Computer Vision and Deep Learning Enabled Real-Time Liquid Level Detection and Measurement in Transparent Containers
Laboratories, particularly those in large oil companies, require a fast and reliable system for detecting and measuring liquid levels in containers. Current manual methods and some of the pure vision based methods are time-consuming, tedious, and prone to errors leading to delays in product development and increased risk of errors. There is a critical need for a fast and reliable system that can detect and measure liquid levels in real-time and improve the efficiency and reducing human errors in laboratory testing procedures.
Moreover, with the increase in the trend of Industry 4.0 the capability to detect and measure the liquid levels in the transparent flasks/test tubes is a crucial part in the whole perception system of an autonomous robot and by the use of the Computer vision and deeplearning we can easily help solve this problem. The final developed system can be used in various applications across various industries, including pharmaceutical, manufacturing and chemical processing making it a crucial component in the perception system of an autonomous robot in the Industry 4.0.
To solve the problem of manual and slow pure vision based liquid level measurement in laboratories [1], we propose to develop an fast and accurate automated system that uses the state-of-the-art deep learning technology [2] to provide accurate and real-time feedback on liquid levels in containers from various viewing angles. The system consists of a realsense d435 camera that collects data [4], which is then analyzed by a state-of-the-art deep learning model and angle correction by devising a novel algorithm to correct the errors in any viewing angle and then to determine the liquid level in real-time. This technology will reduce the risk of errors and increase efficiency in laboratory testing procedures, allowing for faster product development and improved quality control. Additionally, the system can be extended to handle datasets with different types of containers and liquids [3] to ensure its effectiveness across various laboratory testing scenarios. The system will be robot-friendly, with a simple interface that can easily pass the real-time measurement data to the microprocessor to further control a robotic arm to pick up the container which is with appropriate liquid level. Once developed, the system will be tested and optimized to ensure its accuracy and reliability, and can be further enhanced with training heavier deep learning models using different types of containers dataset to improve the accuracy of the liquid level measurement over time.
- Classical CV based solution Advantages: 1. Fast, less computational cost 2. Easy to implement DisAdvantages: 1. Not adaptive 2. Extensive tuning of thresholds etc 3. Less effective in different environments. 4. Very difficult to detect transparent liquid.
- Deep Learning based solution Advantages: 1. State-of-the-art performance 2. They can learn features and representations directly from data 3. More flexible and adaptable in variations in the objects DisAdvantages: 1. They require large amount of labeled data to train effectively 2. Computationally expensive 3. Prone to over-fitting in-case of noisy data 4. less likely to understand how they system is making decisions 5. They may struggle with rare Below is our methodology for the deeplearning model + classical computer vision based == Robust solution
