Open Policy Agent (OPA) is an open-source policy engine designed for policy-based control and decision-making in modern, cloud-native applications. It provides a unified, declarative language for expressing policies across different layers of your software stack.
-
Declarative Policies: OPA allows you to express policies using a high-level, human-readable language called Rego (Policy Language) rather than writing complex code.
-
Fine-Grained Control: OPA enables fine-grained control over authorization and access control, making it suitable for microservices and containerized environments.
-
Policy as Code: You can version, test, and manage policies as code, making it easier to maintain and enforce complex security and compliance requirements.
-
Integration Flexibility: OPA can be integrated with various cloud-native tools, services, and APIs, making it versatile for enforcing policies in different environments.
-
Access Control: OPA helps define and enforce access control policies, ensuring that only authorized users or services can access specific resources.
-
Authorization: It allows you to determine whether a given request or action is authorized based on defined policies.
-
Data Filtering: OPA can filter and transform data in real-time, enabling data-driven policy decisions.
-
Compliance and Security: OPA can enforce security and compliance policies, ensuring that your applications adhere to organizational standards and best practices.
OPA evaluates policies against incoming requests or data. It can be integrated into your application's code or deployed as a standalone service. When a request or data is sent to OPA, it uses the defined policies to make access control and authorization decisions.
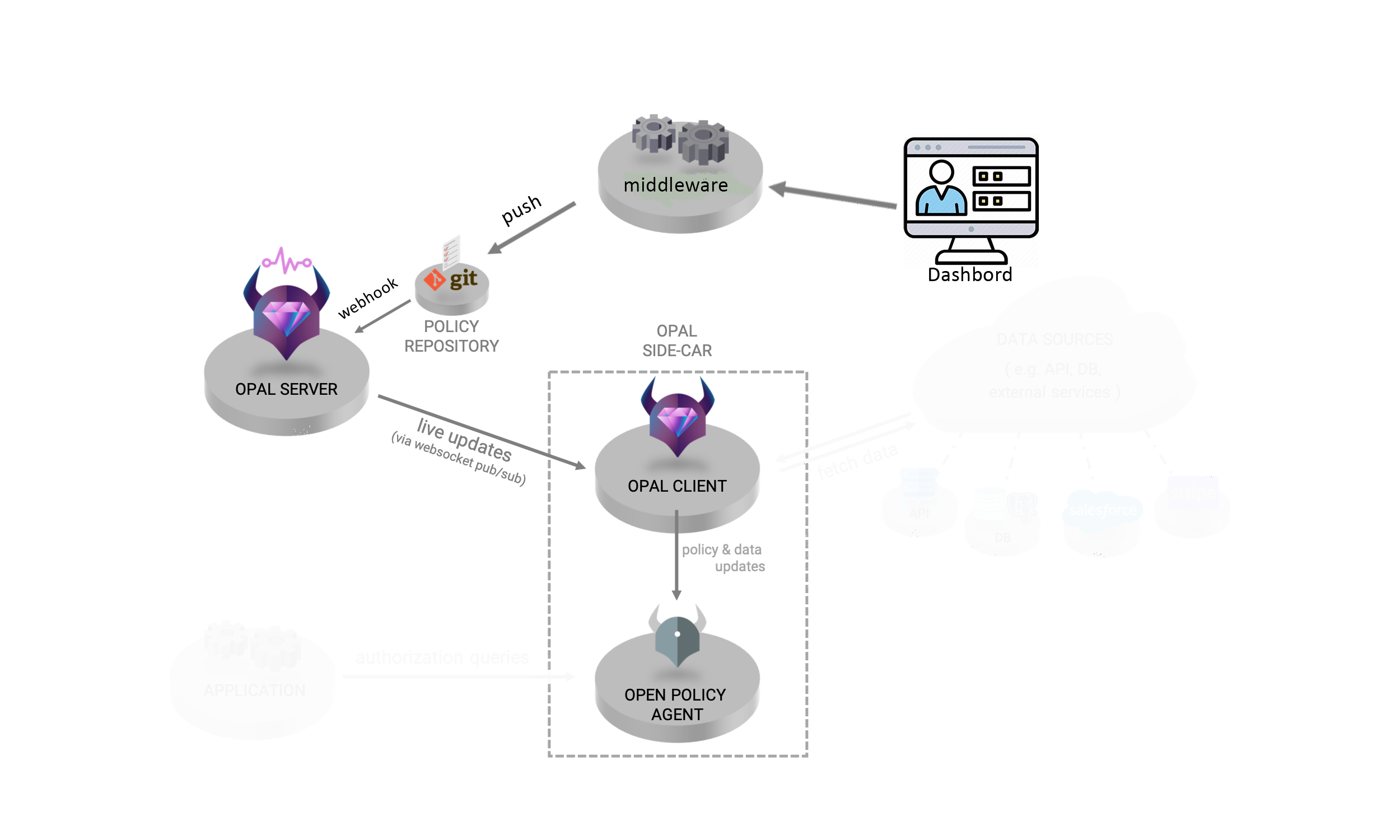
About OPAL, an open-source project developed by permit io. OPAL was initially designed to be an integral part of the permit.io website. Its primary aim is to facilitate real-time aggregation of Open Policy Agent (OPA) policies and data using real-time WebSockets. The core architecture of OPAL consists of three main components: the OPAL server, OPAL client, and broadcast channel.
-
OPAL Server: The OPAL server acts as the central synchronization hub for all agents. It enables seamless distribution of updates to agents without directly transmitting the data. Instead, the server provides the resource location from which the OPAL client can retrieve the data. This approach is particularly advantageous for efficiently managing and distributing large datasets.
-
