A blazingly fast JSON serializing & deserializing library, accelerated by JIT (just-in-time compiling) and SIMD (single-instruction-multiple-data).
- Go 1.15/1.16/1.17
- Linux/darwin OS
- Amd64 CPU with AVX instruction set
- Runtime object binding without code generation
- Complete APIs for JSON value manipulation
- Fast, fast, fast!
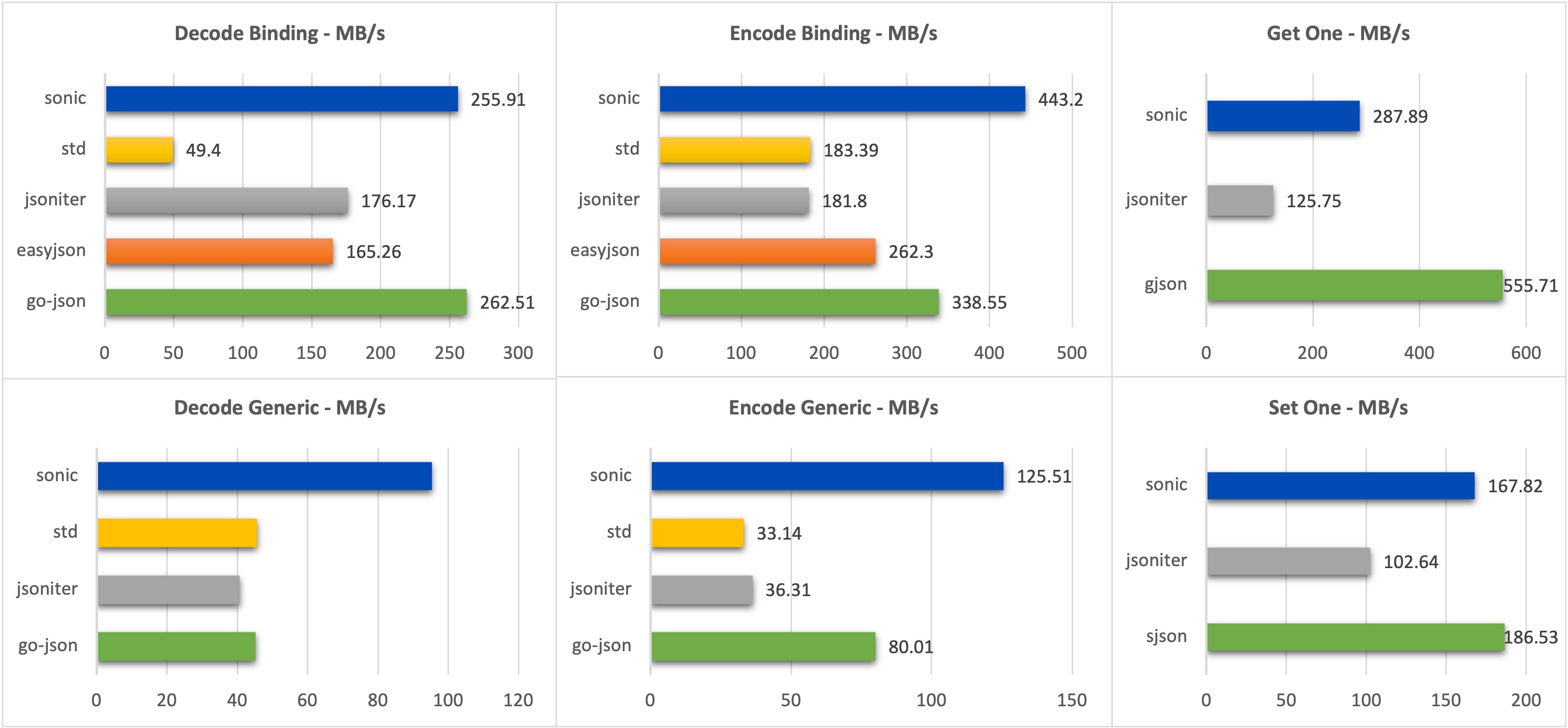
For all sizes of json and all scenarios of usage, Sonic performs best.