This section is divided into 4 main subsections:
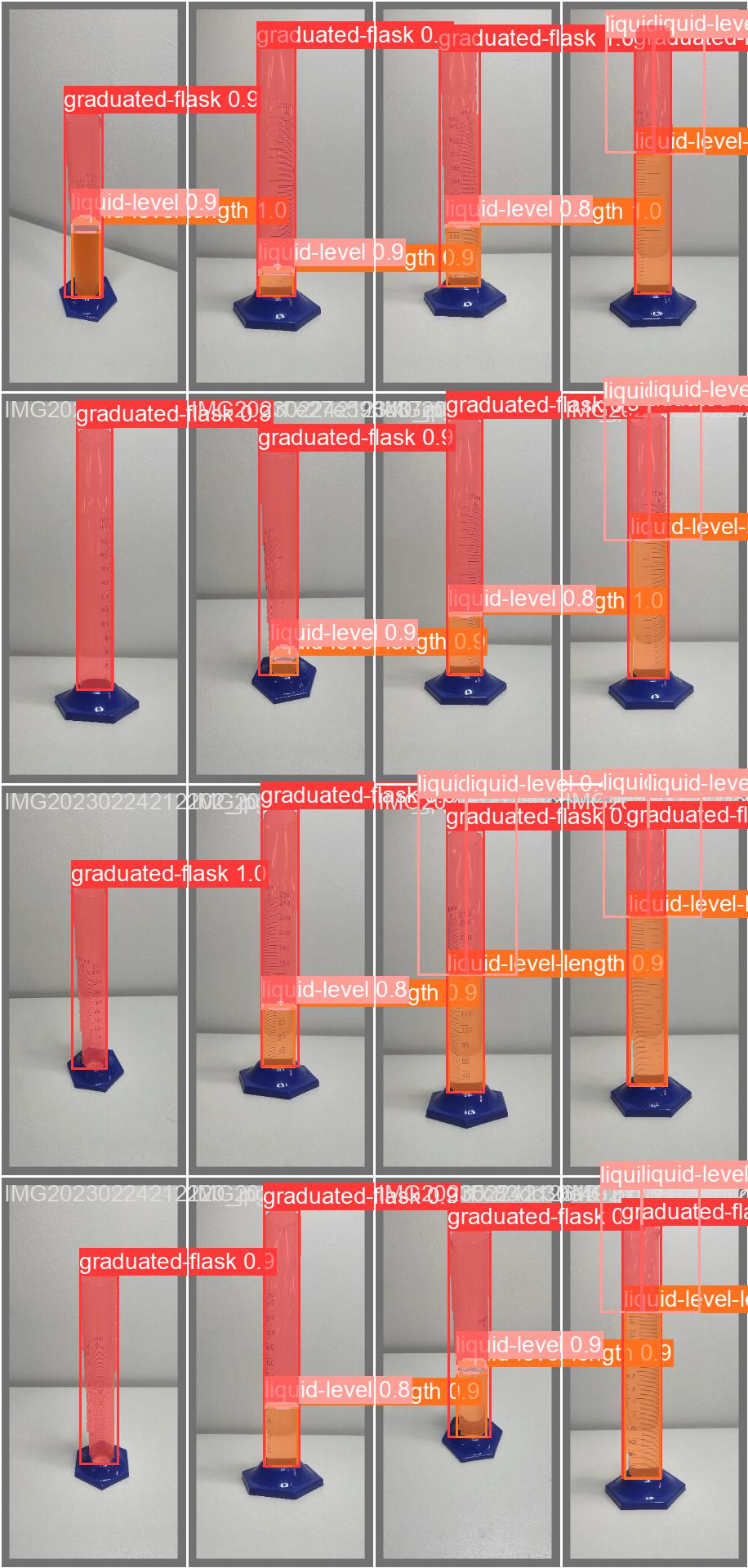
For dataset creation we choose the roboflow platform as it have tools which will make the process of the annotation of the images seemless. We took 214 images of the graduated flask with different liquid levels at various orientations and annotated it on Roboflow[3].
After creating our dataset now it was time to train a large model of Yolo v8 (yolov8l-seg.pt) with 100 epochs input image size as 640x640 pixels.





To ensure robust measurements, we have to calibrate our camera’s intrinsic and extrinsic parameters to match their default values. The process of calibration usually requires the aid of a paper with a checkerboard pattern. For this step, we take several photos from different angels of the checkerboard and input them to our application. The idea of using such a pattern in common is that it has sharp corner and is easy to distinct by the camera lens [8].


After calibration, we can use the camera parameters to reduce the skew and other artifacts and have a rectified image that can later be used with further computer vision processes. Rectifying the image parameters is a crucial step to do before using the camera. The output of the process reduces the camera to the simple pinhole model, which simplifies the calculations further and enhances the accuracy overall due to correct parameters.
The project is a synthesis of different units that are prepared and responsible for different tasks each. The target containers mainly consist of liquids that are desired to be monitored through the sensory unit, the camera. The sensory unit monitors the liquid and generates a digital image that is later handed to the detection unit. The unit that handles the detection process is mainly based on a deep learning model.
The Liquid containers which we are training out model is only for the transparent liquid level containers only, the proposed solution will not work for the liquid level containers which aren't transparent. There can be any number of container types but as long as they are transparent then there is not an issue.
Given the variety of camera parameters and the complexity of interfacing it with the computer, choosing the sensory unit is a crucial step as it influences the overall accuracy process. For this application we choose the Intel RealSense D435 camera due to its pioneering in 3d scanning and detecting facial-features. Furthermore, there is package for python with API for quicker interfacing with python.[9]
Deep learning is a powerful tool that utilizes the usage of neural networks to predict and regulate the output model. Recently deep learning has been noticed in many fields, most famous of which is computer vision. Nowadays there are many tools that combine deep learning with computer vision, one of them is YOLOv8. The reason we choose to work with YOLOv8 is due to the fact that it is the state-of-the-art model, and faster when it comes to instance segmentation and object detection.