OPAL Client: Responsible for maintaining up-to-date OPA policies and data, the OPAL client operates in the background. It ensures that the OPA instances are consistently aligned with the latest changes, enhancing the overall accuracy of policy enforcement.
-
Broadcast Channel: The broadcast channel establishes a connection bridge between the OPAL client and OPAL server. It facilitates efficient transmission of updates, ensuring that policy and data changes are promptly delivered and applied.
-
Data Sharding: OPAL supports data sharding, allowing efficient division and management of data. This feature is particularly useful for handling extensive datasets, ensuring streamlined storage and retrieval.
-
Low Latency: With a focus on minimal latency, OPAL ensures swift propagation of policy and data updates throughout the system. This is crucial for maintaining the real-time nature of policy enforcement.
-
CLI Tools: Both the OPAL server and OPAL client come with command-line interface (CLI) tools, simplifying various management, configuration, and monitoring tasks.
-
Git Repository Sync: OPAL's integration with Git repositories enhances version control for policies, streamlining collaboration and providing a history of policy modifications.
OPAL provides versatile methods to accommodate changes and updates:
-
API-based Data Changes: OPAL supports API-based changes specifically for data updates. Through the API interface, you can programmatically modify data, offering flexibility and automation in data management.
-
Git Repository Tracking: For managing data and policy changes, OPAL supports tracking data and policy modifications via Git repositories. By monitoring repository commits and updates, OPAL ensures that data and policies remain synchronized with the latest changes.
In cases of network disruptions, the OPAL client implements a fail-safe mechanism. Upon reconnection, it refetch all changes and updates from the OPAL server, guaranteeing that no critical updates are missed.
Edit OPA Code
Add Tag
-
Real-time Adaptability: Enables real-time updates in OPA for agile policy adjustments.
-
Version Control: Manages code versions for auditability and rollback capability.
-
Stability Assurance: Implements validation and error handling for OPA stability.
-
Error Prevention: Rigorous testing prevents logical and compilation errors.
-
Git Repository Compatibility: Supports various Git platforms for flexibili
If test failed we discord changes and send failed response
This guide provides comprehensive instructions for setting up and running the OPAL along with the accompanying Node.js server. OPAL enables real-time management policies.
