-compound 385
Prepared according to the method of example 10, substituting acrylonitrile with methyl acrylate to give 6.50g (48.0%), mp 90-92 ℃.
The following biological activity experiments further illustrate the present invention.
Biological Activity test example 1 test of antioxidant Effect of novel Compounds of the general formula I of the present invention on Cu in vitro2+The effect of inhibition of the production of thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS), the final product that induces the oxidation of normal human low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
Normal human low density lipoprotein and Cu as shown in FIG. 12+Incubation can induce LDL oxidation modification, and oxidation end product thereof is thiobarbituric acidThe reaction mass is increased significantly. The concentration of the new structure compound is 25 mu mol-1When incubated with LDL for 5h in an LDL oxidation reaction system, the inhibition rates for TBARS production were compound 2 (50.72%), compound 4 (33.75%), VitE (27.67%), compound 135 (20.08%), compound 149 (17.74%), compound 155 (17.67%), compound 148 (13.87%), and compound 134 (6.21%), respectively. The concentration is 250 mu mol.L-1When incubated with LDL for 5h in an LDL oxidation reaction system, the inhibition rates for TBARS production were 149 (82.06%), 2 (74.32%), 155 (70.88%), 133 (65.66%), 1 (48.65%), 135 (44.31%), 4 (30.71%), 148 (24.50%), 134 (15.04%), 5 (8.97%), and 136 (8.90%), respectively.
Biological Effect Experimental example 1. experiment of antioxidant effect of the novel Compounds suggests that the compounds of formula I of the present invention have significant antioxidant effect, and that representative compounds 2 and 4 have a stronger antioxidant effect than VitE. Studies have shown that drugs having an antioxidant action, such as probucol, can both block the development of atherosclerotic lesions and have an effect of promoting regression of the lesions (see document 1). The strong antioxidation effect of the compound 2 is hopeful to be used for treating atherosclerotic diseases and diseases related to free radicals.
Reference 1Nagano Y, Naramura T, Matsuzawa Y, et al Probucol and thermalserosis in the WHHR lane term anti atheroscerotic effect and artifacts on anaerobic substrates et al atheroscerosis, 1992; 92: 131.
biological Effect test example 1. method for investigating the antioxidant Effect of novel Compounds: dialyzing with Phosphate Buffer Solution (PBS) without EDTA to adjust protein concentration to 2.0 mg.L-1Adding equal volume of PBS (blank control), Vit E (positive control) and different concentrations of the sample to be tested (final concentration is 250 and 25 mu mol. L) in turn-1) Then adding Cu respectively2+LDL oxidation was induced by incubation at 37 ℃ and samples were taken every 1 h. Adding a certain amount of sulfur to the sample to be testedBarbituric acid is reacted and the amount of the oxidation product produced is determined colorimetrically. The antioxidant effect of the drug was observed.
Biological effects experiment example 2 effect of compound 2 representative of the formula of the present invention on inhibition of high cholesterol-induced blood lipid elevation.
As shown in Table 1, the effect of the drug on hyperlipidemia induced by high cholesterol feeding was observed by feeding the white rabbits with high cholesterol while orally administering 210mg/kg of the compound to the white rabbits with high cholesterol. The compound 2 can remarkably reduce the increase of plasma total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol induced by high cholesterol feeding, and has the tendency of inhibiting the increase of TG. The TC and LDL-C, TG levels of the rabbits are obviously increased by one month after high-fat diet, compared with the normal diet group, the increase ranges are respectively 53 times, 95 times and 1.5 times, the corresponding increase ranges of the TC and the LDL-C of the compound 2 administration group are respectively 14.52 times and 27.47 times, and TG is not different from the normal diet group. It is suggested that compound 2 can significantly reduce the increase of TC and LDL-C induced by high cholesterol (P <0.01 compared with high fat diet group), and has the tendency of inhibiting TG increase.
TABLE 1 Effect of Compound 2 on blood lipids in rabbits raised at 1 month with high cholesterol
Note: blood lipid concentration is mmol.L-1Data expressed in x ± s, compared to normal diet group:*P<0.05,**P<0.01. comparison with the group of high fat diets: # P<0.05,##P<0.01. The data processing application is a SAS software D2P8 program.
Biological effect experiment example 2 suggests that compound 2 has significant effect in regulating blood lipid. In recent years, several large series of clinical studies have demonstrated that lowering plasma TC, especially LDL, reduces the risk of coronary heart disease, and that lowering serum LDL in high risk populations promises to reduce the incidence and mortality of CHD in the21 st century by one third (see documents 2, 3, 4). The compound 2 has obvious blood fat regulating effect and shows good prospect of preventing and treating coronary heart disease.
Document 2 Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival study group, Rnadirected formulated tertiary of cholestrol lower in 4444 patents with a cardio heart disease: the scandinavian simvastatin sumivavalstudy (4s) [ J ]. Lancet, 1994; 344: 1383-389.
Document 3 Shepherd J, Cbbesm, Ford L, et al, prediction of coronary disease with pravastatin in men with hypercholestrolememawest of scotland coronary prediction study group [ J ]. N Engl J Med; 1995, 333: 1301-307.
