We designed this framework to be as simple as possible, while still providing you with the tools you need to build powerful apps. It is compatible with Symfony and Laravel.
We are working to expand the support of different LLMs. Right now, we are supporting OpenAI and Ollama that can be used to run LLM locally such as Llama 2.
If you want to use other LLMs, you can use genossGPT as a proxy.
We want to thank few amazing projects that we use here or inspired us:
- the learnings from using LangChain and LLamaIndex
- the excellent work from the OpenAI PHP SDK.
We can find great external resource on LLPhant (ping us to add yours):
- 🇫🇷 Construire un RAG en PHP avec la doc de Symfony, LLPhant et OpenAI : Tutoriel Complet
- 🇫🇷 Retour d'expérience sur la création d'un agent autonome
Requires PHP 8.1+
First, install LLPhant via the Composer package manager:
composer require theodo-group/llphantYou may also want to check the requirements for OpenAI PHP SDK as it is the main client.
There are plenty use cases for Generative AI and new ones are creating every day. Let's see the most common ones. Based on a survey from the MLOPS community and this survey from Mckinsey the most common use case of AI are the following:
- Create semantic search that can find relevant information in a lot of data. Example: Slite
- Create chatbots / augmented FAQ that use semantic search and text summarization to answer customer questions. Example: Quivr is using such similar technology.
- Create personalized content for your customers (product page, emails, messages,...). Example Carrefour.
- Create a text summarizer that can summarize a long text into a short one.
Not widely spread yet but with increasing adoption:
- Create personal shopper for augmented ecommerce experience. Example: Madeline
- Create AI agent to perform various task autonomously. Example: AutoGpt
- Create coding tool that can help you write or revie code. Example: Code Review GPT
If you want to discover more usage from the community, you can see here a list of GenAI Meetups. You can also see other use cases on Qdrant's website.
You can use OpenAI or Ollama as LLM.
The most simple to allow the call to OpenAI is to set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable.
export OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-XXXXXXYou can also create an OpenAIConfig object and pass it to the constructor of the OpenAIChat or OpenAIEmbeddings.
$config = new OpenAIConfig();
$config->apiKey = 'fakeapikey';
$chat = new OpenAIChat($config);If you want to use Ollama, you can just specify the model to use using the OllamaConfig object and pass it to the OllamaChat.
$config = new OllamaConfig();
$config->model = 'llama2';
$chat = new OllamaChat($config);💡 This class can be used to generate content, to create a chatbot or to create a text summarizer.
You can use the OpenAIChat or OllamaChat to generate text or to create a chat.
We can use it to simply generate text from a prompt. This will ask directly an answer from the LLM.
$response = $chat->generateText('what is one + one ?'); // will return something like "Two"If you want to display in your frontend a stream of text like in ChatGPT you can use the following method.
return $chat->generateStreamOfText('can you write me a poem of 10 lines about life ?');You can add instruction so the LLM will behave in a specific manner.
$chat->setSystemMessage('Whatever we ask you, you MUST answer "ok"');
$response = $chat->generateText('what is one + one ?'); // will return "ok"This feature is amazing and is available only for OpenAI.
OpenAI has refined its model to determine whether tools should be invoked. To utilize this, simply send a description of the available tools to OpenAI, either as a single prompt or within a broader conversation.
In the response, the model will provide the called tools names along with the parameter values, if it deems the one or more tools should be called.
One potential application is to ascertain if a user has additional queries during a support interaction. Even more impressively, it can automate actions based on user inquiries.
We made it as simple as possible to use this feature.
Let's see an example of how to use it. Imagine you have a class that send emails.
class MailerExample
{
/**
* This function send an email
*/
public function sendMail(string $subject, string $body, string $email): void
{
echo 'The email has been sent to '.$email.' with the subject '.$subject.' and the body '.$body.'.';
}
}You can create a FunctionInfo object that will describe your method to OpenAI. Then you can add it to the OpenAIChat object. If the response from OpenAI contains a tools' name and parameters, LLPhant will call the tool.
