This project has been retired.
The original README is below.
(Code-name) Halite is a Salt GUI.
For best results, it is recommended to use Halite with the develop branch of Salt.
Halite is, however, known to work with Salt version greater than Hydrogen.
To install the develop branch of Salt:
$ git clone -b develop https://github.com/saltstack/salt.git
$ cd salt && python setup.py install
$ salt-master --version
$ salt-master -l debugThis version of Halite is designed to work out of the box with SaltStack when
the PyPi package version of Halite is installed. The PyPi (PIP) version of Halite
is a minified version tailored for this purpose. (https://pypi.python.org/pypi/halite)
Halite makes use of the Bottle (WSGI) web framework. Servers that are tested and
known to work with Halite are paste, cherrypy and gevent.
To pip install Halite.
$ pip install -U haliteThis purpose of the repository is to enable development of custom versions of the UI that could be deployed with different servers, different configurations, etc. and also for development of future features for the Salt packaged version.
Halite can poll for highstate consistency. This is similar to executing
salt \* state.highstate test=True and checking for the results.
Polling is turned OFF by default.
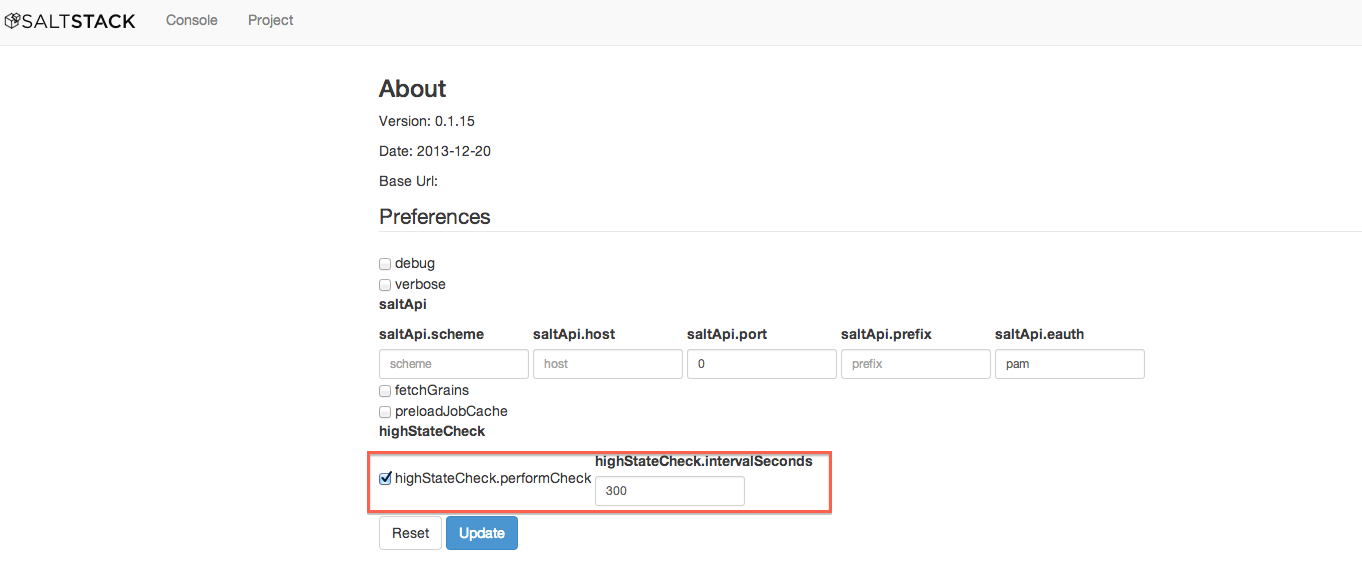
To switch polling ON, navigate to the Preferences tab and check
highStateCheck.performCheck. The poll timer can be adjusted using
highStateCheck.intervalSeconds and is set to 300 seconds (5 minutes) by
default. Once these settings are updated, click Update and reload the page.
These options are depicted in the screenshot below.
Highstate consistency check results can be seen on the minion view. Minions that have inconsistent state have a flag next to them as shown in the screenshot.