- Medium (13KB, 300+ key, 6 layers)
goversion: 1.17.1
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-9880H CPU @ 2.30GHz
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_Sonic-16 42688 ns/op 305.36 MB/s 15608 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 30043 ns/op 433.87 MB/s 14638 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 46461 ns/op 280.56 MB/s 13433 B/op 77 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_GoJson-16 73608 ns/op 177.09 MB/s 23219 B/op 16 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_StdLib-16 122622 ns/op 106.30 MB/s 49137 B/op 827 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_Sonic-16 8190 ns/op 1591.61 MB/s 16175 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 7365 ns/op 1769.85 MB/s 14367 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 23326 ns/op 558.81 MB/s 9487 B/op 2 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_GoJson-16 9412 ns/op 1384.93 MB/s 9480 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_StdLib-16 18510 ns/op 704.22 MB/s 9479 B/op 1 allocs/op
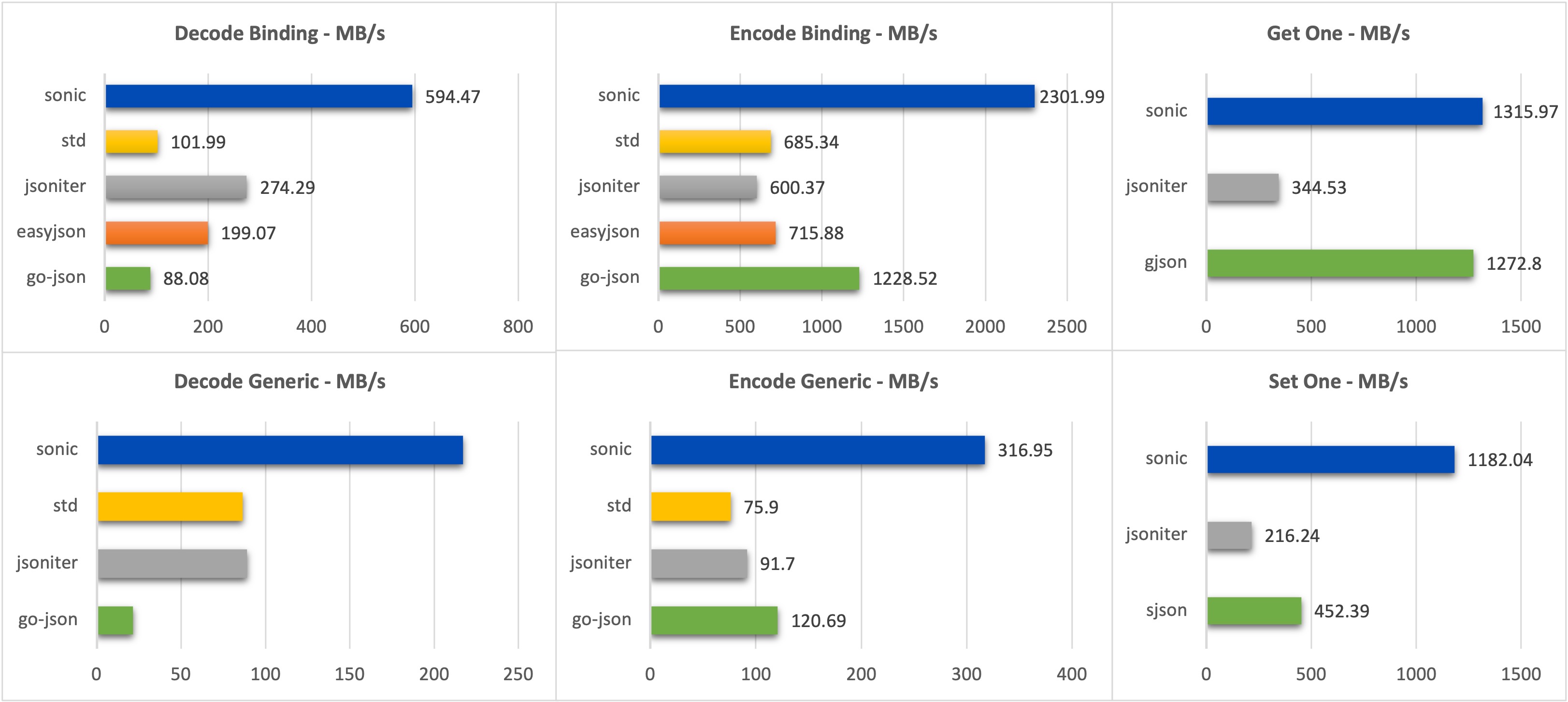
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic-16 7716 ns/op 1689.37 MB/s 12812 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 4791 ns/op 2720.47 MB/s 10884 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_JsonIter-16 10505 ns/op 1240.85 MB/s 13455 B/op 77 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_GoJson-16 24086 ns/op 541.19 MB/s 23379 B/op 17 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_StdLib-16 65697 ns/op 198.41 MB/s 49164 B/op 827 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic-16 2085 ns/op 6251.53 MB/s 12933 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 1612 ns/op 8087.31 MB/s 11177 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_JsonIter-16 6169 ns/op 2112.84 MB/s 9494 B/op 2 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_GoJson-16 3492 ns/op 3733.14 MB/s 9492 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_StdLib-16 5170 ns/op 2521.50 MB/s 9482 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_Sonic-16 71589 ns/op 182.08 MB/s 57531 B/op 723 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 57653 ns/op 226.10 MB/s 49743 B/op 313 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_StdLib-16 143584 ns/op 90.78 MB/s 50870 B/op 772 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 94775 ns/op 137.54 MB/s 55783 B/op 1068 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_GoJson-16 88647 ns/op 147.04 MB/s 66371 B/op 973 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_Sonic-16 