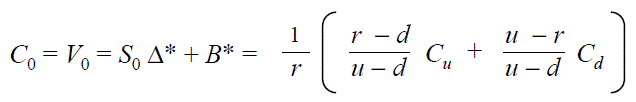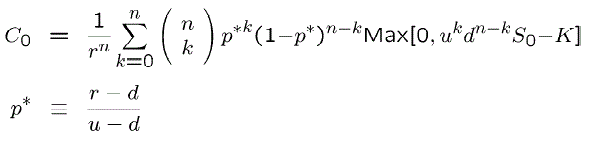- Vanilla: Bottom-UP DP + 2D numpy Array
- Time complexity: N^2
- Space complexity: N^2
- Knock-out: Bottom-UP DP + 1D numpy Array
- Time complexity: N^2
- Space complexity: N
- Knock-in:
- Vanilla 2D numpy Array + DFS with memo
- Time complexity: N^2
- Space complexity: N^2
- (TODO) Bottom-up DP to calculate (1) activated node(i,j)'s vanilla price Or (2) if not activated, do as usual
- Time complexity: K x N^2
- Space complexity: N
- Vanilla 2D numpy Array + DFS with memo
- N cannot be too large (i.e N=500 is used in test cases)
- losses of precision vs Speed
- float vs decimal
- Error Propagation vs iterative algorithm
# Initialise parameters
S0 = 100 # initial stock price
K = 110 # strike price
T = 0.5 # time to maturity in years
r = np.log(1+0.06) # annual risk-free rate
sigma = np.log(1+0.3) # Annualised stock price volatility
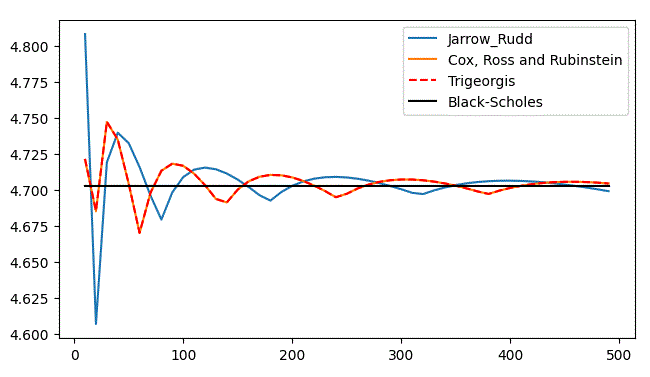
periods = range(10, 500, 10) ============================= test session starts =============================
collecting ... collected 1 item
test_options.py::MyTestCase::test_knockin_knockout_parity
============================== 1 passed in 1.77s ==============================
Process finished with exit code 0
PASSED [100%]
--------------------Input Parameter-----------------------------------------------------------
risk_free_rate= 0.009950330853168092 vol= 0.26236426446749106 N= 500 spot= 100.0 K= 95.0 T= 1.0 H= 105.0 shares= 1
--------------------Computation---------------------------------------------------------------
Vanilla Call PV at t=0: 13.371077462005541
Up-And-In Call PV at t=0: 13.318153535622839
Up-And-out Call PV at t=0: 0.05292392638270593
--------------------Equality for Knock-out + Knock-in = Vanilla --------------------------
knock_out_pv+knock_in_pv = 13.371077462005545 , vanilla_pv = 13.371077462005541 BS_Model= 13.370147046851775
--------------------End ------------------------------------------------------------------
============================= test session starts =============================
collecting ... collected 1 item
test_options.py::MyTestCase::test_knockout_fast_slow_version
============================= 1 passed in 28.12s ==============================
Process finished with exit code 0
PASSED [100%]
--------------------Input Parameter-----------------------------------------------------------
risk_free_rate= 0.009950330853168092 vol= 0.26236426446749106 spot= 100.0 K= 95.0 T= 1.0 H= 105.0 shares= 1
--------------------Logger---------------------------------------------------------------
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = False , model = CRR , N = 3', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 0.0000 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = True , model = CRR , N = 3', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 0.0000 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = False , model = CRR , N = 50', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 0.0000 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = True , model = CRR , N = 50', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 0.0040 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = False , model = CRR , N = 100', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 0.0080 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = True , model = CRR , N = 100', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 0.0040 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = False , model = CRR , N = 1000', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 1.0186 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = True , model = CRR , N = 1000', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 0.0559 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = False , model = CRR , N = 5000', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 25.1035 sec
'Up-And-out Call, fast_version = True , model = CRR , N = 5000', func:'price' args:[(), {'initSpot': 100.0, 'noShares': 1}] took: 0.9749 sec-
Parameters (used in code)
- T = Tenor(Years)
- n = #no of periods (e.g days)
- i = period i (n...0) //0 is 0th(start of day), i is ith(end of day), n is nth(end of day)
- j = node j at period i (0...i)
- r = continuously compounded interest rate log(1+x)
- df = e^-h*r #discount factor for 1 period
- k = strike
- b = barrier
- move = movement (up/down)
- opt = option type (call/put)
- sigma = std of continuously compounded stock return (annualized)
- h = T/n
- p = risk neutral prob. for up move
- u = e^sqrt(h)*sigma #up move
- d = 1/u #down move
- s0 = initial stock price
-
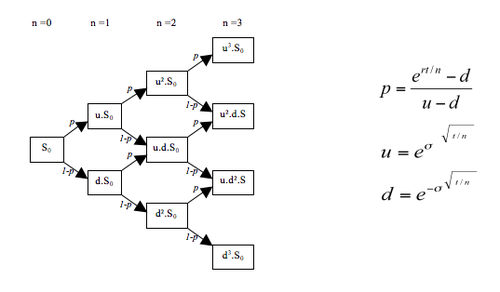
Binomial Tree
- Overlapped(u * d = 1) nodes
- At i = 3(4th day), 4 leaf nodes.
