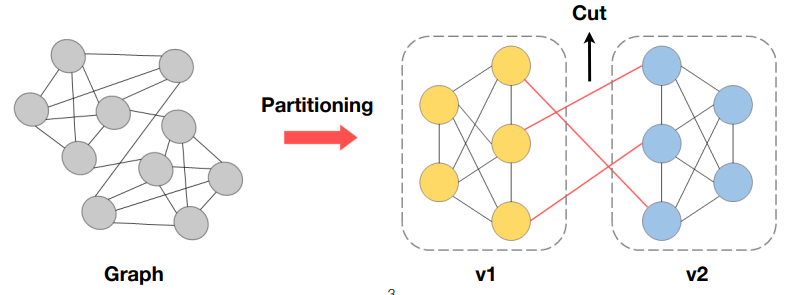
Graph partioning is a one of the NP-complete combinatorial optimization problems. We can find many papers applying genetic algorithm to the graph partiioning problem. In here, I decided to apply the method from the journal paper "Genetic Algorithm and Graph Partitioning" written by Thang Nguyen Bui and Byung Ro Moon.
Why Graph Partitioning is important?
Break down a large scale graph problem into smaller subproblems to be solved independently and in parallel
→ faster processing
Many real-world applications (ex. parallel processing, VLSI design)
- Google maps, where the partitioning algorithm is used to efficiently compute routes.
(Paper link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/508322)
To given an undirected graph G = (V, E) where V is the set of n nodes and E is the set of edges between the nodes, it divides the graph into two disjoint subsets of nodes v1 and v2 so that the number of edges between the nodes in the different subsets is minimized, and the sizes of the subsets are equal.
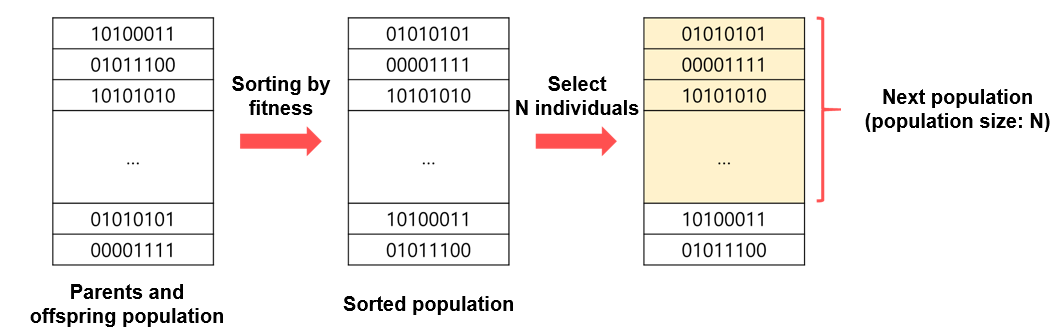
There are 5 parameters in the program.
POP_SIZE
- Initial population size
- Type : INT
- Range : [1, INF)
NUM_NODES
- The number of nodes in the graph which will be generated randomly.
- It should be an even number.
- Type : INT
- Range : [2, INF)
CONNECT_PROB
- The probability to connect two nodes with edge
- Type : FLOAT
- Range : [0., 1.)
MUT_PROB
- The probability to execute mutation
- Type : FLOAT
- Range : [0., 1.)
STOPPING_COUNT
- Stopping criteria
- If there is no improvement within STOPPING_COUNT times, the program will be terminated.
- Type : INT
- Range : (1, INF)
K_IND
- How many individuals are selected for the tournament
- Type : INT
- Range : [1, NUM_NODES)
- If there's no improvement within 10 times, the program will be terminated.
- How many times you accept it without the improvement can be adjusted with the parameter STOPPING_COUNT.
- Fitness of each individual will be calculated by the equation below.
The cut is the set of edges between the partitions.
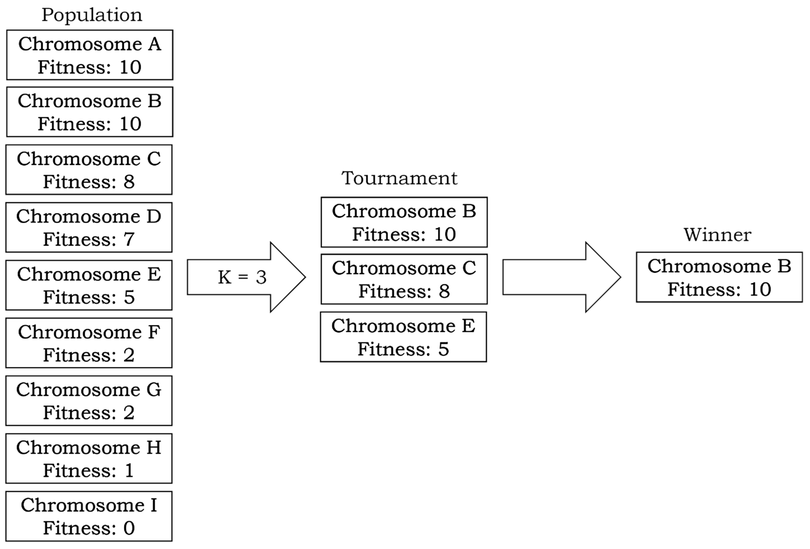
Tournament selection
- Select k random individuals from the population and pick the best out of them
- random number k can be adjusted with the parameter K_IND
(© https://medium.com/pragmatic-programmers/implementing-common-selection-strategies-37c6f99795a6)
I replaced single point crossover to multi-point crossover.