Document 4 Scott MG. Cholesterol and coronary heart disease-the21th center [ J ]. Arch Intern Med; 1997, 157: 1177-184
Biological Effect experiment example 3 Effect of compound 2 representative of the formula of the present invention on atherosclerosis induced by elevated blood lipids in hypercholesterolemic rabbits.
The effect of the drug on the formation of aortic plaques in rabbits was observed by feeding the white rabbits with high cholesterol while orally administering 210mg/kg of the compound to the white rabbits. The arterial wall of the hypercholesterolemic feeding group was significantly thickened, and the raised cream yellow plaque on the intimal surface was fused into a sheet covering the entire thoracic and abdominal aortic surfaces. The arterial wall of the group administered with compound 2 was slightly thickened, the lesion was heavier at the root and arch of the aorta, spread to the entire thoracic aorta, spread to the abdominal aorta in a small amount, and the plaque was not fused into a piece. Suggesting that the compound 2 can inhibit atherosclerosis caused by hyperlipemia induced by high cholesterol feeding.
Biological effect experiment example 3 suggests that high cholesterol feeding can induce hyperlipidemia and cause atherosclerosis, and that compound 2 can inhibit atherosclerosis formation caused by hyperlipidemia.
Biological effect experiment the study methods of example 2 and example 3: the big ear white rabbits are kept for the whole male, and the body weight is about 2 kg. Each dosing was given high fat diet 120g.d-1(containing 1.2 g of bile)Sterol), basal diet 120g.d was given to the normal diet group-1. The administration group orally administered compound 210 mg/kg.d. At 1 month of experiment, rabbit ear vein blood specimen is collected, serum is separated, and total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride in blood plasma are measured. The effect of the drug on high cholesterol-induced elevation of blood lipids was observed. At 1.5 months of the experiment, animals were sacrificed, the aorta was treated routinely, and the effect of the drug on the general distribution of atherosclerotic plaque formation caused by hypercholesterolemia induced rabbit hyperlipidemia was visually observed.
The experimental methods are detailed in the references: chenkai, Zhang Yan Fang, Wanqian, etc. Hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis induced by high cholesterol raising of rabbits, quails and rats; free military pharmacology, 17 (3): 117-124
Claims (7)
1. Application of compound shown in general formula I or medicinal salt thereof in preparing medicine for preventing or treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases or application of compound shown in general formula I or medicinal salt thereof as tool medicine for researching the diseases
Wherein:
R1R2n is piperazinyl, 4-methylpiperazinyl, 4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-methyl-2-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4)-piperidinylmethyl-2-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-pyridyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-pyrimidinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-pyrimidinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (5-pyrimidinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (6-pyrimidinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-pyridazinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4, 6-dimethoxy-2-triazinyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-chlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3-chlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-chlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-fluorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3-fluorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-pyridyl) piperazinyl, and the like, 4- (2-chlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3, 4-dichlorophenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (5-chloro-2-methylphenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (2-methoxyphenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (3-methoxyphenyl) piperazinyl, 4- (4-methoxyphenyl) piperazinyl, 4-bis (4-fluorophenyl) methylpiperazinyl;
R3represents C6-12Aryl, substituted C6-12An aromatic hydrocarbon group, wherein the substituent of each substituent-bearing group is selected from: halogen, hydroxy, cyano, nitro, C1-6Hydrocarbyl radical, C4-6Aryl radical, C1-6Alkoxy radical, C1-6Alkylthio, mono-, di-or trihalo-C1-6Alkyl, amino, C1-10Alkylamino radical, C1-10Hydrocarbon acyloxy, C6-10Aroyloxy radical or C1-10A hydrocarboxamide group, the substituent can have one, two, three or four, and can be the same or different;
y represents phosphonic acid group, C1-10Hydrocarbyloxyphosphonyl, di-C1-10Hydrocarbyloxyphosphonyl radical, C1 -10Hydrocarbyloxy group C1-10Hydrocarbylaminophosphonyl radical, C1-10Hydrocarbylaminophosphonyl, di-C1-10A hydrocarbyl aminophosphonyl group.
2. The use of claim 1, wherein R is1R2N is 4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl and Y is diethoxyphosphonyl.
3. The use of claim 1, wherein the pharmaceutically acceptable salt is a pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt selected from the group consisting of hydrochloride, sulfate, phosphate, hydrobromide; or an acetate, oxalate, citrate, gluconate, succinate, tartrate, p-toluenesulfonate, methanesulfonate, benzoate, lactate or maleate salt.
4. The use according to claim 1, wherein the pharmaceutically acceptable salt is a salt with a base selected from an alkali metal salt, an alkaline earth metal salt, a salt with an organic base or a salt with a chiral base.
5. Use according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the compound of formula I is selected from
2- (3, 5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl) -2- [4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl ] methylphosphonic acid diethyl ester;
2- (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) -2- [4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl ] methylphosphonic acid diethyl ester;
diethyl 2- (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazinyl) methylphosphonate.