32399 ns/op 402.33 MB/s 27814 B/op 137 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 28655 ns/op 454.89 MB/s 25127 B/op 34 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_StdLib-16 116617 ns/op 111.78 MB/s 7344 B/op 103 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 36206 ns/op 360.02 MB/s 14673 B/op 385 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_GoJson-16 29396 ns/op 443.43 MB/s 22042 B/op 49 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic-16 12243 ns/op 1064.68 MB/s 57135 B/op 723 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 10101 ns/op 1290.48 MB/s 49440 B/op 313 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_StdLib-16 57352 ns/op 227.28 MB/s 50877 B/op 772 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_JsonIter-16 58693 ns/op 222.09 MB/s 55814 B/op 1068 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_GoJson-16 45245 ns/op 288.10 MB/s 66430 B/op 974 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic-16 7035 ns/op 1852.89 MB/s 27731 B/op 137 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 6510 ns/op 2002.33 MB/s 24841 B/op 34 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_StdLib-16 33086 ns/op 393.97 MB/s 7344 B/op 103 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_JsonIter-16 17827 ns/op 731.18 MB/s 14680 B/op 385 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_GoJson-16 16813 ns/op 775.29 MB/s 22268 B/op 49 allocs/op
BenchmarkGetOne_Sonic-16 11328 ns/op 1149.64 MB/s 29 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkGetOne_Gjson-16 12970 ns/op 1004.07 MB/s 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkGetOne_Jsoniter-16 59928 ns/op 217.31 MB/s 27936 B/op 647 allocs/op
BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Sonic-16 1447 ns/op 9002.23 MB/s 114 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Gjson-16 1171 ns/op 11125.73 MB/s 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Jsoniter-16 15545 ns/op 837.75 MB/s 27940 B/op 647 allocs/op
BenchmarkSetOne_Sonic-16 16922 ns/op 769.57 MB/s 1936 B/op 17 allocs/op
BenchmarkSetOne_Sjson-16 42683 ns/op 305.11 MB/s 52181 B/op 9 allocs/op
BenchmarkSetOne_Jsoniter-16 91104 ns/op 142.95 MB/s 45861 B/op 964 allocs/op
BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Sonic-16 2065 ns/op 6305.03 MB/s 2383 B/op 17 allocs/op
BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Sjson-16 11526 ns/op 1129.87 MB/s 52175 B/op 9 allocs/op
BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Jsoniter-16 35044 ns/op 371.61 MB/s 45887 B/op 964 allocs/opSee bench.sh for benchmark codes.