- total number of up and down movement = n-1
- At i = 3(4th day), max no. of up = 3 or max no. of down = 3
- Overlapped(u * d = 1) nodes
-
Recursion Relations for PV
PV(i,j) = df * [ p*PV(i+1, j+1) + (1-p)*PV(i+1,j) ]
-
Stock Price at jth node and ith period
s(i,j) = s0 * u^j * d^i-j
-
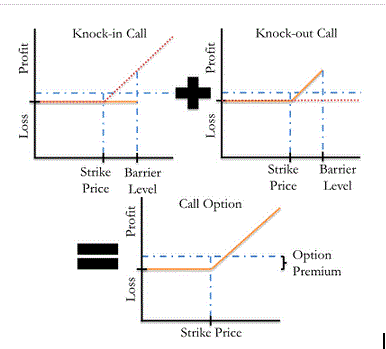
Existence of options at ith period
If inout=knock-out
If (move=up and s(i,j)>=H) or (move=down and s(i,j)<=H)
Then PV(i,j) = 0 # terminated
If inout=knock-in
If (move=up and s(i,j)>=H) or (move=down and s(i,j)<=H)
Then PV(i,j) = vanilla(i,j) # becomes vanilla options at (i,j)
-
Base case: Payoff at n-1th period (European)
If opt=call ,
Then PV(n, j) = max{0, s(n,j)-K}
If opt=put ,
Then PV(n, j) = max{0, K - s(n,j)}
Use of Numpy vectorization (the absence of any explicit looping, indexing, etc., in the code - these things are taking place, of course, just “behind the scenes” in optimized, pre-compiled C code)
-
Stock Price at jth node and ith period: 1D Row Vector*scalar
S = s0 * u**np.arange(0,i+1,1) * d**np.arange(i,-1,-1)
-
Recursion Relations for PV: Integer indexing + in-place and augmented assignments
PV[:i+1] = df * (p*PV[1:i+2] + (1-p)*PV[0:i+1] ) #update the view (instead of a new copy)
PV = PV[:-1] #shrink
-
Base Case (https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.maximum.html)
- np.maximum(x1, x2)
- Compare two arrays and returns a new array containing the element-wise maxima.
- Parameters: x1, x2 (array_like)
- The arrays holding the elements to be compared.
- If x1.shape != x2.shape, they must be broadcastable to a common shape (which becomes the shape of the output).
- The arrays holding the elements to be compared.
- np.maximum(x1, x2)
If opt=call ,
Then PV = np.maximum(0, S - K)
If opt=put ,
Then PV = np.maximum(0, K - S)
-
Existence of options at ith period: Boolean Indexing with S > (scaler) output 1D dimensional result + in-place and augmented assignments
PV[move=="up" & (S>=H)] = 0 # terminated for knock-out call options
- https://blog.slcg.com/2013/01/barrier-options.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binomial_options_pricing_model
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black%E2%80%93Scholes_model
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Array_programming
- https://docs.python.org/3/library/functools.html#functools.wraps
- https://vollib.org/
- https://pythonspeed.com/articles/vectorization-python-alternatives/
- https://towardsdatascience.com/dont-assume-numpy-vectorize-is-faster-dd7e455dba2