This PHP script will most likely call the sendMail method that we pass to OpenAI.
$chat = new OpenAIChat();
// This helper will automatically gather information to describe the tools
$tool = FunctionBuilder::buildFunctionInfo(new MailerExample(), 'sendMail');
$chat->addTool($tool);
$chat->setSystemMessage('You are an AI that deliver information using the email system.
When you have enough information to answer the question of the user you send a mail');
$chat->generateText('Who is Marie Curie in one line? My email is [email protected]');If you want to have more control about the description of your function, you can build it manually:
$chat = new OpenAIChat();
$subject = new Parameter('subject', 'string', 'the subject of the mail');
$body = new Parameter('body', 'string', 'the body of the mail');
$email = new Parameter('email', 'string', 'the email address');
$tool = new FunctionInfo(
'sendMail',
new MailerExample(),
'send a mail',
[$subject, $body, $email]
);
$chat->addTool($tool);
$chat->setSystemMessage('You are an AI that deliver information using the email system. When you have enough information to answer the question of the user you send a mail');
$chat->generateText('Who is Marie Curie in one line? My email is [email protected]');You can safely use the following types in the Parameter object: string, int, float, bool. The array type is supported but still experimental.
💡 Embeddings are used to compare two texts and see how similar they are. This is the base of semantic search.
An embedding is a vector representation of a text that captures the meaning of the text. It is a float array of 1536 elements for OpenAI for the small model.
To manipulate embeddings we use the Document class that contains the text and some metadata useful for the vector store.
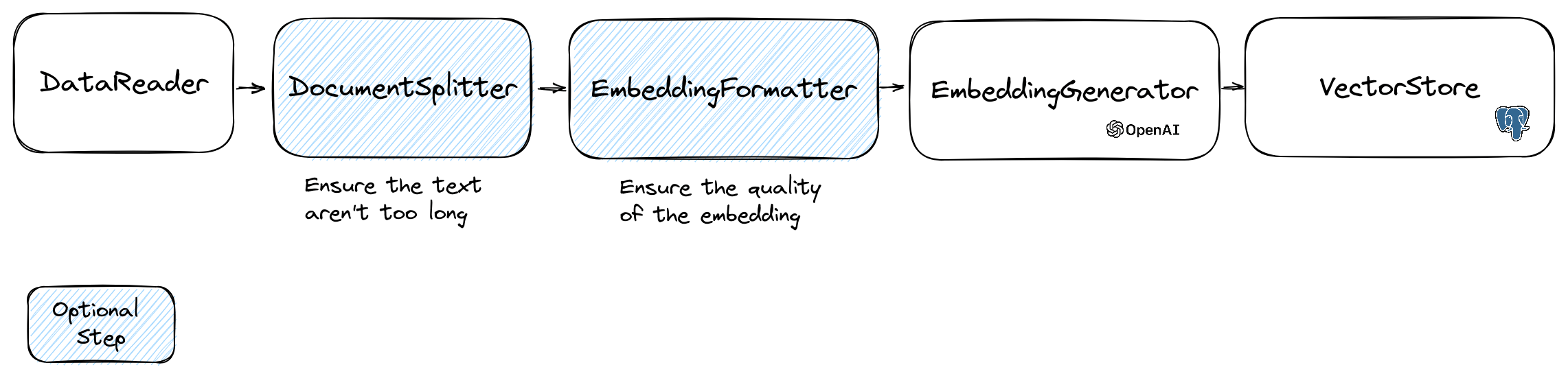
The creation of an embedding follow the following flow:
The first part of the flow is to read data from a source. This can be a database, a csv file, a json file, a text file, a website, a pdf, a word document, an excel file, ... The only requirement is that you can read the data and that you can extract the text from it.
For now we only support text files, pdf and docx but we plan to support other data type in the future.
You can use the FileDataReader class to read a file. It takes a path to a file or a directory as parameter.
The second parameter is the class name of the entity that will be used to store the embedding.
The class needs to extend the Document class
and even the DoctrineEmbeddingEntityBase class (that extends the Document class) if you want to use the Doctrine vector store.