The Highstate subtab for each minion displays the state items that lack
consistency. All of the inconsistent items will be displayed here for easy
visualization. The screenshot below shows a message that might appear
when highstate consistency is disturbed.
The cog icon that appears in the Monitor section can be clicked to perform
highstate consistency check. The on demand check only works in the
scenario where polling is off. In the case where polling is switched on (as
discussed above) the cog icon will appear to be spinning (and does not respond
to clicks).
This section explains installation of the development version of Halite. If you are interested in installing Halite as an end user, please follow the tutorial instead.
- Setup permissions for users who will use Halite
For example in master config:
external_auth:
pam:
myusername:
- .*
- '@runner'
- '@wheel'Halite uses the runner manage.present to get the status of minions so runner
permissions are required. Currently Halite allows but does not require any
wheel modules.
- Clone the Halite repository:
git clone https://github.com/saltstack/halite- Run halite/halite/server_bottle.py (use with -h option to get parameters)
The simplest approach is to run the server with it dynamically generating the main web app load page (main.html) in coffescript mode, where the coffeescript is transpiled to javascript on the fly. In each case the appropriate server package must be installed.
$ ./server_bottle.py -d -C -l debug -s cherrypy
$ ./server_bottle.py -d -C -l debug -s paste
$ ./server_bottle.py -d -C -l debug -s gevent- Navigate HTML5 compliant browser to https://localhost:8080/app
- Login
The default eauth method is 'pam'. To change, go to the Preferences page.
The navbar has a login form. Enter the eauth username and password to login to salt.
Once logged in, the navbar will display the username highlighted in blue and a logout button.
To logout click on the Logout button.
Click on the SaltStack logo to go to the preferences page
On this page, one can change the eauth method to something other than 'pam' such as 'ldap'.
Check fetchGrains if you want grains data to be loaded when Halite loads.
Checking preloadJobCache will fetch all previously completed, cached jobs.
Once all changes are made, click Update and refresh the browser page.
To navigate to the console, view click on the Console tab.
This view has two sections. The Command section and the Monitor section.
The Command section is collapsed by default. Clicking on the downward chevron will
expand the Command section.
The top section of the Console view has controls for entering basic salt commands. The target field will target minions with the command selected. There is ping button with the bullhorn icon and the action menu has some preselected common commands.
Click on the downward chevron button to expand the Command form with additional
fields for entering any salt module function. To enter "runner" functions, prepend
"runner." to the function name. For example, "runner.manage.status". To enter wheel
functions, prepend "wheel." to the wheel function name. For example, "wheel.config.values".
For commands that require arguments, enter them in the arguments fields. The number of argument
fields equals the number of arguments accepted by the function.
Click on the Execute button or press the Return key to execute the command.
You can choose the Target Format which will be used by the Target field to target minions.
There is a ping button with the bullhorn icon and the Macro menu has some preselected commands for "speed dial".
There is also a history feature which appears as a book icon on the top right corner of the Command panel.
Checking Live Doc Search will show the documentation related to the command being
entered in the Function field. Un-check it to conserve screen real estate.
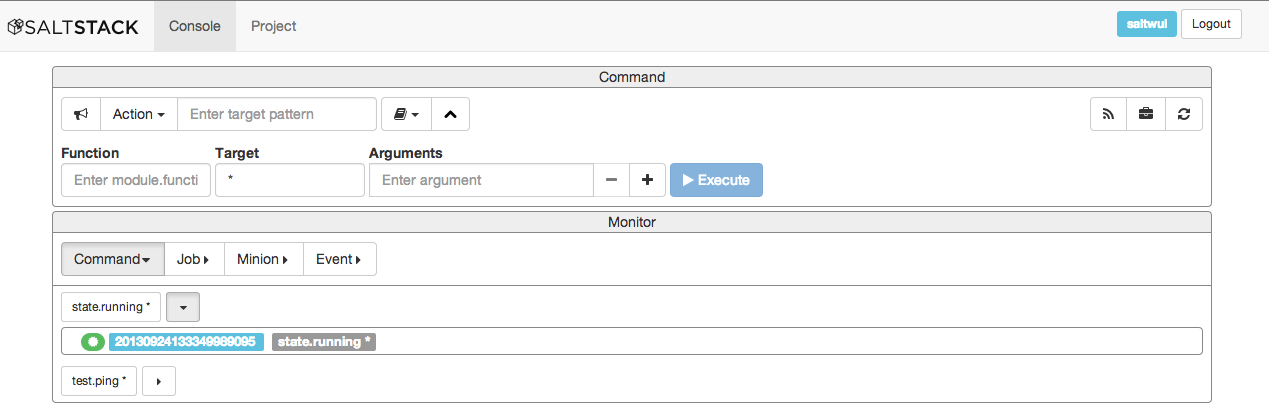
The bottom section of the console view has monitor view buttons. Each button will show panels with the associated information.
