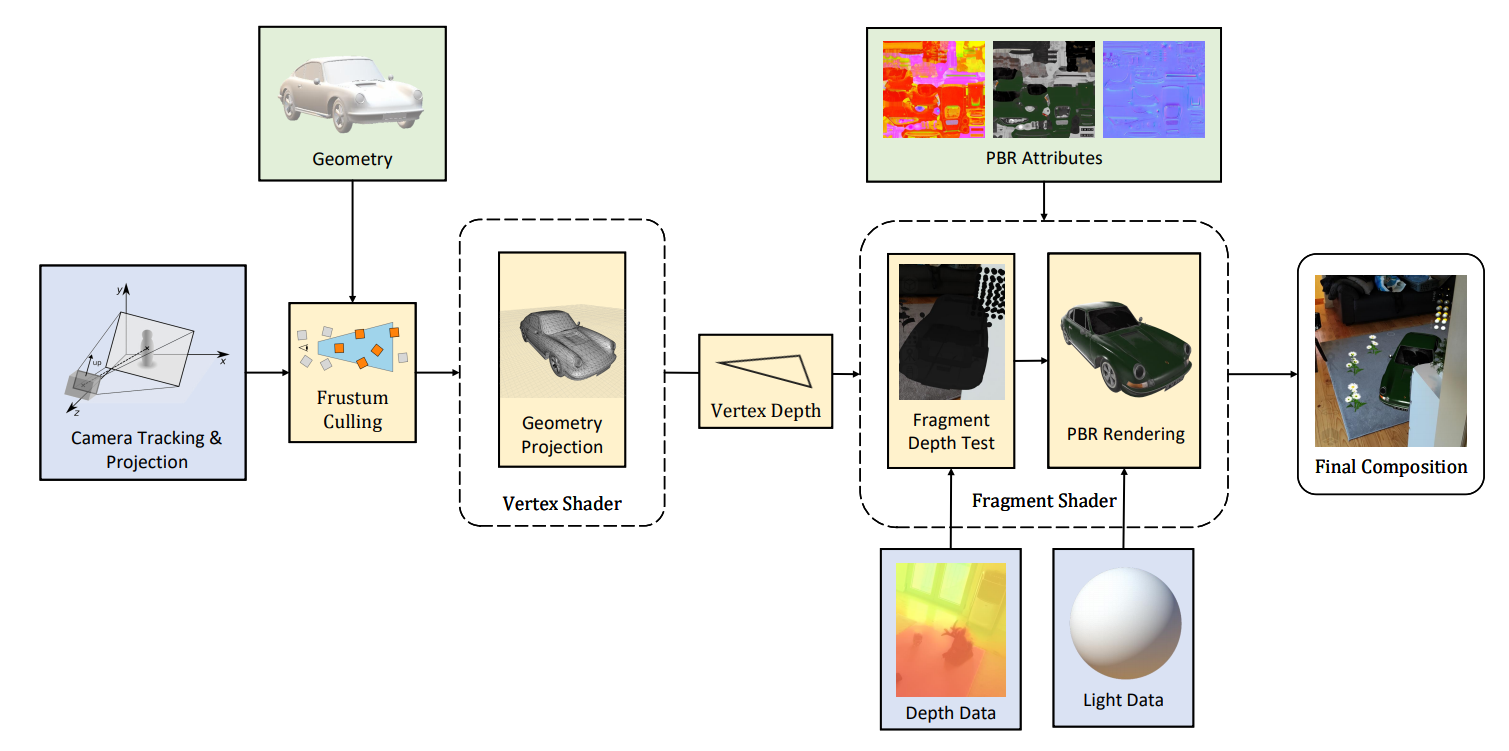
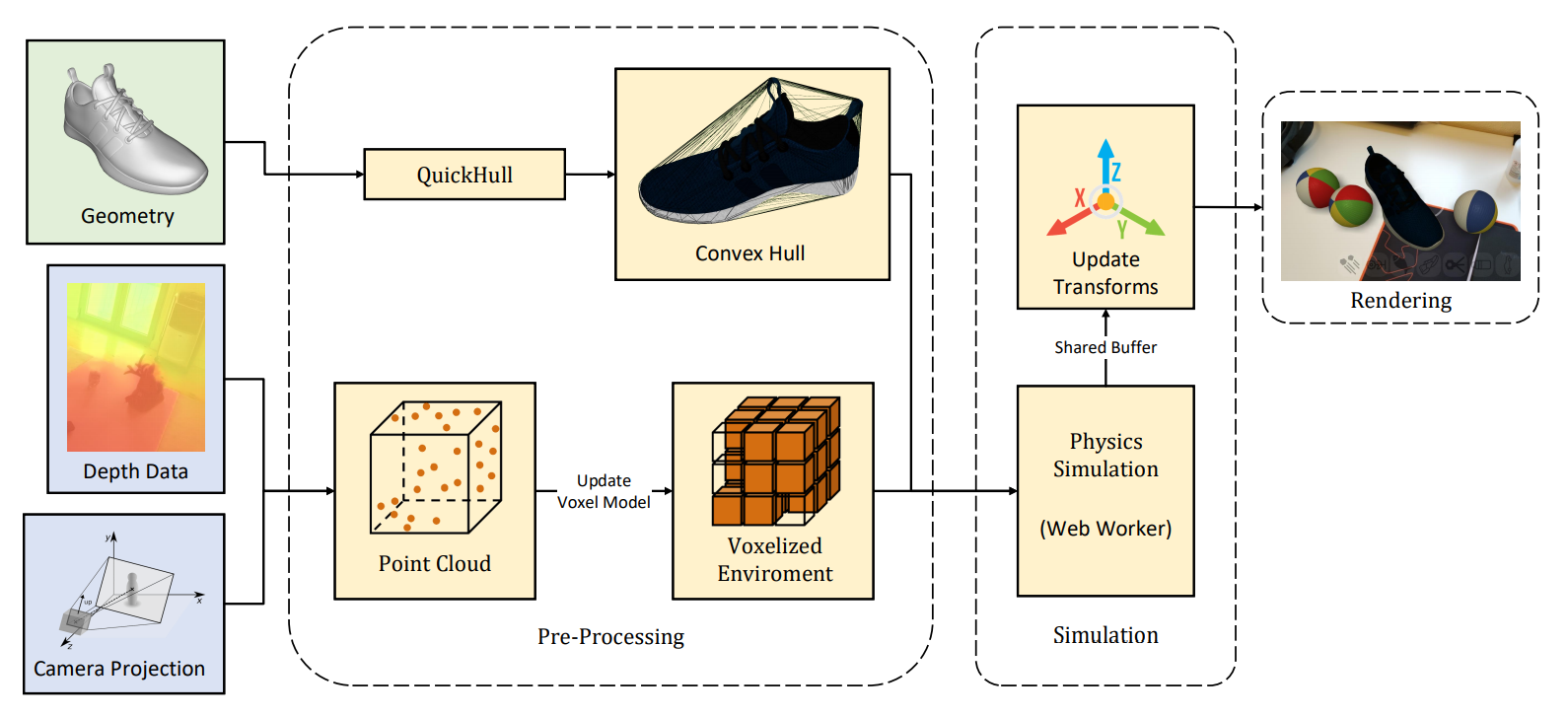
- Web-based framework for environment-aware rendering and interaction in augmented reality based on WebXR using three.js
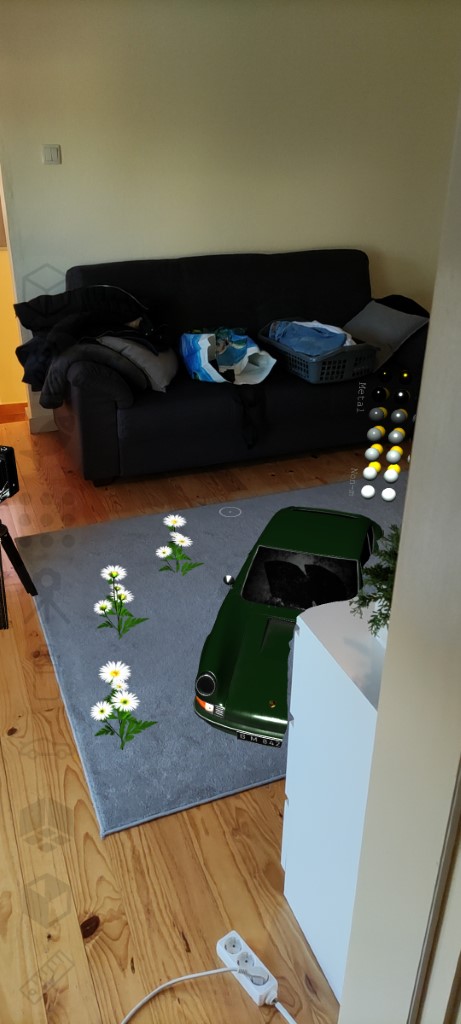
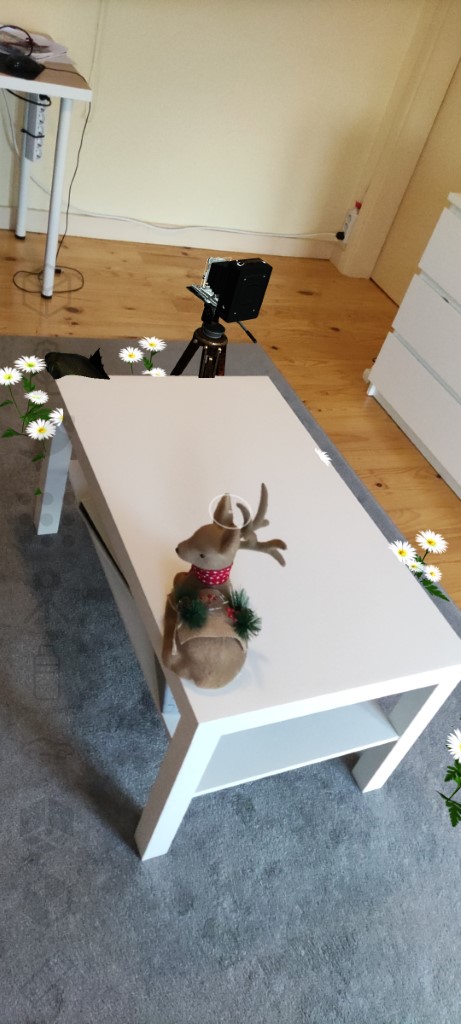
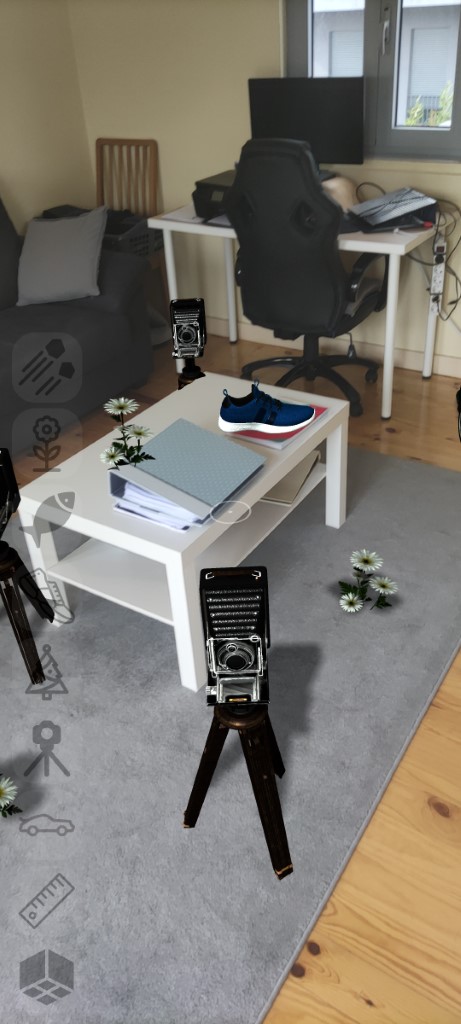
- The framework handles geometry occlusions, matches the lighting of the environment, casts shadows, and provides physics interaction with real-world objects.
- Material from three.js can be reused the shader code required for AR occlusion is injected into the existing shaders using the
onBeforeCompilecallback. - Capable of obtaining over 20 frames per second even on middle-range devices.
- WebXR AR features supported by the framework
- Download the repository from git
gh repo clone tentone/enva-xr - Install Node and NPM.
- Ensure that your browser is compatible with WebXR and check features support (e.g.
depth-estimation,hit-test,lighting). - Install dependencies from NPM by running
