This project uses the ESP32 as the primary controller and the MG995 as the servo motor to create an automated outdoor fish feeder.
- Voice-controlled feeding via Xiao Ai.
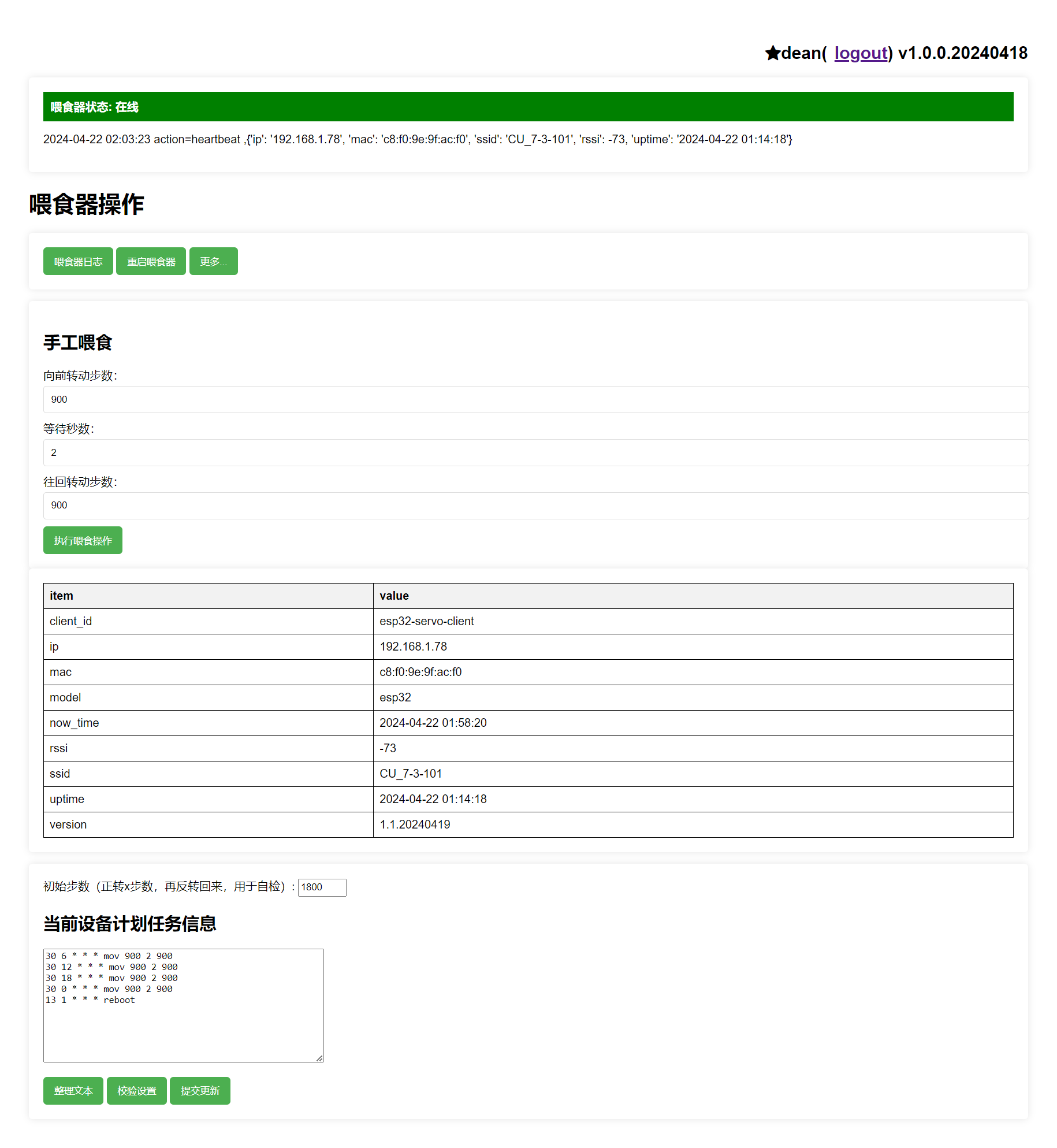
- Web-based interface for status viewing, logging, feed operations, and scheduling.
- Scheduled tasks allow for automated operations like feeding or restarting based on set times.
- Operation video
1. ESP32 Module:
Upon booting, the ESP32 initializes the servo by rotating it forwards and backwards for set periods. It then sends status updates (e.g., start notifications, action executions) to its MQTT server and subscribes to relevant topics (/xxx/servo/action). Upon receiving commands:
- 'query': Fetches current connection and task scheduling information, and posts it to /xxx/servo/data on MQTT.
- 'reboot': Restarts the device.
- 'do': Executes a fish feeding operation.
- 'set_cfg': Retrieves configuration data for scheduled tasks, writes it to boot.ini, and restarts to apply new settings. Due to ESP32's Micropython lacking threading support, it's advisable to use a while loop for multitasking. The task scheduling syntax is similar to Linux's crontab but simplified.
2. Web Server Module:
Built with Flask, it handles:
- Static file hosting (CSS, JS, images).