$filePath = __DIR__.'/PlacesTextFiles';
$reader = new FileDataReader($filePath, PlaceEntity::class);
$documents = $reader->getDocuments();To create your own data reader you need to create a class that implements the DataReader interface.
The embeddings models have a limit of string size that they can process.
To avoid this problem we split the document into smaller chunks.
The DocumentSplitter class is used to split the document into smaller chunks.
$splittedDocuments = DocumentSplitter::splitDocuments($documents, 800);The EmbeddingFormatter is an optional step to format each chunk of text into a format with the most context.
Adding a header and links to other documents can help the LLM to understand the context of the text.
$formattedDocuments = EmbeddingFormatter::formatEmbeddings($splittedDocuments);This is the step where we generate the embedding for each chunk of text by calling the LLM.
30 january 2024 : Adding Mistral embedding API
You need to have a Mistral account to use this API. More information on the Mistral website.
And you need to set up the MISTRAL_API_KEY environment variable or pass it to the constructor of the MistralEmbeddingGenerator class.
25 january 2024 : New embedding models and API updates OpenAI has 2 new models that can be used to generate embeddings. More information on the OpenAI Blog.
| Status | Model | Embedding size |
|---|---|---|
| Default | text-embedding-ada-002 | 1536 |
| New | text-embedding-3-small | 1536 |
| New | text-embedding-3-large | 3072 |
You can embed the documents using the following code:
$embeddingGenerator = new OpenAI3SmallEmbeddingGenerator();
$embededDocuments = $embeddingGenerator->embedDocuments($formattedDocuments);You can also create a embedding from a text using the following code:
$embeddingGenerator = new OpenAI3SmallEmbeddingGenerator();
$embedding = $embeddingGenerator->embedText('I love food');
//You can then use the embedding to perform a similarity searchOnce you have embeddings you need to store them in a vector store. The vector store is a database that can store vectors and perform a similarity search. There are currently 4 vectorStore class:
- MemoryVectorStore stores the embeddings in the memory
- FileSystemVectorStore stores the embeddings in a file
- DoctrineVectorStore stores the embeddings in a postgresql database. (require doctrine/orm)
- QdrantVectorStore stores the embeddings in a Qdrant vectorStore. (require hkulekci/qdrant)
- RedisVectorStore stores the embeddings in a Redis database. (require predis/predis)
- ElasticsearchVectorStore stores the embeddings in a Elasticsearch database. (require elasticsearch/elasticsearch)
- MilvusVectorStore stores the embeddings in a Milvus database.
Example of usage with the DoctrineVectorStore class to store the embeddings in a database:
$vectorStore = new DoctrineVectorStore($entityManager, PlaceEntity::class);
$vectorStore->addDocuments($embededDocuments);Once you have done that you can perform a similarity search over your data. You need to pass the embedding of the text you want to search and the number of results you want to get.
$embedding = $embeddingGenerator->embedText('France the country');
/** @var PlaceEntity[] $result */
$result = $vectorStore->similaritySearch($embedding, 2);To get full example you can have a look at Doctrine integration tests files.
One simple solution for web developers is to use a postgresql database as a vectorStore with the pgvector extension. You can find all the information on the pgvector extension on its github repository.
We suggest you 3 simple solutions to get a postgresql database with the extension enabled:
- use docker with the docker-compose-pgvector.yml file
- use Supabase
- use Neon
In any case you will need to activate the extension:
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector;Then you can create a table and store vectors. This sql query will create the table corresponding to PlaceEntity in the test folder.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_place (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
content TEXT,
type TEXT,
sourcetype TEXT,
sourcename TEXT,
embedding VECTOR
);OpenAI3LargeEmbeddingGenerator class, you will need to set the length to 3072 in the entity.
Or if you use the MistralEmbeddingGenerator class, you will need to set the length to 1024 in the entity.