However, a single point crossover is still available.
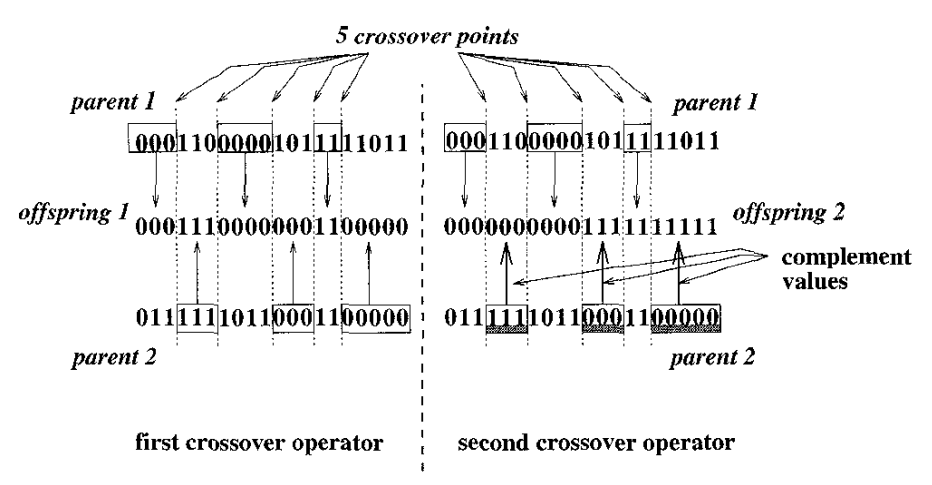
Multi-point crossover
- From the tournament selection, two chromosomes are selected as parents.
- 5 cut points for crossover are selected randomly
- Offspring 1 and 2 will be generated in different way (described in below image).
- If the partitions of new offspring don't have the same size, the offspring will be discarded
Single point crossover
From the tournament selection, two chromosomes are selected as parents.The crossover point is selected randomly.If the partitions of new offspring don't have the same size, the offspring will be discarded.
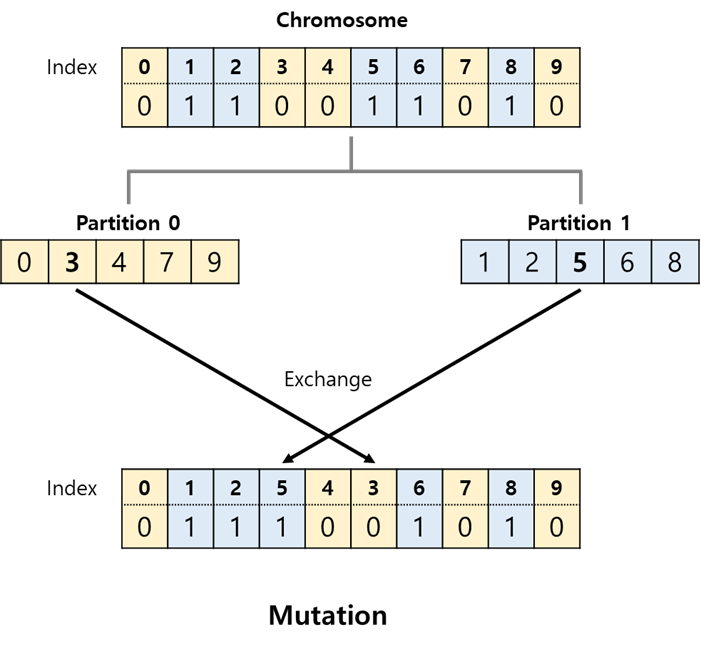
- Replace one node in a graph with a different, compatible type.
- The node randomly chosen from partition 0 will be exchanged with the node randomly chosen from partition 1.
cd src python3 main.pynetworkx numpyInstallation
pip3 install networkx pip3 install numpyParameters are defined as global variables in main.py.
POP_SIZE = 300 NUM_NODES = 100 CONNECT_PROB = 0.1 MUT_PROB = 0.3 STOPPING_COUNT = 10 K_IND = int(POP_SIZE * 0.1)You can adjust the parameters by modifying the values of them.
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
yoooooola/GraphPartitioning-GA
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
About
Assignment for Advanced Software Analysis, KNU (2021)