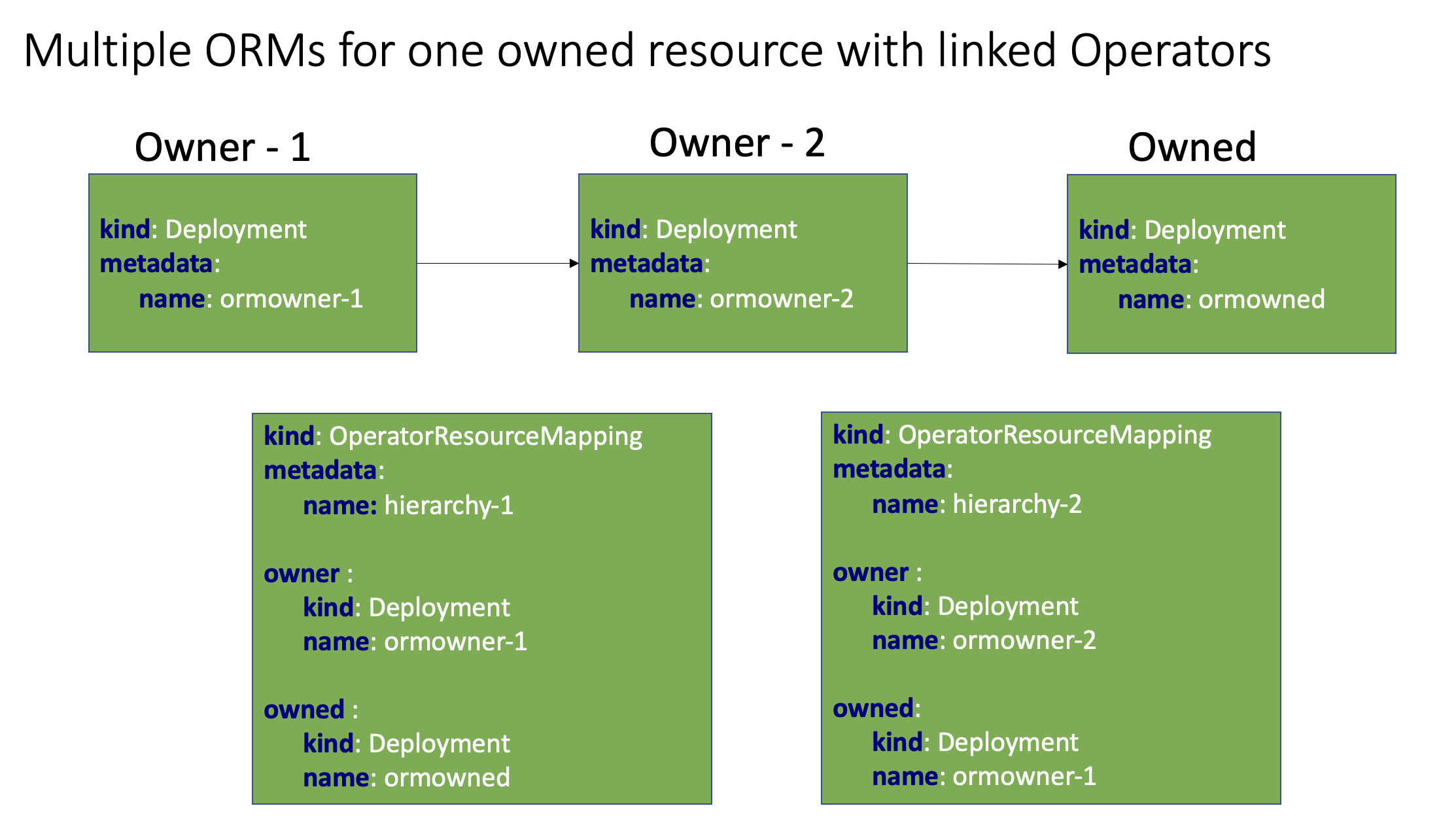
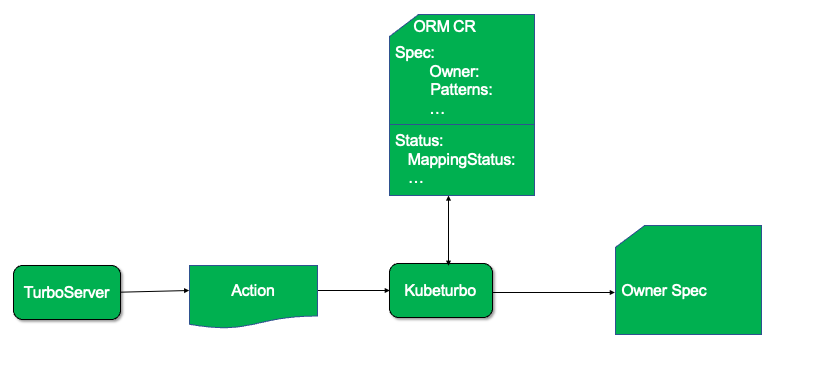
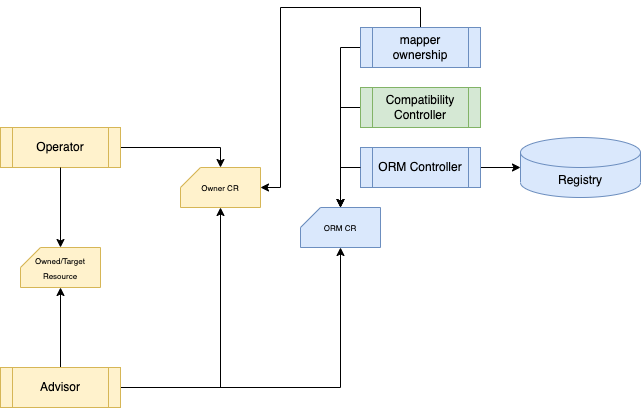
Previous ORM CRD and Samples are moved to archive, please find doc for compatibility here.
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
- Overview
- ORM Schema
- Use Cases
- QuickStart to Test Your ORM CR with Turbonomic/Kubeturbo
- QuickStart to Test Your ORM CR with ORM Controllers
- Next Step