- Command Monitor
Shows panels, one per command that has been executed by this user on this console. Clicking on the dropdown button will show the associated job ids that have been run with this command and the completion status via an icon. Red is fail, green is success. Clicking on the button on the panel will rerun the command.
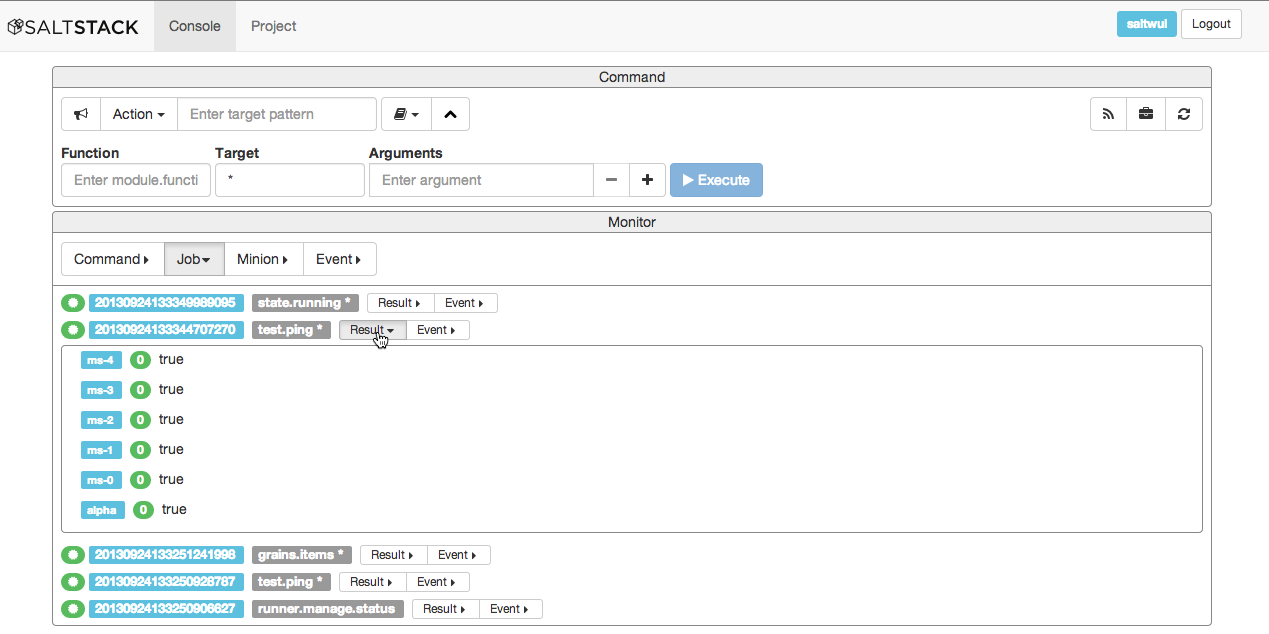
- Job Monitor
Shows panels, one per job that has been run by any minion associated with this
master. Clicking on the associated dropdown button with expand to show Result and Event data.
Selecting the Result button will show the returner and return data
for each minion targeted by the job.
Selecting the Event button will show the events associated with the job.