6. The use according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the compound is diethyl 2- (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) -2- [4- (2-pyridyl) piperazinyl ] methylphosphonate hydrochloride.
7. The use of claim 6, wherein the use is in the preparation of a medicament for preventing or treating atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, and stroke.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB011372737A CN100486981C (en) | 2001-11-02 | 2001-11-02 | Compound possessing function for preventing and curing atherosclerosis and its application in biologic pharmacological science |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB011372737A CN100486981C (en) | 2001-11-02 | 2001-11-02 | Compound possessing function for preventing and curing atherosclerosis and its application in biologic pharmacological science |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1415617A CN1415617A (en) | 2003-05-07 |
| CN100486981C true CN100486981C (en) | 2009-05-13 |
Family
ID=4674110
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB011372737A Expired - Lifetime CN100486981C (en) | 2001-11-02 | 2001-11-02 | Compound possessing function for preventing and curing atherosclerosis and its application in biologic pharmacological science |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN100486981C (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2041088B1 (en) | 2006-06-28 | 2014-01-08 | Amgen Inc. | Glycine transporter-1 inhibitors |
| EP2268616A1 (en) * | 2008-03-21 | 2011-01-05 | Chlorion Pharma, Inc. | Substituted pyrrolidine and piperidine compounds, derivatives thereof, and methods for treating pain |
| CN101717416B (en) * | 2008-10-09 | 2014-03-12 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院毒物药物研究所 | Derivative of alpha-amino phosphonic acid containing saccharide groups, preparation method and medical application thereof |
| CN102731574B (en) * | 2011-03-30 | 2016-03-02 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院毒物药物研究所 | Thienopyridines α-amido benzyl phosphonic acid ester, Preparation Method And The Use |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3925245A (en) * | 1971-06-26 | 1975-12-09 | Ciba Geigy Corp | Corrosion inhibiting composition containing an aminoalkyl-phosphonic acid and an inorganic nitrite |
| US3954761A (en) * | 1968-10-17 | 1976-05-04 | Petrolite Corporation | Piperazine phosphonic acids |
-
2001
- 2001-11-02 CN CNB011372737A patent/CN100486981C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3954761A (en) * | 1968-10-17 | 1976-05-04 | Petrolite Corporation | Piperazine phosphonic acids |
| US3925245A (en) * | 1971-06-26 | 1975-12-09 | Ciba Geigy Corp | Corrosion inhibiting composition containing an aminoalkyl-phosphonic acid and an inorganic nitrite |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1415617A (en) | 2003-05-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU2293733C2 (en) | Novel 1,2,4-triazole compounds, methods for their preparing and medicaments containing thereof | |
| JP2009504722A (en) | Production and use of tetrahydropyrrolo [3,2-C] pyridin-4-one derivatives for the treatment of obesity, psychiatric disorders and neurological disorders | |
| EP3348548A1 (en) | Nitric oxide-releasing prodrug molecule | |
| CN102731574B (en) | Thienopyridines α-amido benzyl phosphonic acid ester, Preparation Method And The Use | |
| JP2020528924A (en) | 1,3-Disubstituted ketene compounds and their use | |
| WO2015134701A1 (en) | Dihydropyridinone mgat2 inhibitors for use in the treatment of metabolic disorders | |
| PT862562E (en) | BENZOXAZEPINE COMPOUNDS ITS PRODUCTION AND USE AS AGENTS FOR REDUCING LIPID LEVELS | |
| AU2005217174A1 (en) | Hydrazide type compounds and the use thereof in pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases | |
| JP2002500663A (en) | Novel orally active iron (III) chelators | |
| EP2496230B1 (en) | Ire-1 alpha inhibitors | |
| EP0266989B1 (en) | Dihydropyridine anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory agents | |
| JP4832897B2 (en) | Ester derivatives and their pharmaceutical uses | |
| CN111170884B (en) | Salicylamide compound, preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN100486981C (en) | Compound possessing function for preventing and curing atherosclerosis and its application in biologic pharmacological science | |
| CN113248427B (en) | Sulfonyl nicotinic acid derivative, amido nicotinic acid derivative, preparation method and application thereof | |
| JPH02229168A (en) | Pyrazolone derivative | |
| CN114805263B (en) | 3- (hydroxybenzyl) phthalide compound, preparation method and application thereof | |
| KR19990044478A (en) | 2-acylaminobenzamide derivatives and preventive and therapeutic agents for diseases caused by vascular endothelial hyperplasia | |
| US4994465A (en) | Antihyperlipidemic and antiatherosclerotic trisubstituted urea compounds | |
| JPS62155253A (en) | Guanidinobenzoic acid ester derivative | |
| CN109748914B (en) | Pyridopyrimidine compound and application thereof | |
| CN100500679C (en) | Compound for adjusting functional activity of vascular endothelial cell, its preparation method as well as usage | |
| CN100486982C (en) | Compound possessing function for preventing and curing thrombus disease, its pharmacy composition and usage in medication | |
| JP2009051731A (en) | New ascochlorin derivative compound and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same | |
| JP2015519334A5 (en) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term |
Granted publication date: 20090513 |
|
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term |