Operator Resource Mapping (ORM) is designed to map identifying exactly how to update a Custom Resource so that assets like Kubeturbo can programmatically update workload specifications that are controlled by an Operator, for example to vertically scale containers by updating container specs or horizontally scale pods by managing the number of replicas.
In this setup, an Operator oversees the lifecycle of microservice-based applications using a declarative approach to maintain their intended state (e.g., Pod replicas, memory limits, etc.). However, any direct interventions by Turbo to alter the size of workload controllers such as StatefulSet, DaemonSet, Deployment, either vertically or horizontally, will be reverted by the Operator.
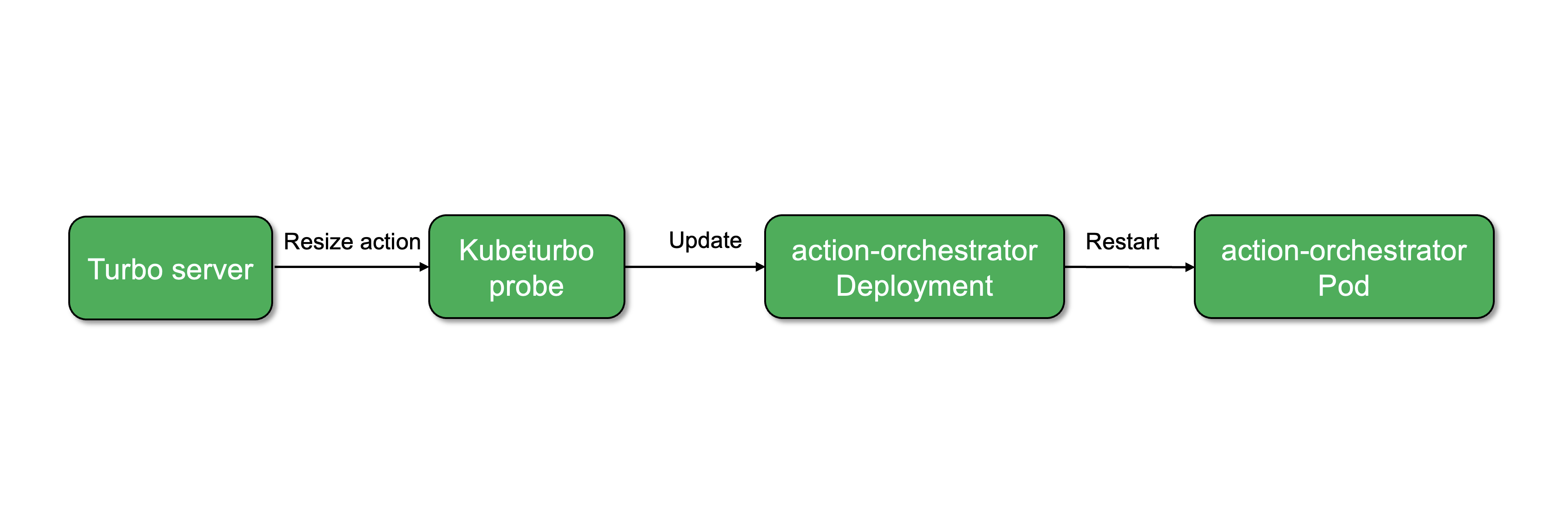
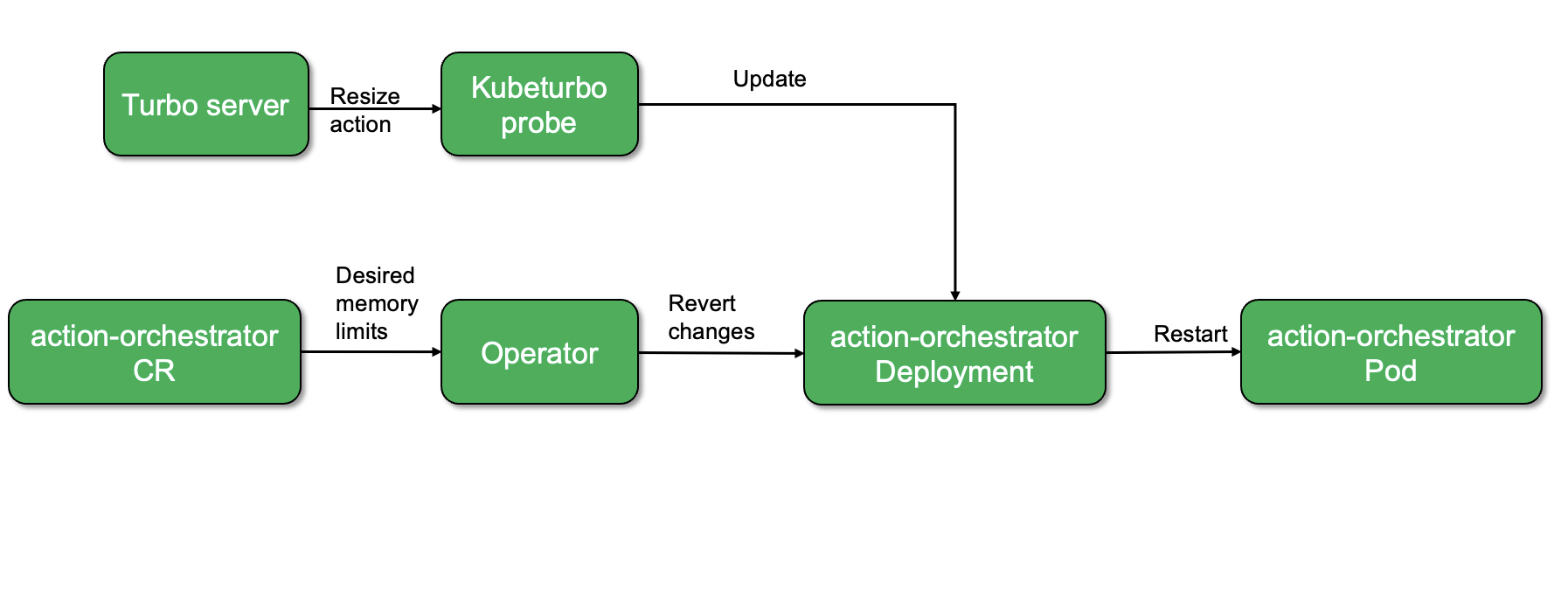
To better understand this, let's examine two different scenarios involving container resizing actions in Kubeturbo, with and without an Operator.