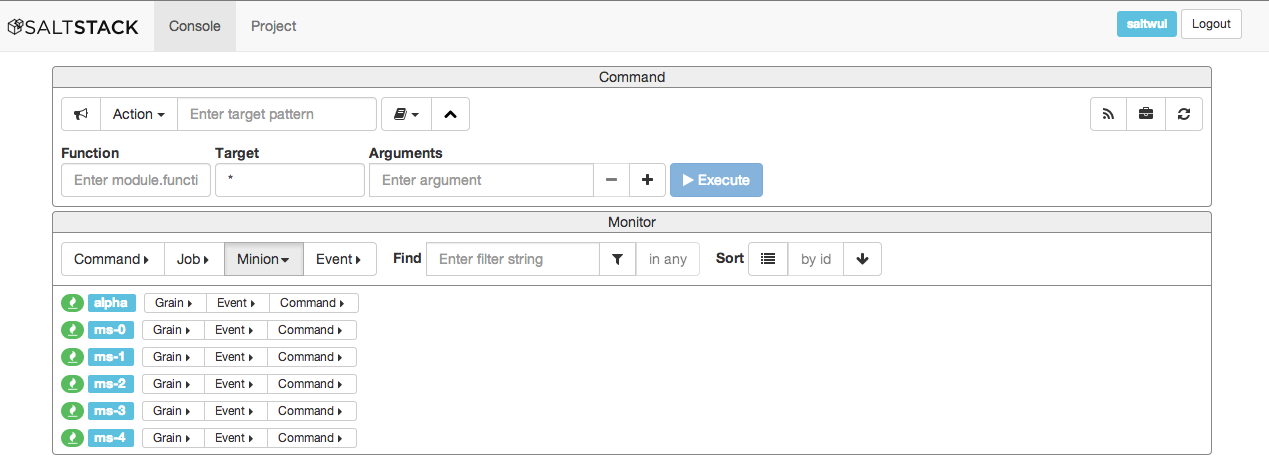
- Minion Monitor
Shows panels, one per minion that have keys associated with this master. The minion panels have icons to show the up/down status of the minion and the grains status. Selecting dropdown buttons will show grains data as well as minion (not job) generated events.
With the Grains button selected, one can see all the grains for the minion.
- Event Monitor
Shows panels, one per event associated with this Master.
More details coming. TBD
Support for ES5 and HTML5 is required. This means any modern browser or IE10+.
- The static media for this app is server-agnostic and may be served from any web server at a configurable URL prefix.
- This app uses the HTML5 history API.
Client side web application requirements:
- AngularJS framework (https://angularjs.org/)
- Bootstrap layout CSS (https://twbs.github.io/bootstrap/)
- AngularUI framework (https://angular-ui.github.io/)
- Underscore JS module (https://underscorejs.org/)
- Underscore string JS module (https://epeli.github.io/underscore.string/)
- Font Awesome Bootstrap Icon Fonts (https://fortawesome.github.io/Font-Awesome/)
- CoffeeScript Python/Ruby like javascript transpiler (https://coffeescript.org/)
- Karma Test Runner (https://karma-runner.github.io/0.8/index.html)
- Jasmine unit test framework (https://pivotal.github.io/jasmine/)
- Protractor E2E test framework for angular apps (https://github.com/angular/protractor)
Optional dependencies:
- Cherrypy web server (https://https://www.cherrypy.org/)
- Paste web server (https://pythonpaste.org/)
- Gevent web server(https://www.gevent.org/)
For nodejs testing:
- Express javascript web server
There are two approaches to deploying Halite.
1) Use it from Salt. The 0.17 release of salt will run halite automatically if the Halite package is installed. So for example, after installing SaltStack, one can install the Halite python package with
$ pip install -U haliteConfigure the master config for halite as follows.
halite:
level: 'debug'
server: 'cherrypy'
host: '0.0.0.0'
port: '8080'
cors: False
tls: True
certpath: '/etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt'
keypath: '/etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.key'
pempath: '/etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.pem'The "cherrypy" and "gevent" servers require the certpath and keypath files to run tls/ssl. The .crt file holds the public cert and the .key file holds the private key. Whereas the "paste" server requires a single .pem file that contains both the cert and key. This can be created simply by concatenating the .crt and .key files.
