- kustomize (tested with
v4.4.1) - kubectl (tested with
v1.21.1) - kubectl must be authenticated and the current context should be set to the cluster that you will be updating
This repo contains a set of base kubernetes that you'll adapt using kustomize.
Create an overlay for your cluster. Choose a cluster name and then create a new overlay directory.
CLUSTER_NAME=replacethis
mkdir -p resources/k8s/overlays/${CLUSTER_NAME}
Create a file named resources/k8s/overlays/${CLUSTER_NAME}/endpoint.env.
The file will start out like this.
apiKey=<replace this>
url=<replace this>The apiKey and url should be filled in with your workspace's values. Find these in the atomist app and replace them in the file.
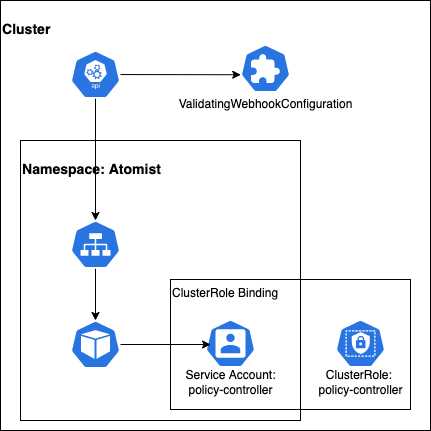
The communication between the api-server and the admission controller will be over HTTPS. This will be configured by running 3 kubernetes jobs in the cluster.
- policy-controller-cert-create job - this job will create SSL certs and store them in a secret named
policy-controller-admission-certin the atomist namespace - policy-controller-cert-path job - this will patch the admission controller webhook with the ca cert (so that the api-server will trust the new policy-controller)
- keystore-create job - this will read the SSL certs created by the policy-controller-cert-create job and create a keystore for the policy-controller HTTP server. The keystore is also stored in a secret named
keystorein the atomist namespace.
You can do steps 1 and 3 now.
# creates roles and service account for running jobs
kustomize build resources/k8s/certs | kubectl apply -f -
kubectl apply -f resources/k8s/jobs/create.yaml
kubectl apply -f resources/k8s/jobs/keystore_secret.yaml
This procedure will create a service account, a cluster role binding, two secrets, a service, and a deployment. All of these will be created in a new namespaced called atomist.
Use the same overlay that you created above (resources/k8s/overlays/${CLUSTER_NAME}). Copy in a template kustomization.yaml file.
cp resources/templates/default_controller.yaml resources/k8s/overlays/${CLUSTER_NAME}/kustomization.yaml
This kustomization file will permit you to change the CLUSTER_NAME environment variable.
In the initial copy of the file, the value will be "default", but it should be changed to the name of your cluster. This change is made to the final line in your new kustomization file.
resources:
- ../../controller
secretGenerator:
- name: endpoint
behavior: merge
envs:
- endpoint.env
patchesJson6902:
- target:
group: apps
version: v1
kind: Deployment
name: policy-controller
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0/env/2/value
value: "default"Deploy the admission controller into the the current kubernetes context using the command shown below.
kustomize build resources/k8s/overlays/sandbox | kubectl apply -f -At this point, the admission controller will be running but the cluster will not be routing any admission control requests to it. Create a configuration to start sending admission control requests to the controller using the following script.
# skip the kube-system namespace
k label namespace kube-system policy-controller.atomist.com/webhook=ignore
# validating webhook configuration
kubectl apply -f resources/k8s/admission/admission.yaml
# finally, patch the admission webhook with the ca certificate generated earlier
kubectl apply -f resources/k8s/jobs/patch.yaml