Here, updates made to the deployment will persist successfully.
In this scenario, the Operator will reverse any updates made to the Deployment, because the changes were not handled through the Operator's CR(Custom Resource).
The proposed solution involves updating workload specifications via the CR allowing the operator to roll out the changes. But in order for any component, such as the Kubeturbo probe, to make changes to the CR, there must be a guide or a map provided that directs how changes can be made.
ORM works at an operand basis. The user will define within the ORM which operand provides the desired status of which resources that can be managed. The user will provide information on the parameters that directs how other assets can programmatically make changes to the Custom Resource.
This repo provides new ORM resource scheme, legacy ORM CRD and examples are in archive folder. Controllers in this repo are
- helping users to compose and test ORMs with the operands and deployed resources only.
- generating ORM resource from legacy ORM resources for backward compatibility
Advisor: Tools providing recommendations to workloads (e.g. Turbonomic, HorizontalPodAutoscaler, VerticalPodAutoScaler). In this phase 1, Advisor can get the mapping from ORM resource and modify the owner for recommendation.
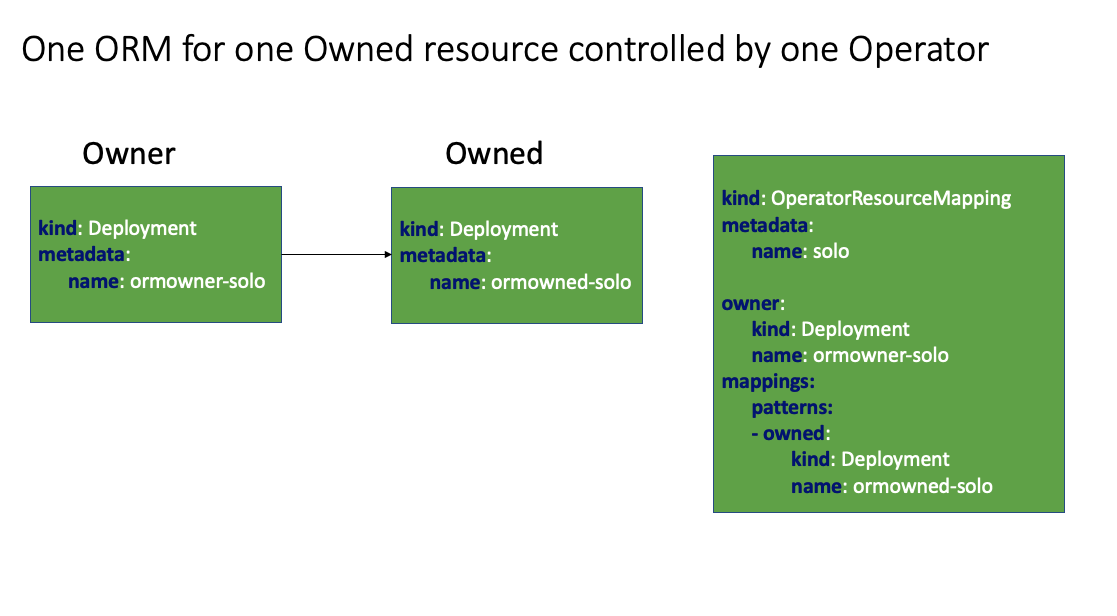
Owner: the operator resource who owns actual deployed resources. Changes in owner trigger operator to update deployed/owned resources
Owned resource: resources deployed by operator, answer to changes in operand/owner
Mapping: pair of paths in owner and owned resources
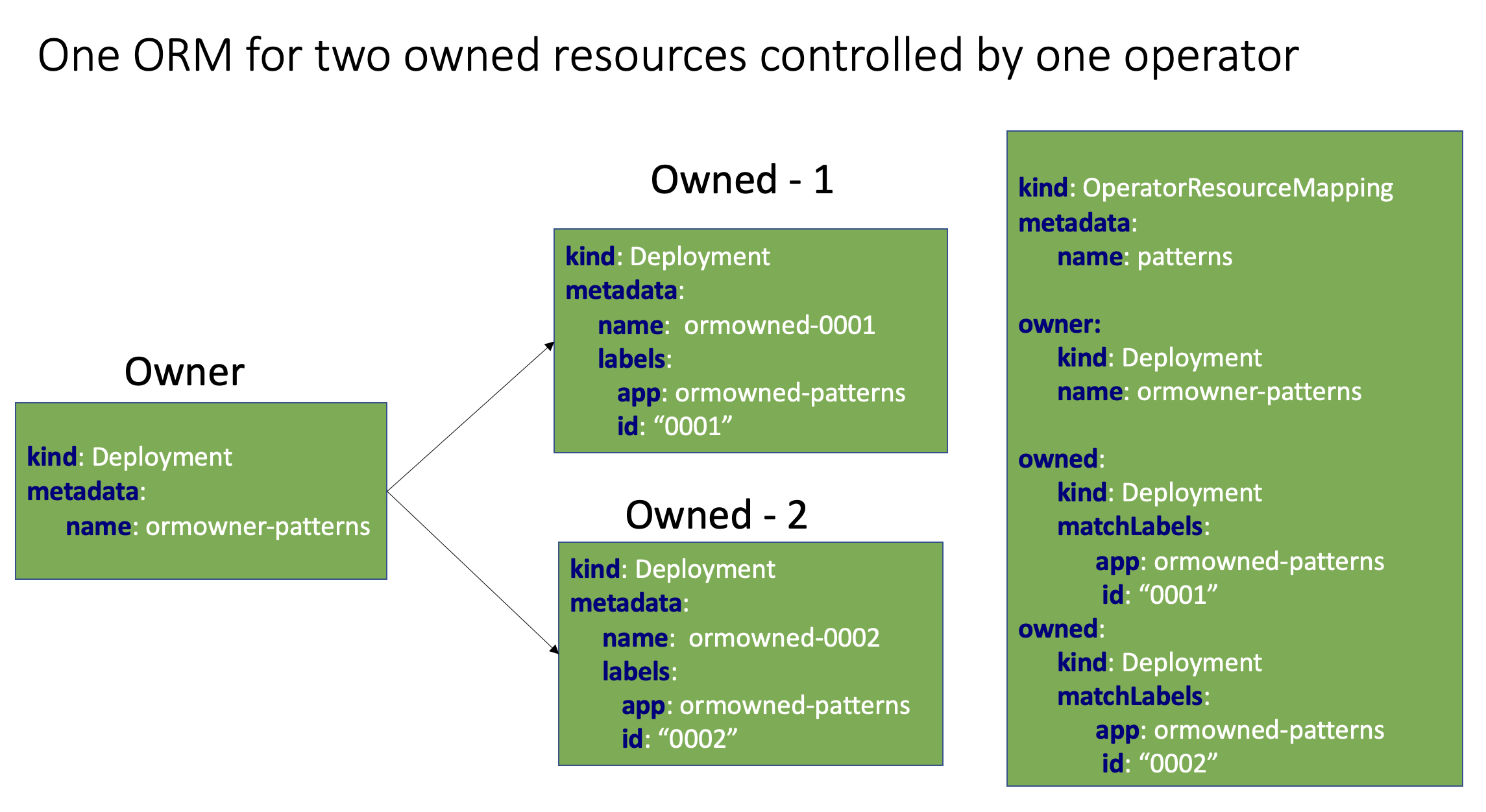
Pattern: pair of paths in owner and owned resource. Parameters can be defined in patters in order to generate multiple mapping from one pattern.