If you want to use a self signed cert, you can create one using the Salt tls module
salt '*' tls.create_ca_signed_cert test localhostWhen using self signed certs, browsers will need approval before accepting the cert. If the web application page has been cached with a non https version of the app, then the browser cache will have to be cleared before it will recognize and prompt to accept the self signed certificate.
You will also need to configure the eauth method to be used by users of the Web UI. See quickstart above for an example.
Install the appropriate HTTP WSGI server selected in the master config above. In this case it is "cherrypy". The other tested servers are "paste" and "gevent". The server must be multi-threaded, asynchronous, or multi-processing in order to support the Server Sent Event (SSE) streaming connection used by the Web UI.
Restart the SaltStack Master and navigate your HTML5 compliant browser to https://localhost:8080/app or however you have configured your master above.
If you have problems look for "Halite:" in the SaltStack master log output.
The Halite Github repository provides a skeleton framework for building your own custom deployment. One can run the default bottle.py framework from the command line:
$ ./server_bottle.py -g
$ ./server_bottle.py -s cherrypyor from a python application
import halite
halite.start()The full set of options is given by
$ ./server_bottle.py -h
usage: server_bottle.py [-h] [-l {info,debug,critical,warning,error}]
[-s SERVER] [-a HOST] [-p PORT] [-b BASE] [-x] [-t]
[-c CERT] [-k KEY] [-e PEM] [-g] [-f LOAD] [-C] [-d]
Runs localhost web application wsgi service on given host address and port.
Default host:port is 0.0.0.0:8080. (0.0.0.0 is any interface on localhost)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l {info,debug,critical,warning,error}, --level {info,debug,critical,warning,error}
Logging level.
-s SERVER, --server SERVER
Web application WSGI server type.
-a HOST, --host HOST Web application WSGI server ip host address.
-p PORT, --port PORT Web application WSGI server ip port.
-b BASE, --base BASE Base Url path prefix for client side web application.
-x, --cors Enable CORS Cross Origin Resource Sharing on server.
-t, --tls Use TLS/SSL (https).
-c CERT, --cert CERT File path to tls/ssl cacert certificate file.
-k KEY, --key KEY File path to tls/ssl private key file.
-e PEM, --pem PEM File path to tls/ssl pem file with both cert and key.
-g, --gen Generate web app load file. Default is 'app/main.html'
or if provided the file specified by -f option.
-f LOAD, --load LOAD Filepath to save generated web app load file upon -g
option.
-C, --coffee Upon -g option generate to load coffeescript.
-d, --devel Development mode.The HTTP server provides two functions.
1) Provide content delivery network for the base load of the web application static content such as html and javascript files.
2) Provide dynamic REST API interface to salt/client/api.py module that is used by the web application via AJAX and SSE connections. Because SSE and CORS (Cross Origin Resource Sharing) are not universally supported even among HTML5 compliant browsers, a single server has to serve both the static content and the rest API. An alternative approach would be to to use a web socket to stream the events, this would not require CORS, so it may be a future option for Halite.
To deploy with apache, modify server_bottle.startServer so it creates the app but
does not call bottle.run on it but returns it to MOD_WSGI.
See (https://bottlepy.org/docs/dev/deployment.html) for other details in using bottle.py
with Apache and Mod_wsgi.
Doing a custom deployment with other frameworks like Django, etc. would involve replicating the endpoints from server_bottle.
