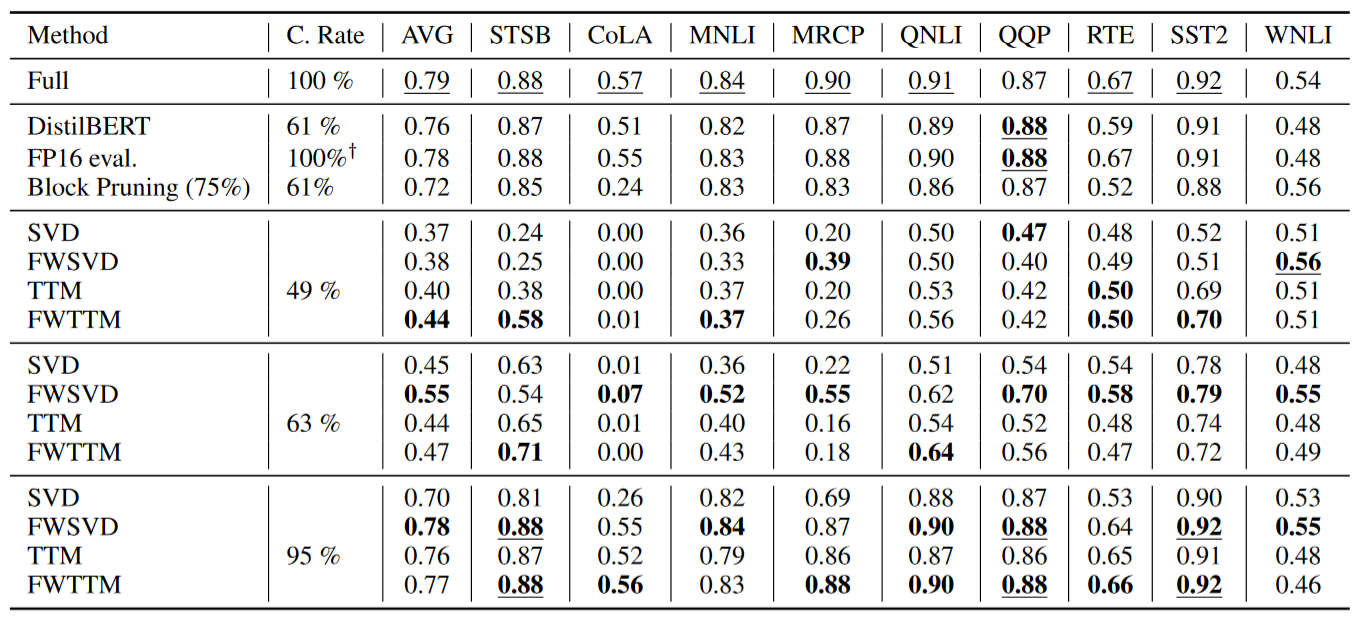
This repository contains code for reproducing experiments from the PACLIC-2023 paper A Computational Study of Matrix Decomposition Methods for Compression of Pre-trained Transformer. In this paper we studied different matrix decompositions to compress Fully-Connected layers of a Transformer models (BERT and BART). Specifically, we apply Singular Value Decomposition(SVD) and Tensor Train Matrix(TTM) decomposition to represent the fully connected layers in a compressed form. We extend the FWSVD approach by adding Fisher information to the TTM decomposition and present a novel method called FWTTM.
Code was tested on Python 3.10. To install needed dependencies, run:
pip install -r requirements.txtAlso, you might want to use logging:
pip install wandbOur code is based on the HuggingFace code for GLUE. So most of args should work for this script too.
Benchmark based on GLUE which is made up of a total of
model = "bert-base-uncased"
random = 814084
python glue_trainer.py \
--model_name_or_path $model \
--run_name $model-full-$random \
--comp_func 'none' \
--save_strategy "epoch" \
--logging_strategy no \
--do_bench --bench_on_eval \
--bench_on_train \
--max_bench_iter 1 \
--batch_sizes 1 16 32 \
--sequence_lengths 128 \
--max_seq_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 32 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 128 \
--learning_rate 5e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--evaluation_strategy 'epoch' \
--seed $random \
--output_dir ./data_eval/ \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--do_train \
--do_eval This script will train and eval bert-base model for GLUE, and then output the results with GPU and CPU utilization. To train model with compression function you can change script to:
for model in "bert-base-uncased"
do
for ranks in 10 60 110
do
for random in 39512
do
python glue_trainer.py \
--model_name_or_path $model \
--run_name $model-TTM-$ranks-$random \
--comp_func 'ttm_ffn' --rank $ranks \
--save_strategy "no" \
--logging_strategy "no" \
--do_bench --bench_on_eval \
--bench_on_train \
--max_bench_iter 1 \
--batch_sizes 1 16 32 \
--sequence_lengths 128 \
--max_seq_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 32 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 128 \
--learning_rate 5e-5 \
--tt_ranks $ranks $ranks $ranks \
--tt_input_dims 12 2 2 16 \
--tt_output_dims 32 3 2 16 \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--evaluation_strategy 'epoch' \
--seed $random \
--output_dir './bert-base-uncased-ttm_ffn/'\
--do_train \
--double_train \
--do_eval \
--overwrite_output_dir
done
done
doneHere svd_ffn_w is SVD (all models available at exps/models.py) and __rank__ is SVD rank. --double_train is the function for additional training after svd compression, in some cases gives better results.
