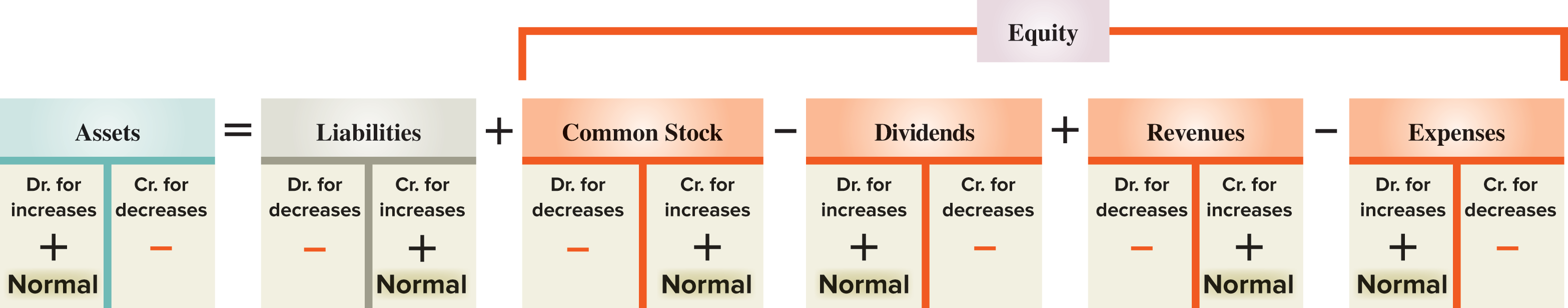
- Assets = Liability + Shareholder's Equity
- cash: coins, checks, money orders, and checking account balances
- Retained Earning <- Retained Earning + Net Income - Dividend
- Net income = Revenue - Expense
- B beginning balance
- A add revenue
- S substract expense
- E ending balance
- Cash <- Cash + Net increase in cash.
| Debit | Credit |
|---|---|
| Asset, expense, dividend | liability, revenue, equity |
- Debit must always equal credit.
- Just remember: asset moves up is debit. Anything that moves in order to keep balance must be credit.
- Prepaid insurance
- Unearned service revenue.
- Dividend does not appear on income income. It is not an expense.

- Receive money, debit asset, credit revenue
- Closing revenue account, debit revenue, credit income summary
- Incur expense, credit expense, debit income summary
- Closing book: debit (decrease) income summary, credit retained earning.
- Credit cash, debit dividend
- closing: credit dividend, debit retained earning.
Corner case: if overpaying liability, the excess is treated as asset (prepaid expense/rent/insurance), not liability.
- Creditors are individuals and organizations that have rights to receive payments from a company
- Customers and others who owe a company are called its debtors.
- accrued expense: taxes payable, and interest payable
- A journal gives a complete record of each transaction in one place. It also shows debits and credits for each trans
- date of transaction
- b titles of affected accounts
- c dollar amount of each debit and credit
- and d explanation of the transaction
- The process of transferring journal entry information to the ledger is called posting
- When entries are posted to the ledger, the debits in journal entries are transferred into ledger accounts as debits, and credits are transferred into ledger accounts as credits.
- A trial balance is a list of all ledger accounts and their balances (either debit or credit) at a point in time.
- Expense is triggers by expiration of future benefits.
- Revenue incurred when service is delivered.
- no impact on income statement when cash is received
- Receiving cash doesn't mean revenue.
Adjusting entries
- Prepaid expense/rent/insurance: asset; paid cash before expense is incurred.