The PlaceEntity
#[Entity]
#[Table(name: 'test_place')]
class PlaceEntity extends DoctrineEmbeddingEntityBase
{
#[ORM\Column(type: Types::STRING, nullable: true)]
public ?string $type;
#[ORM\Column(type: VectorType::VECTOR, length: 3072)]
public ?array $embedding;
}Prerequisites :
- Redis server running (see Redis quickstart)
- Predis composer package installed (see Predis)
Then create a new Redis Client with your server credentials, and pass it to the RedisVectorStore constructor :
use Predis\Client;
$redisClient = new Client([
'scheme' => 'tcp',
'host' => 'localhost',
'port' => 6379,
]);
$vectorStore = new RedisVectorStore($redisClient, 'llphant_custom_index'); // The default index is llphantYou can now use the RedisVectorStore as any other VectorStore.
Prerequisites :
- Elasticsearch server running ( see Elasticsearch quickstart)
- Elasticsearch PHP client installed ( see Elasticsearch PHP client)
Then create a new Elasticsearch Client with your server credentials, and pass it to the ElasticsearchVectorStore constructor :
use Elastic\Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder;
$client = (new ClientBuilder())::create()
->setHosts(['https://localhost:9200'])
->build();
$vectorStore = new ElasticsearchVectorStore($client, 'llphant_custom_index'); // The default index is llphantYou can now use the ElasticsearchVectorStore as any other VectorStore.
Prerequisites : Milvus server running (see Milvus docs)
Then create a new Milvus client (LLPhant\Embeddings\VectorStores\Milvus\MiluvsClient) with your server credentials,
and pass it to the MilvusVectorStore constructor :
$client = new MilvusClient('localhost', '19530', 'root', 'milvus');
$vectorStore = new MilvusVectorStore($client);You can now use the MilvusVectorStore as any other VectorStore.
A popular use case of LLM is to create a chatbot that can answer questions over your private data.
You can build one using LLPhant using the QuestionAnswering class.
It leverages the vector store to perform a similarity search to get the most relevant information and return the answer generated by OpenAI.
Here is one example using the MemoryVectorStore:
$dataReader = new FileDataReader(__DIR__.'/private-data.txt');
$documents = $dataReader->getDocuments();
$splittedDocuments = DocumentSplitter::splitDocuments($documents, 500);
$embeddingGenerator = new OpenAIEmbeddingGenerator();
$embeddedDocuments = $embeddingGenerator->embedDocuments($splittedDocuments);
$memoryVectorStore = new MemoryVectorStore();
$memoryVectorStore->addDocuments($embeddedDocuments);
//Once the vectorStore is ready, you can then use the QuestionAnswering class to answer questions
$qa = new QuestionAnswering(
$memoryVectorStore,
$embeddingGenerator,
new OpenAIChat()
);
$answer = $qa->answerQuestion('what is the secret of Alice?');You can now make your AutoGPT clone in PHP using LLPhant.
Here is a simple example using the SerpApiSearch tool to create an autonomous PHP agent. You just need to describe the objective and add the tools you want to use. We will add more tools in the future.
use LLPhant\Chat\FunctionInfo\FunctionBuilder;
use LLPhant\Experimental\Agent\AutoPHP;
use LLPhant\Tool\SerpApiSearch;
require_once 'vendor/autoload.php';
// You describe the objective
$objective = 'Find the names of the wives or girlfriends of at least 2 players from the 2023 male French football team.';
// You can add tools to the agent, so it can use them. You need an API key to use SerpApiSearch
// Have a look here: https://serpapi.com
$searchApi = new SerpApiSearch();
$function = FunctionBuilder::buildFunctionInfo($searchApi, 'search');
$autoPHP = new AutoPHP($objective, [$function]);
$autoPHP->run();Why use LLPhant and not directly the OpenAI PHP SDK ?
The OpenAI PHP SDK is a great tool to interact with the OpenAI API. LLphant will allow you to perform complex tasks like storing embeddings and perform a similarity search. It also simplifies the usage of the OpenAI API by providing a much more simple API for everyday usage.
Thanks to our contributors:
LLPhant is sponsored by Theodo a leading digital agency building web application with Generative AI.