One of the main goals of this research is to detect and measure the liquid level even if the camera is at a particular range of angles with the liquid container, which means we don’t want the angle of the camera to the liquid container to affect our reading of the volume of liquid inside the container. The distortion in the dimensions of the object when observed from a specific angle is known as foreshortening or perspective distortion and it is caused by the changing distances between the object and the camera, as well as the varying viewing angles that affect the projection of the object onto the 2D image plane [].
We developed an Algorithm based on simple geometry, this algorithm is aimed to eliminate any perspective distortions which are bound to occur in a dynamic environment and when the camera is moving. The Algorithm is as follows
- Get the measured_flask_height of the container (y2-y1) in pixels
- PIXEL_PER_MM_HEIGHT_RATIO = measured_flask_height/ACTUAL_HEIGHT_OF_FLASK
- Get the measured_width and measured_height of the container
- theta = arcsin(measured_height/measured_width)
- Apparant_Flask_height = (measured_flask_height/PIXEL_PER_MM_HEIGHT_RATIO)*cos(theta)
- APPARANT_HEIGHT (diameter)= ACTUAL_DIAMETER_OF_FLASK * (measured_height/measured_width)
- Get the measured_liquid_height of the liquid in the container
- Height correction due to the model detecting the height of the liquid from the middle of the liquid when the camera is at an angle - > measured_liquid_height = measured_liquid_height - (measured_height/2)
- measured_liquid_height_mm = measured_liquid_height/PIXEL_PER_MM_HEIGHT_RATIO
- ACTUAL_LIQUID_HEIGHT = measured_liquid_height_mm/np.cos(theta)
- MILLILITER = (pi *((inner_dia_of_container/2)**2)*ACTUAL_LIQUID_HEIGHT)/1000 + offset
To implement such a project, it is difficult to experience the prototype directly on the actual chemical tanks. Therefore we design an experience that simulates the real process. Below we will discuss the used devices and how the experience was conducted.
Our Hardware setup is as shown below

- Transparent graduated flask: With a total volume approximately 1000 ml
- Intel Realsense camera: advanced camera for 3d scanning and recognition
- Tripod: For fixing camera position at various orientations and distances from the liquid containers
- Software: Deep learning model and our Algorithm
The flask is filled with a certain value of water, this value is to be measured and compared later with the actual to obtain accuracy. After, we place the flask at a given distance and angle from the camera since the model already takes into account the effects of changing projection of angle and distance. Finally, we monitor the flask through real-time stream and detect the approximated water level in the flask
In Conclusion, we have firstly tried to detect and measure the liquid level using the classical computer vision approaches and then we used the combination of both classical computer vision based and deep learning based approach which makes the detection and measurement of the liquid level in the flask seamless.
- More Research on related work done (2-Weeks) - done
- Create dataset (Taking images and doing annotations) (1-Weeks) - done
- Train the deep learning model (0.5-Week) - done
- Devise an algorithm for measuring exact level of liquid in the container (2-Weeks) - done
- Test, evaluate and Optimize the system, Deploy (1.5-Week) - done
- Deep Learning Model (e.g. YOLOv8)
- Computer Vision (e.g. OpenCV)
- Realsense D435 camera
- Roboflow
- Sprinkle of Geometry and Logic;)
- Ma, H. and Peng, L., 2019, December. Vision based liquid level detection and bubble area segmentation in liquor distillation. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST) (pp.1-6). IEEE.
- State-of-the-art Deep learning platform YOLOv8
- Tool to create Dataset and Annotations Roboflow
- Realsense depth camera D435
- Bobovnik, G., Mušič, T. and Kutin, J., 2021. Liquid level detection in standard capacity measures with machine vision. Sensors, 21(8), p.2676.
- Qiao, G., Yang, M. and Wang, H., 2022. A Water Level Measurement Approach Based on YOLOv5s. Sensors, 22(10), p.3714.
- Pithadiya, K.J., Modi, C.K. and Chauhan, J.D., 2010, February. Machine vision based liquid level inspection system using ISEF edge detection technique. In Proceedings of the International Conference and Workshop on Emerging Trends in Technology (pp. 601-605).
- Zhang, Z., 2000. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 22(11),pp.1330-1334.
- pyrealsense2 2.53.1.4623
- opencv-python 4.7.0.72