See INTRODUCTION.md.
Default behaviors are mostly consistent with encoding/json, except HTML escaping form (see Escape HTML) and SortKeys feature (optional support see Sort Keys) that is NOT in conformity to RFC8259.
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
var data YourSchema
// Marshal
output, err := sonic.Marshal(&data)
// Unmarshal
err := sonic.Unmarshal(output, &data) import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
var input = `1`
var data interface{}
// default float64
dc := decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.Decode(&data) // data == float64(1)
// use json.Number
dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.UseNumber()
dc.Decode(&data) // data == json.Number("1")
// use int64
dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.UseInt64()
dc.Decode(&data) // data == int64(1)
root, err := sonic.GetFromString(input)
// Get json.Number
jn := root.Number()
jm := root.InterfaceUseNumber().(json.Number) // jn == jm
// Get float64
fn := root.Float64()
fm := root.Interface().(float64) // jn == jmOn account of the performance loss from sorting (roughly 10%), sonic doesn't enable this feature by default. If your component depends on it to work (like zstd), Use it like this:
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/encoder"
// Binding map only
m := map[string]interface{}{}
v, err := encoder.Encode(m, encoder.SortMapKeys)
// Or ast.Node.SortKeys() before marshal
var root := sonic.Get(JSON)
err := root.SortKeys()On account of the performance loss (roughly 15%), sonic doesn't enable this feature by default. You can use encoder.EscapeHTML option to open this feature (align with encoding/json.HTMLEscape).
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
v := map[string]string{"&&":{"<>"}}
ret, err := Encode(v, EscapeHTML) // ret == `{"\u0026\u0026":{"X":"\u003c\u003e"}}`Sonic encodes premitive objects (struct/map...) as compact-format JSON by default, except marshaling json.RawMessage or json.Marshaler: sonic ensures validating their output JSON but DONOT compacting them for performance concern. We provide option encoder.CompactMarshaler to add compacting process.
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
var data interface{}
err := sonic.Unmarshal("[[[}]]", &data)
if err != nil {
/*one line by default*/
println(e.Error())) // "Syntax error at index 3: invalid char\n\n\t[[[}]]\n\t...^..\n"
/*pretty print*/
if e, ok := err.(decoder.SyntaxError); ok {
/*Syntax error at index 3: invalid char
[[[}]]
...^..
*/
print(e.Description())
}
}Sonic/ast.Node is a completely self-contained AST for JSON. It implements serialization and deserialization both, and provides robust APIs for obtaining and modification of generic data.
Search partial JSON by given paths, which must be non-negative integer or string or nil
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
input := []byte(`{"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}`)
// no path, returns entire json
root, err := sonic.Get(input)
raw := root.Raw() // == string(input)
// multiple pathes
root, err := sonic.Get(input, "key1", 1, "key2")
sub := root.Get("key3").Index(2).Int64() // == 3Tip: since Index() uses offset to locate data, which is much faster than scanning like Get(), we suggest you use it as much as possible. And sonic also provides another API IndexOrGet() to underlying use offset as well as ensuring the key is matched.