- HTML templates for different web pages.
- MQTT subscriptions for logging and interactivity.
- Database management for web authentication. Files include:
- webroot/: Contains static files.
- templates/: Contains HTML template files like index.html (homepage), logs.html (logs page), and others.
- server_web.py: Main Flask application.
- config.py: Configuration settings for the server.
- MyDB.py: Database management.
- log2sqlite.py: Logs MQTT messages to SQLite.
- bemfa.py: Subscription interaction for monitoring Bafa Cloud.
- MyMQTT.py: Encapsulated MQTT modules.
3. Personal Computer Section:
Manages firmware updates with scripts like op_firmware.py, providing options for pushing or fetching files via MQTT topics. Usage examples and error handling are outlined.
File Storage Directory:
- Laptop: Contains scripts and configuration files for managing the ESP32 firmware.
This README aims to provide clear instructions and explanations for operating and maintaining the automated fish feeder. Further updates will refine these details and add new features as necessary.
本项目基于ESP32做主控+MG995做舵机,做一个户外给鱼自动喂食的装置。
可以通过小爱同学,进行语音控制喂食;
可以通过web页面,进行状态查看,日志查看,喂食操作,定时设置;
可以根据定时设置情况,按定时计划,执行对应操作(比如喂食,比如重启自己);
1. ESP32部分
在ESP32启动时,舵机先做一个初始化,正转一定时间,反转一定时间;
然后ESP32开始向自己的MQTT服务器发送一些状态信息(启动通知,执行动作通知等),订阅相关的主题(/xxx/servo/action),当收到类似{'act':'xx'}请求时,
act为query:查询当前连接信息,计划任务信息,将信息扔给MQTT的/xxx/servo/data;
act为reboot:重启自己;
act为do:执行一次喂鱼操作;
act为set_cfg:获得cfg_data(计划任务配置信息),将之写入boot.ini,然后重启自己,确保新任务生效;
由于ESP32的micropython不支持threading,在执行多个任务时,尽可能通过while循环来进行某个任务的执行;
计划任务的配置格式,参考linux的crontab配置格式(只是一个简易实现,仅完成部分简化功能);
由于之前没有操作过舵机,看淘宝上MG995是360度的,想着360度比180度的好,就买的这个。调试时发现,它没法儿像其它舵机那样,精确到某个角度。
MG995只能给它正转指令或者反转指令。然后它就开始转起来,停不下来了。
直到你再给它一个停止指令,它再停下来。
MG995舵机的中点位置是1500微秒(usec), 脉冲宽度范围是500到2500微秒,死区宽度是8微秒。
舵机的控制信号通常遵循以下规律: 当脉冲宽度小于中点位置时,舵机向一个方向转动。 当脉冲宽度大于中点位置时,舵机向相反方向转动。
当脉冲宽度等于中点位置时,舵机停止转动。 因此由脉冲宽度范围是500到2500微秒可知,
当设置pwm.duty_ns(2500*1000)时,舵机反转速度最大
当设置pwm.duty_ns(500*1000)时,舵机正转速度最大
先期也就这么将就着用了。
后面发现这样转几天后,精度不够的原因,食料瓶子就头朝下了,这样再加上瓶子身上雨衣,下雨天时,鱼食会被淋湿,堵死出孔。 后面还是换成180度的MG995舵机了。 1s=1000ms 1ms=1000us 1us=1000000ns 给舵机设置频率50Hz,意味着一个时钟周期是20ms,在这个时钟周期内,给0.5ms的高电平,就会让MG995舵机返回0度,给2.ms的高电平,就会转到180度。 #0.5ms--0度 #1.0ms--45度 #1.5ms--90度 #2.0ms--135度 #2.5ms--180度 做角度映射的话: ns=int(angle/(180/(2500000-500000))+500000) pwm.duty_ns(ns) 这样给定一个角度angle,就算出要给定多少ns的高电平就可以调整它的角度了。
