Chemistry:Iofetamine (123I)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | <10% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
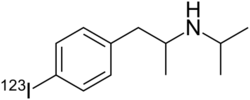
| Formula | C12H18123IN |
| Molar mass | 299.278 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Iofetamine (iodine-123, 123I), brand names Perfusamine, SPECTamine), or N-isopropyl-(123I)-p-iodoamphetamine (IMP), is a lipid-soluble amine and radiopharmaceutical drug used in cerebral blood perfusion imaging with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).[1][2][3] Labeled with the radioactive isotope iodine-123, it is approved for use in the United States as a diagnostic aid in determining the localization of and in the evaluation of non-lacunar stroke and complex partial seizures, as well as in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.[1][2]
An analogue of amphetamine, iofetamine has shown to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine as well as induce the release of these neurotransmitters and of dopamine with similar potencies to other amphetamines like d-amphetamine and p-chloroamphetamine.[4][5] In addition, on account of its high lipophilicity, iofetamine rapidly penetrates the blood-brain-barrier.[6] Accordingly, though not known to have been reported in the medical literature, iofetamine likely possesses psychostimulant and possibly entactogenic effects.[citation needed] However, based on structure-activity relationships, it may also be highly neurotoxic to serotonergic and dopaminergic neurons similarly to most other para-halogenated amphetamines.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis US. 2000. p. 562. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA562. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Iofetamine hydrochloride I 123: a new radiopharmaceutical for cerebral perfusion imaging". DICP: The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 23 (1): 19–24. January 1989. doi:10.1177/106002808902300103. PMID 2655294.
- ↑ "Brain imaging with emission computed tomography and radiolabeled amines". Investigative Radiology 17 (3): 206–15. 1982. doi:10.1097/00004424-198201730-00002. PMID 6811496.
- ↑ "N-isopropyl-[123I p-iodoamphetamine: single-pass brain uptake and washout; binding to brain synaptosomes; and localization in dog and monkey brain"]. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 21 (10): 947–52. October 1980. PMID 6775056. https://jnm.snmjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=6775056.
- ↑ "Serotonin uptake in cerebral cortex cultures: imipramine-like inhibition by N-isopropyl-p-iodoamphetamine". Experimental Neurology 103 (3): 297–9. March 1989. doi:10.1016/0014-4886(89)90055-1. PMID 2920796.
- ↑ "Development of I-123-labeled amines for brain studies: localization of I-123 iodophenylalkyl amines in rat brain". Journal of Nuclear Medicine 21 (10): 940–6. October 1980. PMID 7420195. https://jnm.snmjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=7420195.
 |