Modify the json content by Set()/Unset()
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
// Set
exist, err := root.Set("key4", NewBool(true)) // exist == false
alias1 := root.Get("key4")
println(alias1.Valid()) // true
alias2 := root.Index(1)
println(alias1 == alias2) // true
// Unset
exist, err := root.UnsetByIndex(1) // exist == true
println(root.Get("key4").Check()) // "value not exist"To encode ast.Node as json, use MarshalJson() or json.Marshal() (MUST pass the node's pointer)
import (
"encoding/json"
"github.com/bytedance/sonic"
)
buf, err := root.MarshalJson()
println(string(buf)) // {"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}
exp, err := json.Marshal(&root) // WARN: use pointer
println(string(buf) == string(exp)) // true- validation:
Check(),Error(),Valid(),Exist() - searching:
Index(),Get(),IndexPair(),IndexOrGet(),GetByPath() - go-type casting:
Int64(),Float64(),String(),Number(),Bool(),Map[UseNumber|UseNode](),Array[UseNumber|UseNode](),Interface[UseNumber|UseNode]() - go-type packing:
NewRaw(),NewNumber(),NewNull(),NewBool(),NewString(),NewObject(),NewArray() - iteration:
Values(),Properties(),ForEach(),SortKeys() - modification:
Set(),SetByIndex(),Add()
Since Sonic uses golang-asm as a JIT assembler, which is NOT very suitable for runtime compiling, first-hit running of a huge schema may cause request-timeout or even process-OOM. For better stability, we advise to use Pretouch() for huge-schema or compact-memory application before Marshal()/Unmarshal().
import (
"reflect"
"github.com/bytedance/sonic"
"github.com/bytedance/sonic/option"
)
func init() {
var v HugeStruct
// For most large types (nesting depth <= 5)
err := sonic.Pretouch(reflect.TypeOf(v))
// If the type is too deep nesting (nesting depth > 5),
// you can set compile recursive depth in Pretouch for better stability in JIT.
err := sonic.Pretouch(reflect.TypeOf(v), option.WithCompileRecursiveDepth(depth))
}When decoding string values without any escaped characters, sonic refers them from origin JSON buffer instead of mallocing a new buffer to copy. This helps a lot for CPU performance, but may leave the whole JSON buffer in memory as long as the decoded objects are being used. In practice, we found the extra memory introduced by referring JSON buffer is usually 20% ~ 80% of decoded objects. Once a application holds these objects for a long time (for example, cache the decoded objects for reusing), its inuse memory on server may go up. We provide option decoder.CopyString() for users to choose not to refer the JSON buffer, which may cause the decline of CPU performance in some degree.
For alignment to encoding/json, we provide API to pass []byte as an argument, but the string-to-bytes copy is conducted at the same time considering safety, which may lose performance when origin JSON is huge. Therefore, you can use UnmarshalString() and GetFromString() to pass a string, as long as your origin data is a string or nocopy-cast is safe for your []byte. We also provides API MarshalString() for convenient nocopy-cast of encoded json []byte, which is safe since sonic's output bytes is always duplicated and unique.
To ensure data security, sonic.Encoder quotes and escapes string values from encoding.TextMarshaler interfaces by default, which may degrade performance much if most of your data is in form of them. We provide encoder.NoQuoteTextMarshaler to skip these operations, which means you MUST ensure their output string escaped and quoted in accordance with RFC8259.
In fully-parsed scenario, Unmarshal() performs better than Get()+Node.Interface(). But if you only have a part of schema for specific json, you can combine Get() and Unmarshal() together:
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
node, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson, "statuses", 3, "user")
var user User // your partial schema...
err = sonic.UnmarshalString(node.Raw(), &user)Even if you don't have any schema, use ast.Node as the container of generic values instead of map or interface:
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
root, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson)
user := root.GetByPath("statuses", 3, "user") // === root.Get("status").Index(3).Get("user")
err = user.Check()
// err = user.LoadAll() // only call this when you want to use 'user' concurrently...
go someFunc(user)Why? Because ast.Node stores its children using array:
Array's performance is much better thanMapwhen Inserting (Deserialize) and Scanning (Serialize) data;- Hashing (
map[x]) is not as efficient as Indexing (array[x]), whichast.Nodecan conduct on both array and object; - Using
Interface()/Map()means Sonic must parse all the underlying values, whileast.Nodecan parse them on demand.
CAUTION: ast.Node DOESN'T ensure concurrent security directly, due to its lazy-load design. However, your can call Node.Load()/Node.LoadAll() to achieve that, which may bring performance reduction while it still works faster than converting to map or interface{}