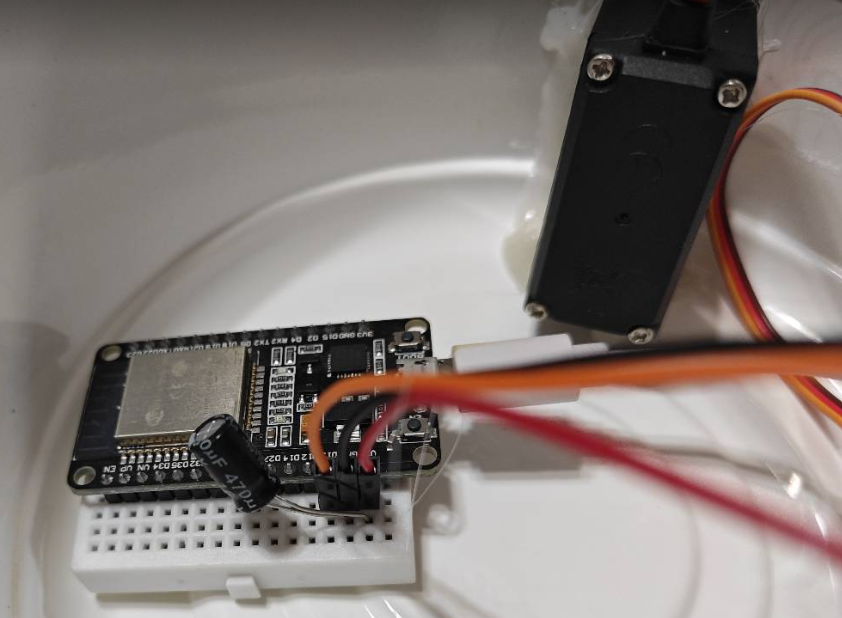
考虑舵机功率,从ESP32的VIN和GND引电(有5V)。
怕舵机启动时电流过大,给它正负极之间加了一个470uF的电容。
实际测了下,不加电容的话,带负载情况下启动舵机,电压在5V,电流在90mA-220mA之间,基本也还能接受。
连接如图:
为了在户外防雨,是把esp32和舵机放在外卖汤盒里面。
给汤盒钻了两个眼儿,一个插usb线供电,一个把舵机那个转轴露出到外面。
漏眼儿的地方,用热熔胶封上,避免进水。
矿泉水瓶子上把舵机戴的帽子用热熔胶固定在矿泉水瓶上。
矿泉水瓶上方瓶身处,用烧红的铁丝,扎许多洞洞,将来倒置它时,鱼食从此处流出来。
为了防止下雨等情况,给瓶身脖子处,拿塑料袋剪裁一个小裙子,也是热熔胶固定下。
下面是整个喂鱼器的完整外观,如下图:
esp32会每隔一分钟,向主题/xxx/servo/log向mqtt服务器发送自己的心跳信息。
考虑到可能在线升级程序代码,给esp32增加了通过mqtt传送文件的部分,实现自己的“OTA”
esp32涉及的程序文件目录为:iot_dev
-
pwm_servo.py 这个是舵机操控部分代码
-
act_mqtt.py 这个是响应mqtt协议发过来的各种指令部分
-
iot_config.py 这个是配置文件部分,所有的关键参数,在这里进行配置
-
main.py 这个是主程序部分
-
function.py 这个是封装的一些常用函数部分。另外由于ESP32的RAM不大,有时会莫名其妙的内存不够,把一些功能拆分到function.py这里面后,这个情况就没有了。
2. 公网服务器部分
这部分部署在一个公网服务器上(我自己的VPS,上面装mosquitto的MQTT服务器),用于做web前端展现以及后端监听mqtt的几个主题进行响应。
监听是/xxx/servo/log的信息: 将esp32发来的日志,入库到本地的sqlite3数据库中。在载入web管理页面时,通过本地sqlite3数据库的记录,判断ESP32是在线状态还是离线状态;
监听巴法云的对应主题FeedFish001信息: 收到巴法云的指令(或者小爱同学),操作mqtt想/xxx/servo/action发送开机指令给esp32执行动作;
公网服务器涉及的程序文件目录为:pub_server
-
static/ 这个目录是放javascript脚本,css等素材,很多历史遗留的东西,抄来抄去也就没去除无用东西了。
-
templates 这个目录存放html的模板文件;
-
login_templ.html 是登录模板文件;
-
index.html 是首页模板文件;
-
logs.html 是日志展示页面模板文件;
- servo_web.py 这个是WEB的主页面
- config.py 这个是公网服务器上涉及配置的各个参数
- MyDB.py 这个是web鉴权的数据库管理模块
- log2sqlite.py 这个是监听/xxx/servo/log的mqtt订阅,然后存入本地sqlite库
- bemfa.py 这个是监听巴法云的订阅交互
- MyMQTT.py 这个是封装的mqtt的一些模块
3. 个人电脑部分
这个主要是封装一个程序更新操作:
d:\>op_firmware.py
usage: op_firmware.py [-h] [-t TOPIC] [-a ACTION] [-sf SOURCE_FILE] [-tf TARGET_FILE]
op_firmware.py: error: No topic specified, add --topic /x/x/x or -t /x/x/x
d:\perl_wrk\ESP32_init\python带伺服电机\laptop>op_firmware.py -h
usage: op_firmware.py [-h] [-t TOPIC] [-a ACTION] [-sf SOURCE_FILE] [-tf TARGET_FILE]
Manage IoT device operations
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-t TOPIC, --topic TOPIC
which iot topic should be selected
-a ACTION, --action ACTION
get/push/cmd
-sf SOURCE_FILE, --source_file SOURCE_FILE
source file to be deal
-tf TARGET_FILE, --target_file TARGET_FILE
target file to be deal
example1, update local main.py to remote ESP32's main.py:
op_firmware.py -a push -t /dean/servo -sf main.py -tf main.py
example2, get remote ESP32's main.py to local main_t.py:
op_firmware.py -a get -t /dean/servo -sf main.py -tf main_t.py
相关文件存放的目录为:laptop
-
op_firmware.py 这个是操作ESp32程序微码主程序
-
pc_config.py 这个是对应的配置文件