To get started, ensure you have the following prerequisites installed on your system:
- Docker
- Docker Compose
- Node.js (for running the Node.js server)
OPAL:
- Edit the
server/docker-compose.yaml:
cd server
nano docker-compose.yaml- Set the following environment variables inside OPAL server:
environment:
- OPAL_POLICY_REPO_URL: <your_rego_code_repo_url>
- OPAL_POLICY_REPO_WEBHOOK_SECRET: <your_webhook_secret>
- OPAL_POLICY_REPO_MAIN_BRANCH: branch that opal will track
- OPAL_POLICY_REPO_WEBHOOK_PARAMS: webhook parameter
- Set the following environment variables inside OPAL client:
environment:
- OPAL_POLICY_STORE_URL: OPA url
- OPAL_POLICY_STORE_AUTH_TYPE: TOKEN or OAuth
- OPAL_POLICY_STORE_AUTH_TOKEN: token to connect to OPA if Authorization layer added to opa
- OPAL_DEFAULT_UPDATE_CALLBACKS: {"callbacks":["middleware_server_URL"]}
- OPAL_SHOULD_REPORT_ON_DATA_UPDATES: TrueNodeJs server:
- Open the
server/.envfile in an editor and set the required environment variables:GIT_REPO=<your_rego_code_repo_url_with_token> OPAL_URL=https://opalHostName:7002 RUN_TESTS=#true or false if you want it to run test before push REMOTE_NAME=#the name of the git remote MAIN_BRANCH=#branch that contain the policies GIT_EMAIL=#Provide the email address associated with your Git commits. This is used for authorship and identification purposes in Git history. DATA_PATH= #path of data file (should be in root) PORT: <port_to_run_the_server_default_3000> OPA_COMMAND: opa(linux) or opa.exe(if you run on Windows)
-
Clone the OPAL repository:
git clone https://github.com/tactful-ai/OPA.git
-
Navigate to the OPAL server directory:
cd OPA/server -
Start OPAL using Docker Compose:
docker-compose up
-
OPAL should now be up and running, tracking the specified policy repository.
-
Webhook Configuration:
- Access the settings of your GitHub repository.
- Go to "Webhooks" or "Hooks" depending on your GitHub version.
- Add a new webhook:
- Payload URL:
https://opalHostName:7002/webhook - Content type:
application/json - Secret: Use the same value as
OPAL_POLICY_REPO_WEBHOOK_SECRET - Choose the events you want to trigger the webhook for (e.g., "Push" events).
- Payload URL:
-
Navigate to the OPAL server directory:
cd OPA/server -
Install the Node.js server dependencies:
npm install
-
Start the Node.js server:
npm run build npm start
or for development
npm run dev
-
The Node.js server should now be running and communicating with the OPAL dashboard.
- Can access full API docs through https://documenter.getpostman.com/view/28376829/2s9Y5WwiNq.
Managing permissions in OPAL is a straightforward process that empowers you to finely control resource access. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to add a new resource, create a corresponding role, and define permissions:
-
Adding a New Resource:
Let's assume you want to add a new resource, like a DB resource, and grant specific access to it.
-
Creating a New Role - DB-administrator:
To enable read and write access to the DB resource, follow these steps:
-
Send a POST request to
/roles. -
Include the following JSON data to create a DB-administrator role:
{ "role": "DB-administrator", "description": "Responsible for managing the database" }
-
-
Creating the DB Resource:
After creating the DB-administrator role, proceed to create the DB resource:
-
Send a POST request to
/resources. -
Include the following JSON data to create the DB resource with read and write scopes:
{ "resource": "DB-resource", "scopes": ["read", "write"] }
-
-
Defining Permissions:
With the role and resource in place, you can define the permissions:
-
To allow the DB-administrator role to read the DB resource:
-
Send a POST request to
/permissions. -
Include the following JSON data to create a permission for reading:
{ "resource": "DB-resource", "scope": "read", "role": "DB-administrator" }
-
-
To allow the DB-administrator role to write to the DB resource:
-
Send another POST request to
/permissions. -
Include the following JSON data to create a permission for writing:
{ "resource": "DB-resource", "scope": "write", "role": "DB-administrator" }
-
-
-
Congratulations! You've now configured the permissions. The DB-administrator role can effectively manage and access the DB resource based on the specified permissions.