Selectors: predefined label selectors to be reused in patterns
Parameters: predefined list of strings for mapping generation
Predefined Parameters - all predefined parameters starts with "."
.owned.name: refer to the name of the owned resource. Together with label selector ofownedresource, a pattern can generate lots of mappings if the naming is right.
apiVersion: devops.turbonomic.io/v1alpha1 # version of the api that manifest is using
kind: OperatorResourceMapping # type of kubernetes resource
metadata:
name: orm # name of the resource
namespace: # namespace where this resource is located
...
spec:
mappings:
patterns:
- owned:
apiVersion: # api version for owned resource
kind: # type of owned resource
path: # The JSON path to the resource property to be mapped, targeting specific containers within an owned resource.
selector: # reference to the selector
ownerPath: #JSON path to the resource location in the owner object, where the values should be reflected
selectors: # Defines label selectors for identifying resources.
xyz: # A named selector.
matchLabels: # Label selectors used to identify resources
...
owner:
apiVersion: # The API version of the owner resource
kind: # The kind of the owner resource
name: # The name of the owner resource
status:
lastTransitionTime: # The timestamp of the last status change
owner:
apiVersion: # Details of owner resource specified in 'spec.owner'
kind:
name:
namespace:
ownerValues: # The values from the owner resource that correspond to the mappings.
- owned: # Details of the owned resource specified in 'spec.mappings.patterns.owned'
apiVersion:
kind:
name:
namespace:
path: # The JSON path to the resource property to be mapped, targeting specific containers within an owned resource.
ownerPath: #JSON path to the resource location in the owner object, where the values should be reflected
value:
resources: {}
state: # The status of the resource mapping indicates whether it is 'ok' or if there have been any errors with a reason during the discovery of ORM's and building the ORM mapping registry .Sample Operator resource mappings can be found here
Example for this use case can be found here
Example for this use case can be found here
Example for this use case can be found here
System architecture for ORM CR with Turbonomic/Kubeturbo is described in the figure below:
mkdir turbonomic
cd turbonomic
git clone https://github.ibm.com/turbonomic/orm.git
cd orm
- Create the ORM Customer Resource Definition (CRD) in the kubernetes cluster (where kubeturbo is also running):
kubectl apply -f config/crd/bases/devops.turbonomic.io_operatorresourcemappings.yamlThis CRD supports kubnernetes 1.16 and higher.
- Next deploy the ORM Custom Resource (CR) for your application in the namespace of that app. Sample CRs are located here. In our example, to allow for resizing of Turbonomic Server app services, we will deploy the Turbonomic XL ORM CR into the namespace where the Turbonomic Server is running:
kubectl -n turbonomic apply -f library/ibm/turbo_operator_resource_mapping_sample_cr.yaml- Rediscover Kubeturbo target from Turbonomic UI and NO need to restart the corresponding Kubeturbo pod in cluster. ORM CR will be successfully discovered when you see a log message from Kubeturbo like this:
I0118 22:34:08.013144 1 k8s_discovery_client.go:327] Discovered 1 v2 ORM Resources.
In order for Kubeturbo to access Operator managed CR's from CRD and map the resources using ORM, Kubeturbo should run with cluster-admin role. You can find more details about Kubeturbo Cluster roles here
System architecture is described in the figure below:
ORM Controller – watch ORM resource and update registry with mappings
Mapper Ownership – retrieve value from owner resource and update ORM status
Compatibility Controller - Generate new ORM from legacy ORM
ORM leverages operator sdk to create/build project, follow the standard operator sdk approach to run it locally or generate images to deploy to a target cluster with right RBAC settings.
mkdir turbonomic
cd turbonomic
git clone https://github.ibm.com/turbonomic/orm.git
cd orm
You're able to run the orm controllers if you have access to a kubernetes cluster. Please ensure the rbac of your current access is able to cover the resources you want map.
make install runYou terminal is occupied by the controller after it is started, you need to start another terminal to try examples
Feel free to try other approaches in Operator SDK such as OLM deployment, Direct deployment.