| model | score | size(MB) | size(M param) | SPS | train speed | inf speed | used_cpu | used_cpu_mem | used_gpu | used_gpu_mem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bert | 0.79508 | 417.6553 | 109.483778 | 513.44118 | 0.21948 | 0.078 | 35.40032 | 2644.8 | 44.9 | 1599 |
| stsb | cola | mnli | mrpc | qnli | qqp | rte | sst2 | wnli | ||
| 0.88816 | 0.57574 | 0.84928 | 0.90352 | 0.91338 | 0.87682 | 0.67508 | 0.92432 | 0.5493 |
First script is same as huggingface run_summarization.py. This script will train model on any bart-based seq2seq task, and generate model with additional fisher weight coefs
for random in 585534
do
python ./xsum_trainer.py \
--model_name_or_path "facebook/bart-base" \
--tokenizer_name "facebook/bart-base" \
--run_name bart-xsum-wttm-dt-$ranks \
--dataset_name xsum \
--dataset_config "3.0.0" \
--do_train \
--do_predict \
--comp_func "none" \
--predict_with_generate \
--seed $random \
--evaluation_strategy "epoch" \
--max_source_length 512 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 16 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 32 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_strategy "no" \
--source_prefix "" \
--output_dir ./experiments_BART/BART_XSUM_$random
doneSecond script is for compression and training a compressed model:
for ranks in 10 60 110
do
for random in 585534
do
python ./xsum_trainer.py \
--model_name_or_path ./experiments_BART/BART_XSUM_$random \
--tokenizer_name ./experiments_BART/BART_XSUM_$random \
--run_name bart-xsum-wttm-dt-$ranks \
--dataset_name xsum \
--dataset_config "3.0.0" \
--do_train \
--do_predict \
--tt_input_dims 8 12 8 \
--tt_output_dims 12 16 16 \
--tt_ranks $ranks $ranks \
--comp_func "ttm_ffn_bart" \
--rank $ranks \
--predict_with_generate \
--seed $random \
--evaluation_strategy "epoch" \
--max_source_length 512 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 16 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 32 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_strategy "no" \
--source_prefix "" \
--output_dir ./experiments_BART/BART_XSUM_$random/BART_XSUM_dt_ttm_ffn_bart_$ranks_$random
done
doneFor evaluate gpu/cpu metrics we use pynvml library. Model only evaluate during evalatuation process.
You can also get scores without training model by directly using synthetic_benchmark.py script.
python synthetic_benchmark.py \
--model_name_or_path 'gpt2' \
--run_name 'gpt2-full' \
--comp_func 'none' \
--do_bench --bench_on_eval \
--bench_on_train \
--max_bench_iter 1 \
--batch_sizes 1 16 32 \
--sequence_lengths 128 \
--max_seq_length 128 \
--seed 42 \
--output_dir ./data_eval_gpt/Data folder contains evaluation results for gpt2/bert-base-cased/distilbert/pruned-bert on 3090. This can be used as example.
All the discussed in paper compression methods are located in the exps folder and can be applied in the main GLUE evaluation script using --comp_func flag :
- Attnetion head pruning, based on the paper "Are Sixteen Heads Really Better than One?" and its implementation
random_head. - Vanilla SVD
our_ffn. - Fisher-Weighted SVD introduced in "Language model compression with weighted low-rank factorization"
svd_ffn_w_Torsvd_ffn_w. - TTM (we use our own implementation)
ttm_ffn. - FWTTM (our proposed method)
ttm_ffn_w.
For sequence-to-sequence models:
- Vanilla SVD
svd_ffn_bart. - Fisher-Weighted SVD
svd_ffn_w_bart. - TTM
ttm_ffn_bart. - FWTTM
ttm_ffn_w_bart.
Additional methods can be found in exps/models.py and exps/models_bart.py.
Due to the specifics of GPUs, drivers and architectures the benchmark should only be performed on immutable environment. The same script running on different gpus will give different results. So, the quality and speed of compression can be compared only within one environment. The environment setup for the experiments in the paper is available in /data_eval/env_info.csv.
Below we present the results from our paper:
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/aist/PletenevMCSZP23,
author = {Sergey Pletenev and
Daniil Moskovskiy and
Viktoria Chekalina and
Mikhail Seleznyov and
Sergey Zagoruyko and
Alexander Panchenko},
editor = {Dmitry I. Ignatov and
Michael Yu. Khachay and
Andrey Kutuzov and
Habet Madoyan and
Ilya Makarov and
Irina Nikishina and
Alexander Panchenko and
Maxim Panov and
Panos M. Pardalos and
Andrey V. Savchenko and
Evgenii Tsymbalov and
Elena Tutubalina and
Sergey Zagoruyko},
title = {Transformers Compression: {A} Study of Matrix Decomposition Methods
Using Fisher Information},
booktitle = {Analysis of Images, Social Networks and Texts - 11th International
Conference, {AIST} 2023, Yerevan, Armenia, September 28-30, 2023,
Revised Selected Papers},
series = {Lecture Notes in Computer Science},
volume = {14486},
pages = {36--48},
publisher = {Springer},
year = {2023},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-54534-4\_3},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-54534-4\_3},
timestamp = {Fri, 29 Mar 2024 23:01:34 +0100},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/conf/aist/PletenevMCSZP23.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}@inproceedings{pletenev-etal-2023-computational,
title = "A Computational Study of Matrix Decomposition Methods for Compression of Pre-trained Transformers",
author = "Pletenev, Sergey and
Chekalina, Viktoriia and
Moskovskiy, Daniil and
Seleznev, Mikhail and
Zagoruyko, Sergey and
Panchenko, Alexander",
editor = "Huang, Chu-Ren and
Harada, Yasunari and
Kim, Jong-Bok and
Chen, Si and
Hsu, Yu-Yin and
Chersoni, Emmanuele and
A, Pranav and
Zeng, Winnie Huiheng and
Peng, Bo and
Li, Yuxi and
Li, Junlin",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 37th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation",
month = dec,
year = "2023",
address = "Hong Kong, China",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2023.paclic-1.73",
pages = "723--742",
}