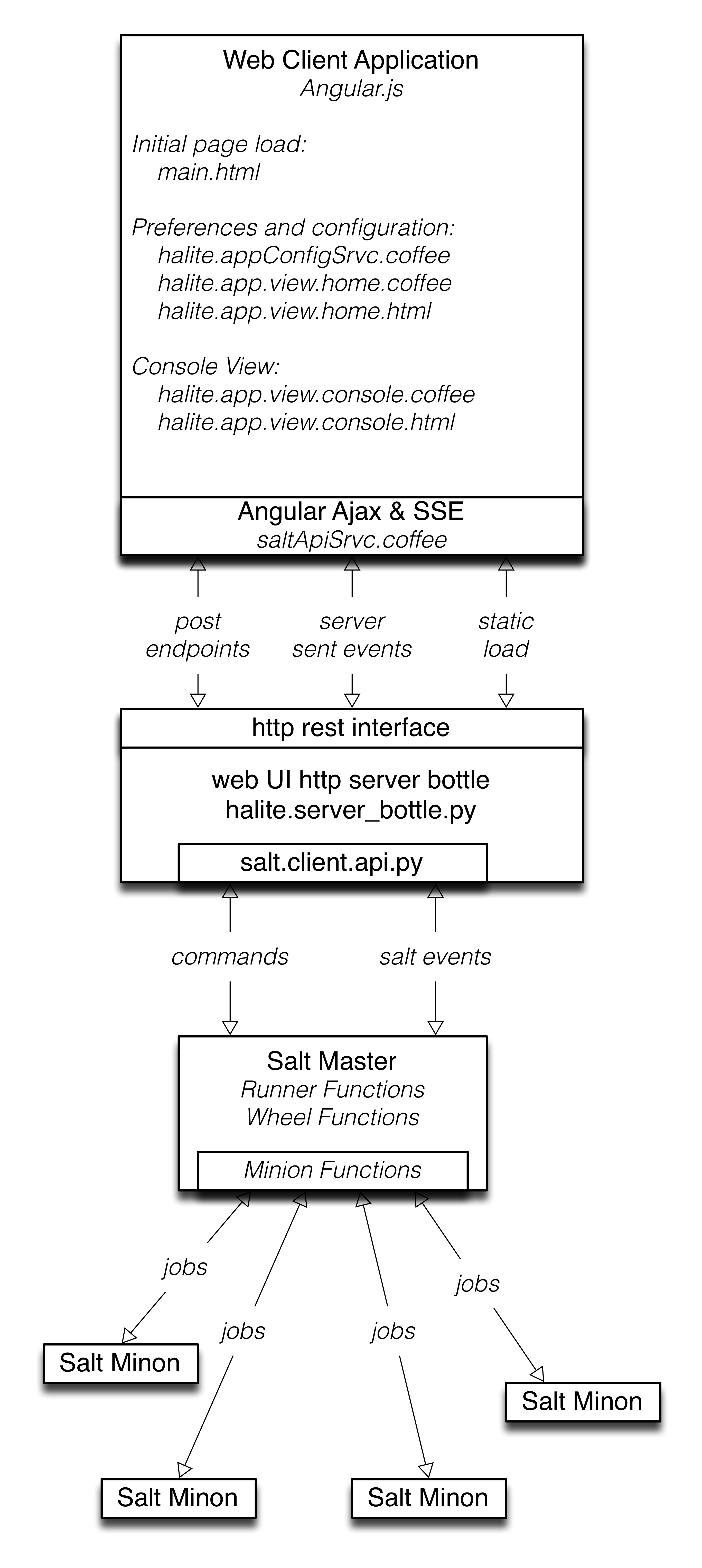
The following diagram illustrates how the various pieces to Halite interact.
To run the karma jasmine unit test runner
$ cd halite
$ karma start karma_unit.conf.jsTo run the protractor e2e test runner first start up a web server. More information
about using protractor can be found on their website.
Make sure that the end to end test is setup to login to Halite
In that file change the following
login =
username: 'your_halite_username'
password: 'your_halite_password'Now you can run the tests using the following commands.
Make sure you have the webdriver-manager started.
More info can be found on the Protractor
webpage.
$ cd halite
$ protractor protractor.conf.jsTo run the functional tests make sure you have the Python webtest
and nose modules installed.
Enter your credentials and the minion name in a new file called
halite/test/functional/config/override.conf
[login]
username = your_user_name
password = your_password
[minions]
apache = minion_connected_to_this_masterThe functional tests can be run via nose.
$ cd halite
$ nosetestsYou might have to build the distribution (for development)
$ cd halite
$ ./prep_dist.pySubtree can be fetched by running git subtree pull --prefix=halite/lattice lattice master --squash