- to adjust account, increase (debit) expense, decrease (credit) asset
- book value: cost - accumulated depreciation
- Accrued revenue: asset (account receivable)
- to adjust, debit cash, credit accrued revenue (account receivable)
- Unearned revenue: liability
- to adjust account, decrease (debit) unearned revenue, increase revenue (credit)
- Accrued expense: liability
- as future economic benefits expire
Borrow cash:
- debit cash, credit note payable
- accrue interest:
- debit interest expense (same direction as asset)
- credit interest payable (liability)
Pay salary
- accrue salary: debit salary expense, credit salary payable (liability)
- pay salary: debit salary payable, credit cash
Asset classes
- current asset (order matters)
- cash
- debt investment
- account receivable
- note receivable (< 12 months)
- inventory
- supplies
- prepaid insurance
- long term invest
- stock investment
- real estate investment
- PPE: land, equipment, less accumulated depreciation
- intangible asset: patents
Liability classes
- current liability,
- note, account payable (< 12 month)
- unearned service revenue
- salary, wages payable
- interest payable
- long term liability
- mortgage payable
- notes payable (> 12 month)
- stockholder equity
current ratio = current assets / current liability
- measure of liquidity
- too high is not good (no economic activity)
- too low means insolvant
- sales revenue - returns & allowance - discount = net sales
- gross profit: net sales - COGS
- operating income: gross margin - operating expense
- net income: operating income + non-operating income
- gross profit/margin ratio: gross margin / net sales
- Straight line (easiest, most common)
- Units of activity (most accurate)
- declining balance method: twice the rate of straight line
- last year takes the residual, do not depreciate below salvage
- DR depreciation expense, CR accumulated depreciation
- amortization: patent
- good will: when business is acquired; cannot create good will; excess payment of asset value
- not depreciated
- Beginning + Cost of Goods Purchased = Ending + cost of good sold
- gross profit/margin = sales - COGS
- 2, 10 net 30: 2% discount if paid in 10 days, or pay full amount in 30 days
- paid within discount period: credit cash & inventory
- Sales: debit AR, credit sales, debit COGS, credit inventory
- returns: debit sales return, credit AR, debit inventory, credit COGS
- Net sales: sales - sales return - sales discount
- Net sales - COGS = gross profit
- Customer pay with discount: debit sales discount, cash, credit AR
- Net income = net sales - operating - non-operating (interest expense, interest revenue, gain/loss of equipment sales)
- FOB shipping point: buyer incurs shipping expense
- buyer increase (debit inventory), credit cash
- FOB destination: seller incurs shipping expense
- seller debit freight out (operating expense), credit cash
- Sale:
- DR cash, CR sales
- DR COGS, CR inventory
- Common stock holders get to vote, but get reward last in liquidation
- authorized stock: how many can issue? = issued stock + treasury stock
- outstanding = issued stock - treasury stock
- only outstanding stock pays dividend
- Par value + paid in val in excess of par = cash debit
- no-par stock: cash = common stock + paid in val in excess of stated value
- treasury stock is a buffer of retained earning
- sell above treasury stock price: add additional to paid in treasury
- sell below purchase price:
- SE = paid in capital + retained earning
- paid in capital = common stock + additional paid in capital
- treasury stock
- subtract from SE
- buy treasury: debit treasury stock, credit cash
- sell treasury: debit cash, credit treasury stock and
- debit paid in treasury stock if selling below (decrease SE),
- if depleted, debit retained earning
- credit paid in treasury stock if selling above (increase SE)
- debit paid in treasury stock if selling below (decrease SE),
- Declaration: DR dividend(Retained Earning) CR payable
- Payment: DR payable, CR cash
CLAD for Operation Cash Flow
- AR increase: decrease cash flow
- AP increase: increase cash flow
- Loss & Gain:
- loss: add to cash flow
- gain: subtract from cash flow
- add depreciation
- don't care about expense
Dr dep exp
Cr accu dep
Operating acticity (income statement):
- AR, Payable
- inventory
- depreciation
- collecting interest, dividend
Financing activity (long term SE):
- issuing stocks / repurchase treasury stock
- paying Dividend
- issuing/redeem bond, debt (borrow money)
investment (long term asset)
- lending money, collecting cash on loan (not borrowing/repaying)
- acquiring/sale investment/property
Final: 4, 8, 11, 12