npm installand start the code runningnpm run start - To allow easier debugging in mobile devices eruda can be used as a development tools alternative.
- Bellow is a simple usage example of the library the
ARRendereris responsible for most of the work required to setup the AR scene. - The
ARRendererreceives a configuration object that indicates wich WebXR features should be enabled. - To enable AR rendering on existing
three.jsmaterials theAugmentedMaterial.transform()method should be used to transform regular materials into AR materials. - The example bellow demonstrates how to create a simple AR scene with occlusion and lighting enabled.
LightProbeobject replicates the envornment lighting and position main light source position and direction. Internaly contains a three.js LightProbe and DirectionalLight with shadow casting enabled by default.
const renderer = new ARRenderer({
depthSensing: true,
depthTexture: true,
lightProbe: true
});
let material: any = new MeshPhysicalMaterial({color: (Math.random() * 0xFFFFFF)});
material = AugmentedMaterial.transform(material);
let box = new Mesh(new BoxGeometry(), material);
box.receiveShadow = true;
box.castShadow = true;
renderer.scene.add(box);
const probe = new LightProbe();
renderer.scene.add(probe);
const floor = new FloorPlane();
renderer.scene.add(floor);
renderer.onFrame = function(time: number, renderer: ARRenderer) {
box.rotation.x += 0.01;
};
renderer.start();- Depth data provided by WebXR can be used for occlusion in the 3D scene.
- Occlusion is calculated in the shader code injected using the
AugmentedMaterial.transform()method. - To enable realistic rendering of the scene the
MeshPhysicalMaterialmaterial should be used alonside PBR assets.
- cannon.js can be used for physics interaction between objects.
- The
VoxelEnvironmentprovides a probabilistic voxel based model that maps the environment from depth data that is updated every frame. - Alternativelly physics can rely on plane detection using the
FloorPlaneorPlanesobjects. - Currently performance is limited might be improved using WebXR Real World Geometry API
- The code from the project is MIT licensed. The license is available on the project repository,