In order to show relationship between operator and the resource it manages we use Redis operator from OT_CONTAINER-KIT. We created redis standalone.
helm list -ANAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
redis ot-operators 1 2023-05-04 12:27:31.051399 -0400 EDT deployed redis-0.14.2 0.14.0
redis-operator ot-operators 1 2023-03-13 12:31:40.264923 -0400 EDT deployed redis-operator-0.14.3 0.14.0
kubectl get statefulset -n ot-operators -oyamlapiVersion: v1
items:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
annotations:
redis.opstreelabs.in: "true"
redis.opstreelabs.instance: redis-standalone
creationTimestamp: "2024-01-25T21:48:58Z"
generation: 1
labels:
app: redis-standalone
redis_setup_type: standalone
role: standalone
name: redis-standalone
namespace: ot-operators
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: redis.redis.opstreelabs.in/v1beta1
controller: true
kind: Redis
name: redis-standalone
uid: 6dd0759d-0c67-48e7-903b-bf74b9c8e4a1
resourceVersion: "41508623"
uid: 256b404c-1961-471e-9d1c-5085d44e2de2
spec:
podManagementPolicy: OrderedReady
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis-standalone
redis_setup_type: standalone
role: standalone
serviceName: redis-standalone-headless
template:
metadata:
annotations:
redis.opstreelabs.in: "true"
redis.opstreelabs.instance: redis-standalone
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: redis-standalone
redis_setup_type: standalone
role: standalone
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: REDIS_ADDR
value: redis:https://localhost:6379
- name: SERVER_MODE
value: standalone
- name: SETUP_MODE
value: standalone
image: quay.io/opstree/redis:v7.0.5
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- bash
- /usr/bin/healthcheck.sh
failureThreshold: 3
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
name: redis-standalone
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- bash
- /usr/bin/healthcheck.sh
failureThreshold: 3
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
requests:
cpu: 20m
memory: 24Mi
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext: {}
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
updateStrategy:
rollingUpdate:
partition: 0
type: RollingUpdate
status:
availableReplicas: 1
collisionCount: 0
currentReplicas: 1
currentRevision: redis-standalone-799b86b4b5
observedGeneration: 1
readyReplicas: 1
replicas: 1
updateRevision: redis-standalone-799b86b4b5
updatedReplicas: 1
kind: List
metadata:
resourceVersion: ""
kubectl get redis redis-standalone -n ot-operators -oyamlapiVersion: redis.redis.opstreelabs.in/v1beta1
kind: Redis
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
creationTimestamp: "2024-01-25T21:48:58Z"
finalizers:
- redisFinalizer
generation: 2
name: redis-standalone
namespace: ot-operators
resourceVersion: "41508397"
uid: 6dd0759d-0c67-48e7-903b-bf74b9c8e4a1
spec:
kubernetesConfig:
image: quay.io/opstree/redis:v7.0.5
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
requests:
cpu: 20m
memory: 24Mi
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
redisExporter:
image: quay.io/opstree/redis-exporter:v1.44.0
securityContext: {}
Apply the redis standalone orm from library and you can see the pattern defined in spec are located in the cluster. Details are showed in status.
kubectl get orm -n ot-operators redis-orm -o yamlapiVersion: devops.turbonomic.io/v1alpha1
kind: OperatorResourceMapping
metadata:
name: redis-orm
namespace: ot-operators
...
spec:
mappings:
patterns:
- owned:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
path: .spec.template.spec.containers[?(@.name=="redis")].resources
selector: my_redis_sts
ownerPath: .spec.kubernetesConfig.resources
selectors:
my_redis_sts:
matchLabels:
app: redis
owner:
apiVersion: redis.redis.opstreelabs.in/v1beta1
kind: Redis
name: redis
status:
lastTransitionTime: "2023-05-04T17:27:05Z"
owner:
apiVersion: redis.redis.opstreelabs.in/v1beta1
kind: Redis
name: redis
namespace: ot-operators
ownerValues:
- owned:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
name: redis
namespace: ot-operators
path: .spec.template.spec.containers[?(@.name=="redis")].resources
ownerPath: .spec.kubernetesConfig.resources
value:
resources: {}
state: ok