Dead simple way to run LLaMA on your computer.
- Powered by llama.cpp and llama-dl CDN
- Hackable web app included
- Ships with JavaScript API
- Ships with Socket.io API
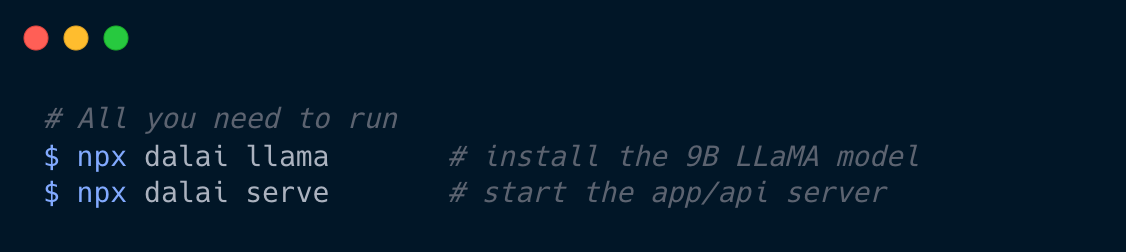
Install the 7B model (default) and start a web UI:
npx dalai llama
npx dalai serve
Then go to http:https://localhost:3000
Above two commands do the following:
- First installs the 7B module (default)
- Then starts a web/API server at port 3000
Basic install (7B model only)
npx dalai llama
Install all models
npx dalai llama 7B 13B 30B 65B
The install command :
- Creates a folder named
dalaiunder your home directory (~) - Installs and builds the llama.cpp project under
~/llama.cpp - Downloads all the requested models from the llama-dl CDN to
~/llama.cpp/models - Runs some tasks to convert the LLaMA models so they can be used
Dalai is also an NPM package:
- programmatically install
- locally make requests to the model
- run a dalai server (powered by socket.io)
- programmatically make requests to a remote dalai server (via socket.io)
Dalai is an NPM package. You can install it using:
npm install dalai
const dalai = new Dalai(home)home: (optional) manually specify the llama.cpp folder
By default, Dalai automatically stores the entire llama.cpp repository under ~/llama.cpp.
However, often you may already have a llama.cpp repository somewhere else on your machine and want to just use that folder. In this case you can pass in the home attribute.
Creates a workspace at ~/llama.cpp
const dalai = new Dalai()Manually set the llama.cpp path:
const dalai = new Dalai("/Documents/llama.cpp")dalai.request(req, callback)req: a request object. made up of the following attributes:prompt: (required) The prompt stringmodel: (required) The model name to query ("7B", "13B", etc.)url: only needed if connecting to a remote dalai server- if unspecified, it uses the node.js API to directly run dalai locally
- if specified (for example
ws:https://localhost:3000) it looks for a socket.io endpoint at the URL and connects to it.
threads: The number of threads to use (The default is 8 if unspecified)n_predict: The number of tokens to return (The default is 128 if unspecified)seed: The seed. The default is -1 (none)top_ktop_prepeat_last_nrepeat_penaltytemp: temperaturebatch_size: batch sizeskip_end: by default, every session ends with\n\n<end>, which can be used as a marker to know when the full response has returned. However sometimes you may not want this suffix. Setskip_end: trueand the response will no longer end with\n\n<end>
callback: the streaming callback function that gets called every time the client gets any token response back from the model
Using node.js, you just need to initialize a Dalai object with new Dalai() and then use it.
const Dalai = require('dalai')
new Dalai().request({
model: "7B",
prompt: "The following is a conversation between a boy and a girl:",
}, (token) => {
process.stdout.write(token)
})To make use of this in a browser or any other language, you can use thie socket.io API.
First you need to run a Dalai socket server:
// server.js
const Dalai = require('dalai')
new Dalai().serve(3000) // port 3000Then once the server is running, simply make requests to it by passing the ws:https://localhost:3000 socket url when initializing the Dalai object:
const Dalai = require("dalai")
new Dalai().request({
url: "ws:https://localhost:3000",
model: "7B",
prompt: "The following is a conversation between a boy and a girl:",
}, (token) => {
console.log("token", token)
})Starts a socket.io server at port
dalai.serve(port)const Dalai = require("dalai")
new Dalai().serve(3000)connect with an existing http instance (The http npm package)
dalai.http(http)http: The http object
This is useful when you're trying to plug dalai into an existing node.js web app
const app = require('express')();
const http = require('http').Server(app);
dalai.http(http)
http.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server started")
})await dalai.install(model1, model2, ...)models: the model names to install ("7B"`, "13B", "30B", "65B", etc)
Install the "7B" and "13B" models:
const Dalai = require("dalai");
const dalai = new Dalai()
await dalai.install("7B", "13B")returns the array of installed models
const models = await dalai.installed()const Dalai = require("dalai");
const dalai = new Dalai()
const models = await dalai.installed()
console.log(models) // prints ["7B", "13B"]